Effect of Ice Storage on Freshness and Biochemical, Physical, Chemical, and Microbiological Quality of Leg Muscle Samples from Bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Bullfrogs
2.2. Analysis of Samples During Storage on Ice
2.3. Analytical Determinations
2.3.1. ATP and Degradation Products
2.3.2. Calculation of K-Value
2.3.3. Determination of the pH of Frog Leg Muscle
2.3.4. Color
2.3.5. Texture
2.3.6. Water Retention Capacity (WHC)
2.3.7. Total Volatile Bases (TVB-N)
2.3.8. Aerobic Mesophilic and Psychrophilic Bacteria Count
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Estimation of the Concentrations of ATP and Its Degradation Products
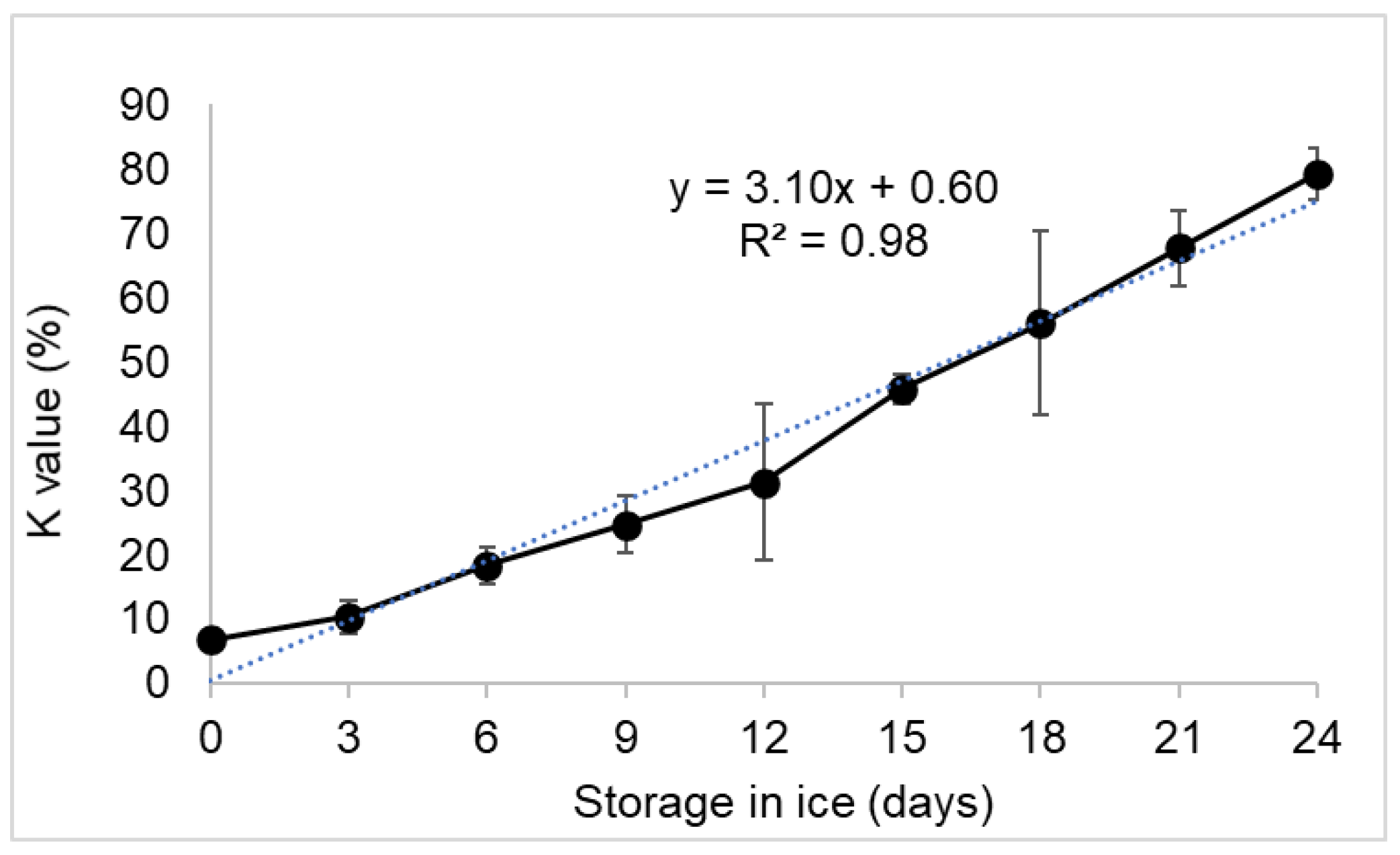
3.2. Estimation of K-Value
