Tailored Polylactic Acid/Polycaprolactone Blends with Excellent Strength–Stiffness and Shape Memory Capacities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PLA/PCL Composite Polymer Blends
2.3. Elaboration of Test Samples
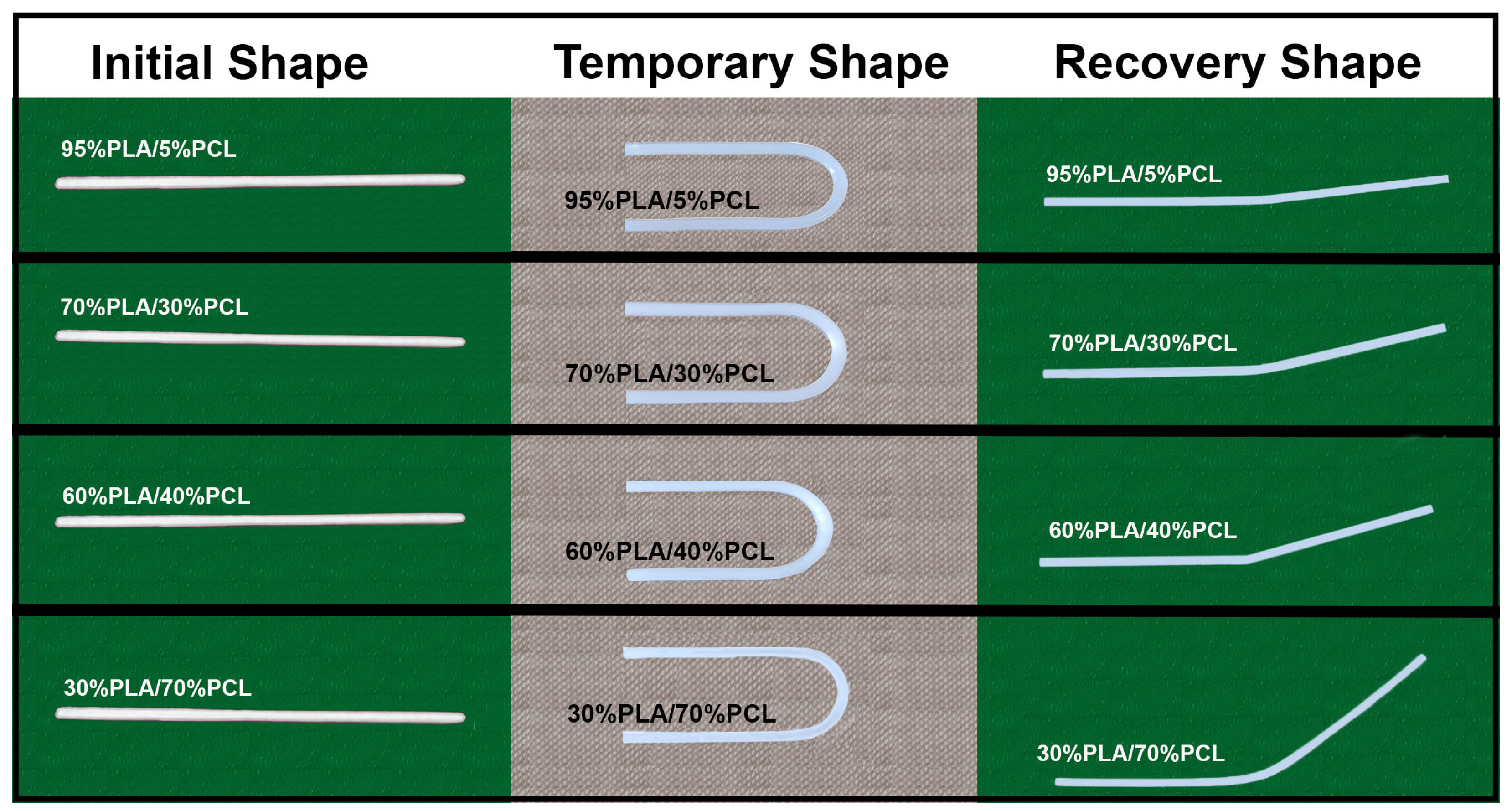
2.4. Shape Memory Experiments
- Sinking the strip for 10 s in a water bath already heated to 60 °C to ensure a uniform sample warming. This temperature was not randomly selected, as the glass transition (Tg) of PLA and the melting temperature of PCL (Tm) were defined by DSC analysis to be 59.7 °C and 63.8 °C, respectively [21]. Standing immersed in the hot water, the sample was bent to an angle of 180° by means of a metallic brace.
