Greening the Gas Grid—Evaluation of the Biomethane Injection Potential from Agricultural Residues in Austria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- The first stage is the “theoretical biogas potential” from agricultural residues. No restrictions are placed on land use or the amount of agricultural manure in this stage.
- The second stage, the “technical biogas potential” includes restrictions to consider technical limitations. Therefore, minimum amounts for catch crops (≥300 ha per municipality) and farm manure (≥12,000 tFM per municipality) are defined to take logistic limitations into account. Moreover, 300 ha of catch crops or 12,000 t of farm manure are necessary to meet the methane demand of a biogas plant with an electric capacity of 100 kW and 7200 full-load hours (200,000 m³CH4). Sugar beet leaves are harvested if sufficient catch crops and/or farm manure is available in a community. In addition, restrictions are placed on the use of straw as feedstock. Since a dry matter content of over 9% in the fermenter requires a special agitator technology [36] and the amount of water or recyclate that can be added is limited by the fermenter volume, the dry matter content of the feedstock mixture is limited to 30%. With a dry matter content of 30%, the necessary amount of water corresponds to the amount of feedstock to achieve a dry matter content of 15% in the fermenter. More water or recyclate as well as biological degradation reduce the dry matter content in the fermenter to below 15%. The amount of straw that can be added, which has a dry matter content of around 86%, is therefore corrected for technical reasons.
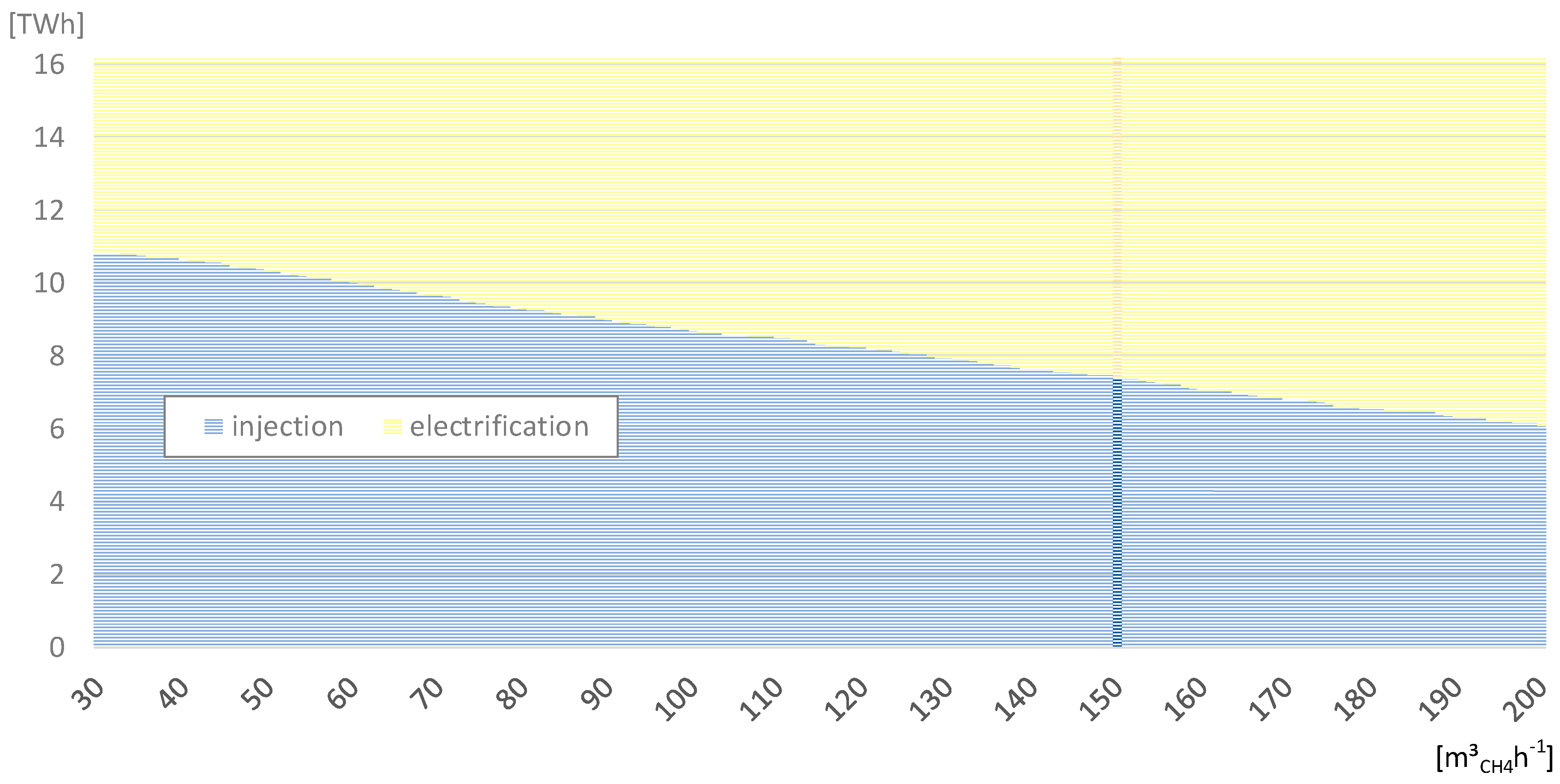
- In the third stage, the biomethane injection potential was calculated. In addition to the limitations regarding the technical potential, assumptions for the derivation of the biomethane potential are included: in communities where a gas supply is available, an annual minimum quantity of 1,200,000 m³CH4 is required to operate a biomethane injection plant with 150 m³CH4 h−1 (8000 full load hours), which is a common feed-in capacity in Austria [37]. In municipalities where this requirement is not met, or that do not have a gas supply, the resulting gas volume is processed in biogas plants for combined heat and power generation.