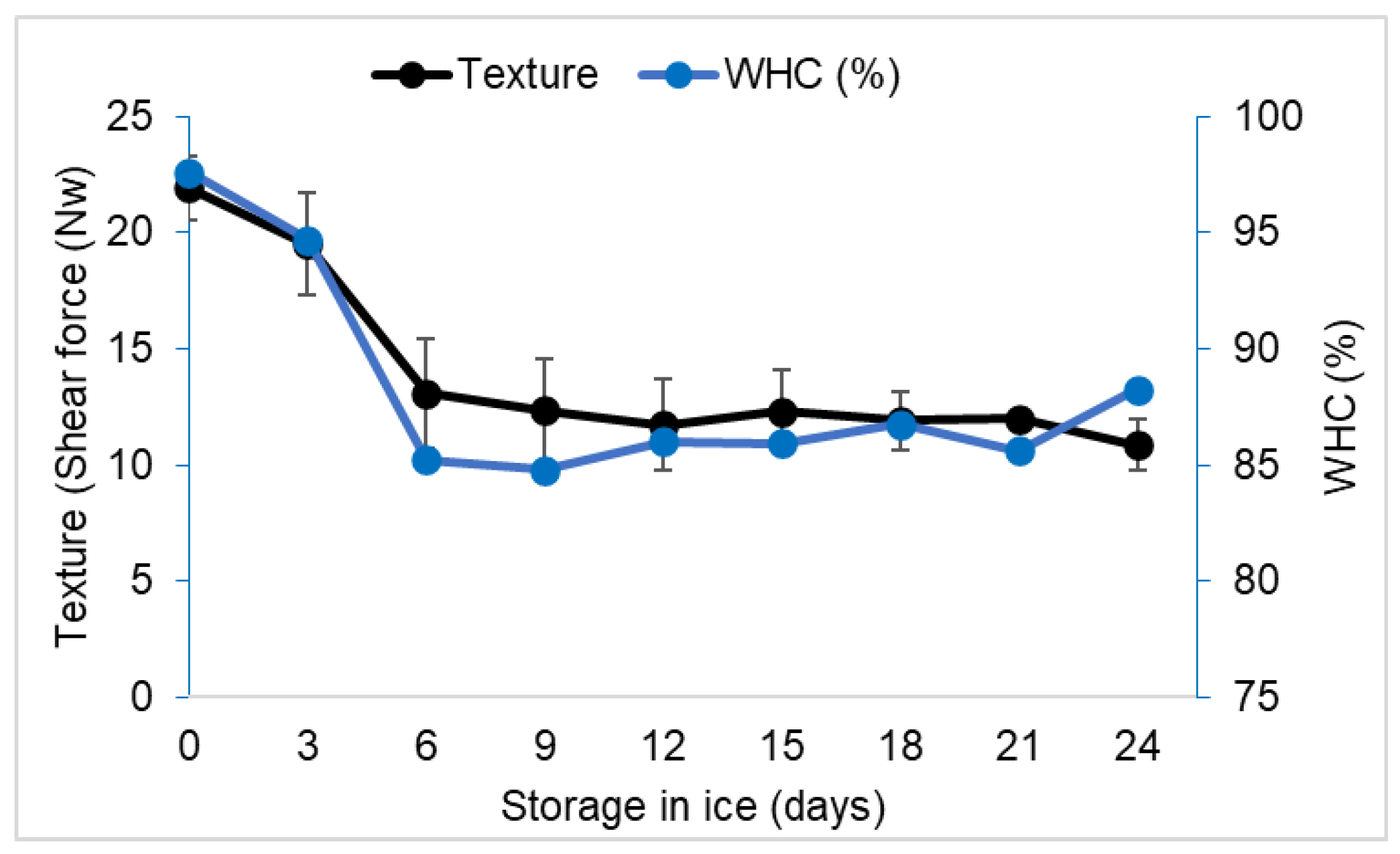
3.3. Texture and WHC of the Frog Leg Muscle
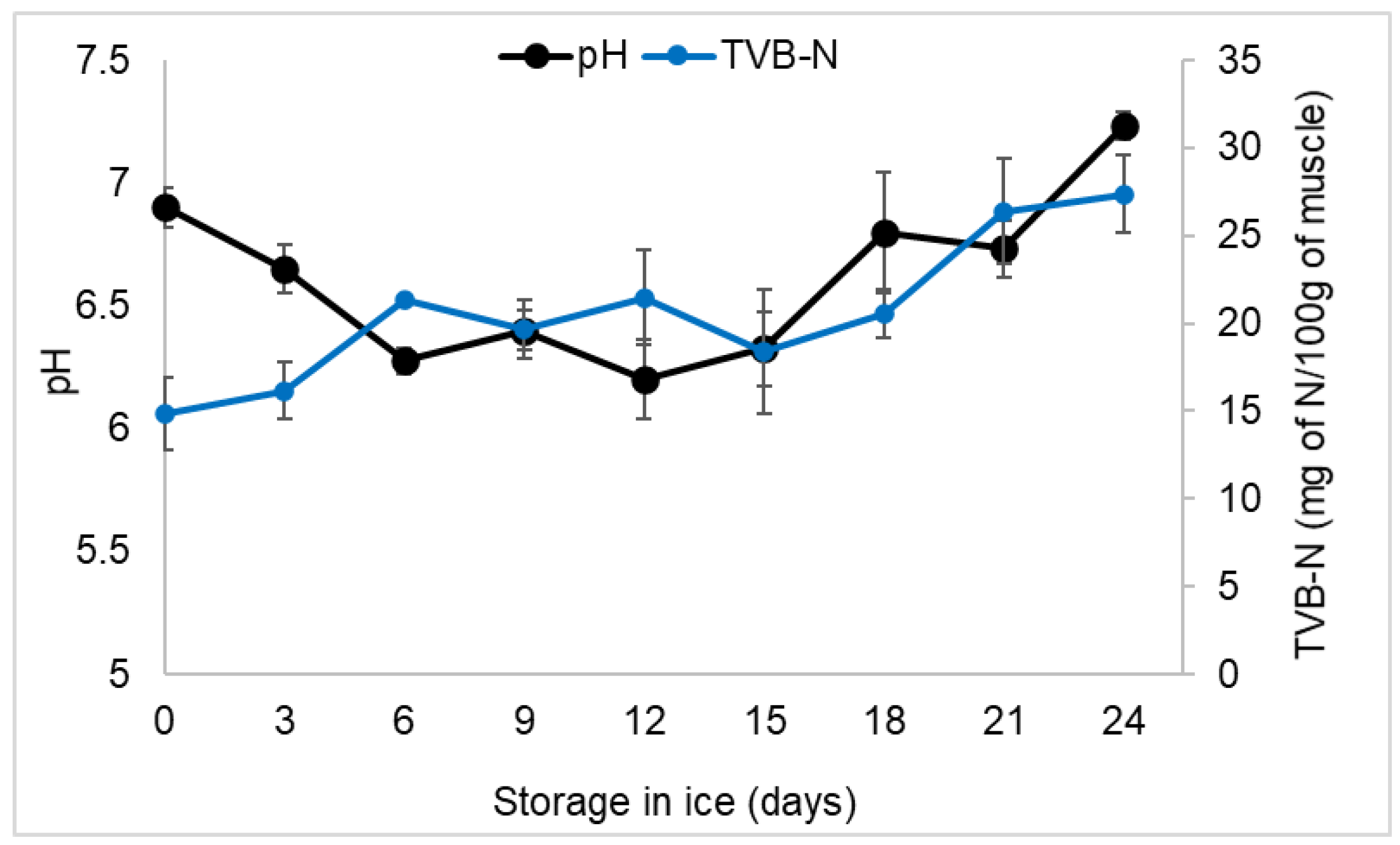
3.4. Estimation of pH and TVB-N
3.5. Color of the Frog Leg Muscle
3.6. Effect of Storage on Microbiological Content
3.7. Degree of Association Among the Different Quality Parameters
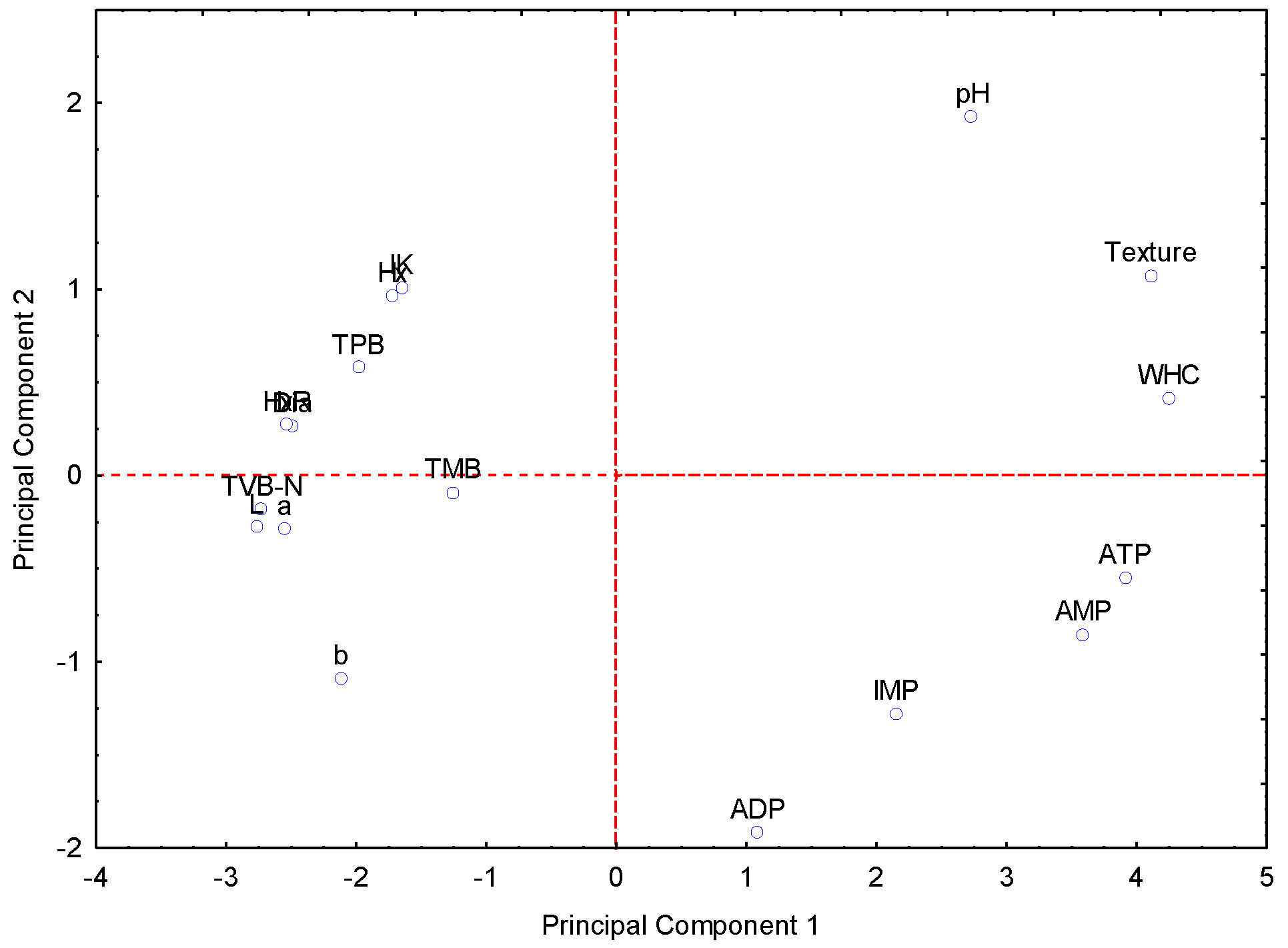
3.8. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Between the Different Quality Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Estimation of the Concentrations of ATP and Its Degradation Products
4.2. Estimation of K-Value
4.3. Texture and WHC of the Frog Leg Muscle
4.4. Estimation of pH and TVB-N
4.5. Color of the Frog Leg Muscle
4.6. Effect of Storage on Microbiological Content
