An Online Blast Furnace Condition Recognition Method Based on Spatiotemporal Texture Feature Coupling and Diffusion Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Classification of BF Conditions and Color Rendering of BF Burden Surface Images
2.1. Classification and Feature Description of BF Conditions
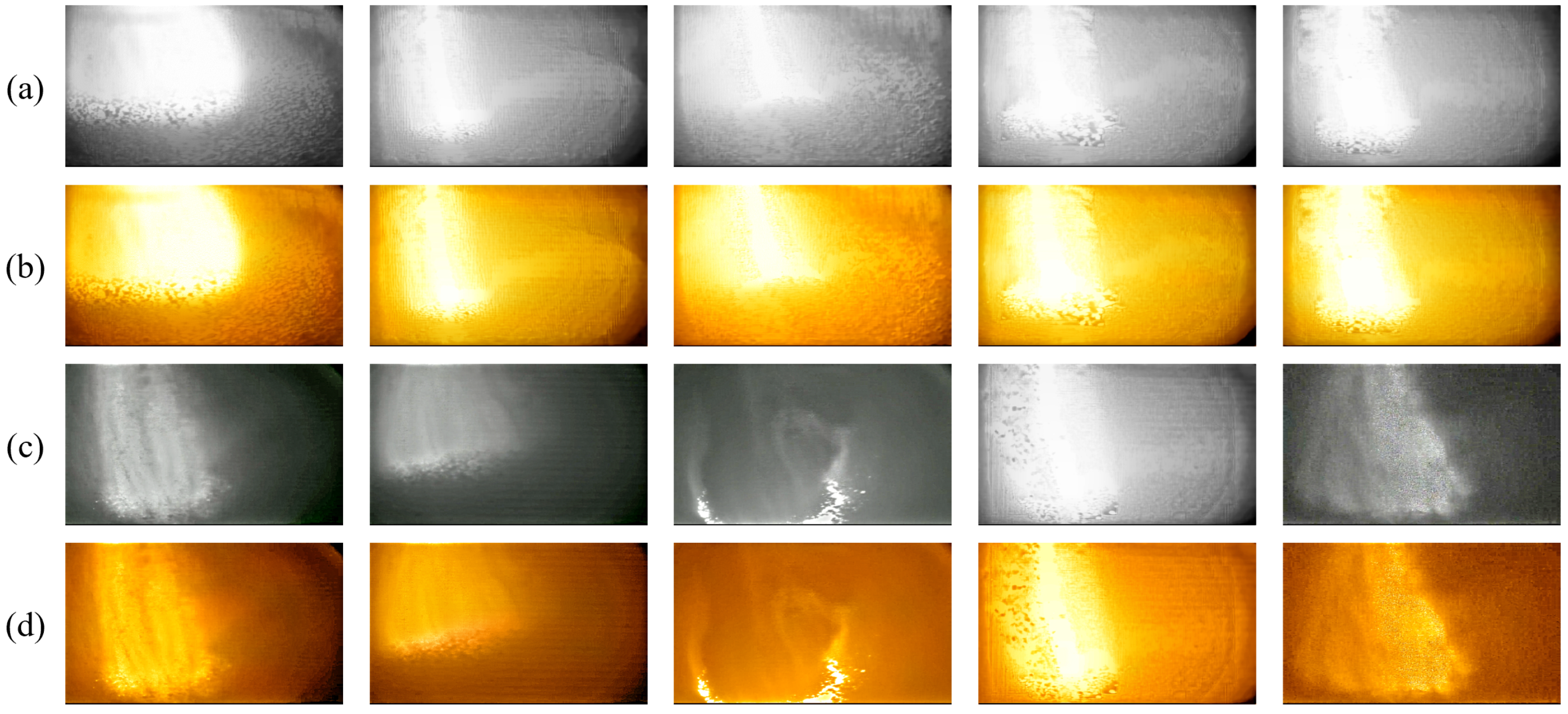
2.2. Image Enhancement and Color Rendering of BF Burden Surface
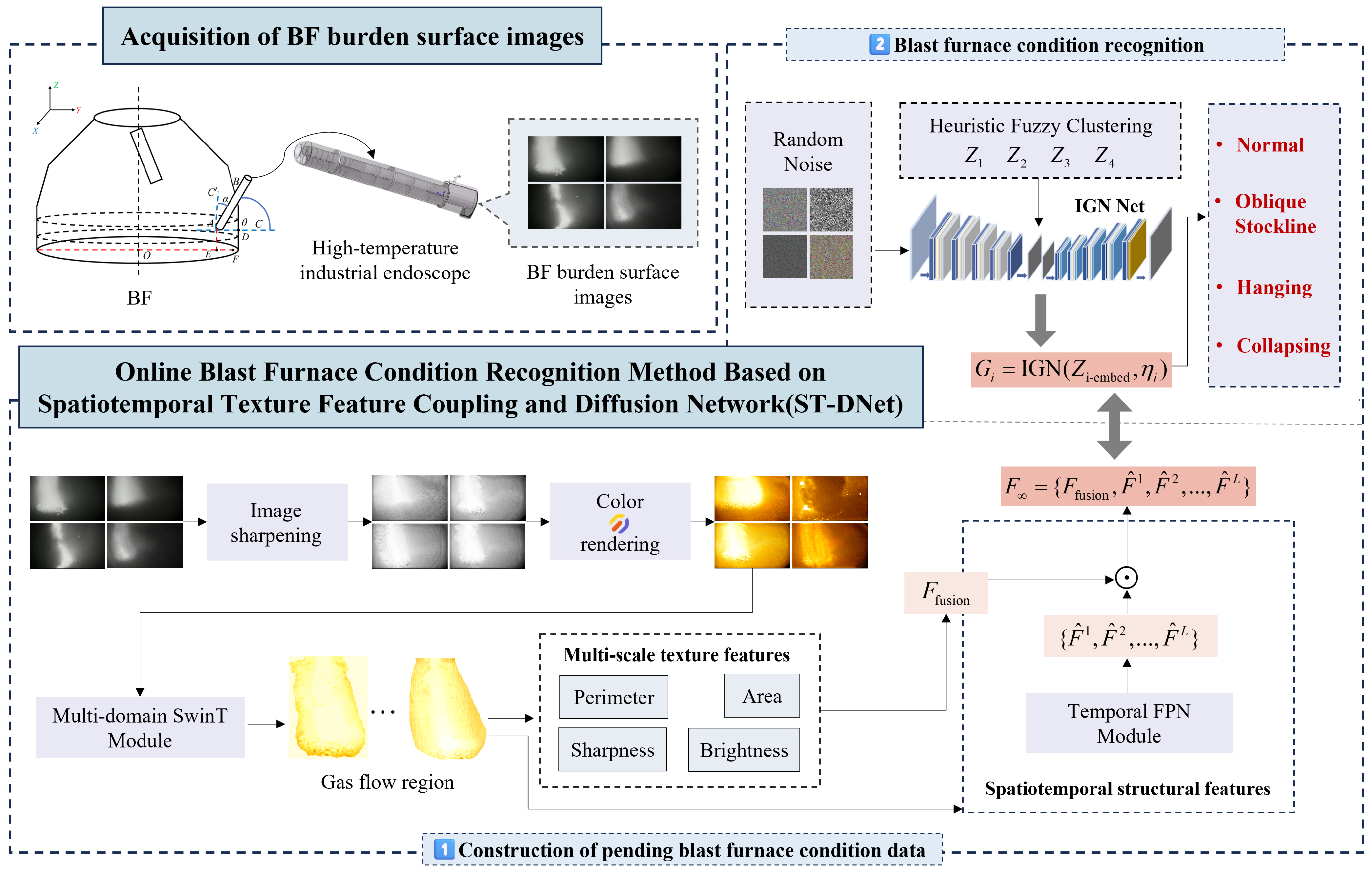
3. Methods
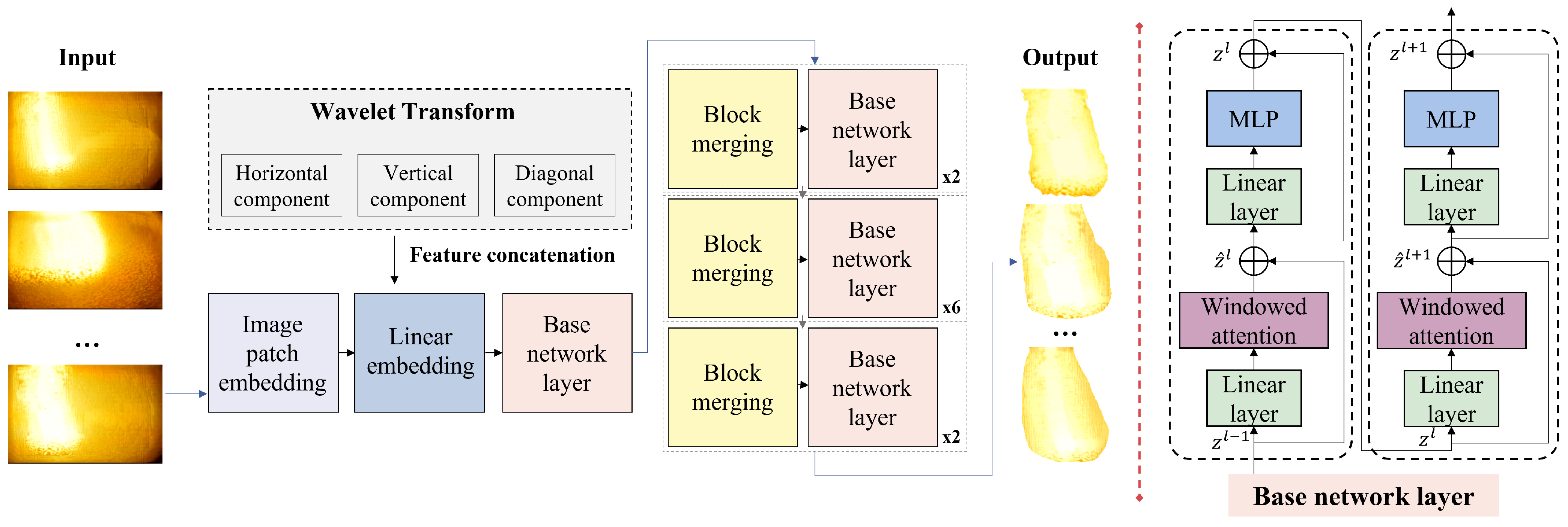
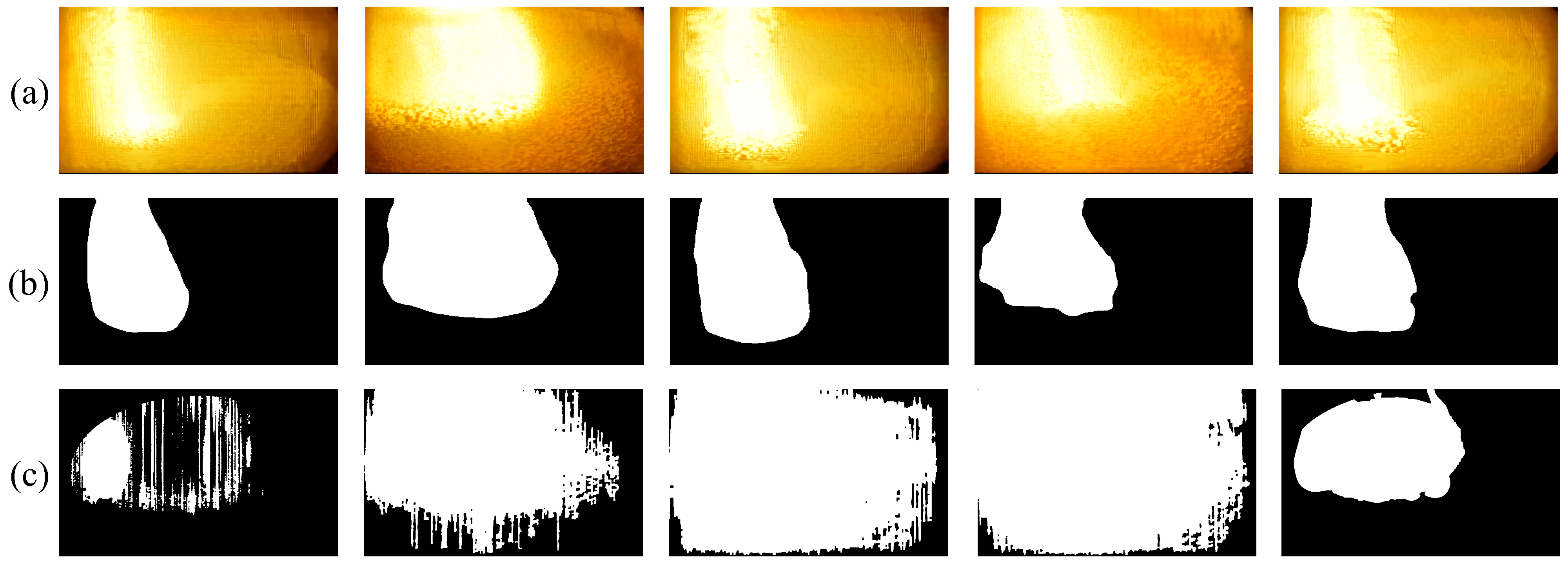
3.1. Gas Flow Region Extraction Based on Multi-Domain Swin-Transformer Module (MDSTM)
3.2. Feature Computation of Gas Flow Regions
3.2.1. Multi-Scale Texture Features
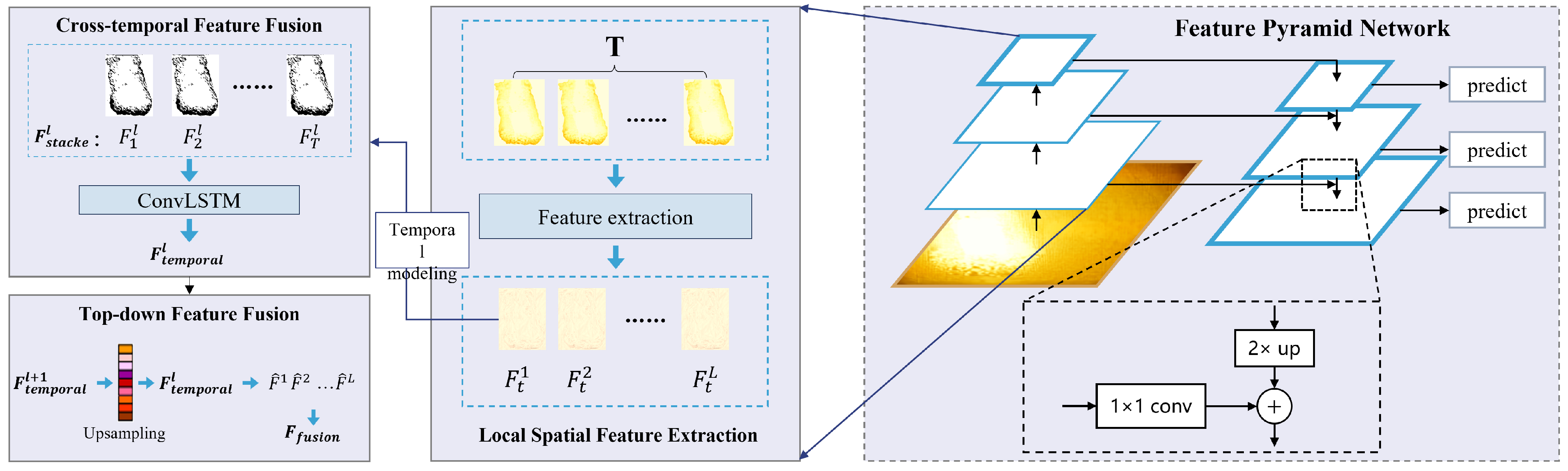
3.2.2. Spatiotemporal Structural Feature Extraction Based on Temporal FPN Module (T-FPNM)
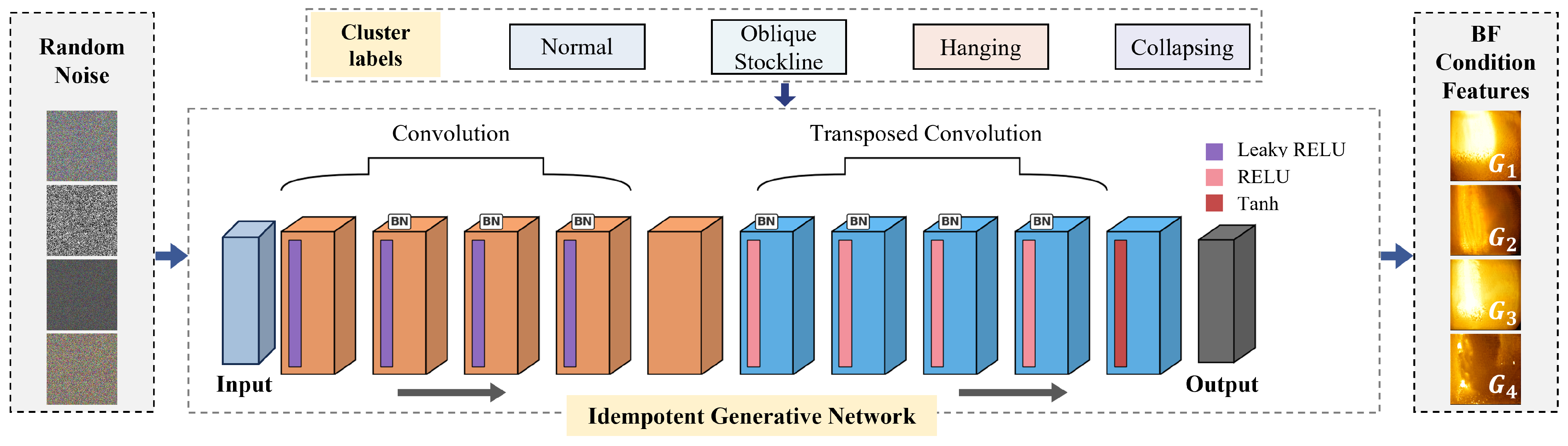
3.3. Intelligent BF Condition Recognition Method Based on Feature Generation
4. Experiments
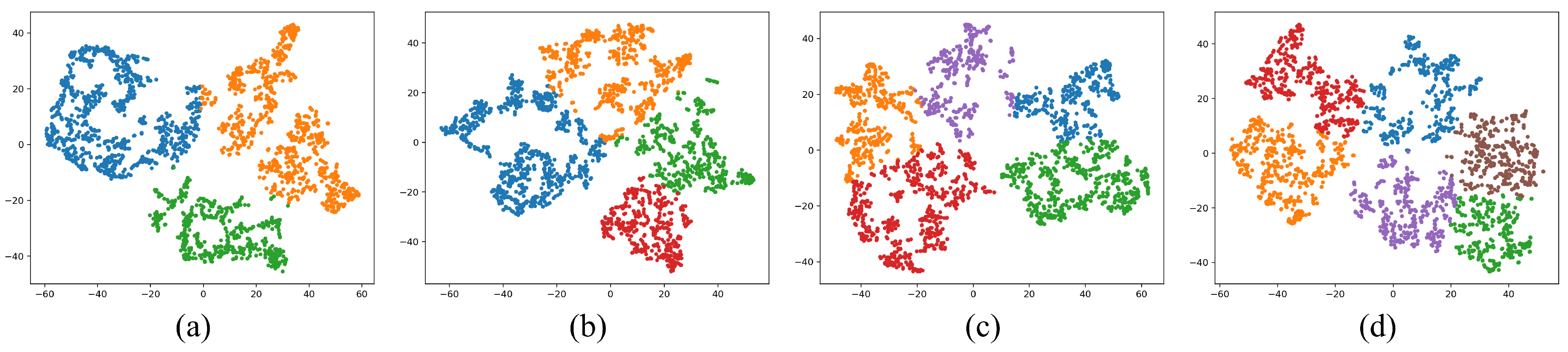
4.1. Generation of BF Condition Clustering Labels
4.2. Accuracy and Efficiency in BF Condition Recognition
4.3. Feature Analysis and Ablation Experiments of High-Temperature Gas Flow Regions
4.3.1. Multi-Scale Feature Computation of High-Temperature Gas Flow
