Abstract
Engineered nanomaterials (ENMs), such as copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs), are emerging as pollutants extensively used in many commercial and industrial applications, thus raising environmental concerns due to their release into water bodies. It is, therefore, essential to remove these pollutants from water bodies in order to minimize the potential threat to the aquatic environment and human health. The objective of this study was to investigate the removal of CuO NPs from waters by the coagulation process. This study also explored the efficiency of coagulation to remove hydrophobic/hydrophilic dissolved organic matter (DOM) and turbidity with varying polyaluminum chloride (PACl) doses. According to the results, a high concentration of DOM affects both the CuO NPs zeta potential and hydrodynamic diameter, thereby decreasing the agglomeration behavior. At effective coagulation zone (ECR), high removal of CuO NPs (>95%) was observed for all studied waters (hydrophobic and hydrophilic waters), above ECR excess charge induced by coagulant restabilized particles in solution. Furthermore, waters containing hydrophobic DOM and those with high UV254nm values needed more coagulant dose than hydrophilic waters to obtain similar CuO NP removals. The primary mechanism involved in CuO NPs removal might be charge neutralization. These findings suggest that PACl is an effective coagulant in the removal of CuO NPs; however, water characteristics are an influencing factor on the removal performance of ENMs during the coagulation process.
1. Introduction
Engineered nanomaterials (ENMs) are widely used in many consumer products and industrial applications, such as cosmetics, electronics, energy technology, drug delivery, agriculture and environmental sciences [1]. Amongst many ENMs, copper oxide (CuO) is the most extensively used nanoparticle (NP) because of its application as an antimicrobial agent in textile and coatings, and also in the materials used for energy technology process [2,3]. In 2010, the global production of CuO was approximately 570 tons/year and is estimated to reach 1600 tons/year by 2025. According to Keller et al., 54% of the produced ENMs may be released during their usage and disposal phase and are likely to enter wastewater treatment plants (WWTP) [4]. A recent study [5] reported the presence of ENMs in wastewater treatment effluents and biosolids, which further suggests that NPs might eventually end up in freshwater bodies. At present, data on the measure environmental concentration of most ENMs in surface waters are not available; however, researchers have estimated the concentration to be in the range of 21–10,000 ng/L [6]. Therefore, if the conventional WWTP are incapable of removing ENMs from water, NPs may find their ways into water bodies, thereby increasing the associated potential risks of exposure to aquatic organisms and humans.
Various studies [7,8] have demonstrated that ENMs are a potential threat and may adversely affect the aquatic biota and human health. CuO NPs can attach on the surface of micro-organisms such as lymphocytes, Fagopyrum esculentum, and Pseudokirchneriella, thereby affecting their life cycle [9,10]. Dimkpa et al. demonstrated the adverse effect of released Cu2+ ions on the growth rate of Triticum aestivum and Dreher et al. showed acute toxic effects of ENMs (i.e., oxidative stress in human cells and damage to DNA) [11,12]. In the natural environment, the transport behavior of ENMs mostly depends on their physiochemical properties such as particle size, shape, surface charge, coating, media properties (e.g., pH, ionic strength), and dissolved organic matter (DOM) [13]. For instance, media pH can affect the surface potential via a pH-dependent protonation/deprotonation of surface hydroxyl groups, thus affecting the aggregation and mobility of NPs [14]. Peng et al. reported that a higher concentration of metal cation increases the agglomeration by compressing the electrical double layer (EDL) around the NPs surface [15]. Conversely, DOM such as humic acid (HA) and fulvic acid (FA) can be attached to the surface of NPs through hydrophobic interaction, and H-bonding thereby promotes the colloidal stability of suspension [16,17]. Thus, it is important to understand the transport and removal performance of the ENMs in the water treatment process to control the associated risk of exposure to the ecosystem.
Presently, advanced techniques such as ultra-filtration process are widely used to remove the ENMs from water. However, the membrane fouling significantly impacts the treatment performance leading to an increased operation cost [18]. ENMs can be removed through the activated sludge process; however, they are toxic to microbes and adversely impact the sludge treatment [19]. Conventional drinking water treatment plants include coagulation, flocculation and sedimentation steps. Coagulation is an efficient technique for removing the suspended solids, organic and inorganic matter from aqueous solution. Various studies [20,21,22,23] have demonstrated the removal of commercially available ENMs such as CdTe, C60, MWCNT and titanium dioxide (TiO2) by coagulation process. Abbott Chalew et al. reported the residual concentration of different commercial ENMs such as Ag (2%–21%), TiO2 (2%–9%) and ZnO (48%–98%) in synthetic WWTP [24]. Previous studies demonstrated the high removal of CuO, Ag and TiO2 NPs using iron-based or aluminum-based coagulants, but these studies used a high coagulant dose (up to 50 mg/L) [23,25,26]. DOM has been known to impede agglomeration and reduce NP removal by coagulation. For example, ENMs coated with DOM such as humic acid (HA) showed remarkable adsorption capacities, thereby reduce the NPs removal efficiency because of the steric hindrance effect of adsorbed DOM molecules [27]. The findings of the various previous studies suggested that coagulation seems to be an efficient process for removing CuO NPs from the aqueous environment. However, most of the earlier studies reported in the literature are limited to ENMs removal in the presence of DOM. Furthermore, the studies also appear inadequate in elucidating the influence of characteristic of hydrophobic/hydrophilic DOM on the interactive behavior of CuO NPs. Thus, it is important to comprehensively understand the effect of DOM characteristics on the agglomeration and removal behavior of CuO NPs by coagulation in heterogenous water environments.
Accordingly, the objective of this study was to explore the removal of CuO NPs by coagulation process and understand the effect of DOM characteristics on the agglomeration and overall removal performance of the coagulation process. The obtained data were then used to predict the possible transportation and removal mechanism of CuO NPs during water treatment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
The CuO NPs (diameter < 50 nm) humic acid (HA) and salicylic acid (SA) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) and were used without additional purification. The analytical grade chemicals—potassium chloride (KCl), magnesium chloride (MgCl2), sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrochloric acid (HCl)—were procured from Samchun (Samchun pure Chemicals Co., Ltd., Pyeongtaek-si, Korea). The coagulation experiments were conducted using a commercial coagulant i.e., polyaluminum chloride (PACl) with relative basicity of (65–70%) in stock solution with 850 mg/L Al2O3 was procured from WAC HB (Elf Atochem). Pure water (18.2 MΩ) was prepared using Synergy ultra-pure water system (Milli-Q, Millipore, USA) and used for the preparation of all experimental solutions.