4.7. Degree of Association Among the Different Quality Parameters
4.8. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Between the Different Quality Parameters
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anuario Estadístico de Pesca. Comisión Nacional de Acuicultura y Pesca. 2021. Available online: https://nube.conapesca.gob.mx/sites/cona/dgppe/2021/ANUARIO_ESTADISTICO_DE_ACUACULTURA_Y_PESCA_2021.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2024).
- Helfrich, L.A.; Neves, R.J.; Parkhurst, J. Commercial Frog Farming; Virginia Cooperative Association: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2017; Publication 420-255. [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta, C.Y.; Reisfeld, L.; Silvatti, B.; Salvagni, F.A.; de Paula, C.D.; Pessier, A.P.; Ferreira Neto, J.S. Tuberculosis caused by Mycobacterium bovis infection in a captive-bred American bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeiana). BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. Rana catesbeiana. In Cultured Aquatic Species Information Programme; Flores Nava, A., Ed.; Fisheries and Aquaculture Division: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cifuentes Lemus, J.L.; Torres-García, M.P.; Frías Mondragón, M. El Océano y Sus Recursos, XI. Acuicultura, 3rd ed.; Instituto Latinoamericano de la Comunicación Educativa: Ciudad de México, Mexico, 1999; p. 160. Available online: https://bibliotecadigital.ilce.edu.mx/sites/ciencia/volumen2/ciencia3/090/html/sec_12.html (accessed on 29 November 2024).
