Syngas Production Improvement of Sugarcane Bagasse Conversion Using an Electromagnetic Modified Vacuum Pyrolysis Reactor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Biomass Sample
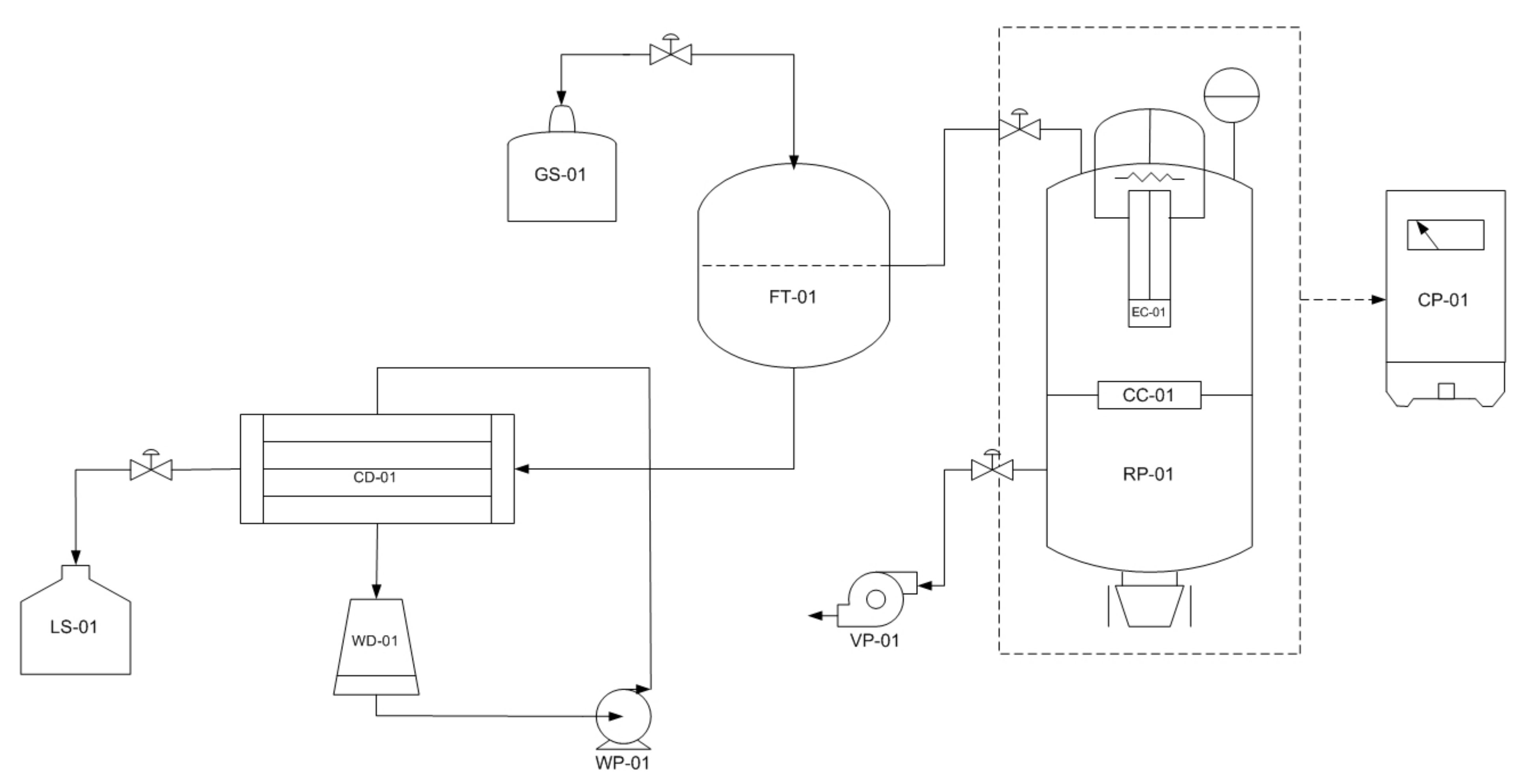
2.2. Bagasse Pyrolysis Using Modified-Vacuum Pyrolysis Reactor
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aydin, M. The effect of biomass energy consumption on economic growth in BRICS countries: A country-specific panel data analysis. Renew.Energy 2019, 138, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, K.; Sharma, V.K.; Dhingra, S.; Braccio, G.; Ahmad, M.; Sofia, S. Assessing the lignocellulosic biomass resources potential in developing countries: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 682–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balat, M.; Ayar, G. Biomass Energy in the World, Use of Biomass and Potential Trends. Energy Sources 2005, 27, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea-Moreno, M.A.; Samerón-Manzano, E.; Perea-Moreno, A.J. Biomass as renewable energy: Worldwide research trends. Sustainability 2019, 11, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, L.W.; Ngoh, G.C.; Chua, A.S.M.; Patah, M.F.A.; Teoh, W.H. Process intensification of cellulase and bioethanol production from sugarcane bagasse via an integrated saccharification and fermentation process. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2019, 142, 107528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, N.P.; Machin, E.B.; Pedroso, D.T.; Antunes, J.S.; Silveira, J.L. Fluid-dynamic assessment of sugarcane bagasse to use as feedstock in bubbling fluidized bed gasifiers. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 73, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, G.F.; Justo, O.R.; Perez, V.H.; Garcia-Perez, M. Thermochemical conversion of sugarcane bagasse by fast pyrolysis: High yield of levoglucosan production. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis. 2018, 133, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavasoli, A.; Barati, M.; Karimi, A. Sugarcane bagasse supercritical water gasification in presence of potassium promoted copper nano-catalysts supported on γ-Al2O3. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Che, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Shao, J.; Chen, H. Recent developments in lignocellulosic biomass catalytic fast pyrolysis: Strategies for the optimization of bio-oil quality and yield. Fuel Process. Technol. 2019, 196, 106180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, L.; Zhou, J.; Liang, K.; Song, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lan, X. Products optimization by FeS2 catalyst for low-rank coal microwave pyrolysis. Fuel 2019, 255, 115759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantrell, K.B.; Martin, J.H.; Ro, K.S. Application of Thermogravimetric Analysis for the Proximate Analysis of Livestock Wastes. J. Am. Soc. Test. Mater. Int. 2010, 7, 102583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.; Nasir, S.; Said, M.; Kurniawan, I.; Huda, A. A New Prototype Design and Experimental Study for Assessing Spontaneous Coal Combustion. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlavsová, A.; Corsaro, A.; Raclavská, H.; Juchelková, D.; Škrobánková, H.; Frydrych, J. Syngas Production from Pyrolysis of Nine Composts Obtained from Nonhybrid and Hybrid Perennial Grasses. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffar, M.M.; Nahil, M.A.; Williams, P.T. Methane Production from the Pyrolysis–Catalytic Hydrogenation of Waste Biomass: Influence of Process Conditions and Catalyst Type. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 7443–7457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, S.; Liu, S.; Yang, C.; Lu, Q. Fast pyrolysis of biomass in free-fall reactor for hydrogen-rich gas. Fuel Process. Technol. 2004, 85, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellens, C.J.; Brown, R.C. Optimization of a free-fall reactor for the production of fast pyrolysis bio-oil. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 103, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, L.; Mohan, D.; Bricka, M.; Steele, P.; Strobel, D.; Crocker, D.; Mitchell, B.; Mohammad, J.; Cantrell, K.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Pyrolysis of wood and bark in an auger reactor: Physical properties and chemical analysis of the produced bio-oils. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosavljevic, I.; Oja, V.; Suuberg, E.M. Thermal effects in cellulose pyrolysis: Relationship to char formation processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1996, 35, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Gao, Z.; Jin, J.; Zhou, H.; Cohron, M.; Zhao, H.; Liu, H.; Pan, W. Synthesis Gas Production with an Adjustable H2/CO Ratio through the Coal Gasification Process: Effects of Coal Ranks And Methane Addition. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 1720–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.M.; Prieto, P.; de la Hoz, A.; Díaz-Ortiz, Á.; Martín, D.R.; Garcia, J.I. Influence of Polarity and Activation Energy in Microwave-Assisted Organic Synthesis (MAOS). ChemistryOpen 2015, 4, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huda, A.; Suman, P.H.; Torquato, L.D.M.; Silva, B.F.; Handoko, C.T.; Gulo, F.; Zanoni, M.V.B.; Orlandi, M.O. Visible light-driven photoelectrocatalytic degradation of acid yellow 17 using Sn3O4 flower-like thin films supported on Ti substrate (Sn3O4/TiO2/Ti). J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2019, 376, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, R.K.; Nam, W.L.; Chong, M.Y.; Phang, X.Y.; Su, M.H.; Yek, P.N.Y.; Ma, N.L.; Cheng, C.K.; Chong, C.T.; Lam, S.S. Oil palm waste: An abundant and promising feedstock for microwave pyrolysis conversion into good quality biochar with potential multi-applications. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 115, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Components of Proximate Analysis | Standard Method | Value a | Components of Ultimate Analysis | Standard Method | Value b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture (%) | ASTM E 871-82 | 3.01 | Carbon/C (%) | ASTM E 777 | 45.01 |
| Volatile (%) | ASTM E 872-82 | 72.66 | Oxygen/O (%) | By difference | 41.73 |
| Fixed Carbon (%) | ASTM D 3172-02 | 12.89 | Hydrogen/H (%) | ASTM E 777 | 5.59 |
| Ash (%) | ASTM D1102-84 | 8.98 | Nitrogen/N (%) | ASTM E 778 | 0.29 |
| Sulphur/S (%) | ASTM # 775 | 1.08 |
| Applied Current (A) | Temperature (°C) | Pyrolysis Time (Minutes) | H2/CO Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 210 | 60 | 0.13 |
| 1 | 0.66 | ||
| 2 | 0.89 | ||
| 3 | 1.98 | ||
| 4 | 3.18 | ||
| 5 | 4.40 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bustan, M.D.; Haryati, S.; Hadiah, F.; Selpiana, S.; Huda, A. Syngas Production Improvement of Sugarcane Bagasse Conversion Using an Electromagnetic Modified Vacuum Pyrolysis Reactor. Processes 2020, 8, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8020252
Bustan MD, Haryati S, Hadiah F, Selpiana S, Huda A. Syngas Production Improvement of Sugarcane Bagasse Conversion Using an Electromagnetic Modified Vacuum Pyrolysis Reactor. Processes. 2020; 8(2):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8020252
Chicago/Turabian StyleBustan, Muhammad Djoni, Sri Haryati, Fitri Hadiah, Selpiana Selpiana, and Adri Huda. 2020. "Syngas Production Improvement of Sugarcane Bagasse Conversion Using an Electromagnetic Modified Vacuum Pyrolysis Reactor" Processes 8, no. 2: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8020252
APA StyleBustan, M. D., Haryati, S., Hadiah, F., Selpiana, S., & Huda, A. (2020). Syngas Production Improvement of Sugarcane Bagasse Conversion Using an Electromagnetic Modified Vacuum Pyrolysis Reactor. Processes, 8(2), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8020252





