Technological Advancement for Efficiency Enhancement of Biodiesel and Residual Glycerol Refining: A Mini Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Conventional Protocols
2.1. Wet/Water Washing
2.2. Physicochemical Treatment
2.3. Distillation
3. State of the Art Technologies
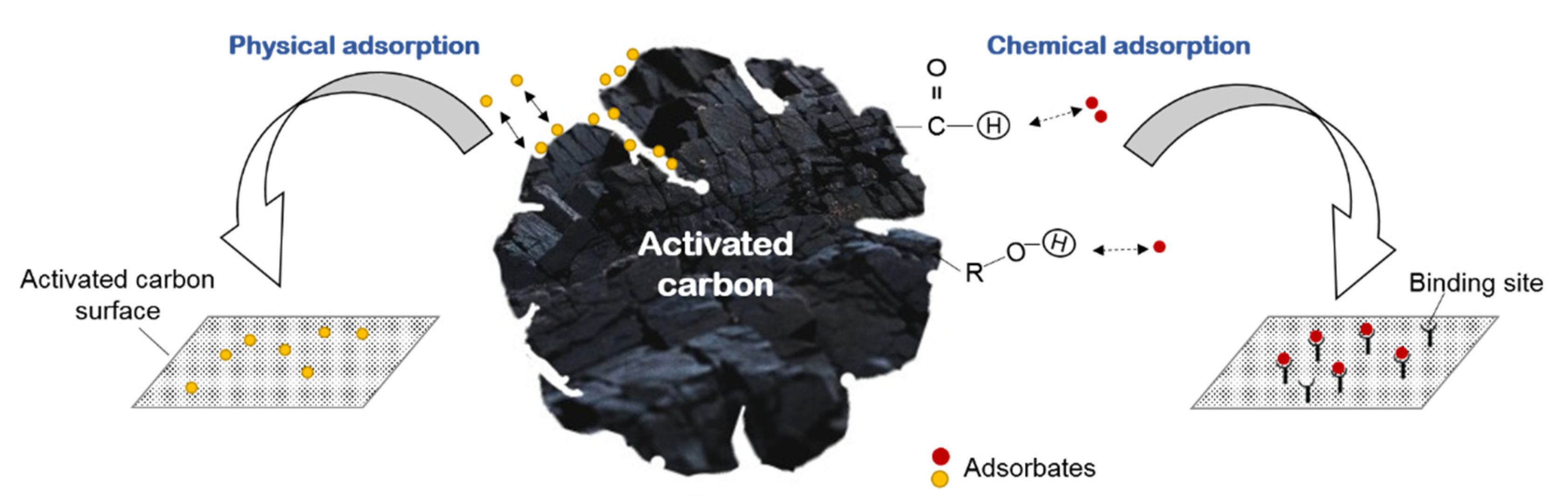
3.1. Dry Washing by Adsorption
3.1.1. Activated Adsorbent Compound
3.1.2. Biomass-Based Adsorbent
3.1.3. Silica-Based Adsorbent
3.2. Dry Washing by Ion-Exchange
3.3. Membrane Filtration
3.3.1. Organic/Polymeric Membrane
3.3.2. Inorganic/Ceramic Membrane
3.3.3. Hybrid Membrane
3.4. Comparison of Processes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sadaf, S.; Iqbal, J.; Ullah, I.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nouren, S.; Nisar, J.; Iqbal, M. Biodiesel production from waste cooking oil: An efficient technique to convert waste into biodiesel. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 41, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SDG Knowledge Hub. World Population to Reach 9.9 Billion by 2050. Available online: https://sdg.iisd.org/news/world-population-to-reach-9-9-billion-by-2050/ (accessed on 16 June 2021).
- BP Global. Statistic Review of World Biofuels Production. Available online: https://www.bp.com/content/dam/bp/business sites/en/global/corporate/pdfs/energy-economics/statistical-review/bp-stats-review-2020-full-report.pdf (accessed on 4 June 2021).
