Evaluation of Nano Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) Activity in Solution and Immobilized in Hydrophilic PVDF Membrane for Drimaren Red X-6BN and Bisphenol-a Removal in Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of Nano Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI)/Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC)
2.3. nZVI/PAA/PVDF Membrane Preparation
2.4. nZVI/CMC and nZVI/PAA/PVDF Membrane Characterization
2.5. nZVI/CMC Activity for Drimaren Red X-6BN (DRX-6BN) and Bisphenol-a (BPA) Removal
2.6. nZVI/PAA/PVDF Membrane Activity for BPA Removal
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nanoparticles’ Characterization
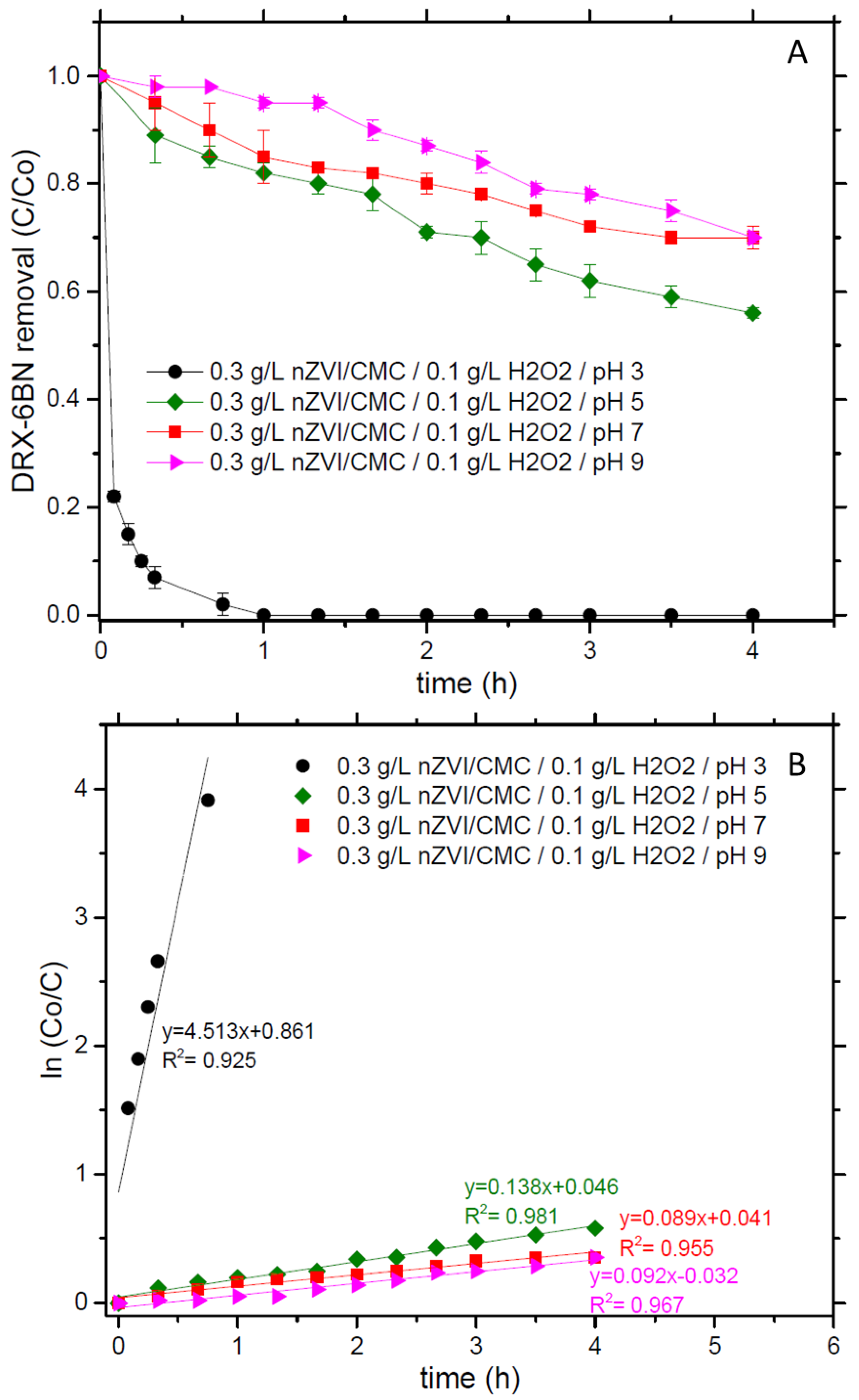
3.2. BPA and Dye Removal by nZVI in Solution
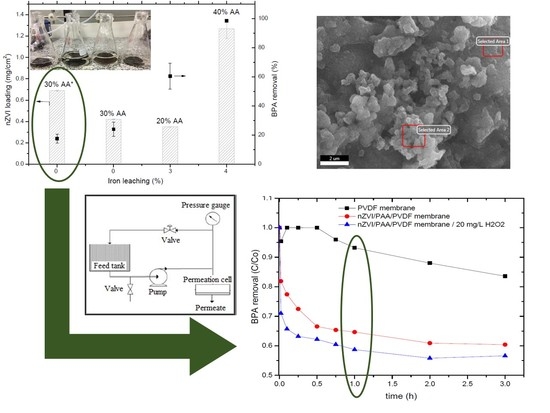
3.3. PAA Functionalized PVDF Membranes and Correlation with nZVI Loading, Iron Leaching, and BPA Removal
3.4. nZVI/PAA/PVDF Membrane Characterization
3.5. BPA Removal in Convective Mode
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Son, H.S.; Im, J.K.; Zoh, K.D. Fenton-like degradation mechanism for 1,4-dioxane using zero-valent iron (Fe0) and UV light. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.-G.; Yoona, H.; Leeb, W.; Kimc, E.; Chang, Y. Comparative study of peroxide oxidants activated by nZVI: Removal of 1,4-Dioxane and arsenic(III) in contaminated waters. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 2511–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Collins, R.N.; Waite, T.D.; Hanna, K. Advances in surface passivation of nanoscale zerovalent iron (NZVI): A critical review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12010–12025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; He, Q.; Zeng, G.; Tang, L.; Zhang, L.; Xie, L.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, F. Degradation of trichloroethene by nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) and nZVI activated persulfate in the absence and presence of EDTA. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Sun, Y.; Qin, H.; Li, J.; Lo, I.M.C.; He, D.; Dong, H. The limitations of applying zero-valent iron technology in contaminants sequestration and the corresponding countermeasures: the development in zero-valent iron technology in the last two decades (1994–2014). Water Res. 2015, 75, 224–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satapanajaru, T.; Chompuchan, C.; Suntornchot, P.; Pengthamkeerati, P. Enhancing decolorization of Reactive Black 5 and Reactive Red 198 during nano zerovalent iron treatment. Desalination 2011, 266, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Peng, L.; Zeng, Q.; Yang, Y.; Song, H.; Shao, J.; Liu, S.; Gu, J. High efficient removal of tetracycline from solution by degradation and flocculation with nanoscale zerovalent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Liu, H. The use of zero-valent iron for groundwater remediation and wastewater treatment: a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 267, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaniuk, M.; Oleszczuk, P.; Ok, Y.S. Review on nano zerovalent iron (nZVI): From synthesis to environmental applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, M.; Smuleac, V.; Ormsbee, L.E.; Sedlak, D.; Bhattacharyya, D. Iron oxide nanoparticle synthesis in aqueous and membrane systems for oxidative degradation of trichloroethylene from water. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Liang, B.; Tsang, E.P. Remediation of hexavalent chromium contaminated soil by stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron prepared from steel pickling waste liquor. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 247, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osegueda, O.; Dafinov, A.; Llorca, J.; Medina, F.; Sueiras, J. Heterogeneous catalytic oxidation of phenol by in situ generated hydrogen peroxide applying novel catalytic membrane reactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Hernández, S.; Wan, H.; Ormsbee, L.; Bhattacharyya, D. Role of membrane pore polymerization conditions for pH responsive behavior, catalytic metal nanoparticle synthesis, and PCB degradation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, H.; Ma, J. Preparation and characterization of PAA/PVDF membrane-immobilized Pd/Fe nanoparticles for dechlorination of trichloroacetic acid. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4656–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sottoc, A.; Lib, J.; Van der Bruggena, B. Progress and perspectives for synthesis of sustainable antifouling composite membranes containing in situ generated nanoparticles. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 502–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Lu, Z.; Sun, X.; Wang, L. Preparation and characterization of ZrO2/PES hybrid ultrafiltration membrane with uniform ZrO2 nanoparticles. Desalination 2014, 332, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.; Li, J.; Wei, K.; Sun, X.; Shen, J.; Han, W.; Wang, L. In Situ preparation of Al-containing PVDF ultrafiltration membrane via sol-gel process. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 364, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, P.; Ma, J.; Liu, H. Preparation of novel composites based on hydrophilized and functionalized polyacrylonitrile membrane-immobilized NZVI for reductive transformation of metronidazole. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 396, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Liu, H.; Ma, J. Investigation of PAA/PVDF-NZVI hybrids for metronidazole removal: synthesis, characterization, and reactivity characteristics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 264, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, J.; Zhu, M.; Wang, X.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Liu, K. Poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane supported nano zero-valent iron for metronidazole removal: Influences of calcium and bicarbonate ions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 49, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, X.; Ma, B.; Qin, A.; He, C. Removal of water contaminants by nanoscale zero-valent iron immobilized in PAN-based oxidized membrane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 321, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanez, J.E.H.; Wang, Z.; Lege, S.; Obst, M.; Roehler, S.; Burkhardt, C.J.; Zwiener, C. Application and characterization of electroactive membranes based on carbon nanotubes and zerovalent iron nanoparticles. Water Res. 2017, 108, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Ma, J.; Liu, H.; Ning, P. Synthesis and characterization of a new hydrophilic boehmite-PVB/PVDF blended membrane supported nano zero-valent iron for removal of Cr(VI). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 205, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smuleac, V.; Bachas, L.; Bhattacharyya, D. Aqueous—Phase Synthesis of PAA in PVDF Membrane Pores for Nanoparticle Synthesis and Dichlorobiphenyl Degradation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 346, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillen, G.R.; Pan, Y.; Li, M.; Hoek, E.M.V. Preparation and Characterization of Membranes Formed by Nonsolvent Induced Phase Separation: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3798–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Dozier, A.; Bhattacharyya, D. Synthesis of Nanoscale Bimetallic Particles in Polyelectrolyte Membrane Matrix for Reductive Transformation of Halogenated Organic Compounds. J. Nanopart. Res. 2005, 7, 449–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Bhattacharyya, D. Fe/Pd Nanoparticle Immobilization in Microfiltration Membrane Pores: Synthesis, Characterization, and Application in the Dechlorination of Polychlorinated Biphenyls. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 2348–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo1, F.V.F.; Yokoyama, L.; Teixeira, L.A.C.; Campos, J.C. Heterogeneous fenton process using the mineral hematite for the discolouration of a reactive dye solution. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 28, 605–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Anastopoulos, I. Adsorptive removal of bisphenol A (BPA) from aqueous solution: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 885–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, T.; Yatagai, T.; Kawase, Y. Hydroxyl radical generation linked with iron dissolution and dissolved oxygen consumption in zero-valent iron wastewater treatment process. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 303, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Zeboril, R. Iron-based green technologies for water remediation. In Advanced Oxidation Processes for Water Treatment; Stefan, M.I., Ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Rani, G.U.; Sen, G. Microwave initiated synthesis and application of polyacrylic acid grafted carboxymethyl cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Xanga, Z.; Quana, S.; Xu, Y.; Jianga, Z.; Shao, L. Exploring the synergetic effects of graphene oxide (GO) and polyvinylpyrrodione (PVP) on poly(vinylylidenefluoride) (PVDF) ultrafiltration membrane performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 316, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Yahya, R.; Hassan, A.; Yar, M.; Azzahari, A.D.; Selvanathan, V.; Sonsudin, F.; Abouloula, C.N. pH Sensitive Hydrogels in Drug Delivery: Brief History, Properties, Swelling, and Release Mechanism, Material Selection and Applications. Polymers 2017, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Mao, S.S. Titanium