Abstract
In petroleum production processes, the water used to maintain formation pressure often plays a key role and is pumped into injection wells to compensate for the pressure drop in the formation after oil extraction and displacement of the remaining petroleum products to the development well. The source of such water may be produced by waters extracted together with oil and previously purified from mechanical impurities and hydrocarbons. However, a significant disadvantage of using such water is the presence of pollutants such as sulphur-reducing bacteria (SRB) and a high content of hydrogen sulfide. Traditional purification methods against them show low efficiency. Hydrogen sulfide and SRB are not only a threat of environmental pollution, but they also pose a high risk to pipelines in the petroleum industry due to an increase in the rate of metal corrosion. In this paper, formation water was treated with a field deployment flow-mode plasma discharge unit. A significant decrease in the growth rate of SRB in treated water was achieved. Bacterial growth was suppressed for up to 14 days after three treatment cycles of treatment. The hydrogen sulfide content was reduced by 33% after one cycle of plasma discharge water treatment.
1. Introduction
Aiming to maintain the required level of formation pressure in an oil field, injection wells designed to inject steam or liquid into the productive formation are used. Under the influence of the injected water, oil is displaced from the rock towards the development well. This makes it possible to maintain a high level of formation productivity and regulate the rate of extraction of minerals, as well as to efficiently develop fields with hard-to-recover oil reserves [1]. However, the use of injection wells entails various risks due to favourable conditions for the development of sulphur-reducing bacteria (SRB) in the well.
SRB are a group of microorganisms that reduce sulphates to sulfides during vital activity [2,3]. A distinctive feature of these microorganisms is their ability for anaerobic respiration due to the use of sulphates as the final electron acceptor instead of oxygen, allowing them to survive in oxygen-free conditions. This property allows SRB to develop their colonies in oil reservoirs, which negatively affects the petroleum production process and oil quality [4].
SRB are one of the main microorganisms in the formation and development of metal corrosion due to the formation of toxic hydrogen sulfide [5,6], hydrogen consumption [7,8], as well as due to the formation of biofilms, which form an environment favorable for the development of corrosion [9,10]. Hydrogen sulfide, which is intensively released during the vital activity of the SRB, is a toxic gas that destroys reinforced concrete and metal pipes, instrumentation and other equipment used in the petroleum industry [11]. The problem of biocorrosion caused by SRB is most pronounced in regions with developing oil and gas industries due to lack of funds and equipment. Some of such regions include some African countries such as Nigeria, Angola, and Algeria, where oil production is a key sector of the economy. SRB activity in oil fields in these countries leads to significant economic losses.
The problem of biological corrosion makes it urgent to develop new methods for suppressing SRB in reservoir waters. Currently, there are various physical, chemical and physico-chemical methods of suppressing the vital activity of SRB in water. Many works have been devoted to the study of the effectiveness of chemical methods of exposure to SRB using such oxidizing agents and bactericides such as nitric acid [12], essential oils [13], formic acid salts [14], and potassium permanganate [15]. In addition, biological methods of SRB control have shown high efficiency [16]. However, despite the relatively high effectiveness against bacteria and a wide range of effects, the use of these methods may cause difficulties associated with the production and transportation of reagents and the formation of toxic by-products [17].
Currently, a group of chemical and physico-chemical methods of water purification, known as Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs), is increasingly developing. These methods are aimed at the decomposition of stable organic and inorganic pollutants, which is made possible by the generation of •OH hydroxyl radicals, as well as other reactive oxygen species, such as superoxide radical O2−, atomic oxygen O2, and hydrogen peroxide H2O2 [18]. AOP methods include photocatalytic oxidation (for example, using TiO2/UV [19,20]), Fenton reactions [21], ozonisation [22,23,24], and ultrasonic oxidation during cavitation [25].
Combined methods, which are a combination of several AOPs or traditional purification methods, are promising in the field of water purification. The implementation of such methods makes it possible to strengthen standard AOP methods, increase their effectiveness and compensate for some of their shortcomings. Ultrasonic cavitation has found wide application in combination with other AOP methods [26], which is capable of enhancing the effect of various oxidizing agents. Thus, when cavitation and ozonisation are used together [27], additional free radicals are formed due to cavitation effects, and then reactions with O3 and water are initiated, which also result in the formation of free radicals. In addition, O3 can be converted to •OH when the cavitation bubble collapses. When combined with H2O2 and cavitation oxidation methods [28], due to the formation of local points with high temperature and pressure in the cavitation field, part of the hydrogen peroxide begins to decompose with the release of an •OH radical, thereby increasing the effectiveness of the method, since the •OH radical is a stronger oxidizer. Cavitation can also play an important role in the generation of a plasma discharge in a liquid, since more favourable conditions for ionization of the medium and breakdown formation appear in the formed liquid–gas phase boundaries in cavitation bubbles, as a result of which the breakdown voltage of the medium decreases to 1–10 kV/cm.
The key advantage of AOP methods lies not only in their ability to suppress the vital activity of a wide class of bacteria but also in their ability to effectively destroy complex organic compounds, including antibiotic residues, pesticides and dyes, to low-molecular-weight products or complete mineralization [29]. However, despite their high efficiency, AOPs have a number of limitations. The main disadvantages include high energy consumption (especially in processes with UV radiation), the need to optimize some chemical parameters of the treated liquid (pH and concentration of reagents) and the potential formation of toxic products as a result of oxidation of certain pollutants [30]. In addition, the use of certain methods, such as the Fenton reaction, requires the subsequent removal of catalyst residues, which may require the development of separate methods [31]. Nevertheless, the expansion of the scope of AOP methods in the field of water treatment, in combination with traditional methods [32,33], can increase the economic efficiency of water treatment and make this process more environmentally friendly in the treatment of industrial effluents. The sonoplasma method of water treatment, based on the combined effect of plasma discharge and hydrodynamic cavitation, provides the energetically efficient use of the advantages of these AOP methods while eliminating some of the disadvantages [34].
In this paper, a unit for sonoplasma water treatment in real oil fields was implemented to purify injection wells water from hydrogen sulfide and SRB. To assess the impact of sonoplasmic water treatment on the vital activity of the SRB, contamination of a water solution was performed by introducing a cumulative culture of the SRB in such a way as to simulate the actual level of contamination of formation water. The results of using a sonoplasma unit for the decomposition of hydrogen sulfide dissolved in water were obtained by introducing a sonoplasma unit into the process of preparing the produced water as the final stage of purification after the ultrafiltration unit.