4.3.2. Ablation Experiments on the Extraction of High-Temperature Gas Flow Regions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scolari, S.; Dall’Osto, G.; Tuveri, A.; Mombelli, D.; Mapelli, C. Optimization of Red Mud and Blast Furnace Sludge Self-Reducing Briquettes Propaedeutic for Subsequent Magnetic Separation. Metals 2025, 15, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J. A dielectric-filled waveguide antenna element for 3D imaging radar in high temperature and excessive dust conditions. Sensors 2016, 16, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yu, L.; Chang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J. Microstructure evolution behavior of blast-furnace coke under different gasification reaction conditions. Coatings 2022, 12, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mio, H.; Narita, Y.; Nakano, K.; Nomura, S. Validation of the burden distribution of the 1/3-scale of a blast furnace simulated by the discrete element method. Processes 2019, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, G.H.; Choi, J.S.; Min, D.J. Investigation on the reaction behaviour of partially reduced iron under blast furnace conditions. Metals 2021, 11, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Yin, Y.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, Z. Data-driven multiobjective optimization for burden surface in blast furnace with feedback compensation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 2233–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Gao, Z.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Liu, X.J.; Lv, Q. Research on Blast Furnace Ingredient Optimization Based on Improved Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm. Metals 2024, 14, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Gui, W.; Yang, C. A novel device for optical imaging of blast furnace burden surface: Parallel low-light-loss backlight high-temperature industrial endoscope. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 6703–6717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Gui, W. A novel 3-D high-temperature industrial endoscope with large field depth and wide field. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 6530–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Gui, W.; Zhu, J.; Yang, C.; Jiang, Z. A novel sensing imaging equipment under extremely dim light for blast furnace burden surface: Starlight high-temperature industrial endoscope. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2024, 11, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, W. Future definition and extraction of the blast furnace 3D burden surface based on intelligent algorithms. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Huang, Y.; Shi, H.; Sun, M. Review on simulation and practice of blast furnace burden distribution process. Metall. Res. Technol. 2025, 122, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Tanaka, A.; Gao, D.; Liu, Z.; Hou, Q.; Chen, X. Characterization of the Blast Furnace Burden Surface: Experimental Measurement and Roughness Statistics. ISIJ Int. 2023, 63, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, J.; Gui, W. A real-time 3D measurement system for the blast furnace burden surface using high-temperature industrial endoscope. Sensors 2020, 20, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Xu, K.; Bai, J.; He, D. On-line detecting the tuyere coke size and temperature distribution of raceway zone in a working blast furnace. Fuel 2022, 316, 123349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, R.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Q. A novel anomaly detection and classification algorithm for application in tuyere images of blast furnace. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 139, 109558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.T.; Yang, T.; Yan, R.; Zhao, H.B. Anomaly detection of the blast furnace smelting process using an improved multivariate statistical process control model. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng. Part B 2022, 166, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, W.D. Classification model for blast furnace status based on multi-source information. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 141, 109728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Shin, M.; Sagingalieva, A.; Tripathi, A.J.; Pinto, K.; Melnikov, A. Predictive control of blast furnace temperature in steelmaking with hybrid depth-infused quantum neural networks. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.12389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi-cheng, H.; Chuan, W.; Hang, Y.; Ming, Z. Image detail enhancement method based on multi-scale bilateral texture filter. Chin. Opt. 2016, 9, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Shocher, A.; Dravid, A.; Gandelsman, Y.; Mosseri, I.; Rubinstein, M.; Efros, A.A. Idempotent generative network. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.01462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Li, X.; Gao, L. A transfer convolutional neural network for fault diagnosis based on ResNet-50. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 6111–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhichri, H.; Alswayed, A.S.; Bazi, Y.; Ammour, N.; Alajlan, N.A. Classification of remote sensing images using EfficientNet-B3 CNN model with attention. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 14078–14094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–19 June 2019; pp. 5693–5703. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Liu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, A.; Xu, C.; Xu, Y.; et al. A survey on vision transformer. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
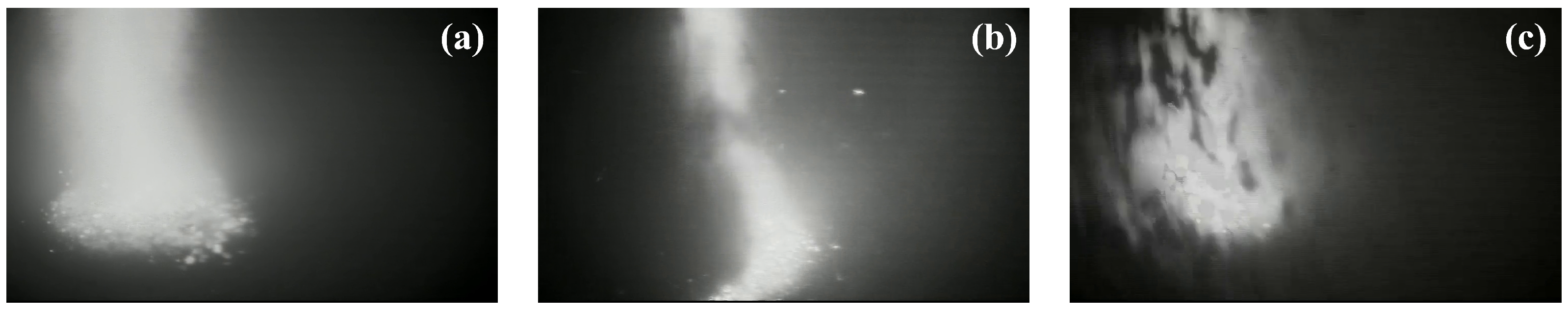
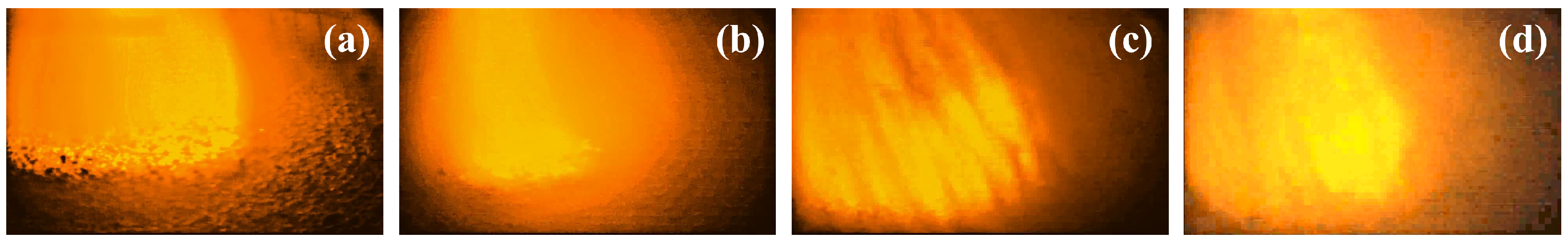

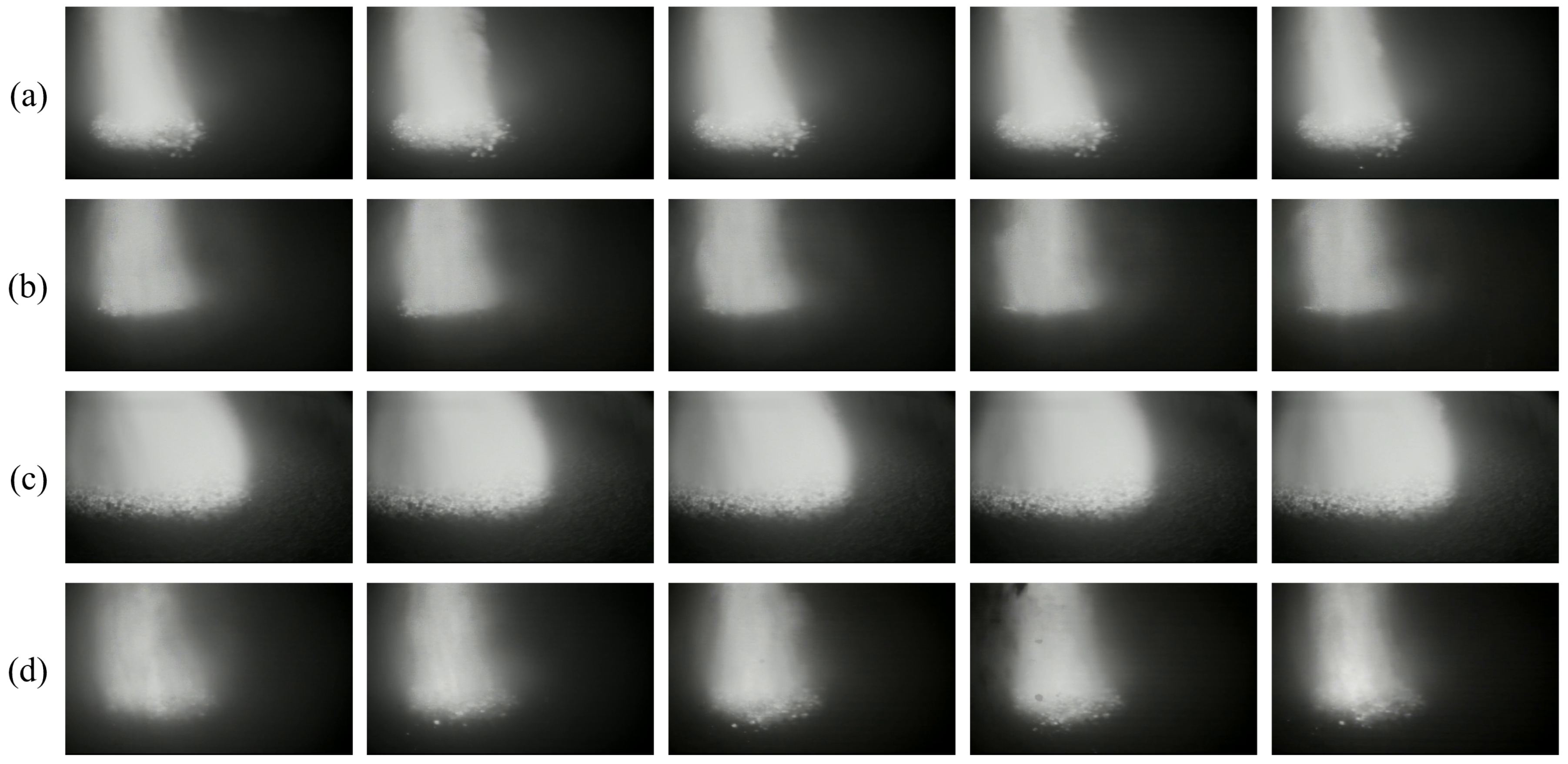
| BF Condition | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Normal condition | Stable combustion inside the BF, uniform gas flow distribution, consistent brightness, clear gas flow morphology, and sharp image display. |
| Hanging | The burden surface cannot descend steadily, permeability decreases, gas flow is obstructed, and central gas flow brightness intensifies. |
| Oblique stockline | Uneven burden descent, unreasonable gas flow distribution, asymmetric gas flow pattern, and low brightness. |
| Collapsing | Sudden massive collapse of burden, chaotic and irregular image appearance, and low brightness. |
| Model | BF Condition | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | Inference Speed (FPS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet-50 | Normal condition | 96.22 | 95.88 | 96.00 | 20.48 |