- Biomethane injection plant: 150 to 300 m³CH4h−1
- Electricity generation plant: up to 150 kW electric
- Electricity generation plant: 150 to 400 kW electric
- Electricity generation plant: 400 to 750 kW electric
- Electricity generation plant: 750 to 1300 kW electric
3. Results
3.1. Theoretical and Technical Biogas Potential
3.2. Biomethane Injection Potential
3.3. Average Haul Distance
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change. The IPCC Response Strategies; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Genf, Switzerland, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Global Warming of 1.5 °C. Summary for Policymakers; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Genf, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- UN. Paris Agreement 2015. Available online: https://unfccc.int/sites/default/files/english_paris_agreement.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- COM 640. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the European Council, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions: The European Green Deal; COM: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- ÖVP/Grüne Regierungsprogramm für die XXVII. Gesetzgebungsperiode 2020. Available online: https://www.dieneuevolkspartei.at/Download/Regierungsprogramm_2020.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Bach, C.; Bütler, T.; Huber, M. Abgasemissionen von Gasfahrzeugen. Aqua Gas 2017, 7/8, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Börjesson, M.; Ahlgren, E.O. Cost-effective biogas utilisation–A modelling assessment of gas infrastructural options in a regional energy system. Energy 2012, 48, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm-Nielsen, J.B.; Al Seadi, T.; Oleskowicz-Popiel, P. The future of anaerobic digestion and biogas utilization. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5478–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrizio, P.; Leduc, S.; Chinese, D.; Dotzauer, E.; Kraxner, F. Biomethane as transport fuel—A comparison with other biogas utilization pathways in northern Italy. Appl. Energy 2015, 157, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasi, S.; Timonen, K.; Joensuu, K.; Regina, K.; Virkajärvi, P.; Heusala, H.; Tampio, E.; Luostarinen, S. Sustainability of Vehicle Fuel Biomethane Produced from Grass Silage in Finland. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakawati, R.; Smyth, B.M.; McCullough, G.; De Rosa, F.; Rooney, D. What is the most energy efficient route for biogas utilization: Heat, electricity or transport? Appl. Energy 2017, 206, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caposciutti, G.; Baccioli, A.; Ferrari, L.; Desideri, U. Biogas from Anaerobic Digestion: Power Generation or Biomethane Production? Energies 2020, 13, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German Biogas Assoziation. Branchenzahlen 2017 und Prognose der Branchenentwicklung 2018; In-House Publication: Freising, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- German Biogas Assoziation. Branchenzahlen—Prognose 2013/2014; In-House Publication: Freising, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- e-control. Ökostrombericht 2018; e-control: Vienna, Austria, 2018; p. 99. [Google Scholar]
- Statistical Report 2016; European Biogas Association: Brussels, Belgium, 2016.
- Stürmer, B. Biogas—Part of Austria’s future energy supply or political experiment? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EBA Statistical Report. European Overview 2019; European Biogas Association: Brussels, Belgium, 2020; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- OeMAG. Ökostrom-Einspeisemengen und -Vergütungen in Österreich. 1.-4. Quartal 2019. Available online: https://www.oem-ag.at/fileadmin/user_upload/Dokumente/statistik/einspeisemengen/2019_Q4_BillingStat.jpg (accessed on 21 May 2020).