Dioxide Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Properties, Modifications, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2891–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, C.; Zhang, G.; Hu, L.; Wang, P. Photocatalytic Fe-doped TiO2/PSF composite UF membranes: Characterization and performance on BPA removal under visible-light irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 319, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalona, I.; Grooth, J.; Font, J.; Nijmeijer, K. Removal of BPA by enzyme polymerization using NF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girit, B.; Dursun, D.; Olmez-Hanci, T.; Arslan-Alaton, I. Treatment of aqueous bisphenol A using nano-sized zero-valent iron in the presence of hydrogen peroxide and persulfate oxidants. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 71, 1859–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Membrane | AA (wt. %) | EG (mol % of AA) | K2S2O8 (wt. %) | Contact Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20% AA | 20 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 5 |
| 30% AA | 30 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 5 |
| 30% AA * | 30 | 1.0 | 1.0 | Filtration (10 mL) 1 |
| 40% AA | 40 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 5 |
| Compound Initial Concentration | nZVI/CMC (g/L) | H2O2 (g/L) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|
| (DRX-6BN)0 = 10 mg/L | 0.1 | 0.1 | 5.0 |
| 0.5 | 0.1 | 5.0 | |
| 1 | 0.1 | 5.0 | |
| 2 | 0.1 | 5.0 | |
| 3 | 0.01 | 3.0 | |
| 3 | 0.05 | 3.0 | |
| 3 | 0.1 | 3.0 | |
| 3 | 0.1 | 5.0 | |
| 3 | 0.1 | 7.0 | |
| 3 | 0.1 | 9.0 | |
| 5 | 0.1 | 5.0 | |
| (BPA)0 = 800 mg/L | 0.1 | 0.02 | 3.0 |
| 0.5 | 0.02 | 3.0 | |
| 1.0 | 0.02 | 3.0 |
| nZVI/CMC (g/L) | BPA Removal (%) |
|---|---|
| 0.1 | 96 |
| 0.5 | 100 |
| 1 | 100 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
L. S. Silva, L.; A. Caldara, J.; Maria Rocco, A.; P. Borges, C.; V. Fonseca, F. Evaluation of Nano Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) Activity in Solution and Immobilized in Hydrophilic PVDF Membrane for Drimaren Red X-6BN and Bisphenol-a Removal in Water. Processes 2019, 7, 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7120904
L. S. Silva L, A. Caldara J, Maria Rocco A, P. Borges C, V. Fonseca F. Evaluation of Nano Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) Activity in Solution and Immobilized in Hydrophilic PVDF Membrane for Drimaren Red X-6BN and Bisphenol-a Removal in Water. Processes. 2019; 7(12):904. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7120904
Chicago/Turabian StyleL. S. Silva, Larissa, Júlio A. Caldara, Ana Maria Rocco, Cristiano P. Borges, and Fabiana V. Fonseca. 2019. "Evaluation of Nano Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) Activity in Solution and Immobilized in Hydrophilic PVDF Membrane for Drimaren Red X-6BN and Bisphenol-a Removal in Water" Processes 7, no. 12: 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7120904
APA StyleL. S. Silva, L., A. Caldara, J., Maria Rocco, A., P. Borges, C., & V. Fonseca, F. (2019). Evaluation of Nano Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) Activity in Solution and Immobilized in Hydrophilic PVDF Membrane for Drimaren Red X-6BN and Bisphenol-a Removal in Water. Processes, 7(12), 904. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7120904