Abstract
The target molecule of this study is haloperidol, a neuroleptic from the butyrophenone family. It is one of the most widely used psychotropic drugs globally and is considered as effective as other low-potency psychotropic medications. The RP-HPLC method employed in this study utilizes a novel mobile phase composed of a 90:10 mixture of methanol and phosphate buffer (pH = 9.8) for isocratic elution. This method has been validated with a correlation coefficient (R) of 0.999 across a concentration range of 2.5 to 50 µg/mL. It exhibits excellent sensitivity, with a relative standard deviation (RSD) of less than 2% for both precision and accuracy. The method is highly effective for the analysis of haloperidol in oral commercial formulations. The mobile phase is cost-efficient, environmentally friendly, and simple to use, making it suitable for analyzing haloperidol in both liquid and powder forms. Additionally, the method is applied to monitor haloperidol degradation under various stress conditions. For powder samples, the maximum degradation observed was 6.20% after 48 h of sunlight exposure. For liquid haloperidol samples, stability was retained only under oxidative stress conditions, with the highest degradation (57.36%) occurring after 48 h of sunlight exposure and the lowest degradation (10.03%) observed under thermal stress at 60 °C over seven days.
1. Introduction
Haloperidol, a neuroleptic from the butyrophenone family, is one of the most widely used psychiatric drugs in many countries. It is expected to perform exactly as effectively as other psychotropic drugs of moderate potency [1]. It is a widely used first-generation antipsychotic, and had over 1 million U.S. prescriptions in 2020 but has seen declining use, with no top rankings in 2022. Global data are limited, but its usage is decreasing worldwide, favoring atypical antipsychotics due to socioeconomic factors [2,3,4]. Haloperidol is used to treat psychotic conditions such as schizophrenia, manic episodes, delusions, and acute and chronic psychosis. Additionally, it is used to manage vocal outbursts in patients with Tourette’s syndrome and to calm the frantic behavior of some individuals. In addition to medications for palliative care such as nausea, it is on the World Health Organization (WHO) ’s list of essential medications [3,5] for vomiting induced by radiotherapy [6]. It is advised to take this medication orally, either as a pill or an oral solution, and in cases of severe symptom, an injectable form should be used [7].
Numerous studies have looked at the measurement of haloperidol in pharmaceutical products that are liquid or solid form [1,8,9,10]. The most used analytical techniques for determining haloperidol in solid form are HPLC [8] and UV–Vis spectrometry in the pharmacopeias [10,11]. In the past, haloperidol has been extracted and complexed in the presence of visible light or chemical derivative methods. However, these processes either involve a lot of chemicals as solvents and reagents during the extraction process or take a very long time in the complexation process [11,12,13,14,15,16]. The new chromatographic methods are more efficient, especially hyphenated instruments, like HPLC coupled with electrospray ionization and HPLC/ESI/MS mass spectrometry. These instruments have been proposed to analyze haloperidol, but it mainly improves the separation of its degradation products. Nevertheless, the mobile phases used are often complex [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25].
Previously, tests were undertaken to investigate the stability of haloperidol. The first research paper on haloperidol stability was published in 1961; it explored the effect of daylight on the stability of drug molecules [26]. It was reported that haloperidol was highly unstable in the presence of sunlight. In fact, a haloperidol solution stored in clear glass vials discolored within a few hours and precipitated a grey substance, but no deterioration or precipitation was observed in amber glass vials even after eighteen months of storage. Janicki and Ko [27] established that haloperidol solution containing lactic acid at pH~3 was stable up to 5 years at room temperature, up to 2 years at 40 °C, and up to 6 months at 60 °C. However, when the solution was exposed to natural light, it soon became cloudy and discolored. A decrease in haloperidol content was observed by assay. In 1983, Panaggio and Greene [19] demonstrated through HPLC analysis that haloperidol is unstable when exposed to high temperatures and light. They concluded that the conversion of haloperidol to degradation product was observed under elevated temperature, light exposure, and reduced solution pH. Ölçer and Hakyemez [28] studied the effect of oxygen and light on haloperidol samples. Some of these samples were saturated with oxygen before sealing, and it was concluded that oxygen did not influence the degradation of haloperidol. However, the stability of haloperidol has not been confirmed and is therefore the purpose of the present study, which aims at establishing a protocol respecting the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) guidelines in order to remedy this lack.
Still, very few research works have examined the process of isolating haloperidol from the byproducts of its breakdown in liquid dosage forms. This approach could be a good substitute for the previously discussed HPLC techniques since it is unambiguous, simple, and practical. It takes less than four minutes, making it easier to estimate the concentration of haloperidol in the presence of its breakdown products.
This study introduces an innovative HPLC method for analyzing haloperidol in liquid dosage forms, particularly focusing on the effective separation of haloperidol from its degradation products. The approach is distinguished by its simplicity, speed, and feasibility, enabling the precise determination of haloperidol in less than 4 min—a significant improvement over previously reported methods. The careful optimization of the mobile phase, based on bibliographic data and laboratory experiments, combined with the use of a newly formulated polar mobile phase in isocratic elution, brings a new dimension to chromatography technology. Notably, this study is the first of its kind in the field, providing an unprecedented contribution to understanding haloperidol’s stability. By examining haloperidol degradation under various stress conditions, it further expands the research scope, solidifying its position as a pioneering work in this area. This research makes a significant contribution by presenting an innovative, practical, comprehensive, and unparalleled method for haloperidol analysis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
SIGMA-ALDRICH provided sodium hydroxide, lactic acid, monobasic phosphate, and methanol (99.9%) of HPLC quality (St. Louis, MO, USA). SCHARLAU (Barcelona, Spain) provided the hydrogen peroxide (99%), PubChem (Bethesda, MD, USA) provided the methylparaben, and BIOCHEM (Berlin, Germany) provided the hydrochloric acid (99%).
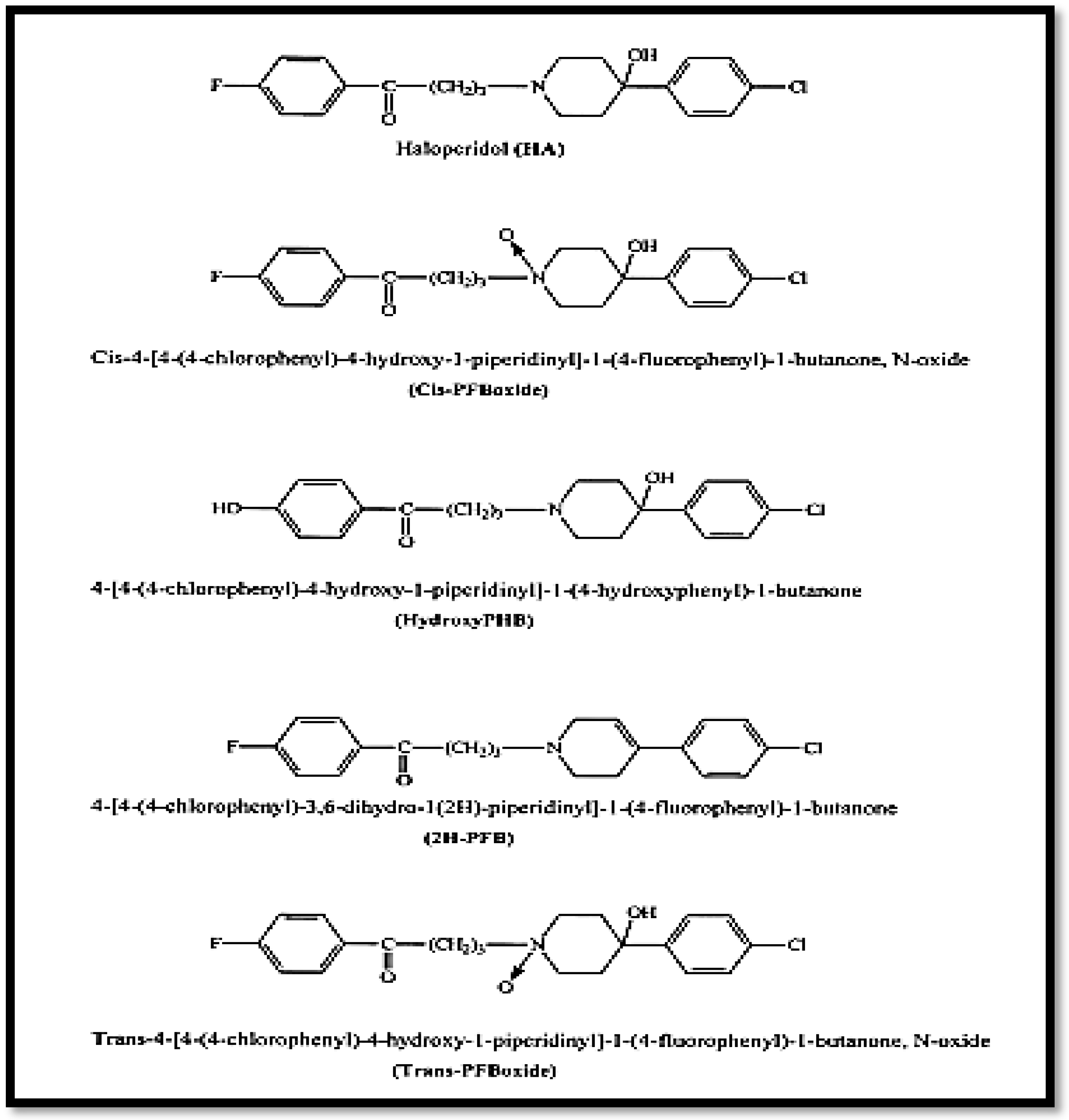
Haloperidol is manufactured by GROUPE SANTE-ALGERIE (Alger, Algeria) with a purity of 99.9%. It is chemically known as 4-[4-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-hydroxy-1-piperidinyl]-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-butanone. It is a white, crystalline powder with the empirical formula C21H23ClFNO2 and a molecular weight of 375.9 g/mol. Haloperidol has a pKa value of 8.3 and its chemical structure is shown in Figure 1.