- Coppo, J.A. El medio interno de la “rana toro” (Rana catesbeiana, Shaw 1802). Rev. Vet. 2016, 14, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büyükdeveci, M.E.; Boga, E.K.; Ozyurt, G. Gamma-irradiation induced effects on biogenic amine formation and quality of frog legs (Rana esculenta) during storage. LWT 2019, 99, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, L.R.; Tejada-Ortigoza, V.; Martín-del-Campo, S.T.; Balderas-León, I.; Morales-de la Peña, M.; Garcia-Amezquita, L.E.; Welti-Chanes, J. Evaluation of nutritional composition and technological functionality of whole American Bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus), its skin, and its legs as potential food ingredients. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.X.; Huang, K.K.; Lu, L.K.; Wang, L.; Song, K.; Zhang, L.; Li, P. Effects of different lipid sources on growth performance, body composition and lipid metabolism of bullfrog Lithobates catesbeiana. Aquaculture 2016, 457, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efenakpo, O.D.; Ijeomah, H.M.; Eniang, E. Assessment of frog meat trade and nutritional composition of selected Anura species in Ibadan, Nigeria. Prod. Agric. Technol. 2015, 11, 203–218. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, A.L.; Gooi, C.T.; Pang, H.K. Proximate composition and fatty acid profile of anurans meat. J. Sci. Technol. 2008, 22, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Wu, Y.; Regenstein, J.M.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, F.; Xu, Y.; Xia, W. Recent advances in quality retention of non-frozen fish and fishery products: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 60, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehira, S.; Uchiyama, H. Determination of Fish Freshness Using the K Value and Comments on Some Other Biochemical Changes in Relation to Freshness; Kramer, D.E., Ed.; Seafood Quality Determination: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 185–207. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Yan, Q.; Li, D.; Xie, J. Degradation mechanism and development of detection technologies of ATP-related compounds in aquatic products: Recent advances and remaining challenges. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 65, 2267690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhuang, S.; Peng, Y.; Tan, Y.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y. Mechanism of Inosine Monophosphate Degradation by Specific Spoilage Organism from Grass Carp in Fish Juice System. Foods 2022, 11, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Choi, H.; Lee, K.G. ATP degradation products as freshness indicator of flatfish during storage. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 1891–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanez, F.J.C.; Ruiz, E.I.J.; Rodriguez, D.F.C.; Rios, E.M.; Camacho, N.M.; Cruz, S.R.; Higuera, V.M.O. Postmortem biochemical changes and evaluation of the freshness in the muscle of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) during the storage in ice. J. Fish Aqua. Sci. 2014, 9, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasalvar, C.; Taylor, K.A.; Shahidi, F. Comparative quality assessment of cultured and wild sea bream (Sparus aurata) stored in ice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2039–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi, F.; Chong, X.; Dunajski, E. Freshness quality of harp seal (Phoca groenlandica) meat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökodlu, N.; Özden, Ö.; Erkan, N. Physical, chemical and sensory analyses of freshly harvested sardines (Sardina pilchardus) stored at 4 °C. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 1998, 7, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ye, X.; Yang, Y. Spoilage potential characterization of Shewanella and Pseudomonas isolated from spoiled large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 64, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, S.I.; Amuzie, C.C. Microbiological quality of Hoplobatrachus occipitalis (Amphibia, Anura) used as meat. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 3192–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.J.; Rajeev, S.; Miller, D.L.; Schmutzer, A.C.; Burton, E.C.; Rogers, E.D.; Hickling, G.J. Preliminary evidence that American bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana) are suitable hosts for Escherichia coli O157: H7. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4066–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasteris, S.E.; Vera Pingitore, E.; Roig Babot, G.; Otero, M.C.; Bühler, M.I.; Nader-Macías, M.E. Characterization of the beneficial properties of lactobacilli isolated from bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) hatchery. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2009, 95, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SENASICA. Manual de Buenas Prácticas de Producción Acuícola de Rana Toro. Cd. México. Servicio Nacional de Sanidad, Inocuidad y Calidad Agroalimentaria. SAGARPA. 