| Hanging | 95.81 | 95.25 | 95.52 | 19.57 | |
| Oblique stockline | 95.18 | 94.54 | 94.85 | 19.67 | |
| Collapsing | 98.95 | 99.00 | 98.97 | 25.49 | |
| EfficientNet-B3 | Normal condition | 96.98 | 96.41 | 96.67 | 13.78 |
| Hanging | 96.36 | 95.93 | 96.11 | 12.64 | |
| Oblique stockline | 95.74 | 95.00 | 95.43 | 12.49 | |
| Collapsing | 99.12 | 98.90 | 99.01 | 14.95 | |
| HRNet-W32 | Normal condition | 95.48 | 94.76 | 95.00 | 24.69 |
| Hanging | 95.27 | 94.37 | 94.88 | 24.13 | |
| Oblique stockline | 94.86 | 93.85 | 94.29 | 23.49 | |
| Collapsing | 98.74 | 98.42 | 98.55 | 25.41 | |
| Vision Transformer | Normal condition | 96.51 | 95.98 | 96.26 | 26.42 |
| Hanging | 96.14 | 95.45 | 95.84 | 25.73 | |
| Oblique stockline | 95.95 | 94.98 | 95.48 | 25.98 | |
| Collapsing | 99.00 | 98.85 | 98.97 | 26.91 | |
| MDSTM | Normal condition | 98.24 | 97.72 | 98.42 | 28.16 |
| Hanging | 97.86 | 97.33 | 97.56 | 27.91 | |
| Oblique stockline | 97.58 | 96.92 | 97.28 | 26.73 | |
| Collapsing | 99.47 | 99.34 | 99.36 | 28.37 |
| BF Condition | Area (/px2) | Perimeter (/px) | Brightness | Sharpness | Spatiotemporal Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal condition | 0.988 | 0.053 | 0.045 | ||
| Hanging | 1.000 | 0.043 | 0.065 | ||
| Oblique stockline | 0.999 | 0.041 | 0.061 | ||
| Collapsing | 0.996 | 0.001 | 0.094 |
| Model | Condition | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Hanging | Oblique Stockline | Collapsing | |
| With multi-domain guidance | 98.24% | 97.86% | 97.58% | 99.47% |
| Without multi-domain guidance | 93.22% | 96.81% | 97.36% | 98.64% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, X.; Han, J.; He, J.; Gui, W. An Online Blast Furnace Condition Recognition Method Based on Spatiotemporal Texture Feature Coupling and Diffusion Networks. Processes 2025, 13, 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113416
Ji X, Han J, He J, Gui W. An Online Blast Furnace Condition Recognition Method Based on Spatiotemporal Texture Feature Coupling and Diffusion Networks. Processes. 2025; 13(11):3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113416
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Xiao, Jie Han, Jianjun He, and Weihua Gui. 2025. "An Online Blast Furnace Condition Recognition Method Based on Spatiotemporal Texture Feature Coupling and Diffusion Networks" Processes 13, no. 11: 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113416
APA StyleJi, X., Han, J., He, J., & Gui, W. (2025). An Online Blast Furnace Condition Recognition Method Based on Spatiotemporal Texture Feature Coupling and Diffusion Networks. Processes, 13(11), 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113416






