High Throughput Expression Screening of Arabinofuranosyltransferases from Mycobacteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. High-Throughput Cloning of Arabinofuranosyltransferase Genes
2.2. High-Throughput Expression Screening and Purification
2.3. Large Scale Protein Expression and Purification
3. Results
3.1. Genomic Expansion and High-Throughput Cloning of Arabinofuranosyltransferases
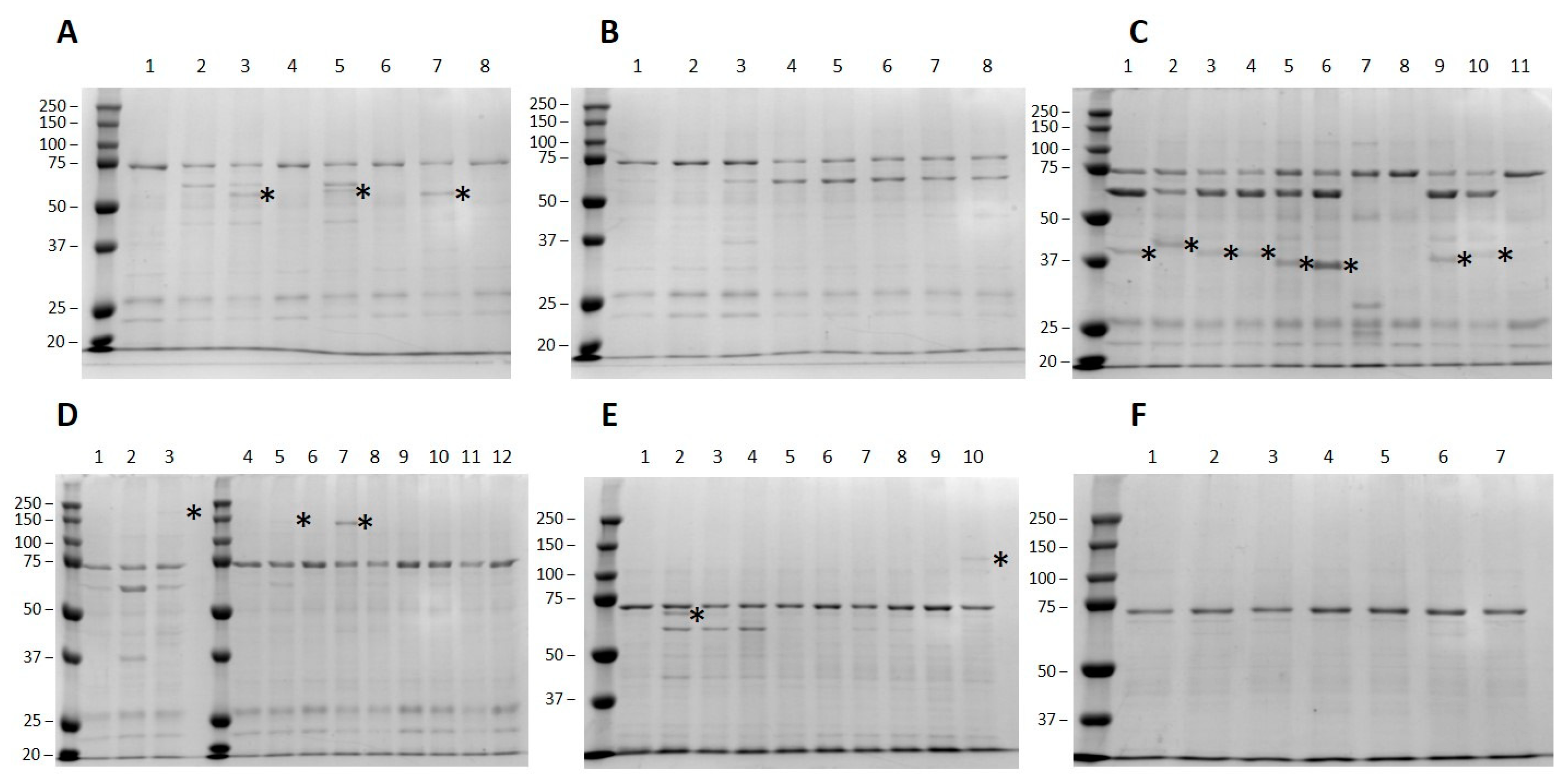
3.2. Small Scale High-Throughput Expression of Arabinofuranosyltransferases
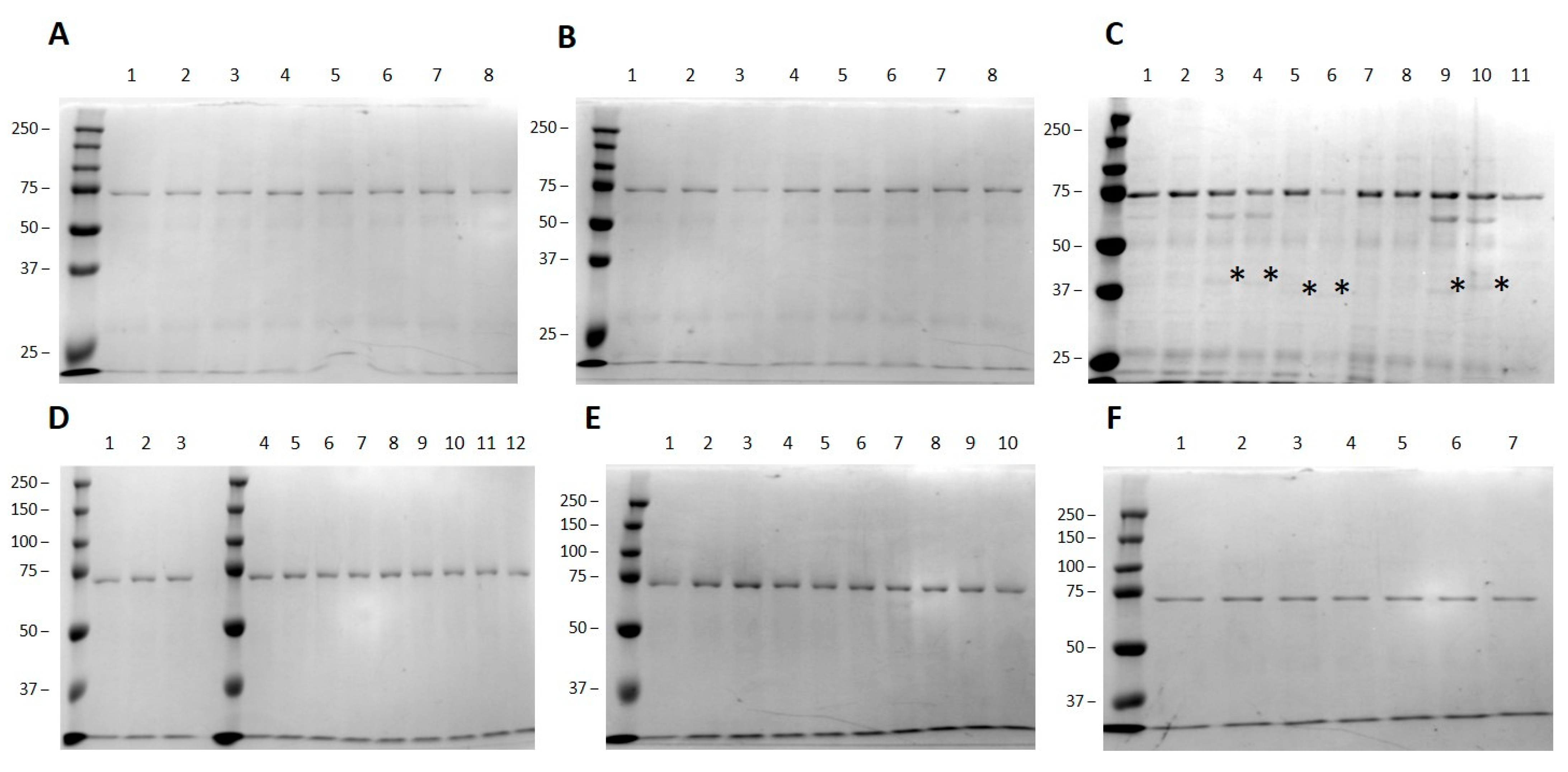
3.3. Validation of HTP Target Selection by Large-Scale Protein Production
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| ID | GenBank ID | Organism | Predicted Protein | C41 | C43 | BL21 (DE3) pLysS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | SIU02450.1 | Mycobacterium bovis AF2122/97 | AftA | − | − | − |
| A8 | EUA63955.1 | Mycobacterium abscessus 1948 | AftA | − | − | + |
| C2 | ABP43658.1 | Mycobacterium gilvum PYR-GCK | AftA | + | − | − |
| C9 | AFC41461.1 | Mycobacterium intracellulare ATCC 13950 | AftA | − | − | − |
| F1 | ABM16394.1 | Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1 | AftA | + | − | + |
| F3 | AGP61782.1 | Mycobacterium yongonense 05-1390 | AftA | − | − | − |
| F7 | CDQ43571.1 | Mycobacterium neoaurum | AftA | + | − | + |
| F8 | AAS02550.1 | Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis K-10 | AftA | − | − | − |
| A2 | SIU02464.1 | Mycobacterium bovis AF2122/97 | AftB | − | − | − |
| A9 | EUA63936.1 | Mycobacterium abscessus 1948 | AftB | − | − | − |
| C7 | CCP46634.1 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv | AftB | − | − | − |
| D9 | AGP61763.1 | Mycobacterium yongonense 05-1390 | AftB | − | − | − |
| D10 | AFC41442.1 | Mycobacterium intracellulare ATCC 13950 | AftB | − | − | − |
| D11 | ABM16411.1 | Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1 | AftB | − | − | − |
| E2 | AIR19061.1 * | Mycobacterium kansasii 662 | AftB | − | − | − |
| E5 | CDQ43590.1 | Mycobacterium neoaurum | AftB | − | − | − |
| A3 | AMC65006.1 | Mycobacterium bovis AF2122/97 | AftC | + | − | + |
| A10 | EUA61591.1 | Mycobacterium abscessus 1948 | AftC | + | − | − |
| C11 | AFC44620.1 | Mycobacterium intracellulare ATCC 13950 | AftC | + | + | − |
| C12 | AGZ53302.1 | Mycobacterium kansasii ATCC 12478 | AftC | + | + | − |
| D1 | ABP46386.1 | Mycobacterium gilvum PYR-GCK | AftC | + | + | + |
| D2 | CDQ43952.1 | Mycobacterium neoaurum | AftC | + | + | + |
| E6 | EHB50241.1 | Mycobacterium rhodesiae JS60 | AftC | − | − | − |
| E7 | AFM16967.1 | Mycobacterium chubuense NBB4 | AftC | − | − | − |
| E8 | AAS05110.1 | Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis K-10 | AftC | + | + | − |
| E9 | AGP64972.1 | Mycobacterium yongonense 05-1390 | AftC | + | + | − |
| F9 | ABM13300.1 | Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1 | AftC | − | − | − |
| A4 | CAB5247947.1 | Mycobacterium bovis AF2122/97 | AftD | − | − | − |
| D4 | AGZ51741.1 | Mycobacterium kansasii ATCC 12478 | AftD | − | − | − |
| H11 | EUA63217.1 | Mycobacterium abscessus 1948 F5/8 | AftD | + | − | + |
| A5 | SIU02452.1 | Mycobacterium bovis AF2122/97 | EmbA | − | − | − |
| A11 | EUA63951.1 | Mycobacterium abscessus 1948 | EmbA | + | − | − |
| B4 | AAC45280.1 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv | EmbA | − | − | − |
| B8 | ACC43760.1 | Mycobacterium marinum M | EmbA | + | − | − |
| C5 | ABP43656.1 | Mycobacterium gilvum PYR-GCK | EmbA | − | − | − |
| G5 | AAS02546.1 | Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis K-10 | EmbA | − | − | − |
| G11 | CDQ43576.1 | Mycobacterium neoaurum | EmbA | − | − | − |
| H1 | ABM16396.1 | Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1 | EmbA | − | − | − |
