Fabrication of Ultrathin MoS2 Nanosheets and Application on Adsorption of Organic Pollutants and Heavy Metals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of the MoS2 Nanosheets
2.3. Adsorption Batch Experiments
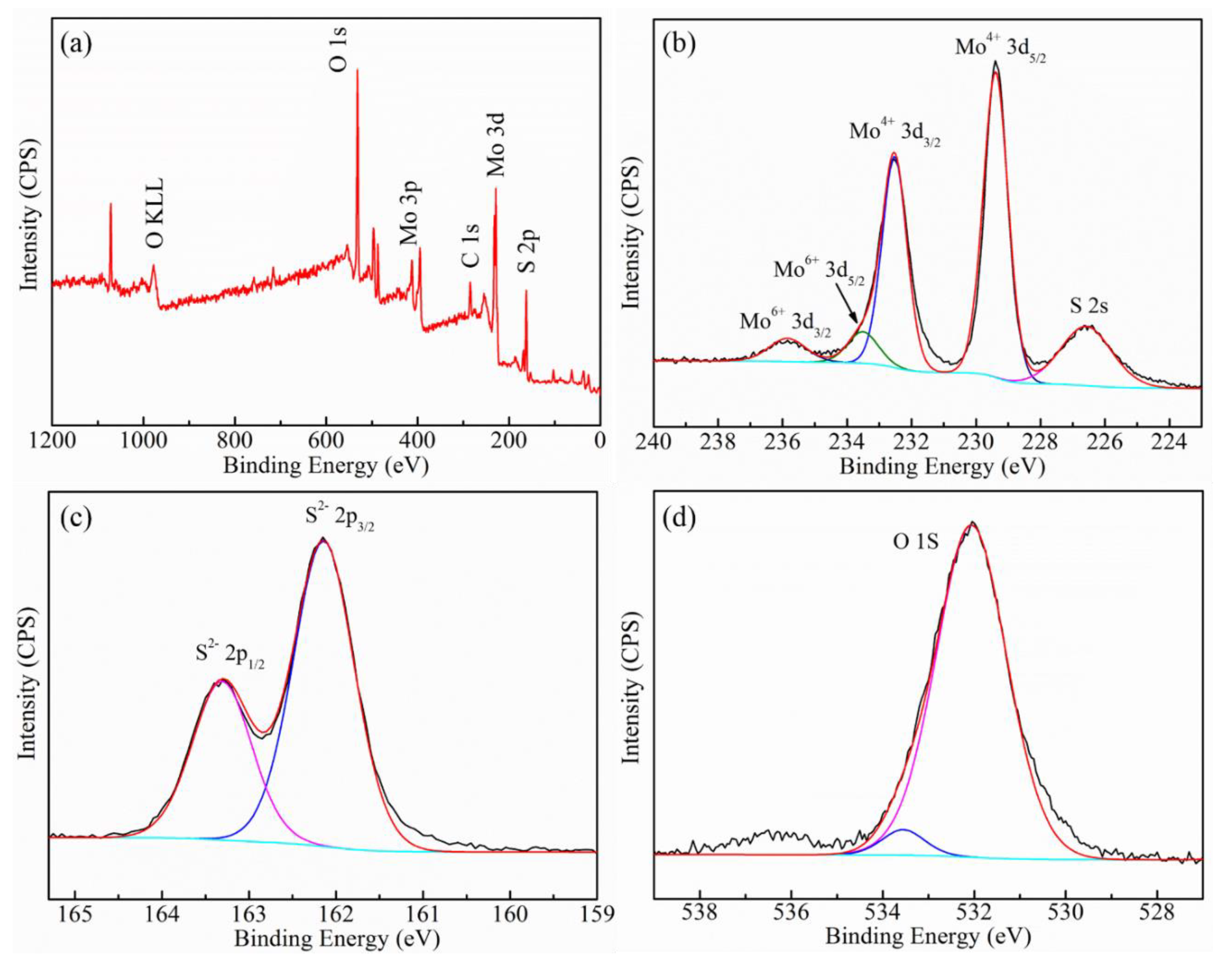
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of MoS2 Nanosheets
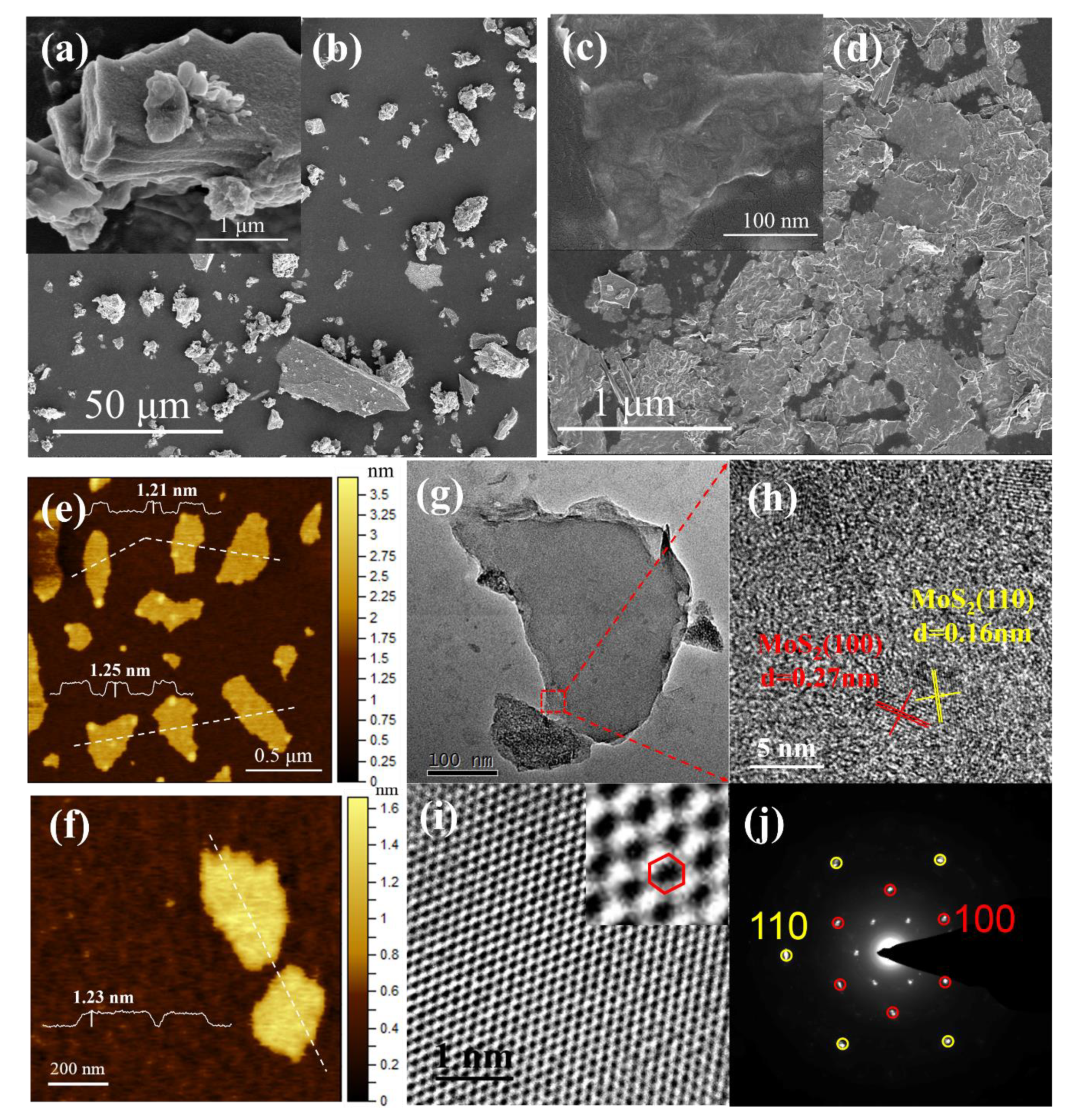
3.1.1. Microstructures and Morphology
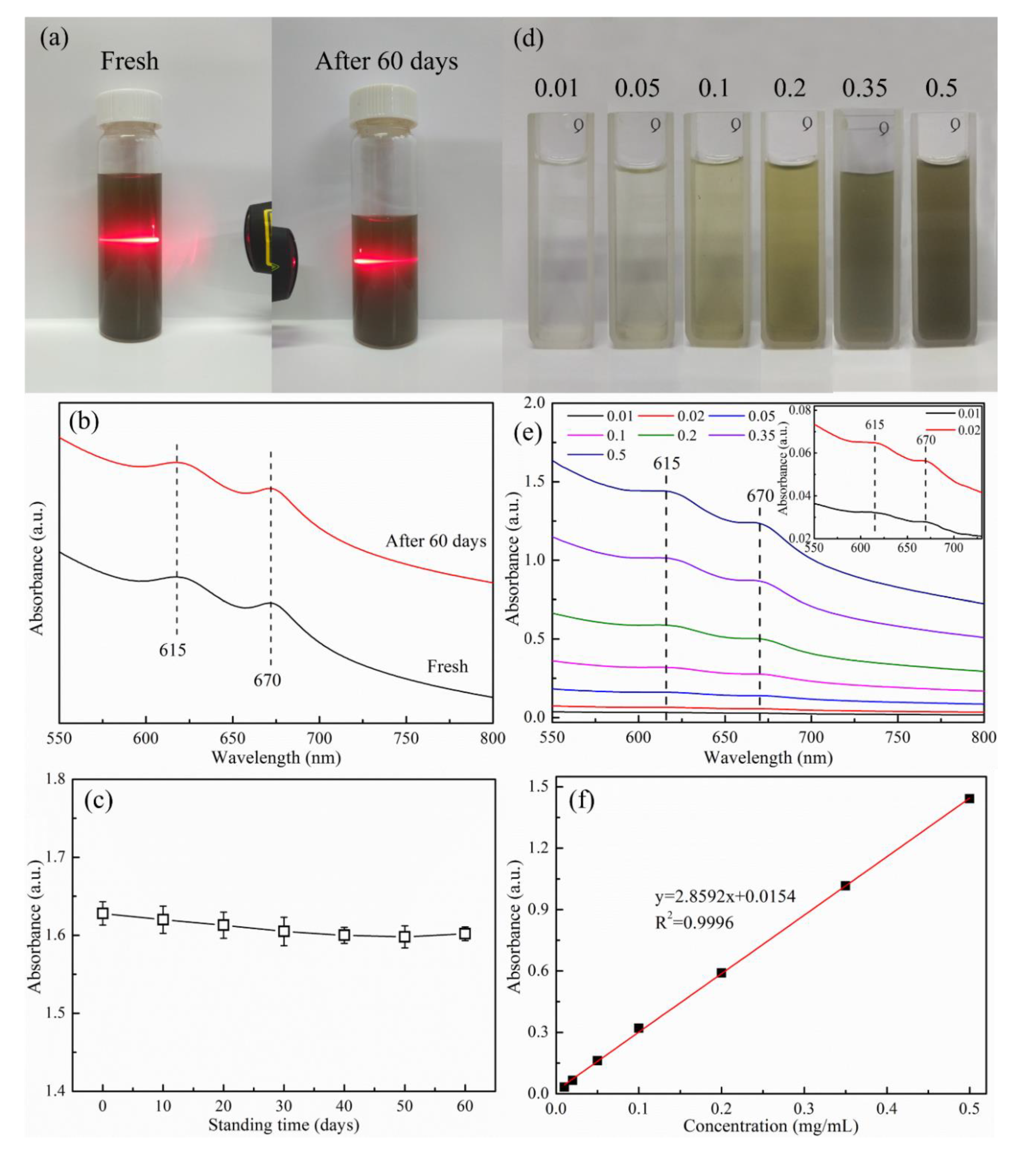
3.1.2. Optical Properties of MoS2 Nanosheets Dispersion
3.2. Adsorption Behavior of MoS2-NS Towards Dyes and Heavy Metals
3.2.1. Adsorption Isotherms and Kinetics
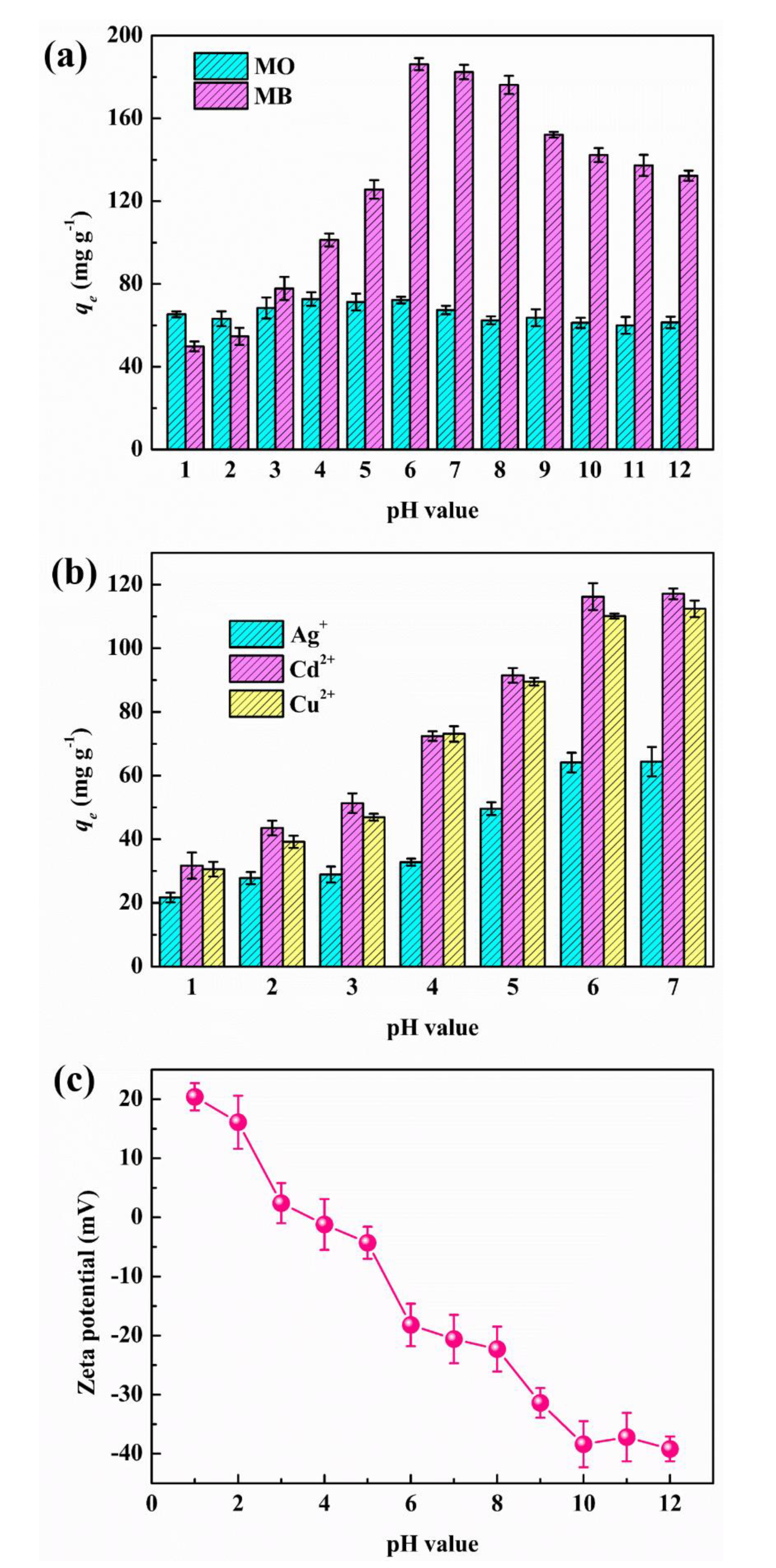
3.2.2. Adsorption Mechanism
Physical Hole-Filling Effects
Electrostatic Interactions
Ion Exchange
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kibsgaard, J.; Chen, Z.; Reinecke, B.N.; Jaramillo, T.F. Engineering the surface structure of MoS2 to preferentially expose active edge sites for electrocatalysis. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakes, L.; Carter, R.; Hanken, T.; Cohn, A.P.; Share, K.; Schmidt, B.; Pint, C.L. Interface strain in vertically stacked two-dimensional heterostructured carbon-MoS2 nanosheets controls electrochemical reactivity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, X.-Q.; Tian, F.-Y.; Hou, D.-F.; Hu, F.-C.; Li, D.-S. Equilibrium and kinetic studies on MB adsorption by ultrathin 2D MoS2 nanosheets. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 11631–11636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Xu, H.; Zhang, D.; Chen, S. Synthesis of bilayer MoS2 nanosheets by a facile hydrothermal method and their methyl orange adsorption capacity. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 55, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yan, H.; Brus, L.E.; Heinz, T.F.; Hone, J.; Ryu, S. Anomalous Lattice Vibrations of Single- and Few-Layer MoS2. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2695–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, J.; Matsuhashi, Y.; Iwasa, Y. Ambipolar MoS2 Thin Flake Transistors. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 1136–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.N.; Lotya, M.; O’Neill, A.; Bergin, S.D.; King, P.J.; Khan, U.; Young, K.; Gaucher, A.; De, S.; Smith, R.J.; et al. Two-Dimensional Nanosheets Produced by Liquid Exfoliation of Layered Materials. Science 2011, 331, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Neill, A.; Khan, U.; Coleman, J.N. Preparation of High Concentration Dispersions of Exfoliated MoS2 with Increased Flake Size. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 2414–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Chai, J.W.; Lü, X.; Wong, L.M.; Wong, T.I.; Pan, J.; Xiong, Q.; Chi, D.; Wang, S. Growth of wafer-scale MoS2 monolayer by magnetron sputtering. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2497–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motola, M.; Baudys, M.; Zazpe, R.; Krbal, M.; Michalicka, J.; Rodriguez-Pereira, J.; Pavlinak, D.; Prikryl, J.; Hromadko, L.; Sopha, H.I.; et al. 2D MoS2 nanosheets on 1D anodic TiO2 nanotube layers: An efficient co-catalyst for liquid and gas phase photocatalysis. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 23126–23131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; He, Y.; Wu, J.; Gao, C.; Keyshar, K.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Ye, M.; Vajtai, R.; Lou, J.; et al. Liquid Phase Exfoliation of Two-Dimensional Materials by Directly Probing and Matching Surface Tension Components. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 5449–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kwon, S.; Cho, D.