Dynamic Modeling of the Human Coagulation Cascade Using Reduced Order Effective Kinetic Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Formulation of Reduced Order Coagulation Models
2.2. Identification of Model Parameters Using Particle Swarm Optimization
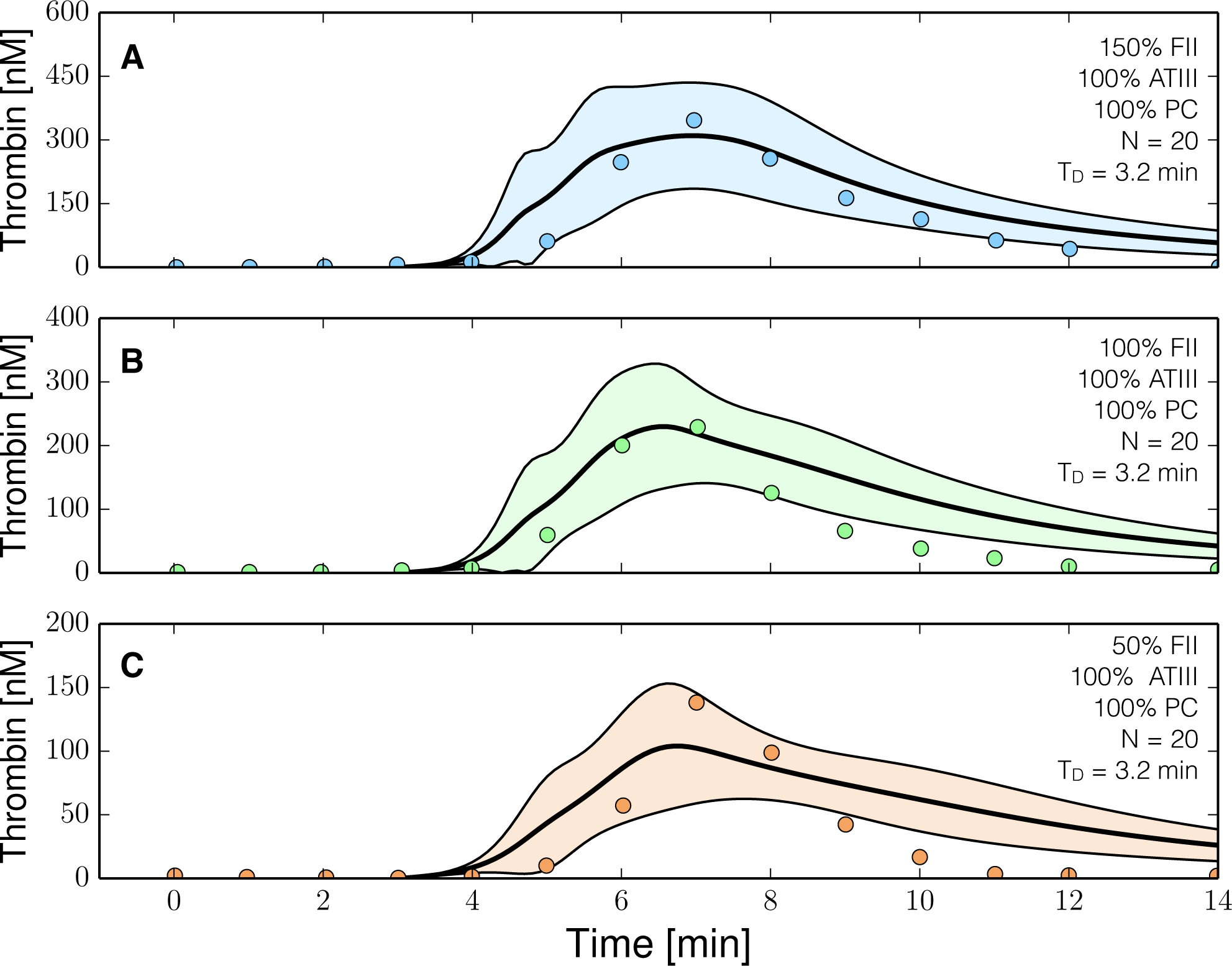
2.3. Validation of the Reduced Order Coagulation Model
2.4. Global Sensitivity Analysis of the Reduced Order Coagulation Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Formulation and Solution of the Model Equations
4.2. Estimation of Model Parameters From Experimental Data
4.3. Global Sensitivity Analysis of Model Performance
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kholodenko, B.; Yaffe, M.B.; Kolch, W. Computational approaches for analyzing information flow in biological networks. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, re1. [Google Scholar]
- Gadkar, K.G.; Varner, J.; Doyle, F.J. Model identification of signal transduction networks from data using a state regulator problem. Syst. Biol. 2005, 2, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, J.E. Complex biology with no parameters. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 503–504. [Google Scholar]
- Machta, B.B.; Chachra, R.; Transtrum, M.K.; Sethna, J.P. Parameter space compression underlies emergent theories and predictive models. Science 2013, 342, 604–607. [Google Scholar]
- Tasseff, R.; Nayak, S.; Song, S.O.; Yen, A.; Varner, J.D. Modeling and analysis of retinoic acid induced differentiation of uncommitted precursor cells. Integr. Biol. 2011, 3(3), 578–591. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, M.K.; Saez-Rodriguez, J.; Sorger, P.K.; Lauffenburger, D.A. Logic-based models for the analysis of cell signaling networks. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 3216–3224. [Google Scholar]
- Saez-Rodriguez, J.; Alexopoulos, L.G.; Zhang, M.; Morris, M.K.; Lauffenburger, D.A.; Sorger, P.K. Comparing signaling networks between normal and transformed hepatocytes using discrete logical models. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5400–5411. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, M.K.; Saez-Rodriguez, J.; Clarke, D.C.; Sorger, P.K.; Lauffenburger, D.A. Training signaling pathway maps to biochemical data with constrained fuzzy logic: Quantitative analysis of liver cell responses to inflammatory stimuli. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1001099. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, M.K.; Shriver, Z.; Sasisekharan, R.; Lauffenburger, D.A. Querying quantitative logic models (Q2LM) to study intracellular signaling networks and cell-cytokine interactions. Biotechnol. J 2012, 7, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Butenas, S.; Mann, K.G. Blood coagulation. Biochemistry 2002, 67, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Schenone, M.; Furie, B.C.; Furie, B. The blood coagulation cascade. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2004, 11, 272–277. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, R.L.C.; Bird, R.J. Review article: Coagulation cascade and therapeutics update: Relevance to nephrology. Part 1: Overview of coagulation, thrombophilias and history of anticoagulants. Nephrology 2009, 14, 462–470. [Google Scholar]
- Hemostasis and Thrombosis: Basic Principles and Clinical Practice; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Colman, R.W.; Clowes, A.W. (Eds.) Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006.