| H2 | AGZ51276.1 | Mycobacterium kansasii ATCC 12478 | EmbA | − | − | − |
| A6 | SIU02453.1 | Mycobacterium bovis AF2122/97 | EmbB | − | − | − |
| A12 | EUA63949.1 | Mycobacterium abscessus 1948 | EmbB | + | − | − |
| B3 | AAC45281.1 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv | EmbB | − | − | − |
| B7 | ACC43761.1 | Mycobacterium marinum M | EmbB | − | − | − |
| C4 | ABP43655.1 | Mycobacterium gilvum PYR-GCK | EmbB | − | − | − |
| G3 | AFC41455.1 | Mycobacterium intracellulare ATCC 13950 | EmbB | − | − | − |
| G6 | AAS02545.1 | Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis K-10 | EmbB | − | − | − |
| G9 | AGP61776.1 | Mycobacterium yongonense 05-1390 | EmbB | − | − | − |
| H7 | KEP38884.1 | Mycobacterium kansasii | EmbB | − | − | − |
| H9 | ABM16397.1 | Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1 | EmbB | + | − | + |
| B1 | EUA63954.1 | Mycobacterium abscessus 1948 | EmbC | − | − | − |
| C3 | ABP43657.1 | Mycobacterium gilvum PYR-GCK | EmbC | − | − | − |
| G4 | AFC41460.1 | Mycobacterium intracellulare ATCC 13950 | EmbC | − | − | − |
| G7 | AAS02549.1 | Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis K-10 | EmbC | − | − | − |
| G10 | AGP61781.1 | Mycobacterium yongonense 05-1390 | EmbC | − | − | − |
| H4 | CDQ43572.1 | Mycobacterium neoaurum | EmbC | − | − | − |
| H5 | AGZ51274.1 | Mycobacterium kansasii ATCC 12478 | EmbC | − | − | − |
| ID | GenBank ID | Organism | Predicted Protein | % Identity (M. tuberculosis) | Predicted Molecular Weight (kDa) | Predicted Transmembrane Helixes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | SIU02450.1 | Mycobacterium bovis AF2122/97 | AftA | 100 | 70 | 13 |
| A2 | SIU02464.1 | Mycobacterium bovis AF2122/97 | AftB | 99 | 69 | 9 |
| A3 | AMC65006.1 | Mycobacterium bovis AF2122/97 | AftC | 99 | 49 | 8 |
| A4 | CAB5247947.1 | Mycobacterium bovis AF2122/97 | AftD | 99 | 146 | 9 |
| A5 | SIU02452.1 | Mycobacterium bovis AF2122/97 | EmbA | 99 | 116 | 13 |
| A6 | SIU02453.1 | Mycobacterium bovis AF2122/97 | EmbB | 99 | 118 | 13 |
| A7 | SIU02451.1 | Mycobacterium bovis AF2122/97 | EmbC | 99 | 118 | 13 |
| A8 | EUA63955.1 | Mycobacterium abscessus 1948 | AftA | 65 | 68 | 13 |
| A9 | EUA63936.1 | Mycobacterium abscessus 1948 | AftB | 67 | 71 | 10 |
| A10 | EUA61591.1 | Mycobacterium abscessus 1948 | AftC | 64 | 47 | 8 |
| A11 | EUA63951.1 | Mycobacterium abscessus 1948 | EmbA | 65 | 114 | 12 |
| A12 | EUA63949.1 | Mycobacterium abscessus 1948 | EmbB | 68 | 73 | 8 |
| B1 | EUA63954.1 | Mycobacterium abscessus 1948 | EmbC | 68 | 117 | 11 |
| B2 | AAC45279.1 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv | EmbC | 100 | 117 | 13 |
| B3 | AAC45281.1 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv | EmbB | 100 | 118 | 12 |
| B4 | AAC45280.1 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv | EmbA | 100 | 116 | 13 |
| B5 | CCP42964.1 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv | AftD | 100 | 146 | 9 |
| B6 | ACC43759.1 | Mycobacterium marinum M | EmbC | 86 | 117 | 14 |
| B7 | ACC43761.1 | Mycobacterium marinum M | EmbB | 89 | 116 | 12 |
| B8 | ACC43760.1 | Mycobacterium marinum M | EmbA | 87 | 118 | 13 |
| B9 | AFM19671.1 | Mycobacterium chubuense NBB4 | EmbB | 72 | 115 | 13 |
| B10 | AFM19669.1 | Mycobacterium chubuense NBB4 | EmbC | 75 | 116 | 12 |
| B11 | AFM19670.1 | Mycobacterium chubuense NBB4 | EmbA | 69 | 115 | 13 |
| B12 | AFM19668.1 | Mycobacterium chubuense NBB4 | AftA | 67 | 71 | 10 |
| C1 | ACC43758.1 | Mycobacterium marinum M | AftA | 83 | 70 | 13 |
| C2 | ABP43658.1 | Mycobacterium gilvum PYR-GCK | AftA | 68 | 67 | 13 |
| C3 | ABP43657.1 | Mycobacterium gilvum PYR-GCK | EmbC | 74 | 115 | 14 |
| C4 | ABP43655.1 | Mycobacterium gilvum PYR-GCK | EmbB | 70 | 115 | 13 |
