Blended Sewage Sludge–Palm Kernel Expeller to Enhance the Palatability of Black Soldier Fly Larvae for Biodiesel Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
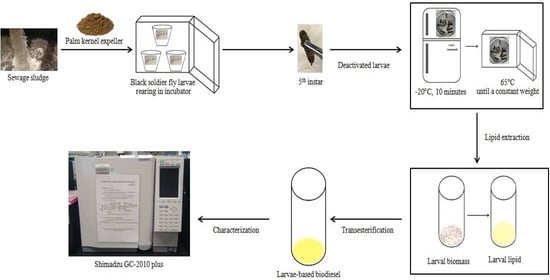
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Blended Substrates
2.2. Experimental Set Up for BSFL Rearing
2.3. Lipid Extraction from BSFL Biomass
2.4. Transesterification of Larval Lipid into BSFL-Based Biodiesel
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Different Ratios of Blended Sewage Sludge on BSFL Growth
3.2. Effect of Different Ratios of Blended Sewage Sludge on BSFL Lipid Yield
3.3. BSFL-Based Biodiesel
3.4. Projection for Large-Scale Production of BSFL-Based Biodiesel
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Souza, M.C.G.; De Oliveira, M.F.; Vieira, A.T.; De Faria, A.M.; Batista, A.C.F. Methylic and ethylic biodiesel production from crambe oil (Crambe abyssinica): New aspects for yield and oxidative stability. Renew. Energy 2021, 163, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.C.; Taouil, D.S.G. Biodiesel: Uma energia alternativa e verde. Vértices 2010, 12, 17–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Sources and Solutions: Fossil Fuels. 4 February 2019. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/nutrientpollution/sources-and-solutions-fossil-fuels (accessed on 13 December 2020).
- Production Statistics. 5 November 2018. Available online: https://www.biodiesel.org/production/production-statistics (accessed on 20 September 2020).
- World Biodiesel Consumption by Country. 6 March 2009. Available online: https://www.indexmundi.com/energy/?product=biodiesel&graph=consumption&display=rank (accessed on 20 September 2020).
- Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Pandey, A. Biological pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass—An overview. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Prakash, A.; Balagurumurthy, B.; Bhaskar, T. Hydrothermal Liquefaction of Biomass. In Recent Advances in Thermo-Chemical Conversion of Biomass; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 269–291. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Yang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Nie, Q.; Xian, M. Biodiesel production from oleaginous microorganisms. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd-Noor, S.-N.; Wong, C.-Y.; Wong, K.C.; Mah-Hussin, M.-I.-A.; Uemura, Y.; Lam, M.-K.; Ramli, A.; Bashir, M.J.; Tham, L. Optimization of self-fermented period of waste coconut endosperm destined to feed black soldier fly larvae in enhancing the lipid and protein yields. Renew. Energy 2017, 111, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Rehman, K.U.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, L.; Li, W.; Cai, M.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z. Insect biorefinery: A green approach for conversion of crop residues into biodiesel and protein. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Zheng, L.; Hou, Y.; Yang, S.; Yu, Z. Insect fat, a promising resource for biodiesel. J. Pet. Environl. Biotechnol. 2011, 2, 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Sun, J.; Konda, N.V.S.N.M.; Shi, J.; Dutta, T.; Scown, C.D.; Simmons, B.A.; Singh, S. Transforming biomass conversion with ionic liquids: Process intensification and the development of a high-gravity, one-pot process for the production of cellulosic ethanol. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 9, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abduh, M.Y.; Manurung, R.; Faustina, A.; Affanda, E.; Siregar, I.R.H. Bioconversion of pandanus tectorius using black soldier fly larvae for the production of edible oil and protein-rich biomass. J. Entomol. Zool Stud. 2017, 5, 803–809. [Google Scholar]