2. Materials and Methods
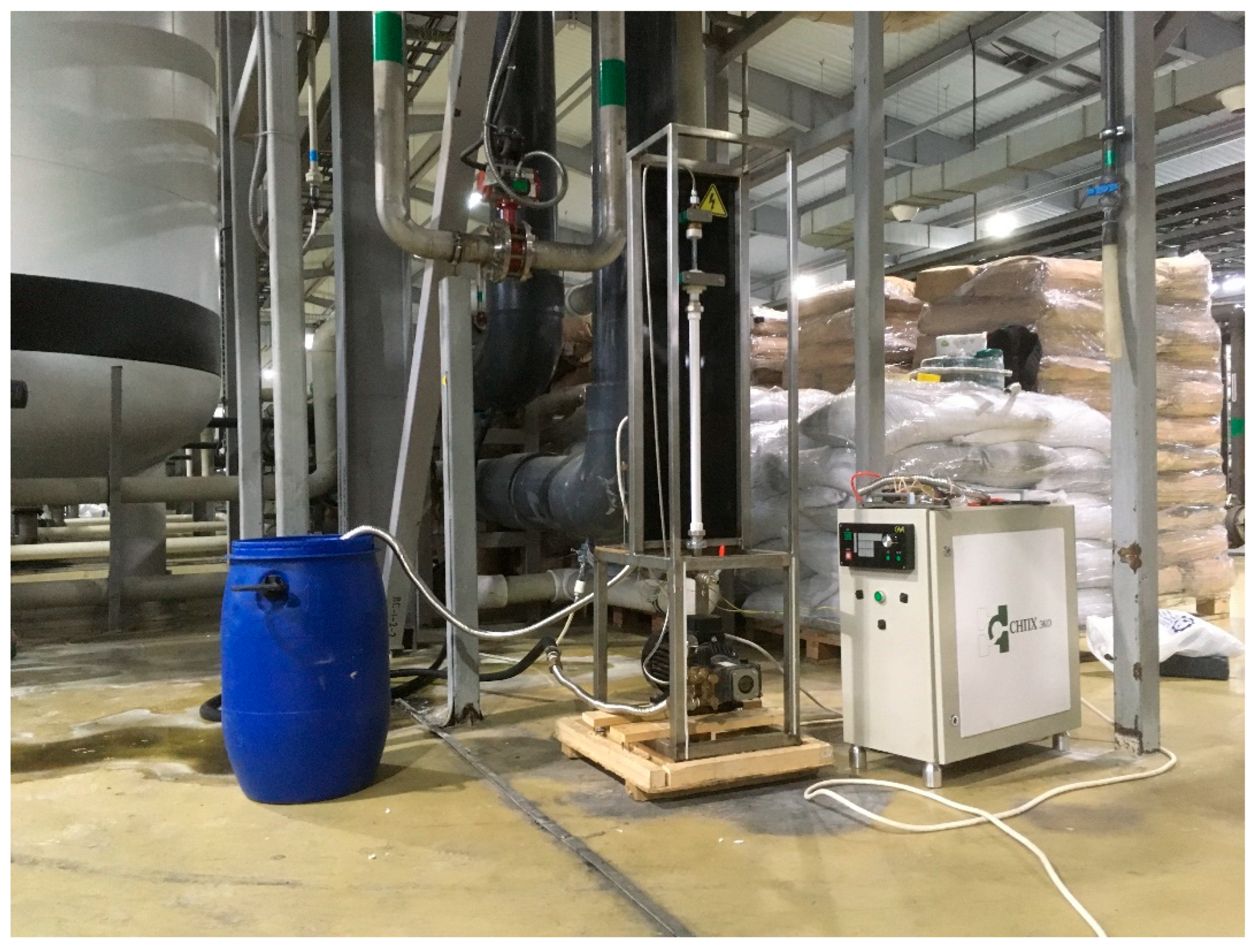
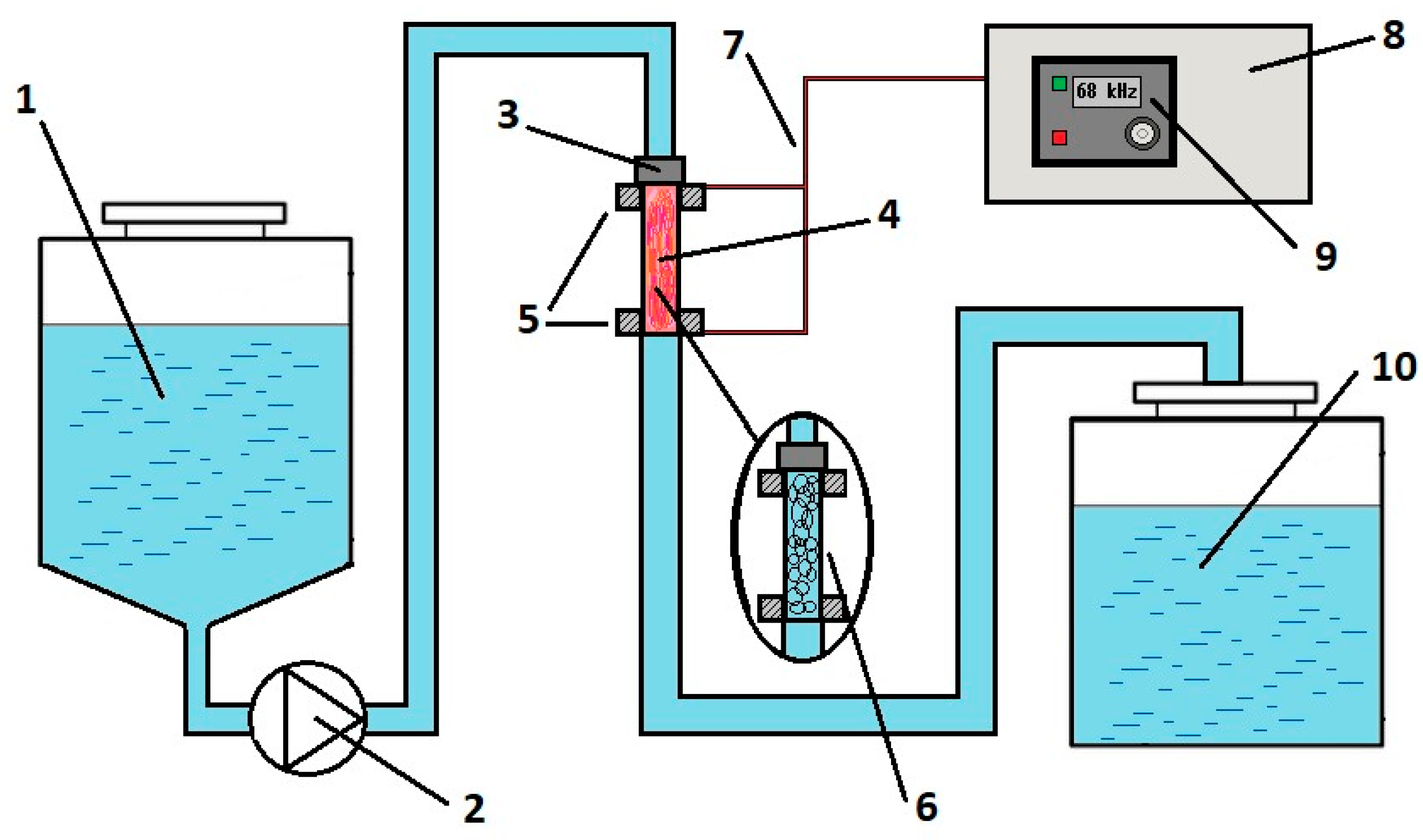
Figure 1 shows a diagram of a sonoplasma unit (Applied Acoustics Center, Moscow, Russia) for water treatment in cavitation conditions. A more detailed description of the mechanisms of the designed unit is presented in one of our earlier articles [34]. In this unit configuration, a constant stream of water pumped at a pressure of 40 bar enters the reactor tube, where a hydrodynamic emitter converts acoustic energy into a cavitation field. When an alternating voltage is applied to the electrodes at the ends of the reactor tube in the frequency range from 30 to 70 kHz with an amplitude of up to 4 kV, a stable plasma discharge is maintained in the reactor. The distance between electrodes is 150 mm. The pulse frequency is adjusted directly on the generator panel. The amplitude of the current of the secondary winding of the high-voltage block during plasma combustion can reach 9 A, depending on the current treatment mode. The capacity of this equipment is 12 L/min. Electrical power measurements were performed using a four-channel Tektronix TPS 2024B (Tektronix, Beaverton, OR, USA) oscilloscope between the generator and the high-voltage unit.
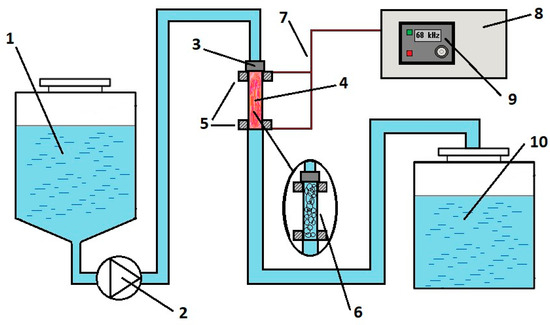
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of an installation for generating plasma in water under cavitation conditions: 1—inlet water tank; 2—pump; 3—hydrodynamic emitter; 4—plasma reactor; 5—electrodes; 6—cavitation field in the reactor in the absence of high-frequency electrical pulses; 7—high-voltage cable; 8—generator; 9—control panel; 10—outlet tank with treated water.
In the present paper, sonoplasma treatment of water contaminated with SRB culture was performed at a power of 4.5 kW and at an electrical pulse frequency of 30 kHz. The object of the research was a mineralized aqueous solution containing SRB, which was an analogue of the waters used to maintain reservoir pressure in oil wells. Before the start of the experiment, all unit components, including the inlet and outlet tanks, were treated by repeated circulation of a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution, followed by clean fresh water to ensure the sterility of the unit.