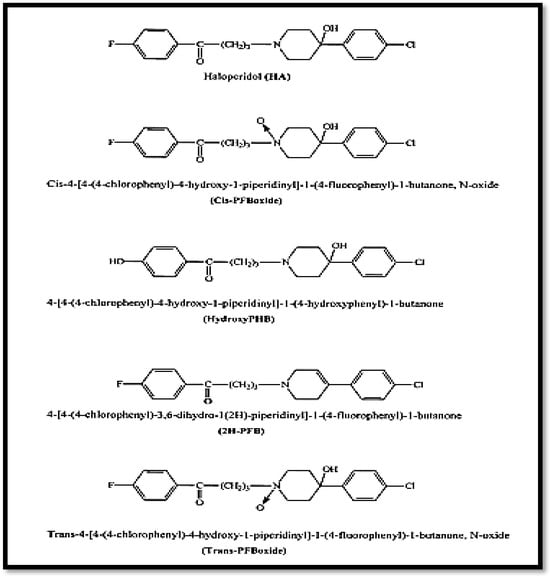
Figure 1.
Structure of haloperidol and its degradation products [22].
Lactic acid was chosen as solvent for the solubility of haloperidol. It can be deemed non-toxic at the concentrations used as an excipient. A 1% (v/v) solution of lactic acid is safe to apply to the skin [2,29,30]. Literature data show its low solubility in water (0.1 mg/mL) and methanol (approximately 16.7 mg/mL at 25 °C) and its good solubility in ethanol, methylene chloride [9,12,31], and lactic acid [27].
2.2. Methods
A chromatograph (Hewlett Packard 1100 series (Hewlett-Packard, Palo Alto, CA, USA)) was equipped with a G1312A binary pump, a G1322A degasser, a UVG1315A detector, and a G1316. A column (reverse phase column C18, 250 mm × 4.6 mm × 5 µm) inserted in an oven was used. The oven temperature varied in the range of 0–55 °C. The sample was injected through a manual syringe injector (volume of injection = 20 µL). ChemStation software (version B.04.03) was used to control the HPLC system, record the results, and prepare the chromatograms.
The lactic acid solution at 1% (v/v) was prepared by diluting 1 mL of lactic acid in 100 mL of purified water. Haloperidol stock solution (100 µg/mL) was prepared by dissolving 10 mg of haloperidol in 100 mL of lactic acid solution. A pH 9.8 buffer solution was created by dissolving 10 mg of monobasic phosphate in 100 mL of filtered water. The pH measured was 9.8 using a pH meter (HANNA instruments model, Cluj-Napoca, Romania).
The optimization tests enabled the selection of a mobile phase composed of 90 mL of HPLC-grade methanol and 10 mL of a buffer solution at pH 9.8. The column employed in this analysis was a C18 with dimensions of 250 mm length and 4.6 mm diameter and a particle size of 5 µm. The study was carried out at a temperature of 25 °C with a flow rate of 1 mL/min, a detection wavelength of 248 nm, and an injection volume of 20 µL.
2.2.1. Method Validation
The validation study of the haloperidol assay was performed according to the ICH guidelines [9,32]. The methodologies’ specificity assured that the presence of excipients would not interfere with the active ingredient’s analysis in the final product. Methylparaben is an antibacterial preservative included in the medicinal liquid version of haloperidol. Using HPLC-grade methanol solvent, haloperidol and methylparaben solutions were injected (20 µL) at the concentration of 50 µg/mL to check for potential interference at 248 nm. This was done to assess the specificity of the procedure.
Linearity
The linearity method was assessed over a range of haloperidol concentrations from 1 to 50 µg/mL, appropriately prepared from the 100 µg/mL stock solution using HPLC-grade methanol as dilution solvent. The peak areas of the different solutions in the range were determined at 248 nm and the calibration curve was constructed by plotting the areas according to the concentrations.
Precision
Precision is determined at two levels, including repeatability and intermediate precision.
Repeatability is estimated by determination of the variation in peak areas obtained by injection of a haloperidol solution of concentration 50 µg/mL with 5 repetitions during the same day. A minimum of 5 determinations should be obtained covering the specified interval for the procedure.
Intermediate precision was determined by inter-day variation, obtained by injecting 3 concentrations of haloperidol of 5, 25, and 50 µg/mL, with 3 repetitions for each concentration but analyzed on 3 different days.
Accuracy
Accuracy expresses the closeness of agreement between the mean value from a series of test results and a theoretical value considered to be true. It reflects the systematic error of a dosage method [32]. It is assessed with three different concentration levels at 5, 25, and 50 µg/mL, and can be inferred once accuracy and linearity have been established.
The accuracy will be studied on the basis of the data obtained during the study of the calibration function. The signal intensity recorded for each range point is used to determine the calculated concentrations Z on the basis of the inverse equation (Z = Y − b/a). The ratio between the concentrations Z and the theoretical concentrations is used to calculate a recovery rate R (%) defined by the following equation R (%) = 100·(Z/X).
Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
The limit of detection (LOD) is defined as the lowest concentration of an analyte that can be detected but not necessarily quantified as an exact value [32].
The limit of quantification (LOQ) is the lowest concentration of an analyte that can be quantitatively determined with acceptable precision and accuracy under the operating conditions specified in the procedure [32].
Application of the Method to the Analysis of the Commercial Product
The proposed method was applied for the analysis of the commercial product of haloperidol oral solution of concentration 2 mg/mL (Vilbar and Isoperidol). The samples were purchased from local pharmacies in Algeria. In order to prepare the sample solution for injection, 0.5 mL of the commercial product was diluted appropriately in 25 mL of methanol. The resultant mixture was then filtered through a 0.22 µm filter (Millex GP syringe filter, Millipore Express® PES syringe filter, Millipore Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA) and subjected to RP-HPLC analysis.
Haloperidol Forced Degradation Studies
Forced degradation, which may also identify a product’s degradation routes, was used to assess the stability capability. The active substance and the dosage determine the kind of forced deterioration, which entails large changes in temperature, oxidation, pH, and photolysis processes.
The protocol does not provide any rules for mandatory degradation testing. The degradation study’s main objective was to accomplish just 20% degradation, which would allow for the simultaneous detection of the molecule and its degradation products, rather than totally destroying the molecules to acquire the ultimate degradation products [33].
Hydrolysis Degradation
Haloperidol exhibited hydrolysis breakdown in both basic and acidic media. In order to achieve this, 100 µg/mL concentrations of haloperidol solutions were tested at different pH levels using various acid and base concentrations (0.1 N HCl, 1 N HCl, 0.1 N NaOH, 1 N NaOH) for a week at 60 °C. The solutions were then neutralized with the appropriate base or acid.
For instance, 2 mL of 1.0 N HCl solution was mixed with 2 mL of haloperidol solution samples at 100 µg/mL. The mixture was neutralized with 2 mL of 1.0 N NaOH solution and then diluted with 4 mL of HPLC-grade methanol following seven days of storage at 60 °C (Mammert UN 110–108 L natural convection oven). Therefore, the final solution was subjected to RP-HPLC analysis, and the percentage of degradation was ascertained by contrasting it with the concentration of the non-degraded haloperidol solution (20 µg/mL).