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.2.1. Preparation of Stock Solution and Model Waters
First, 1 mg of CuO NPs was weighed through microbalance (Mettler Toledo XP26DR; Mettler Toledo AG, Greidensee, Switzerland) and dissolved into 100 mL pure water. Prior to the experiments, the NPs suspension was subjected to probe sonication by ultrasonic cell crusher (Bio-safer 1200-90, Nanjing, China). To simulate diverse natural water characteristics, four synthetic waters (W1–W4) of various organic concentration (moderate/moderate-high) and organic type (hydrophilic/hydrophobic) were used. The inorganic matrix background was maintained in all studied samples, as presented in Table 1. The dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentration was controlled by spiking the HA and SA representing the hydrophobic, high molecular mass (HMM) DOM and the hydrophilic, low molecular mass (LMM) DOM surrogate, respectively. These models, DOM are widely used in water treatment research to provide consistent experimental conditions [28]. HA stock solution was prepared by dissolving the powder in pure water and adjusting the solution pH to 8 by the addition of NaOH. A 100 mg/L stock solution of SA was prepared by dissolving it into 1 L pure water. The characteristics of hydrophilic and hydrophobic DOC were based on specific ultraviolet absorbance (SUVA) with values below 3 L/(m·mg) and above 4 L/(m·mg), respectively [29]. Moderate (2–3 mgC/L) and moderate–high (ca. 6 mgC/L) range DOC concentrations waters were analyzed [30]. In order to simulate moderately-hard water, ionic strength was maintained at 4.0 mM using (mono (KCl) and divalent (MgCl2)) [31]. Water containing hydrophilic DOM showed lower pH values because of the addition of higher SA concentrations (Table 1).

Table 1.
Detailed properties of synthetic waters.
2.2.2. Sedimentation Experiments
To better understand the aggregation behavior of ENMs in waters, the agglomeration rate of CuO NPs was quantitatively determined through the turbidity variation with time, as described in the previous study [27]. Briefly, the suspension was placed in cuvette and turbidity was monitored continuously as a function of time. Since turbidity of suspension increases with increase in NP concentration, the aggregation rate can be determined through normalized NP turbidity (C/C0), where C0 and C is the initial turbidity of suspension at time 0 and time t, respectively. The sedimentation rate constant d(C/C0)/dt can be assessed from an initial 5% decline in (C/C0) NP turbidity, which usually occurs within 1 h for the rapid agglomeration and in 12 h for slow agglomeration experimental environments.
2.2.3. Coagulation Experiments with Synthetic Waters
The coagulation experiments were conducted using a 250 mL sample, in jar tester (Model: SJ10, Young Hana Tech Co., Ltd. Gyeongsangbuk-Do, Korea) with six paddles at 25 ± 1 °C. Prior to the coagulation experiment, the CuO NPs suspension was probe-sonicated then placed into the jars and stirred for 1 min before the addition of coagulant. The operating conditions were set based on the standard procedure used in water treatments plants which include the following: (1) coagulation at 200 rpm for 2 min; (2) flocculation at 20 rpm for 20 min; and (3) settling for 30 min. Once rapid mixing began, the predetermined amount of PACl coagulant was dosed into the jars. The zeta potential of each CuO suspension was measured at suspension was measured during the experiment. An aliquot of 100 mL of the supernatant was collected at the end of the experiment to measure the different water quality parameters. The effects of various (0–10 mg/L) coagulant dose were investigated in all studied waters, where 0 represent the control (absence of coagulant) experiments. The high concentration (10 mg/L) of CuO that was used in all tested waters is much higher than the predicted value in the environment by many researchers. However, this value was selected to obtain good accuracy in dynamic light scattering (DLS) and other measurements. All experiments were performed in triplicate and the relative standard deviations (RSD) are reported.
2.3. Other Analytical Methods
