On the Selective Transport of Nutrients through Polymer Inclusion Membranes Based on Ionic Liquids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Polymer Inclusion Membranes Based on Ionic Liquids
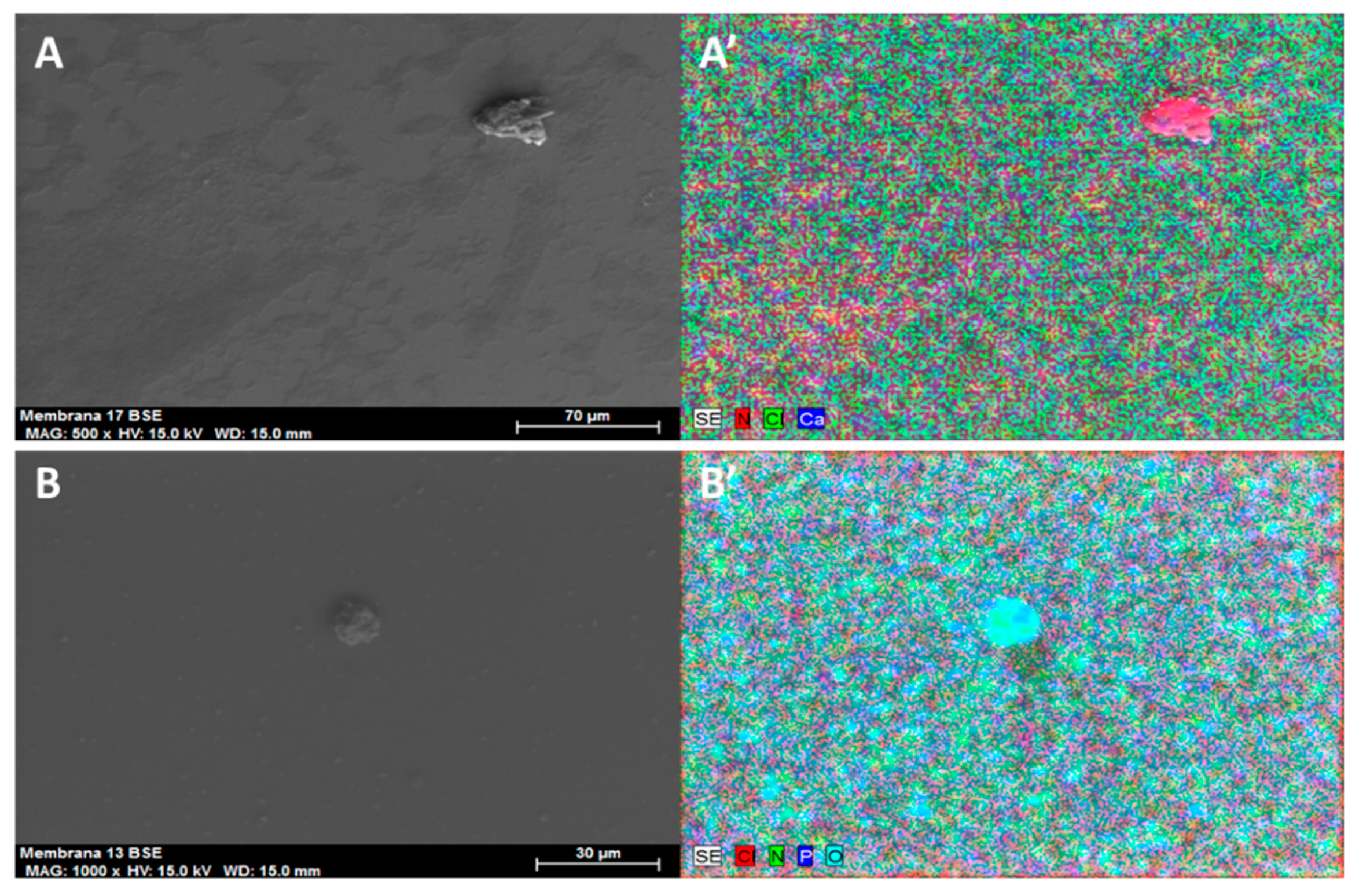
2.2. SEM–EDX and Elemental Mapping Characterization
2.3. Ion Transport Studies
2.4. Ionic Chromatography
2.5. Calculation of Permeability
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Polymer Ionic Liquid Inclusion Membrane Characterization before and after Being Used as Separators
3.2. Transport Studies of CaCl2 and Na2HPO4 through Polymer Inclusion Ionic Liquid Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ortiz, I.; Bringas, E.; Samaniego, H.; San Román, M.F.; Urtiaga, A. Membrane processes for the efficient recovery of anionic pollutants. Desalination 2006, 193, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, L.J.; Godínez, C.; de los Ríos, A.P.; Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; Sánchez-Segado, S.; Alguacil, F.J. Recent advances in supported ionic liquid membrane technology. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 376, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Applications of ionic liquids in the chemical industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de los Ríos, A.P.; Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; Lozano, L.J.; Sánchez, S.; Moreno, J.I.; Godínez, C. Removal of Metal Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Extraction with Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de los Ríos, A.P.; Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; Alguacil, F.J.; Lozano, L.J.; Ginestá, A.; García-Díaz, I.; Sánchez-Segado, S.; López, F.A.; Godínez, C. On the use of imidazolium and ammonium-based ionic liquids as green solvents for the selective recovery of Zn(II), Cd(II), Cu(II) and Fe(III) from hydrochloride aqueous solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 97, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de los Ríos, A.P.; Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; Tomás-Alonso, F.; Rubio, M.; Gómez, D.; Víllora, G. On the importance of the nature of the ionic liquids in the selective simultaneous separation of the substrates and products of a transesterification reaction through supported ionic liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 307, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, A.; Arce, A.; Khoshkbarchi, M.K. Partitioning of antibiotics in a two-liquid phase system formed by water and a room temperature ionic liquid. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 44, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de los Ríos, A.P.; Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; Presa, H.; Gómez, D.; Víllora, G. Tailoring supported ionic liquid membranes for the selective separation of transesterification reaction compounds. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 328, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, R.D.; Gin, D.L. Perspective on ionic liquids and ionic liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 369, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Noble, R.D.; Gin, D.L.; Zhang, X.; Deng, L. Combination of ionic liquids with membrane technology: A new approach for CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 497, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Bai, L.