Oxidative Degradation
The oxidative stress study of haloperidol in solution was conducted with 1 mL of haloperidol solution with a concentration of 1 mg/mL and 9 mL of hydrogen peroxide solutions with concentrations of 0.3% and 3% for one week at temperatures of 25 °C and 60 °C. After diluting each solution by around 1.0 mL in 25 mL of HPLC-grade methanol, the resultant solutions were subjected to analysis to ascertain the percentage of degradation in comparison to the non-degraded haloperidol solution.
Thermal Degradation
The thermal degradation study was conducted for powder as well as solution (100 µg/mL) forms of haloperidol. Thus, haloperidol samples were placed in a hot air oven at 60 °C and 80 °C for one week (solution form) and two weeks (powder form). The active ingredient in powdered form was tested. Additionally, a solution was prepared using the same method as for the 100 µg/mL haloperidol stock solution, followed by dilution to obtain a 20 µg/mL haloperidol solution in methanol. The prepared solutions of pre- and post-degradation were analyzed by RP-HPLC and compared with the initial non-degraded solution to calculate the degradation percentage.
Photolytic Degradation
Forced photodegradation was studied by exposing the haloperidol samples (in powder form and as a solution of 100 µg/mL) to natural daylight for 48 h [18,34,35] and UV light using a UV lamp (Ultraviolet light UVA 24 W (Philips PL/L, Amsterdam), 270 nm, 20 mW/cm2) for 48 h. After exposing the sample to light for a predetermined amount of time, the concentration of haloperidol was determined by making a 100 µg/mL solution in 1% lactic acid (using the same method as the one used to make the 100 µg/mL haloperidol stock solution). To ascertain the percentage of degradation, haloperidol’s RP-HPLC analysis in the samples exposed to light before and after was compared.
3. Results
3.1. HPLC Analysis of Haloperidol
Maximum absorbance at the wavelength (λmax) of 248 nm is seen in the UV–Vis spectroscopic scanning of a haloperidol solution produced in 1% lactic acid solution in the wavelength range of 200 to 400 nm. The UV/Vis spectrophotometer used was an OPTIZEN 3220UV double beam equipped with paired 1 cm quartz cells from Daejeon, South Korea. Other researchers also reported a similar wavelength (λmax) for spectrophotometric determination of haloperidol in solutions [11,14,15,36,37]. Thus, 248 nm (λmax) was selected for the RP-HPLC detector’s detection wavelength.
The analysis of haloperidol was tested with different mobile phase solvents. First, a 50:50 ratio of methanol/acetonitrile [38] was used as a mobile phase solvent. The chromatogram for haloperidol was not satisfactory because of low retention time (~2.32 min) and no proper separation of degraded products peaks. Then, only methanol was used as a mobile phase solvent, but this gave an irregular pattern of chromatogram peaks for haloperidol and 1% lactic acid. After that, methanol/phosphate buffer (pH 9.8) solvent in the ratio of 90:10 was used as the mobile phase. The reason for selecting the phosphate buffer (pH 9.8) solution in the mobile phase is the pKa (8.3) of haloperidol, which allows clear and well-resolved peaks in the chromatogram. The obtained peaks have a retention time of 3.3 min and well-separated peaks for the degraded product of haloperidol. Therefore, this method can be applied to study the forced degradation of haloperidol drug samples. The mixture of methanol and phosphate buffer (pH 9.8) solution in the ratio of 90:10 (v/v) with a flow rate of 1 mL/min gave better peak resolution, shape, and symmetry than other mobile phase solvents used.
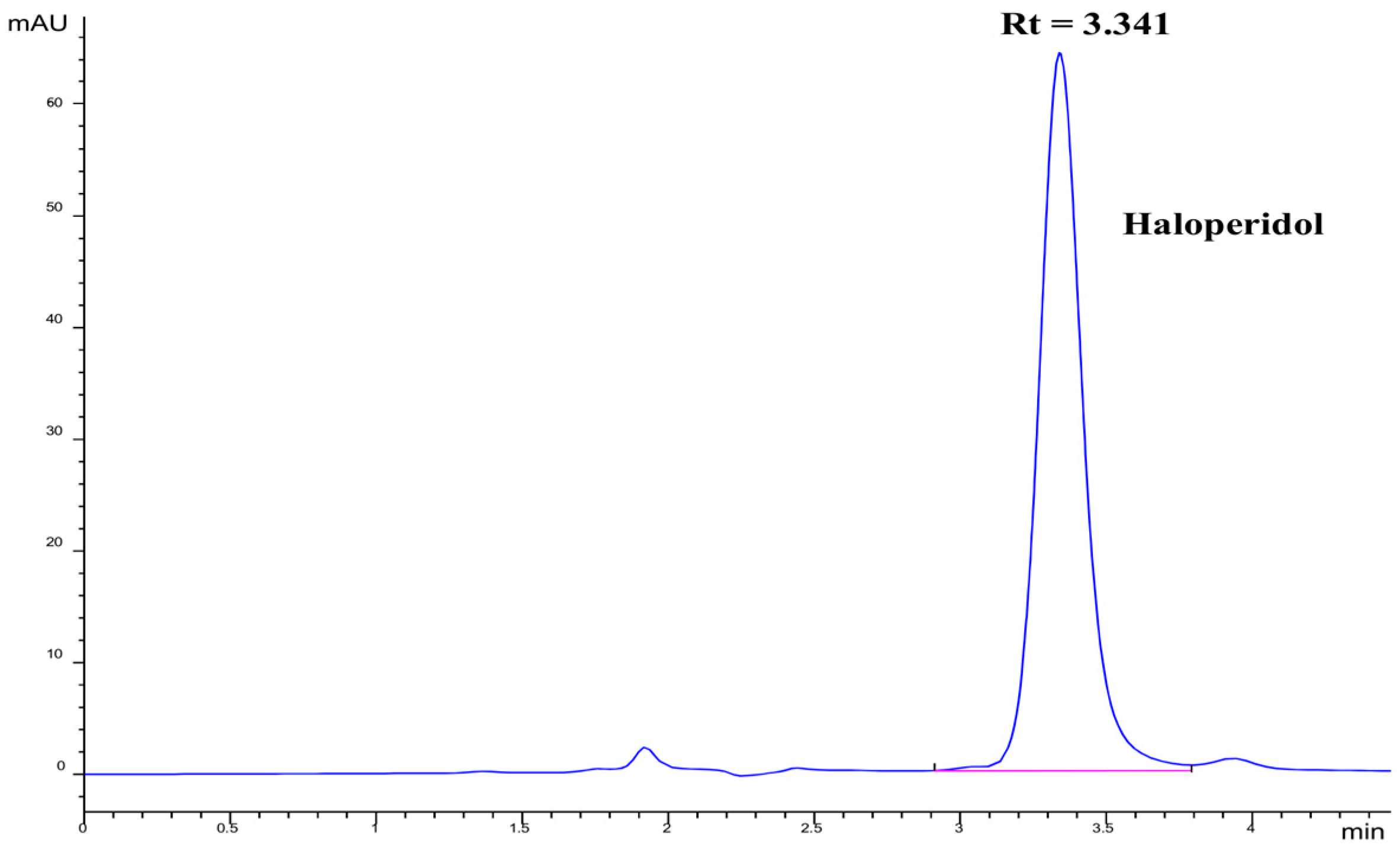
The retention time for haloperidol was 3.3 min, with a well-shaped peak, as shown in Figure 2. The repeatability of the results is excellent. In another attempt to develop the RP-HPLC method, Petkovska and Dimitrovska [39] developed the simultaneous determination method of haloperidol with six other related compounds using phosphate buffer (pH 6.5) and acetonitrile (in different ratios) in the mobile phase of RP-HPLC. A Zorbax Eclipse XDB C18 column was used with a mobile phase flow rate of 1.5 mL/min, and a chromatogram was observed at 230 nm wavelength using a UV detector. The well-separated chromatogram peaks were observed in a total analysis time of 7.0 min, and the retention time for haloperidol analysis was reported to be 3.77 min, which was very close to the haloperidol retention time (3.30 min) observed in the current study.

Figure 2.
Chromatogram of haloperidol.
