Aristolochic Acid I Adsorption onto Activated Carbon: Kinetics, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Reagents and Chemicals
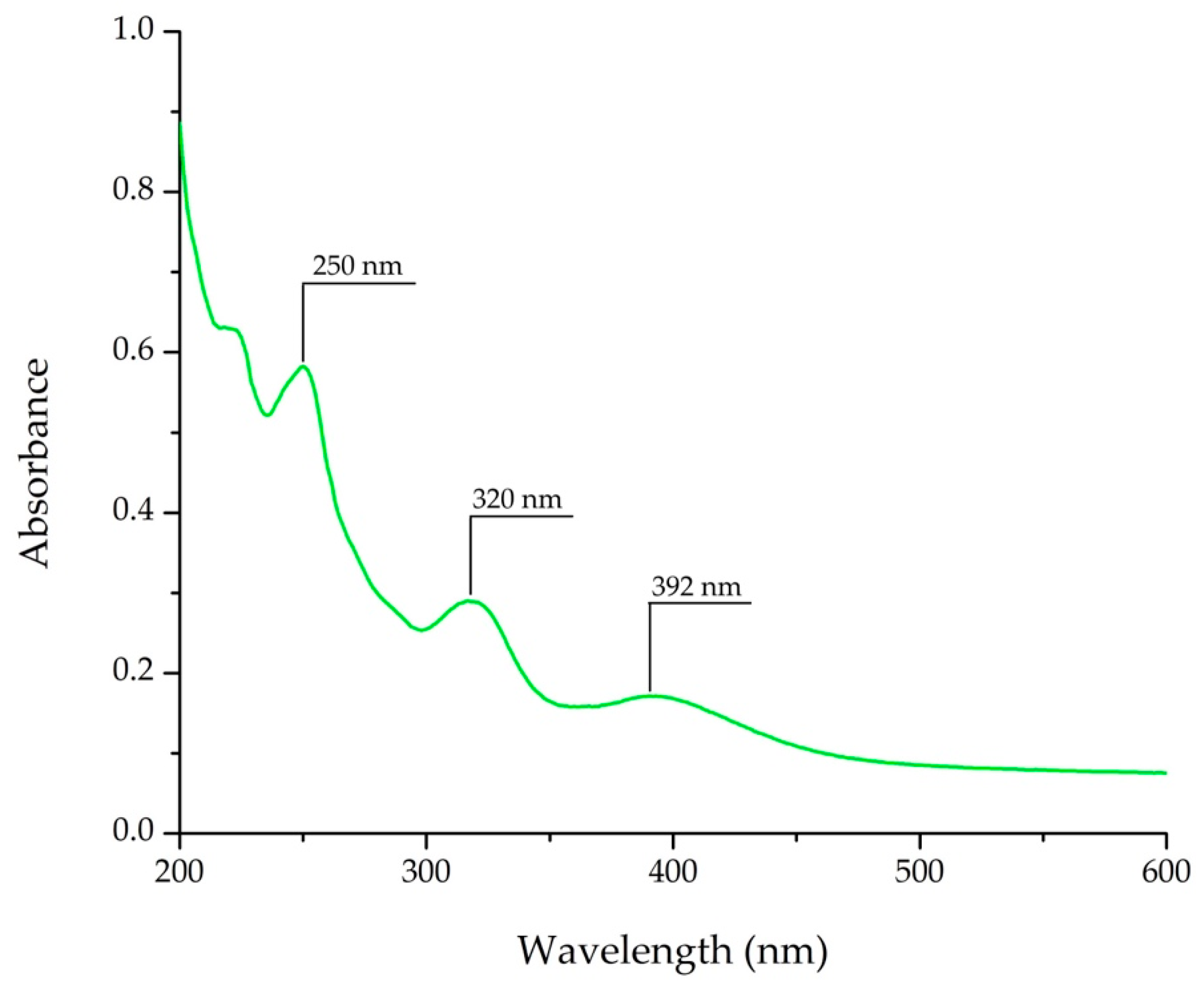
2.3. AAI Detection
2.4. Adsorption Studies
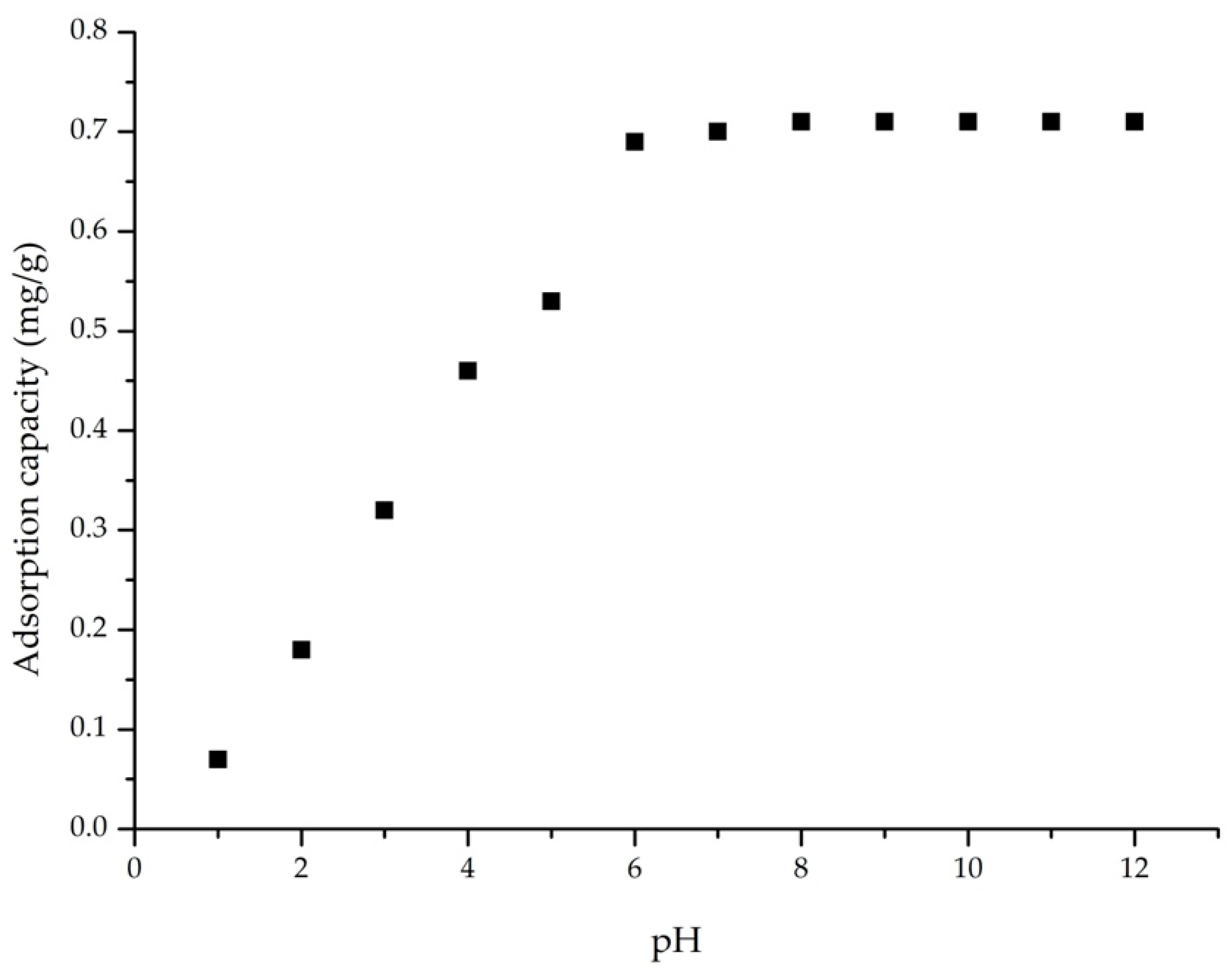
2.4.1. Influence of pH
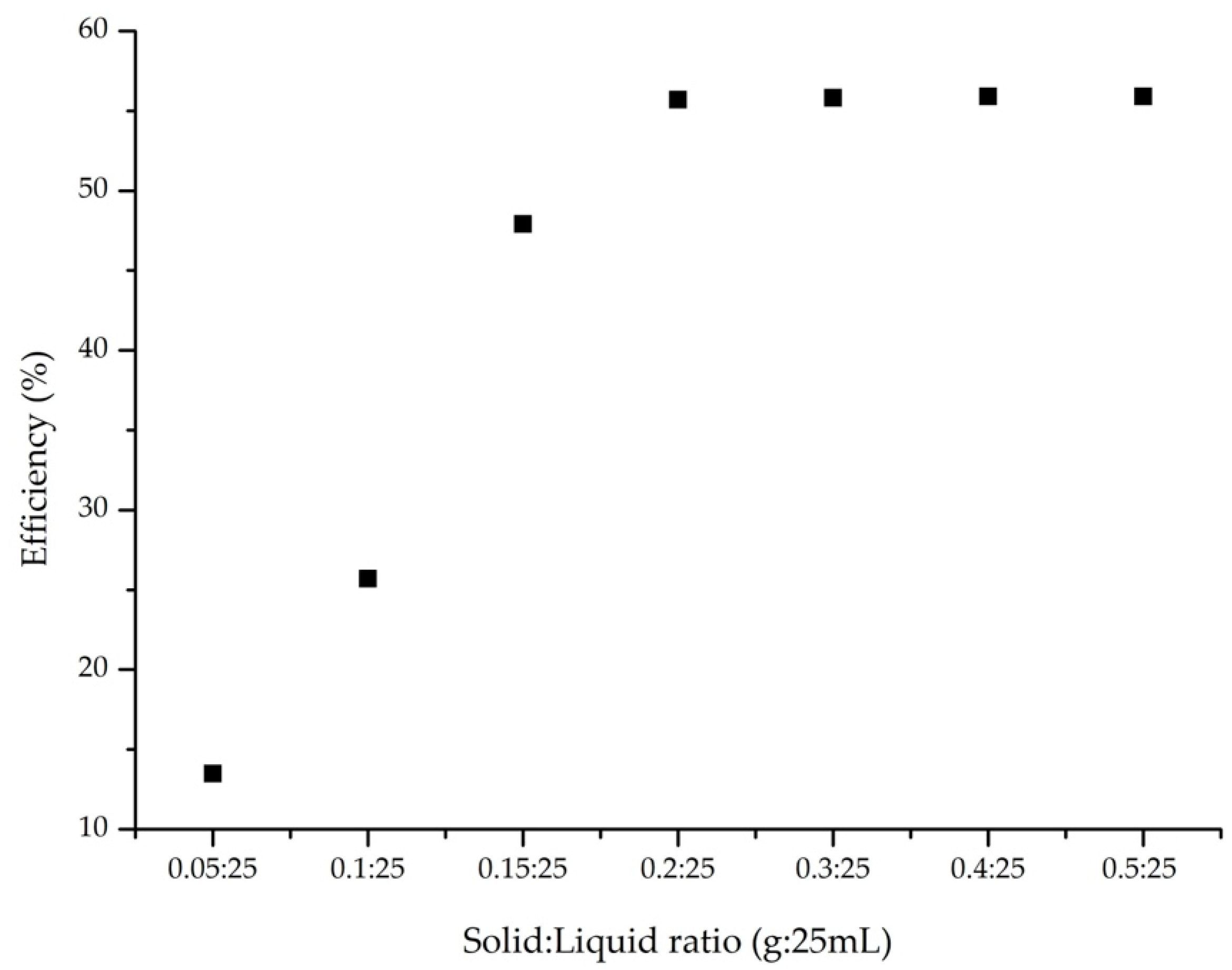
2.4.2. Influence of Solid/Liquid Ratio
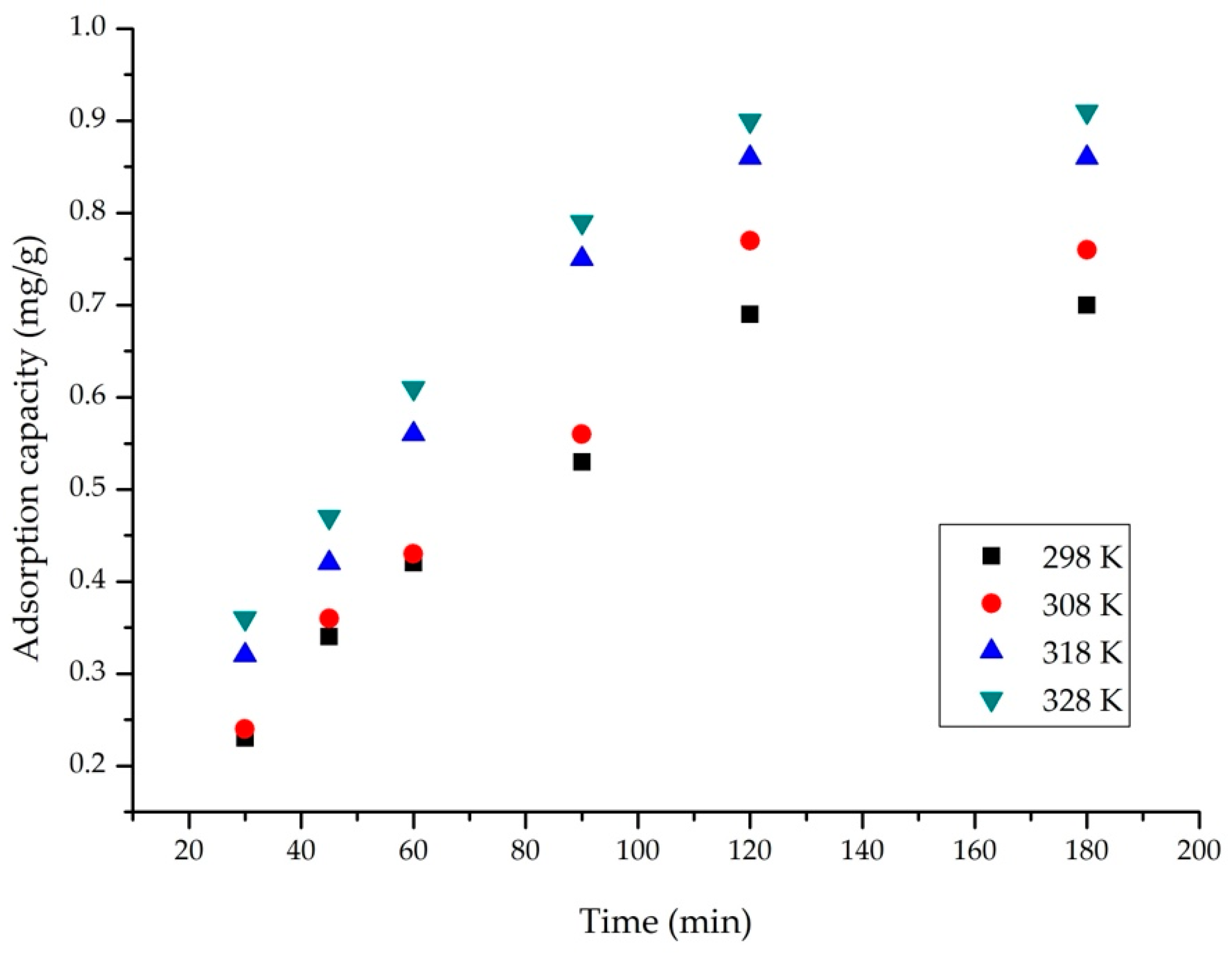
2.4.3. Influence of Temperature and Contact Time
2.4.4. Influence of the Initial Concentration
2.5. Kinetic Studies
2.6. Thermodynamic Studies
2.7. Equilibrium Studies
3. Results
3.1. Detection of AAI
3.2. Adsorption Studies and Kinetic, Thermodynamic, and Equilibrium Studies
3.2.1. pH Influence on the Adsorption Process
3.2.2. Influence of Solid/Liquid Ratio
3.2.3. Influence of Contact Time and Temperature
3.2.4. Kinetic Studies
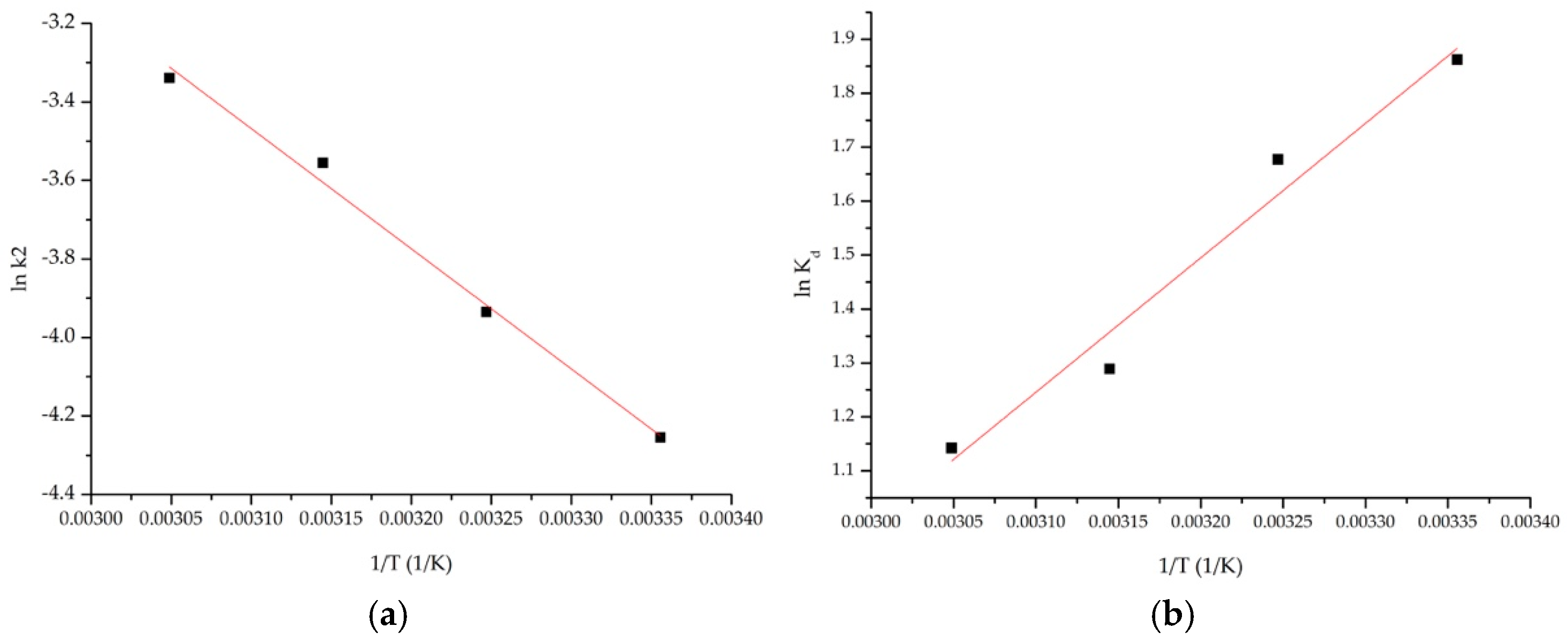
3.2.5. Thermodynamics Studies
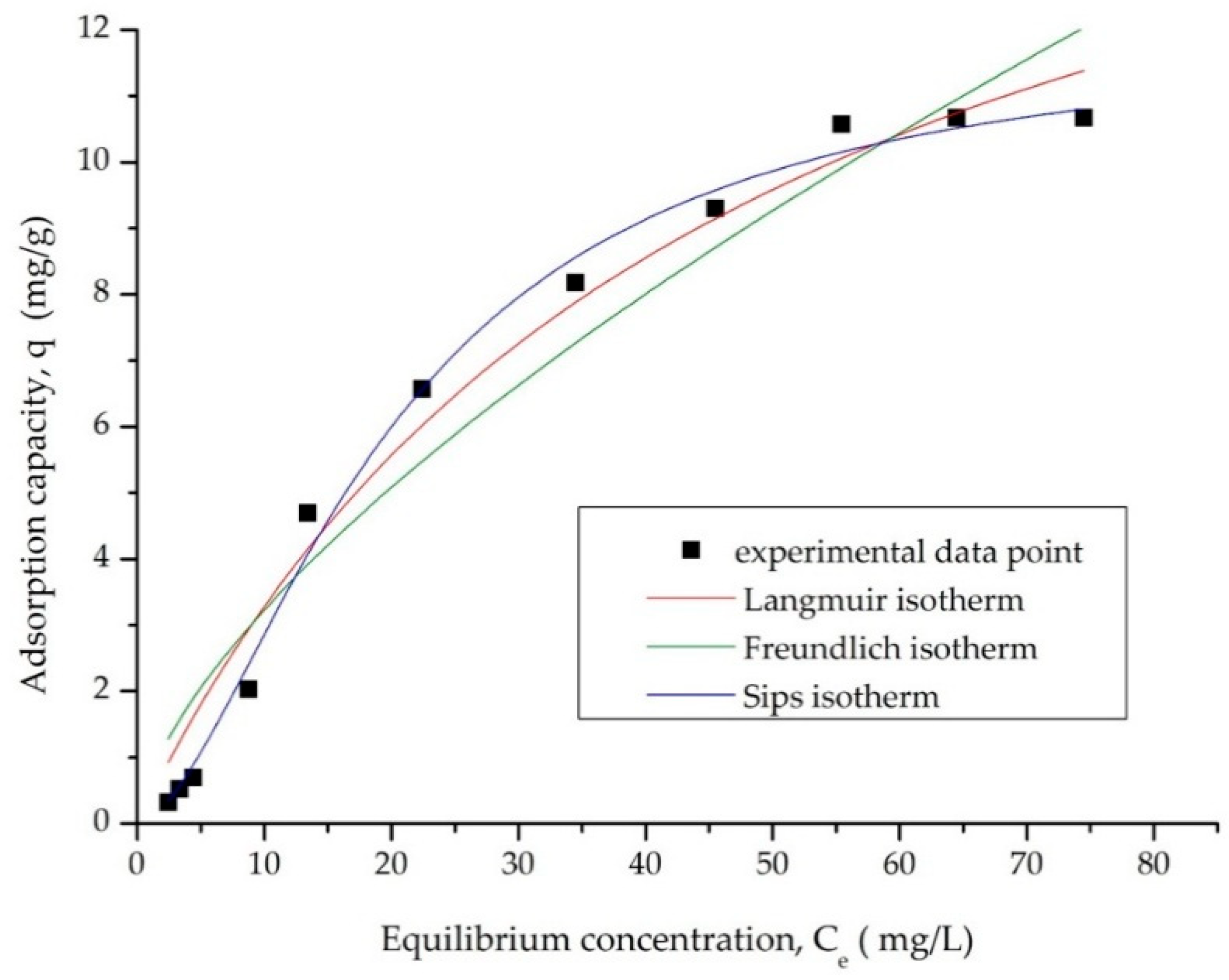
3.2.6. Equilibrium Studies—Adsorption Isotherms
4. Discussion
Strengths, Limitations, and Future Perspectives of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | Aristolochic acid |
| AAs | Aristolochic acids |
| AAI | Aristolochic acid I |
| AC | Activated carbon |
| AAN | Aristolochic Acid Nephropathy |
| BEN | Balkan Endemic Nephropathy |
| CHN | Chinese Herbal Nephropathy |
| CMC | Carbon microcoils |
| CNT | Carbon nanotubes |
| EME | Electromembrane extraction |
| IND | Indomethacin |
| MIP | Molecularly imprinted polymers |
| MOF | Metal–Organic Frameworks |
| S:L | Solid/Liquid |
| UV-VIS | Ultraviolet–visible |
References
- Ioset, J.-R.; Raoelison, G.E.; Hostettmann, K. Detection of Aristolochic Acid in Chinese Phytomedicines and Dietary Supplements Used as Slimming Regimens. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.W.T.; Poon, S.L.; Huang, M.N.; Lim, J.Q.; Boot, A.; Yu, W.; Suzuki, Y.; Thangaraju, S.; Ng, C.C.Y.; Tan, P.; et al. Aristolochic Acids and Their Derivatives Are Widely Implicated in Liver Cancers in Taiwan and throughout Asia. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan6446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Han, J.; Li, W.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y. Detection and Removal of Aristolochic Acid in Natural Plants, Pharmaceuticals, and Environmental and Biological Samples: A Review. Molecules 2023, 29, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, D.; Shi, Q.; Ren, G.; Liu, C. Microbial Degradation of Aristolochic Acid I by Endophytic Fungus A.h-Fs-1 of Asarum Heterotropoides. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 917117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Tian, M.; Row, K.H.; Yan, X.; Xiao, W. Isolation of Aristolochic Acid I from Herbal Plant Using Molecular Imprinted Polymer Composited Ionic Liquid-based Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-67. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 3047–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Han, Y.; Bai, L.; Yan, H. On-Line Enrichment and Determination of Aristolochic Acid in Medicinal Plants Using a MOF-Based Composite Monolith as Adsorbent. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1159, 122343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, M.; Dai, L. Interaction between Chlortetracycline and Calcium-Rich Biochar: Enhanced Removal by Adsorption Coupled with Flocculation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Chen, G.; Wang, L.; Cui, X.; Luo, Z.; Jing, W.; Chang, C.; Zeng, A.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Q. Metal-Organic Framework Grafted with Melamine for the Selective Recognition and Miniaturized Solid Phase Extraction of Aristolochic Acid I from Traditional Chinese Medicine. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1647, 462155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Gao, J.