| C5 | ABP43656.1 | Mycobacterium gilvum PYR-GCK | EmbA | 69 | 114 | 12 |
| C6 | AIU11367.1 | Mycobacterium smegmatis str. MC2 155 | AftA | 68 | 67 | 12 |
| C7 | CCP46634.1 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv | AftB | 100 | 69 | 9 |
| C8 | AAS02532.1 | Mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis | AftB | 82 | 70 | 9 |
| C9 | AFC41461.1 | Mycobacterium intracellulare ATCC 13950 | AftA | 77 | 68 | 13 |
| C10 | ABK72123.1 | Mycobacterium smegmatis str. MC2 155 | AftC | 70 | 49 | 8 |
| C11 | AFC44620.1 | Mycobacterium intracellulare ATCC 13950 | AftC | 84 | 50 | 8 |
| C12 | AGZ53302.1 | Mycobacterium kansasii ATCC 12478 | AftC | 89 | 49 | 8 |
| D1 | ABP46386.1 | Mycobacterium gilvum PYR-GCK | AftC | 70 | 48 | 9 |
| D2 | CDQ43952.1 | Mycobacterium neoaurum | AftC | 70 | 48 | 8 |
| D3 | ABK71542.1 | Mycobacterium smegmatis str. MC2 155 | AftD | 71 | 148 | 12 |
| D4 | AGZ51741.1 | Mycobacterium kansasii ATCC 12478 | AftD | 82 | 148 | 13 |
| D5 | ACC38960.1 | Mycobacterium marinum | AftD | 80 | 146 | 7 |
| D6 | AFM15049.1 | Mycobacterium chubuense NBB4 | AftD | 70 | 145 | 12 |
| D7 | ADT97050.1 | Mycobacterium gilvum Spyr1 | AftD | 70 | 148 | 13 |
| D8 | ABP43645.1 | Mycobacterium gilvum PYR-GCK | AftB | 71 | 70 | 9 |
| D9 | AGP61763.1 | Mycobacterium yongonense 05-1390 | AftB | 82 | 72 | 10 |
| D10 | AFC41442.1 | Mycobacterium intracellulare ATCC 13950 | AftB | 82 | 72 | 10 |
| D11 | ABM16411.1 | Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1 | AftB | 70 | 72 | 9 |
| D12 | EHB54870.1 | Mycobacterium rhodesiae JS60 | AftB | 68 | 73 | 10 |
| E1 | CDM79377.1 | Mycobacterium marinum E11 | AftB | 85 | 73 | 10 |
| E2 | AIR19061.1 * | Mycobacterium kansasii 662 | AftB | 86 | 73 | 10 |
| E3 | ABK75671.1 | Mycobacterium smegmatis str. MC2 155 | AftB | 73 | 70 | 9 |
| E4 | AFM19681.1 | Mycobacterium chubuense NBB4 | AftB | 68 | 72 | 11 |
| E5 | CDQ43590.1 | Mycobacterium neoaurum | AftB | 67 | 67 | 11 |
| E6 | EHB50241.1 | Mycobacterium rhodesiae JS60 | AftC | 71 | 49 | 7 |
| E7 | AFM16967.1 | Mycobacterium chubuense NBB4 | AftC | 71 | 49 | 9 |
| E8 | AAS05110.1 | Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis K-10 | AftC | 83 | 49 | 8 |
| E9 | AGP64972.1 | Mycobacterium yongonense 05-1390 | AftC | 83 | 50 | 8 |
| E10 | ACC40492.1 | Mycobacterium marinum | AftC | 87 | 50 | 8 |
| E11 | AAS06236.1 | Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis K-10 | AftD | 79 | 145 | 9 |
| E12 | EHB55421.1 | Mycobacterium rhodesiae JS60 | AftD | 71 | 149 | 13 |
| F1 | ABM16394.1 | Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1 | AftA | 67 | 68 | 13 |
| F2 | CDQ42439.1 | Mycobacterium neoaurum F5/8 | AftD | 67 | 148 | 13 |
| F3 | AGP61782.1 | Mycobacterium yongonense 05-1390 | AftA | 77 | 68 | 13 |
| F4 | EHB54850.1 | Mycobacterium rhodesiae JS60 | AftA | 71 | 66 | 13 |
| F5 | AGZ51273.1 | Mycobacterium kansasii ATCC 12478 | AftA | 84 | 70 | 13 |
| F6 | AGP66385.1 | Mycobacterium yongonense 05-1390 | AftD | 80 | 146 | 13 |
| F7 | CDQ43571.1 | Mycobacterium neoaurum | AftA | 67 | 67 | 11 |
| F8 | AAS02550.1 | Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis K-10 | AftA | 79 | 75 | 11 |
| F9 | ABM13300.1 | Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1 | AftC | 69 | 48 | 9 |
| F10 | ABM11102.1 | Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1 | AftD | 70 | 147 | 10 |
| F11 | AFP42646.1 | Mycobacterium smegmatis str. MC2 155 | EmbA | 69 | 117 | 13 |
| F12 | ABK72840.1 | Mycobacterium smegmatis str. MC2 155 | EmbB | 69 | 117 | 13 |
| G1 | ABK72375.1 | Mycobacterium smegmatis str. MC2 155 | EmbC | 75 | 115 | 10 |
| G2 | AFC41456.1 | Mycobacterium intracellulare ATCC 13950 | EmbA | 83 | 115 | 14 |
| G3 | AFC41455.1 | Mycobacterium intracellulare ATCC 13950 | EmbB | 85 | 115 | 12 |