- Kumar, S.; Shamsuddin, M.R.; Farabi, M.A.; Saiman, M.I.; Zainal, Z.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H. Production of methyl esters from waste cooking oil and chicken fat oil via simultaneous esterification and transesterification using acid catalyst. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 226, 113366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiwot, B.; Maryo, M. Evaluation of land use patterns across agro-ecological and slope classes using GIS and remote sensing: The case of Gedeo Zone, Southern Ethiopia. Intl. J. Adv. Remote Sens. GIS 2015, 4, 1385–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaki, K.; Portugal-Pereira, J. The effect of biofuel production on greenhouse gas emission reductions. In Biofuels and Sustainability. Science for Sustainable Societies; Takeuchi, K., Shiroyama, H., Saito, O., Matsuura, M., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2018; pp. 53–71. ISBN 978-4-431-54895-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ardi, M.S.; Aroua, M.K.; Awanis Hashim, N. Progress, prospect and challenges in glycerol purification process: A review. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asikin-Mijan, N.; AbdulKareem-Alsultan, G.; Izham, S.M.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H. Biodiesel production via simultaneous esterification and transesterification of chicken fat oil by mesoporous sulfated Ce supported activated carbon. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 141, 105714. [Google Scholar]
- Hazmi, B.; Rashid, U.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Ibrahim, M.L.; Nehdi, I.A. Supermagnetic nano-bifunctional catalyst from rice husk: Synthesis, characterization and application for conversion of used cooking oil to biodiesel. Catalysts 2020, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Farid, M.A.; Hassan, M.A.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Ibrahim, M.L.; Othman, M.R.; Ali, A.A.M.; Shirai, Y. Production of methyl esters from waste cooking oil using a heterogeneous biomass-based catalyst. Renew. Energy 2017, 114, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Farid, M.A.; Roslan, A.M.; Hassan, M.A.; Hasan, M.Y.; Othman, M.R.; Shirai, Y. Net energy and techno-economic assessment of biodiesel production from waste cooking oil using a semi-industrial plant: A Malaysia perspective. Sustain. Energy Technol. 2020, 39, 100700. [Google Scholar]
- Demirbas, A. Progress and recent trends in biodiesel fuels. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrios, M.; Skelton, R.L. Comparison of purification methods for biodiesel. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 144, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Farid, M.A.; Hassan, M.A.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Shirai, Y.; Hasan, M.Y.; Zakaria, M.R. Waterless purification using oil palm biomass-derived bioadsorbent improved the quality of biodiesel from waste cooking oil. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figoli, A.; Cassano, A.; Basile, A. Membrane Technologies for Biorefining; Elseiver: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; p. 294. [Google Scholar]
- Chongkhong, S.; Tongurai, C.; Chetpattananondh, P. Continuous esterification for biodiesel production from palm fatty acid distillate using economical process. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; He, Q.; Niu, H.; Corscadden, K.; Caldwell, C. A comparative study on the performance of fiber-based biosorbents in the purification of biodiesel derived from Camelina sativa. J. Technol. Innov. Renew. Energy 2017, 5, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaya, N.; Ethirajulu, K. Kinetic studies of heterogeneously catalysed transesterification of cottonseed oil to biodiesel. J. Environ. Res. Develop. 2011, 5, 689–695. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti, H.; Hanif, M.; Qasim, M.; Rehman, A. Biodiesel production from waste tallow. Fuel 2008, 87, 2961–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.; Bordado, J.; Santos, R. Upgrading the glycerol from biodiesel production as a source of energy carriers and chemicals—A technological review for three chemical pathways. Energies 2017, 10, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongjao, S.; Damronglerd, S.; Hunsom, M. Purification of crude glycerol derived from waste used-oil methyl ester plant. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 27, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, T.L.; Yong, K.C.; Dzulkefly, K.; Wan Yunus, W.M.Z.; Hazimah, A.H. Crude glycerine recovery from glycerol residue waste from a palm kernel oil methyl ester plant. J. Oil Palm Res. 2001, 13, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Tianfeng, C.; Huipeng, L.; Hua, Z.; Kejian, L. Purification of crude glycerol from waste cooking oil-based biodiesel production by orthogonal test method. China Pet. Process. Petrochem. Technol. 2013, 15, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Hájek, M.; Skopal, F. Treatment of glycerol phase formed by biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 101, 3242–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javani, A.; Hasheminejad, M.; Tahvildari, K.; Tabatabaei, M. High quality potassium phosphate production through step-by-step glycerol purification: A strategy to economise biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 104, 788–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, R.D.; Terry, P.A. Principles of Chemical Separations with Environmental Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Surrod, T.; Pattamaprom, C. Purification of glycerine by-product from biodiesel production using electrolysis process. In Proceedings of the Second TSME International Conference on Mechanical Engineering, Krabi, Thailand, 19–21 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, K.C.; Ooi, T.L.; Dzulkefly, K.; Wan Yunus, W.M.Z.; Hazimah, A.H. Refining of crude glycerine recovered from glycerol residue by simple vacuum distillation. J. Oil Palm Res. 2001, 13, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Nasir, N.; Mirus, M.; Ismail, M. Purification of crude glycerol from transesterification reaction of palm oil using direct method and multistep method. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 243, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccini, C.S.; Cunha, M.E.D.; Moraes, M.S.A.; Krause, L.C.; Manique, M.C.; Rodrigues, M.R.A.; Benvenutti, E.V.; Caramão, E.B. Dry washing in biodiesel purification: A comparative study of adsorbents. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2011, 22, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Farid, M.A.; Hassan, M.A.; Roslan, A.M.; Ariffin, H.; Norrrahim, M.N.F.; Othman, M.R.; Yoshihito, S. Improving the decolorization of glycerol by adsorption using activated carbon derived from oil palm biomass. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Li, X.; Xing, J.; Xu, G. Adsorption of potentially toxic elements in water by modified biochar: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.L.; Chin, K.L.; H’ng, P.S.; Rashid, U.; Maminski, M.; Khoo, P.S. Effect of pretreatment conditions on the chemical–structural characteristics of coconut and palm kernel shell: A potentially valuable precursor for eco-efficient activated carbon production. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atadashi, I.M. Purification of crude biodiesel using dry washing and membrane technologies. Alex. Eng. J. 2015, 54, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, R.F.; Rashid, U.; Ibrahim, M.L.; Hazmi, B.; Alharthi, F.A.; Nehdi, I.A. Bifunctional nano-catalyst produced from palm kernel shell via hydrothermal-assisted carbonization for biodiesel production from waste cooking oil. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.F.; Pendleton, P.; Badalyan, A. Effects of surface functional groups of activated carbon on adsorption of triclosan from aqueous solution. Int. J. Environ. Technol. Manag. 2009, 10, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, A.A.; Hassan, M.A.; Farid, M.A.A.; Yasim-Anuar, T.A.T.; Samsudin, M.H.; Yusoff, M.Z.M.; Zakaria, M.R.; Mokhtar, M.N.; Shirai, Y. Adsorption mechanism and effectiveness of phenol and tannic acid removal by biochar produced from oil palm frond using steam pyrolysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnaief, M.; Sandouqa, A.; Altarawneh, I.; Al-Shannag, M.; Alkasrawi, M.; Al-hamamre, Z. Adsorption characteristics and potential of olive cake alkali residues for biodiesel purification. Energies 2021, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, M.; Dhobale, A. Complete utilisation of Pongamia pinnata: Preparation of activated carbon, biodiesel and its purification. Int. J. Chemtech. Res. 2014, 6, 3672–3676. [Google Scholar]