- Keeping the applied force unchanged, the sample was transferred to cold water at 5 °C, where it was held for 10 s. After cooling, the external load was withdrawn in order to ascertain the temporary shape of the polymer strip and to record the bending angle of fixation as .
- In the third step, after leaving it to rest for 20 min at room temperature, the specimen was placed again in a warm water bath at 60 °C to recover its permanent state. Then, the strip was pulled off the bath, and the bending angle of recovery was measured and written down as .
- Both bending angles and , which were needed to calculate and , were measured using ImageJ software (version 1.54k).
2.5. Instrumental Methods
3. Results and Discussion
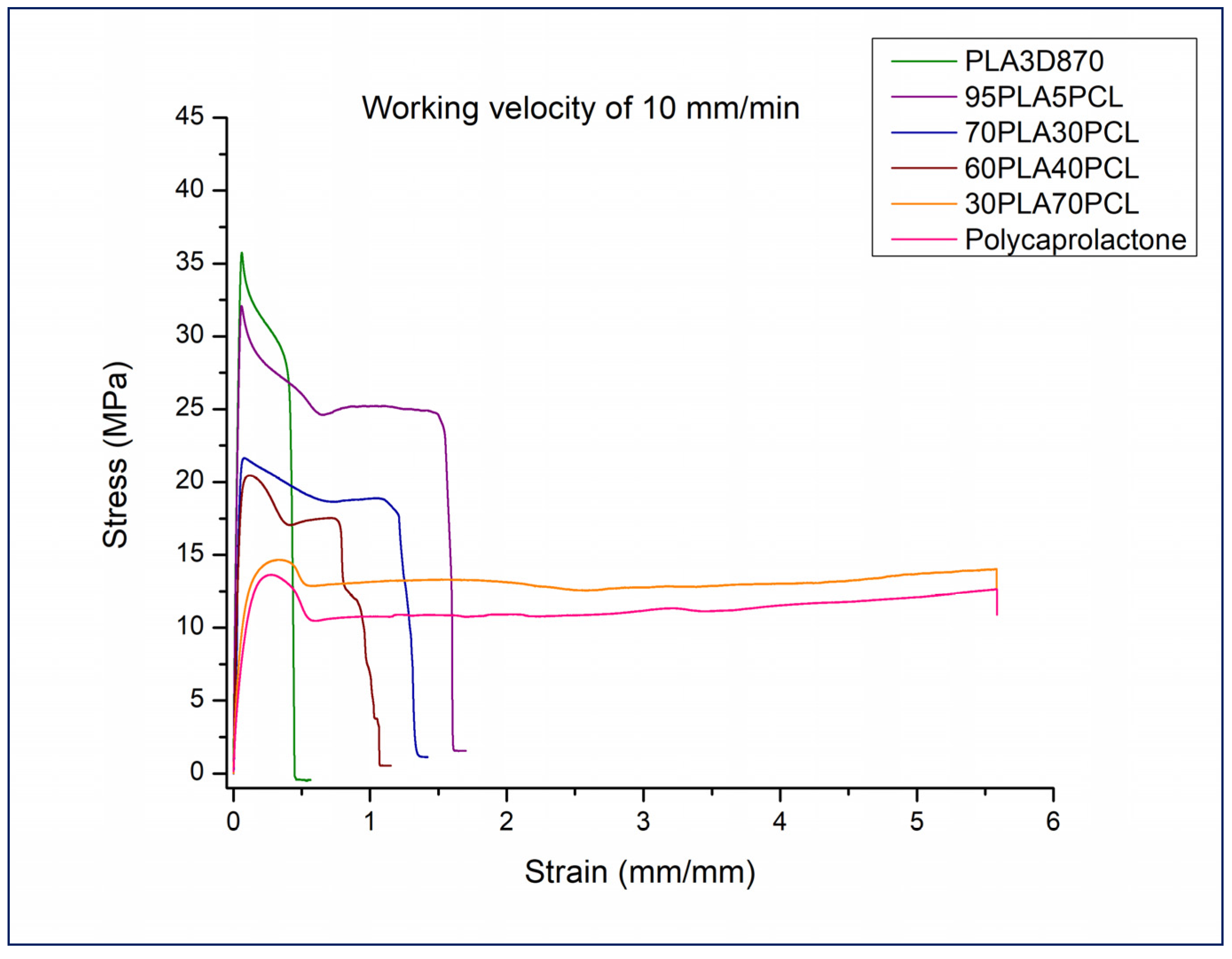
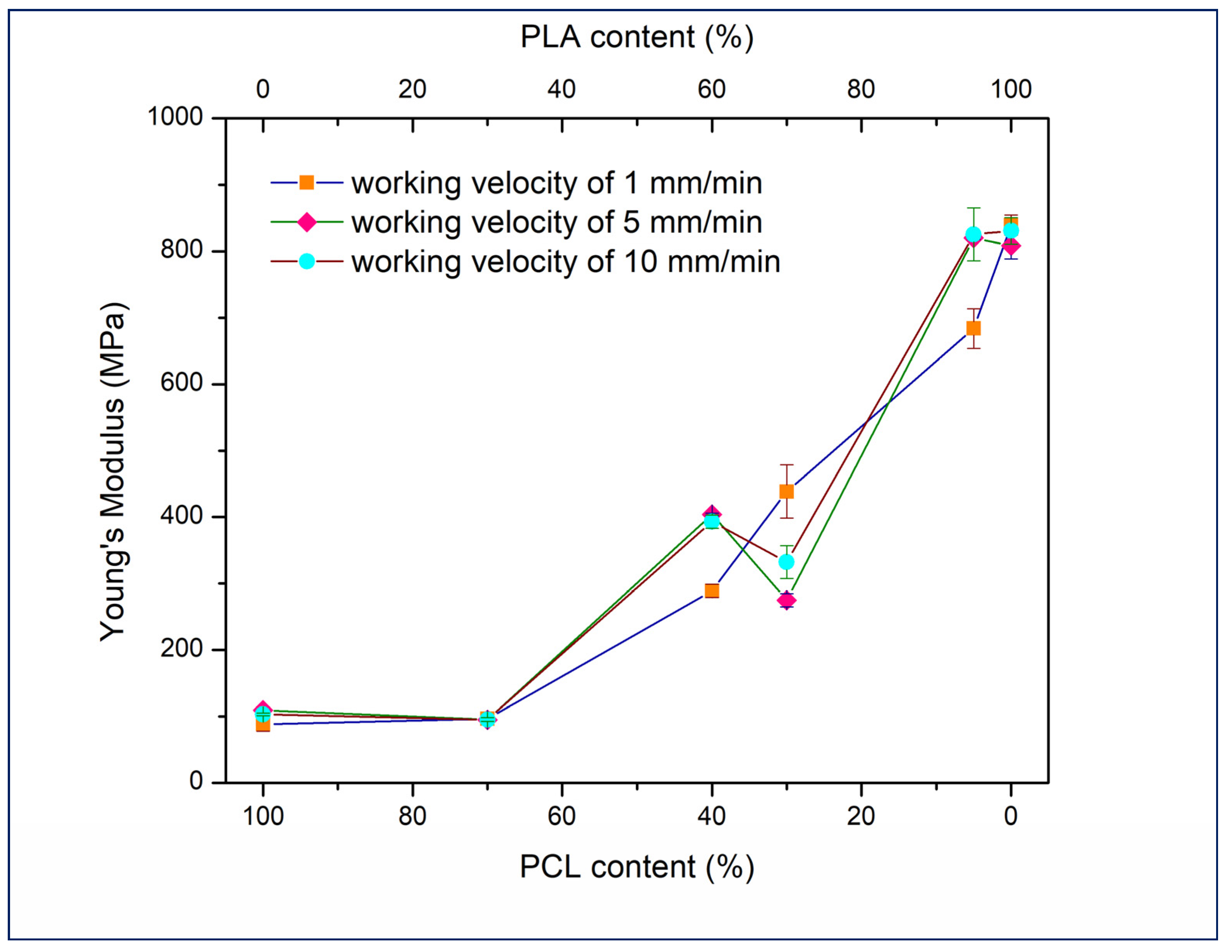
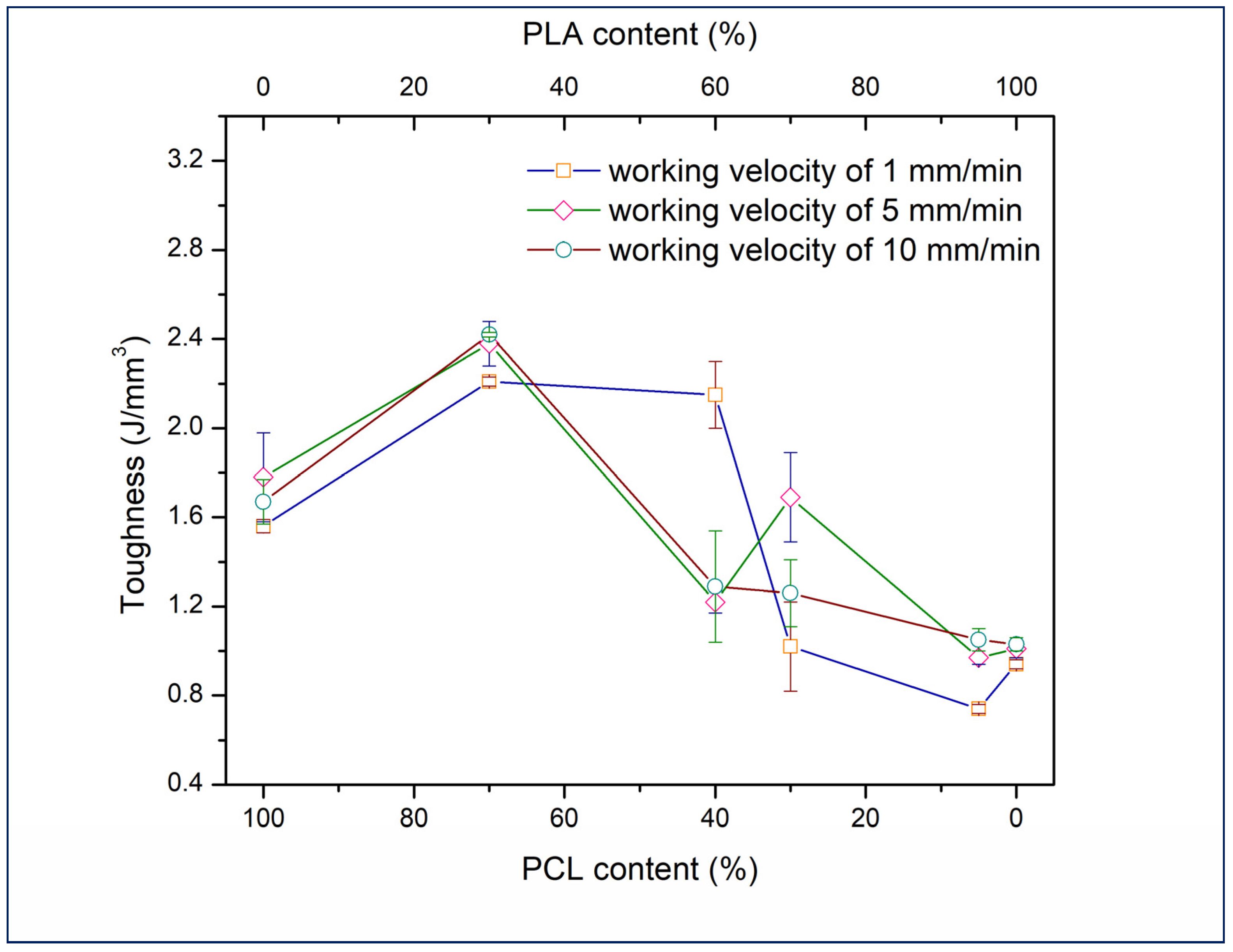
3.1. Tensile Testing Analysis
3.2. Shape Memory Characterization of PLA/PCL Strips
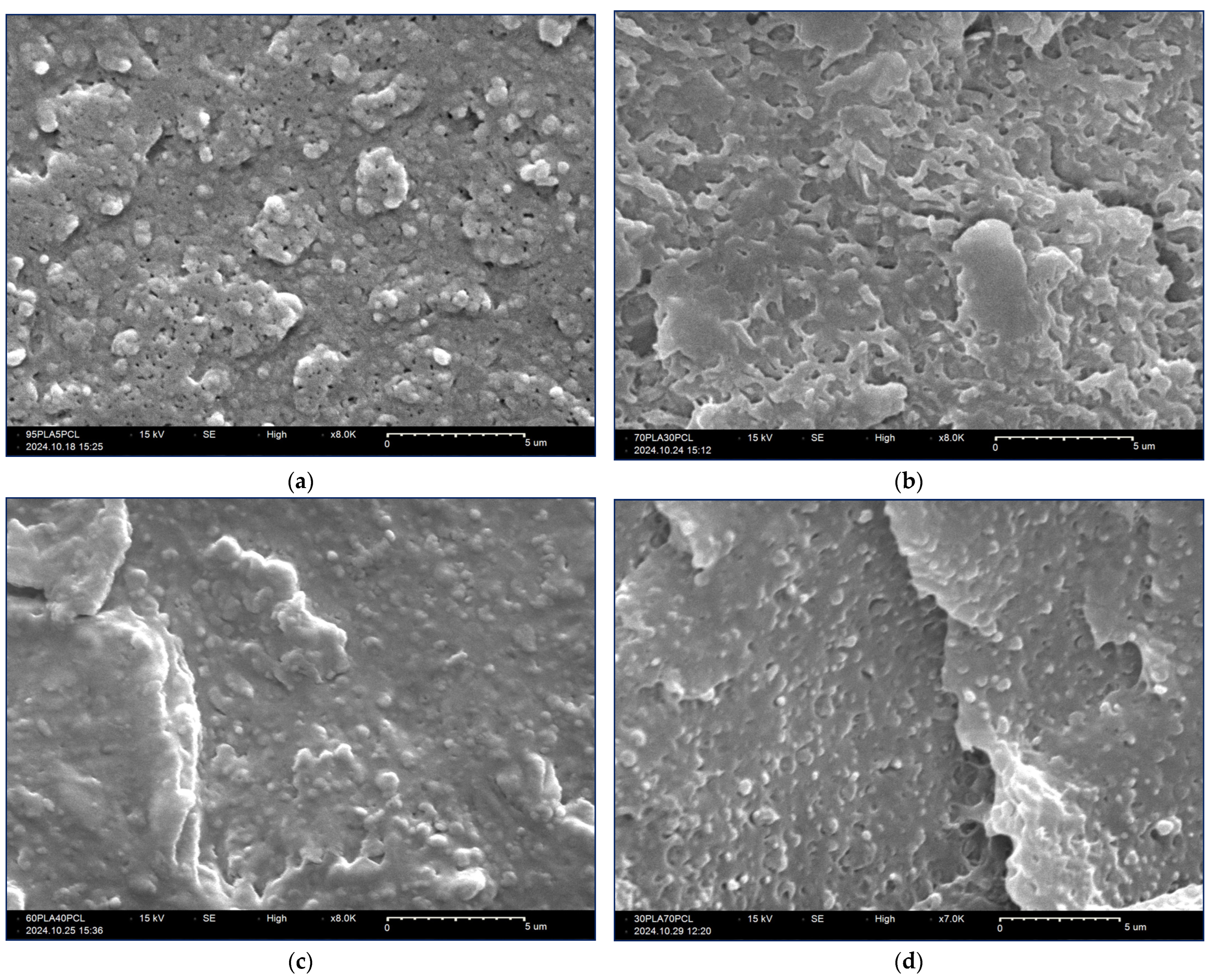
3.3. SEM Analysis of PLA/PCL Blends
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yusoff, R.B.; Takagi, H.; Nakagaito, A.N. Tensile and flexural properties of polylactic acid-based hybrid green composites reinforced by kenaf, bamboo and coir fibers. React. Funct. Polym. 2016, 94, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Baena, I.; Sessini, V.; Dominici, F.; Torre, L.; Kenny, J.M.; Peponi, L. Design of biodegradable blends based on PLA and PCL: From morphological, thermal and mechanical studies to shape memory behavior. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 132, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Gu, T.; Chen, B.; Bi, H.; Hu, Y. Mechanical, thermal properties and shape memory behaviors of PLA/PCL/PLA-g-GMA blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2023, 63, 2084–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molavi, F.K.; Ghasemi, I.; Messori, M.; Esfandeh, M. Nanocomposites based on poly(L-lactide)/poly(ε-caprolactone) blends with triple-shape memory behavior: Effect of the incorporation of graphene nanoplatelets (GNps). Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 151, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, R.; Kumar, V.; Ranjan, N.; Gupta, J.; Bhura, N. On 3D printed thermoresponsive PCL-PLA nanofibers based architected smart nanoporous scaffolds for tissue reconstruction. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 119, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, H.; Dijkstra, P.; Loos, K. The recent development in biobased polymers toward general and engineering applications; polymers that are upgraded from biodegradable polymers, analogous to petroleum-derived polymers, and newly developed. Polymers 2017, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri, S.E.; Mousavi, S.R.; Khakestani, M.; Mozaffari, S.; Ajami, N.; Khonakdar, H.A. Electrospun nanofibers of poly (lactic acid)/poly (ε-caprolactone) blend for the controlled release of levetiraceta. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatu, R.R.; Oria, M.; Rao, M.B.; Peiro, J.L.; Chia-Ying, L. Biodegradation of poly(L-lactic acid) and poly(ε-caprolactone) patches by human amniotic fluid in an in- vitro simulated fetal environment. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, B.G.; Ocón, G.; Silva, F.M.; Iribarren, J.I.; Armelin, E.; Alemán, C. Thermally-induced shape memory behavior of polylactic acid/polycaprolactone blends. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 196, 112230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Pandey, P.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Toughening of polylactic acid: An overview of research progress. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2016, 55, 1623–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortelny, I.; Ujcic, A.; Fambri, L.; Slouf, M. Phase Structure, Compatibility, and Toughness of PLA/PCL Blends: A Review. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urquijo, J.; Guerrica-Echavarria, G.; Eguiazabal, J.I. Melt processed PLA/PCL blends: Effect of processing method on phase structure, morphology, and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, C.L.; Viana, J.C.; Cunha, A.M. Mechanical Properties of Poly(ε-caprolactone) and Poly(lactic acid) Blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Sheng, Y.; Mo, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, B.; Huang, C.; Duan, Q.; Zhao, H. Poly(lactic acid)/polycaprolactone-based self-programmed photothermal responsive shape memory polymers. React. Funct. Polym. 2024, 202, 105990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, J.; Lei, M.; Li, M.; Li, D. Effects of the composition ratio on the properties of PCL/PLA blends: A kind of thermo-sensitive shape memory polymer composites. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, J.; Yang, J.; Cao, X. Preparation and Properties of Biodegradable Shape Memory Polylactic Acid/Poly(ε-caprolactone) Blends under Volume Elongational Deformation. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2023, 308, 2200342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Chen, X.-G.