-H.; Kang, B.; Kwon, H.; Kim, Y.; Park, S.O.; Jung, G.Y.; Shin, E.; Kim, W.-G.; et al. Direct exfoliation and dispersion of two-dimensional materials in pure water via temperature control. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Lin, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, C.; Yang, D.; Lu, H. Spontaneous exfoliation and tailoring of MoS2 in mixed solvents. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 15936–15939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.-G.; Mao, N.-N.; Wang, H.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, H.-L. A Mixed-Solvent Strategy for Efficient Exfoliation of Inorganic Graphene Analogues. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 10839–10842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardia, L.; Paredes, J.I.; Rozada, R.; Villar-Rodil, S.; Martinez-Alonso, A.; Tascón, J.D. Production of aqueous dispersions of inorganic graphene analogues by exfoliation and stabilization with non-ionic surfactants. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 14115–14127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.J.; King, P.J.; Lotya, M.; Wirtz, C.; Khan, U.; De, S.; O’Neill, A.; Duesberg, G.S.; Grunlan, J.C.; Moriarty, G.; et al. Large-Scale Exfoliation of Inorganic Layered Compounds in Aqueous Surfactant Solutions. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3944–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Dong, S.; Liu, Y.; Nai, C.T.; Shin, H.S.; Jeong, H.Y.; Liu, B.; Loh, K.P. High yield exfoliation of two-dimensional chalcogenides using sodium naphthalenide. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuc, W.; Gao, X.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Chao, Y.; Li, M.; Mahurin, S.M.; Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Dai, S. Controlled Gas Exfoliation of Boron Nitride into Few-Layered Nanosheets. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 10766–10770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Tian, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, R.; Qiao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Fu, H. Facile fabrication of high quality graphene from expandable graphite: Simultaneous exfoliation and reduction. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.B.; Lee, C.-S.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, G.D.; Kang, Z.H.; Luo, L.B.; Song, H.S.; Liu, Y.; He, Z.; Zhang, W.; et al. High-Quality Graphenes via a Facile Quenching Method for Field-Effect Transistors. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1374–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Thanh, D.; Pan, C.-C.; Chu, C.-W.; Wei, K.-H. Production of few-layer MoS2nanosheets through exfoliation of liquid N2–quenched bulk MoS2. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 15586–15589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Xing, B. Adsorption of Phenanthrene on Multilayer Graphene as Affected by Surfactant and Exfoliation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Huang, F.; Zhuang, Z.; Lin, Z. A study of the potential application of nano-Mg(OH)2 in adsorbing low concentrations of uranyl tricarbonate from water. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.-Q.; Chai, J.-X.; Jia, Y.-X.; Wang, L.-J.; Zhao, Z.-L.; Cao, M. Facile Preparation of Few-layer MoS2-NS by Liquid-Phase Ultrasonic Exfoliation. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Manufacturing Engineering and Intelligent Materials (ICMEIM 2017), Guangzhou, China, 25–26 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hai, X.; Chang, K.; Pang, H.; Li, M.; Li, P.; Liu, H.; Shi, L.; Ye, J. Engineering the Edges of MoS2 (WS2) Crystals for Direct Exfoliation into Monolayers in Polar Micromolecular