3.2. Method Validation
3.2.1. Linearity
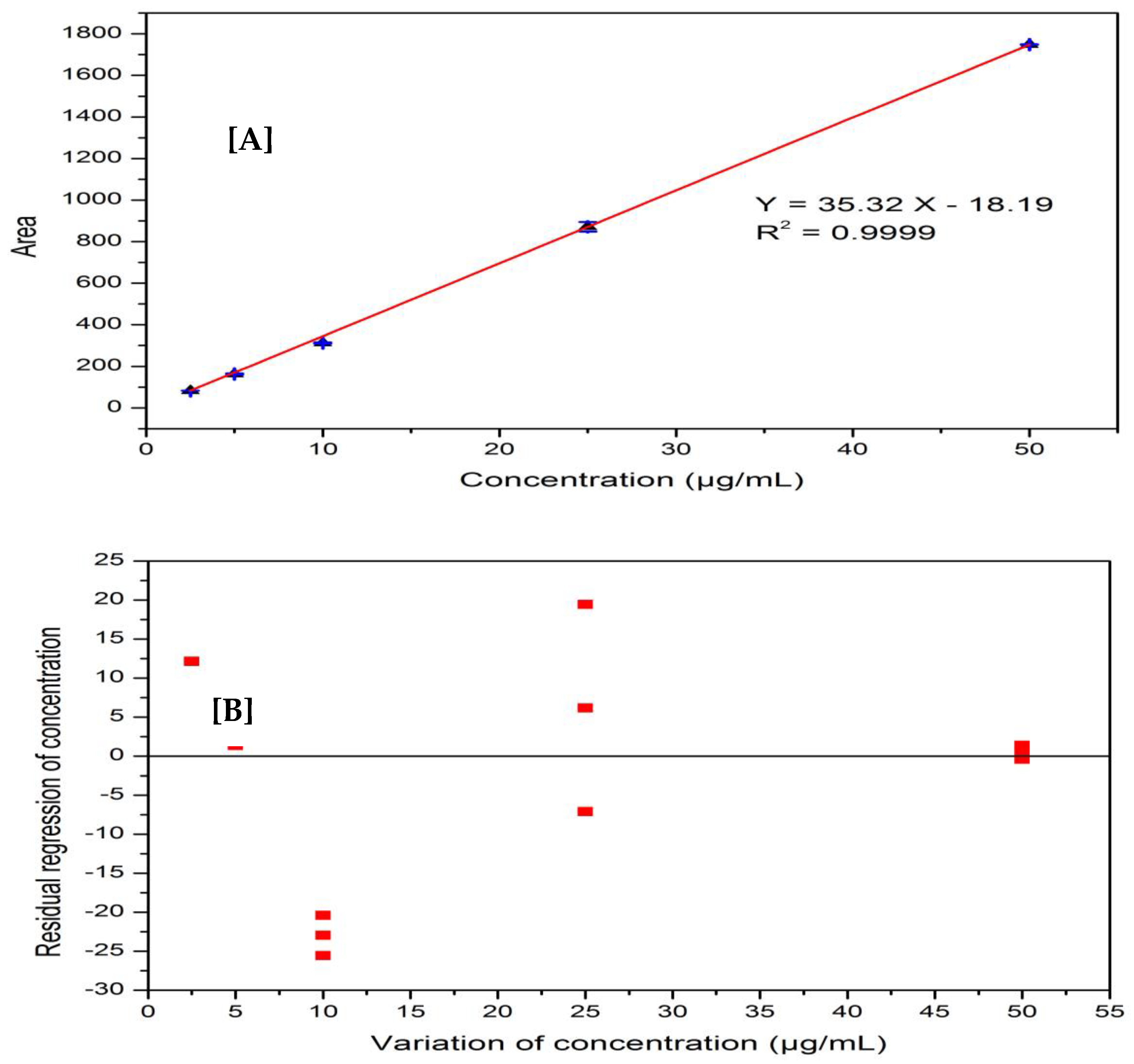
The linearity of the method was established through the calibration curve of the standard solution of known concentration range (2.5 µg/mL to 50 µg/mL). The chromatograms obtained by injecting in the standard solutions (n = 2) were recorded, the area of each chromatogram was calculated and is presented in Table 1. The calibration curve was obtained by plotting the chromatogram area of each standard solution against standard concentrations, as shown in Figure 3A. The correlation coefficient (R) between concentration and area in the plotted data is 0.999 and the relative standard deviation (RSD) is less than 2%, which is very close to the perfect linearity (R = 1.000). The statistical test results of the obtained data are well accepted in the criteria of ICH guidelines.

Table 1.
Method linearity results.
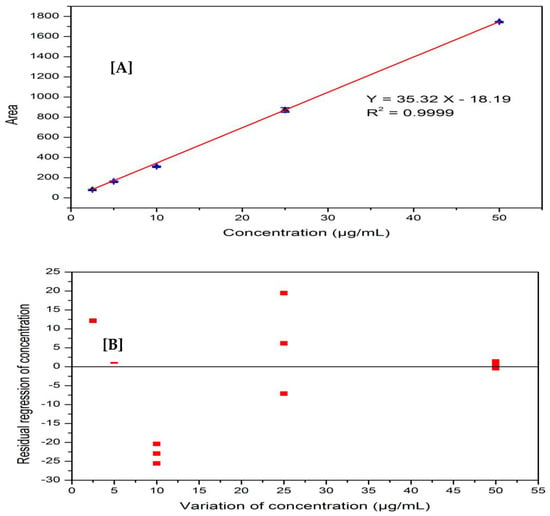
Figure 3.
(A) Linearity of the method; (B) residual graph showing the method’s linearity.
The industrial guidelines for method validation require residual plots of random data around zero line and Fisher’s test values in addition to the correlation coefficient and relative standard deviation [40,41]. Figure 3B displays the residual graph for the haloperidol determination and Table 2 displays the statistical parameters and results from the Fisher’s test. The regression diagram for the haloperidol determination data shows an irregular distribution around the zero line, and the regression is 95% linear according to Fisher’s test, with an F-value greater than the F-critical value.

Table 2.
Statistical results of linearity.
3.2.2. Precision
The precision in the results with the novel mobile phase in the proposed RP-HPLC method for haloperidol determination and quantification are summarized in Table 3 and Table 4. The low coefficients of variation obtained (<2%) for both repeatability and intermediate precision demonstrate the good precision of the proposed method for haloperidol analysis.

Table 3.
Repeatability results.

Table 4.
Intermediate precision results of the method.
3.2.3. Accuracy
The statistical parameters of the accuracy of haloperidol concentration using the proposed RP-HPLC methods are summarized in Table 5. The results show that the recovery percentage lay in the range from99 to 110%, with a maximum relative standard deviation (RSD) of 1.74% for the lowest concentration solution. The low RSD with high recovery rates indicates that the method is accurate.

Table 5.
Method accuracy results and recovery rate.
3.2.4. Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) values are equal to 0.31 µg/mL and 0.95 µg/mL, respectively. These low values indicate the good sensitivity of the proposed RP-HPLC method for the analysis of haloperidol.
