Abstract
There were three main issues of long start-up period, nitrate build-up and sludge loss during the operation of combined partial-nitritation anammox (CPNA). To fully start up the CPNA reactor, the fast achievement of partial-nitritation (PN) was the first step. Firstly, the PN process was successfully achieved within 22 days by 2 mg·L−1 hydroxylamine (NH2OH) addition and online intermittent aeration control at 0.2~0.3 mg·L−1 dissolved oxygen (DO). Then, a novel strategy of adding anoxic stirring phase between feeding and aeration period during CPNA operation was applied. It was shown effective to control nitrate build-up since the mole ratio of NO3−-N production and NH4+-N removed (MNRR) was mostly below 15%. Also, the procedure adjustment was proven useful to alleviate sludge loss by sustaining filamentous bacteria that could act as biomass framework and reduce nitrate substrate. The filamentous denitrifying bacteria could cause sludge bulking. The total nitrogen removal rate (TNRR) varied from 0.20 to 0.45 kg·m−3·d−1 during CPNA operation. In Stage III, after adding anoxic stirring phase, the abundance of nitrogen transformation functional microorganism’s nitrite oxidizing bacteria (NOB) was below 1.6%, which was one order of magnitude lower than Anammox and ammonia oxidizing bacteria (AOB).
1. Introduction
Since the first discovery of autotrophic anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) in early 1990s [1], the research and application of anammox–based technologies have been widely reported [2]. The single–stage anammox systems such as combined partial–nitritation anammox (CPNA) require much lower investment costs and skips of adjusting two reactors, making it the most frequently adopted anammox process. However, there were three main issues during the operation of CPNA, namely long start-up period, nitrate build–up and sludge loss. The slow-growth physiological characteristics of anammox bacteria makes the anammox inocula scarce, affecting the start-up duration. Lackner et al. [1] investigated the practical engineering of Anammox installations and found that 50% of wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) had experienced nitrate build-up which lasted up to several weeks. Some of them even confronted nitrate build-up repeatedly [3]. The investigation of full-scale Anammox plants also showed that about 45% of them confronted the sludge retention, settling or solids separation problems, which lasted up to 21 days [1]. The study at the WWTP Strass, Austria experienced significant sludge concentration decrease and severe loss of solids [4].
The most effective way to fast start up CPNA system is to inoculate fresh or preserved anammox sludge [5]. But the scarcity of anammox inoculation makes this approach impractical. Besides, trying to shorten the start-up period of partial-nitritation (PN) with conventional activated sludge and then established CPNA process could be also an alternative for CPNA fast start-up. Fast start-up of partial nitritation can be realized by high dissolved oxygen (DO) supply [6] or high free ammonia (FAN) [7], but the operation was not always stable and reliable. PN was stably achieved within 20 days by 10 mg·L−1 hydroxylamine (NH2OH) addition in aerobic granules under high DO concentration (above 5 mg/L) [8]. The study by Li et al. [9] also showed that 4.5 mg·L−1 NH2OH addition with 1.0 mg·L−1 DO could reduce the start-up period of PN to 19 days. However, NH2OH’s effect on floccular sludge under low DO condition was scarcely reported, especially with low NH2OH dosage.
To alleviate the nitrate build-up, NOB inhibition should be executed. The conventional methods to inhibit NOB were DO control, FAN and free nitrous acid (FNA) inhibition, but these methods have limitations or defects in engineering applications. For example, low DO [10] was reported to greatly inhibit AOB, but only slightly inhibited NOB, making DO control less effective for rapid start-up of partial nitrification process. The concentrations of FAN and FNA were significantly affected by substrate (ammonium or nitrous nitrogen), pH and temperature (T). Bacteria may adapt to high-intensity FAN or FNA [11]. NH2OH, as one of the intermediates of anammox, was shown an inhibitory effect on NOB [12] without adverse effects on AOB or anammox. By 20 mg·L−1 NH2OH dosing and a 40-day sludge retention time (SRT) control, the effluent nitrate of CPNA declined drastically from more than 500 mg·L−1 to 65 mg·L−1 [13]. However, NH2OH could reduce the particle size of sludge, causing sludge loss. The typical sequencing batch reactor (SBR) cycle for one-stage CPNA process is feeding →aeration →stirring →sedimentation →discharge [13,14]. Under this operational procedure, process instabilities included nitrate build-up and sludge loss were reported in both lab-scale reactors and WWTPs [1,14,15]. To change this adverse condition, operational procedure adjustment could be a promising choice.
The reasons for sludge loss include poor sedimentation of filamentous sludge, abnormal operation of sedimentation tank and excessive foaming caused by aeration [1,4]. In addition, the accumulation of nitrite or ammonia can exhibit toxic inhibition on sludge, resulting in the disintegration of flocculent sludge. Besides, filamentous bacteria could accommodate well to the low chemical oxygen demand (COD) and DO environment in the CPNA system [16]. The overgrowth of these microorganisms led to sludge bulking and sludge loss. In the study of Wang et al. [17], the massive proliferation of filamentous bacteria, i.e., Haliscomenobacter and Ignavibacterium in the CPNA process were found when the high concentration of nitrate was accumulated, resulting in a severe sludge loss. The accumulated nitrate offered substrate for denitrifying filamentous bacteria, which facilitated their growth, causing filamentous bulking. Besides, the chemical reagents addition could also cause sludge loss. For example, Wang et al. [13] studied the nitrate build-up recovery of the CPNA system by NH2OH dosing, they found the sludge concentration decreased from 3.36 g·L−1 to 2.82 g·L−1 in the lab-scale study. Sludge loss was also found in full-scale Anammox installations, i.e., at the WWTP Zürich (1400 m3), voluminous and fluffy sludge flocs were formed when the mixed liquid volatile suspended solids (MLVSS) was lower than 2.0 mg·L−1, the sedimentation was impaired by small bubbles of N2, resulting in sludge loss [14]. Sludge aggregation and biofilm formation are the most important measures to prevent sludge loss. Therefore, the control of sludge loss can be realized by cultivating a granular sludge system with good sedimentation [18] or adding carriers to form a biofilm system or installing a membrane module [19]. In addition, adding flocculants such as nano flocs, or adopting sludge retention devices such as cyclone separator, drum screen could be alternative measures. However, these methods are hindered by technical challenges or incremental costs, and are often impractical. The sludge loss can also be controlled by prolonging the sedimentation duration or conducting multiple periodic sedimentation before drainage. So, the onsite adjustment of SBR procedures could possibly be a practical approach. In the fields of software and online process monitoring equipment, more online control systems were applied in WWTPs for accurate control, which improved the operational performance and reduced the costs [13,15].
To solve the above mentioned three operational issues during the CPNA life cycle respectively, this study aims to control nitrate build-up and sludge loss by adding anoxic stirring stage in the SBR operational procedures and adjusting online control modes. And also realize fast start-up of PN for the CPNA by NH2OH addition as well. Meanwhile, the evolution of microbial community was investigated in the CPNA process.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Lab-Scale Reactor Setup and Its Operation
2.1.1. Set-Up
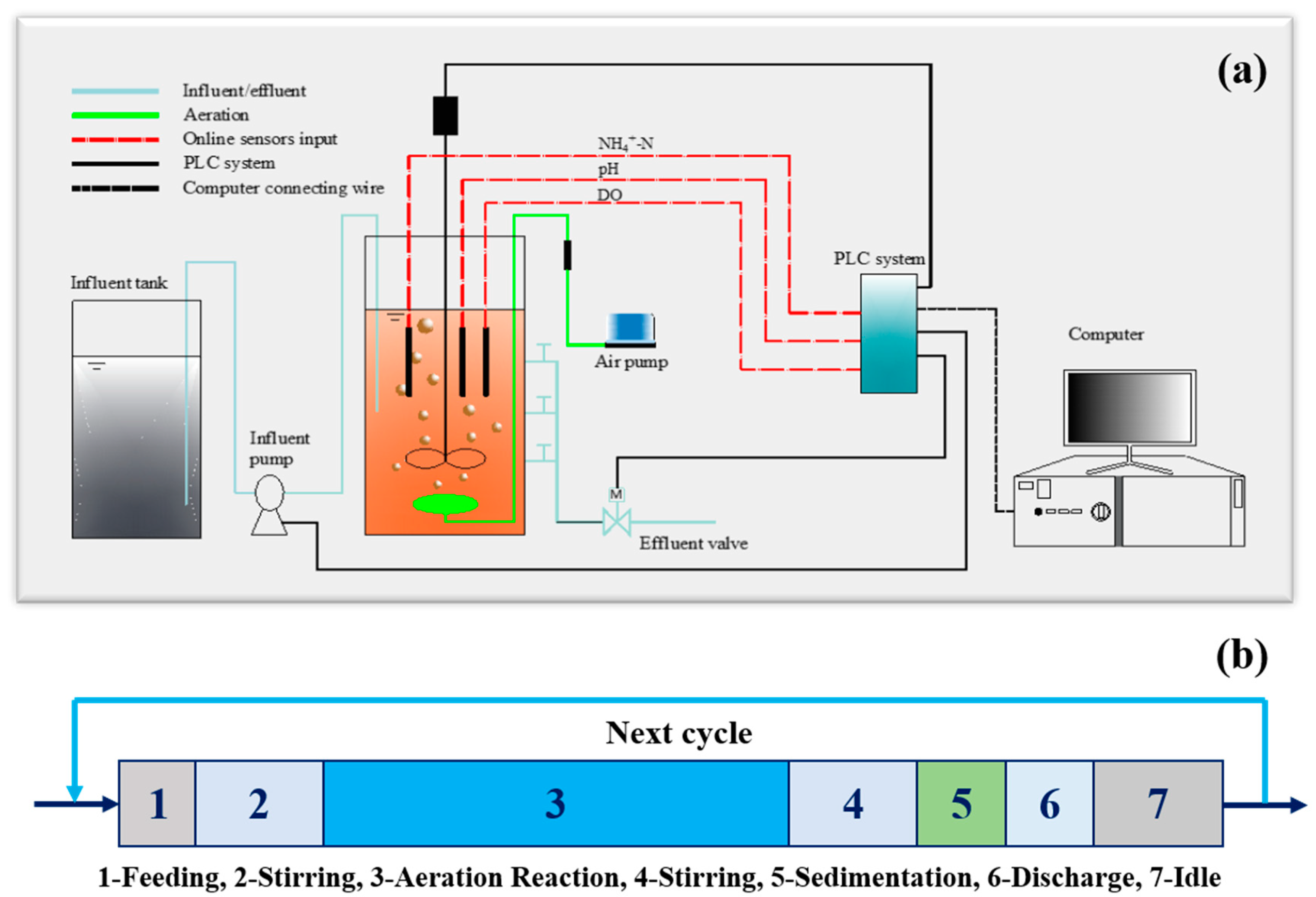
The schematic diagram of the CPNA is shown in Figure 1a. A cylindrical reactor made of Plexi glass, with an effective volume of 15.0 L (ϕ 250 mm × H 400 mm), was designed [13]. The reactor was maintained at 33 ± 1 °C with a water jacket system (SC-15, SCIENTZ, Ningbo, China). A black shading fabric was wrapped around the outside of the reactor to prevent light from reaching the AOB and Anammox bacteria and to inhibit the growth of photosynthetic microorganisms that could produce oxygen. The sludge and substrates were fully mixed by a mechanical stirrer, which was installed in the middle of the reactor and controlled by a programmable logic controller (PLC) system (S7-300, SIEMENS, Munich, Germany). The DO, pH and ORP probes are all bought from HACH (Loveland, USA). All of them are connected to the PLC system. The stirrer was consisted of three steel impellers with diameter of 5 cm. The stirring speed was controlled at 150 rpm to mix the substrates completely and drive produced N2 out.
