A Thermodynamic Model for Performance Prediction of an Ejector with an Adjustable Nozzle Exit Position
Abstract
:1. Introduction
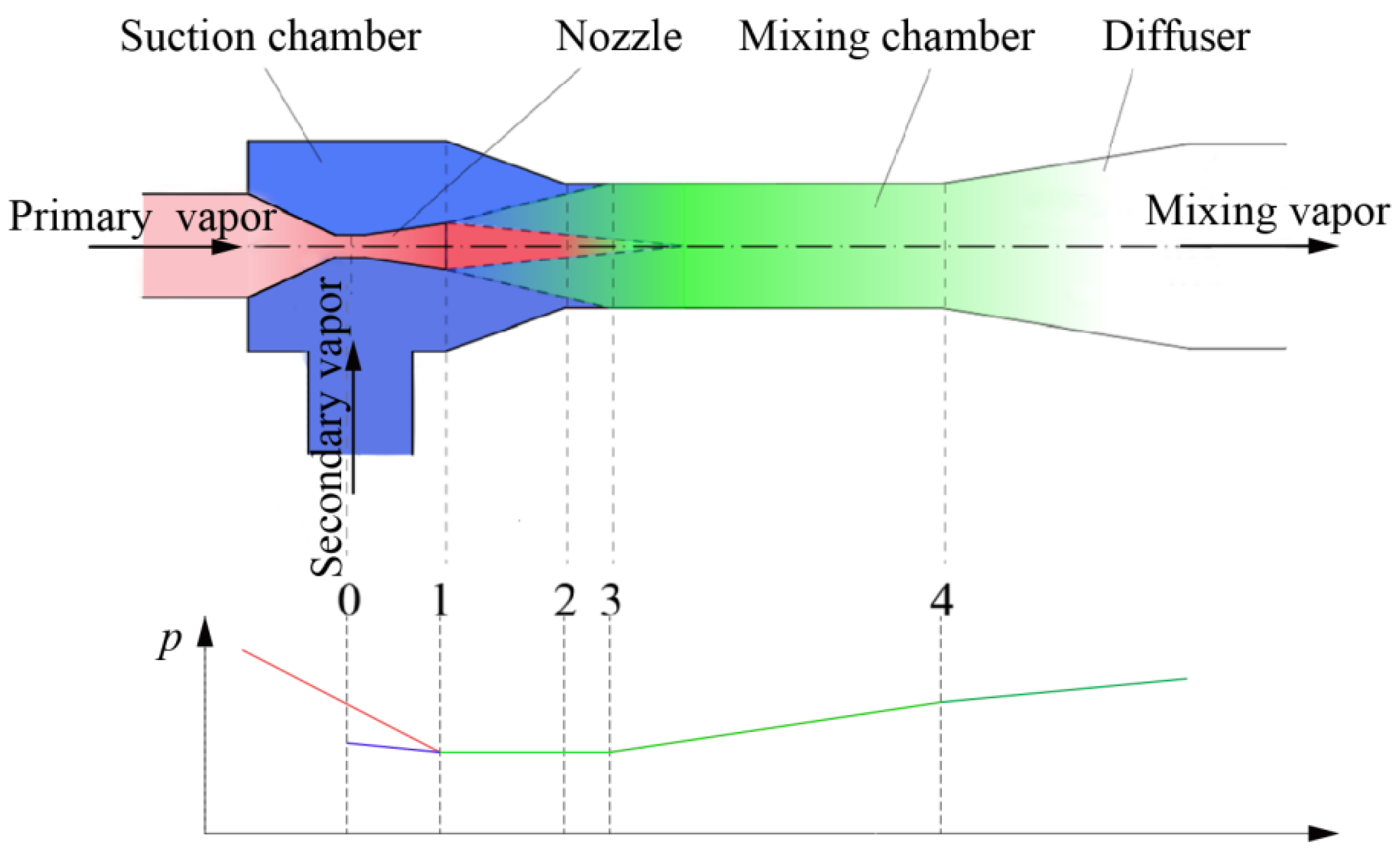
2. Mathematical Model of Vapor Ejector
2.1. The Model of the Vapor Ejector Under the Single-Choking Mode
2.2. The Entrainment Ratio of the Ejector Under the Double-Choking Mode
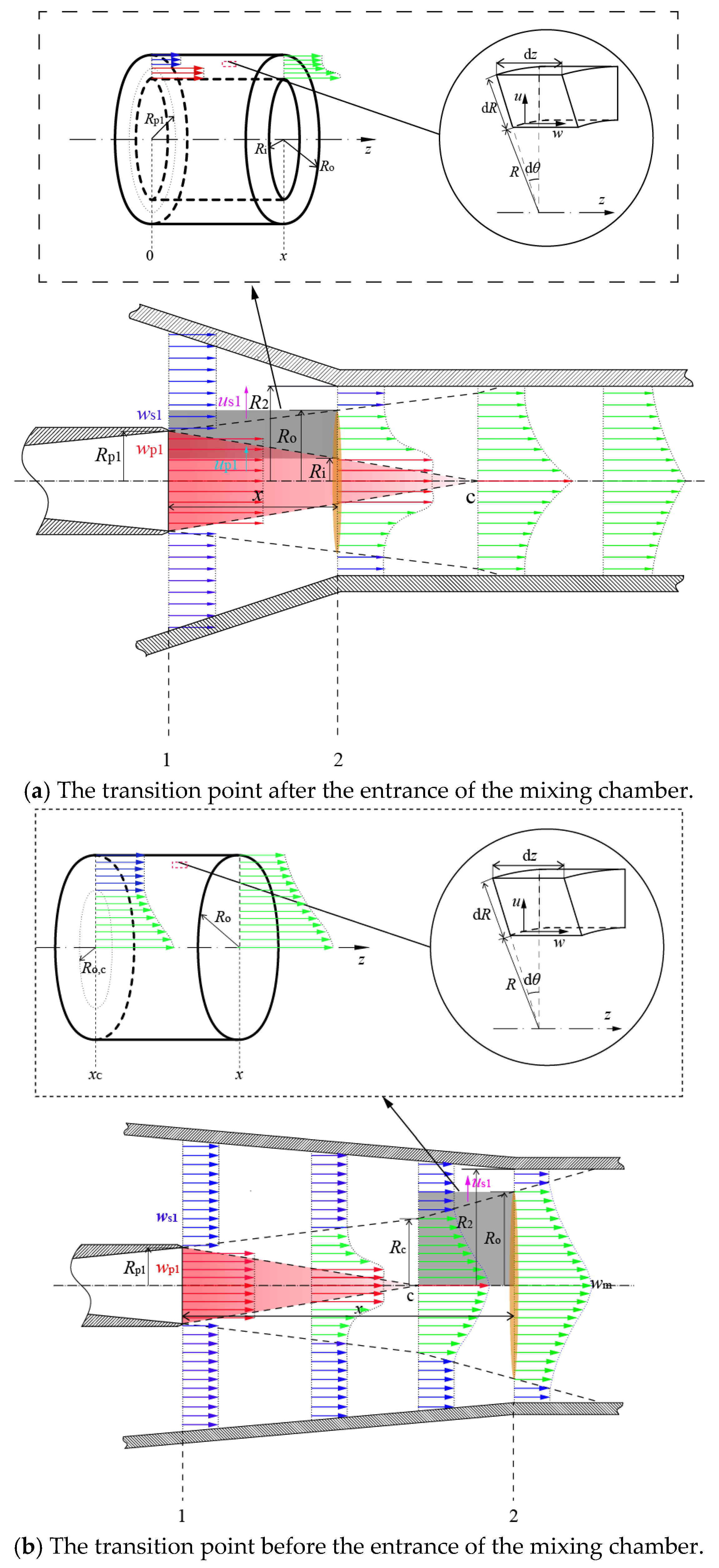
2.2.1. Situation with the Transition Point Inside the Mixing Chamber
2.2.2. Situation with the Transition Point Outside the Mixing Chamber
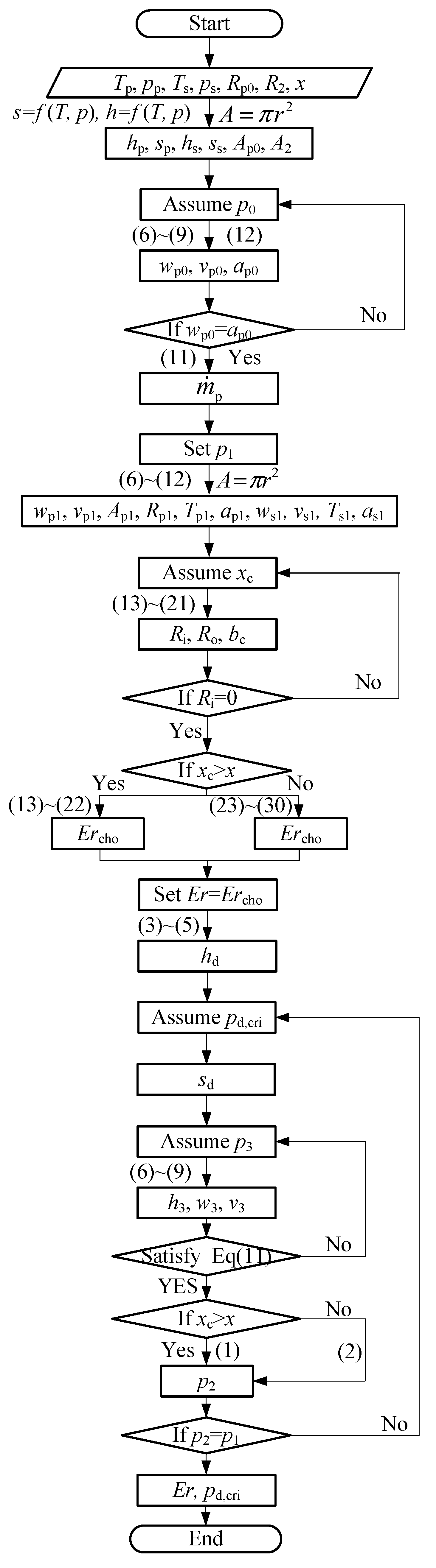
2.3. Calculation Process
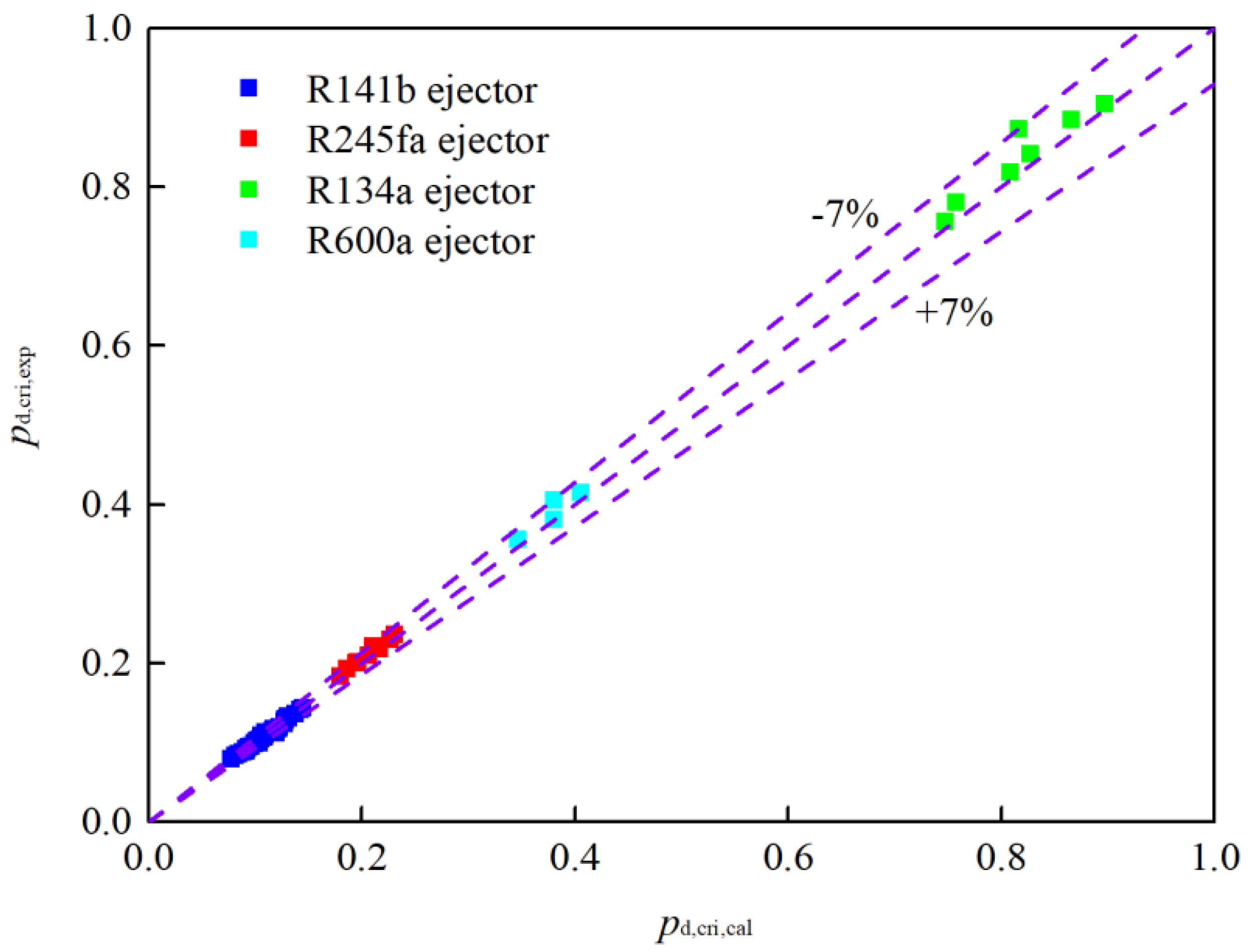
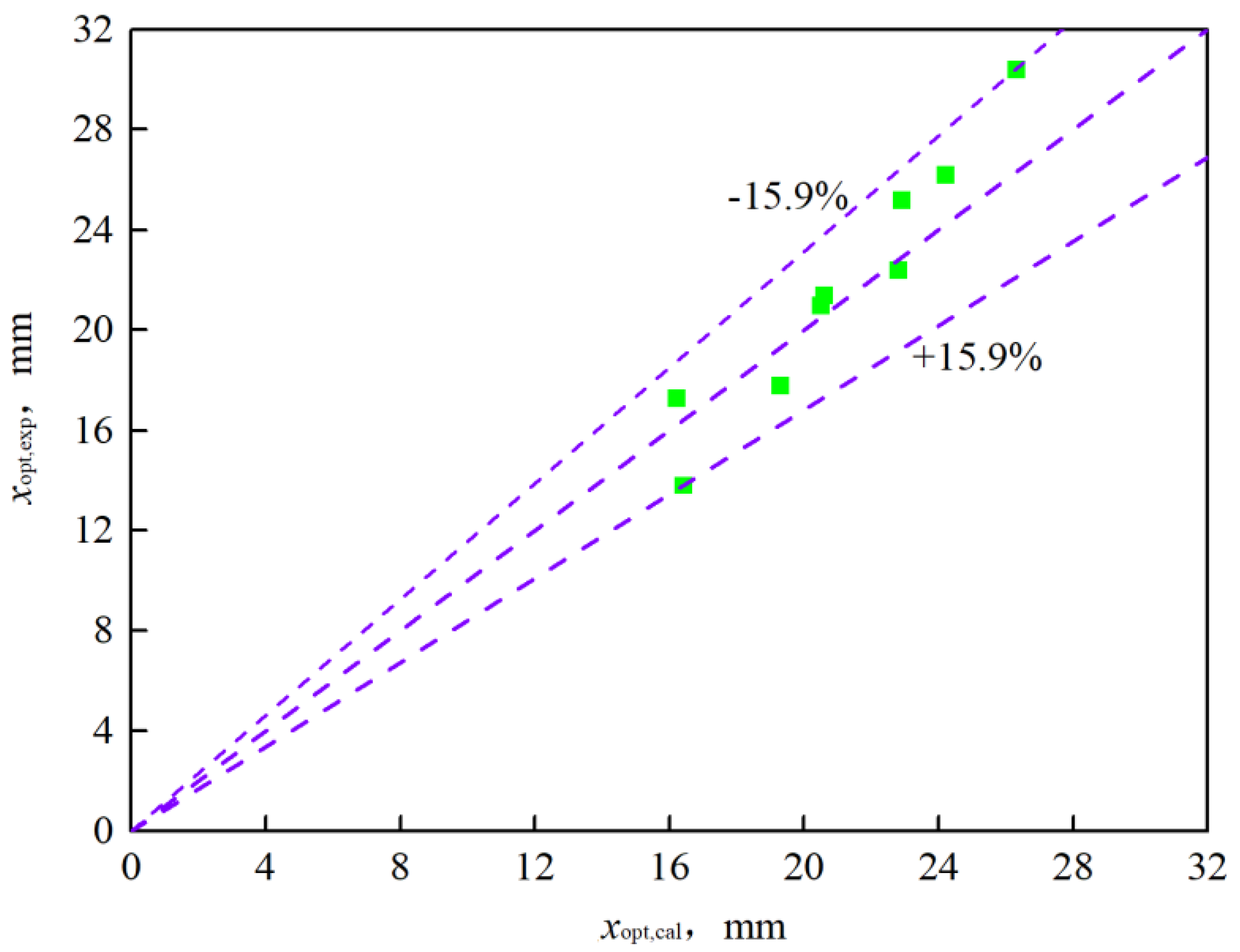
2.4. Verification of the Model
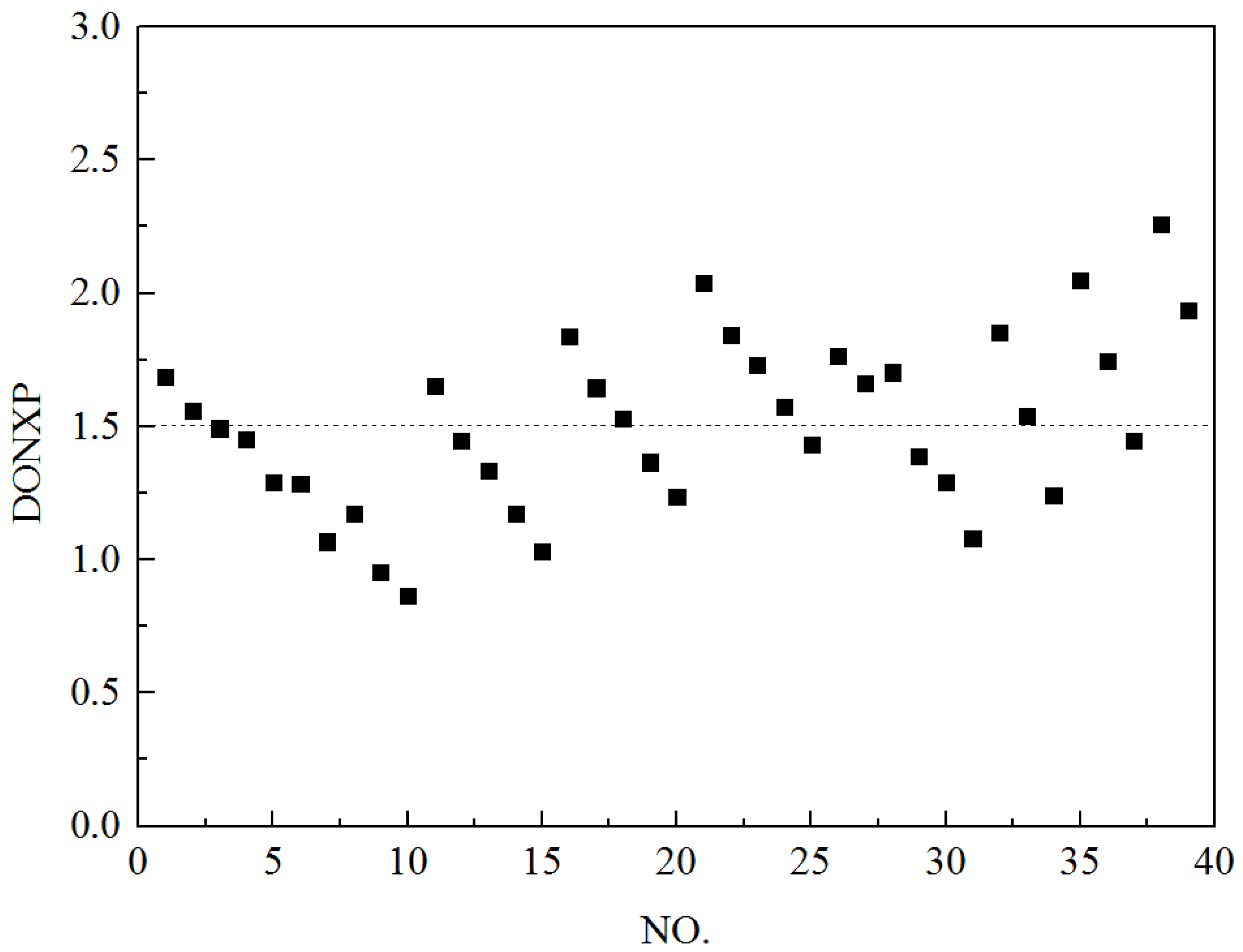
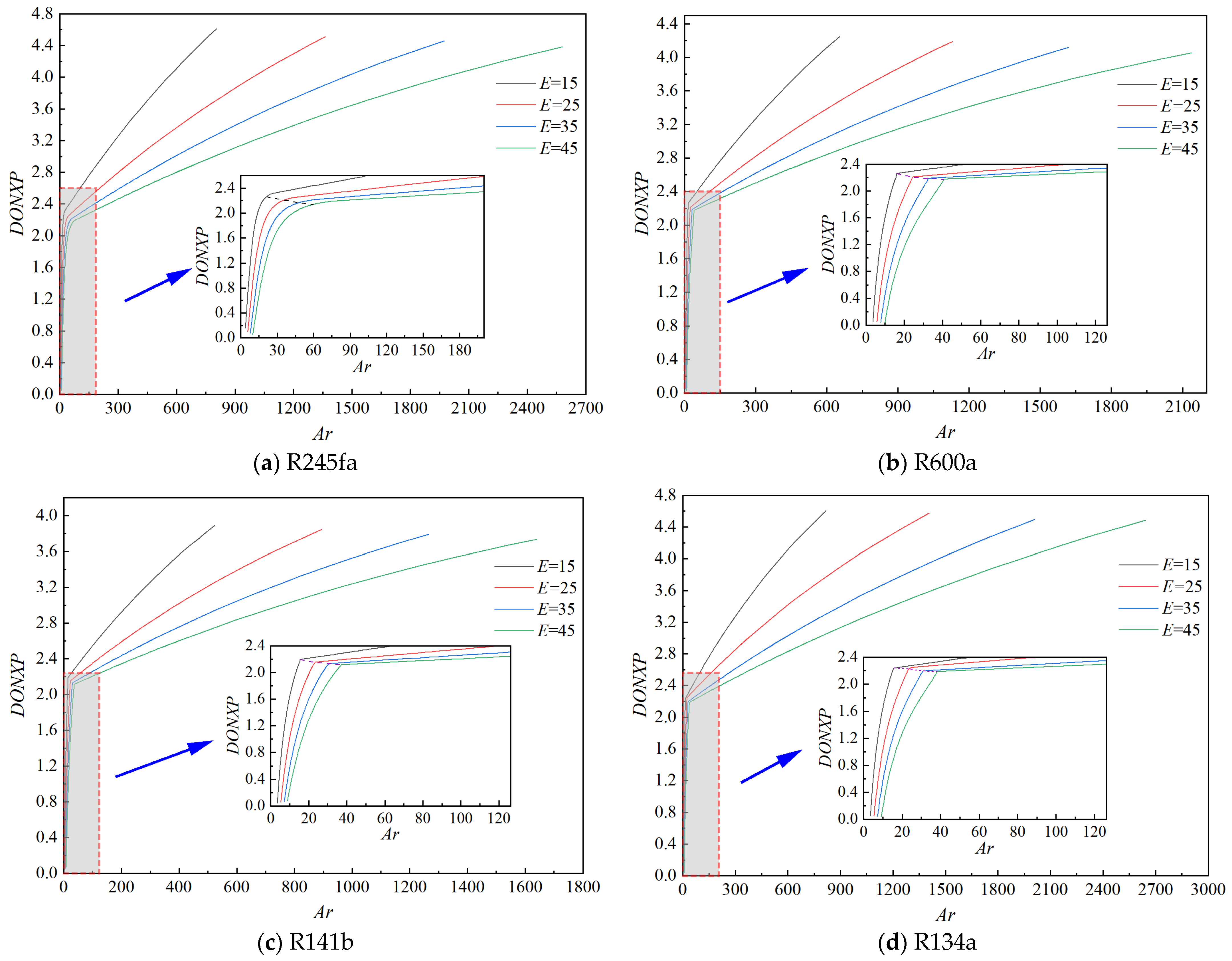
3. Functions for the DONXP of the Gas Ejector
3.1. The Key Factors Influencing the DONXP
3.2. Construction of Functional Relation
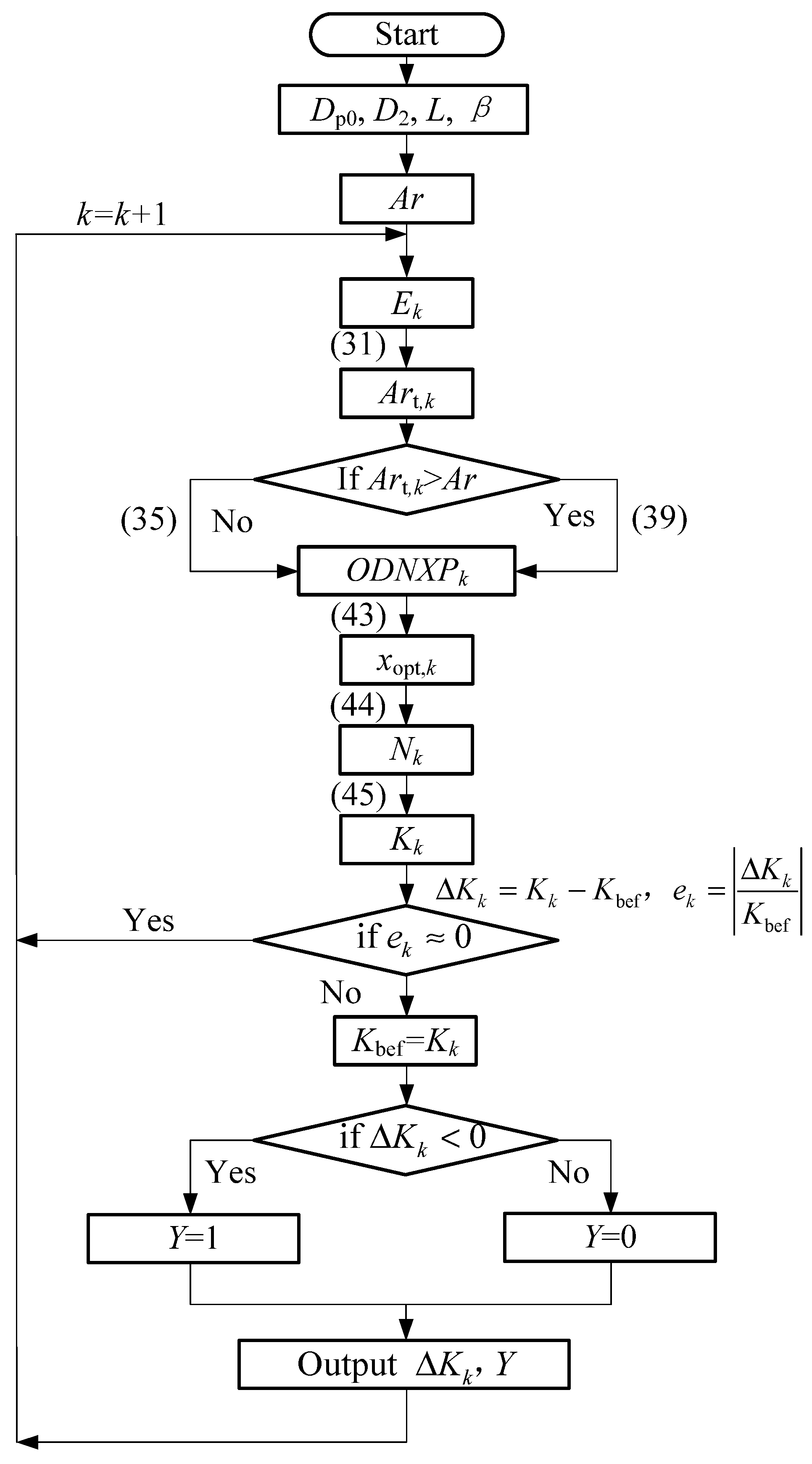
4. Application of Functions in Automatic Adjustment of Ejectors
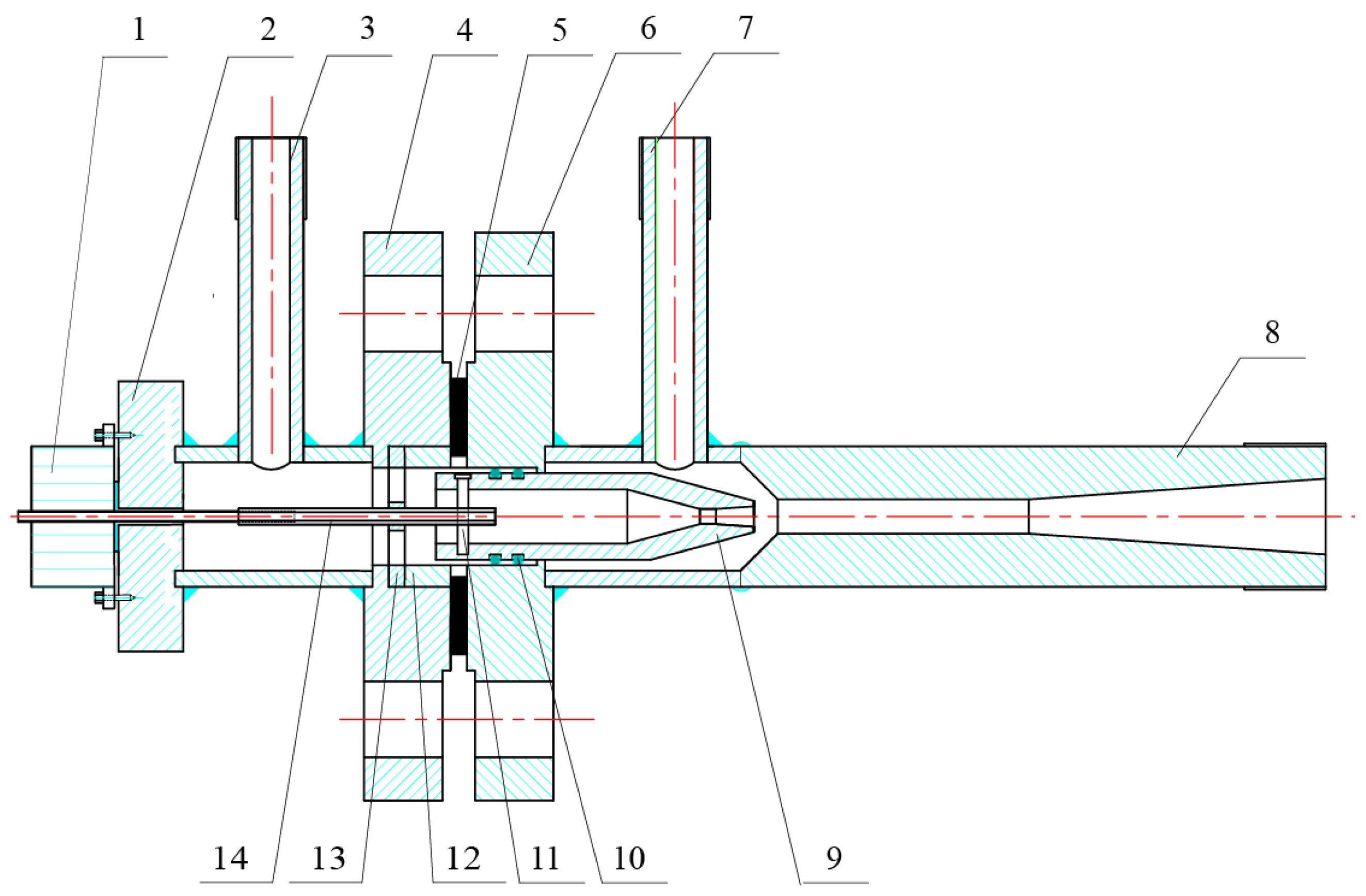
4.1. Structure of Ejector with Automatic Adjustment of Nozzle Exit Position
4.2. Automatic Adjustment Method of Nozzle Exit Position Under Variable Working Conditions
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The proposed theoretical model demonstrates reliable accuracy, with the maximum errors in the entrainment ratio, critical back pressure, and nozzle exit position within ±10.70%, ±7%, and ±15.85%, respectively, when compared to the available experimental data.