3.2.5. Specificity
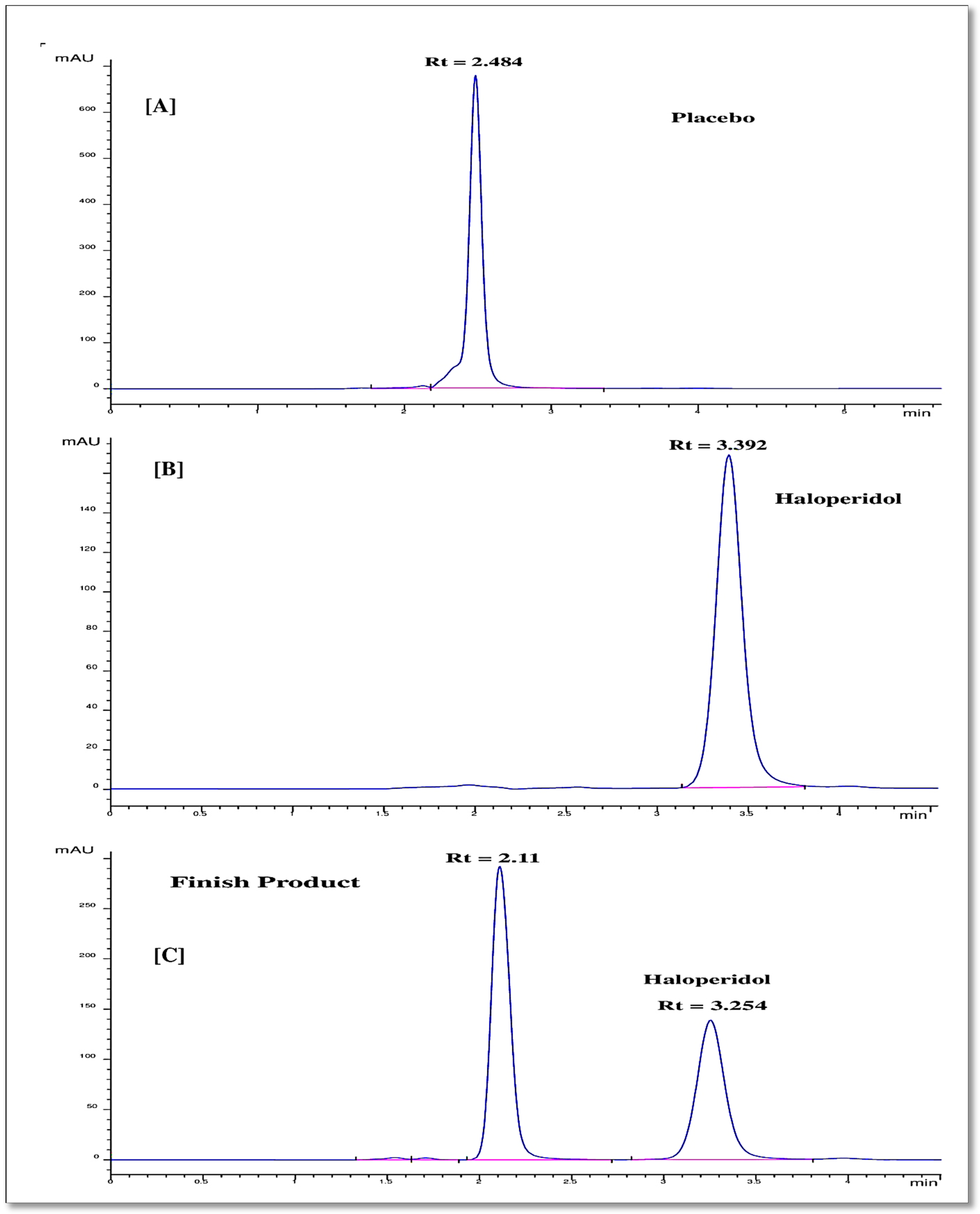
The commercial haloperidol drug samples with concentration 2 mg/mL were selected to analyze through the proposed RP-HPLC method. The drug samples after dilution and placebo (solution containing methylparaben and lactic acid) samples were injected into the chromatograph and the elution peak were observed through a UV-detector at wavelength 248 nm as shown in Figure 4A,B. A clear peak separation was observed with a time difference of nearly 1 min of retention time. Haloperidol and methylparaben were eluted well with retention times of approximately 3.3 min and 2.4 min, respectively.

Figure 4.
Chromatograms of proposed RP-HPLC method for placebo (A), haloperidol (B), and commercial product (haloperidol oral solution 2 mg/mL) (C).
The validation of haloperidol analysis results through the proposed RP-HPLC method are summarized in Table 6. The validation parameters such as specificity, linearity range, correlation coefficient (R2), precision, accuracy, LOD, and LOQ of this study meet the guidelines of the ICH for drug analysis [32]. The LOD (0.31 µg/mL) and LOQ (0.95 µg/mL) of this method are better than some HPLC methods reported in the literature [24,38,39]. The recovery percent (99–100%) and RSD (0.05–1.74%) of this method are comparable to chromatographic methods reported in the literature [8]. Thus, the proposed RP-HPLC method is sensitive, accurate, precise, and reproducible for the determination of haloperidol in liquid dosage form.

Table 6.
Method validation results.
3.3. Application of the Proposed RP-HPLC Method for Commercial Drugs
The sample solution for injection into the chromatograph was obtained by one-time dilution of 0.5 mL liquid commercial product Vibar (Biopharm pharmaceutical industry, concentration 2 mg/mL) in 25 mL methanol. The oral solution, containing haloperidol, methylparaben, and lactic acid, revealed the presence of two chromatographic peaks at around 3.25 min and 2.11 min corresponding to haloperidol and placebo (mixture of methylparaben and lactic acid 1%), respectively, as shown in Figure 4. Both compounds are well-eluted and well-separated with a resolution time more than 2 min. The concentration of haloperidol in the commercial product was found to be 2 ± 0.84 mg/mL (n = 3), corresponding to a percentage estimate of 102.5% (Figure 4C). This is in line with the standards specified in the British Pharmacopoeia [42], which are between 95% and 105% [43].
For the control of haloperidol oral solution at a concentration of 2 mg/mL, the HPLC technique suggested in this study for haloperidol analysis is accurate and precise. Its advantages are related to the simplicity of the mobile phase compared to those stated in the literature [20,24,44] and proposed by the pharmacopeias. It can therefore be used as an alternative analytical method in pharmaceutical quality control laboratories.
Table 7 summarizes the chromatographic methods already used for the estimation of haloperidol in the various liquid and solid dosage forms in view of the complexity of the mobile phase.

Table 7.
Haloperidol content in pharmaceutical preparations as determined by HPLC [8].
3.4. Forced Degradation Study of Haloperidol
The forced degradation of haloperidol molecules was examined using the suggested RP-HPLC approach, which involved tracking the chromatogram peak profile and determining the degradation percentage in relation to the starting concentration of haloperidol molecules. A specific methodology was followed in the forced deterioration investigation. This study demonstrated the stability of the haloperidol molecule in pharmaceutical formulations such as solid and liquid solutions rather than being primarily focused on determining the breakdown products [46]. The forced degradation stress used in this study were hydrolytic, oxidative, thermal, and photolytic.
3.4.1. Hydrolysis Degradation
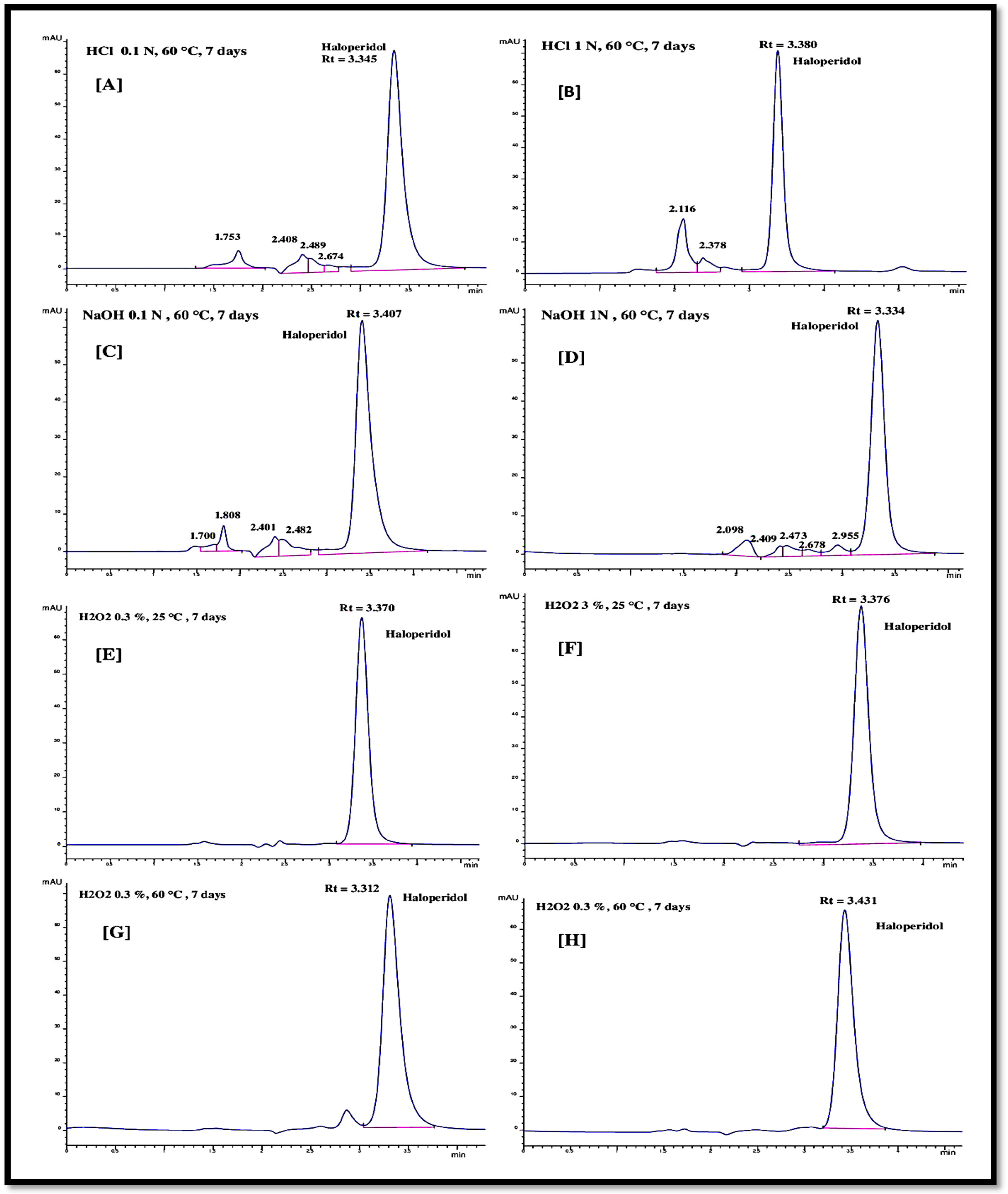
The hydrolysis of the haloperidol was performed through acid (HCl) and base (NaOH) solutions with varying concentrations at two levels (0.1 N and 1.0 N). Hydrolysis temperature (60 °C) and time (7 days) were fixed for both the hydrolysis agents (NaOH and HCl). The injection of the haloperidol solutions, after hydrolytic degradation in acid and base medium, gave the chromatograms as represented in Figure 5A–D. In acid medium at low concentration (0.1 N), four minor peaks at retention times of 1.7, 2.4, 2.5, and 2.6 min were observed other than a large haloperidol peak at the retention time of 3.3 min (Figure 5A). The low area of the minor peaks appeared before the dominant peak of haloperidol. The degraded haloperidol molecules had a smaller molecular weight than the parent haloperidol molecule and, therefore, their elution peaks appeared before the parent haloperidol chromatogram peak (Figure 5B). With the increase in the acid concentration from 0.1 N to 1.0 N, the degradation of the haloperidol increased from 16.02% to 24.82%, respectively. Only two minor peaks (at a retention time of 2.1 min and 2.3 min) appeared before the haloperidol peak. Furthermore, the peak areas of the minor peaks were more important compared to low-concentration HCl (0.1 N) hydrolyzed haloperidol chromatogram peaks. Hydrolysis with 0.1 N and 1.0 N NaOH solution did not give much difference in the degraded chromatogram peaks. For both concentrations of NaOH, the numbers of minor chromatogram peaks are equal (as seen in Figure 5C,D). The haloperidol degradation with 0.1 N and 1.0 N NaOH solution was 15.80 and 17.26%, respectively. Under the hydrolytic stress, a decrease in the chromatogram peak area was observed, reflecting a partial degradation of haloperidol molecules in the solution. Table 8 provides a summary of the degradation percentage data, showing that a 1.0 N HCl medium produced the highest percentage of degradation. The results of haloperidol’s hydrolytic breakdown are consistent with the data reported in the literature [21,24].