2016. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/senasica/documentos/buenas-practicas-de-produccion-acuicola-de-rana-de-toro (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Ryder, J.M. Determination of adenosine triphosphate and its breakdown products in fish muscle by highperformance liquid chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1985, 33, 678–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Regenstein, J.M.; Luo, Y. The importance of ATP-related compounds for the freshness and flavor of post-mortem fish and shellfish muscle: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1787–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagedhal, A.; Busalmen, J.P.; Roldán, H.A.; Paredi, M.E.; Crupkin, M. Post-mortem changes in adenosine triphosphate and related compounds in mantle of squid (Illex argentinus) at different stages of sexual maturation. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 1997, 6, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyewoda, A.D.; Shaw, S.J.; Ke, P.J.; Burns, B.G. Recommended Laboratory Methods for Assessment of Fish Quality; Canadian Technical Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences. No. 1448; Department of Fisheries and Oceans: Halifax, NS, Canada, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.S.; Hamann, D.D.; Webb, N.B.; Sidwell, V. Effects of species and storage time on minced fish gel texture. J. Food Sci. 1979, 44, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NORMA Oficial Mexicana. NOM-092-SSA1-1994, Bienes y Servicios. Método Para la Cuenta de Bacterias Aerobias en Placa. México, D.F. Available online: https://dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=4886029&fecha=12/12/1995#gsc.tab=0 (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Ocaño-Higuera, V.M.; Maeda-Martínez, A.N.; Marquez-Ríos, E.; Canizales-Rodríguez, D.F.; Castillo-Yáñez, F.J.; Ruíz-Bustos, E.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M. Freshness assessment of ray fish stored in ice by biochemical, chemical and physical methods. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.-H.; Sun, D.-W.; Han, Z.; Zeng, X.-A. Texture and Structure Measurements and Analyses for Evaluation of Fish and Fillet Freshness Quality: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarahi, M.; Abdolalizadeh, L.; Hedayati, S. Mung bean protein isolate: Extraction, structure, physicochemical properties, modifications, and food applications. Food Chem. 2024, 444, 138626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocaño-Higuera, V.M.; Marquez-Ríos, E.; Canizales-Dávila, M.; Castillo-Yáñez, F.J.; Pacheco-Aguilar, R.; Lugo-Sánchez, M.E.; Graciano-Verdugo, A.Z. Postmortem changes in cazon fish muscle stored on ice. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.S.; Roth, B.; Jessen, F.; Jakobsen, A.N.; Lerfall, J. Water holding properties of Atlantic salmon. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 477–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-Y.; Park, S.-W.; Shin, H.-S. Fish Freshness Indicator for Sensing Fish Quality during Storage. Foods 2023, 12, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, K.A.; Saeed, M.; Jamilah, B.; Ebrahimian, M. A review on correlations between fish freshness and pH during cold storage. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2008, 4, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhit, A.E.D.A.; Holman, B.W.; Giteru, S.G.; Hopkins, D.L. Total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) and its role in meat spoilage: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 280–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Sakaguchi, M. Storage of yellowtail (Seriola quinquerediata) white and dark muscles in ice. Changes in content of adenina nucleotides and related compounds. J. Food Sci. 1986, 55, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.S.; McCormick, M.C.; Robergs, R.A. Interaction among skeletal muscle metabolic energy systems during intense exercise. J. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 2010, 905612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocano-Higuera, V.M.; Maeda-Martínez, A.N.; Lugo-Sánchez, M.E.; Pacheco-Aguilar, R. Postmortem biochemical and textural changes in the adductor muscle of catarina scallop stored at 0 °C. J. Food Biochem. 2006, 30, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.V.; Fitts, R.H. Muscle fatigue in the frog semitendinosus: Role of the high-energy phosphates and Pi. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 263 Pt 1, C803–C809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haard, N. Biochemistry and chemistry of color and color change in seafood. In Advances in Seafood Biochemistry, Composition and Quality; Flinck, J., Ed.; Technomic Publishing Co.: Lancaster, PA, USA, 1992; pp. 305–360. [Google Scholar]