- Shumo, M.; Osuga, I.M.; Khamis, F.M.; Tanga, C.M.; Fiaboe, K.K.M.; Subramanian, S.; Ekesi, S.; Van Huis, A.; Borgemeister, C. The nutritive value of black soldier fly larvae reared on common organic waste streams in Kenya. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinasih, I.; Putra, R.E.; Permana, A.D.; Gusmara, F.F.; Nurhadi, M.Y.; Anitasari, R.A. Growth performance of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) fed on some plant based organic wastes. Hayati 2018, 25, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Spranghers, T.; Ottoboni, M.; Klootwijk, C.; Ovyn, A.; Deboosere, S.; De Meulenaer, B.; Michiels, J.; Eeckhout, M.; De Clercq, P.; De Smet, S. Nutritional composition of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) prepupae reared on different organic waste substrates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2594–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalander, C.; Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C.; Vinnerås, B. Effects of feedstock on larval development and process efficiency in waste treatment with black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens). J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano-Agugliaro, F.; Sánchez-Muros, M.J.; Barroso, F.G.; Sánchez, A.I.M.; Pérez-Ben, C.; Pérez-Bañòn, C. Insects for biodiesel production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 3744–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, Q.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Z. Conversion of Solid Organic Wastes into Oil via Boettcherisca peregrine (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) Larvae and Optimization of Parameters for Biodiesel Production. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.; Yang, D.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhu, L. Biodiesel from Zophobas morio Larva Oil: Process Optimization and FAME Characterization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 51, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, Z. Pilot-scale biodegradation of swine manure via Chrysomya megacephala (Fabricius) for biodiesel production. Appl. Energy 2014, 113, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowling, J.J.; Anderson, J.B.; Armbrust, K.L.; Hamann, M.T. Evaluation of potential biodiesel feedstock production from oleaginous insect Solenopsis sp. Fuel 2014, 117, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Hou, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, S.; Li, Q.; Yu, Z. Exploring the potential of grease from yellow mealworm beetle (Tenebrio molitor) as a novel biodiesel feedstock. Appl. Energy 2013, 101, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, Q.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Z. Biodiesel production from swine manure via housefly larvae (Musca domestica L.). Renew. Energy 2014, 66, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zheng, L.; Cai, H.; Garza, E.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, S. From organic waste to biodiesel: Black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens, makes it feasible. Fuel 2011, 90, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Tomberlin, J.K.; VanLaerhoven, S. Influence of Resources on Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larval Development. J. Med. Èntomol. 2013, 50, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diener, S.; Lalander, C.; Zurbrügg, C.; Vinnerås, B. In Opportunities and constraints for medium-scale organic waste treatment with fly larvae composting. In Proceedings of the 15th International Waste Management and Landfill Symposium, Cagliari, Sardinia, Italy, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Caruso, D.; Devic, E.; Subamia, I.; Talamond, P.; Baras, E. Technical Handbook of Domestication and Production of Diptera Black Soldier Fly (bsf), Hermetia illucens, Stratiomyidae; PT Penerbit IPB Press, Kampus IPB Taman Kencana: Bogor, Indonesia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ushakova, N.A.; Brodskii, E.S.; Kovalenko, A.A.; Bastrakov, A.I.; Kozlova, A.A.; Pavlov, D.S. Characteristics of lipid fractions of larvae of the black soldier fly Hermetia illucens. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 468, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Chen, J.-H.; Luo, Y.-M. Complementary biodiesel combination from Tung and medium-chain fatty acid oils. Renew. Energy 2012, 44, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, S.Y.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Malakahmad, A.; Tan, C.K. Feasibility study of biodiesel production using lipids of Hermetia illucens larva fed with organic waste. Waste Manag. 