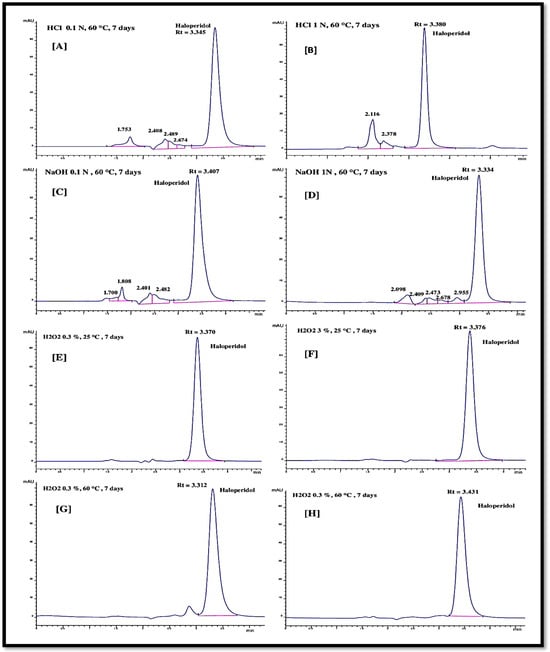
Figure 5.
Forced degradation of haloperidol in the presence of (A) HCl 0.1 N, 60 °C and 7 days; (B) HCl 1.0 N, 60 °C and 7 days; (C) NaOH 0.1 N, 60 °C and 7 days; (D) NaOH 1.0 N, 60 °C and 7 days; (E) H2O2 0.3%, 25 °C and 7 days; (F) H2O2 3.0%, 25 °C and 7 days; (G) H2O2 0.3%, 60 °C and 7 days; (H) H2O2 3.0%, 60 °C and 7 days.

Table 8.
Forced degradation results of haloperidol.
Hydrolysis of haloperidol is a chemical reaction in which the drug undergoes degradation when it interacts with water. This process is influenced by factors such as pH, temperature, and the presence of enzymes.
Haloperidol’s functional groups, including a ketone (>C=O) and a hydroxyl (-OH), make it vulnerable to hydrolytic attack. Hydrolysis can break ester bonds (if present), releasing carboxylic acids and alcohols. The ketone group can be transformed under acidic or basic conditions.
The reaction produces hydroxylated or carboxylated compounds, which are often pharmacologically inactive, reducing therapeutic efficacy.
Techniques such as HPLC and mass spectrometry are used to detect and quantify the products of hydrolysis. Understanding hydrolysis is crucial for guaranteeing drug stability and optimizing formulations.
3.4.2. Oxidative Degradation
The oxidative degradation was performed in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) solution for a fixed duration of 7 days. The variation in the degradation experiment was conducted by increasing the H2O2 concentration from 0.3% to 3.0% and the solution temperature from 25 °C to 60 °C. After exposing the haloperidol solution samples to a set of H2O2 concentrations and temperatures for 7 days, the resultant solution was injected to the chromatograph with the proposed RP-HPLC method. The obtained chromatogram peaks are shown in Figure 5E–H, showing no change in the chromatogram. Only one peak appeared for the undegraded haloperidol molecule at the retention time of 3.3 min and zero percent degradation was observed under all the variations of oxidative degradation as reported in Table 8. This reflects the stability of the haloperidol molecule under oxidative stress [25,36,37]. Nevertheless, some researchers reported oxidative degradation of haloperidol up to 18% under more severe conditions. Gadhavi et al. [24] reported 18.83% oxidative degradation of haloperidol in the presence of 3% H2O2 solution under a very high solution temperature of 80 °C. Trabelsi et al. [21] studied the haloperidol oxidative degradation with high concentration (30%) H2O2 solution at 70 °C for 5 h. After oxidative degradation, the authors observed the cis- and trans-haloperidol N-oxide molecules as degraded molecules, but the percentage degradation of haloperidol after oxidative degradation was not specified.