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, X.; Nie, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhang, S. Ether-functionalized ionic liquid based composite membranes for carbon dioxide separation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 45184–45192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Chen, J. Preparation of poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-tetrafluoroethylene)-based polymer inclusion membrane using bifunctional ionic liquid extractant for Cr(VI) transport. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 2714–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Fernandez, F.J.; de Los Rios, A.P.; Salar-Garcia, M.J.; Ortiz-Martinez, V.M.; Lozano-Blanco, L.J.; Godinez, C.; Tomas-Alonso, F.; Quesada-Medina, J. Recent progress and perspectives in microbial fuel cells for bioenergy generation and wastewater treatment. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 138, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Shinde, V.N.; Deopurkar, R.L.; Kale, S.P.; Patil, S.A.; Pant, D. Recent advances in the use of different substrates in microbial fuel cells toward wastewater treatment and simultaneous energy recovery. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 706–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Martínez, V.M.; Salar-García, M.J.; Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; de los Ríos, A.P. Development and characterization of a new embedded ionic liquid based membrane-cathode assembly for its application in single chamber microbial fuel cells. Energy 2015, 93, 1748–1757. [Google Scholar]
- Baicha, Z.; Salar-García, M.J.; Ortiz-Martínez, V.M.; Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; de los Ríos, A.P.; Labjar, N.; Lotfi, E.; Elmahi, M. A critical review on microalgae as an alternative source for bioenergy production: A promising low cost substrate for microbial fuel cells. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 154, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salar-García, M.J.; Ortiz-Martínez, V.M.; de los Ríos, A.P.; Hernández-Fernández, F.J. A method based on impedance spectroscopy for predicting the behavior of novel ionic liquid-polymer inclusion membranes in microbial fuel cells. Energy 2015, 89, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez Fernandez, F.; de los Rios, A.P.; Rubio, M.; Tomas Alonso, F.; Gomez, D.; Villora, G. A novel application of supported liquid membranes based on ionic liquids to the selective simultaneous separation of the substrates and products of a transesterification reaction. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 293, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de los Ríos, A.P.; Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; Tomás-Alonso, F.; Palacios, J.M.; Gómez, D.; Rubio, M.; Víllora, G. A SEM–EDX study of highly stable supported liquid membranes based on ionic liquids. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 300, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Fortunato, R.; González-Muñoz, M.J.; Kubasiewicz, M.; Luque, S.; Alvarez, J.R.