- Brummel, K.E.; Paradis, S.G.; Butenas, S.; Mann, K.G. Thrombin functions during tissue factor-induced blood coagulation. Blood 2002, 100, 148–152. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, K.; Nesheim, M.; Church, W.; Haley, P.; Krishnaswamy, S. Surface-dependent reactions of Vitamin K-dependent enzyme complexes. Blood 1990, 76, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, H.; Monroe, D.; Oliver, J.; Chang, J.; Hoffman, M. Newer Concepts of Blood Coagulation. Haemophilia 1998, 4, 331–334. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, K. Biochemistry and Physiology of Blood Coagulation. Thromb. Haemost. 1999, 82, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Khanin, M.A.; Semenov, V.V. A mathematical model of the kinetics of blood coagulation. J. Theor. Biol. 1989, 136, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Willems, G.M.; Lindhout, T.; Hermens, W.T.; Hemker, H.C. Simulation model for thrombin generation in plasma. Haemostasis 1991, 21, 197–207. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, S.A.; Basmadjian, D. A mathematical model of thrombin production in blood coagulation, Part I: The sparsely covered membrane case. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 1994, 22, 357–370. [Google Scholar]
- Leipold, R.J.; Bozarth, T.A.; Racanelli, A.L.; Dicker, I.B. Mathematical model of serine protease inhibition in the tissue factor pathway to thrombin. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 25383–25387. [Google Scholar]
- Kuharsky, A.L.; Fogelson, A.L. Surface-mediated control of blood coagulation: The role of binding site densities and platelet deposition. Biophys. J 2001, 80, 1050–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, D.; Zai, M.; Varner, J.D. Computationally derived points of fragility of a human cascade are consistent with current therapeutic strategies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2007, 3(3), e142. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, D.; Szlam, F.; Tanaka, K.A.; Barie, P.S.; Varner, J.D. Ensembles of uncertain mathematical models can identify network response to therapeutic interventions. Mol. Biosyst. 2010, 6, 2272–2286. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, K.C.; Mann, K.G. A model for the tissue factor pathway to thrombin. II. A mathematical simulation. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 23367–23373. [Google Scholar]
- Hockin, M.F.; Jones, K.C.; Everse, S.J.; Mann, K.G. A model for the stoichiometric regulation of blood coagulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 18322–18333. [Google Scholar]
- Butenas, S.; Orfeo, T.; Gissel, M.T.; Brummel, K.E.; Mann, K.G. The significance of circulating factor IXa in blood. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 22875–22882. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, K.; Denney, W.S.; Diamond, S.L. Stochastic modeling of blood coagulation initiation. Pathophysiol. Haemost Thromb. 2005, 34, 80–90. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, M.S.; Denney, W.S.; Jing, H.; Diamond, S.L. Systems biology of coagulation initiation: Kinetics of thrombin generation in resting and activated human blood. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrophanov, A.Y.; Wolberg, A.S.; Reifman, J. Kinetic model facilitates analysis of fibrin generation and its modulation by clotting factors: Implications for hemostasis-enhancing therapies. Mol. Biosyst. 2014, 10, 2347–2357. [Google Scholar]
- Stalker, T.J.; Traxler, E.A.; Wu, J.; Wannemacher, K.M.; Cermignano, S.L.; Voronov, R.; Diamond, S.L.; Brass, L.F. Hierarchical organization in the hemostatic response and its relationship to the platelet-signaling network. Blood 2013, 121, 1875–1885. [Google Scholar]
- Leiderman, K.; Fogelson, A. An overview of mathematical modeling of thrombus formation under flow. Thromb. Res. 2014, 133, S12–S14. [Google Scholar]
- Bannish, B.E.; Keener, J.P.; Fogelson, A.L. Modelling fibrinolysis: A 3D stochastic multiscale model. Math. Med. Biol. 2014, 31, 17–44. [Google Scholar]
- Voronov, R.S.; Stalker, T.J.; Brass, L.F.; Diamond, S.L. Simulation of intrathrombus fluid and solute transport using in vivo clot structures with single platelet resolution. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, K.; Gavaises, M.; Atkin, C. A simplified mathematical model for thrombin generation. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 196–204. [Google Scholar]
