Reckoning the Dearth of Bioinformatics in the Arena of Diabetic Nephropathy (DN)—Need to Improvise
Abstract
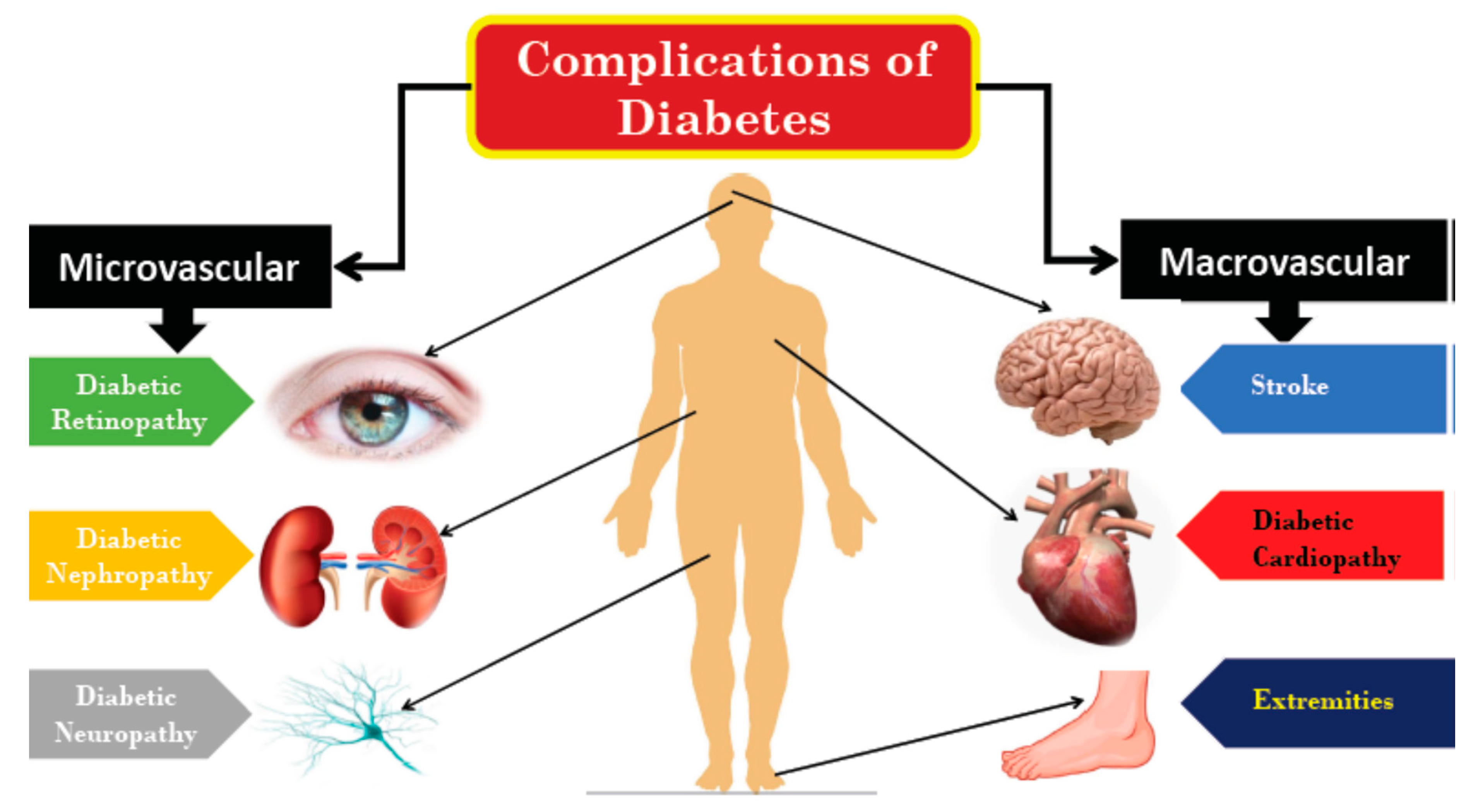
:1. Introduction
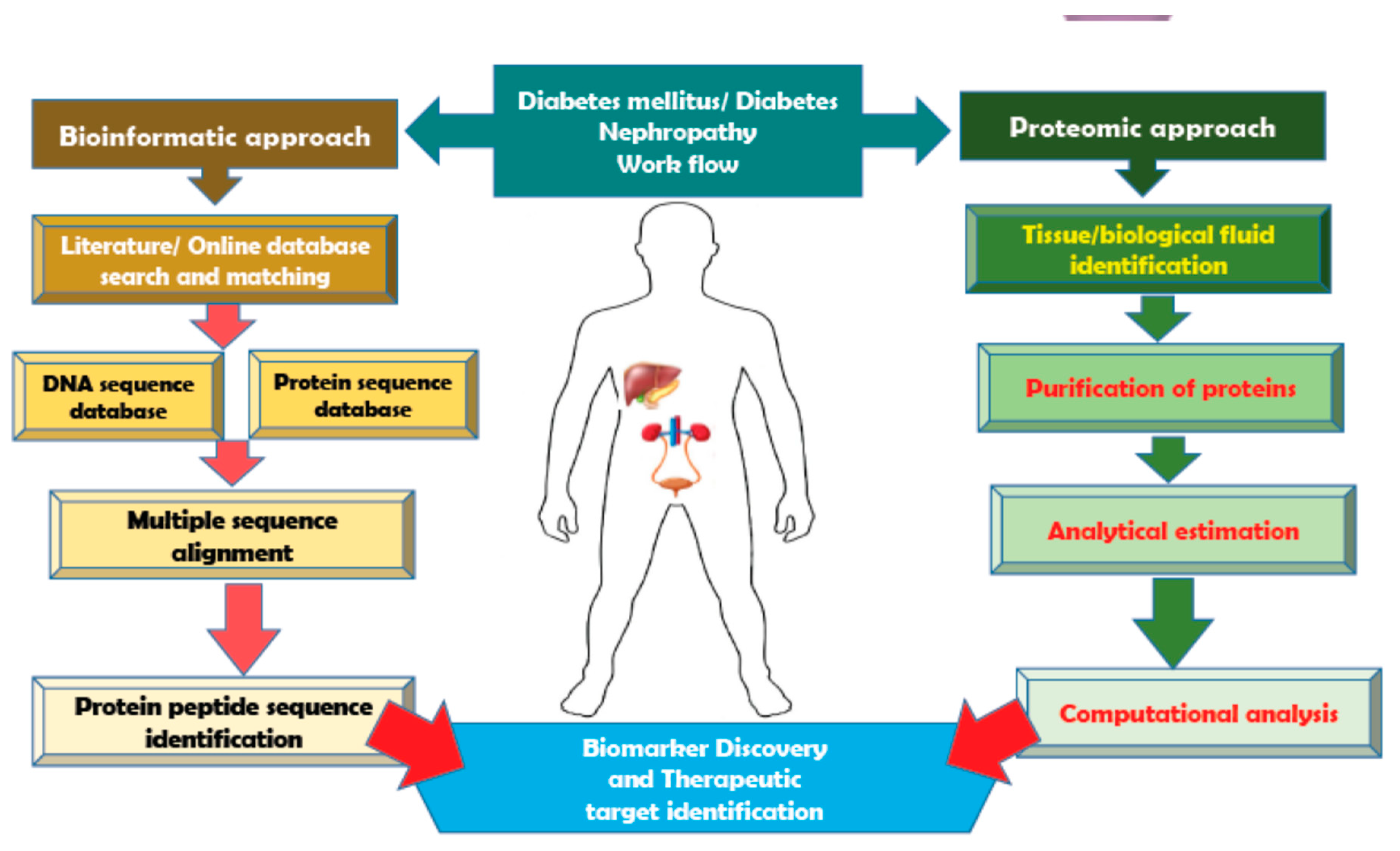
2. A Snapshot of Bioinformatic Tools Used for Diabetes Mellitus
3. Proteomic Advances Made in the Area of Diabetic Nephropathy
4. Future Perspective: Bioinformatics Applications into DN
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gross, J.L.; de Azevedo, M.J.; Silveiro, S.P.; Canani, L.H.; Caramori, M.L.; Zelmanovitz, T. Diabetic nephropathy: Diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Felehgari, V.; Rahimi, Z.; Mozafari, H.; Vaisi-Raygani, A. ACE gene polymorphism and serum ACE activity in Iranians type II diabetic patients with macroalbuminuria. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 346, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molitch, M.E.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Franz, M.J.; Keane, W.F.; Mogensen, C.E.; Parving, H.H.; Steffes, M.W.; American Diabetes Association. Nephropathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, S79–S83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van, J.A.; Scholey, J.W.; Konvalinka, A. Insights into Diabetic Kidney Disease Using Urinary Proteomics and Bioinformatics. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Gaur, V.; Khurana, S.; Bose, S.; Kiran, M.; Kiran, M.; Sharawat, S.K. Proteomics Tools—An Update. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 2, 1358. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Ameur, R.; Molina, L.; Bolvin, C.; Kifagi, C.; Jarraya, F.; Ayadi, H.; Molina, F.; Granier, C. Proteomic approaches for discovering biomarkers of diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 2866–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jungblut, P.; Wittmann-Liebold, B. Protein analysis on a genomic scale. J. Biotechnol. 1995, 41, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, R.N.; Sangoi, M.B.; De Carvalho, J.A.M.; Tatsch, E.; Bochi, G.V. Diabetic nephropathy: Traditional to proteomic markers. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 421, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campion, C.G.; Sanchez-Ferras, O.; Batchu, S.N. Potential Role of Serum and Urinary Biomarkers in Diagnosis and Prognosis of Diabetic Nephropathy. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2017, 4, 2054358117705371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongboonkerd, V. Study of Diabetic Nephropathy in the Proteomic Era. Contrib. Nephrol. 2011, 170, 172–183. [Google Scholar]