3.4.3. Thermal Degradation
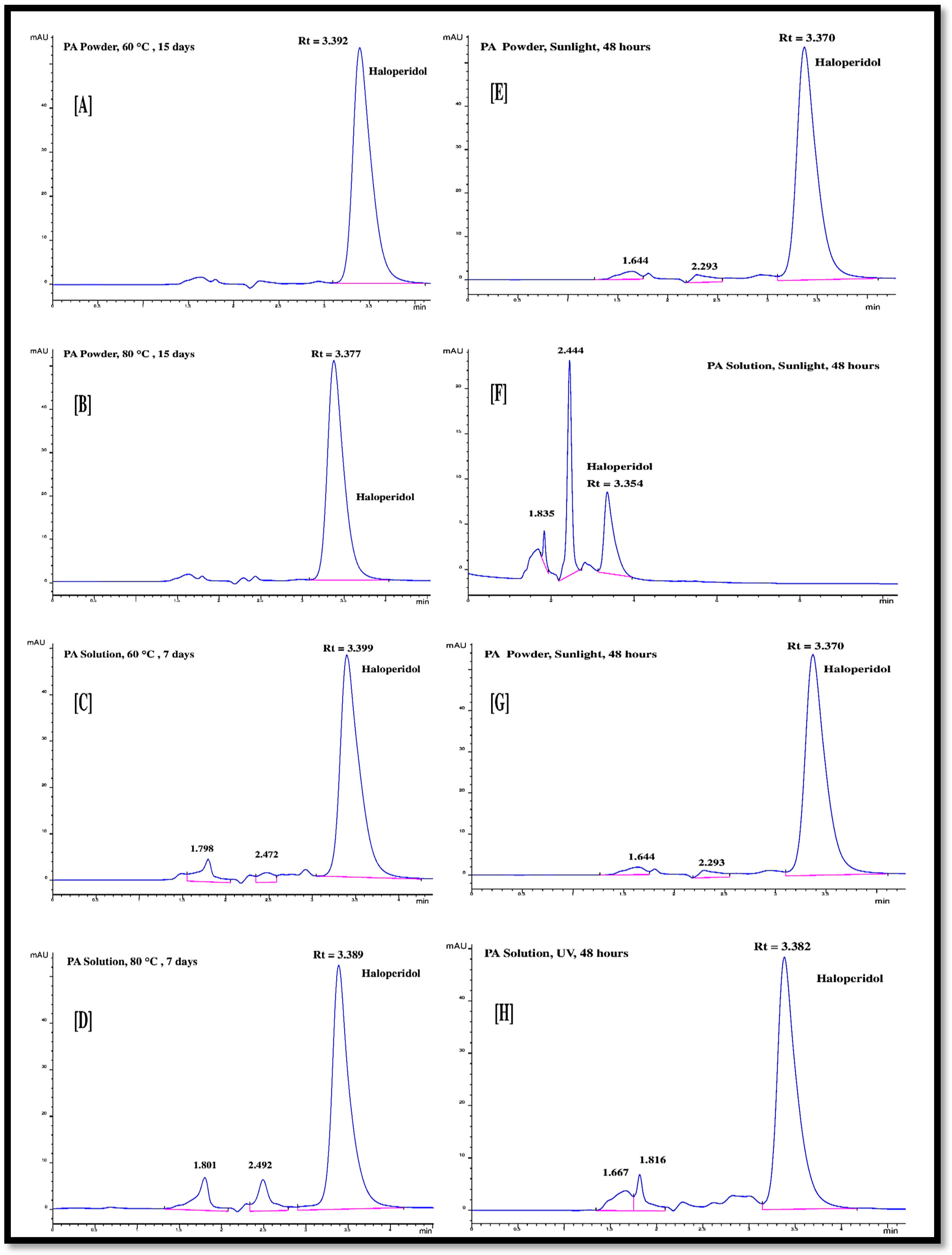
Thermal degradation of powder, as well as solution samples of haloperidol, was performed at temperatures of 60 °C and 80 °C. The powder samples were exposed to the selected temperature for 15 days, and the liquid samples were exposed for seven days. The post-degradation samples were analyzed through the proposed RP-HPLC method. The chromatograms of post-thermal degradation samples of haloperidol in powder and liquid solution forms are shown in Figure 6A–D. The powder samples of haloperidol are quite stable up to thermal stress of 80 °C. No degradation peaks were observed, and only one peak appeared at a retention time of 3.3 min in the chromatogram (as shown in Figure 6A,B), which belongs to undegraded haloperidol molecule. However, the liquid solution form of haloperidol exposed to thermal degradation was unstable. The RP-HPLC analysis results showed 10% and 17% degradation after thermal stress of 60 °C and 80 °C, respectively. Two secondary peaks appeared in the chromatogram before the haloperidol peak. The degradation product peaks were observed at about 1.8 min and 2.5 min retention times, as shown in Figure 6C,D. The degradation percentage calculated through the chromatogram area of each peak is reported in Table 8. The stability of the haloperidol molecules decreased with the increase in thermal stress temperature and exposure time [20,21]. However, the thermal stability of haloperidol molecules at room temperature has been established in previous studies [24,28,37].

Figure 6.
Forced degradation of haloperidol through (A) thermal degradation of active principal (PA) powder at 60 °C in 15 days; (B) thermal degradation of PA powder at 80 °C in 15 days; (C) thermal degradation of PA solution at 60 °C in 7 days; (D) thermal degradation of PA solution at 80 °C in 7 days; (E) photolytic degradation of PA powder in the presence of sunlight in 48 h; (F) photolytic degradation of PA solution in the presence of sunlight in 48 h (G) photolytic degradation of PA powder in the presence of UV light in 48 h; (H) photolytic degradation of PA solution in presence of UV light in 48 h.
3.4.4. Photolytic Degradation
The photolytic degradation of powder and liquid solution samples of haloperidol was conducted in the presence of UV light and natural sunlight with an exposure time of 48 h. The exposed samples were analyzed by the proposed RP-HPLC method. The powder sample was found stable under photolytic stress for 48 h, no degradation was observed under UV light as shown in Figure 6G and only 6% degradation was calculated through the peak area evaluation of sunlight-exposed samples (shown in Figure 6E). The liquid solution samples were highly susceptible to degradation under photolytic stress. The maximum degradation (57%) was observed when the liquid solution of haloperidol was exposed to sunlight for 48 h. The degradation is illustrated in Figure 6F, which vividly shows the smaller area chromatogram peak at a retention time 3.3 min corresponding to haloperidol. The degraded molecules peak appeared at the retention time of 2.4 min and 1.8 min with large peak area. In pure UV light, nearly 13% of the haloperidol solution sample was degraded. The minor degradation peaks appeared at the retention time of 1.6 and 1.8 min. The degradation percentage calculated from the peak area of the chromatograms is reported in Table 8.
In summary, in dry powder form, haloperidol molecules remain mostly stable under thermal and photolytic stress conditions and only slightly degraded (~6%) in the presence of sunlight. Haloperidol molecule in liquid solution is only stable against oxidative stress. It degrades partially under hydrolysis (~15–24%) and thermal stress (~10–16%). The liquid solution sample was highly unstable against the photolytic stress induced by sunlight, with 57% degradation within 48 h of exposure time. This justifies the choice of the amber glass bottle for the primary packaging of the liquid dosage form of this compound.
4. Discussion
A novel RP-HPLC method using an isocratic mobile phase (90:10 methanol/phosphate buffer, pH 9.8) was developed for the analysis of haloperidol. The method was validated based on regulatory pharmaceutical standards [42], demonstrating linearity, precision, sensitivity, and specificity. Linearity was confirmed over a haloperidol concentration range of 1–50 µg/mL, with a correlation coefficient of 0.999 and a mean relative standard deviation (RSD) of less than 2%. This method was successfully used to determine the dosage of commercial haloperidol liquid drug samples (2 mg/mL) without requiring any extraction or pre-treatment.
The RP-HPLC method was also applied to monitor the forced degradation of haloperidol under various physico-chemical stress conditions, including hydrolytic, oxidative, thermal, and photolytic stresses. It effectively identified and separated haloperidol degradation products in the chromatogram, with clear and distinct peaks. The forced degradation study showed that haloperidol liquid solutions were highly susceptible to hydrolytic, thermal, and photolytic degradation, with the highest degradation (57%) occurring after 48 h of sunlight exposure. However, the liquid solution remained stable under oxidative stress in up to 3% hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) at temperatures below 60 °C for seven days. In contrast, haloperidol in its dry powdered form was significantly more stable, with only 6% degradation observed after 48 h of sunlight exposure under photolytic stress. These findings highlight the importance of selecting the most stable form of haloperidol to minimize degradation and ensure drug efficacy during storage and use.