- (2)
- At a certain expansion ratio, the DONXP increases as the area ratio increases. However, there is a transition point in the rate of increase of the DONXP. When the area ratio increases, with the transition point located in the mixing chamber, the increase rates of the DONXP are within 0.068~0.195 for the R245fa, R600a, R141b, and R134a ejectors, whereas with the transition point located before the mixing chamber, the increase rates are within 0.0009~0.0034. Additionally, when the area ratio is fixed, the larger the expansion ratio, the smaller the DONXP.
- (3)
- The DONXP can be fitted according to different cases where the turning point is located either before or after the entrance of the mixing chamber, resulting in a relational equation associated with the expansion ratio and the area ratio, which can be used for the automatic adjustment of the nozzle exit position.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| a | Speed of sound, m/s |
| A | Cross-sectional area, m2 |
| Ar | Area ratio |
| b | Mixing layer thickness |
| D | Diameter, m |
| e | Relative error |
| E | Expansion ratio |
| Er | Entrainment ratio |
| h | Specific enthalpy, kJ/kg |
| K | Number of pulses driving stepping motor |
| L | Screw pitch, m |
| Mass flow rate, kg/s | |
| M | Convective Mach number |
| N | Number of motor turns |
| p | Pressure, Pa |
| R | Radius, m |
| u | Radial velocity |
| v | Specific volume, m3/kg |
| w | Axial velocity |
| s | Specific entropy, kJ/(kg·K) |
| T | Temperature, K |
| x | Value of nozzle exit position, m |
| Y | Criterion for controlling pulse direction |
| Greek letters | |
| β | Step angle of stepping motor, ° |
| η | Isentropic efficiency |
| μ | Momentum efficiency |
| ρ | Density, kg/m3 |
| ψ | Cross section coefficient |
| Φ | Compressibility factor |
| Subscripts | |
| bef | Previous calculated value |
| c | Value of turning point |
| cri | Critical value |
| cal | Calculated value |
| cho | Value of double-choking mode |
| d | Mixed vapor |
| d4 | Mixed vapor on cross section 4 |
| exp | Experimental value |
| i | Parameter of inner boundary of mixing layer |
| is | Parameter after isentropic process |
| k | Loop count |
| m | Parameter on axis |
| o | Parameter of external boundary of mixing layer |
| opt | Optimal value |
| p | Primary vapor |
| p0 | Parameter of primary vapor on cross section 0 |
| p1 | Parameter of primary vapor on cross section 1 |
| s | Secondary vapor |
| s1 | Parameter of secondary vapor on cross section 0 |
| 0 | Parameter on cross section 0 |
| 1, 2, 3, 4 | Parameter on cross sections 1, 2, 3, 4 |