| G4 | AFC41460.1 | Mycobacterium intracellulare ATCC 13950 | EmbC | 85 | 114 | 13 |
| G5 | AAS02546.1 | Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis K-10 | EmbA | 83 | 117 | 14 |
| G6 | AAS02545.1 | Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis K-10 | EmbB | 84 | 115 | 12 |
| G7 | AAS02549.1 | Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis K-10 | EmbC | 85 | 117 | 13 |
| G8 | AGP61777.1 | Mycobacterium yongonense 05-1390 | EmbA | 83 | 116 | 14 |
| G9 | AGP61776.1 | Mycobacterium yongonense 05-1390 | EmbB | 85 | 115 | 12 |
| G10 | AGP61781.1 | Mycobacterium yongonense 05-1390 | EmbC | 85 | 114 | 13 |
| G11 | CDQ43576.1 | Mycobacterium neoaurum | EmbA | 69 | 116 | 13 |
| G12 | EHB54852.1 | Mycobacterium rhodesiae JS60 | EmbA | 72 | 116 | 13 |
| H1 | ABM16396.1 | Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1 | EmbA | 70 | 116 | 13 |
| H2 | AGZ51276.1 | Mycobacterium kansasii ATCC 12478 | EmbA | 88 | 115 | 13 |
| H3 | AEV72559.1 | Mycobacterium rhodesiae NBB3 | EmbC | 76 | 114 | 14 |
| H4 | CDQ43572.1 | Mycobacterium neoaurum | EmbC | 72 | 115 | 13 |
| H5 | AGZ51274.1 | Mycobacterium kansasii ATCC 12478 | EmbC | 88 | 117 | 14 |
| H6 | ABM16395.1 | Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1 | EmbC | 73 | 116 | 10 |
| H7 | KEP38884.1 | Mycobacterium kansasii | EmbB | 90 | 117 | 11 |
| H8 | AEV72557.1 | Mycobacterium rhodesiae NBB3 | EmbB | 76 | 114 | 13 |
| H9 | ABM16397.1 | Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1 | EmbB | 70 | 115 | 13 |
| H10 | AHC23140.2 | Mycobacterium neoaurum VKM Ac-1815D | EmbB | 69 | 115 | 13 |
| H11 | EUA63217.1 | Mycobacterium abscessus 1948 F5/8 | AftD | 62 | 149 | 12 |
| H12 | AFC46048.1 | Mycobacterium intracellulare ATCC 13950 | AftD | 79 | 146 | 13 |
| AftA | A1 | A8 | C2 | C9 | F1 | F3 | F7 | F8 | |||
| AftB | A2 | A9 | C7 | D9 | D10 | D11 | E2 | E5 | |||
| AftC | A3 | A10 | C11 | C12 | D1 | D2 | E6 | E7 | E8 | E9 | F9 |
| AftD | A4 | D4 | H11 | ||||||||
| EmbA | A5 | A11 | B4 | B8 | C5 | G5 | G11 | H1 | H2 | ||
| EmbB | A6 | A12 | B3 | B7 | C4 | G3 | G6 | G9 | H7 | H9 | |
| EmbC | B1 | C3 | G4 | G7 | G10 | H4 | H5 |
| OD of Induction | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL21 (DE3) pLysS | AftA | 0.92 | 0.99 | 1.04 | 0.85 | 1.03 | 1.05 | 0.80 | 1.10 | |||
| AftB | 0.82 | 0.87 | 1.00 | 0.75 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.58 | 0.65 | ||||
| AftC | 1.02 | 0.64 | 0.72 | 0.80 | 1.05 | 0.84 | 0.88 | 1.07 | 0.86 | 0.75 | 1.23 | |
| AftD | 0.93 | 1.00 | 0.61 | |||||||||
| EmbA | 0.87 | 0.72 | 0.79 | 0.74 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 1.16 | 1.11 | 0.89 | |||
| EmbB | 1.06 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.97 | 0.82 | 0.56 | 0.90 | 0.30 | 0.70 | ||
| EmbC | 1.03 | 0.47 | 1.12 | 0.96 | 1.06 | 0.46 | 0.40 | |||||
| C41 | AftA | 1.19 | 1.00 | 0.77 | 0.57 | 0.68 | 0.63 | 0.76 | 0.60 | |||
| AftB | 0.43 | 0.46 | 0.78 | 0.75 | 0.81 | 0.79 | 0.72 | 0.60 | ||||
| AftC | 1.01 | 0.55 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 1.14 | 0.84 | 0.85 | 1.06 | 0.66 | 0.59 | 0.86 | |
| AftD | 0.55 | 0.75 | 0.62 | |||||||||
| EmbA | 0.51 | 0.72 | 0.64 | 0.74 | 0.51 | 0.52 | 0.62 | 0.53 | 0.58 | |||
| EmbB | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.37 | 0.67 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 0.50 | 0.53 | 0.74 | 0.68 | ||
| EmbC | 0.76 | 0.97 | 0.70 | 0.63 | 0.81 | 0.63 | 0.40 | |||||
| C43 | AftA | 0.73 | 0.80 | 0.88 | 0.71 | 0.84 | 0.81 | 0.92 | 0.81 | |||
| AftB | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.52 | 0.83 | 0.78 | 0.85 | 0.79 | 0.76 | ||||
| AftC | 0.79 | 0.76 | 0.75 | 0.72 | 0.82 | 1.04 | 0.83 | 0.87 | 0.80 | 0.78 | 0.83 | |
| AftD | 0.66 | 0.52 | 0.74 | |||||||||