- Cutillas, P.R.; Biber, J.; Marks, J.; Jacob, R.; Stieger, B.; Cramer, R.; Waterfield, M.; Burlingame, A.L.; Unwin, R.J. Proteomic analysis of plasma membrane vesicles isolated from the rat renal cortex. Proteomics 2005, 5, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magni, F.; Sarto, C.; Valsecchi, C.; Casellato, S.; Bogetto, S.F.; Bosari, S.; Di Fonzo, A.; Perego, R.A.; Corizzato, M.; Doro, G.; et al. Expanding the proteome two-dimensional gel electrophoresis reference map of human renal cortex by peptide mass fingerprinting. Proteomics 2005, 5, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, Y.; Miyazaki, K.; Kamiie, J.; Sato, M.; Okuizumi, S.; Kenmochi, A.; Kamijo, K.; Nabetani, T.; Tsugita, A.; Xu, B.; et al. Two-dimensional electrophoretic profiling of normal human kidney glomerulus proteome and construction of an extensible markup language (XML)-based database. Proteomics 2005, 5, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barile, M.; Pisitkun, T.; Yu, M.-J.; Chou, C.-L.; Verbalis, M.J.; Shen, R.-F.; Knepper, M.A. Large-Scale Protein Identification in Intracellular Aquaporin-2 Vesicles from Renal Inner Medullary Collecting Duct. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2005, 4, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dihazi, H.; Asif, A.R.; Agarwal, N.K.; Doncheva, Y.; Müller, G.A. Proteomic Analysis of Cellular Response to Osmotic Stress in Thick Ascending Limb of Henle’s Loop (TALH) Cells. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2005, 4, 1445–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.-J.; Cho, E.-H.; Yoo, J.-H.; Kim, P.-K.; Shin, J.-S.; Kim, M.-R.; Kim, C.W. Proteome Analysis of Serum from Type 2 Diabetics with Nephropathy. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zürbig, P.; Jerums, G.; Hovind, P.; MacIsaac, R.J.; Mischak, H.; Nielsen, S.E.; Panagiotopoulos, S.; Persson, F.; Rossing, P. Urinary Proteomics for Early Diagnosis in Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes 2012, 61, 3304–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossing, K.; Mischak, H.; Dakna, M.; Zürbig, P.; Novak, J.; Julian, B.A.; Good, D.M.; Coon, J.J.; Tarnow, L.; Rossing, P.; et al. Urinary proteomics in diabetes and CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.V.; Lu, X.; Standley, M.; Pattee, P.; Neelima, G.; Girisesh, G.; Dakshinamurthy, K.; Roberts, J.C.T.; Nagalla, S.R. Proteomic