An aliquot of 100 mL was collected for the measurement of pH and conductivity (HACH: HQ40d Portable pH, conductivity, oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) and ion selective electrode (ISE) Multi-Parameter Meter, Hach Company, Loveland, CO, USA), turbidity (HACH 2100N with detection range, 0.001 NTU), UV absorbance at 254 nm wavelength (Optizen 2120 UV, Mecasys, Daejeon, Korea) and DOC (TOC-5000A, Shimadzu Corp, Kyoto, Japan) by standard methods of analysis. The residual concentrations of Cu2+ and Al were analyzed using (ICP-OES: Model Varian, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The electrophoretic mobility (EPM) and hydrodynamic diameters (HD) of CuO NPs were analyzed through laser Doppler electrophoresis and DLS method using a Malvern Zetasizer (NanoZS, Worcestershire, UK).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of CuO NPs
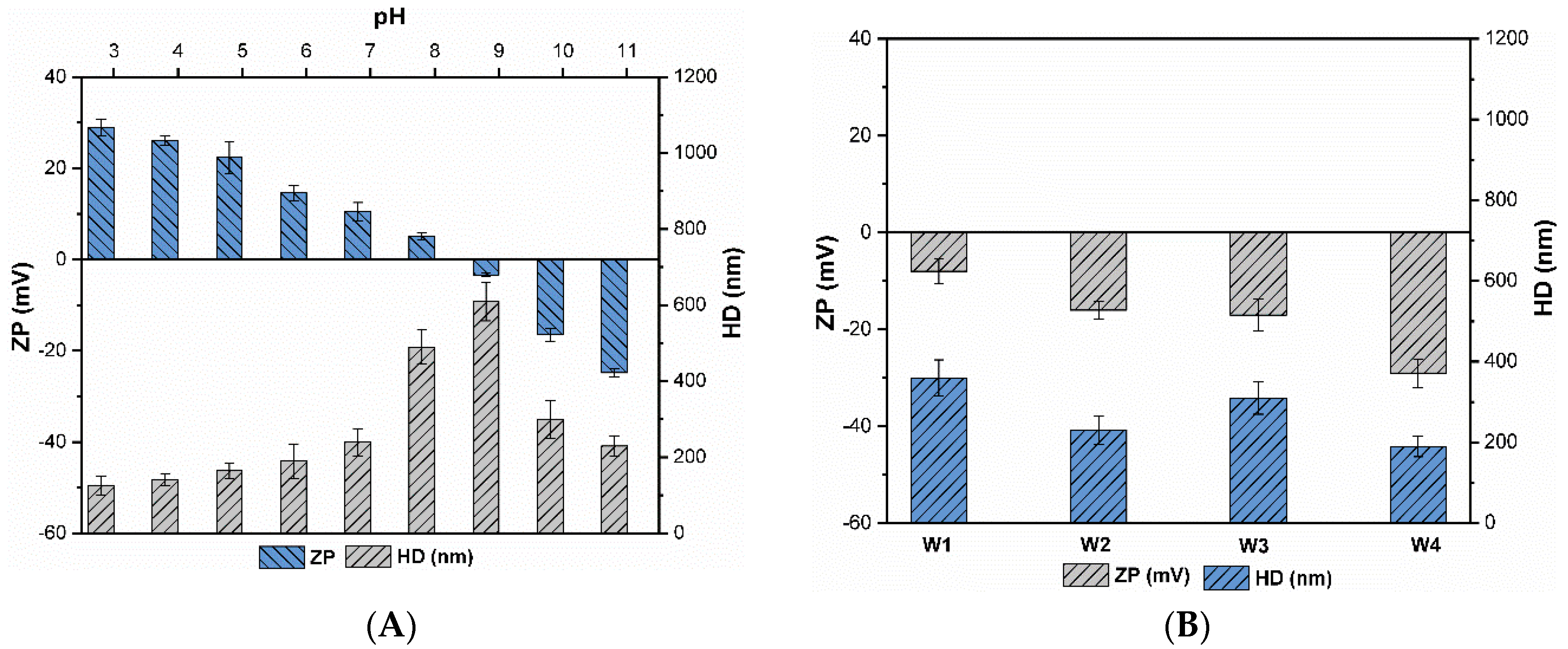
Figure 1A shows the effect of pH on the hydrodynamic diameters (HD) and zeta potential (ZP) in pure water. For all the tested pH, a larger HD of CuO NPs (approximately 150 nm) was found in pure water as compared to the vendor reported size (50 nm), thus indicating that most of NPs form larger agglomerates when suspended in the aqueous environment. The interaction among NPs and surrounding media might promote the formation of larger size NPs aggregates [32]. The surface potential and subsequently, HD of NPs, might be modified by altering the solution pH or IS. The zeta potential and HD were significantly influenced by suspension pH (Figure 1A). The surface charge was positive between pH 3.0 to 8.0 and became negative for pH values above 8 (32.1 ± 2.6 to −28.3 ± 0.9 mV). The point of zero charge (pzc) was found approximate to (pH ≈ 8.2), where the charge of a particle is negligible or zero. These findings are consistent with those contained in the literature [13,15,17], which reported that the pzc of CuO NPs was between pH 7.0 and 8.5. Moreover, zeta potential at pH values below pzc was positive, then negative at pH values above pzc. Furthermore, it was assumed that CuO NPs with zeta potential within ±15 mV would be unstable and will tend to aggregate under pure electrostatic interaction, while NPs having surface charge of ±15 mV to ±30 mV would be in a transitional state. The NPs with zeta potential above (±30 mV) would be predominantly stable in the suspension [13].

Figure 1.
Zeta potential (ZP) and hydrodynamic diameter (HD) of CuO NPs (10 mg/L); (A) under various pH values (pH 3–11); (B) different synthetic waters (W1–W4).
As illustrated in Figure 1A, the highest aggregates size was observed between pH 8–9 (510.3 ± 51.4 to 630.7 ± 85.2 nm), where the zeta potential was (5.1 ± 1.5 to −1.8 ± 1.1 mV), while the lowest was observed at pH 3.0 (148.9 ± 35.9 nm), where the zeta potential was (28.3 ± 3.9 mV). At or near pzc (pH ≈ 8.2), NPs had negligible or zero surface charge, resulting in a significant weakening of the repulsive forces among NPs, implying that each collision between primary NPs and/or aggregates may cause colloids adherence [17]. Thus, CuO NPs present the highest HD (630.7 ± 85.2 nm, Figure 1A) at this pH, due to gravitational force the larger size aggregates settle quickly in the solution. CuO NPs were highly charged and stable for pH values between 3.0 and 5.0 (28.3 ± 3.9 mV and 20.3 ± 2.4 mV); thus, agglomeration was minimized with HD values less than 150 nm due to high repulsive forces. An increase in pH led to enhanced in repulsive forces among NPs, thus resulting in stabilization of particles and consequently decrease in the HD of particles. Moreover, electrostatic repulsive forces predominate over the van der Waals (vdW) forces at these pH conditions [15]. Prior to the pzc, particles are in an intermediate state, so the size values ranged from 250.3 ± 108.1 nm to 510.3 ± 51.4, as shown in Figure 1A.
The measured polydispersity index (PdI) for synthetic waters was 0.31 ± 0.03 for W1, 0.30 ± 0.02 for W2, 0.32 ± 0.01 for W3 and 0.28 ± 0.03 for W4, which indicated a high accuracy level for this DLS device. As illustrated in Figure 1B, the presence of DOM shifts the zeta potential and HD of CuO NPs. CuO NPs were negatively charged and the HD values in all the studied waters ranged from 190 ± 35 to 310 ± 65 nm. Consequently, DOM increased the absolute surface potential by imparting a negative charge to the particle surface. These results coincide with previous studies, which reported a stabilizing effect of DOM [32,33]. Peng et al. reported that DOM may be adsorbed onto the NPs surface and might decrease or alter the surface charge from positive to negative at appropriate concentrations [15].