- Özogul, Y.; Özogul, F. Degradation products of adenine nucleotides in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) stored in ice in modified atmosphere packaging. Turk. J. Zool. 2002, 26, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Howgate, P. A review of the kinetics of degradation of inosine monophospate in some species of fish during chilled storage. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 41, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srirangsan, P.; Hamada-Sato, N.; Kawai, K.; Watanabe, M.; Suzuki, T. Improvement of fish freshness determination method by the application of amorphous freeze-dried enzymes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12456–12461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, H.; Nakazato, K.; Hamada-Sato, N. Adenosine monophosphate degradation and inosinic acid accumulation in the shrimp Penaeus japonicus. Int. Aquat. Res. 2017, 9, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Ruíz, E.I.; Ocaño-Higuera, V.M.; Valdez-Hurtado, S.; Cruz-Guzmán, J.A.; Otero-León, C.B.; Ruíz-Cruz, S.; Garzón-García, A.M.; Barrales-Cureño, H.J.; Canizales-Rodríguez, D.F.; Pérez-Martínez, C.J.; et al. Quality Improvement and Shelf-Life Extension of Iced Nile Tilapia Fillets Using Natural Garlic Extract. Fishes 2023, 8, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huss, H.H. Quality and Quality Changes in Fresh Fish; Fisheries Technical Document No. 348; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1995; p. 202. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Yáñez, F.J.; Pacheco-Aguilar, R.; Márquez-Ríos, E.; Lugo-Sánchez, M.E.; Lozano-Taylor, J. Freshness loss in sierra fish (Scomberomorus sierra) muscle stored in ice as affected by poscapture handling practices. J. Food Biochem. 2007, 31, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, I.S. Chemical, sensory and shelf life evaluation of sliced salmon treated with salts of organic acids. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özogul, Y.; Özogul, F.; Kuley, E.; Özkutuk, A.S.; Gökbulut, C.; Köse, S. Biochemical, sensory and microbiological attributes of wild turbot (Scophthalmus maximus), from the Black Sea, during chilled storage. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Arai, K.; Matsuyoshi, M. A new method for estimating the freshness of fish. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1959, 24, 749–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanam, P.T.; Gopakumar, K. K-value, an index for estimating fish freshness and quality. Curr. Sci. 1999, 76, 400–404. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, K.; Ohashi, C.; Ohtuki, K.; Kawabata, M. Type V collagen in trout (Salmo gairdneri) muscle and its solubility change during chilled storage of muscle. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, U.B.; Thomassen, M.S.; Rora, M.B. Texture properties of farmed rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Effects of diet, muscle fat content and time of storage in ice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1997, 74, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, K.; Smith, J. The effect of slaughter method on the quality of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) during storage on ice. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1998, 24, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, P.; Borderias, J. Effect of rigor mortis and ageing on collagen in trout (Salmo irideus) muscle. J. Food Agric. 1990, 52, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, I.; Taylor, R.; Astier, C.; Ventre, F.; Lebart, M.; Roustan, C.; Ouali, A.; Benyamin, Y. Dystrophin cleavage and sarcolemma detachment are early post mortem changes on sea bass (Dicentrachus labrax) white muscle. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, J.; Bermell, S. Propiedades funcionales de las proteínas miofibrilares: Capacidad de retención de agua. Agroquímica Tecnol. Aliment. 1984, 24, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Hamm, R. Funcional properties of the myofibrillar system and their measurements. In Muscle as Food: Food Science and Technology a Series of Monographs; Bechtel, P.J., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: Orlando, FL, USA, 1986; pp. 135–199. [Google Scholar]
- Pastoriza, L.; Sampedro, G. Influence of ice storage on ray (Raja clavata) wing muscle. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1994, 64, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, R. Processing cod: The influence of season and fishing ground. In Torry Advisory Note No.71; Torry Research Station: Aberdeen, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher, S.D.; Feng, Y.; Hultin, H.O.; Livingston, M.B. Role of initial muscle pH on the solubility of fish muscle proteins in water. J. Food Biochem. 