5. Conclusions
This study developed and validated an innovative chromatographic method (RP-HPLC) using an isocratic mobile phase composed of methanol and phosphate buffer (pH 9.8) in a 90:10 ratio. The method proved reliable, precise, sensitive, and compliant with pharmaceutical validation standards [42], enabling the effective analysis of haloperidol in commercial liquid formulations without requiring complex pre-treatment. Forced degradation studies revealed high stability of haloperidol in its powdered form under thermal and photolytic stress conditions, with a maximum degradation of only 6% after sunlight exposure. In contrast, the liquid form was more sensitive, showing significant degradation of 57% after 48 h of sunlight exposure. The stability of the liquid solution under oxidative stress was confirmed, even with hydrogen peroxide concentrations up to 3%. These findings highlight the importance of formulation and packaging in ensuring haloperidol stability. The proposed method provides a robust tool for the quality control of pharmaceutical products and can serve as an alternative to existing methods due to its simplicity and efficiency. It also opens new avenues for the rapid and accurate analysis of other pharmaceutical compounds under similar conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.D., R.M., M.D., M.H., Z.A.M., H.T., O.B., J.Z. and A.A. (Abdeltif Amrane); Data curation, K.D.; Formal analysis, K.D., R.M., M.D., M.H., Z.A.M., M.S.O., A.A. (Ahmad Ali), J.Z. and A.A. (Abdeltif Amrane); Funding acquisition, M.S.O. and A.A. (Ahmad Ali); Investigation, K.D., R.M., M.D., S.L., M.H., Z.A.M., H.T., O.B., M.S.O., J.Z. and A.A. (Abdeltif Amrane); Methodology, K.D., R.M., M.D., S.L., M.H., Z.A.M., H.T., O.B., M.S.O., A.A. (Ahmad Ali), J.Z. and A.A. (Abdeltif Amrane); Project administration, H.T., M.S.O., A.A. (Ahmad Ali), J.Z. and A.A. (Abdeltif Amrane); Resources, K.D., M.D., M.H., Z.A.M., H.T., M.S.O., A.A. (Ahmad Ali), J.Z. and A.A. (Abdeltif Amrane); Software, K.D., R.M., S.L., M.H., H.T. and O.B.; Supervision, R.M., J.Z. and A.A. (Abdeltif Amrane); Validation, K.D., R.M., M.D., M.H., Z.A.M., H.T., O.B., M.S.O., A.A. (Ahmad Ali), J.Z. and A.A. (Abdeltif Amrane); Visualization, K.D., R.M., M.D., S.L., Z.A.M., H.T., O.B., M.S.O., A.A. (Ahmad Ali), J.Z. and A.A. (Abdeltif Amrane); Writing—original draft, K.D.; Writing—review and editing, R.M., M.D., S.L., M.H., Z.A.M., H.T., O.B., M.S.O., A.A. (Ahmad Ali), J.Z. and A.A. (Abdeltif Amrane). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, Researchers Supporting Project Number (RSPD2025R710).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to extend their sincere gratitude to the Center for Scientific and Technical Research in Physical and Chemical Analysis (CRAPCC) in Algeria for allowing to use instruments for this work. The authors also extends thanks to the Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM), Penang, Malaysia, and the University of Science and Technology Houari Boumediene, Algiers-Bab Ezzouar, Algeria, for providing the facilities and resources used in this research work. The authors extend their appreciation to King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, for funding this work through Researchers Supporting Project Number (RSPD2025R710).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tardy, M.; Huhn, M.; Kissling, W.; Engel, R.R.; Leucht, S. Haloperidol versus low-potency first-generation antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD009268. [Google Scholar]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Sayeeda, Z.; et al. DrugBank 5.0: A major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J. PubMed 2.0. Med. Ref. Serv. Q. 2020, 39, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinCalc. ClinCalc DrugStats Database. 2020. Available online: https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/ (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Piggott, T.; Moja, L.; Huttner, B.; Okwen, P.; Raviglione, M.; Kredo, T.; Schünemann, H. WHO Model list of essential medicines: Visions for the future. Bull. World Health Organ. 2024, 102, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prommer, E. Role of haloperidol in palliative medicine: An update. Am. J. Hosp. Palliat. Med. 2012, 29, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafi, I.; Arafat, S.; Al Zayed, L.; Sukkar, M.; Albeirakdar, A.; Krayem, D.; Essali, A. Haloperidol (route of administration) for people with schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 2017, CD012833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.S.; Nalini, C. Analytical determinations of haloperidol and its combinations in pharmaceutical dosage forms and biological matrices. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2021, 44, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharmacopeial, U.S. The United States Pharmacopeia 2018: USP 41. In The National Formulary; American Pharmaceutical Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, N.; Sameen, S.; Kashif, M. Spectroscopic study on the interaction of haloperidol and 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine and its application for the quantification in drug formulations. Anal. Chem. Lett. 2016, 6, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Sara, U. Development and validation of UV spectrophotometric method for the estimation of haloperidol. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2014, 4, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The British Pharmacopoeia. The British Pharmacopoeia Commission Secretariat of the Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA); TSO (The Stationery Office): London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, N.; Khatoon, A.; Rahman, H. Studies on the development of spectrophotometric method for the determination of haloperidol in pharmaceutical preparations. Quim. Nova 2012, 35, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambamurty Raju, S.; Raju, P.N.; Ashok Babu, R.; Anjani Devi, A. Validated UV and Visible Spectrophotometric Methods for the quantification of Haloperidol in Pharmaceutical dosage forms. Actapharmica 2015, 2, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Wate, S.; Borkar, A. Simultaneous spectrophotometric estimation of haloperidol and trihexyphenidyl in tablets. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 72, 265. [Google Scholar]
- Ouanes, S.; Kallel, M.; Trabelsi, H.; Safta, F.; Bouzouita, K. Zero-crossing derivative spectrophotometry for the determination of haloperidol in presence of parabens. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1998, 17, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maślanka, A.; Krzek, J.; Stolarczyk, M.; Walczak, M.; Głogowska, A. Stability studies of clonazepam, diazepam, haloperidol, and doxepin with diverse polarities in an acidic environment. J. AOAC Int. 2011, 94, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennickent, S.; Pino, L.; Vega, M.; de Diego, M. Chemical stability of haloperidol injection by high performance thin-layer chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panaggio, A.; Greene, D.S. High Pressure Liquid Chromatographic Determination of Haloperidol Stability. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1983, 9, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driouich, R.; Trabelsi, H.; Bouzouita, K.A. Stability—Indicating assay for haloperidol syrup by high-performance liquid chromatography. Chromatographia 2001, 53, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, H.; Bouabdallah, S.; Bouzouita, K.; Safta, F. Determination and degradation study of haloperidol by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 29, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monser, L.; Trabelsi, H. A rapid LC method for the determination of haloperidol and its degradation products in pharmaceuticals using a porous graphitic carbon column. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2003, 26, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Fast Determination of Haloperidol in Pharmaceutical Preparations Using HPLC with a Monolithic Silica Column. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2005, 28, 3169–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhavi, R.; Patel, J. Development and validation of stability indicating assay method of haloperidol in oral solution. JPSBR 2014, 4, 319–329. [Google Scholar]
- Goud, E.S.; Reddy, V.K.; Krishnadevaraya, S. Development and validation of a reverse-phase liquid chromatographic method for assay and related substances of haloperidol for 50 mg/mL and 100 mg/mL. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 5, 389–396. [Google Scholar]
- Demoen, P.J. Properties and analysis of haloperidol and its dosage forms. J. Pharm. Sci. 1961, 50, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicki, C.A.; Ko, C.Y. Haloperidol. Anal. Profiles Drug Subst. 1981, 9, 341–369. [Google Scholar]
- Ölçer, M.; Hakyemez, G. Investigations of some physicochemical properties of haloperidol which may affect its activity. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 1988, 13, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- (EDQM), an institution of the Council of Europe. European pharmacopoeia. Eur. Dir. Qual. Med. Health Care Counc. Eur. (EDQM) 2017, 9, 3104–3105. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, R.C.; Sheskey, P.; Quinn, M. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients; Libros Digitales-Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. European Pharmacopoeia, 5th, ed.; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology Q2 (R1). Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/9781118971147.ch5 (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Guidelines for Drug Stability and Stability Testing. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/117092767/Guidelines_for_Drug_Stability_and_Stability_Testing9 (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- European Medical Agency. Photostability Testing of New Active Substances and Medicinal Products, ICH Topic Q1B; European Medical Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Trawiński, J.; Skibiński, R. Studies on photodegradation process of psychotropic drugs: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 1152–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djilali, K.; Maachi, R.; Mesbah, Z.A.; Nasrallah, N.; Touzout, N.; Tahraoui, H.; Zhang, J.; Amrane, A. Breaking Barriers in Pharmaceutical Analysis: Streamlined UV Spectrometric Quantification and Stability Profiling of Haloperidol and Methylparaben in Liquid Formulations. Anal. Biochem. 2024, 695, 115632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djilali, K.; Maachi, R.; Tahraoui, H.; Mesbah, Z.A.; Amrane, A. Advancing Thermal Stability Analysis of Haloperidol: Integrative Approaches and Optimization Strategies for Enhanced Pharmaceutical Formulations. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1315, 138870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Dubey, B.; Basedia, D.; Dhakar, S.; Ahirwar, M.; Jain, P. Comparison of RP-HPLC and UV Spectrophotometric Methods for Estimation of Haloperidol in Pure and Pharmaceutical Formulation. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2018, 8, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovska, R.; Dimitrovska, A. Use of chemometrics for development and validation of an RP-HPLC method for simultaneous determination of haloperidol and related compounds. Acta Pharm. 2008, 58, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.N. Basic statistical methods for analytical chemistry. Part 2. Calibration and regression methods. A review. Analyst 1991, 116, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöckl, D.; Dewitte, K.; Thienpont, L.M. Validity of linear regression in method comparison studies: Is it limited by the statistical model or the quality of the analytical input data? Clin. Chem. 1998, 44, 2340–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartwright, A.C. The British Pharmacopoeia, 1864 to 2014: Medicines, International Standards and The State; Routledge: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vallender, M.; Gaur, R.; Azizi, M.; Gan, J.; Hansal, P.; Harper, K.; Mannan, R.; Panchal, A.; Patel, K.; Rana, J. British Pharmacopoeia 2009; The Stationery Office: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Raggi, M.; Casamenti, G.; Mandrioli, R.; Sabbioni, C.; Volterra, V. A rapid LC method for the identification and determination of CNS drugs in pharmaceutical formulations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 23, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Stewart, J. HPLC analysis of haloperidol and its related compound in the drug substance and a tablet dosage form using a non-porous silica octadecylsilane column. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 1999, 22, 1857–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blessy, M.; Patel, R.D.; Prajapati, P.N.; Agrawal, Y.K. Development of forced degradation and stability indicating studies of drugs—A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2014, 4, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).