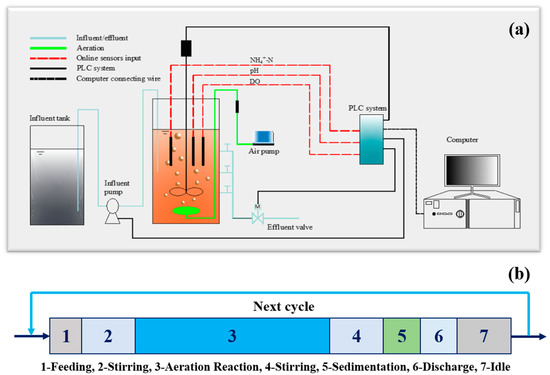
Figure 1.
Experimental set-up (a) and operational pattern (b) of the CPNA.
2.1.2. Influent and Seeding Sludge
The SBR was fed with synthetic wastewater by an influent diaphragm pump (DP-35, XINXISHAN, Shanghai, China). Synthetic wastewater contained mainly NH4Cl and NaHCO3 with the molar ratio of 1:2, and the ammonia concentration was controlled at the range of 60~600 mg·L−1. The mineral elements and trace elements in the influent were listed in Table S1.
The seeding sludge for Stage I was the mixture of activated sludge in the anaerobic, anoxic and oxic tanks of Qinghe Reclaimed Wastewater Treatment Plant in Beijing. The sludge was washed by PBS (pH = 7.0) and tap water three times, respectively, to remove the remaining substrate and the buffering solution before added to the reactor. The final MLSS in the beginning of the reactor was around 8.0 g·L−1. In Stage II, both air flow and aeration time was controlled, trying to transform PN to Anammox. In Stage III, 3.5 L (MLSS = 10.0 g·L−1) anammox sludge was inoculated in the reactor, resulting in a final MLSS of 6.9 g·L−1.
2.1.3. Experimental Operation
The CPNA was operated in an SBR mode. Its operational pattern was demonstrated in Figure 1b. In each SBR cycle, 5 L of synthetic wastewater was pumped into the reactor during the feeding period. Then the stirrer was operated for a certain period (Figure 1b-2) without aeration to remove the remained nitrite or nitrate in CPNA, differing from normal operation [13,14] without this period. The reaction periods (Figure 1b-3) of intermittent and continuous aeration control mode were different. The start/stop of aeration pump (HAILEA® V-10, Guangdong, China) was controlled by a timer in the intermittent mode. And this period consisted of several sub-cycles including aeration period and stirring period. However, in continuous aeration control mode, it was operated by aeration continuously. The DO protection logic, which meant to stop aeration once the DO concentration was higher than the threshold, and then continued to aerate when the DO concentration was lower than the setting value, was contained in both of the two control modes. The operation termination and end of reaction stage were controlled by an ammonium online sensor (Ammolyt® Plus Set, WTW, Munich, Germany), which was used to indicate the completion of ammonia oxidation and anammox. A 30-min anoxic stirring, 30-min settling, 5-min discharge and idle (Figure 1b-4–7) were the following operational periods.
To shorten the start-up period of partial nitritation, realize the Anammox transformation, and investigate the CPNA operational stability, the total operation period of this study was divided into three operational stages (Table S2):
Stage I (Day1–22), Partial nitritation. Under intermittent aeration control mode (Figure S1a), 2 mg N/(L·d) NH2OH was added to the reactor on day6–10 and day16–21 to accelerate the start-up of partial nitritation, respectively.
Stage II (Day23–73), Anammox transition. Various DO concentrations and different stirring periods combined with online intermittent aeration control (Figure S1a) were applied to transform PN system to a mixed biomass consisted of AOB and Anammox biomass. No NH2OH dosing was carried out in this stage.
Stage III (Day74–272), CPNA operation. To accelerate the Anammox transition process, a quantity of anammox sludge was added to the SBR system. The reactor was then operated under continuous aeration mode (Figure S1b). No NH2OH dosing was carried out in this stage.
The CPNA was operated over 300 days with 35 d, 70 d and 210 d in each stage. The reactor was equipped with a PLC for automatic operation and NH4+-N, DO, oxidation-reduction potential (ORP), pH and T data acquisition through online probes. The designed logic program of the real-time control for the SBR operation is shown in Figure S1.
2.2. Activity Analysis of AOB, NOB and Anammox
The activities of AOB, NOB and Anammox were determined by batch tests of our previous studies [13,20]. A working volume of 1 L reactor was used for aerobic batch test to evaluate the ammonia reduction, nitrite accumulation and nitrate production, which could reflect activities of AOB and NOB comprehensively. 0.5 L of the mixed liquor were collected from the SBR with approximate 100 mg·L−1 of ammonium for the aerobic batch tests. The water temperature was controlled at 33 ± 1 °C and DO was always kept above 4.0 mg·L−1. Water samples were taken every 10 min and filtered through 0.45 μm micropore polyether sulfone (PES) membrane (Membrana, Wuppertal, Germany). The filtrates were used to determine concentrations of ammonium, nitrite and nitrate. Sludge samples were collected at the end of each batch test.
Anammox activity batch test was conducted in the SBR directly. Through the manual control on PLC system, the SBR was maintained in the mixing stage with the ammonium concentration of 50 mg·L−1. Nitrite stock solution (NaNO2, Sino pharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) was added to the SBR to obtain the initial nitrite concentration of 30 mg·L−1. Water samples were taken every 30 min and filtered through 0.45 μm micropore polyether sulfone (PES) membrane (Membrana, Wuppertal, Germany). The measurements of water and sludge samples were the same as those in the aerobic batch test. The three activities RAOB, RNOB and RAnammox (g N·(g MLVSS·d) −1) for functional bacteria AOB, NOB and Anammox were calculated as follows,
here, C represents the concentration, inf represents influent, eff represents effluent, t is the time.
RAOB = (CNH4+-N, inf − CNH4+-N, eff)/(t⋅CMLVSS)
RNOB = (CNO3−-N, eff − CNO3−-N, inf)/(t⋅CMLVSS)
RAnammox = [(CNH4+-N, inf + CNO2−-N, inf) − (CNH4+-N, eff + CNO2−-N, eff)]/(t⋅CMLVSS)
2.3. Sludge Sampling, High-Throughput Sequencing and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
Activated sludge samples were collected from the SBR during the mixing state on day 2, 33, 56, 77, 109, 208 and 269, respectively, to investigate the evolution of microbial community. The samples were stored at −20 °C before DNA extraction.
0.5 mL sludge sample was firstly centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 min, then the pellet was used for the DNA extraction by FAST DNA Spin Kit for Soil (MP Biomedicals, Southern California, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. DNA extraction of each sample was conducted in duplicate, and the corresponding DNA extracts were then merged together for further analysis. Extracted genomic DNA was detected and quantified using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and NanoDrop 2000 (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), respectively, and then stored at −80 °C before use.
PCR primers 515F/806R targeting bacteria and archaeal 16S rRNA V4 region were selected for the microbial community analysis [21] in activated sludge samples taken on day 2, 33, 56, 109 and 269, respectively. The high throughput sequencing was conducted by Sango Co., Ltd., in Shanghai through the small-fragment library construction and pair-end sequencing using the Illumina Miseq sequencing system. The sequencing reads were assigned to each sample according to the unique barcode, and pair-end reads were merged using FLASH and filtered with QIIME quality filters [22,23]. PCR chimeras were filtered out using UCHIME [24]. Clean sequences were deposited into the NCBI sequence read archive (SRA) database under the project number of PRJNA487973. The taxonomic classification of the sequences in each sample was carried out using RDP Classifier at the cutoff of 50% [25], and then operational taxonomic units (OTUs) with an abundance below 0.01% were removed.