The zeta potential of CuO NPs in hydrophobic waters (W2 and W4) showed higher negative values as compared to the hydrophilic waters (W1 and W3) (Figure 1B). This shows that the hydrophilic DOM (SA) contributed less to the negativity of the CuO NPs surface charge than the hydrophobic DOM. Baalousha et al. also reported the enhanced absorption and thickness of surface coating of organic molecules with an increase in DOM concentration [34]. Sorption of DOM molecules enhanced the effect of steric stabilization combined with the effect on the surface charge that controls NPs interactions in solution. A recent study reported that the primary driving forces of sorption of DOM onto the NPs surface might be a result of the combination of electrostatic repulsive and attractive interactions [23]. In general, in the presence of heterogeneous compounds such as humic acid and salicylic acid, vdW interactions and steric effects also played a critical role in colloidal stability.
3.2. Agglomeration of CuO NPs
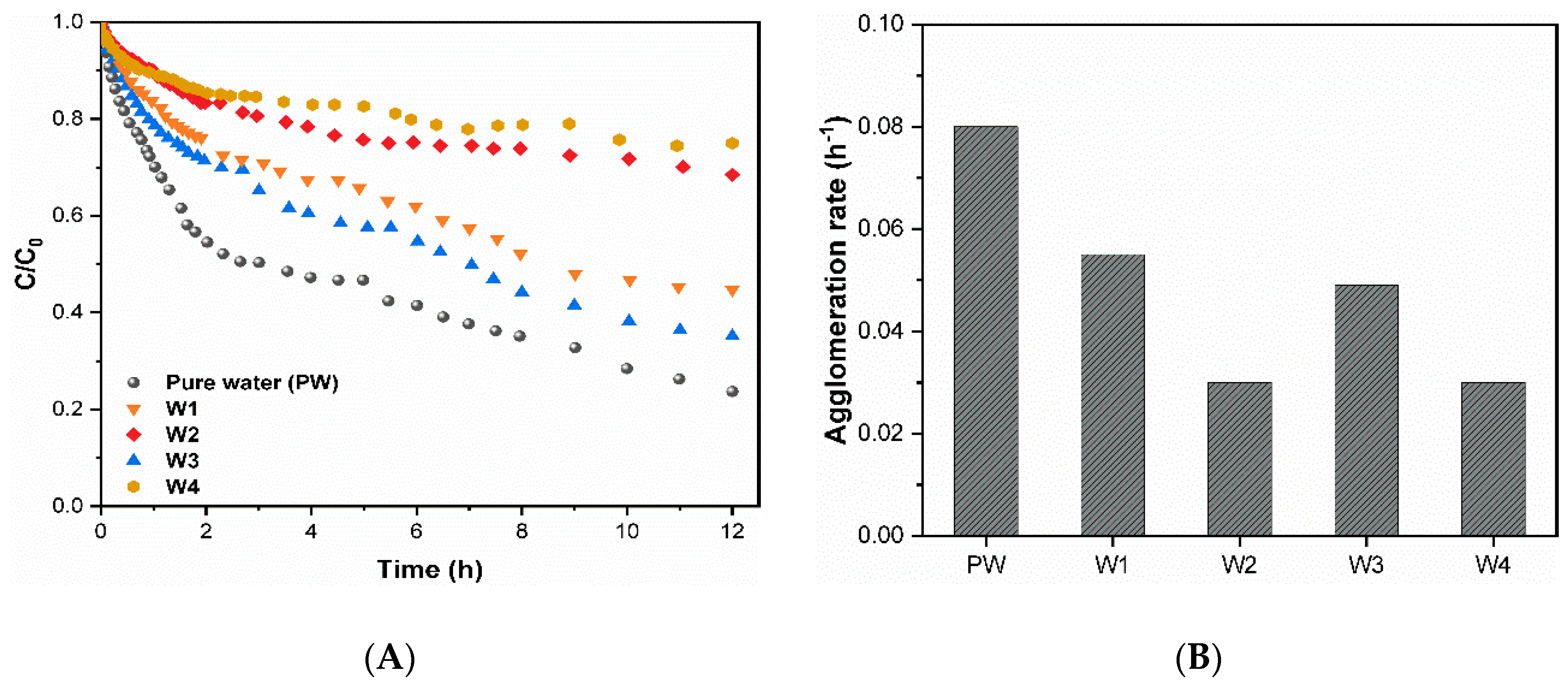
The agglomeration behavior of CuO NPs (10 mg/L) observed in various aqueous matrices is presented in Figure 2. The higher agglomeration rate (~0.08 h−1) (Figure 2B) shows that CuO NPs suspended in pure water settled faster as compared to the remaining waters (Figure 2A). This might be attributed to the absence of repulsive force, where CuO NPs form large aggregates, thereby resulting in a higher sedimentation rate (Figure 2B). Particles with a greater size tend to agglomerates faster due to gravitational force. In addition, CuO NPs spiked in water containing hydrophobic DOM (W2 and W4) present a small HD size (Figure 1B); hence, the settling is less pronounced and, subsequently, shows the lowest agglomeration rate (0.03 h−1) (Figure 2B). However, hydrophilic waters (W1 and W3) show higher aggregation and settling rates (~0.05 h−1) than hydrophobic waters. In general, the aggregation and settling rate of CuO NPs were found to be higher in hydrophilic DOM containing waters.

Figure 2.
(A) CuO aggregation kinetics; (B) agglomeration rates (h−1) in the studied waters (10 mg/L CuO NPs).