Identification of Urinary Biomarkers of Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papale, M.; Di Paolo, S.; Magistroni, R.; Lamacchia, O.; Di Palma, A.M.; De Mattia, A.; Rocchetti, M.T.; Furci, L.; Pasquali, S.; De Cosmo, S.; et al. Urine Proteome Analysis May Allow Noninvasive Differential Diagnosis of Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2409–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roscioni, S.S.; de Zeeuw, D.; Hellemons, M.E.; Mischak, H.; Zürbig, P.; Bakker, S.J.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Reinhard, H.; Persson, F.; Lajer, M.; et al. A urinary peptide biomarker set predicts worsening of albuminuria in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2012, 56, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Overgaard, A.J.; Hansen, H.G.; Lajer, M.; Pedersen, L.; Tarnow, L.; Rossing, P.; McGuire, J.N.; Pociot, F. Plasma proteome analysis of patients with type 1 diabetes with diabetic nephropathy. Proteome Sci. 2010, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fliser, D.; Novak, J.; Thongboonkerd, V.; Argilés, A.; Jankowski, V.; Girolami, M.A.; Jankowski, J.; Mischak, H. Advances in Urinary Proteome Analysis and Biomarker Discovery. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 1057–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varghese, S.A.; Powell, T.B.; Budisavljevic, M.N.; Oates, J.C.; Raymond, J.R.; Almeida, J.S.; Arthur, J. Urine biomarkers predict the cause of glomerular disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoemaker, D.D.; Linsley, P.S. Recent developments in DNA microarrays. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlai, R. Phenomics: Fiction or the future? Trends Neurosci. 2002, 25, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyers, M.; Mann, M. From genomics to proteomics. Nature 2003, 422, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedela, S.; Rao, A.A.; Medicherla, N.R. Identification of Biomarkers for Type 2 Diabetes and Its Complications: A Bioinformatic Approach. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. IJBS 2007, 3, 229–236. [Google Scholar]
- Tamimi, N.A.; Ellis, P. Drug Development: From Concept to Marketing! Nephron Clin. Pract. 2009, 113, c125–c131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profile: Pharmaceutical Research Industry. PhRMA Website. 2013. Available online: http://www.phrma.org/sites/default/files/pdf/PhRMA%20Profile%202013.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2014).