7 nitrogen transformation functional genes including nitrification (amoA, hao, nxrB, NSR), anammox (hzsA, hzo) and denitrification (narG) were quantified on day 2, 33, 56, 109, 208 and 269, respectively. The detailed procedure was referred to our previous study [17]. The main nitrogen processes and the corresponding functional genes were in Figure S4. The primers and annealing temperature used in this study and their corresponding mechanisms were summarized in Table S3. The detailed information of q-PCR for each target gene was shown in Table S4.
2.4. Analysis of Physical-Chemical Parameters
Water samples were collected and analyzed regularly to evaluate nitrogen removal performance of the CPNA process. Concentrations of NH4+-N, NO2−-N, NO3−-N, total nitrogen (TN) and MLSS were determined according to the standard methods [26]. The NH4+-N concentrations, pH, DO, ORP and temperature in the SBR were real-time monitored with online sensors. The particle size distributions of the activated sludge were measured with a Malvern Mastersizer 2000 (Malvern Co., Worcestershire, UK). Sludge property was observed with a scanning electronic microscopy (SEM) (SEM, Quattro C, thermoscientific) equipped with EDAX (Element, AMETEK).
The nitrite accumulation rate (NAR) was calculated by Equation (1) to analyze the nitrite build-up.
The MNRR in each SBR cycle was determined by Equation (2) to identify the nitrate build-up.
In Equations (1) and (2), NO2−eff, NO3−eff, NH4+eff were the effluent NO2−-N, NO3−-N and NH4+-N concentrations in the SBR cycles, mg/L, while NO3−inf and NH4+inf were the influent NO3−-N and NH4+-N concentrations, mg/L.
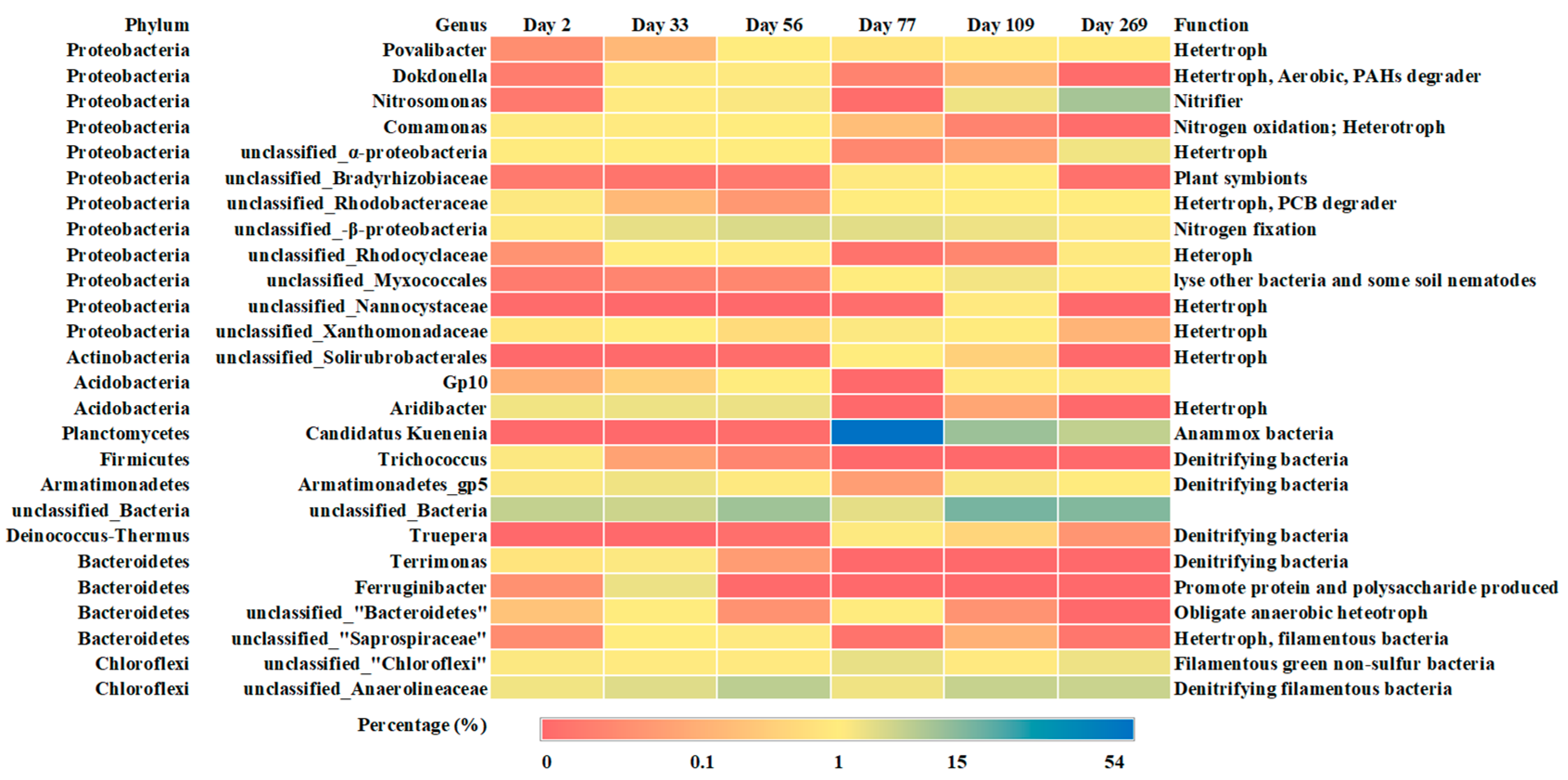
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The results of chemical parameters and the genes copy concentrations were visualized through Origin 2019b (OriginLab, Northampton, MA, USA). A heat map of the top 10 genera in each sample based on relative abundance percentage was built using Excel 2019 (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Performance of Reactor Start-Up and Nitrogen Removal
3.1.1. Start-Up of PN
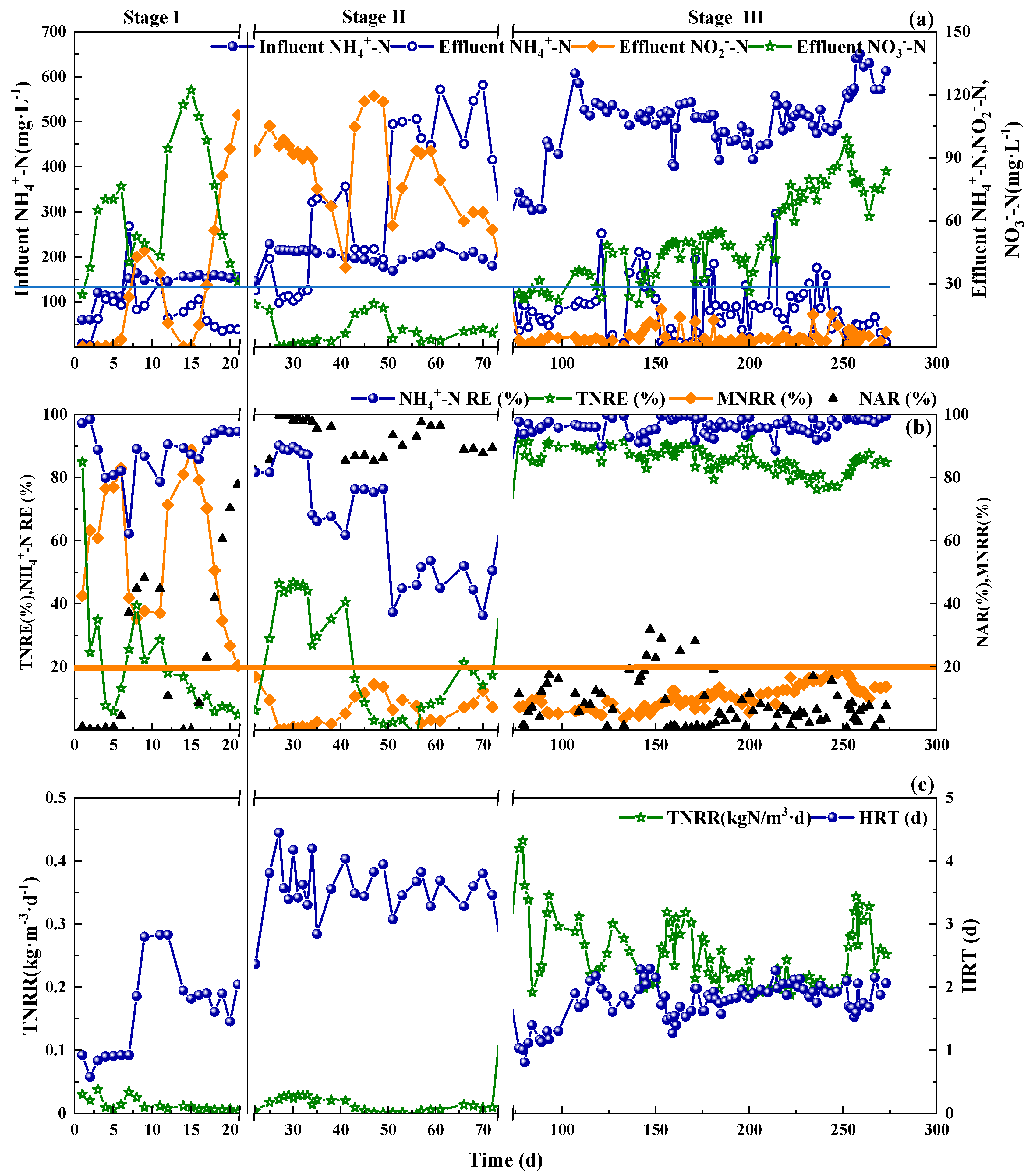
As shown in Figure 2a, in Stage I, under intermittent aeration control mode, with the addition of 2 mg·L−1 NH2OH on Day 6–10, the produced nitrate declined and more ammonia was oxidized to nitrite, indicating the inhibition of NOB and promotion of AOB. The NAR of 50% indicated the success of PN. While during day 11–15 without NH2OH addition, the nitrite concentration decreased and the effluent nitrate increased immediately. This phenomenon indicated that the inhibition effect of NH2OH on NOB was reversible, which was in accordance with results of Wang et al. [13]. The second dosing of NH2OH on Day 16–21 caused the same nitrogen species variations trends as that on Day 6–10. However, stable nitrite production was maintained with an average NAR of 80% (Figure 2b). Theoretically, around 50% NH4+-N to nitrite conversion [27] was enough for PN, which could further shorten the start-up period by NH2OH addition and online control. To fully start up the CPNA reactor, the fast achievement of PN was the first step, which could save the time for start-up of CPNA on the whole.