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; He, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes for Highly Selective Removal of Aristolochic Acid. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1602, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Huang, C.; Shen, X. Electromembrane Extraction of Aristolochic Acids: New Insights in Separation of Bioactive Ingredients of Traditional Chinese Medicines. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1608, 460424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhou, G.; Jiang, X.; Wang, X. QuEChERS Pretreatment Combined with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Determination of Aristolochic Acids I and II in Chinese Herbal Patent Medicines. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 25319–25324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaclavik, L.; Krynitsky, A.J.; Rader, J.I. Quantification of Aristolochic Acids I and II in Herbal Dietary Supplements by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Multistage Fragmentation Mass Spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2014, 31, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Chow, A.H.L.; Wang, Y.; Tong, H.H.Y.; Zheng, Y. Removal of Toxic Aristolochic Acid Components from Aristolochia Plants by Supercritical Fluid Extraction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 72, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.-K.; Tung, K.-K.; Pavlović, N.M.; Chan, W. Remediation of Aristolochic Acid-Contaminated Soil by an Effective Advanced Oxidation Process. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-Khah, A.; Ansari, R. Activated Charcoal: Preparation, Characterization and Applications: A Review Article. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2009, 1, 859–864. [Google Scholar]
- Mladin, G.; Ciopec, M.; Negrea, A.; Duteanu, N.; Negrea, P.; Svera, P.; Ianăşi, C. Selenite Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Silica–Iron Oxide Nanocomposite Adsorbents. Gels 2023, 9, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.J.; Ashiq, M.N. Adsorption of Dyes from Aqueous Solutions on Activated Charcoal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 139, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihăilescu, M.; Negrea, A.; Ciopec, M.; Davidescu, C.M.; Negrea, P.; Duţeanu, N.; Rusu, G. Gold (III) Adsorption from Dilute Waste Solutions onto Amberlite XAD7 Resin Modified with L-Glutamic Acid. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. About the Theory of So-Called Adsorption of Solution Substances. K. Sven. Vetenskapsakademiens Handl. 1898, 24, 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y. Review of Second-Order Models for Adsorption Systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, D.D. Adsorption Analysis: Equilibria and Kinetics (with CD Containing Computer MATLAB Programs); World Scientific: Singapore, 1998; ISBN 978-1-78326-224-3. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, I. The Adsorption of Gases on Plane Surfaces of Glass, Mica and Platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febrianto, J.; Kosasih, A.N.; Sunarso, J.; Ju, Y.-H.; Indraswati, N.; Ismadji, S. Equilibrium and Kinetic Studies in Adsorption of Heavy Metals Using Biosorbent: A Summary of Recent Studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 616–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Over the Adsorption in Solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Sips, R. On the Structure of a Catalyst Surface. J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khaiary, M.I.; Malash, G.F. Common Data Analysis Errors in Batch Adsorption Studies. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 105, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the Modeling of Adsorption Isotherm Systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, B.D.; Srivastava, A.; Gupta, V.; Tandon, P.; Jain, S. Spectroscopic and Quantum Chemical Study of an Alkaloid Aristolochic Acid I. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 116, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Huang, H.; Xue, W.; Yao, X.; Jin, J. Interaction Studies of Aristolochic Acid I with Human Serum Albumin and the Binding Site of Aristolochic Acid I in Subdomain IIA. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, F.; Cheng, W.; Wang, J.; Ma, J. Adsorption Equilibrium and Kinetics of the Removal of Ammoniacal Nitrogen by Zeolite X/Activated Carbon Composite Synthesized from Elutrilithe. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 1936829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, H.; Salahandish, M.; Sharifi, H.; Mohammadzadehasl, N. Dependence of Extinction Cross-Section, Absorption and Surface Plasmon Resonance of Nanoparticle Surface Size and Concentration of Silica@Gold Nanoparticles. Biomed. Mater. Devices 2025, 3, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oss, C.J.; Good, R.J.; Chaudhury, M.K. The Role of van Der Waals Forces and Hydrogen Bonds in “Hydrophobic Interactions” between Biopolymers and Low Energy Surfaces. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 1986, 111, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehiomogue, P.; Ahuchaogu, I.I.; Ahaneku, I.E. Review of Adsorption Isotherms Models. Acta Tech. Corviniensis Bull. Eng. 2021, 14, 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, H.; Fan, Y.; Mao, X.; Guo, L.; Yan, A.; Guo, X.; Wan, Y.; Wan, H. Thermosensitive and Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Selective Recognition and Extraction of Aristolochic Acid I. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Deng, Q.; Wang, S. Dummy Molecularly Imprinted Silica Materials for Effective Removal of Aristolochic Acid I from Kaempfer Dutchmanspipe Root Extract. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.-H.; Shu, H.; Xu, X.-Y.; Guo, P.-Q.; Liu, R.-L.; Luo, Z.-M.; Chang, C.; Fu, Q. Combined Magnetic Porous Molecularly Imprinted Polymers and Deep Eutectic Solvents for Efficient and Selective Extraction of Aristolochic Acid I and II from Rat Urine. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 97, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Chen, G.; Wang, L.; Cui, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Chang, C.; Guo, Q.; Luo, Z.; Fu, Q. Adenine-Coated Magnetic Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes for the Selective Extraction of Aristolochic Acids Based on Multiple Interactions. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1627, 461382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.-J.; Zhang, J.-B.; Cao, X.-J.; Lu, J. Ionizable Copolymer Functionalized Magnetic Nanocomposite as an Adsorbent for Boosting the Extraction Selectivity of Aristolochic Acids. J. Food Drug Anal. 2024, 32, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Wang, S.; Cui, T.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, H.; Li, X. Sustainable Defect-Engineered Imprinted UiO-66-NH2 for Selective Removal of Aristolochic Acids from Medicinal Herbs. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 11113–11127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Ge, Y.; Xu, X.-Y.; Guo, P.-Q.; Luo, Z.-M.; Du, W.; Chang, C.; Liu, R.-L.; Fu, Q. Hybrid-Type Carbon Microcoil-Chitosan Composite for Selective Extraction of Aristolochic Acid I from Aristolochiaceae Medicinal Plants. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1561, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Jin, R.; Luo, C.; Deng, C.; Hu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Song, G. Fast Determination of Aristolochic Acid I (AAI) in Traditional Chinese Medicine Soup with Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1609, 460455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Bai, Q.; Zheng, C.; Sun, N.; Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Hu, F.; Lu, T. Application of Metal-Organic Framework in Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetes. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
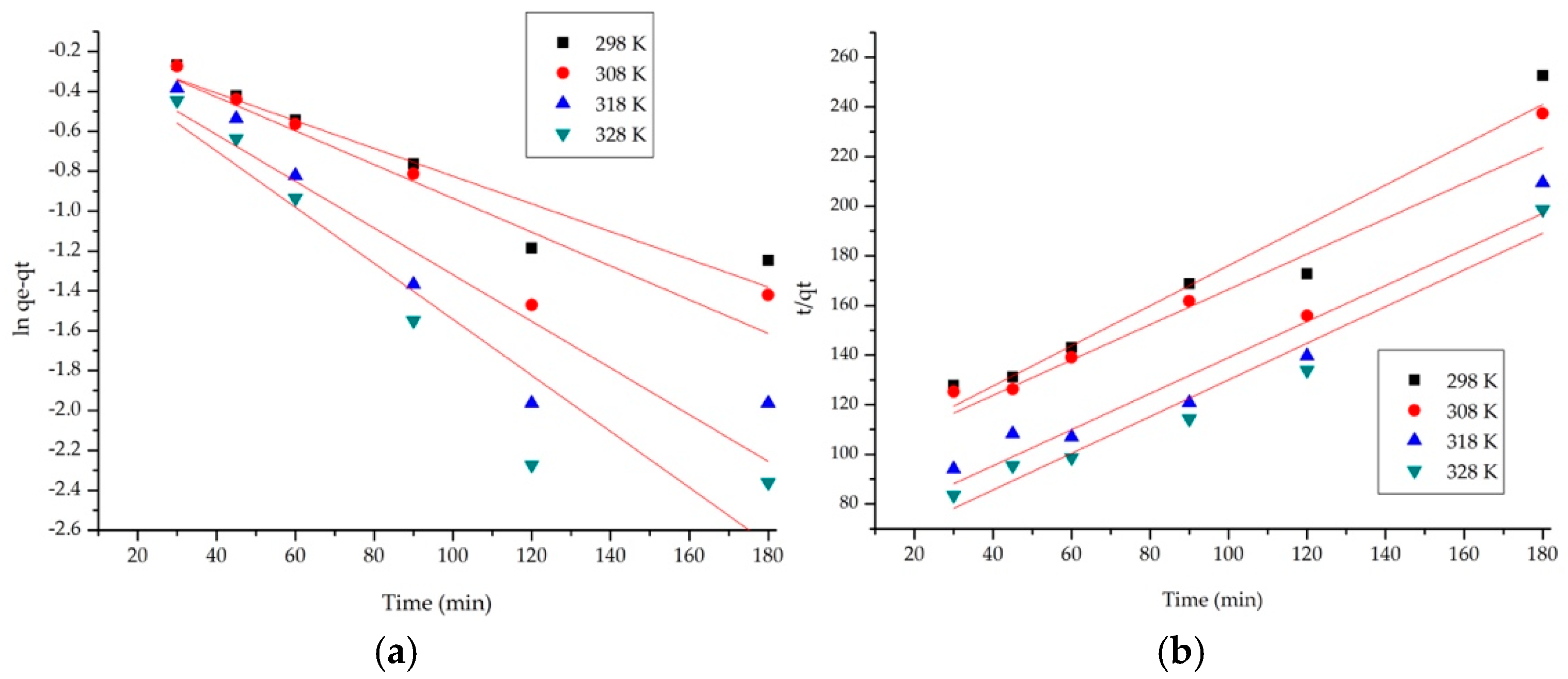
| Pseudo-First-Order Model (Lagergren Model) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (K) | qe, exp (mg·g−1) | k1 (min−1) | qe, calc (mg·g−1) | R2 |
| 298 | 0.69 | 0.0069 | 1.14 | 0.9109 |
| 308 | 0.77 | 0.0081 | 1.10 | 0.8618 |
| 318 | 0.86 | 0.0117 | 1.16 | 0.8710 |
| 328 | 0.89 | 0.0141 | 1.15 | 0.9750 |
| Pseudo-Second-Order Model (Ho and McKay Model) | ||||
| Temperature (K) | qe, exp (mg·g−1) | k2 (min−1) | qe, calc (mg·g−1) | R2 |
| 298 | 0.69 | 0.0142 | 1.16 | 0.9805 |
| 308 | 0.77 | 0.0195 | 1.36 | 0.9812 |
| 318 | 0.86 | 0.0285 | 1.37 | 0.9899 |
| 328 | 0.89 | 0.0354 | 1.41 | 0.9898 |
| ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔS° (J/mol∙K) | ΔG° (kJ/mol) | R2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 K | 308 K | 318 K | 328 K | |||
| 20.70 | 58.83 | −16.02 | −16.55 | −17.09 | −17.63 | 0.9881 |
| Langmuir Isotherm | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| qm, exp (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | qL (mg/g) | R2 |
| 0.67 | 0.0216 | 18.45 | 0.9763 |
| Freundlich Isotherm | |||
| KF (mg/g) | 1/nF | R2 | |
| 0.713 | 0.65 | 0.9430 | |
| Sips Isotherm | |||
| KS | qS (mg/g) | 1/nS | R2 |
| 0.006 | 11.9 | 0.60 | 0.9933 |
| Absorbents | Maximum Adsorption Capacities | Ref |
|---|---|---|
| Molecularly imprinted polymers (TMNIPs) | 2.60 mg/g | [34] |
| Dummy molecularly imprinted silica material (MIS) | 8.12 mg/g | [35] |
| Molecularly imprinted polymers (TMMIPs) | 8.51 mg/g | [34] |
| Magnetic mesoporous carbon (MMC@MIPs) | 8.65 mg/g | [36] |