3.3. Removal of CuO NPs
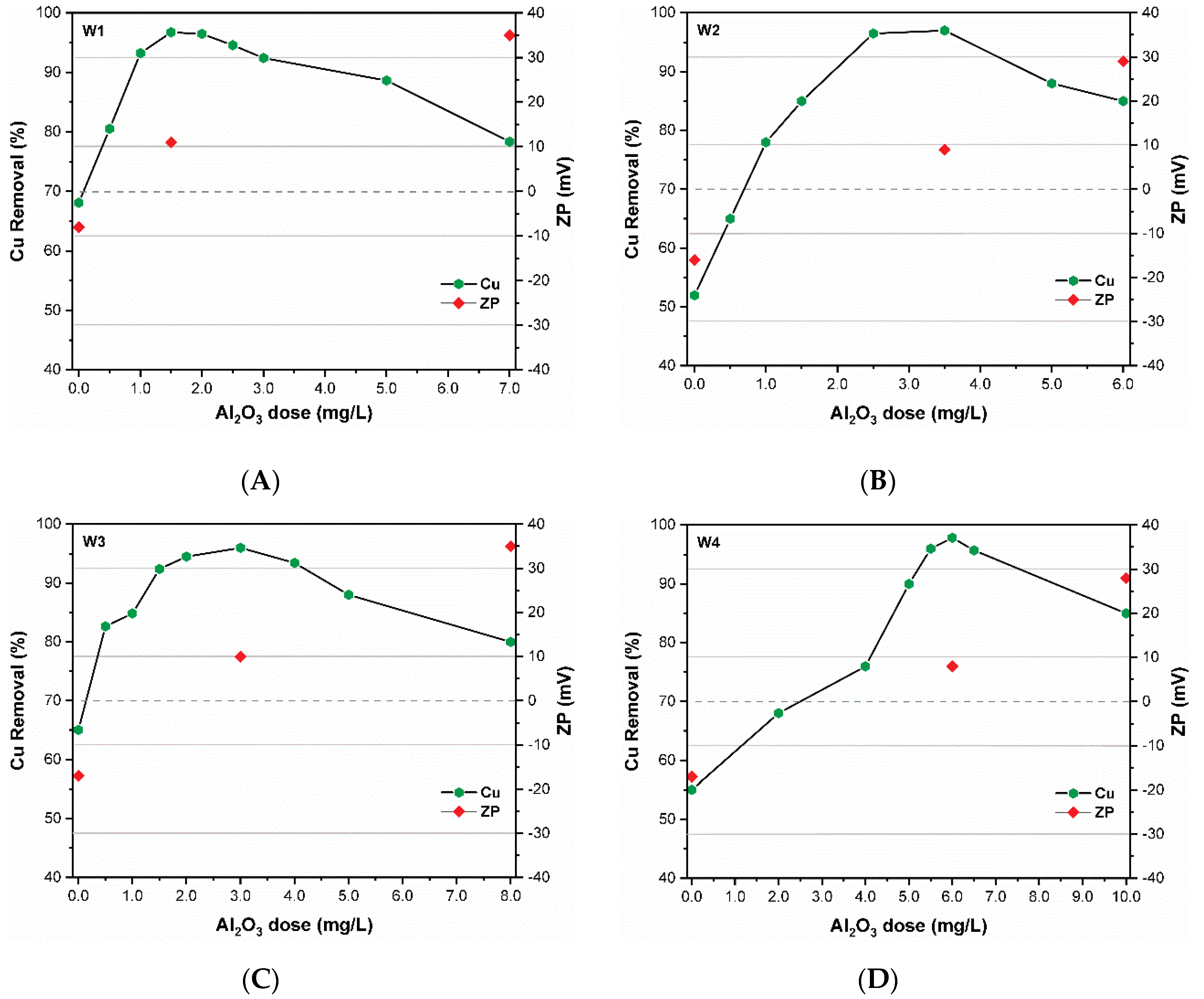
Figure 3 illustrates the removal of CuO NPs and corresponding zeta potential values of synthetic waters (W1–W4) at various coagulant doses after the coagulation process. More Cu was removed in the absence of coagulant in all tested waters. Hydrophilic DOM water (W1, W3) showed Cu removal efficiencies of above 65% compared to 50% for hydrophobic waters. Under these conditions, the CuO NPs form aggregates with HD values ranging between 350 ± 35 and 310 ± 54 nm, confirming the larger HD values for hydrophilic waters (Figure 1B). These observations are consistent with sedimentation experiments, where the hydrophilic waters (W1, W3) indicated a higher agglomeration rate in comparison with hydrophobic waters (W2 and W4). A previous study [35] also reported larger size (300 nm) NPs in the presence of HA auto-precipitated at control condition (without coagulant (AlCl3)). The high removal of CuO NPs in these conditions may also be attributed to the presence of metal cations (K+, Mg2+). Holbrook et al. demonstrated that the specific adsorption of divalent cation increased the NPs agglomeration at a wide range of pH levels in a complex environment [22].

Figure 3.
Cu removal and zeta potential (ZP) under different coagulant dose in synthetic waters (A) W1 (B); W2; (C) W3 and (D) W4.
As presented in Figure 3, the addition of coagulant increased the Cu removal efficiencies in all studied waters. The removal efficiencies increased with an increase in coagulant dose until the removal approached a plateau at ~90%, which is known as the “effective coagulation zone” (ECR) [35]. The ECR for hydrophilic waters varied between 0.5 to 2.5 mg Al2O3/L for W1 with an optimum dose (OD) of 1.5 mg/L Al2O3/L, and between 2.0 and 4.0 mg Al2O3/L for W3 with an OD of 3.0 mg Al2O3/L (Figure 3A,C). In the case of hydrophobic waters such as W2, the ECR was between 2.5 and 4.5 mg Al2O3/L with the OD at 3.5 mg Al2O3/L, while W4 showed an ECR between 4.0 and 7.0 mg Al2O3/L with the OD at 6.0 mg Al2O3/L (Figure 3B,D). Removal of Cu up to 95% was achieved at the OD of coagulant Al2O3/L (Figure 3). These results suggest a dependency of CuO NPs removal on the source water characteristics and dosage of applied coagulant as demonstrated in earlier studies [21,22]. The results in Figure 3 further show the key role of DOM characteristics on the coagulant dose and overall performance of the coagulation process. For instance, water with hydrophobic DOM (W2 and W4) would need a higher coagulant dose to obtain similar Cu removal to that observed in hydrophilic water (W1, W3). With similar DOC content among hydrophilic/hydrophobic waters, high UV254nm values require a higher Al2O3/L dose to obtain similar Cu removals. The addition of coagulant after the ECR zone promoted the restabilization of coagulated colloids because of polyelectrolytes oversaturation, thereby decreasing the removal efficiency [36].