2016, 47, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanum, F.; Yuan, L.C.; Kamahara, H.; Aziz, H.A.; Atsuta, Y.; Yamada, T.; Daimon, H. Treatment of Sewage Sludge Using Anaerobic Digestion in Malaysia: Current State and Challenges. Front. Energy Res. 2019, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.; Agrawal, M. Potential benefits and risks of land application of sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, S.; Tor, A.; Aydin, M.E. Investigation on the Levels of Heavy Metals, Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, and Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Sewage Sludge Samples and Ecotoxicological Testing. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2013, 41, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.-Q.; Wang, D.-F. Immobilization of Heavy Metals in Sewage Sludge during Land Application Process in China: A Review. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fytili, D.; Zabaniotou, A. Utilization of sewage sludge in EU application of old and new methods—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, R.; Green, T.R. Using black soldier fly larvae for processing organic leachates. J. Econ. Èntomol. 2012, 105, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, S.; Zurbrugg, C.; Tockner, K. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens and effects on its life cycle. J. Insects Food Feed. 2015, 1, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gold, M.; Cassar, C.M.; Zurbrügg, C.; Kreuzer, M.; Boulos, S.; Diener, S.; Mathys, A. Biowaste treatment with black soldier fly larvae: Increasing performance through the formulation of biowastes based on protein and carbohydrates. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.Y.; Aris, M.N.M.; Daud, H.; Lam, M.K.; Yong, C.S.; Abu Hasan, H.; Siewhui, C.; Show, P.L.; Hajoeningtijas, O.D.; Ho, Y.-C.; et al. In-Situ Yeast Fermentation to Enhance Bioconversion of Coconut Endosperm Waste into Larval Biomass of Hermetia illucens: Statistical Augmentation of Larval Lipid Content. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, G.-P.; Yu, H.-Q.; Li, X.-Y. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.C.; Mohd-Noor, S.-N.; Wong, C.-Y.; Lam, M.-K.; Goh, P.-S.; Beniers, J.; Da Oh, W.; Jumbri, K.; Ghani, N.A. Palatability of black soldier fly larvae in valorizing mixed waste coconut endosperm and soybean curd residue into larval lipid and protein sources. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.; Khalid, A.; Mahmood, T.; Aziz, I. Anaerobic co-digestion of catering waste with partially pretreated lignocellulosic crop residues. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 117, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Lar, J.S.; He, Y.; Zhu, B. Anaerobic Codigestion of Kitchen Waste with Cattle Manure for Biogas Production. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 2225–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siew, W. Characteristics and uses of Malaysian palm kernel cake. PORIM Technol. 1989, 14, 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- Tschirner, M.; Simon, A. Influence of different growing substrates and processing on the nutrient composition of black soldier fly larvae destined for animal feed. J. Insects Food Feed. 2015, 1, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, R. Biochemie und stoffwechsel. In Lehrbuch der Entomologie; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 75–89. [Google Scholar]
- Sue, T.T. Quality and characteristics of Malaysian palm kernel cakes/expellers. Palm Oil Dev. 2004, 34, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Brouwer, E. Report of sub-committee on constants and factors. In Proceedings of the 3rd Symposium on Energy Metabolism of Farm Animals; European Association for Animal Production: Rome, Italy; Academic Press: London, UK, 1965; pp. 441–443. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, F.N. Supplementation of Palm Kernel Expeller to Grazing Dairy Farms in New Zealand: A Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Animal Science at Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand. Ph.D. Thesis, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Palmquist, D.L. Use of fats in diets for lactating dairy cows. In Proceedings of the Fats in Animal Nutrition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 357–381. [Google Scholar]