- Runyon, M.K.; Johnson-Kerner, B.L.; Ismagilov, R.F. Minimal functional model of hemostasis in a biomimetic microfluidic system. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2004, 43, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar]
- Kastrup, C.J.; Runyon, M.K.; Shen, F.; Ismagilov, R.F. Modular chemical mechanism predicts spatiotemporal dynamics of initiation in the complex network of hemostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15747–15752. [Google Scholar]
- Runyon, M.K.; Johnson-Kerner, B.L.; Kastrup, C.J.; van Ha, T.G.; Ismagilov, R.F. Propagation of blood clotting in the complex biochemical network of hemostasis is described by a simple mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7014–7015. [Google Scholar]
- Runyon, M.K.; Kastrup, C.J.; Johnson-Kerner, B.L.; Ha, T.G.V.; Ismagilov, R.F. Effects of shear rate on propagation of blood clotting determined using microfluidics and numerical simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 3458–3464. [Google Scholar]
- Butenas, S.; van’t Veer, C.; Mann, K.G. Normal thrombin generation. Blood 1999, 94, 2169–2178. [Google Scholar]
- Van’t Veer, C.; Golden, N.J.; Kalafatis, M.; Mann, K.G. Inhibitory Mechanism of the Protein C Pathway on Tissue Factor-induced Thrombin Generation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 7963–7994. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, G.A.; Hoffman, M.; Roberts, H.R.; Monroe, D.M. Manipulation of prothrombin concentration improves response to high-dose factor VIIa in a cell-based model of haemophilia. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 134, 314–319. [Google Scholar]
- Kuepfer, L.; Peter, M.; Sauer, U.; Stelling, J. Ensemble modeling for analysis of cell signaling dynamics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.O.; Varner, J. Modeling and analysis of the molecular basis of pain in sensory neurons. PLoS One 2009, 4, e6758. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.O.; Chakrabarti, A.; Varner, J.D. Ensembles of signal transduction models using Pareto Optimal Ensemble Techniques (POETs). Biotechnol. J 2010, 5, 768–780. [Google Scholar]
- Tasseff, R.; Nayak, S.; Salim, S.; Kaushik, P.; Rizvi, N.; Varner, J.D. Analysis of the molecular networks in androgen dependent and independent prostate cancer revealed fragile and robust subsystems. PLoS One 2010, 5, e8864. [Google Scholar]
- Lequieu, J.; Chakrabarti, A.; Nayak, S.; Varner, J.D. Computational modeling and analysis of insulin induced eukaryotic translation initiation. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1002263. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, L.M.; Rizk, M.L.; Liao, J.C. Ensemble modeling of metabolic networks. Biophys. J 2008, 95, 5606–5617. [Google Scholar]
- Hansson, G.K. Inflammation, Atherosclerosis and Coronary Artery Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, K.A.; Key, N.S.; Levy, J.H. Blood coagulation: Hemostasis and thrombin regulation. Anesth. Anal. 2009, 108, 1433–1446. [Google Scholar]
- Tuddenham, E.; Cooper, D. The Molecular Genetics of Haemostasis and Its Inherited Disorders; Oxford monographs in medical genetics; Oxford University Press: New York NY, USA, 1994; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci, M.P.; Tuddenham, E.G.D. The Hemophilias–From royal genes to gene therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, J.; Phillott, A. Haemophilia and inhibitors 1: diagnosis and treatment. Nurs. Times. 2008, 104, 26–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tomokiyo, K.; Nakatomi, Y.; Araki, T.; Teshima, K.; Nakano, H.; Nakagaki, T.; Miyamoto, S.; Funatsu, A.; Iwanaga, S. A novel therapeutic approach combining human plasma-derived factors VIIa and X for haemophiliacs with inhibitors: Evidence of a higher thrombin generation rate in vitro and more sustained haemostatic activity in vivo than obtained with factor VIIa alone. Vox Sanguinis 2003, 85, 290–299. [Google Scholar]
- Hedner, U. Factor VIIa and its potential therapeutic use in bleeding-associated pathologies. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 100, 557–562. [Google Scholar]