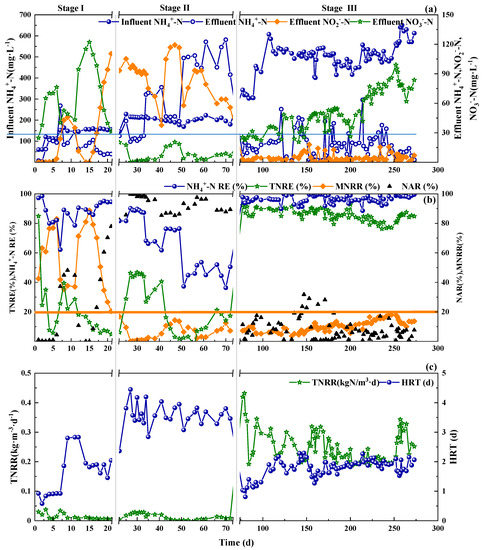
Figure 2.
Influent NH4+-N, effluent NH4+-N, NO2−-N and NO3−-N (a), NH4+-N RE, TNRE, MNRR and NAR (b), TNRR and HRT (c) during the whole operational stages of SBR.
3.1.2. Nitrogen Removal
The total nitrogen removal efficiency (TNRE) in the Stage II and Stage III were 0~40% and 78%~90%, respectively. Correspondingly, the TNRR were also very low in Stage II (0~0.04 kg·m−3·d−1), indicating the difficulty in transforming the PN biomass to anammox system by DO and aeration control. With the inoculation of anammox in the beginning of Stage III, the TNRR for the whole stage was around 0.20~0.43 kg·m−3·d−1.
In Stage II, although higher hydraulic retention time (HRT) was applied, less than 40% TNRE (Figure 2b) was achieved under various DO concentrations and different stirring periods. There were several denitrifying bacteria from the WWTPs’ inoculation, which could perform denitrification with the organics of dead cells or soluble microbial products (SMP) as the carbon source. So, the higher TNRE could be mainly contributed by denitrification. After around 70 days’ transition, no apparent anammox activity occurred in the system by DO concentration and online control.
During the first 7 days in Stage III, certain amount of nitrite was added to the system in each SBR cycle to ensure the normal growth of anammox bacteria. With the increase of influent NH4+-N concentration, the effluent nitrate showed a stable rising trend (Figure 2a). In each SBR cycle, approximately 20 mg·L−1 nitrate was produced. The normal value of MNRR calculated by CPNA equation was 15% [28], and values higher than 15% indicated nitrate build-up. Countermeasures should be taken when the MNRR value exceeded 20% [14]. The MNRR values in Stage III were mainly less than 15%, some were even less than 10%, meaning an effective control of NOB and nitrate build-up. Compared with the study of Wang et al. [13], the key point for achieving higher TNRE and less nitrate build-up in this study was the adjustment of SBR operational procedure. The addition of stirring period between feeding and aeration paved the way to denitrification with the organics offered by bacteria debris and the residual nitrate as substrates. Besides, this stirring period alleviated the DO inhibition on Anammox bacteria, contributing to higher TNRE and TNRR.
3.1.3. Activity of AOB, NOB and Anammox
The activities of functional bacteria including AOB, NOB and Anammox were plotted in Figure S2. The AOB activity increased significantly from 0.15 to 0.35 kg N·kg MLVSS−1·d−1 in the first two intermittent aeration stages, and further increased to 0.4 kg N·kg MLVSS−1·d−1 in the beginning of continuous aeration stage (Stage III), and remained stable subsequently. The higher DO supply, NH2OH addition [20] and mesophilic temperature facilitated its increase in the first two stages. In Stage III, although continuous aeration mode was applied, lower DO concentration limited AOB activity increase. The NOB activity was one order of magnitude lower than that of AOB. With 2 mg·L−1 NH2OH addition in Stage I, the NOB activity was reduced to zero in Stage II and recovered until day 129 under low DO concentration and continuous aeration conditions. The NOB activity variations on Day 1 to Day 56 proved that the NH2OH inhibition had a lag influence on NOB, and the inhibition effect would last for a period of time. Due to the inoculation of Anammox sludge, the Anammox activity began to appear in Stage III. The Anammox and AOB activities were 13.8 and 22.2 times of NOB activity in this stage, making them dominant microorganisms in the CPNA reactor. The Anammox activity did not change a lot in Stage III because no environmental parameters or operational procedures were adjusted.
3.2. Sludge Loss
3.2.1. Sludge Loss
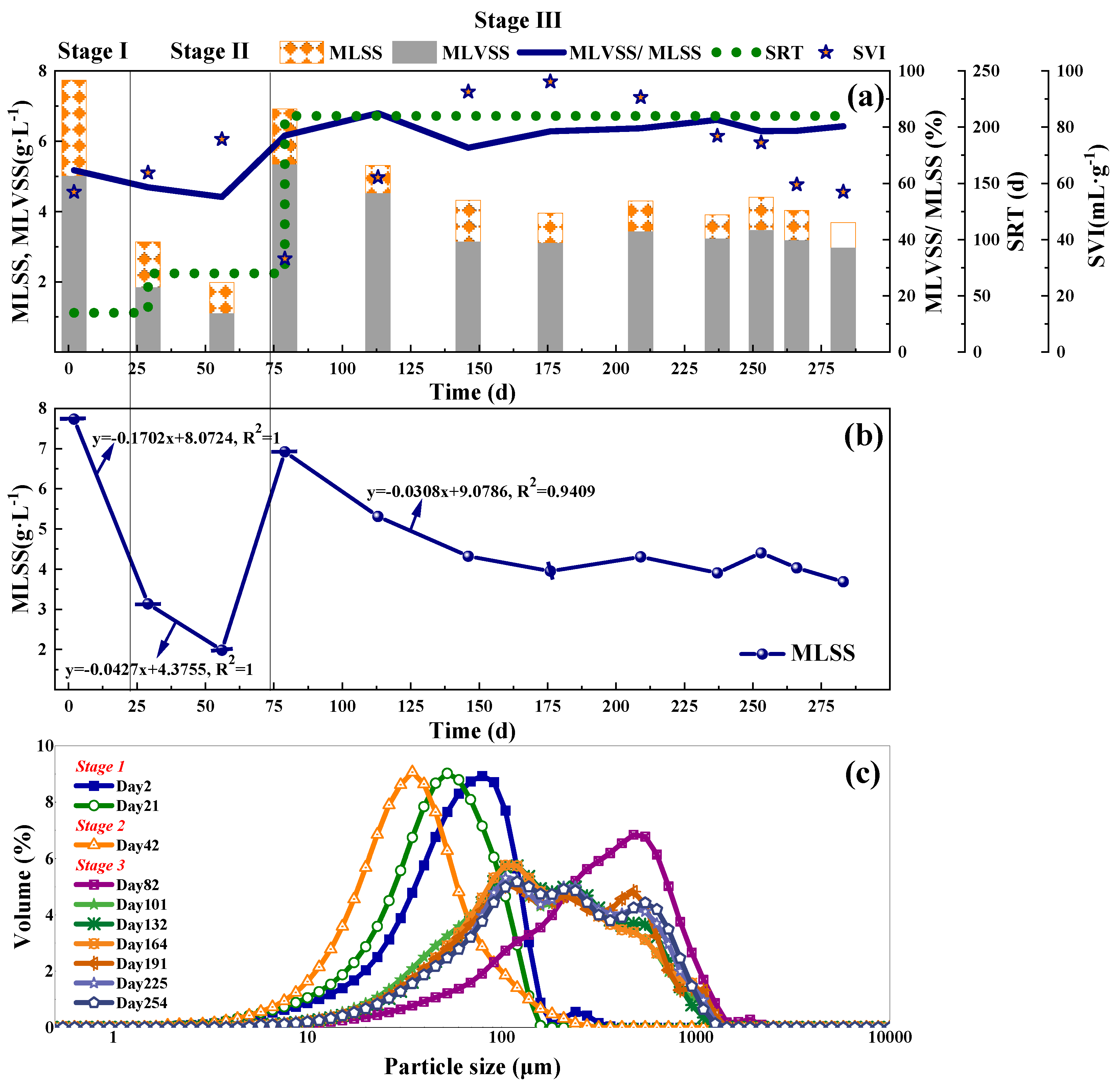
The biomass characteristics including ML(V)SS, settling volume index (SVI), particle size distribution (PSD) curves were shown in Figure 3. In the first two stages, the MLSS declined 59.38% and 36.48%, separately. The SVI increased from 57.00 to 63.78 mL·g−1 and from 63.78 to 76.00 mL·g−1. Both the MLSS decrease and SVI raise represented significant biomass washout rate of 0.17 and 0.04 g·L−1·d−1 (Figure 3b), indicating serious sludge loss. The inocula for Stage I were performed to DO around 4.0 mg·L−1 before put into this reactor. But the DO supply was far less with only 0.2~0.3 mg·L−1 during the operation in PN. The adaptation of inocula to the new low DO environment caused bacterial death and sludge loss. Besides, NH2OH was reported to reduce the sludge particle size [29]. Smaller biomass size caused a lower settling velocity value, resulting in a higher SVI. Moreover, sludge bulking caused by the overgrowth of filamentous bacteria [30] could also affect the SVI. The study by Ma et al. [31] showed the accumulation of nitrite deteriorated the sludge settleability. While the average nitrite concentration and NAR in Stage II were 67.97 mg·L−1 and 93.13%, respectively. Higher nitrite concentration and NAR could be the main reasons for SVI increase and sludge loss.