- Herper, M. The Cost of Creating a New Drug Now $5 Billion, Pushing Big Pharma to Change. Forbes Website. Available online: http://www.forbes.com/sites/matthewherper/2013/08/11/how-the-staggering-cost-of-inventing-new-drugs-is-shaping-thefuture-of-medicine/ (accessed on 6 March 2014).
- Katara, P. Role of bioinformatics and pharmacogenomics in drug discovery and development process. Netw. Model. Anal. Health Inform. Bioinform. 2013, 2, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Expert Committee on the, D.; Classification of Diabetes, M. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2002, 26, S5–S20. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO/CONRAD Technical Consultation on Nonoxynol-9, World Health Organization, Geneva, 9–10 October 2001: Summary Report. Reprod. Health Matters 2002, 10, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabetes: The Cost of Diabetes. Retrieved. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs236/en/ (accessed on 16 January 2005).
- Spengler, S.J. Techview: Computers and biology. Bioinformatics in the information age. Science 2000, 287, 1221–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thippakorn, C.; Schaduangrat, N.; Nantasenamat, C. Proteomic and bioinformatic discovery of biomarkers for diabetic nephropathy. EXCLI J. 2018, 17, 312–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Csordas, A.; Bai, J.; Bernal-Llinares, M.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Inuganti, A.; Griss, J.; Mayer, G.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: Improving support for quantification data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D442–D450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The Effect of Intensive Treatment of Diabetes on the Development and Progression of Long-term Complications in Insulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 14, 286–287. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Huang, H.; Wu, C.H. Protein Bioinformatics Databases and Resources. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1558, 3–39. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, D.A.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 42, D32–D37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brosch, M.; Yu, L.; Hubbard, T.; Choudhary, J. Accurate and Sensitive Peptide Identification with Mascot Percolator. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 3176–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vázquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeats, C.; Maibaum, M.; Marsden, R.; Dibley, M.; Lee, D.; Addou, S.; Orengo, C.A. Gene3D: Modelling protein structure, function and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D281–D284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, J.; Jupp, S.; Moulos, P.; Fernandez, M.; Buffin-Meyer, B.; Casemayou, A.; Chaaya, R.; Charonis, A.; Bascands, J.L.; Stevens, R.; et al. The KUPKB: A novel Web application to access multiomics data on kidney disease. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 2145–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attwood, T.K. PRINTS and its automatic supplement, prePRINTS. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, M.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Sun, Y.; Shao, C.; Li, M.; Sun, W.; Gao, Y. A comprehensive analysis and annotation of human normal urinary proteome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaraman, M.M.; Al-Yousif, N.S.H.; Singh Mann, A.; Dolinsky, V.W.; Rabbani, R.; Zarychanski, R.; Abou-Setta, A.M. Resveratrol for adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 1, CD011919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khetan, S.; Kursawe, R.; Youn, A.; Lawlor, N.; Jillette, A.; Marquez, E.J.; Ucar, D.; Stitzel, M.L. Type 2 Diabetes–Associated Genetic Variants Regulate Chromatin Accessibility in Human Islets. Diabetes 2018, 67, 2466–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barale, M.S.; Shirke, D.T. Cascaded Modeling for PIMA Indian Diabetes Data. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2016, 139, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whetzel, P.L.; Grethe, J.S.; Banks, D.E.; Martone, M.E. The NIDDK Information Network: A Community Portal for Finding Data, Materials, and Tools for Researchers Studying Diabetes, Digestive, and Kidney Diseases. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nesvizhskii, A.I.; Keller, A.; Kolker, E.; Aebersold, R. A Statistical Model for Identifying Proteins by Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 4646–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogland, C.; Mostaguir, K.