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-F. Temperature and Infill Density Effects on Thermal, Mechanical and Shape Memory Properties of Polylactic Acid/Poly(ε-caprolactone) Blends for 4D Printing. Materials 2022, 15, 8838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; He, H.; Huang, B. Favorable Thermoresponsive Shape Memory Effects of 3D Printed Poly(Lactic Acid)/Poly(epsilon-Caprolactone) Blends Fabricated by Fused Deposition Modeling. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 2000295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xia, Y.; Mu, G.; Gao, Y.; Liang, S.; Li, G.; Yang, Q.; Lin, X.; Qian, F. The preparation and characterization of biodegradable PCL/PLA shape memory blends. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Pure Appl. Chem. 2021, 58, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.M.; Wu, S.H.; Lin, G.G.; Don, T.M. Unusual mechanical properties of melt blended poly(lactic acid) (PLA)/clay nanocomposites. Euro. Polym. J. 2014, 52, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, E.; Kotsilkova, R.; Georgiev, V.; Batakliev, T.; Angelov, V. Advanced Rheological, Dynamic Mechanical and Thermal Characterization of Phase-Separation Behavior of PLA/PCL Blends. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2025, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostafinska, A.; Fortelny, I.; Nevoralova, M.; Hodan, J.; Kredatusova, J.; Slouf, M. Synergistic effects in mechanical properties of PLA/PCL blends with optimized composition, processing, and morphology. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 98971–98982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostafinska, A.; Fortelny, I.; Hodan, J.; Krejcikova, S.; Nevoralova, M.; Kredatusova, J.; Kruliš, Z.; Kotek, J.; Slouf, M. Strong synergistic effects in PLA/PCL blends: Impact of PLA matrix viscosity. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 69, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Li, L.; Shi, X.; Yeh, J.-M.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, P. Conductive Stretchable Shape Memory Elastomers Combining with Electrical Stimulation for Synergistic Osteogenic Differentiation. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, J.; Shi, M.; Zhang, H.; Ma, P.X.; Guo, B. Electroactive anti-oxidant polyurethane elastomers with shape memory property as non-adherent wound dressing to enhance wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 121999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunes, I.S.; Cao, F.; Jana, S.C. Evaluation of nanoparticulate fillers for development of shape memory polyurethane nanocomposites. Polymer 2008, 49, 2223–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, L.; Gigante, V.; Geerinck, R.; Coltelli, M.-B.; Lazzeri, A. Micromechanical analysis and fracture mechanics of poly(lactic acid) (PLA)/polycaprolactone (PCL) binary blends. Polym. Test. 2023, 121, 107984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Huang, C.; Xiu, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Toughening of poly(L-lactide) with poly(epsilon-caprolactone): Combined effects of matrix crystallization and impact modifier particle size. Polymer 2013, 54, 5257–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broz, M.E.; VanderHart, D.L.; Washburn, N.R. Structure and mechanical properties of poly(D,L-lactic acid)/poly(ε-caprolactone) blends. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4181–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Polymer Blend | PLA, wt% | PCL, wt% |