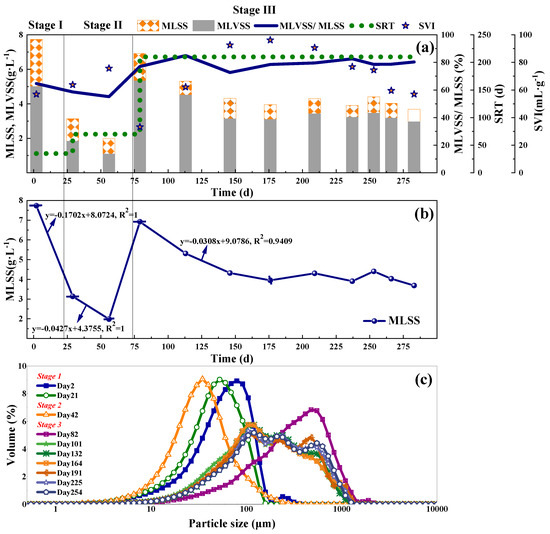
Figure 3.
The sludge concentration, SRT, SVI (a), MLSS dynamic variations (b), and laser particle size distribution (c) of the SBR biomass.
Compared with the first two stages, good sludge settleability included the increased MLSS and decreased SVI, at the beginning of Stage III, which was mainly benefitted from anammox biomass addition. During Day 73~146, the MLSS declined and the SVI increased. The unadaptability of inoculated microorganisms led to the death of bacteria and sludge disintegration, affecting the sludge concentration in this period, which was the same as the above description in Stage I. Besides, the filamentous bacteria could also contribute to the sludge loss which would be discussed below. Subsequently, the MLSS was stabilized at around 4 mg·L−1 on Day 146~280 with an average MLVSS/MLSS ratio of 79.5%, which could be the combined effects of microbes and operation control. Due to the addition of stirring step (anoxic operation) in the SBR operational procedure, the accumulation of nitrate in the CPNA system was less. Therefore, during the long-term operation of the CPNA, the amount of nitrate substrate that could be exploited by denitrifying filamentous bacteria [32] was reduced, thus reducing the sludge loss caused by filamentous sludge bulking.
3.2.2. Sludge PSD and Morphology
The sludge PSD curves shifted to the left from Stage I to Stage II (Figure 3c), representing a decline of sludge particle size. It can be calculated from Table S5 that with comparison to Stage I, the median aggregate size in Stage II reduced by 30.42%, and its shape of PSD increased up to 1.32 times of that in Stage I. These findings were in accordance with a previous study [29]. In their research, when 15 mg·L−1 NH2OH was added to nitrifying cultures in 6-h batch tests, a 20–40% decrease in the median aggregate size, up to 2.3 times broaden the shape of particle size distribution and more dispersed microcolonies were found. So, in Stage I, NH2OH addition mainly contributed to the particle size decrease. Differently, in Stage II, the high nitrite concentration and lower biomass size together contributed to the higher SVI and lower MLSS. The data in Table S5 showed an increase in sludge particle size to some extent in Stage III as shown in Figure 3c. The spans in this stage was much higher than Stage I and II, indicating a much wider shape of particle size distribution (Figure 3c, Table S5). Finally, the sludge in the SBR was a mixture of flocs and granules, and the MLSS remained stable (around 4.0 g·L−1), incorporating roughly 210–250 μm large granules and 75–90 μm small flocs, respectively. The decrease of sludge particle size will affect the sedimentation rate and cause sludge loss. Besides, it also affected the nitrogen removal performance. A simulation by Hao et al. [33] confirmed that decrease in sludge particle size would cause considerable loss of nitrogen removal and nitrite accumulation. Probably, the nitrogen removal performance was related to the microbes’ activity at different sludge particle sizes. For example, a higher Anammox activity was measured in granules with diameters above 500–1000 μm [34]. By size fraction, Gilbert et al. [35] found the highest anammox abundance in the range of 100–315 μm and they confirmed that both the measured nitrogen conversion rates and the detected functional microorganisms’ abundances decreased with increasing size fraction. The study by Choi et al. [36] also showed that granules larger than 100 μm in the SBR increased the TNRR. So, in this study, with the stabilization of sludge concentration and the PSD, the TNRR of Stage III was significantly higher than that of the first two stages (Figure 2c).
SEM was used to investigate the surface changes of activated sludge throughout the experiment. As was shown in Figure S3, on day 2 of Stage I, the surfaces of biomass were mainly consisted of Bacilli and Brevibacterium. Bacterial cells were surrounded by fine strands of supportive connective tissue, and some dead cells were shown. These may be associated with the autolysis of bacteria in the reactor. On day 16 of Stage I, after a short period of NH2OH addition, the surface of biomass became much looser. In Stage II of anammox acclimation, the quantity of microbes increased in Figure S3c,d. Besides, fine strands of supportive connective tissue were also found. There were some obvious slime or gel substances observed in Figure S3e, which were probably extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). Jia et al. [19] performed a study on structure and composition of EPS to elucidate factors for the anammox aggregation property. The results showed that slime secreted from Anammox cells may easily formed the gel network to aggregate for their higher viscosity to the sludge surface. Also, large amounts of hydrophobic groups of protein in EPS promoted the microbial aggregation. The tightly bound EPS concentrations in CPNA sludge were in the range of 107.82~350.51 mg·L−1, which increased as the operational period grew. In sum, slime and tightly bound EPS were closely related with sludge morphology, and could be used as the indicators for anammox microbial survival ability. On day 113 and day 136 in Stage III, filamentous bacteria were found (Figure S3f,g) because low DO concentration and less nutrient (C and P) facilitated the growth of filamentous bacteria [37]. Besides, some denitrifying bacteria belonged to filamentous bacteria, which could also help remove nitrogen [38]. Similar to Figure S3g,h some slime or gel substances were also observed in both in Figure S3g,h. On Day 269, except few filamentous bacteria, SEM observations showed the granules with a high degree of compactness, explaining the higher TNRR in Figure 2c.