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Coelhoso, I.M.; Crespo, J.G. Liquid membranes using ionic liquids: The influence of water on solute transport. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 249, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, R.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Reis, M.A.M.; Crespo, J.G. Supported liquid membranes using ionic liquids: Study of stability and transport mechanisms. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 242, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.G.; Santos, L.M.N.B.F.; Fernandes, A.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Marrucho, I.M. An overview of the mutual solubilities of water–imidazolium-based ionic liquids systems. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2007, 261, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás-Alonso, F.; Rubio, A.M.; Giménez, A.; de los Ríos, A.P.; Salar-García, M.J.; Ortiz-Martínez, V.M.; Hernández-Fernández, F.J. Influence of ionic liquid composition on the stability of polyvinyl chloride-based ionic liquid inclusion membranes in aqueous solution. AIChE J. 2017, 63, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Compound | Structure |
|---|---|
| Methyltrioctylammonium Chloride |  |
| Polyvinyl Chloride |  |
| Permeability (×106 cm.s−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Membrane | Na+ | HPO42− | Ca+2 | Cl− |
| 70% w/w [MTOA+][Cl−] | 25.671 | 18.463 | 0.000 | 2.669 |
| 30% w/w [MTOA+][Cl−] | 4.216 | 5.351 | 0.000 | 1.573 |
| Permselectivity (rPi) | Average Permselectivity (rP) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Membrane | Na+/HPO4−2 | Na+/Cl− | Cl−/HPO4−2 | |
| 70% w/w [MTOA+][Cl−] | 1.39 | 9.62 | 6.92 | 5.98 |
| HPO4−2/Na+ | Na+/Cl− | HPO4−2/Cl− | ||
| 30% w/w [MTOA+][Cl−] | 1.27 | 2.68 | 3.4 | 2.45 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baicha, Z.; Salar-García, M.J.; Ortiz-Martínez, V.M.; Hernández-Fernández, F.J.; de los Ríos, A.P.; Maqueda Marín, D.P.; Collado, J.A.; Tomás-Alonso, F.; El Mahi, M. On the Selective Transport of Nutrients through Polymer Inclusion Membranes Based on Ionic Liquids. Processes 2019, 7, 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7080544
Baicha Z, Salar-García MJ, Ortiz-Martínez VM, Hernández-Fernández FJ, de los Ríos AP, Maqueda Marín DP, Collado JA, Tomás-Alonso F, El Mahi M. On the Selective Transport of Nutrients through Polymer Inclusion Membranes Based on Ionic Liquids. Processes. 2019; 7(8):544. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7080544
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaicha, Z., M.J. Salar-García, V.M. Ortiz-Martínez, F.J. Hernández-Fernández, A.P. de los Ríos, D.P. Maqueda Marín, J.A. Collado, F. Tomás-Alonso, and M. El Mahi. 2019. "On the Selective Transport of Nutrients through Polymer Inclusion Membranes Based on Ionic Liquids" Processes 7, no. 8: 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7080544
APA StyleBaicha, Z., Salar-García, M. J., Ortiz-Martínez, V. M., Hernández-Fernández, F. J., de los Ríos, A. P., Maqueda Marín, D. P., Collado, J. A., Tomás-Alonso, F., & El Mahi, M. (2019). On the Selective Transport of Nutrients through Polymer Inclusion Membranes Based on Ionic Liquids. Processes, 7(8), 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7080544