- Supriyatna, A.; Manurung, R.; Esyanti, R.R.; Putra, R.E. Growth of black soldier larvae fed on cassava peel wastes, an agriculture waste. J. Entomol. Zool Stud. 2016, 4, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Nijhout, H.F. Physiological Control of Molting in Insects. Am. Zool. 1981, 21, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhout, H.F.; Williams, C.M. Control of moulting and metamorphosis in the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta (L.): Growth of the last-instar larva and the decision to pupate. J. Exp. Biol. 1974, 61, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Riddiford, L.M.; Truman, J.W. Hormone Receptors and the Regulation of Insect Metamorphosis. Am. Zool. 1993, 33, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, Y.J.; Koyama, T.; Hiruma, K.; Riddiford, L.M.; Truman, J.W. A molt timer is involved in the metamorphic molt in Manduca sexta larvae. Proc. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12518–12525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bennett, G. Is There a Specific Appetite for Protein? CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bentancourt, C.M.; Scatoni, I.B.; González, Á; Franco, J. Effects of larval diet on the development and reproduction of Argyrotaenia sphaleropa (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Neotrop. Èntomol. 2003, 32, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Wyngaard, J.; Meeske, R. Palm kernel expeller increases milk fat content when fed to grazing dairy cows. South Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 47, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danieli, P.P.; Lussiana, C.; Gasco, L.; Amici, A.; Ronchi, B. The Effects of Diet Formulation on the Yield, Proximate Composition, and Fatty Acid Profile of the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.) Prepupae Intended for Animal Feed. Animals 2019, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos, M.J.; Fernández, C.M.; Casas, A.; Rodríguez, L.; Pérez, Á. Influence of fatty acid composition of raw materials on biodiesel properties. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendra, K.; Olivier, R.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Jha, R.; Khanal, S.K. Bioconversion of organic wastes into biodiesel and animal feed via insect farming. Renew. Energy 2016, 98, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ewald, N.; Vidakovic, A.; Langeland, M.; Kiessling, A.; Sampels, S.; Lalander, C. Fatty acid composition of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens)—Possibilities and limitations for modification through diet. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, S.; Aziz, A.A.; Aroua, M.K. Reactive extraction of solid coconut waste to produce biodiesel. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013, 44, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biodiesel Fuel Quality. 3 April 2019. Available online: https://farm-energy.extension.org/biodiesel-fuel-quality/#:~:text=Biodiesel%20usually%20has%20a%20higher,than%20biodiesel%20from%20unsaturated%20oil (accessed on 13 December 2020).
- Tesfamariam, E.H.; Ogbazghi, Z.M.; Annandale, J.G.; Gebrehiwot, Y. Cost–Benefit Analysis of Municipal Sludge as a Low-Grade Nutrient Source: A Case Study from South Africa. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobelak, A.; Czerwińska, K.; Murtaś, A. General considerations on sludge disposal, industrial and municipal sludge. Ind. Munic. Sludge 2019, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.-D.; Shie, J.-L.; Chang, C.-Y.; Huang, S.-H.; Pai, C.-Y.; Yu, Y.-H.; Chang, C.H. Economic Cost Analysis of Biodiesel Production: Case in Soybean Oil. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulqarnain; Yusoff, M.H.M.; Ayoub, M.; Jusoh, N.; Abdullah, A.Z. The Challenges of a Biodiesel Implementation Program in Malaysia. Processes 2020, 8, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, M.N.A.M.; Zulkifli, N.W.M.; Sukiman, N.L.; Chyuan, O.H.; Hassan, M.H.; Hasnul, M.H.; Zulkifli, M.S.A.; Abbas, M.M.; Zakaria, M.Z. Sustainability of Palm Biodiesel in Transportation: A Review on Biofuel Standard, Policy and International Collaboration between Malaysia and Colombia. Bioenergy Res. 2020, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, O.T. Cheaper to Use Biodiesel Now. 31 October 2018. Available online: https://www.nst.com.my/business/2018/10/426997/cheaper-use-biodiesel-now (accessed on 22 January 2021).