3.3. Abundances of Functional Bacteria and Genes Related to Nitrogen Transformation
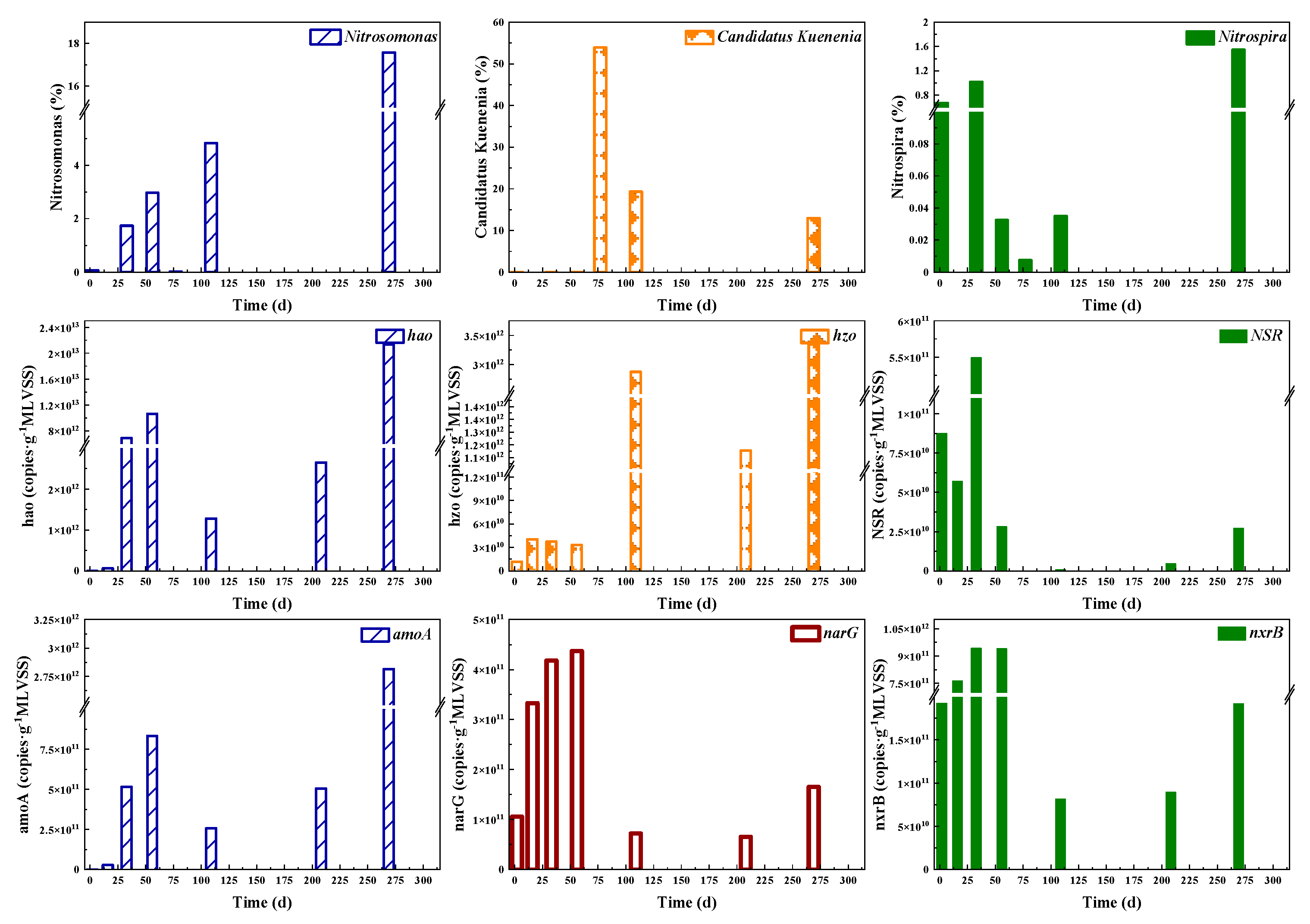
To explore the underlying reasons for nitrogen transformation process, key genes and relative abundance of functional bacteria including AOB, NOB and Anammox were determined as shown in Figure 4. According to the results of high-throughput sequencing analysis, Nitrosomonas, Nitrospira and Candidatus Kuenenia were the dominant genera of AOB, NOB and Anammox, respectively. The relative abundance of Nitrosomonas increased significantly from 0.07% to 17.58% during the whole CPNA operational stages. Nitrosomonas and Ca. Kuenenia eventually became dominant bacteria in the CPNA reactor. Nitrosomonas and Ca. Kuenenia were the sole genus of AOB and Anammox in the CPNA reactor, respectively. After the addition of anammox sludge, the relative abundance of Ca. Kuenenia decreased to 12.93% on day 269. The abundance of Nitrospira increased in Stage I, but decreased significantly in Stage II and early period of Stage III, which indicated that the effect of NH2OH on Nitrospira was delayed. However, the inhibition effect of NH2OH on NOB was evident and the NAR increased rapidly (Figure 2b). In the last period of Stage III, the relative abundance of Nitrospira increased, and this showed that long period of low DO and nitrite shortage could be conducive for Nitrospira growth, which is consistent with others study [39].
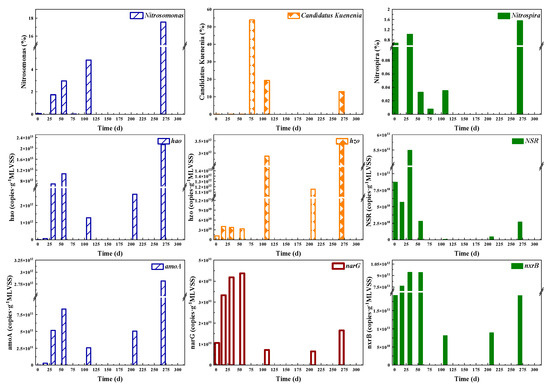
Figure 4.
The abundances of nitrogen conversion functional bacteria and genes abundance.
As shown in Figure 4, the numbers of functional genes and functional bacteria were consistent with the bacteria activities. The functional genes of AOB including amoA and hao increased dramatically on day 33 because of NH2OH addition. The NH2OH addition rapidly increased hao encoding NH2OH oxidoreductase. Correspondingly, the abundance of Nitrosomonas increased from 0.07% to 1.73% on day 33 due to NH2OH addition. The enhancement of AOB was achieved by both NH2OH and DO and substrate supply. The NOB functional genes (nxrB and NSR) were relatively low, with the abundances of 8.17 × 1010–9.42 × 1011 and 7.72 × 108–5.49 × 1011, respectively. Nitrobacter, a typical NOB, was under the detection limit (0.003%) in all samples, while Nitrospira as the predominant NOB (0–1.55% in abundance) was significantly affected by NH2OH addition. The nxrB abundance was much higher in the first two stages compared with Stage III, in addition, after the NH2OH addition, its abundance was not reduced, thus the decrease of nxrB abundance during day 109~208 was mainly caused by DO shortage. With a high nitrite and DO affinity and low growth rate, Nitrospira (k-strategist) would win the competition against Nitrobacter with a lower nitrite and DO affinity and higher growth rate (r-strategist) [39], thus Nitrospira could survive in the CPNA system. The nxrB was one of the functional genes of Nitrobacter, so its abundance could be affected by DO variations. However, as the functional gene of Nitrospira, NSR abundance was decreased on day 16 after the first time of NH2OH addition. From day 33~56, although higher DO was supplied, the abundance of NSR declined by nearly 95%, and was further dropped by 4.72 × 109 on day 208. Even on day 269, this value was less than 5% of that on day 33. It showed that the effects of NH2OH on different genus of NOB were distinct, NH2OH addition could not inhibit Nitrobacter, while it could inhibit Nitrospira for a long time. Compared with the Anammox functional gene hzsA, another gene hzo encoding N2H4 oxidoreductase in Anammox, could be detected even at low values in the first two stages. Besides, the abundance of hzo was an order of magnitude higher than hzsA in stage III. Although the Anammox activity did not change much in Stage III, its functional genes’ abundances declined due to the adaption of Anammox to the new micro-aeration environment.
3.4. Evolution in Microbial Communities
High-throughput sequencing results revealed high microbial diversity in the SBR (Figure 5). The diversity indexes of the microbial community concerned in this study was shown in Table S6. All of the samples showed better heterogeneity for the higher Shannon index. Based on the OUT number and chao index, the microbe species in first two stages were higher than Stage III. This is probably caused by the inoculation of anammox sludge and the following stable operation of CPNA. The most abundant phyla in the CPNA system were Proteobacteria, Chloroflexi, Armatimonadetes, Acidobacteria, Firmicutes and Planctomycetes, respectively. Microbial community analysis at the genus level helped speculate the community function. Despite no COD introduction from influent, heterotrophs constituted to a small percentage of microorganisms in CPNA reactor, especially in the first two stages (Figure 5). The microbes in WWTP was their origin. Over time, these heterotrophs could utilize the soluble microbial products (SMP) excreted by bacteria or the dead cells for growth. It was reported that unclassified_Anaerolineaceae, which belonged to Chloroflexi phylum, could utilize glucose and N-acetylglucosamine (a main component of cell wall peptidoglycan of most bacteria) from autotrophs [32,40,41]. It was also reported to utilize SMP and the nitrate produced by Candidate Kuenenia (Ca. Kuenenia), to form the biomass framework and to serve as the cellular micro-aggregate carriers [32,42]. Therefore, the presence of heterotrophs could effectively prevent the accumulation of SMP and cell decay substances released by autotrophic bacteria such as nitrifying bacteria and anammox bacteria [40]. Povalibacter, Dokdonella, unclassified_Rhodobacteraceae and Aridibacter were the most abundant genera in the reactor (Figure 4). All these bacteria are heterotrophs, which were capable of utilizing complex carbon sources like PAHs and PCB. Dokdonella was responsible for nitrite transformation in a simultaneous anammox and denitrification system [41]. Besides, the genus of Truepera, Trichococcus, Armatimonadetes_gp5, Terrimonas are capable of heterotrophic denitrification [41,43,44]. They may also contribute to the nitrogen removal of CPNA reactor through the pathway of nitrite or nitrate reduction. In addition, heterotrophs could also facilitate maintaining sludge integrity, because several genus of filamentous Chloroflexi could serve as carrier of micro-aggregates of cells and form the framework of granular sludge [42].
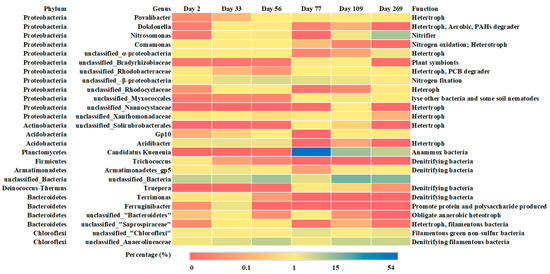
Figure 5.
Heatmap of the core genera in the sludge samples on various days.