Sonoplasmic treatment of water containing hydrogen sulfide in concentrations from 300 to 440 mg/L was performed in 5 modes with different power levels (from 2.6 to 4.5 kW), differing in the frequency of electrical pulses supplied from the generator to the reactor electrodes through the high-voltage part of the unit (Figure 2).
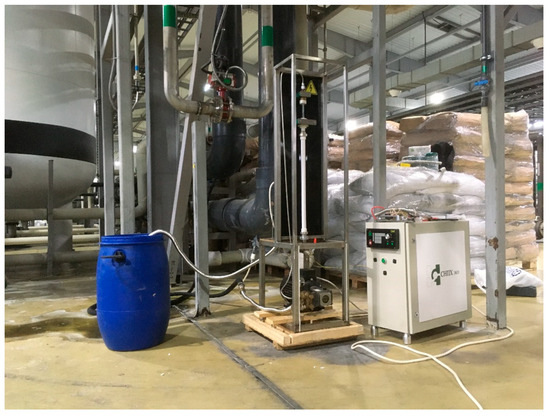

Figure 2.
Industrial plant including a sonoplasma unit in an oil field in the produced water treatment unit.
The hydrogen sulfide content in the water was determined by the iodometric method [35], based on the oxidation of hydrogen sulfide in an acidic environment with iodine (UralHimInvest, Ufa, Russia) in excess. The amount of iodine spent on oxidation was calculated by the difference between the added amount of iodine and its excess, determined by titration with thiosulfate (UralHimInvest, Ufa, Russia):
Contamination of the solution was performed by adding an estimated amount of a cumulative culture of SRB. The culture was replanted several times so that, with extreme replanting, the growth of SRB (blackening of the Postgate medium [36]) was observed on the second day. A culture of 4–5-day exposure of SRB was used for testing. To infect mineralized water with a volume of 15.0 L, a cumulative culture of SRB with an infection rate 108–109 cells per 1.0 mL was used.
The level of contamination with SRB in water was determined as follows. For the first dilution, the selected water at an amount of 1.0 mL, in compliance with the rules of sterility, was added to the first matrass with a Postgate medium; the contents were mixed. Next, 1.0 mL was taken from the first matrass with a new sterile syringe and inserted into the second one. Thus, a number of successive dilutions were obtained: 1:10, 1:100, 1:1000, etc., up to 1:108 in three parallel studies.