- Özçimen, D.; Yucel, S. Novel methods in biodiesel production. Marco Aurélio Santos Bernardes Biofuel’s Eng. Process Technol. 2011, 1, 353–384. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, J. Costs of biodiesel production. Energy Effic. Conserv. Auth. 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Moradi-Kheibari, N.; Ahmadzadeh, H.; Talebi, A.F.; Hosseini, M.; Murry, M.A. Recent Advances in Lipid Extraction for Biodiesel Production. In Advances in Feedstock Conversion Technologies for Alternative Fuels and Bioproducts; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 179–198. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; He, B.; Thompson, J.; Van Gerpen, J. Process optimization of biodiesel production using alkaline catalysts. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2006, 22, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Blended Sewage Sludge Medium | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | G5 | Control | |
| Overall degradation (%) | 73.34 ± 5.41 | 67.39 ± 2.68 | 62.45 ± 4.31 | 75.91 ± 3.30 | 84.85 ± 3.03 | 85.74 ± 0.20 |
| Waste reduction index (g/d) | 0.54 ± 0.04 | 0.61 ± 0.02 | 0.83 ± 0.06 | 1.08 ± 0.05 | 1.31 ± 0.05 | 1.32 ± 0.00 |
| Efficiency of conversion of digested feed (%) | 1.14 ± 0.32 | 1.94 ± 0.23 | 2.71 ± 1.20 | 5.11 ± 0.22 | 3.65 ± 0.13 | 4.26 ± 0.29 |
| FAMEs | Blended Sewage Sludge | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | G5 | Control | |
| C10:0 | 0.86 | 5.56 | 4.48 | 18.90 | 16.35 | 5.73 |
| C12:0 | 19.56 | 24.28 | 53.36 | 21.37 | 7.91 | 16.92 |
| C14:0 | 10.26 | 16.35 | 12.52 | 6.62 | 16.06 | 11.01 |
| C14:1 | 8.93 | 7.18 | 2.79 | 14.15 | 7.85 | 16.11 |
| C16:0 | 15.34 | 10.24 | 9.89 | 16.13 | 11.93 | 5.28 |
| C16:1 | 12.83 | 1.37 | 4.40 | 6.26 | 5.24 | 5.46 |
| C18:0 | - | 2.56 | 1.23 | 8.67 | 5.82 | 10.30 |
| C18:1 | 24.37 | 20.29 | 9.22 | 5.0 | 18.56 | 11.91 |
| C18:2 | 7.86 | 12.17 | 2.11 | 2.89 | 10.30 | 17.28 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raksasat, R.; Kiatkittipong, K.; Kiatkittipong, W.; Wong, C.Y.; Lam, M.K.; Ho, Y.C.; Oh, W.D.; Suryawan, I.W.K.; Lim, J.W. Blended Sewage Sludge–Palm Kernel Expeller to Enhance the Palatability of Black Soldier Fly Larvae for Biodiesel Production. Processes 2021, 9, 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020297
Raksasat R, Kiatkittipong K, Kiatkittipong W, Wong CY, Lam MK, Ho YC, Oh WD, Suryawan IWK, Lim JW. Blended Sewage Sludge–Palm Kernel Expeller to Enhance the Palatability of Black Soldier Fly Larvae for Biodiesel Production. Processes. 2021; 9(2):297. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020297
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaksasat, Ratchaprapa, Kunlanan Kiatkittipong, Worapon Kiatkittipong, Chung Yiin Wong, Man Kee Lam, Yeek Chia Ho, Wen Da Oh, I Wayan Koko Suryawan, and Jun Wei Lim. 2021. "Blended Sewage Sludge–Palm Kernel Expeller to Enhance the Palatability of Black Soldier Fly Larvae for Biodiesel Production" Processes 9, no. 2: 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020297
APA StyleRaksasat, R., Kiatkittipong, K., Kiatkittipong, W., Wong, C. Y., Lam, M. K., Ho, Y. C., Oh, W. D., Suryawan, I. W. K., & Lim, J. W. (2021). Blended Sewage Sludge–Palm Kernel Expeller to Enhance the Palatability of Black Soldier Fly Larvae for Biodiesel Production. Processes, 9(2), 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020297