|---|---|---|
| 95PLA/5PCL | 95 | 5 |
| 70PLA/30PCL | 70 | 30 |
| 60PLA/40PCL | 60 | 40 |
| 30PLA/70PCL | 30 | 70 |
| Polymer Blend | [%] | [%] at 60 °C | [%] at 70 °C | [s] at 60 °C | [s] at 70 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95PLA/5PCL | 96.7 | 92.4 | 96.0 | 70 | 7 |
| 70PLA/30PCL | 97.8 | 91.2 | 92.7 | 70 | 7 |
| 60PLA/40PCL | 98.3 | 79.5 | 82.2 | 70 | 7 |
| 30PLA/70PCL | 97.2 | 78.5 | 79.2 | 70 | 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Batakliev, T.; Georgiev, V.; Ivanov, E.; Angelov, V.; Kotsilkova, R. Tailored Polylactic Acid/Polycaprolactone Blends with Excellent Strength–Stiffness and Shape Memory Capacities. Processes 2025, 13, 1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051328
Batakliev T, Georgiev V, Ivanov E, Angelov V, Kotsilkova R. Tailored Polylactic Acid/Polycaprolactone Blends with Excellent Strength–Stiffness and Shape Memory Capacities. Processes. 2025; 13(5):1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051328
Chicago/Turabian StyleBatakliev, Todor, Vladimir Georgiev, Evgeni Ivanov, Verislav Angelov, and Rumiana Kotsilkova. 2025. "Tailored Polylactic Acid/Polycaprolactone Blends with Excellent Strength–Stiffness and Shape Memory Capacities" Processes 13, no. 5: 1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051328
APA StyleBatakliev, T., Georgiev, V., Ivanov, E., Angelov, V., & Kotsilkova, R. (2025). Tailored Polylactic Acid/Polycaprolactone Blends with Excellent Strength–Stiffness and Shape Memory Capacities. Processes, 13(5), 1328. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051328