The genus of Caldilinea in Chloroflexi phylum, which was also filamentous bacteria, showed a higher relative abundance (0.86% on day 2) in Stage I, indicating the contribution of filamentous bacteria on SVI increase. The relative abundance of family of unclassified_Saprospiraceae in phylum Bacteroidetes from Day 2 to Day 33 increased from zero to 2%. The SVI during this period increased from 56.91 to 63.78 mL/g, while the MLSS declined from 7.73 to 3.14 g/L. The study by Xu et al. showed that the unclassified_Saprospiraceae could adhere to Chloroflexi and cause sludge bulking [45]. The sludge loss could be the results of filamentous unclassified_Saprospiraceae increase. The relative abundance of filamentous bacteria Type 0803 in phylum Chloroflexi in Stage II was 0.64%, which was much higher than in Stage I (0.09%). Furthermore, the relative abundance of Caldilinea was 0.64% and 0.56% on day 33 and 56 in Stage II, respectively. Both showed effects of filamentous bacteria on SVI increase. In Stage III, the relative abundance of unclassified_Saprospiraceae was decreased, meaning the alleviation of sludge bulking caused by this kind of filamentous bacteria. The relative abundance of unclassified_Anaerolineaceae in Stage III was increased to around 20% (Figure 5). As the carrier of micro-aggregates of cells, this could be the main reasons for the stable sludge particle size from day 176 to day 272 (Figure 3c).
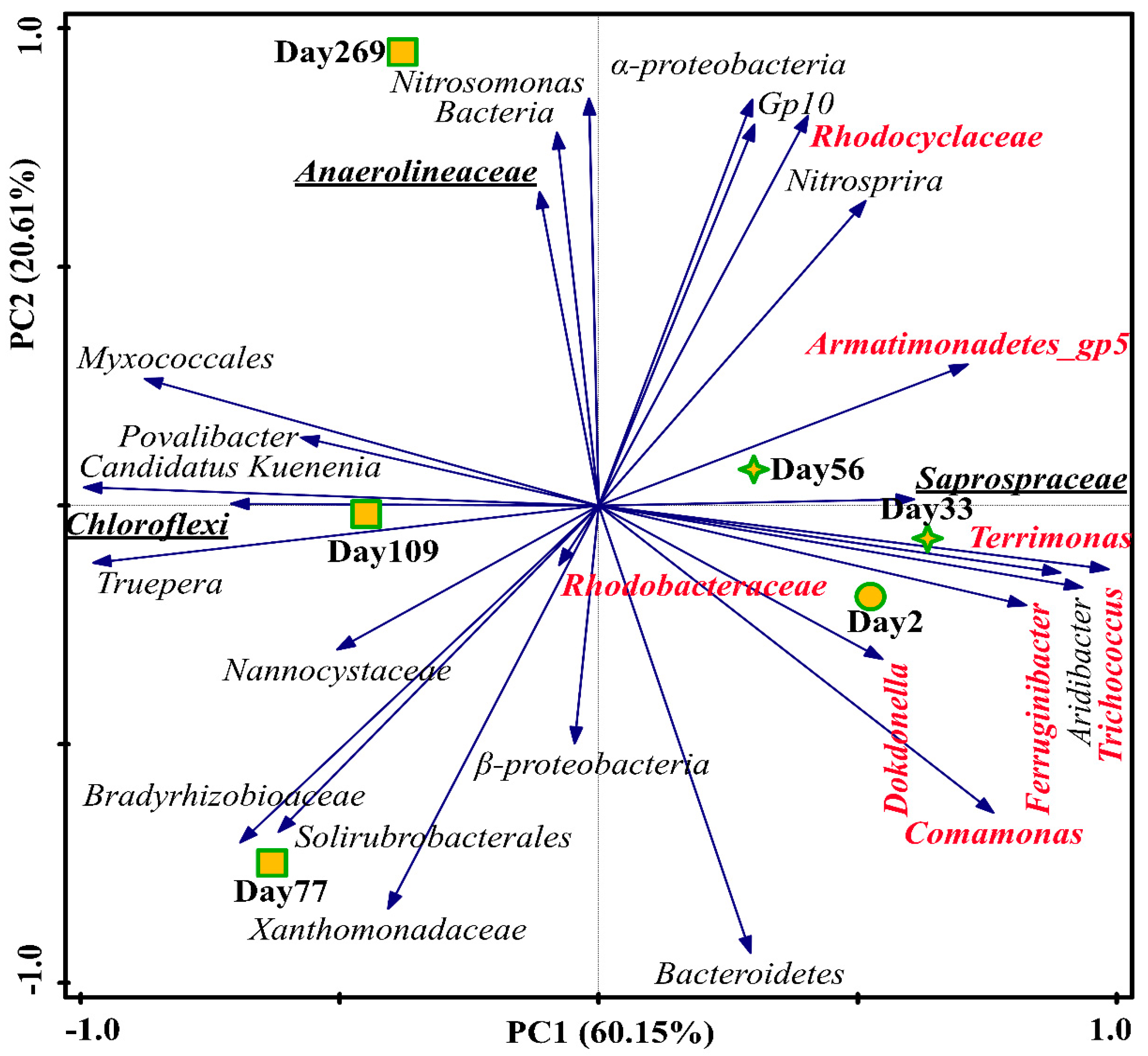
PCA based on the dominant genera in each sample is shown in Figure 6. From day 2 to 272, Nitrosomonas become more abundant with the shift of control mode from intermittent aeration to continuous aeration. Candidatus Kuenenia was remarkably high on day 77, while it decreased due to the environment adaption as mentioned above. The shifts of functional bacteria (AOB and Anammox) were consistent with the changes in functional genes. The microbial communities in the samples on day 2, day 33 and day 56 were close and greatly different from the samples on day 77–269. Samples in the first two stages were closely distributed in the PCA plot, with high abundance of denitrifying bacteria including Armatimonadetes_gp5, Comamonas, Terrimonas, Ferruginibacter, Trichococcus and Rhodocyclaceae, which evidenced the previous stating that the TNRE in Stage II was mainly caused by denitrification. The main functions of the dominant genera in the CPNA process are listed in Table S7. Trichococcus and Saprospiraceae were filamentous bacteria, which could cause sludge bulking [45,46]. In Stage III, filamentous bacteria Anaerolineaceae in phylum of Chloroflexi was highly abundant on Day 269, which supported the observation in the SEM image in Figure S3i. In the end, the dominant bacteria in the CPNA were AOB and Anammox. Meantime, several heterotrophs (Myxococcales) and filamentous bacteria (Anaerolineaceae) were also present in the system.
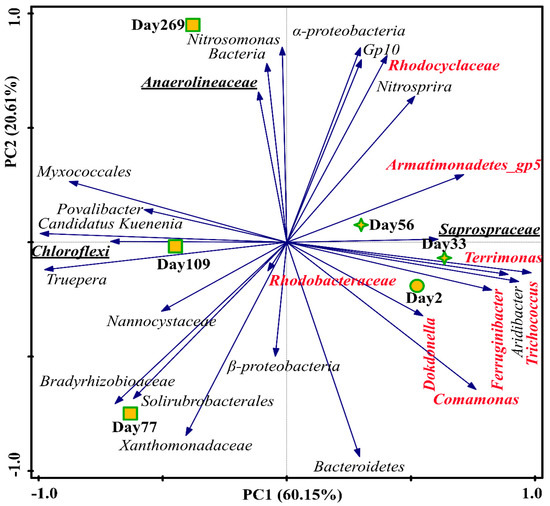
Figure 6.
Microbial communities for the three stages based on the top 10 abundant genera in each sample (species marked in red represents denitrifying bacteria; bold underlined species represents filamentous bacteria).
3.5. The Analysis of NH2OH’s Effect and Possible Sludge Loss Reasons in the CPNA System
In our previous study, the in-situ recovery was successfully achieved from the deteriorated CPNA system caused by nitrate build-up through NH2OH addition [13]. In this study, the nitrate build-up in the long-term operation of the CPNA system was avoided by SBR operational procedure adjustment through adding the anoxic stirring phase between feeding and aeration, which was simple and easy compared to DO or FAN control. In the anoxic phase, denitrifiers in the inocula could utilize the influent low COD from real wastewater or the dead cells as electron donor, and the remained nitrate in the system as the electron acceptor, to remove both organic matters and nitrate simultaneously through denitrification process. Interestingly, the adjustment of SBR procedure also helped to maintain several beneficial filamentous bacteria like unclassified_Anaerolineaceae which could act as sludge framework to keep stable biomass morphology, preventing sludge loss. Compared to normal measurements to control sludge loss such as chemicals addition, biomass acclimatization or equipment upgrading, this method was simple, cost-effective, and thus more competent.
NH2OH addition could increase SVI by inhibiting NOB activity and affect the relative abundance of filamentous bacteria which could act as the sludge framework, resulting in the decrease of sludge morphology stability, particle size and settling property. Besides, it could also help accelerate the process of PN as was shown in Figure 2. The accumulated nitrate could serve as denitrification substrate for filamentous bacteria, which utilized cell decay materials produced by autotrophs. So, the increase of filamentous bacteria caused sludge settling problems, and finally led to biomass loss. Besides, the adaption of autotrophic anammox to the microaeration environment in the first few days of Stage III could also cause sludge loss. The effects of NH2OH addition and possible reasons for sludge loss in the nitrogen removal system was plotted in Figure S3. Several optional methods to control sludge loss in CPNA system are to promote the growth of microorganisms that can act as the sludge framework, do not add toxic chemicals like hydroxylamine, adjust the operation process and control the mechanical action (aeration, agitation).