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Hochstrasser, D.F.; Appel, R.D. SWISS-2DPAGE, ten years later. Proteomics 2004, 4, 2352–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, S.K.; Berman, H.M.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.; Chen, L.; Di Costanzo, L.; Christie, C.; Duarte, J.M.; Dutta, S.; Feng, Z.; et al. Protein Data Bank: The single global archive for 3D macromolecular structure data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D520–D528. [Google Scholar]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Wyder, S.; Forslund, K.; Heller, D.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Santos, A.; Tsafou, K.P.; et al. STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 43, D447–D452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.; Pethica, R.; Zhou, Y.; Talbot, C.; Vogel, C.; Madera, M.; Chothia, C.; Gough, J. SUPERFAMILY--sophisticated comparative genomics, data mining, visualization and phylogeny. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D380–D386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Thiessen, P.A.; Bolton, E.E.; Chen, J.; Fu, G.; Gindulyte, A.; Han, L.; He, J.; He, S.; Shoemaker, B.A.; et al. PubChem Substance and Compound databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 44, D1202–D1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnovsky, A.; Weymouth, T.; Hull, T.; Tarcea, V.G.; Scardoni, G.; Laudanna, C.; Sartor, M.A.; Stringer, K.A.; Jagadish, H.V.; Burant, C.; et al. Metscape 2 bioinformatics tool for the analysis and visualization of metabolomics and gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duren, W.; Weymouth, T.; Hull, T.; Omenn, G.S.; Athey, B.; Burant, C.; Karnovsky, A. MetDisease—Connecting metabolites to diseases via literature. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2239–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D457–D462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, P.D.; Campbell, M.J.; Kejariwal, A.; Mi, H.; Karlak, B.; Daverman, R.; Diemer, K.; Muruganujan, A.; Narechania, A. PANTHER: A Library of Protein Families and Subfamilies Indexed by Function. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2129–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Vasaikar, S.V.; Shi, Z.; Greer, M.; Zhang, B. WebGestalt 2017: A more comprehensive, powerful, flexible and interactive gene set enrichment analysis toolkit. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W130–W137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smigielski, E.M.; Sirotkin, K.; Ward, M.; Sherry, S.T. dbSNP: A database of single nucleotide polymorphisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Habib, M.; Xia, J. Xeno-miRNet: A comprehensive database and analytics platform to explore xeno-miRNAs and their potential targets. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Mamidipalli, S.; Huan, T. HAPPI: An online database of comprehensive human annotated and predicted protein interactions. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, S1–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karolchik, D.; Hinrichs, A.S.; Kent, W.J.; Speir, M.L.; Zweig, A.S.; Rosenbloom, K.R.; Raney, B.J.; Paten, B.; Nejad, P.; Lee, B.T.; et al. The UCSC Genome Browser. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2012, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Aguilar, R.; Benmezroua, Y.; Vaillant, E.; Balkau, B.; Marre, M.; Charpentier, G.; Sladek, R.; Froguel, P.; Neve, B. Analysis of KLF transcription factor family gene variants in type 2 diabetes. BMC Med Genet. 2007, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashurst, J.L.; Chen, C.K.; Gilbert, J.G.; Jekosch, K.; Keenan, S.; Meidl, P.; Searle, S.M.; Stalker, J.; Storey, R.; Trevanion, S.; et al. The Vertebrate Genome Annotation (Vega) database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D459–D465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivula, R.W.; Heggie, A.; Barnett, A.; Cederberg, H.; Hansen, T.H.; Koopman, A.D.; Ridderstråle, M.; Rutters, F.; Vestergaard, H.; Gupta, R.; et al. Discovery of biomarkers for glycaemic deterioration before and after the onset of type 2 diabetes: Rationale and design of the epidemiological studies within the IMI DIRECT Consortium. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Choi, M.E. Urinary biomarkers for early diabetic nephropathy: Beyond albuminuria. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2015, 30, 1063–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagtalunan, M.E.; Miller, P.L.; Jumping-Eagle, S.; Nelson, R.G.; Myers, B.D.; Rennke, H.G.; Coplon, N.S.; Sun, L.; Meyer, T.W. Podocyte loss and progressive glomerular injury in type II diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mauer, S.M. Structural-functional correlations of diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1994, 45, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chavers, B.M.; Bilous, R.W.; Ellis, E.N.; Steffes, M.W.; Mauer, S.M. Glomerular Lesions and Urinary Albumin Excretion in Type I Diabetes without Overt Proteinuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320, 966–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, C.E.; Christensen, C.K.; Vittinghus, E. The Stages in Diabetic Renal Disease: With Emphasis on the Stage of Incipient Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes 1983, 32, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satirapoj, B.; Adler, S.G. Comprehensive approach to diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Res. Clin. Pr. 2014, 33, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Starkey, J.M.; Tilton, R.G. Proteomics and systems biology for understanding diabetic nephropathy. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2012, 5, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Senatorski, G.; Paczek, L.; Kropiewnicka, E.; Bartłomiejczyk, I. [Cytokines in noninvasive diagnostics of diabetic nephropathy progression]. Polski Merkur. Lek. Organ Polskiego Towar. Lek. 2002, 13, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Merchant, M.L.; Perkins, B.A.; Boratyn, G.M.; Ficociello, L.H.; Wilkey, D.W.; Barati, M.T.; Bertram, C.C.; Page, G.P.; Rovin, B.H.; Warram, J.H.; et al. Urinary peptidome may predict renal function decline in type 1 diabetes and microalbuminuria. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 2065–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wołkow, P.P.; Niewczas, M.A.; Perkins, B.; Ficociello, L.H.; Lipinski, B.; Warram, J.H.; Krolewski, A.S. Association of urinary inflammatory markers and renal decline in microalbuminuric type 1 diabetics. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mischak, H.; Kaiser, T.; Walden, M.; Hillmann, M.; Wittke, S.; Herrmann, A.; Knueppel, S.; Haller, H.; Fliser, D. Proteomic analysis for the assessment of diabetic renal damage in humans. Clin. Sci. 2004, 107, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, D.M.; Zürbig, P.; Argilés, A.; Bauer, H.W.; Behrens, G.; Coon, J.J.; Dakna, M.; Decramer, S.; Delles, C.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. Naturally Occurring Human Urinary Peptides for Use in Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease *. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010, 9, 2424–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Yi, Z.; D’Agati, V.D.; Sun, Z.; Zhong, F.; Zhang, W.; Wen, J.; Zhou, T.; Li, Z.; He, L.; et al. Comparison of Kidney Transcriptomic Profiles of Early and Advanced Diabetic Nephropathy Reveals Potential New Mechanisms for Disease Progression. Diabetes 2019, 68, 2301–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobin, A.; Gingeras, T.R. Mapping RNA-seq Reads with STAR. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2015, 51, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa-Silva, J.; Domingues, D.; Lopes, F.M. RNA-Seq differential expression analysis: An extended review and a software tool. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0190152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- The Gene Ontology, C. Expansion of the Gene Ontology knowledgebase and resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, D331–D338. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Diehn, M. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clough, E.; Barrett, T. The Gene Expression Omnibus Database. Breast Cancer 2016, 1418, 93–110. [Google Scholar]
- Maere, S.; Heymans, K.; Kuiper, M. BiNGO: A Cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of Gene Ontology categories in Biological Networks. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3448–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merico, D.; Isserlin, R.; Stueker, O.; Emili, A.; Bader, G.D. Enrichment Map: A Network-Based Method for Gene-Set Enrichment Visualization and Interpretation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, J.A.; Guan, M.; Ng, M.C.; Palmer, N.D.; Hicks, P.J.; Keaton, J.M.; Lea, J.P.; Langefeld, C.D.; Freedman, B.I.; Bowden, D.W. The ras esponsive transcription factor RREB1 is a novel candidate gene for type 2 diabetes associated end-stage kidney disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 6441–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pezzolesi, M.G.; Poznik, G.D.; Mychaleckyj, J.C.; Paterson, A.D.; Barati, M.T.; Klein, J.B.; Ng, D.P.; Placha, G.; Canani, L.H.; Bochenski, J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Scan for Diabetic Nephropathy Susceptibility Genes in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sandholm, N.; Salem, R.M.; McKnight, A.J.; Brennan, E.P.; Forsblom, C.; Isakova, T.; McKay, G.J.; Williams, W.W.; Sadlier, D.M.; Mäkinen, V.