After plating, all matrasses were placed in a thermostat with a chamber temperature ranging from +32 °C to +35 °C and kept for 15 days; the change in appearance (the appearance of blackening) was monitored every day. The growth and development of SRB cells was accompanied by the formation of hydrogen sulfide and a clearly visible black sediment: iron sulfide. The number of SRB cells was estimated from the last matrass in which SRB growth was observed. The number of SRB cells in 1.0 mL of the source water was calculated using the following formula:
where
M = 10n−1/V,
M—the number of SRB cells contained in 1.0 mL of the specimen.
n—serial number of the last dilution where bacterial growth was observed;
V—the volume of water used for plating.
The bacterial activity index was taken into account during the period of monitoring the growth of SRB. When observing the growth of SRB on the next day, the activity index was equal to 100 conventional units.
A mineralized solution for further contamination and treatment in a sonoplasma unit was prepared by adding sodium chloride to fresh water in a predetermined proportion (1.2 kg/15.0 L). The solution was kept for 24 h until the salt was completely dissolved in volume with periodic stirring. Contamination of 15.0 L of saline solution with a concentration of 90 g/L was performed in the feed tank by adding the calculated amount of suspension of the accumulative culture of SRB. The liquid in the feed tank was thoroughly mixed for 15–20 min at room temperature (20–25 °C). Samples were then taken to determine the contamination level, density and pH.
3. Results and Discussion
The results of determining the density and pH of the solution (monitored parameters) before and after passing through the sonoplasma unit are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Monitored indicators of contaminated water (salt concentration: 90 g/L).