| EmbA | 0.71 | 0.65 | 0.62 | 0.70 | 0.67 | 0.61 | 0.57 | 0.60 | 0.56 | |||
| EmbB | 0.74 | 0.66 | 0.68 | 0.70 | 0.48 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 0.71 | 0.60 | 0.82 | ||
| EmbC | 0.88 | 0.78 | 0.72 | 0.61 | 0.48 | 0.63 | 0.65 | |||||
| OD Variation | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL21(DE3) pLysS | AftA | 9.36 | 6.43 | 8.44 | 7.87 | 3.82 | 4.13 | 1.47 | 8.71 | |||
| AftB | 7.94 | 8.33 | 8.26 | 6.76 | 5.51 | 7.11 | 7.80 | 5.70 | ||||
| AftC | 8.94 | 6.73 | 7.39 | 1.55 | 7.17 | 6.97 | 6.96 | 6.82 | 7.20 | 7.44 | 8.25 | |
| AftD | 5.15 | 6.75 | 5.44 | |||||||||
| EmbA | 8.54 | 6.51 | 7.85 | 8.08 | 7.78 | 8.30 | 7.71 | 7.60 | 7.58 | |||
| EmbB | 6.92 | 8.33 | 5.19 | 5.35 | 8.20 | 7.70 | 7.18 | 8.37 | 5.23 | 1.58 | ||
| EmbC | 6.76 | 7.65 | 6.41 | 7.38 | 7.13 | 8.14 | 7.94 | |||||
| C41 | AftA | 9.14 | 8.19 | 6.40 | 9.16 | 8.97 | 9.07 | 7.70 | 8.41 | |||
| AftB | 7.43 | 9.65 | 10.67 | 14.87 | 7.48 | 9.07 | 6.12 | 6.45 | ||||
| AftC | 9.15 | 8.89 | 10.06 | 9.60 | 8.45 | 10.17 | 7.93 | 7.38 | 9.27 | 9.06 | 7.52 | |
| AftD | 5.62 | 7.52 | 5.03 | |||||||||
| EmbA | 7.09 | 6.39 | 6.57 | 5.75 | 8.32 | 9.60 | 6.29 | 3.40 | 6.45 | |||
| EmbB | 6.67 | 7.67 | 4.15 | 5.01 | 5.28 | 5.41 | 4.00 | 5.22 | 7.18 | 6.98 | ||
| EmbC | 6.56 | 8.90 | 7.96 | 8.69 | 9.38 | 9.45 | 7.72 | |||||
| C43 | AftA | 6.97 | 7.06 | 6.96 | 6.82 | 6.66 | 6.76 | 7.70 | 7.25 | |||
| AftB | 7.31 | 6.85 | 12.09 | 8.64 | 7.66 | 7.27 | 7.22 | 7.09 | ||||
| AftC | 7.24 | 9.82 | 7.95 | 11.34 | 7.62 | 12.73 | 7.83 | 8.02 | 8.80 | 7.64 | 7.38 | |
| AftD | 6.61 | 10.16 | 7.21 | |||||||||
| EmbA | 6.70 | 10.83 | 7.38 | 7.06 | 7.56 | 7.82 | 6.82 | 7.30 | 6.60 | |||
| EmbB | 7.06 | 8.08 | 8.86 | 7.99 | 7.43 | 7.32 | 7.43 | 7.62 | 6.90 | 8.50 | ||
| EmbC | 7.21 | 7.12 | 6.87 | 6.89 | 6.68 | 7.46 | 7.01 | |||||

References
- Wallin, E.; Von Heijne, G. Genome-wide analysis of integral membrane proteins from eubacterial, archaean, and eukaryotic organisms. Protein Sci. 1998, 7, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden markov model: Application to complete genomes11Edited by F. Cohen. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Von Heijne, G. The membrane protein universe: What’s out there and why bother? J. Intern. Med. 2007, 261, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasi, E.A.; Kruyer, N.S.; Peralta-Yahya, P. Advances in G protein-coupled receptor high-throughput screening. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 64, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arinaminpathy, Y.; Khurana, E.; Engelman, D.M.; Gerstein, M.B. Computational analysis of membrane proteins: The largest class of drug targets. Drug Discov. Today 2009, 14, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davey, J. G-Protein-Coupled Receptors: New Approaches to Maximise the Impact of GPCRs in Drug Discovery. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2004, 8, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlegel, S.; Löfblom, J.; Lee, C.; Hjelm, A.; Klepsch, M.; Strous, M.; Drew, D.; Slotboom, D.J.; de Gier, J.-W. Optimizing Membrane Protein Overexpression in the Escherichia coli strain Lemo21 (DE3). J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 423, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubellini, F.; Verdon, G.; Karpowich, N.K.; Luff, J.D.; Boël, G.; Gauthier, N.; Handelman, S.K.; Ades, S.E.; Hunt, J.F. Physiological Response to Membrane Protein Overexpression in E. coli. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2011, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunte, C. Specific protein–lipid interactions in membrane proteins. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005, 33, 938–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.G. How lipids affect the activities of integral membrane proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2004, 1666, 62–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hardy, D.; Mandon, E.D.; Rothnie, A.J.; Jawhari, A. The yin and yang of solubilization and stabilization for wild-type and full-length membrane protein. Methods 2018, 147, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M. Strategies for the Purification of Membrane Proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1485, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drew, D.; Lerch, M.; Kunji, E.; Slotboom, D.-J.; De Gier, J.-W. Optimization of membrane protein overexpression and purification using GFP fusions. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 3, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, L.E.; Rada, H.; Verma, A.; Gasper, R.; Birch, J.; Jennions, M.; Löwe, J.; Moraes, I.; Owens, R.J. Green fluorescent protein-based expression screening of membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 95, e52357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eshaghi, S.; Hedrén, M.; Nasser, M.I.A.; Hammarberg, T.; Thornell, A.; Nordlund, P. An efficient strategy for high-throughput expression screening of recombinant integral membrane proteins. Protein Sci. 2005, 14, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, P.; Varela, F.; Magoch, M.; Silva, A.R.; Rosário, A.L.; Brito, J.; Oliveira, T.F.; Nogly, P.; Pessanha, M.; Stelter, M.; et al. An Efficient Strategy for Small-Scale Screening and Production of Archaeal Membrane Transport Proteins in Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsliger, M.-A.; Deacon, A.M.; Godzik, A.; Lesley, S.A.; Wooley, J.; Wüthrich, K.; Wilson, I.A. The JCSG high-throughput structural biology pipeline. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2010, 66, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, R.; Anderson, S.; Aramini, J.; Belote, R.; Buchwald, W.A.; Ciccosanti, C.; Conover, K.; Everett, J.K.; Hamilton, K.; Huang, Y.J.; et al. The high-throughput protein sample production platform of the Northeast Structural Genomics Consortium. J. Struct. Biol. 2010, 172, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Love, J.; Mancia, F.; Shapiro, L.; Punta, M.; Rost, B.; Girvin, M.; Wang, D.-N.; Zhou, M.; Hunt, J.F.; Szyperski, T.; et al. The New York Consortium on Membrane Protein Structure (NYCOMPS): A high-throughput platform for structural genomics of integral membrane proteins. J. Struct. Funct. Genom. 2010, 11, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mancia, F.; Love, J. High-throughput expression and purification of membrane proteins. J. Struct. Biol. 2010, 172, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellinzoni, M.; Riccardi, G. Techniques and Applications: The heterologous expression of Mycobacterium tuberculosis genes is an uphill road. Trends Microbiol. 2003, 11, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankute, M.; Grover, S.; Rana, A.K.; Besra, G.S. Arabinogalactan and lipoarabinomannan biosynthesis: Structure, biogenesis and their potential as drug targets. Futur. Microbiol. 2012, 7, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umesiri, F.E.; Sanki, A.K.; Boucau, J.; Ronning, D.R.; Sucheck, S.J. Recent advances toward the inhibition of mAG and LAM synthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Med. Res. Rev. 2010, 30, 290–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolucka, B.; McNeil, M.; De Hoffmann, E.; Chojnacki, T.; Brennan, P. Recognition of the lipid intermediate for arabinogalactan/arabinomannan biosynthesis and its relation to the mode of action of ethambutol on mycobacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 23328–23335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankute, M.; Cox, J.A.; Harrison, J.; Besra, G.S. Assembly of the Mycobacterial Cell Wall. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 69, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abrahams, K.A.; Besra, G.S. Mycobacterial cell wall biosynthesis: A multifaceted antibiotic target. Parasitology 2018, 145, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruni, R.; Kloss, B. High-Throughput Cloning and Expression of Integral Membrane Proteins in Escherichia coli. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2013, 74, 29.6.1–29.6.34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Punta, M.; Love, J.; Handelman, S.; Hunt, J.F.; Shapiro, L.; Hendrickson, W.A.; Rost, B. Structural genomics target selection for the New York consortium on membrane protein structure. J. Struct. Funct. Genom. 2009, 10, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rath, A.; Glibowicka, M.; Nadeau, V.G.; Chen, G.; Deber, C.M. Detergent binding explains anomalous SDS-PAGE migration of membrane proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreland, N.; Ashton, R.; Baker, H.M.; Ivanović, I.; Patterson, S.; Arcus, V.L.; Baker, E.N.; Lott, J.S. A flexible and economical medium-throughput strategy for protein production and crystallization. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2005, 61, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashiri, G.; Baker, E.N. Production of recombinant proteins inMycobacterium smegmatisfor structural and functional studies. Protein Sci. 2014, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goldstone, R.M.; Moreland, N.J.; Bashiri, G.; Baker, E.N.; Lott, J.S. A new Gateway® vector and expression protocol for fast and efficient recombinant protein expression in Mycobacterium smegmatis. Protein Expr. Purif. 2008, 57, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewinson, O.; Lee, A.T.; Rees, D.C. The Funnel Approach to the Precrystallization Production of Membrane Proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 377, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kieser, K.J.; Rubin, E.J. How sisters grow apart: Mycobacterial growth and division. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 12, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroux, B.; Walker, J.E. Over-production of Proteins inEscherichia coli: Mutant Hosts that Allow Synthesis of some Membrane Proteins and Globular Proteins at High Levels. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 260, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Studier, F. Use of bacteriophage T7 lysozyme to improve an inducible T7 expression system. J. Mol. Biol. 1991, 219, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, K.; Javed, W.; Vallet, S.; Lesterlin, C.; Candusso, M.-P.; Ding, F.; Xu, X.N.; Ebel, C.; Jault, J.-M.; Orelle, C. Functionality of membrane proteins overexpressed and purified from E. coli is highly dependent upon the strain. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Klepsch, M.M.; Schlegel, S.; Appel, A.; Draheim, R.; Tarry, M.; Högbom, M.; Van Wijk, K.J.; Slotboom, D.J.; Persson, J.O.; et al. Tuning Escherichia coli for membrane protein overexpression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14371–14376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, J.; Heng, J.; Dai, S.; Shaw, N.; Zhou, B.; Huang, B.; He, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Li, X.; et al. An efficient strategy for high throughput screening of recombinant integral membrane protein expression and stability. Protein Expr. Purif. 