| Molecular carbon nanotubes (MCNTs@AAI-MIPs) | 18.54 mg/g | [9] |
| Magnetic nanocomposite (CNT/Fe3O4@SiO2-AzI) | 24.5 mg/g | [37] |
| Magnetic nanocomposite (MNs@SiO2T-DvbDam) | 37.30 mg/g | [38] |
| Metal–organic framework (UiO-66-NH2) | 42.74 mg/g | [39] |
| Chitosan-modified carbon microcoils (CMCs@CS) | 77.72 mg/g | [40] |
| Magnetic solid phase extraction (Fe3O4@SiO2-TPM@StVp) | n.d.a | [41] |
| AC | 10.67 mg/g | This paper |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pricop, M.-A.; Negrea, A.; Ciopec, M.; Pascu, I.B.; Oprean, C.; Lukinich-Gruia, A.T.; Cristea, I.-M.; Ivan, A.; Păunescu, V.; Tatu, C.A. Aristolochic Acid I Adsorption onto Activated Carbon: Kinetics, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies. Processes 2025, 13, 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113397
Pricop M-A, Negrea A, Ciopec M, Pascu IB, Oprean C, Lukinich-Gruia AT, Cristea I-M, Ivan A, Păunescu V, Tatu CA. Aristolochic Acid I Adsorption onto Activated Carbon: Kinetics, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies. Processes. 2025; 13(11):3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113397
Chicago/Turabian StylePricop, Maria-Alexandra, Adina Negrea, Mihaela Ciopec, Ioan Bogdan Pascu, Camelia Oprean, Alexandra Teodora Lukinich-Gruia, Iustina-Mirabela Cristea, Alexandra Ivan, Virgil Păunescu, and Călin Adrian Tatu. 2025. "Aristolochic Acid I Adsorption onto Activated Carbon: Kinetics, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies" Processes 13, no. 11: 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113397
APA StylePricop, M.-A., Negrea, A., Ciopec, M., Pascu, I. B., Oprean, C., Lukinich-Gruia, A. T., Cristea, I.-M., Ivan, A., Păunescu, V., & Tatu, C. A. (2025). Aristolochic Acid I Adsorption onto Activated Carbon: Kinetics, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies. Processes, 13(11), 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113397