-P.; et al. New Susceptibility Loci Associated with Kidney Disease in Type 1 Diabetes. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Väremo, L.; Scheele, C.; Broholm, C.; Mardinoglu, A.; Kampf, C.; Asplund, A.; Nookaew, I.; Uhlen, M.; Pedersen, B.K.; Nielsen, J. Proteome- and Transcriptome-Driven Reconstruction of the Human Myocyte Metabolic Network and Its Use for Identification of Markers for Diabetes. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marinković, T.; Oresic, M. Modeling strategies to study metabolic pathways in progression to type 1 diabetes—Challenges and opportunities. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 589, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, M.; Gheisari, Y. Nodes with high centrality in protein interaction networks are responsible for driving signaling pathways in diabetic nephropathy. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saito, R.; Rocanin-Arjo, A.; You, Y.-H.; Darshi, M.; Van Espen, B.; Miyamoto, S.; Pham, J.; Pu, M.; Romoli, S.; Natarajan, L.; et al. Systems biology analysis reveals role of MDM2 in diabetic nephropathy. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e87877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uhlen, M.; Oksvold, P.; Fagerberg, L.; Lundberg, E.; Jonasson, K.; Forsberg, M.; Zwahlen, M.; Kampf, C.; Wester, K.; Hober, S.; et al. Towards a knowledge-based Human Protein Atlas. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 1248–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.-M.; Huang, K.-Y.; Lee, T.-Y.; Weng, J.T.-Y. An interpretable rule-based diagnostic classification of diabetic nephropathy among type 2 diabetes patients. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, B.H.; Yu, H.; Kim, K.-W.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, I.Y.; Kim, S.I. Application of irregular and unbalanced data to predict diabetic nephropathy using visualization and feature selection methods. Artif. Intell. Med. 2008, 42, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrava, S.; Mardekian, J.; Sadosky, A.; Bienen, E.J.; Parsons, B.; Hopps, M.; Markman, J. Using Random Forest Models to Identify Correlates of a Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Diagnosis from Electronic Health Record Data. Pain Med. 2016, 18, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sl. No | Function | Bioinformatic Tool | Location | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Proteomics Identification database | PRIDE | https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/ | Perez-Riverol et al., 2019 [38] |
| 2 | Medical Calculators, Clinical Resources for diabetic data | diabetic-database | https://globalrph.com/medcalcs/diabetic-database/ | [39] |
| 3 | Protein sequence Database | UniProt | www.uniprot.org | Chen, C. et al., 2017 [40] |
| 4 | Genetic sequence database | GenBank | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/ | Benson, D.A. et al., 2013 [41] |
| 5 | Proteomic fragments analysis | MASCOT | https://www.sanger.ac.uk/science/tools | Brosch, M. et al., 2009 [42] |
| 6 | Human Metabolome Database | hmdb | https://hmdb.ca/ | Wishart, D.S. et al., 2018 [43] |
| 7 | Structural, functional annotation of proteins | Gene3D | http://gene3d.biochem.ucl.ac.uk/Gene3D/ | Yeats et al., 2006 [44] |
| 8 | miRNA, mRNA, protein, phosphoproteins and metabolite expression data sets | KUPKB | http://www.kupkb.org/ | Klein et al., 2012 [45] |
| 9 | Protein Motif fingerprinting | PRINTS database | http://www.bioinf.manchester.ac.uk/dbbrowser/PRINTS/ | Attwood et al., 2003 [46] |
| 10 | Gene expression | GEO dataset | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/ | Zhao et al., 2013 [47] |
| 11 | Knowledge portal for type 2 diabetics | Type 2 Diabetes | http://www.type2diabetesgenetics.org/ | Jeyaraman, M.M. et al., 2020 [48] |
| 12 | Resources for genomic and epigenetic studies of type 2 diabetes and associated issues | Diabetes Epigenome Atlas | https://www.diabetesepigenome.org/ | Khetan et al., 2018 [49] |
| 13 | Database for diabetes based diagnostic methods | pima | https://www.kaggle.com/uciml/pima-indians-diabetes-database | Barale, M. and Shirke, D.T., 2016 [50] |
| 14 | National Diabetes Information | NIDDK | http://diabetes.niddk.nih.gov/about/ | Whetzel et al., 2015 [51] |
| 15 | Protein identification using peptide information from MS/MS | ProteinProphetTM | http://proteinprophet.sourceforge.net/ | Nesvizhskii, A.I. et al., Anal Chem. 2003 [52] |