2011, 78, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, M.S.; Koth, C.M. Structural Proteomics of Membrane Proteins: A Survey of Published Techniques and Design of a Rational High Throughput Strategy. In Advanced Structural Safety Studies; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; Volume 426, pp. 277–295. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, R.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Gurcha, S.S.; Veerapen, N.; Batt, S.M.; et al. Cryo-EM snapshots of mycobacterial arabinosyltransferase complex EmbB2-AcpM2. Protein Cell 2020, 11, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.Z.; Rodrigues, J.; Keener, J.E.; Zheng, R.B.; Brunton, R.; Kloss, B.; Giacometti, S.I.; Rosário, A.L.; Zhang, L.; Niederweis, M.; et al. Cryo-EM structure of arabinosyltransferase EmbB from Mycobacterium smegmatis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wu, L.; Gao, R.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Wu, F.; Gurcha, S.S.; et al. Structures of cell wall arabinosyltransferases with the anti-tuberculosis drug ethambutol. Science 2020, 368, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.Z.; Zhang, L.; Rodrigues, J.; Zheng, R.B.; Giacometti, S.I.; Rosário, A.L.; Kloss, B.; Dandey, V.P.; Wei, H.; Brunton, R.; et al. Cryo-EM Structures and Regulation of Arabinofuranosyltransferase AftD from Mycobacteria. Mol. Cell 2020, 78, 683–699.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderwick, L.J.; Seidel, M.; Sahm, H.; Besra, G.S.; Eggeling, L. Identification of a Novel Arabinofuranosyltransferase (AftA) Involved in Cell Wall Arabinan Biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 15653–15661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Angala, S.K.; Pramanik, P.K.; Li, K.; Crick, D.C.; Liav, A.; Jozwiak, A.; Swiezewska, E.; Jackson, M.; Chatterjee, D.; et al. Reconstitution of Functional Mycobacterial Arabinosyltransferase AftC Proteoliposome and Assessment of Decaprenylphosphorylarabinose Analogues as Arabinofuranosyl Donors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favrot, L.; Ronning, D.R. Targeting the mycobacterial envelope for tuberculosis drug development. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2012, 10, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Number | Success Rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Targets | 96 | - |
| Positive Clones (pNYCOMPS-N23) | 56 | 58 |
| 1 Positive Clones (pNYCOMPS-C23) | 40 | 42 |
| Proteins purified (total) | 17 | 18 |
| E. coli C41::pNYCOMPS-N23 | 16 | 17 |
| E. coli C43::pNYCOMPS-N23 | 6 | 6 |
| E. coli BL21 (DE3) pLysS::pNYCOMPS-N23 | 8 | 8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigues, J.; Almeida, V.T.; Rosário, A.L.; Tan, Y.Z.; Kloss, B.; Mancia, F.; Archer, M. High Throughput Expression Screening of Arabinofuranosyltransferases from Mycobacteria. Processes 2021, 9, 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040629
Rodrigues J, Almeida VT, Rosário AL, Tan YZ, Kloss B, Mancia F, Archer M. High Throughput Expression Screening of Arabinofuranosyltransferases from Mycobacteria. Processes. 2021; 9(4):629. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040629
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigues, José, Vanessa T. Almeida, Ana L. Rosário, Yong Zi Tan, Brian Kloss, Filippo Mancia, and Margarida Archer. 2021. "High Throughput Expression Screening of Arabinofuranosyltransferases from Mycobacteria" Processes 9, no. 4: 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040629
APA StyleRodrigues, J., Almeida, V. T., Rosário, A. L., Tan, Y. Z., Kloss, B., Mancia, F., & Archer, M. (2021). High Throughput Expression Screening of Arabinofuranosyltransferases from Mycobacteria. Processes, 9(4), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9040629