- Talbot, M.; Tien, H.C. The use of recombinant factor VIIa in trauma patients. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2009, 17, 477–481. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, A.D. Single-dose recombinant activated factor VII for the treatment of joint bleeds in hemophilia patients with inhibitors. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2008, 6, 579–586. [Google Scholar]
- Duchesne, J.C.; Mathew, K.A.; Marr, A.B.; Pinsky, M.R.; Barbeau, J.M.; McSwain, N.E. Current evidence based guidelines for factor VIIa use in trauma: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Am. Surg. 2008, 74, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Butenas, S.; Brummel, K.E.; Branda, R.F.; Paradis, S.G.; Mann, K.G. Mechanism of factor VIIa-dependent coagulation in hemophilia blood. Blood 2002, 99, 923–930. [Google Scholar]
- Danforth, C.M.; Orfeo, T.; Everse, S.J.; Mann, K.G.; Brummel-Ziedins, K.E. Defining the boundaries of normal thrombin generation: Investigations into hemostasis. PLoS One. 2012, 7, e30385. [Google Scholar]
- Brummel-Ziedins, K.E.; Orfeo, T.; Callas, P.W.; Gissel, M.; Mann, K.G.; Bovill, E.G. The prothrombotic phenotypes in familial protein C deficiency are differentiated by computational modeling of thrombin generation. PLoS One 2012, 7, e44378. [Google Scholar]
- Mitrophanov, A.Y.; Reifman, J. Kinetic modeling sheds light on the mode of action of recombinant factor VIIa on thrombin generation. Thromb. Res. 2011, 128, 381–390. [Google Scholar]
- Naito, K.; Fujikawa, K. Activation of Human Blood Coagulation Factor XI Independent of Factor XII. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 7353–7358. [Google Scholar]
- Gailani, D.; Broze, G.J., Jr. Factor XI activation in a revised model of blood coagulation. Science 1991, 253, 909–912. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.A.; Mutch, N.J.; Baskar, D.; Rohloff, P.; Docampo, R.; Morrissey, J.H. Polyphosphate modulates blood coagulation and fibrinolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 903–908. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, E.; Oliphant, T.; Peterson, P. SciPy: Open source scientific tools for Python. Available online: http://www.scipy.org/ accessed on 13 March 2015.
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization, Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November-1 December 1995; pp. 1942–1948.
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Sobol, I. Global sensitivity indices for nonlinear mathematical models and their Monte Carlo estimates. Math. Comput. Simul. 2001, 55, 271–280. [Google Scholar]
- Saltelli, A.; Annoni, P.; Azzini, I.; Campolongo, F; Ratto, M.; Tarantola, S. Variance based sensitivity analysis of model output. Design and estimator for the total sensitivity index. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2010, 181, 259–270. [Google Scholar]
- Herman, J.D. Available online: https://github.com/jdherman/SALib accessed 13 March 2015.








© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
Share and Cite
Sagar, A.; Varner, J.D. Dynamic Modeling of the Human Coagulation Cascade Using Reduced Order Effective Kinetic Models. Processes 2015, 3, 178-203. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr3010178
Sagar A, Varner JD. Dynamic Modeling of the Human Coagulation Cascade Using Reduced Order Effective Kinetic Models. Processes. 2015; 3(1):178-203. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr3010178
Chicago/Turabian StyleSagar, Adithya, and Jeffrey D. Varner. 2015. "Dynamic Modeling of the Human Coagulation Cascade Using Reduced Order Effective Kinetic Models" Processes 3, no. 1: 178-203. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr3010178
APA StyleSagar, A., & Varner, J. D. (2015). Dynamic Modeling of the Human Coagulation Cascade Using Reduced Order Effective Kinetic Models. Processes, 3(1), 178-203. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr3010178