- AGCS Biomethanregister Austria. Statistik Biomethan 2019. Available online: https://www.biomethanregister.at/de/download/statistik/2019 (accessed on 21 May 2020).
- Stürmer, B. Feedstock change at biogas plants–Impact on production costs. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 98, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dißauer, C.; Rehling, B.; Strasser, C. Machbarkeitsuntersuchung Methan aus Biomasse. 2019. Available online: https://www.initiative-gas.at/fileadmin/content/Studien/BioEnergy2020.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Lindorfer, J.; Fazeni, K.; Tichler, R.; Steinmüller, H. Erhöhung des Einsatzes von erneuerbarem Methan im Wärmebereich. 2017, p. 109. Available online: https://www.initiative-gas.at/fileadmin/content/user_upload/Bericht_Modul1_2_Erneuerbares_Methan_EIJKU_Ma__rz2017.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Szerencsits, M.; Neubauer, E.; Friedl, R.; Dersch, G.; Erhart, E.; Hartl, W.; Höckner, J.; Legath, S.; Mottl, K.; Siegl, T.; et al. Synergetische Biogaserzeugung aus Zwischenfrüchten und nachhaltigen Fruchtfolgesystemen. 2014. Available online: https://www.energieforschung.at/assets/project/final-report/Syn-EnergyII-829732-endbericht-publizierbar.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Council regulation (EEC) No 3508/92 of 27 November 1992 establishing an integrated administration and control system for certain Community aid schemes. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?qid=1590306548309&uri=CELEX:31992R3508 (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- AGGM. Areas Currently Supplied with Gas. Personal Communication, 12 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Statistik Austria. Regionale Gliederungen-Gemeinden. Available online: https://www.statistik.at/web_de/klassifikationen/regionale_gliederungen/gemeinden/index.html (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Grüner Bericht 2019; Federal Ministry of Sustainability and Tourism: Vienna, Austria, 2019; p. 299.
- Amon, T.; Amon, B.; Kryvoruchko, V.; Machmüller, A.; Hopfner-Sixt, K.; Bodiroza, V.; Hrbek, R.; Friedel, J.; Pötsch, E.; Wagentristl, H.; et al. Methane production through anaerobic digestion of various energy crops grown in sustainable crop rotations. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 3204–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KTBL. Wirtschaftlichkeitsrechner Biogas. Available online: https://daten.ktbl.de/biogas/startseite.do?zustandReq=3&selectedAction=showMona#start (accessed on 11 May 2020).
- Méndez-Hernández, J.E.; Loera, O.; Méndez-Hernández, E.M.; Herrera, E.; Soto-Cruz, N.Ó. Coupling energy-production processes: The use of residues from bioethanol production to improve the anaerobic digestion of corn stover. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 128, 105322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersson, A.; Thomsen, M.H.; Hauggaardnielsen, H.; Thomsen, A.-B. Potential bioethanol and biogas production using lignocellulosic biomass from winter rye, oilseed rape and faba bean. Biomass Bioenergy 2007, 31, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richtlinien für die sachgerechte Düngung; Federal Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, Environment and Water Management: Vienna, Austria, 2006.
- LfL. Biogasausbeuten Mobil & Interaktiv: Einzelabfrage-Vergleich–Substitutionswert. Available online: https://www.lfl.bayern.de/appl/biogas/ausbeute/ (accessed on 11 May 2020).
- AMA. Anhänge zur Sonderrichtlinie für das Österreichische Programm zur Förderung einer Umweltgerechten, Extensiven und den Natürlichen Lebensraum Schützenden Landwirtschaft. Anhang C: GVE-Schlüssel 2018. Available online: https://www.ama.at/getattachment/d8f82210-c511-4b86-a7c8-0bf9fbcfd38e/SRL_OEPUL_2015_20180801_Anhang_C.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2020).
- Kamarád, L.; Pohn, S.; Bochmann, G.; Harasek, M. Determination of mixing quality in biogas plant digesters using tracer tests and computational fluid dynamics. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2013, 61, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stürmer, B.; Novakovits, P.; Luidolt, A.; Zweiler, R. Potential of renewable methane by anaerobic digestion from existing plant stock—An economic reflection of an Austrian region. Renew. Energy 2019, 130, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GSNE-VO 2013. Verordnung der Regulierungskommission der E-Control, mit der die Entgelte für die Systemnutzung in der Gaswirtschaft bestimmt werden (Gas-Systemnutzungsentgelte-Verordnung 2013. Volume BGBl. II Nr. 309/2012, p. 24. Available online: https://news.wko.at/news/oesterreich/GSNE-VO-Novelle-2016_Begutachtung.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2020).