Solvents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 14962–14969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Huang, G.; Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; Ye, J.; Li, H.; Chen, D.; Lee, J.Y. Cationic surfactant-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of few-layer molybdenum disulfide/graphene composites: Microstructure and electrochemical lithium storage. J. Power Sources 2014, 264, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yap, C.C.R.; Tay, B.K.; Edwin, T.H.T.; Olivier, A.; Baillargeat, D. From Bulk to Monolayer MoS2: Evolution of Raman Scattering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korn, T.; Heydrich, S.; Hirmer, M.; Schmutzler, J.; Schüller, C. Low-temperature photocarrier dynamics in monolayer MoS2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 102109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, B.; Matte, H.R.; Sood, A.K.; Ra, C.N.R. Layer-dependent resonant Raman scattering of a few layer MoS2. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2013, 44, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnall, A.; Liang, W.; Marseglia, E.; Welber, B. Raman studies of MoS2 at high pressure. Phys. B+C 1980, 99, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.S.; De, I.; Kim, J.; Byun, S.; Dykstra, C.; Yu, J.; Huang, J.; Dravid, V.P. Ligand Conjugation of Chemically Exfoliated MoS2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4584–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Xu, Z.; Wang, W.; Bai, X. Atomic Mechanism of Dynamic Electrochemical Lithiation Processes of MoS2 Nanosheets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6693–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcoxon, J.P.; Newcomer, P.P.; Samara, G.A. Synthesis and optical properties of MoS2 and isomorphous nanoclusters in the quantum confinement regime. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81, 7934–7944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; Cai, Y.; Low, M.; Teng, C.P.; Phang, I.Y.; Cheng, Y.; Duei, K.L.; Srinivasan, B.M.; et al. Protein Induces Layer-by-Layer Exfoliation of Transition Metal Dichalcogenides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6152–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, K.F.; Lee, C.; Hone, J.; Shan, J.; Heinz, T.F. Atomically Thin MoS2: A New Direct-Gap Semiconductor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, P.; Yin, N.; Li, P.; Cheng, W.; Huang, M. The adsorption and diffusion behavior of noble metal adatoms (Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag and Au) on a MoS2 monolayer: A first-principles study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 20713–20722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; Jia, F.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C.; Sun, K.; Yang, B.; Song, S. Controllable incorporation of oxygen in MoS2 for efficient adsorption of Hg2+ in aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zeng, S.; Liu, K.; Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Xu, P.; Lin, C.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, M. Removal of p-arsanilic acid by an amino-functionalized indium-based metal–organic framework: Adsorption behavior and synergetic mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 339, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yuan, H.; Hu, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhang, D. Synthesis of mesoporous C/MoS2 for adsorption of methyl orange and photo-catalytic sterilization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 504, 144445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Fu, K.; Sun, M.; Yin, K.; Wang, D.; Liu, X.; Crittenden, J.C. Phase-Mediated Heavy Metal Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions Using Two-Dimensional Layered MoS2. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 38789–38797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Jang, J. Heavy metal ion adsorption onto polypyrrole-impregnated porous carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 325, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xie, F.; Li, W.; Fahlman, B.D.; Chen, M.; Li, W. Preparation and adsorption capacity of porous MoS2 nanosheets. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 105222–105230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Tran, H.N.; Chao, H.-P.; Lin, C.-C. Activated Carbons Derived from Teak Sawdust-Hydrochars for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue, Copper, and Cadmium from Aqueous Solution. Water 2019, 11, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Deng, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.J.; Awasthi, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, R.; Zhou, B.; Du, J.; Zhang, Z. High-efficiency removal of Pb(II) and humate by a CeO2–MoS2 hybrid magnetic biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 273, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Chen, B.; Zhu, X.; Xing, B. Aggregation, Adsorption, and Morphological Transformation of Graphene Oxide in Aqueous Solutions Containing Different Metal Cations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11066–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Yang, R.; Wang, H. Synthesis of ZIF-8/Fly Ash Composite for Adsorption of Cu2+, Zn2+ and Ni2+ from Aqueous Solutions. Materials 2020, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


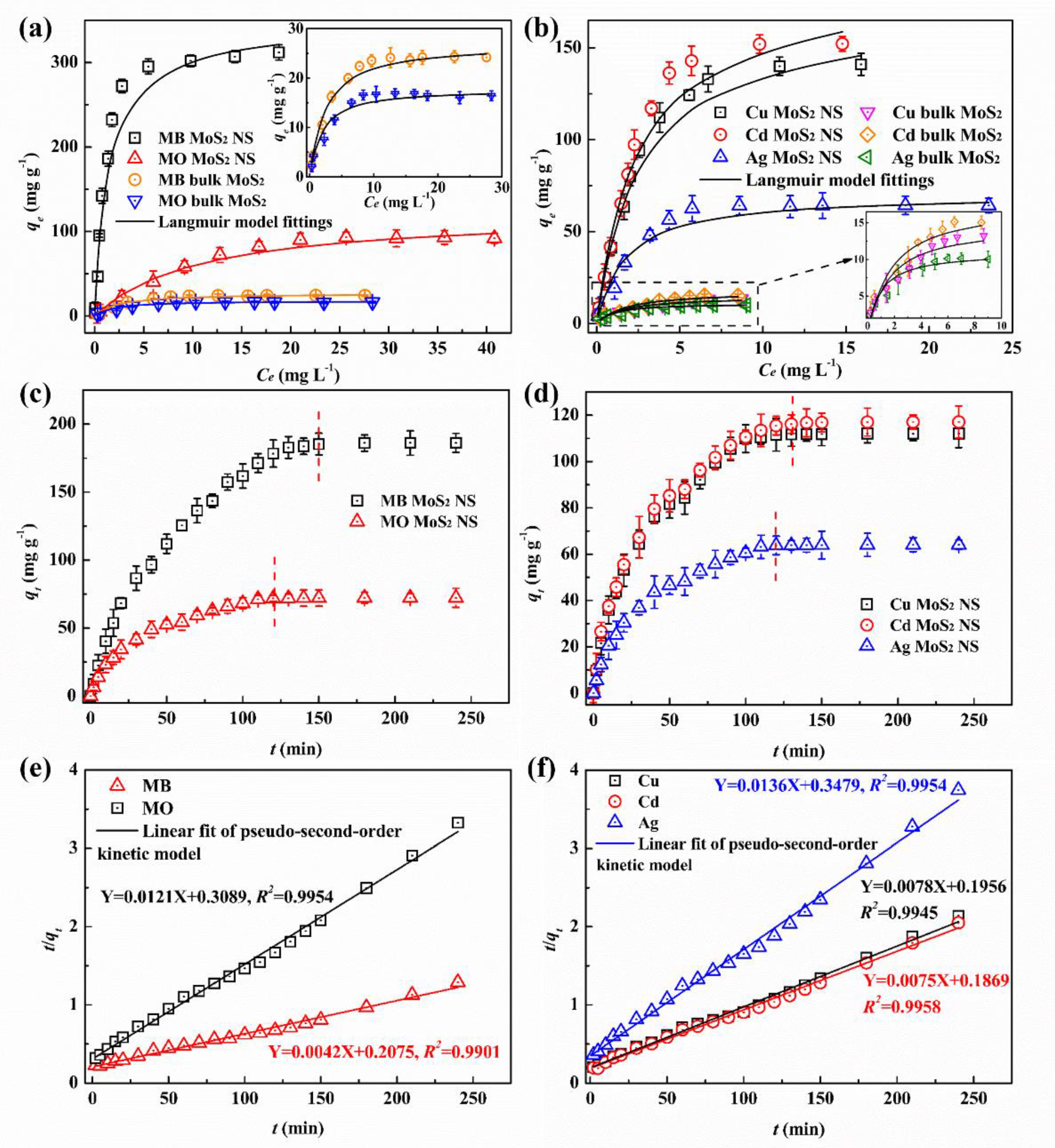
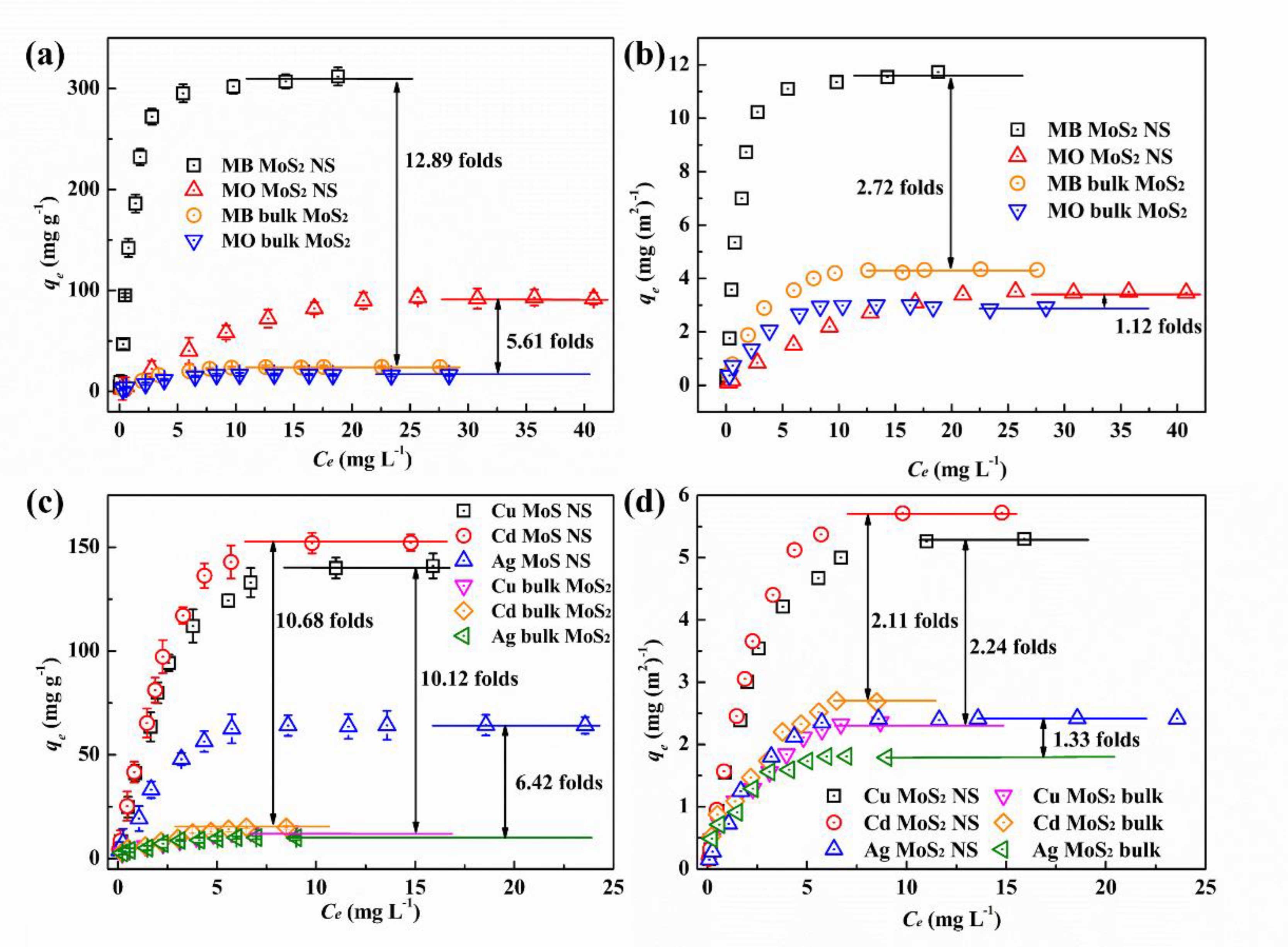
| Samples | Targets | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg g−1) | KL (L mg−1) | R2 | 1/n | Kf (L g−1) | R2 | ||