As can be seen from the data presented in Table 1, the sonoplasmic water treatment did not affect the density and concentration of salt in the water. The pH value began to increase after the second and third treatment cycles, which may be due both to the decomposition of organic compounds and directly to the plasma treatment, since during the combustion of the discharge in the plant reactor, OH radicals and other compounds were formed in the water, affecting the total pH of the water.
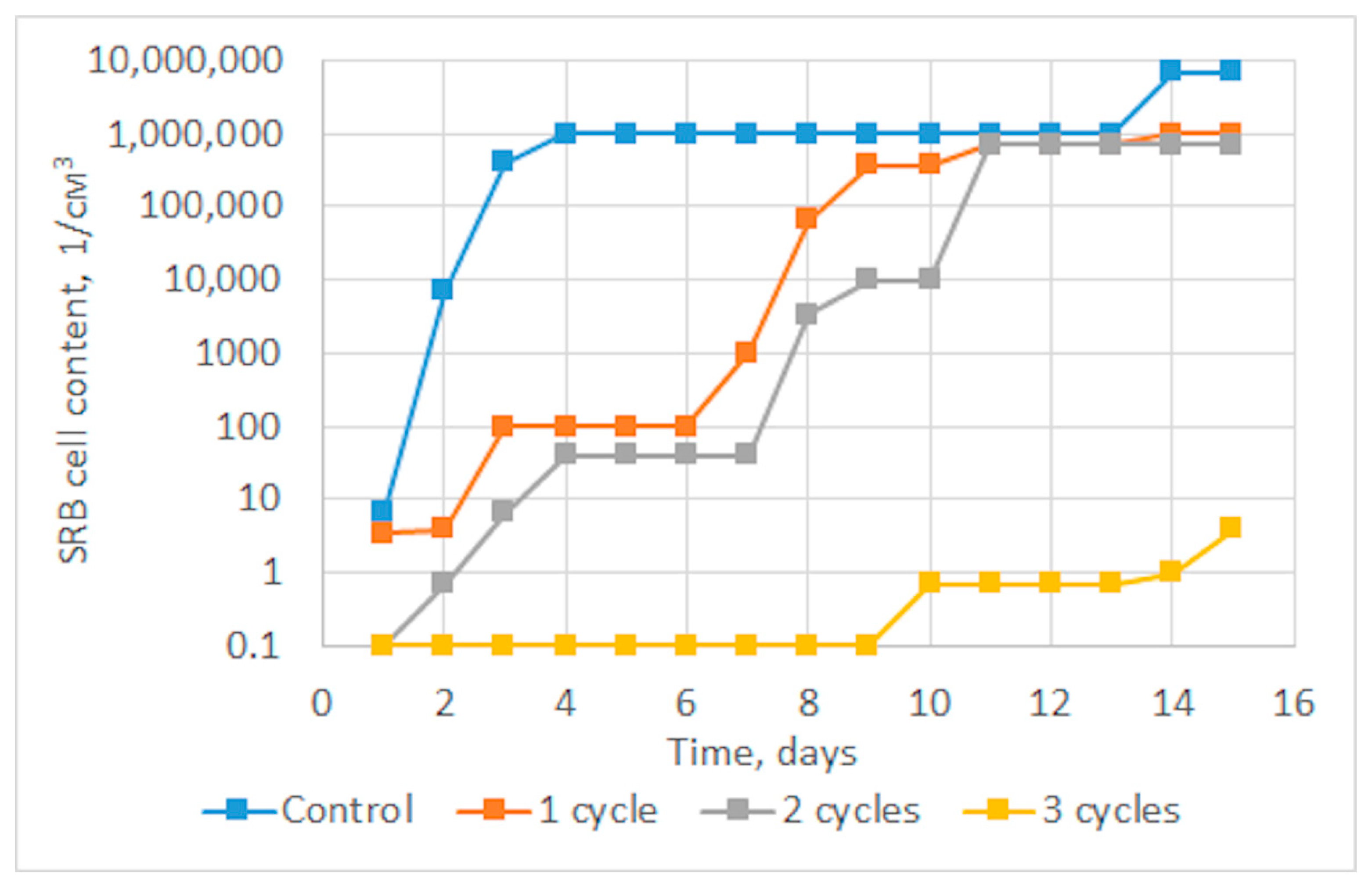
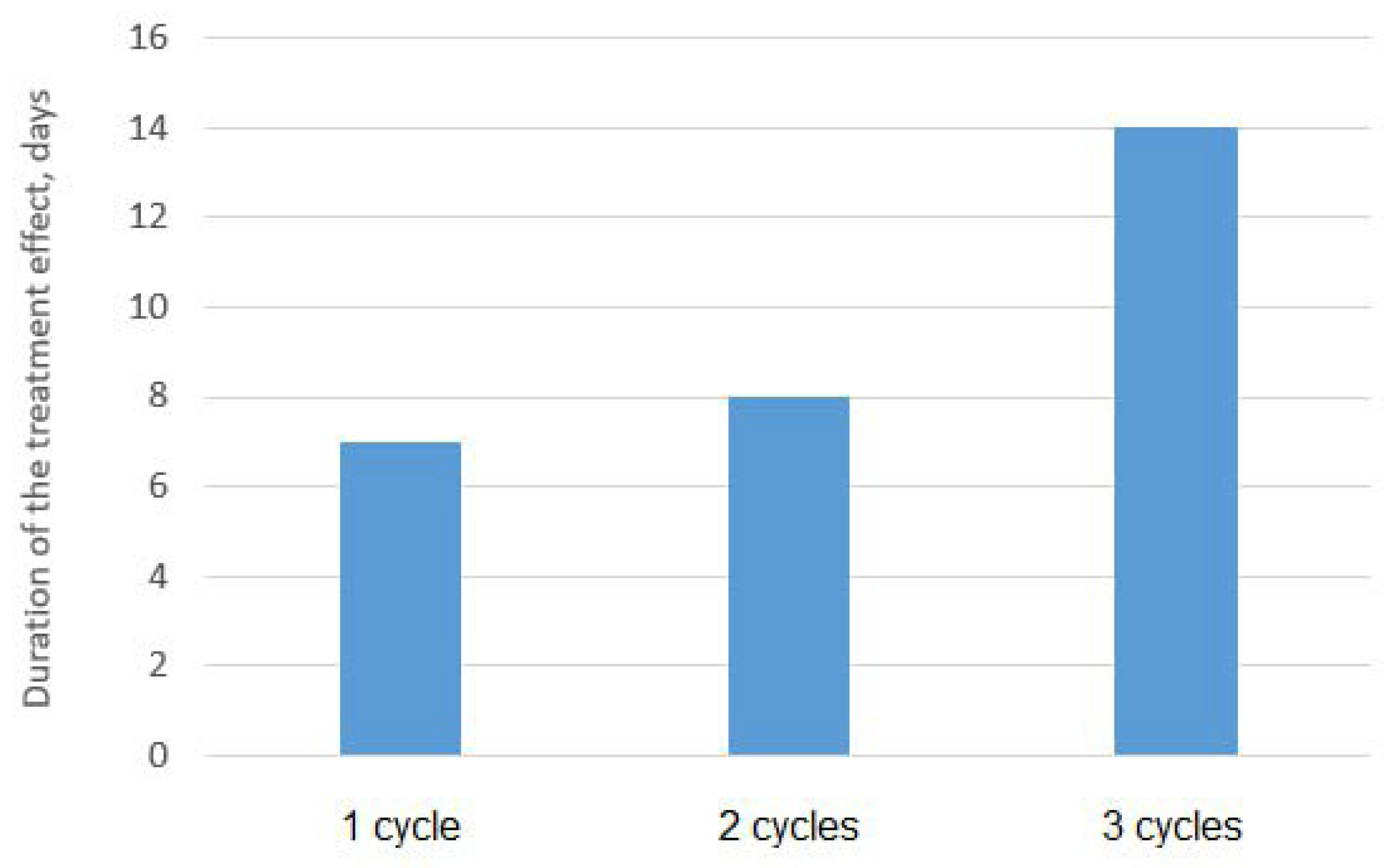
Figure 3 shows graphs of the dependence of the average content of SRB cells in three parallel experiments for several treatment cycles on time. It can be seen from the graph below that a significant decrease in the growth rate of SRB colonies is achieved already during the first and second cycles of sonoplasma treatment, and after the third treatment cycle, bacterial growth is suppressed up to 14 days. The diagram shown in Figure 4 shows the prolonged effect of suppressing the vital activity of SRB colonies during water treatment, depending on the number of treatment cycles. After one cycle of water treatment, a decrease in SRB growth is observed for about 7 days, and the duration of this effect increases with an increase in the number of cycles to 14 days after three treatment cycles.
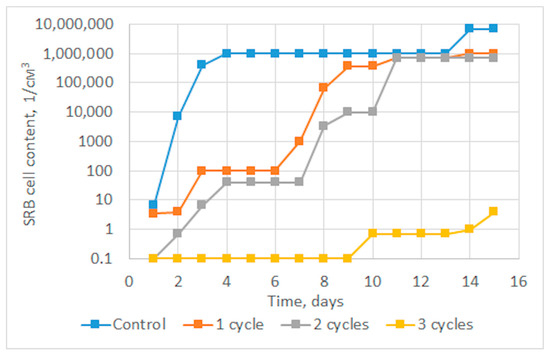
Figure 3.
Average dynamics of SRB cell growth according to the results of three parallel experiments.
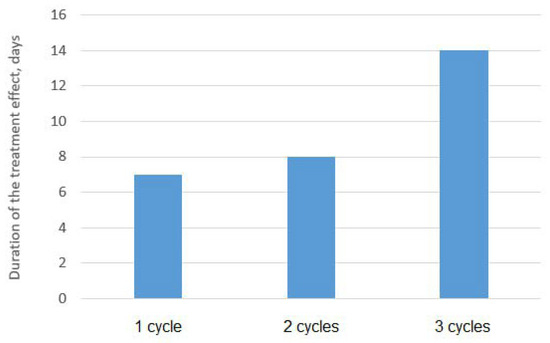
Figure 4.
Number of passages through the sonoplasma treatment and the effect on the suppression of the vital activity of SRB.
In Table 2, the results of the analysis of samples of water produced from an oil field after their treatment in a sonoplasma unit are presented. A significant decrease in the hydrogen sulfide content was detected, up to 20% in the third mode and up to 33.3% in the fifth mode of operation of the unit. There was also an increase in the SO42− content for all treatment modes.

Table 2.
Results of the determination of the content of hydrogen sulfide, hydrosulfides and ions in water before and after treatment in the sonoplasma unit in various modes of electrical pulse frequency and power consumption.