- Overend, R.P. The average haul distance and transportation work factors for biomass delivered to a central plant. Biomass 1982, 1982, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zethner, G.; Süßenbacher, E. Vergärung von Wirtschaftsdüngern in Biogasanlagen. Evaluierung hinsichtlich Klimaschutzrelevanz; Umweltbundesamt: Wien, Austria, 2012; ISBN 978-3-99004-180-2. [Google Scholar]
- Statistik Austria. Energiebilanzen. 2018. Available online: www.stat.at/web_de/statistiken/energie_umwelt_innovation_mobilitaet/energie_und_umwelt/energie/energiebilanzen/index.html (accessed on 11 May 2020).
- Walla, C.; Schneeberger, W. The optimal size for biogas plants. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stürmer, B.; Schmid, E.; Eder, M.W. Impacts of biogas plant performance factors on total substrate costs. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 1552–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiz, R.; Ammenberg, J.; Björn, A.; Guo, Y.; Karlsson, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shizue Moriga Masuda, L.; Enrich-Prast, A.; Rohracher, H.; et al. Biogas Potential for Improved Sustainability in Guangzhou, China—A Study Focusing on Food Waste on Xiaoguwei Island. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidaki, I.; Treu, L.; Tsapekos, P.; Luo, G.; Campanaro, S.; Wenzel, H.; Kougias, P.G. Biogas upgrading and utilization: Current status and perspectives. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 452–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah Khan, I.; Hafiz Dzarfan Othman, M.; Hashim, H.; Matsuura, T.; Ismail, A.F.; Rezaei-DashtArzhandi, M.; Wan Azelee, I. Biogas as a renewable energy fuel—A review of biogas upgrading, utilisation and storage. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 150, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandfort, V.; Trabold, B.; Abdolvand, A.; Bolwien, C.; Russell, P.; Wöllenstein, J.; Palzer, S. Monitoring the Wobbe Index of Natural Gas Using Fiber-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Sensors 2017, 17, 2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, N.; Kvist, T. Alternative of Biogas Injection into the Danish Gas Grid System—A Study from Demand Perspective. ChemEngineering 2018, 2, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, W. Macro-economic impacts of biogas production in Austria. Biogas J. 2016, 9, 26–29. [Google Scholar]




| Yield [tDM ha−1] | Specific Methane Yield [m³CH4 tDM−1] | |
|---|---|---|
| Cereal straw | 4.2 | 174 |
| Maize stover | 5.0 | 308 |
| Rapeseed straw | 2.8 | 188 |
| Beet leaves | 3.6 | 275 |
| Catch crops | 2.6 | 280 |
| Mean Value [tFM per LU *] | Standard Deviation [tFM per LU] | Specific Methane Yield [m³CH4 tDM−1] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cattle | 18.5 | 1.53 | 167 |
| Pigs | 5.5 | 1.03 | 186 |
| Poultry | 7.4 | 1.31 | 225 |
| Sheep and Goats | 6.7 | 0.81 | 330 |
| Other livestock | 6.3 | 3.77 | 125 |
| Theoretical Biogas Potential | Technical Biogas Potential | Dißauer et al. [22] | Lindorfer et al. [23] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 106 tDM | TWhCH4 | 106 tDM | TWhCH4 | 106 tDM | 106 tDM | |
| Catch crops | 1.9 | 6.1 | 1.7 | 5.4 | -- | -- |
| Straw | 3.5 | 8.4 | 2.2 | 5.3 | 4.0 | 1.7 |
| Beet leaves | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.25 | 0.1 |
| Farm manure | 3.1 | 6.2 | 2.6 | 5.1 | 8.5 | 3.9 |
| Sum | 8.7 | 21.0 | 6.6 | 16.2 | 12.75 | 6.1 |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stürmer, B. Greening the Gas Grid—Evaluation of the Biomethane Injection Potential from Agricultural Residues in Austria. Processes 2020, 8, 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8050630
Stürmer B. Greening the Gas Grid—Evaluation of the Biomethane Injection Potential from Agricultural Residues in Austria. Processes. 2020; 8(5):630. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8050630
Chicago/Turabian StyleStürmer, Bernhard. 2020. "Greening the Gas Grid—Evaluation of the Biomethane Injection Potential from Agricultural Residues in Austria" Processes 8, no. 5: 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8050630
APA StyleStürmer, B. (2020). Greening the Gas Grid—Evaluation of the Biomethane Injection Potential from Agricultural Residues in Austria. Processes, 8(5), 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8050630