2004, 28, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Zhang, B.; Du, J.; Zhu, S.; Xu, X.; Xie, J. Synergistic Effect of Combined Treatment with Allicin and Antioxidant of Bamboo Leaves and Preservation of Bullfrogs (Lithobates catesbeiana) during Refrigeration Storage. Foods 2023, 12, 3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baygar, T.; Ozgur, N. Sensory and chemical changes in smoked frog (Rana esculanta) leg during cold storage (4 °C ± 1). J. Anim. Adv. 2010, 9, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, E.M.; Gomide, L.A.M.; Fontes, P.R.; Ramos, A.L.S.; Peternelli, L.A. Meat color evaluation and pigment levels in bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) slaughtered by different methods. Aquaculture 2005, 245, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICMSF. Microorganisms in Foods 2: Sampling for Microbiological Analysis: Principles and Specific Applications, 2nd ed.; University of Toronto Press: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1986; p. 131. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelnaby, T.; Feng, T.; Tiantian, Z.; Jiang, X.; Yuming, W.; Li, Z.; Xue, C. Impact of frozen storage on physicochemical parameters and quality changes in cooked crayfish. Heliyon 2024, 2024, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| L | a | b | Texture | pH | WHC | TVB-N | ATP | ADP | AMP | IMP | HxR | Hx | KV | TPB | TMB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | 1.00000 | |||||||||||||||
| a | 0.99435 | 1.00000 | ||||||||||||||
| b | 0.90962 | 0.87377 | 1.00000 | |||||||||||||
| Texture | −0.94709 | −0.95345 | −0.91945 | 1.00000 | ||||||||||||
| pH | −0.46596 | −0.49383 | −0.59029 | 0.72525 | 1.00000 | |||||||||||
| WHC | −0.98375 | −0.96195 | −0.96714 | 0.94319 | 0.49321 | 1.00000 | ||||||||||
| TVB-N | 0.99967 | 0.99319 | 0.90433 | −0.93858 | −0.44321 | −0.98233 | 1.00000 | |||||||||
| ATP | −0.97815 | −0.95773 | −0.88456 | 0.86466 | 0.28706 | 0.96926 | −0.98266 | 1.00000 | ||||||||
| ADP | −0.57261 | −0.51384 | −0.48395 | 0.29432 | −0.41174 | 0.58389 | −0.59187 | 0.73034 | 1.00000 | |||||||
| AMP | −0.96383 | −0.94565 | −0.84048 | 0.82787 | 0.21549 | 0.94412 | −0.97025 | 0.99612 | 0.76489 | 1.00000 | ||||||
| IMP | −0.76715 | −0.70665 | −0.74268 | 0.55884 | −0.09811 | 0.80144 | −0.77986 | 0.88026 | 0.94502 | 0.88921 | 1.00000 | |||||
| HxR | 0.97488 | 0.94984 | 0.90252 | −0.86514 | −0.29629 | −0.97534 | 0.97905 | −0.99865 | −0.73374 | −0.99158 | −0.89076 | 1.00000 | ||||
| Hx | 0.90611 | 0.86928 | 0.82125 | −0.73489 | −0.08565 | −0.90885 | 0.91543 | −0.97418 | −0.86422 | −0.98048 | −0.96181 | 0.97591 | 1.00000 | |||
| KV | 0.89924 | 0.86165 | 0.81338 | −0.72370 | −0.06959 | −0.90205 | 0.90894 | −0.97048 | −0.87231 | −0.97781 | −0.96518 | 0.97222 | 0.99987 | 1.00000 | ||
| TPB | 0.92171 | 0.88096 | 0.87693 | −0.77701 | −0.16951 | −0.93953 | 0.92879 | −0.97858 | −0.82649 | −0.97513 | −0.95525 | 0.98474 | 0.99382 | 0.99252 | 1.00000 | |
| TMB | 0.83052 | 0.76670 | 0.91503 | −0.72357 | −0.22267 | −0.90171 | 0.83473 | −0.89128 | −0.77017 | −0.86854 | −0.93366 | 0.91275 | 0.92041 | 0.91898 | 0.95303 | 1.00000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiménez-Ruíz, E.I.; Valdez-Hurtado, S.; Ocaño-Higuera, V.M.; Canizales-Rodríguez, D.F.; Garzón-García, A.M.; Marquez-Rios, E.; Ruíz-Cruz, S.; Del-Toro-Sanchez, C.L.; Valdez-Álvarez, E.G.; Paredes Quijada, G.T. Effect of Ice Storage on Freshness and Biochemical, Physical, Chemical, and Microbiological Quality of Leg Muscle Samples from Bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus). Processes 2025, 13, 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030910
Jiménez-Ruíz EI, Valdez-Hurtado S, Ocaño-Higuera VM, Canizales-Rodríguez DF, Garzón-García AM, Marquez-Rios E, Ruíz-Cruz S, Del-Toro-Sanchez CL, Valdez-Álvarez EG, Paredes Quijada GT. Effect of Ice Storage on Freshness and Biochemical, Physical, Chemical, and Microbiological Quality of Leg Muscle Samples from Bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus). Processes. 2025; 13(3):910. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030910
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiménez-Ruíz, Edgar Iván, Santiago Valdez-Hurtado, Víctor Manuel Ocaño-Higuera, Dalila Fernanda Canizales-Rodríguez, Alba Mery Garzón-García, Enrique Marquez-Rios, Saúl Ruíz-Cruz, Carmen Lizette Del-Toro-Sanchez, Estefania Guadalupe Valdez-Álvarez, and Gerardo Trinidad Paredes Quijada. 2025. "Effect of Ice Storage on Freshness and Biochemical, Physical, Chemical, and Microbiological Quality of Leg Muscle Samples from Bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus)" Processes 13, no. 3: 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030910
APA StyleJiménez-Ruíz, E. I., Valdez-Hurtado, S., Ocaño-Higuera, V. M., Canizales-Rodríguez, D. F., Garzón-García, A. M., Marquez-Rios, E., Ruíz-Cruz, S., Del-Toro-Sanchez, C. L., Valdez-Álvarez, E. G., & Paredes Quijada, G. T. (2025). Effect of Ice Storage on Freshness and Biochemical, Physical, Chemical, and Microbiological Quality of Leg Muscle Samples from Bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus). Processes, 13(3), 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030910