As presented in Figure 1B, the CuO NPs in the model waters were negatively charged (between −10.7 ± 0.9 and −28 ± 1.5 mV) at the experimental pH. When added to the aqueous system, the hydrolyzed product of PACl (Al3+) effectively neutralized the negatively charged CuO NPs, causing destabilization of colloids. Therefore, adsorption of Al hydrolysis products on the surface of NPs decreases the zeta potential towards zero trajectory. At the OD of coagulant, NPs were effectively destabilized, the absolute zeta potential was neutral and NPs formed precipitate owing to the reduction in the electrosteric repulsion among them (Figure 3). Zhang et al. reported that NPs can be effectively destabilized and removed when the zeta potential is in the range of ±20 mV [35]. However, after the ECR, the zeta potential increased with increasing coagulant dose and became more positive to values greater than (+20 mV). Thus, the NPs surface becomes highly positive with increasing coagulant dose, resulting in restabilization of the CuO NPs; hence, low removal efficiency was observed in all studied waters (Figure 3A,D). These results indicate that the dominant removal mechanism of CuO NPs from water containing DOM might be charge neutralization. This is in accordance with the mechanism proposed by several studies working on the removal of NPs using iron- and aluminum-based coagulants [20,23,26,27]. The pH of the suspension was monitored after the completion of the experiment, which showed insignificant variation (Supplementary Figure S1). In contrast, a slight decrease in the pH values of hydrophobic waters was observed. Previous studies also reported that the pre-polymerization reaction might be responsible for decreasing the solution pH during the coagulation process compared to non-pre-polymerized ones [25,35].
3.4. Removal of DOM and Turbidity
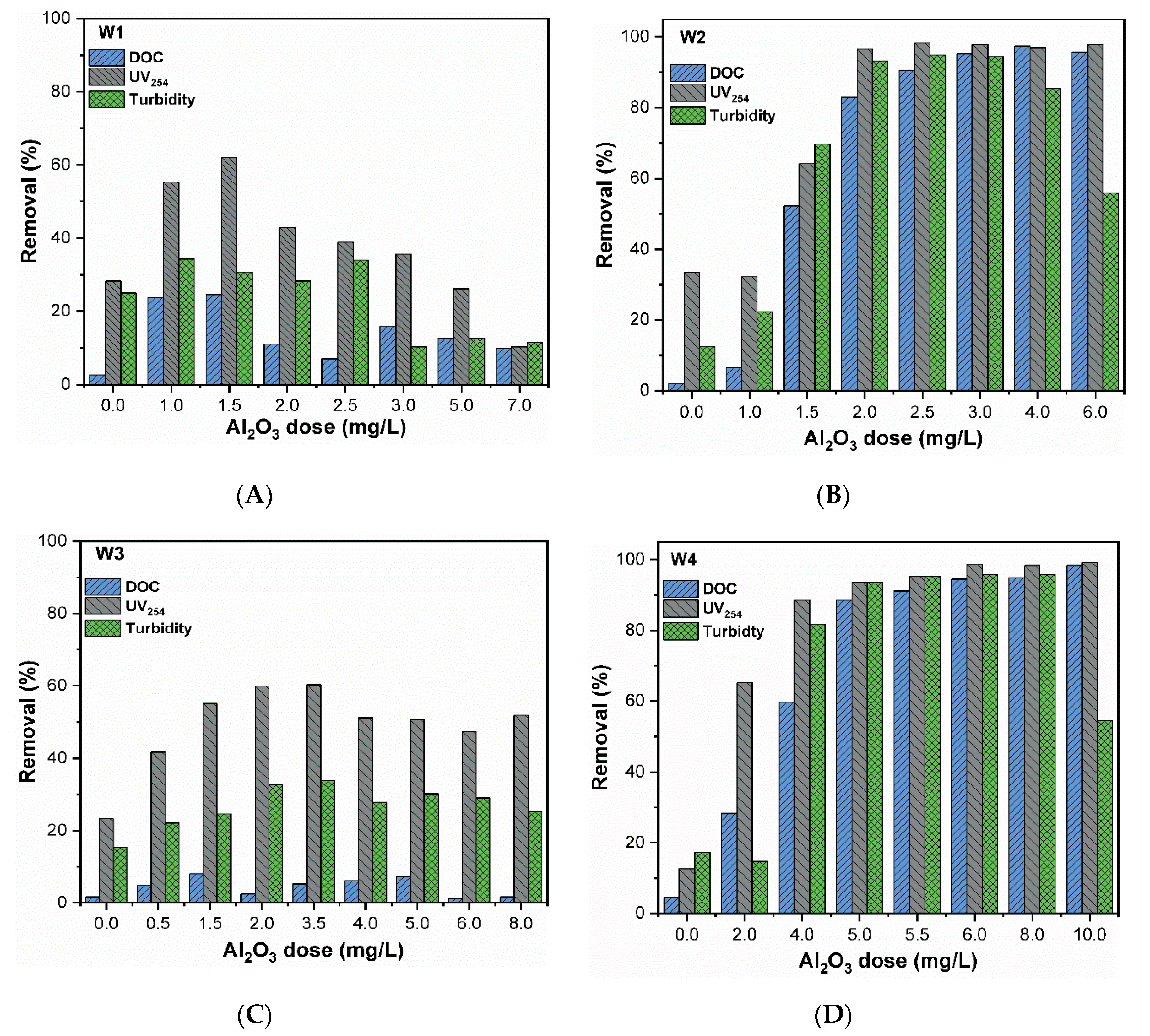
CuO can be efficiently removed through conventional treatment, yet the removal of DOM and turbidity is also necessary in order to evaluate whether or not their coexistence influences the overall performance of the water treatment process. The comparison of removal efficiencies of DOM-related parameters (DOC and UV254nm, and turbidity) for synthetic waters were as shown in Figure 4. According to results, the hydrophobic fraction of DOM was removed more efficiently than the hydrophilic fraction. As observed, the DOC and UV254nm removal were higher in the hydrophobic waters (>95% in ERC, Figure 4B,D for W2 and W4, respectively) than in hydrophilic waters (<25%, Figure 4A,C for W1–W3, respectively). These findings are consistent with Edzwald and Tobiason [37], who report that (i) DOM can control the coagulation process and good DOC removal is obtained when SUVA > 4 in water (mostly higher than 50%) because they are largely composed of humics with high hydrophobicity as well as HMM compounds; (ii) in water with SUVA < 2, DOM has little influence in the process of coagulation and less than 25% DOC removal is achieved, mainly because they contain non-humics with low hydrophobicity and LMM compounds. The amount of DOC reduced was less compared to the amount of UV254nm in all studied waters, revealing that aromatic organic materials are removed more efficiently compared to other DOM fractions. Sharp et al. reported that the hydrophobic DOM fraction has a low isoelectric point (IEP) because of the presence of phenolic and carboxylic groups, which induces a high negative surface potential, as presented in Figure 1B [38]. Charge neutralization with aluminum hydrolysis products removes the hydrophobic DOM more easily because of its increased number of anionic attachment sites compared to in the hydrophilic DOM. Hence, the specific colloidal charge character is dominated by the hydrophobic fraction [39]. A previous study reported that the magnitude of zeta potential affects the removal of hydrophobic fractions. Their finding also demonstrated that under an operational zeta potential window (−10 and +3 mV), the remaining DOC was optimized and stable.