| MoS2 NS | MB | 344.8 | 0.725 | 0.994 | 0.648 | 92.796 | 0.875 |
| MO | 123.5 | 0.393 | 0.980 | 0.724 | 9.023 | 0.969 | |
| Bulk MoS2 | MB | 27.0 | 0.238 | 0.996 | 0.504 | 6.381 | 0.915 |
| MO | 17.8 | 0.187 | 0.992 | 0.449 | 4.988 | 0.904 | |
| MoS2 NS | Cd2+ | 185.2 | 0.606 | 0.985 | 0.708 | 40.496 | 0.943 |
| Cu2+ | 169.5 | 0.588 | 0.989 | 0.693 | 35.848 | 0.938 | |
| Ag+ | 70.4 | 0.339 | 0.993 | 0.533 | 18.326 | 0.914 | |
| Bulk MoS2 | Cd2+ | 18.7 | 0.297 | 0.952 | 0.463 | 6.069 | 0.979 |
| Cu2+ | 16.3 | 0.285 | 0.963 | 0.459 | 5.321 | 0.991 | |
| Ag+ | 11.7 | 0.134 | 0.987 | 0.389 | 4.913 | 0.968 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.; You, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Lv, Y. Fabrication of Ultrathin MoS2 Nanosheets and Application on Adsorption of Organic Pollutants and Heavy Metals. Processes 2020, 8, 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8050504
Huang S, You Z, Jiang Y, Zhang F, Liu K, Liu Y, Chen X, Lv Y. Fabrication of Ultrathin MoS2 Nanosheets and Application on Adsorption of Organic Pollutants and Heavy Metals. Processes. 2020; 8(5):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8050504
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Siyi, Ziyun You, Yanting Jiang, Fuxiang Zhang, Kaiyang Liu, Yifan Liu, Xiaochen Chen, and Yuancai Lv. 2020. "Fabrication of Ultrathin MoS2 Nanosheets and Application on Adsorption of Organic Pollutants and Heavy Metals" Processes 8, no. 5: 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8050504
APA StyleHuang, S., You, Z., Jiang, Y., Zhang, F., Liu, K., Liu, Y., Chen, X., & Lv, Y. (2020). Fabrication of Ultrathin MoS2 Nanosheets and Application on Adsorption of Organic Pollutants and Heavy Metals. Processes, 8(5), 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8050504