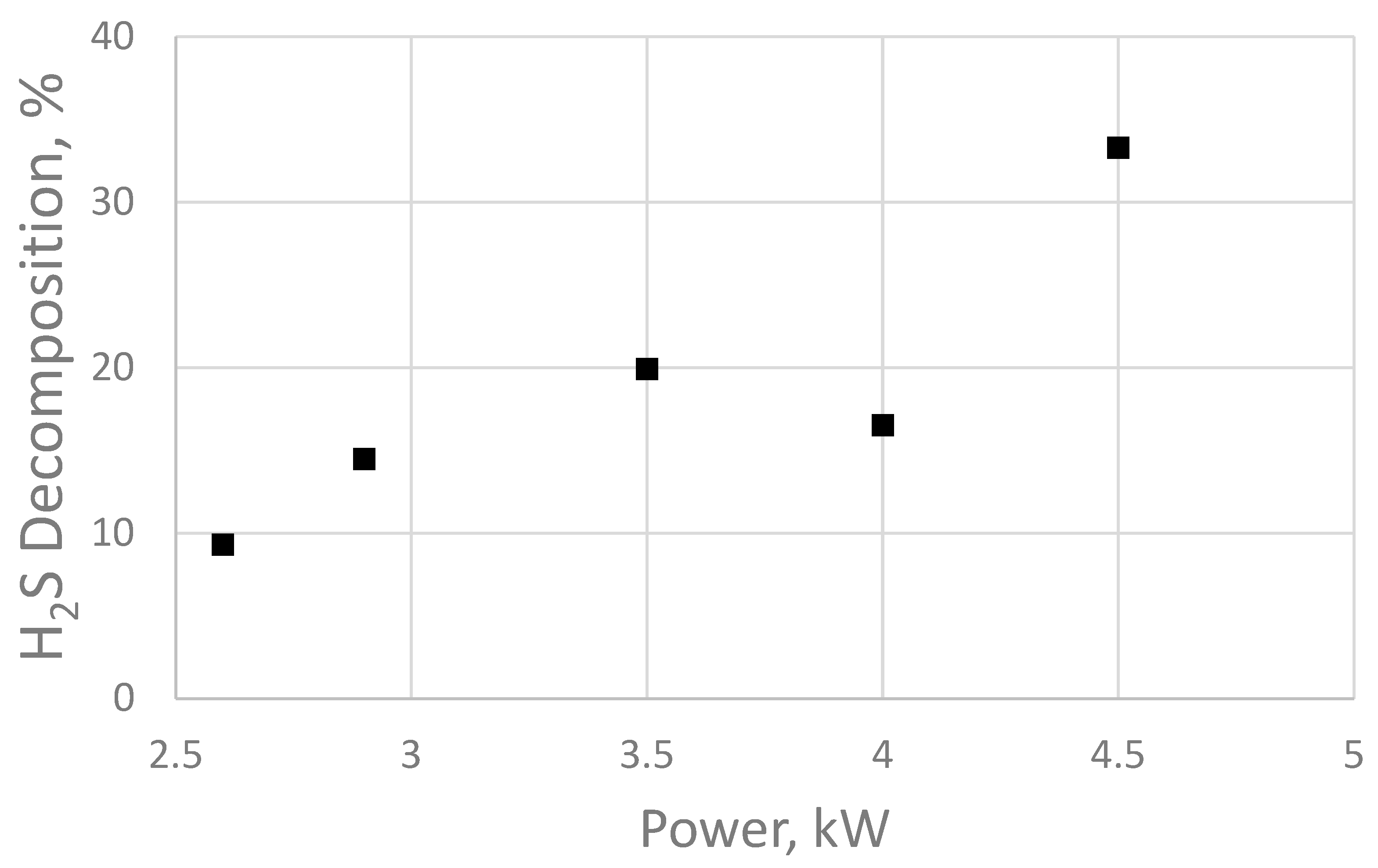
Meanwhile, the pH value and concentration of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions, as well as the content of silicon dioxide, SiO2, in the water did not change significantly compared with the control samples before treatment. Figure 5 provides the dependence of hydrogen sulfide decomposition on the electric pulse power.
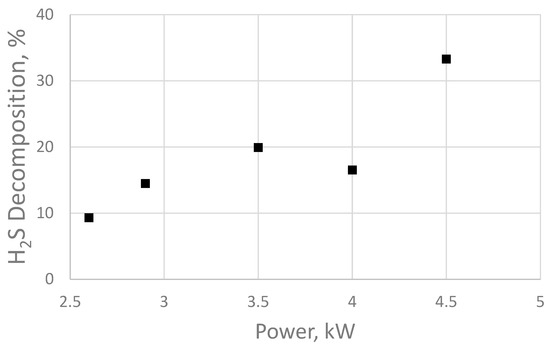
Figure 5.
Decomposition of hydrogen sulfide at different operating powers of the sonoplasma water treatment unit.
Figure 5 demonstrates that the degree of hydrogen sulfide decomposition increases linearly with increasing electrical pulse power; however, the data for 4 kW contradict the general trend. This may indicate that the 4 kW (40 kHz) operating mode is the least energy-efficient from the point of view of the generator electrical circuit. The obtained data correspond to the results of the work in [37], which studied the decomposition of hydrogen sulfide under the influence of dielectric barrier discharge plasma. However, E. Linga Reddy and his research group used a laboratory setup based on the formation of a plasma discharge in gas to obtain these results. Such a system cannot be used for water treatment.
There are several possible mechanisms of the effect of sonoplasma treatment on the bacteria contained in the water. When water enters an area with low pressure in the reactor chamber, a cavitation zone is formed, while cavitation bubbles exert mechanical and thermal effects on bacteria, destroying the cell wall of microorganisms [38]. Such an effect can both inhibit the growth and development of bacteria and significantly reduce their abundance.
One of the main oxidizing agents in AOP methods is the hydroxyl radical •OH, which is formed during decomposition of a water molecule during sonoplasmic discharge treatment [39]. Due to its high reactivity, it is able to destroy persistent organic pollutants. Various sources provide information that •OH radicals can cause lipid peroxidation, which leads to a loss of cellular structure integrity and the disruption of metabolic processes in bacterial cells [40], as well as damage to cell DNA [41]. In addition, the authors of [42] report that the hydroxyl radical not only has high antibacterial efficacy but is also capable of reacting with organic materials included in some biofilms, thereby destroying them.