Figure 4.
Removal of DOM-related parameters (DOC, UV254, and turbidity) from synthetic waters with varying coagulant dose.
The results for hydrophobic waters (W2 and W4) showed high removal of DOC and UV254nm, above 90% when surface potential was approximately +10 mV, for the CuO removal at OD of coagulant. However, removal efficiency decreased at zeta potential ranges of approximately ±30 mV. Interestingly, the removal curves of DOC, UV254nm, and turbidity follow the CuO removal pattern in all tested waters. These results confirmed the removal efficiency of hydrophobic DOM during the chemical coagulation process, as demonstrated in previous studies [40,41]. The removal of DOC and UV254nm in hydrophobic water (W2 and W4) was higher than in hydrophilic water (W1, W3). DOC removal varied between 1% and 25%, while UV254nm removal varied between 10% and 60% (Figure 4A,C). This might be due to the presence of weaker acidic groups and LMW compounds in hydrophilic waters, which impede the competitive interactions among coagulants and DOM.
The OD of turbidity removal follows the same pattern as Cu removal in each studied water (Figure 3 and Figure 4). However, water containing hydrophobic DOM showed higher turbidity removal compared to hydrophilic DOM. The possible explanation for this might be related to the major concentration of HA, which increased the initial turbidity of the hydrophobic waters, thereby improving the removal. The presence of CuO NPs might contribute to the higher removal of DOM and turbidity. For instance, a recent study [42] used the titanium-based NPs as a coagulant in water treatment to remove nutrients and organic matter. The titanium salts successfully achieved high DOM removal with better flocs settling, similar to Al and Fe salts [43]. Thus, the coagulation performance of CuO NPs using polyaluminum coagulant might have a positive impact on the removal of DOM and turbidity. Nevertheless, further analysis and experiments are required to confirm this finding.
4. Conclusions
The objective of this study was to explore the influence of DOM type (hydrophobic/hydrophilic) and its concentration on CuO NPs agglomeration and removal from water by coagulation process. According to the results, hydrophobic DOM, such as HA, remarkably reduced the zeta potential and HD size of CuO NPs compared to hydrophilic DOM because of their greater adsorption potential. The higher DOC concentration hindered the NPs sedimentation owing to the steric repulsion effect of sorbed DOM molecules. The results of coagulation experiments showed that polyaluminum-based coagulants could effectively remove the CuO NPs to values up to 95%. At the OD of coagulant, the high removal of CuO was achieved in all studied waters independently to DOM type and characteristic. However, after the OD, removal of CuO NPs reduced to values less than 70% because of the restabilization of precipitated colloids. Hydrophilic water requires lower coagulant dose to achieve high Cu removal, whereas water with hydrophobic DOM needs more coagulant to obtain the same level of removal. Amongst hydrophilic/hydrophobic waters with the same DOC content, higher UV254nm values required a larger amount of coagulant to obtain similar amount of Cu removals. This indicated that the DOM type plays an important role in determining the applied coagulant dose during the coagulation process. Current results revealed that the primary removal mechanism involved in the CuO NPs composite contaminant might be charge neutralization from waters with various type/concentration of DOM. The findings of this study provide evidence that the characteristic of DOM might affect the fate, mobility and coagulation performance of released CuO NPs during water/wastewater treatment.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9717/7/7/455/s1, Supplementary Figure S1. Difference of water pH with added coagulant for (A) hydrophilic; (B) hydrophobic waters.