| 16 | 2D Gel Database | SWISS-2DPAGE | http://world-2dpage.expasy.org/swiss-2dpage/ | Hoogland, C. et al., 2014 [53] |
| 17 | Protein 3D structure database | PDB | www.rcsb.org | wwPDB Consortium, 2019 [54] |
| 18 | Protein–Protein interaction networks | STRING | http://string-db.org | Szklarczyk, D. et al., 2015 [55] |
| 19 | For structural and functional Annotation | SUPFAM Database | http://supfam.org | Wilson, D. et al., 2009 [56] |
| 20 | Repository for chemical substances and their biological activities | PUBCHEM | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | Kim, S. et al., 2016 [57] |
| 21 | For Visualizing and interpreting metabolomic data | Cytoscape MetScape 3.1 | http://metscape.med.umich.edu/ | Karnovsky, A. et al. 2012 [58] |
| 22 | Literature search based on disease related terms mapped to PubChem compounds for annotating compound networks | MetDisease | http://metdisease.ncibi.org/ | Duren, W. et al.,2014 [59] |
| 23 | Metabolic Pathway Database | KEGG | https://www.kegg.jp/ | Kanehisa, M. et al., 2016 [60] |
| 24 | Gene ontology | PANTHER | http://www.pantherdb.org/ | Thomas, P.D. et al., 2013 [61] |
| 25 | Gene Set Enrichment Analysis | GSEA | http://www.webgestalt.org/ | Wang, J. et al., 2017 [62] |
| 26 | Database for Single Polymorphic data | dbSNP | http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP | Smigielski, M. et al., 2000 [63] |
| 27 | Database for target genes of potential miRNAs | mirnet | https://www.mirnet.ca/ | Fan, Y. et al., 2018 [64] |
| Software Function/Application | Bioinformatics Resources | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Investigating implications of proteins in urine samples from DN patients | using protein–protein interactions (PPI) network analysis-STRINGv10. | Van et al., 2017 [4]; Szklarczyk, D. et al., [55] |
| Biomarkers for DN | PPI for determining interactions within proteins involved in progression of diabetes | Abedi and Gheisari, 2015 [95]; Saito et al., 2016 [96]; Varemo et al., 2015 [93] |
| DN urinary biomarkers in the various nephrons were elucidated and mapping of protein biomarkers in nephron segments | Human Protein Atlas https://www.proteinatlas.org/ determined differences in protein expressions in renal tissues vs. normal tissues | Uhlen et al., 2010 [97]; Van et al. 2017 [4] |
| Identify DN in Type 2 diabetic patients | decision tree-based prediction tool to identify DN in patients with type 2 diabetes | Huang et al., 2015 [98] |
| DN prediction | applied machine learning for early prediction of DN via risk factor analysis | Cho et al., 2008 [99] |
| DN related Factors | random forest learning algorithm (Breiman, 2001) for understanding factors behind diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN). | DuBrava et al. 2017 [100]; Chadinee et al., 2018 [37] |
| RNA sequencing of biopsy kidney samples from early DN and advanced DN patients and that from normal kidney tissue | Gene ontology http://geneontology.org/ CIBERSORT https://cibersortx.stanford.edu/ Gene expression Omnibus https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/ SEURAT https://satijalab.org/seurat/ | The Gene Ontology, 2017 [85]; Newman, A.M. et al., 2015 [86]; Zhao, M. et al., 2017 [47]; Clough, E. and Barrett, T. 2016 [87] |
| Identification of enriched biological processes, 76 differentially expressed proteins in diabetes affected kidneys identified | Cytoscape using plug ins Biological Networks Gene Ontology Enrichment Map | Maere et al., 2005 [88]; Merico et al., 2010 [89]; Van et al., 2017 [4] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, J.-W.; Muthu, M.; Haga, S.W.; Anthonydhason, V.; Paul, P.; Chun, S. Reckoning the Dearth of Bioinformatics in the Arena of Diabetic Nephropathy (DN)—Need to Improvise. Processes 2020, 8, 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070808
Oh J-W, Muthu M, Haga SW, Anthonydhason V, Paul P, Chun S. Reckoning the Dearth of Bioinformatics in the Arena of Diabetic Nephropathy (DN)—Need to Improvise. Processes. 2020; 8(7):808. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070808
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Jae-Wook, Manikandan Muthu, Steve W. Haga, Vimala Anthonydhason, Piby Paul, and Sechul Chun. 2020. "Reckoning the Dearth of Bioinformatics in the Arena of Diabetic Nephropathy (DN)—Need to Improvise" Processes 8, no. 7: 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070808
APA StyleOh, J.-W., Muthu, M., Haga, S. W., Anthonydhason, V., Paul, P., & Chun, S. (2020). Reckoning the Dearth of Bioinformatics in the Arena of Diabetic Nephropathy (DN)—Need to Improvise. Processes, 8(7), 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070808