Due to the formation of hydrogen peroxide in water [43], which has a fairly long lifetime and can persist for up to three weeks at concentrations of about 1–4 mmol/L, water treated with sonoplasma discharge retains its bacteriostatic properties and is able to suppress the growth of colonies of SRB for up to 2 weeks after three treatment cycles. In addition, hydrogen peroxide formed with each new treatment cycle can affect subsequent treatment cycles by decomposing into hydroxide radicals under the influence of sonoplasmic discharge or UV radiation, which occurs simultaneously during plasma discharge. This can be observed in Figure 3 and Figure 4, where the bacteriostatic effect increased significantly with each treatment cycle.
The data shown in Table 2 show that in each mode of sonoplasma treatment, the hydrogen sulfide content decreased, while the concentration of the sulfate ion increased, which can be explained by the destruction of hydrogen sulfide and the subsequent recombination of hydrosulfide ions:
The data obtained show that, due to the high oxidative activity of the hydroxyl ion and hydrogen peroxide, hydrogen sulfide decomposes to atomic sulphur, releasing hydrogen as a gas and forming a sulfate ion. In this paper, the most significant decrease in the concentration of hydrogen sulfide was observed in the maximum processing power mode, from 440 mg/L to 294 mg/L. Thus, in [6], it was shown that reducing the hydrogen sulfide content from 750 mg/L to 50 mg/L makes it possible to achieve a slowdown in the rate of corrosion of pipeline steel equipment by about two times. At the same time, the authors of [44] demonstrated that the corrosion rate of carbon steel can decrease from 19 g/m2h to 8 g/m2h with a decrease in the concentration of hydrogen sulfide from 400 mg/L to 200 mg/L. The rate of corrosion, in addition to the hydrogen sulfide content, may depend on many factors, such as equipment material, temperature, pH, pressure, formation of biofilms on pipe surfaces, etc. However, data from the literature show that a decrease in the hydrogen sulfide content, including the 146 mg/L decrease observed in this paper as a result of the sonoplasma treatment, can significantly reduce the rate of corrosion and thus increase the economic and environmental efficiency of oil-producing wells.
4. Conclusions
In the present work, we report the results of tests conducted on a flow-through sonoplasma unit, aimed at investigating the effects of this treatment on the activity and abundance of SRB in formation water. The sonoplasma treatment was also integrated into a plant for water treatment in order to investigate the reduction in the concentration of hydrogen sulfide in water.
As a result, it was found that water treated with sonoplasma discharge retains its bacteriostatic properties and is able to suppress the growth of SRB colonies for up to 2 weeks. According to various sources in the literature, the reduction in the hydrogen sulfide content in water observed in this work can have a significant impact on the corrosion rate of carbon steel, ranging from a reduction of a few tens of percentage to a reduction in the corrosion rate many times over. The proposed sonoplasma unit for water treatment can thus be effectively used to inactivate SRB and reduce the content of toxic hydrogen sulfide, which not only improves the quality of the wastewater but also allows the treated water to be reused for injection into the formation via an injection well. The reduction in SRB activity and hydrogen sulfide content in the water can also significantly slow down the corrosion rate in oilfield pipelines and increase the economic and environmental efficiency of the oil industry. As the sonoplasma unit operates in a flow-through mode, it can be integrated into existing industrial processes. In this study, the unit was successfully implemented at an oilfield’s production water treatment plant, resulting in a 33% reduction in hydrogen sulfide levels.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.V.K., I.O.A. and G.C.; methodology, R.V.N., I.S.F. and E.S.M.; validation, A.V.K. and V.M.B.; formal analysis, A.V.K.; investigation, E.S.M., R.V.N. and I.S.F.; resources, R.V.N., A.V.K. and V.M.B.; data curation, E.S.M.; writing—original draft preparation, E.S.M.; writing—review and editing, A.V.K., I.O.A. and G.C.; visualization, E.S.M., R.V.N. and I.S.F.; supervision, V.M.B. and G.C.; project administration, A.V.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The article was prepared within the project “The “Clean Water” project as the most important component of cooperation between the Russian Federation and the countries of the Global South: socio-economic and technological dimensions”, supported by the grant from Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation program for research projects in priority areas of scientific and technological development (agreement No. 075-15-2024-546).
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest, including financial, personal or other relationships with anybody or organizations.
References
- Kang, W.L.; Zhou, B.B.; Issakhov, M.; Gabdullin, M. Advances in enhanced oil recovery technologies for low permeability reservoirs. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 1622–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, O.J.; Chen, J.M.; Huang, L.; Buglass, R.L. Sulphate-reducing bacteria. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 26, 155–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Su, P.; Lin, Z. A review of sulphate-reducing bacteria: Metabolism, influencing factors and application in wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cord-Ruwisch, R.; Kleinitz, W.; Widdel, F. Sulphate-reducing bacteria and their activities in oil production. J. Pet. Technol. 1987, 39, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Cheng, X.; Li, G.; Chen, S.; Quan, Z.; Zhao, S.; Niu, L. The influence of hydrogen sulfide on corrosion of iron under different conditions. Corros. Sci. 2000, 42, 1669–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoma, M.S.; Vasyliv, K.B.; Chuchman, M.R. Influence of the hydrogen sulfide concentration on the corrosion and hydrogenation of pipe steels (A Survey). Mater. Sci. 2021, 57, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.H.J. The Influence of Sulphate-Reducing Bacteria on Hydrogen Absorption by Steel During Microbial Corrosion; Cranfield University: Cranfield, UK, 1990; Available online: https://dspace.lib.cranfield.ac.uk/handle/1826/19712 (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Lv, M.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Du, M. Effect of sulphate-reducing bacteria on hydrogen permeation and stress corrosion cracking behavior of 980 high-strength steel in seawater. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 92, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, H.; Benetton, X.D. SRB-biofilm influence in active corrosion sites formed at the steel-electrolyte interface when exposed to artificial seawater conditions. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 1169–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, D. Corrosion behavior of copper under biofilm of sulphate-reducing bacteria. Corros. Sci. 2014, 87, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, M.; Koutnik, P.; Kohout, J. Addressing hydrogen sulfide corrosion in oil and gas industries: A sustainable perspective. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Gutierrez, O.; Yuan, Z. The strong biocidal effect of free nitrous acid on anaerobic sewer biofilms. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3735–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, P.M.D.; Goulart, F.R.D.V.; Marques, J.M.; Bizzo, H.R.; Blank, A.F.; Groposo, C.; Seldin, L. Growth inhibition of sulphate-reducing bacteria in produced water from the petroleum industry using essential oils. Molecules 2017, 22, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voskuhl, L.; Brusilova, D.; Brauer, V.S.; Meckenstock, R.U. Inhibition of sulphate-reducing bacteria with formate. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2022, 98, fiac003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, K.; Guo, H.; Tian, L.; He, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. Potassium permanganate-based advanced oxidation processes for wastewater decontamination and sludge treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Fan, K. Sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (SOB) and sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) in oil reservoir and biological control of SRB: A review. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, R.; Caprio, V.; Insola, A.; Marotta, R. Advanced oxidation processes (AOP) for water purification and recovery. Catal. Today 1999, 53, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarze, M.; Borchardt, S.; Frisch, M.L.; Collis, J.; Walter, C.; Menezes, P.W.; Tasbihi, M. Degradation of phenol via an advanced oxidation process (AOP) with immobilised commercial titanium dioxide (TiO2) photocatalysts. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, C.S.; Kim, T.S.; Park, Y.K.; An, K.H.; Jung, S.C. Degradation of antibiotic tetracycline using H2O2/TiO2/UV/microwave system. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2023, 127, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignatello, J.J.; Oliveros, E.; MacKay, A. Advanced oxidation processes for organic contaminant destruction based on the Fenton reaction and related chemistry. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.Q.; Jothinathan, L.; Deng, S.H.; Ong, S.L.; Ng, H.Y.; Hu, J.Y. Fenton-and ozone-based AOP processes for industrial effluent treatment. In Advanced Oxidation Processes for Effluent Treatment Plants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 199–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikehata, K.; Li, Y. Ozone-based processes. In Advanced Oxidation Processes for Waste Water Treatment; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derco, J.; Gotvajn, A.Ž.; Čižmárová, O.; Dudáš, J.; Sumegová, L.; Šimovičová, K. Removal of Micropollutants by Ozone-Based Processes. Processes 2021, 9, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zeng, T.; Shang, J.; Tao, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, T.; Hu, G. Bubble dynamics model and its revelation of ultrasonic cavitation behavior in advanced oxidation processes: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 63, 105470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, K.; Dinesh, K.; Sun, X.; Soltani, R.D.C.; Wang, Z.; Sonawane, S.; Boczkaj, G. Synergistic effects of hybrid advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) based on hydrodynamic cavitation phenomenon—A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 432, 134191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shi, W.; Xiong, M.; Gao, C.; Cui, M. Hydrodynamic cavitation and its application in water treatment combined with ozonation: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 114, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xia, B.; Zuo, W. Phenol oxidation by combined cavitation water jet and hydrogen peroxide. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 20, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuerda-Correa, E.M.; Alexandre-Franco, M.F.; Fernández-González, C. Advanced Oxidation Processes for the Removal of Antibiotics from Water. An Overview. Water 2020, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Yi, H.; Lai, C.; Liu, X.; Huo, X.; An, Z.; Yang, L. Critical review of advanced oxidation processes in organic wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.M.; Sheng, M.; Niu, W.F.; Fei, Y.L.; Li, D. Regeneration and reuse of iron catalyst for Fenton-like reactions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1446–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesaro, A.; Naddeo, V.; Belgiorno, V. Wastewater treatment by combination of advanced oxidation processes and conventional biological systems. J. Bioremed. Biodegrad. 2013, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajalifard, Z.; Mousazadeh, M.; Khademi, S.; Khademi, N.; Jamadi, M.H.; Sillanpää, M. The efficacious of AOP-based processes in concert with electrocoagulation in abatement of CECs from water/wastewater. NPJ Clean Water 2023, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramov, V.O.; Abramova, A.V.; Cravotto, G.; Nikonov, R.V.; Fedulov, I.S.; Ivanov, V.K. Flow-mode water treatment under simultaneous hydrodynamic cavitation and plasma. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 70, 105323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethge, P.O. On the volumetric determination of hydrogen sulfide and soluble sulfides. Anal. Chim. Acta 1953, 9, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postgate, J.R. Versatile medium for the enumeration of sulfate-reducing bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. 1963, 11, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linga Reddy, E.; Karuppiah, J.; Subrahmanyam, C. Kinetics of hydrogen sulfide decomposition in a DBD plasma reactor operated at high temperature. J. Energy Chem. 2013, 22, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zevnik, J.; Dular, M. Cavitation bubble interaction with compliant structures on a microscale: A contribution to the understanding of bacterial cell lysis by cavitation treatment. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 87, 106053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krystynik, P. Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs)—Utilization of hydroxyl radical and singlet oxygen. In Reactive Oxygen Species; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Yamada, Y.; Ikai, H.; Kanno, T.; Sasaki, K.; Niwano, Y. Bactericidal action of photoirradiated gallic acid via reactive oxygen species formation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10048–10054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toki, T.; Nakamura, K.; Kurauchi, M.; Kanno, T.; Katsuda, Y.; Ikai, H.; Hayashi, E.; Egusa, H.; Sasaki, K.; Niwano, Y. Synergistic interaction between wavelength of light and concentration of H2O2 in bactericidal activity of photolysis of H2O2. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 119, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikai, H.; Nakamura, K.; Shirato, M.; Kanno, T.; Iwasawa, A.; Sasaki, K.; Kohno, M. Photolysis of hydrogen peroxide, an effective disinfection system via hydroxyl radical formation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 5086–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhalev, E.; Kamler, A.; Bayazitov, V.; Sozarukova, M.; Nikonov, R.; Fedulov, I.; Mel’nik, E.; Ildyakov, A.; Smirnov, D.; Volkov, M.; et al. Sonoplasma Frequency Tuning of Electric Pulses to Modulate and Maximise Reactive Oxygen Species Generation. Water 2024, 16, 2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Shao, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, T.; Meng, G.; Wang, F. The effect of H2S concentration on the corrosion behavior of carbon steel at 90 °C. Corros. Sci. 2010, 6, 2050–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).