| Abbreviations | |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| DONXP | Dimensionless optimal nozzle exit position |
| NXP | Nozzle exit position |
References
- Fingas, R.; Haida, M.; Smolka, J.; Croci, L.; Bodys, J.; Palacz, M.; Besagni, G. Experimental analysis of the r290 variable geometry ejector with a spindle. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 258, 124632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Han, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Jia, L.; Wang, L.; Sun, W.; Xue, H. Influence of geometric parameters on ejector acoustics and efficiency in ejector refrigeration system. Int. J. Refrig. 2025, 169, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Li, B.; Elbel, S. Advances in ejector research for multi-effect thermal vapor compression desalination. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 208, 115010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Tang, Y. Numerical study for the influences of primary steam nozzle distance and mixing chamber throat diameter on steam ejector performance. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 132, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, A.S.; Sekhar, S.J. Experimental and numerical investigations on the effect of suction chamber angle and nozzle exit position of a steam-jet ejector. Energy 2018, 164, 1097–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metin, C.; Gök, O.; Atmaca, A.U.; Erek, A. Numerical investigation of the flow structures inside mixing section of the ejector. Energy 2019, 166, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldakamawy, M.H.; Sorin, M.V.; Brouillette, M. Blowdown experimental study on butene ejector. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 160, 114000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, G.; Guo, L.; Tu, J. CFD simulation on the boundary layer separation in the steam ejector and its influence on the pumping performance. Energy 2019, 167, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Cao, H.; Meng, Q.; Li, J.; Jiang, P. Effects of operating conditions and geometries on the performance of nitrogen ejectors for joule–thomson cooling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 212, 118557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, J.; Ge, J.; Lu, W.; Zheng, L. A cylindrical mixing chamber ejector analysis model to predict the optimal nozzle exit position. Energy 2020, 208, 118302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, M. Influence of operating conditions on the optimal nozzle exit position for vapor ejector. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 210, 118377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H. Design and numerical investigation of an adaptive nozzle exit position ejector in multi-effect distillation desalination system. Energy 2017, 140, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, H.; Kong, F.; Liu, G.; Wang, L.; Lai, Y. Synergistic effect of adjustable ejector structure and operating parameters in solar-driven ejector refrigeration system. Sol. Energy 2023, 250, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, C.P.; Croquer, S.; Poirier, M.; Poncet, S. Optimal nozzle exit position for a single-phase ejector (experimental, numerical and thermodynamic modelling). Int. J. Refrig. 2022, 144, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, G.; Hao, X.; Gao, N.; Volovyk, O. Working mechanism and characteristics analysis of a novel configuration of a supersonic ejector. Energy 2023, 278, 128010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Deng, J.; He, Y.; Jiang, P. Dynamic model of a transcritical CO2 ejector expansion refrigeration system. Int. J. Refrig. 2015, 60, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H. Jet Theory and Its Application; Zhejiang University Press: Hangzhou, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Berghe, J.; Dias, B.R.B.; Bartosiewicz, Y.; Mendez, M.A. A 1d model for the unsteady gas dynamics of ejectors. Energy 2023, 267, 126551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, E.Y.; Zinger, N.M. Jet Devices; Energoatomizdat: Moscow, Russia, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, M.; Miao, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, Q. Design and investigation of a dynamic auto-adjusting ejector for the med-tvc desalination system driven by solar energy. Entropy 2022, 24, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.L.; Lemmon, E.W.; Bell, I.H.; Mclinden, M.O. The nist refprop database for highly accurate properties of industrially important fluids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 42, 15449–15472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatski, T.B.; Bonnet, J. Compressibility, Turbulence and High Speed Flow; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, S.; Zhao, Y.; He, L. Supersonic and Hypersonic Nozzle Design; National Defence Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.J.; Chang, J.M.; Wang, C.P.; Petrenko, V.A. A 1-d analysis of ejector performance. Int. J. Refrig. 1999, 22, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shestopalov, K.O.; Huang, B.J.; Petrenko, V.O.; Volovyk, O.S. Investigation of an experimental ejector refrigeration machine operating with refrigerant r245fa at design and off-design working conditions. Part 2. Theoretical and experimental results. Int. J. Refrig. 2015, 55, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, J.G.D.; Jabardo, J.M.S.; Ruiz, F.C.; Alonso, J.F.S.J. An experimental investigation of a r-134a ejector refrigeration system. Int. J. Refrig. 2014, 46, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butrymowicz, D.; Śmierciew, K.; Karwacki, J.; Gagan, J. Experimental investigations of low-temperature driven ejection refrigeration cycle operating with isobutane. Int. J. Refrig. 2014, 39, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Chen, B.; Xu, Z.; Ge, J.; Chen, H.; Zhong, Z. A Thermodynamic Model for Performance Prediction of an Ejector with an Adjustable Nozzle Exit Position. Processes 2025, 13, 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030879
Chen H, Chen B, Xu Z, Ge J, Chen H, Zhong Z. A Thermodynamic Model for Performance Prediction of an Ejector with an Adjustable Nozzle Exit Position. Processes. 2025; 13(3):879. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030879
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hongjie, Bingxu Chen, Zhizhou Xu, Jing Ge, Honghua Chen, and Zhaoqi Zhong. 2025. "A Thermodynamic Model for Performance Prediction of an Ejector with an Adjustable Nozzle Exit Position" Processes 13, no. 3: 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030879
APA StyleChen, H., Chen, B., Xu, Z., Ge, J., Chen, H., & Zhong, Z. (2025). A Thermodynamic Model for Performance Prediction of an Ejector with an Adjustable Nozzle Exit Position. Processes, 13(3), 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030879