Author Contributions
R.K. and I.T.Y. conceived and designed the study; R.K. and M.A.I. performed the experiment and analyzed the data; M.A.I., M.A., A.U. and S.K. provided critical feedback and helped shape the research; R.K. wrote the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
The BK21 plus program supported this work through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education of Korea (Grant No. 22A20152613545). The first and second authors were supported through a scholarship program (HRDI-UESTP) by the Higher Education Commission (HEC), Pakistan.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Vance, M.E.; Kuiken, T.; Vejerano, E.P.; McGinnis, S.P.; Hochella, M.F., Jr.; Rejeski, D.; Hull, M.S. Nanotechnology in the real world: Redeveloping the nanomaterial consumer products inventory. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, M.B.; Goswami, A.; Felpin, F.-X.; Asefa, T.; Huang, X.; Silva, R.; Zou, X.; Zboril, R.; Varma, R.S. Cu and Cu-Based Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications in Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3722–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju-Nam, Y.; Lead, J.R. Manufactured nanoparticles: An overview of their chemistry, interactions and potential environmental implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 396–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, A.A.; Vosti, W.; Wang, H.; Lazareva, A. Release of engineered nanomaterials from personal care products throughout their life cycle. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2014, 16, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, P.; Song, G.; Hristovski, K.; Kiser, M.A. Occurrence and removal of titanium at full scale wastewater treatment plants: Implications for TiO2 nanomaterials. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, N.; Thomas, T.A.; Duncan, J.S. Nanotechnology applications and implications research supported by the US Environmental Protection Agency STAR grants program. J. Environ. Monit. 2007, 9, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Moos, N.; Slaveykova, V.I. Oxidative stress induced by inorganic nanoparticles in bacteria and aquatic microalgae—State of the art and knowledge gaps. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 605–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Vijver, M.G.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Galloway, T.S.; Tyler, C.R. A comparative analysis on the in vivo toxicity of copper nanoparticles in three species of freshwater fish. Chemosphere 2015, 139, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chung, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, I. The genotoxic effect of ZnO and CuO nanoparticles on early growth of buckwheat, fagopyrum esculentum. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruoja, V.; Dubourguier, H.-C.C.; Kasemets, K.; Kahru, A. Toxicity of nanoparticles of CuO, ZnO and TiO2 to microalgae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; McLean, J.E.; Latta, D.E.; Manangón, E.; Britt, D.W.; Johnson, W.P.; Boyanov, M.I.; Anderson, A.J. CuO and ZnO nanoparticles: Phytotoxicity, metal speciation, and induction of oxidative stress in sand-grown wheat. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2012, 14, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreher, K.L. Health and environmental impact of nanotechnology: Toxicological assessment of manufactured nanoparticles. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 77, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.; Vavra, J.; Forbes, V.E. Effects of water quality parameters on agglomeration and dissolution of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO-NPs) using a central composite circumscribed design. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 521, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, Z.; Labbez, C.; Nordholm, S.; Ahlberg, E. Size-dependent surface charging of nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 5715–5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Shen, C.; Zheng, S.; Yang, W.; Hu, H.; Liu, J.; Shi, J. Transformation of CuO Nanoparticles in the Aquatic Environment: Influence of pH, Electrolytes and Natural Organic Matter. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giasuddin, A.B.M.; Kanel, S.R.; Choi, H. Adsorption of humic acid onto nanoscale zerovalent iron and its effect on arsenic removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2022–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Vijver, M.G.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M. Impact of water chemistry on the behavior and fate of copper nanoparticles. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springer, F.; Laborie, S.; Guigui, C. Removal of SiO2 nanoparticles from industry wastewaters and subsurface waters by ultrafiltration: Investigation of process efficiency, deposit properties and fouling mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 108, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiede, K.; Boxall, A.B.A.; Wang, X.; Gore, D.; Tiede, D.; Baxter, M.; David, H.; Tear, S.P.; Lewis, J. Application of hydrodynamic chromatography-ICP-MS to investigate the fate of silver nanoparticles in activated sludge. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2010, 25, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Westerhoff, P.; Crittenden, J.C. Stability and removal of water soluble CdTe quantum dots in water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyung, H.; Kim, J.-H.H. Dispersion of C60in natural water and removal by conventional drinking water treatment processes. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2463–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holbrook, R.D.; Kline, C.N.; Filliben, J.J. Impact of source water quality on multiwall carbon nanotube coagulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1386–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, V.S.; Corniciuc, C.; Teixeira, M.R. The effect of TiO2 nanoparticles removal on drinking water quality produced by conventional treatment C/F/S. Water Res. 2017, 109, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott Chalew, T.E.; Ajmani, G.S.; Huang, H.; Schwab, K.J. Evaluating nanoparticle breakthrough during drinking water treatment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Li, Y.; Tang, T.; Yuan, Z.; Yu, C.-P. Removal of silver nanoparticles by coagulation processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 261, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xue, N.; Chu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yan, H.; Han, Q. CuO nanoparticle-humic acid (CuONP-HA) composite contaminant removal by coagulation/ultrafiltration process: The application of sodium alginate as coagulant aid. Desalination 2015, 367, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Inam, M.; Park, D.; Zam Zam, S.; Shin, S.; Khan, S.; Akram, M.; Yeom, I. Influence of Organic Ligands on the Colloidal Stability and Removal of ZnO Nanoparticles from Synthetic Waters by Coagulation. Processes 2018, 6, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campinas, M.; Rosa, M.J. The ionic strength effect on microcystin and natural organic matter surrogate adsorption onto PAC. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 299, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edzwald, J.K.; Van Benschoten, J.E. Aluminum coagulation of natural organic matter. In Chemical Water and Wastewater Treatment; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1990; pp. 341–359. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA—United States Environmental Protection Agency. Enhanced Coagulation and Enhanced Precipitative Softening Guidance Manual; USEPA—United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Letterman, R. Water Quality and Treatment, a Handbook of Community Water Supplies, 5th ed.; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Oberdörster, G.; Biswas, P. Characterization of size, surface charge, and agglomeration state of nanoparticle dispersions for toxicological studies. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2009, 11, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanello, M.B.; de Cortalezzi, M.M.F. An experimental study on the aggregation of TiO2 nanoparticles under environmentally relevant conditions. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3887–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baalousha, M. Aggregation and disaggregation of iron oxide nanoparticles: Influence of particle concentration, pH and natural organic matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Mao, J.; Zhao, Q.; He, S.; Ma, J. Effect of AlCl3 concentration on nanoparticle removal by coagulation. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 38, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinotti, A.; Zaritzky, N. Effect of aluminum sulfate and cationic polyelectrolytes on the destabilization of emulsified wastes. Waste Manag. 2001, 21, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edzwald, J.K.; Tobiason, J.E. Enhanced coagulation: US requirements and a broader view. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, E.L.; Jarvis, P.; Parsons, S.A.; Jefferson, B. Impact of fractional character on the coagulation of NOM. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 286, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.; Goslan, E.H.; Parsons, S.A.; Jefferson, B. Disinfection by-product formation of natural organic matter surrogates and treatment by coagulation, MIEX® and nanofiltration. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matilainen, A.; Vepsäläinen, M.; Sillanpää, M. Natural organic matter removal by coagulation during drinking water treatment: a review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 159, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, L.; Flora, J.R.V.; Park, Y.-G.; Badawy, M.; Saleh, H.; Yoon, Y. Removal of natural organic matter from potential drinking water sources by combined coagulation and adsorption using carbon nanomaterials. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 95, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Gao, B.Y.; Zhang, G.Z.; Phuntsho, S.; Shon, H.K. Coagulation by titanium tetrachloride for fulvic acid removal: Factors influencing coagulation efficiency and floc characteristics. Desalination 2014, 335, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, H.K.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kim, I.S.; Cho, J.; Kim, G.I.; Kim, J.B.; Kim, J.H. Preparation of titanium dioxide (TiO2) from sludge produced by titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) flocculation of wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).