4. Conclusions
A start-up of PN, its transition to anammox and the stable operation of CPNA process were studied in an SBR. The 2 mg/L NH2OH addition contribute to the fast start-up of PN under low DO conditions for its inhibition effects on Nitrospira and the enhancement of AOB activity. The TNRE in the stage of PN transition to anammox was mainly contributed by denitrification, indicating the transition could hardly succeed within 70 days through DO concentration and aeration period adjustments. The adding of anoxic period to the SBR operationes caused a relatively low NOB abundance during the stable operation of CPNA, which was less than 1.6%. The introduction of anoxic stirring after feeding during the operational procedure of CPNA could be favorable for controlling both nitrate build-up and sludge loss, making it a practical option for stable operation of engineered CPNA plants.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9717/8/9/1053/s1, Figure S1: The intermittent aeration (t-NH4+-N) control mode (a) and the continuous aeration (DO-NH4+-N) control mode (b) of the SBR operation; Figure S2: The activities of nitrogen conversion functional bacteria; Figure S3: Observation of SEM images of the SBR biomass on day 2 (a), day 16 (b), day 29 (c), day 56 (d), day 77 (e), day 113 (f), day 136 (g), day 200 (h), day 269 (i); Figure S4: Main nitrogen process in CPNA system, of which the ones considered in this study and their common corresponding functional genes are shown in blue and red, respectively; Figure S5: The effects of NH2OH addition and possible reasons for sludge loss; Table S1 Compositions of the synthetic wastewater; Table S2 The diversity indexes of microbial community concerned in this study; Table S3 Primers of determined genes and their corresponding annealing temperature and mechanisms; Table S4 The detailed information of q-PCR for each target gene; Table S5 The particle size results of activated sludge in different stages; Table S6 The diversity indexes of microbial community concerned in this study; Table S7 The main functions of the dominant genera in CPNA process.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—Original Draft, H.W.; methodology, Y.W. (Yuanyue Wang); revision, J.Z.; resources, Q.S.; resources, D.H.; resources, F.Z.; conceptualization, supervision, writing—review and editing, Y.W. (Yuansong Wei). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to acknowledge the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment of China (2017ZX07102; 2017ZX07102-003) and Key Research and Development Program of Jiangxi Province (20171ACG70018). Program of China-Sri Lanka Joint Center for Water Technology Research and Demonstration by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS); China-Sri Lanka Joint Center for Education and Research by the CAS.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lackner, S.; Gilbert, E.M.; Vlaeminck, S.E.; Joss, A.; Horn, H.; van Loosdrecht, M.C. Full-scale partial nitritation/anammox experiences-an application survey. Water Res. 2014, 55, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speth, D.R.; In’t Zandt, M.H.; Guerrero-Cruz, S.; Dutilh, B.E.; Jetten, M.S. Genome-based microbial ecology of anammox granules in a full-scale wastewater treatment system. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jardin, N.; Hennerkes, J. Full-scale experience with the deammonification process to treat high strength sludge water—A case study. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wett, B. Solved upscaling problems for implementing deammonification of rejection water. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.C.; Gao, D.W.; Tao, Y. Anammox start-up in sequencing batch biofilm reactors using different inoculating sludge. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 6057–6064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Urata, K.; Wei, Q.; Yamashita, Y.; Hama, T.; Kawagoshi, Y. Fast start-up of partial nitritation as pre-treatment for anammox in membrane bioreactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 105, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, R.; Sheng, X.; Chen, L.; Wu, G.; Hu, H.; Zhan, X. Start up of partial nitritation-anammox process using intermittently aerated sequencing batch reactor: Performance and microbial community dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xu, X.; Yang, F.; Liu, S.; Gao, Y. Partial nitrification adjusted by hydroxylamine in aerobic granules under high DO and ambient temperature and subsequent Anammox for low C/N wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 213, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Lin, J.; Peng, Y. Hydroxylamine addition and real-time aeration control in sewage nitritation system for reduced start-up period and improved process stability. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 294, 122183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yang, D. Evaluating the feasibility of ratio control strategy for achieving partial nitritation in a continuous floccular sludge reactor: Experimental demonstration. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokutomi, T.; Shibayama, C.; Soda, S.; Ike, M. A novel control method for nitritation: The domination of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria by high concentrations of inorganic carbon in an airlift-fluidized bed reactor. Water Res. 2010, 44, 4195–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Star, W.R.; van de Graaf, M.J.; Kartal, B.; Picioreanu, C.; Jetten, M.S.; van Loosdrecht, M.C. Response of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria to hydroxylamine. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2008, 74, 4417–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Chen, M. In-situ restoring nitrogen removal for the combined partial nitritation-anammox process deteriorated by nitrate build-up. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 98, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joss, A.; Salzgeber, D.; Eugster, J.; Konig, R.; Rottermann, K.; Burger, S.; Fabijan, P.; Leumann, S.; Mohn, J.; Siegrist, H.; et al. Full-scale nitrogen removal from digester liquid with partial nitritation and anammox in one SBR. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5301–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joss, A.; Derlon, N.; Cyprien, C.; Burger, S.; Szivak, I.; Traber, J.; Siegrist, H.; Morgenroth, E. Combined nitritation-anammox: Advances in understanding process stability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9735–9742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.M.; Pagilla, K.; Heijnen, J.J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C. Filamentous bulking sludge—A critical review. Water Res. 2004, 38, 793–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yao, L.; Wei, Y.S. Deciphering the evolution of the functional genes and microbial community of the combined partial nitritation-anammox process with nitrate build-up and its in situ restoration. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 111702–111712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongtao, L.V.; Xuan, C.; Wang, L.; Kai, J.; Xiaoqiang, C.; Rui, M.; Xudong, W. Microprofiles of activated sludge aggregates using microelectrodes in completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite (CANON) reactor. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Y. Stratification of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) for aggregated anammox microorganisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3260–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yue, W.; Chen, Y.; Yu, D.; Chen, M.; Wei, Y. Roles of hydroxylamine and hydrazine in the in-situ recovery of one-stage partial nitritation-anammox process: Characteristics and mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Lu, T.; Shen, P.; Zhong, H.; Tong, J.; Wei, Y. Fate of antibiotic resistance genes during anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge: Role of solids retention times in different configurations. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 274, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/nmeth.f.303#supplementary-information (accessed on 11 April 2010). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, A.; Clesceri, L.S.; Greenberg, A.E.; Franson, M.H. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lotti, T.; Kleerebezem, R.; Lubello, C.; van Loosdrecht, M.C. Physiological and kinetic characterization of a suspended cell anammox culture. Water Res. 2014, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliekers, A.O.; Derwort, N.; Gomez, J.L.C.; Strous, M.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S.M. Completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite in one single reactor. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2475–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, W.F., Jr.; Terada, A.; Poly, F.; le Roux, X.; Kristensen, K.; Mazher, M.; Smets, B.F. The effect of hydroxylamine on the activity and aggregate structure of autotrophic nitrifying bioreactor cultures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 102, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriet, O.; Meunier, C.; Henry, P.; Mahillon, J. Filamentous bulking caused by Thiothrix species is efficiently controlled in full-scale wastewater treatment plants by implementing a sludge densification strategy. Sci. Rep. UK 2017, 7, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, X. Achieving nitrogen removal via nitrite in a pilot-scale continuous pre-denitrification plant. Water Res. 2009, 43, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Peng, Y. Microbial community evolution in partial nitritation/anammox process: From sidestream to mainstream. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 251, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.D.; Heijnen, J.J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Model-based evaluation of temperature and inflow variations on a partial nitrification-ANAMMOX biofilm process. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4839–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaeminck, S.E.; Terada, A.; Smets, B.F.; de Clippeleir, H.; Schaubroeck, T.; Bolca, S.; Demeestere, L.; Mast, J.; Boon, N.; Carballa, M.; et al. Aggregate size and architecture determine microbial activity balance for one-stage partial nitritation and anammox. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2010, 76, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, E.M.; Muller, E.; Horn, H.; Lackner, S. Microbial activity of suspended biomass from a nitritation-anammox SBR in dependence of operational condition and size fraction. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 8795–8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Cho, S.; Jung, J. Key operating parameters affecting nitrogen removal rate in single-stage deammonification. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.R.; Du, B.; Fu, H.X.; Wang, R.F.; Shi, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Quan, Z.X. The bacterial diversity in an anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) reactor community. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 32, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, T.R.; Kjellerup, B.V.; Nielsen, J.L.; Hugenholtz, P.; Nielsen, P.H. In situ studies of the phylogeny and physiology of filamentous bacteria with attached growth. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 4, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, M.H.; Boets, P.; Hahne, B.; Goethals, P.; Volcke, E.I. Effect of the dilution rate on microbial competition: R-strategist can win over k-strategist at low substrate concentration. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindaichi, T.; Yuri, S.; Ozaki, N.; Ohashi, A. Ecophysiological role and function of uncultured Chloroflexi in an anammox reactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, T.; Huang, K.; He, X.; Zhang, X.X. Roles and correlations of functional bacteria and genes in the start-up of simultaneous anammox and denitrification system for enhanced nitrogen removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroline, K.; Rolighed, T.T.; Tomasz, M.A.; Halkjær, N.P. Eikelboom’s morphotype 0803 in activated sludge belongs to the genus Caldilinea in the phylum Chloroflexi. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 3, 451–462. [Google Scholar]
- Mielcarek, A.; Rodziewicz, J.; Janczukowicz, W.; Dulski, T.; Ciesielski, S.; Thornton, A. Denitrification aided by waste beer in anaerobic sequencing batch biofilm reactor (AnSBBR). Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.; Guo, J.; Jing, L.; Ngo, H.H.; Yin, P. Effect of fluctuating hydraulic retention time (HRT) on denitrification in the UASB reactors. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 132, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yao, J.; Ainiwaer, M.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of bacterial community structure of activated sludge from wastewater treatment plants in winter. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8278970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheff, G.; Salcher, O.; Lingens, F. Trichococcus flocculiformis gen. nov. sp. nov. A new gram-positive filamentous bacterium isolated from bulking sludge. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1984, 19, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).