- Fadhil, A.B.; Dheyab, M.M. Purification of biodiesel fuels produced from spent frying oils over activated carbons. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2015, 37, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadhil, A.B.; Dheyab, M.M.; Abdul-Qader, A.Q.Y. Purification of biodiesel using activated carbons produced from spent tea waste. Arab. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2012, 11, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, R.S.; Juliantoa, T.S.; Hartono, P.; Puspitasaria, R.D.; Kurniawan, A. Pre-treatment of used-cooking oil as feedstocks of biodiesel production by using activated carbon and clay minerals. Int. J. Renew. Energy Dev. 2014, 3, 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, M.G.; Santos, D.Q.; de Morais, L.C.; Pasquini, D. Purification of biodiesel by dry washing, employing starch and cellulose as natural adsorbents. Fuel 2015, 155, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z. A green route to preparation of silica powders with rice husk ash and waste gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manique, M.C.; Faccini, C.S.; Onorevoli, B.; Benvenutti, E.V.; Caramão, E.B. Rice husk ash as an adsorbent for purifying biodiesel from waste frying oil. Fuel 2012, 92, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.J.; Cavalcanti, Í.V.; de Resende, M.M.; Cardoso, V.L.; Reis, M.H. Biodiesel dry purification with sugarcane bagasse. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 89, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.T. Adsorbents: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzieri, V.A.; Vera, C.R.; Yori, J.C. Adsorptive properties of silica gel for biodiesel refining. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 4281–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuale, D.L.; Mazzieri, V.M.; Torres, G.; Vera, C.R.; Yori, J.C. Non-catalytic biodiesel process with adsorption-based refining. Fuel 2011, 90, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nock, A. Silica Hydrogel and Its Use in Edible Oil Processing. Available online: https://lipidlibrary.aocs.org/edible-oil-processing/silica-hydrogel-and-its-use-in-edible-oil-processing (accessed on 21 October 2019).
- Yori, J.C.; D’ippolito, S.A.; Pieck, C.L.; Vera, C.R. De-glycerolization of biodiesel streams by adsorption over silica beds. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predojević, Z.J. The production of biodiesel from waste frying oils: A comparison of different purification steps. Fuel 2008, 87, 3522–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrios, M.; Siles, J.; Martín, M.; Martín, A. Ion exchange. In Separation and Purification Technologies in Biorefineries; Ramaswamy, S., Huang, H.J., Ramarao, B.V., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zabaruddin, N.H.; Abdullah, L.C.; Mohamed, N.H.; Choong, T.S.Y. Optimization using response surface methodology (RSM) for biodiesel synthesis catalyzed by radiation-induced Kenaf catalyst in packed-bed reactor. Processes 2020, 8, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrios, M.; Martín, M.A.; Chica, A.F.; Martín, A. Purification of biodiesel from used cooking oils. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3625–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, T.M.; Cardoso, N.; Ornelas, M.; Neves, S.; Caetano, N.S. Evaluation of two purification methods of biodiesel from beef tallow, pork lard, and chicken fat. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 4756–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzu, M.; Hidaka, J. Purification to remove leached CaO catalyst from biodiesel with the help of cation-exchange resin. Fuel 2013, 105, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, J.; Van Gerpen, J.; Thompson, J. Soap and glycerin removal from biodiesel using waterless processes. Trans. ASABE 2011, 54, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.M.; Santos, E.; Santo, F.; Carvalho, F.; Alvim-Ferraz, M.C.M.; Almeida, M.F. Study of an ethylic biodiesel integrated process: Raw-materials, reaction optimisation and purification methods. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 124, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mänttäri, M.; Van Der Bruggen, B.; Nyström, M. Nanofiltration. In Separation and Purification Technologies in Biorefineries; Ramaswamy, S., Huang, H.J., Ramarao, B.V., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.Y.; Guo, X.; Zhu, S.L. Comparison of membrane extraction with traditional extraction methods for biodiesel production. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2006, 83, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, J.; Dubé, M.A.; Tremblay, A.Y. Effect of soap, methanol, and water on glycerol particle size in biodiesel purification. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 6179–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorno, F.; Mazzei, R.; Giorno, L. Purification of triacylglycerols for biodiesel production from Nannochloropsis microalgae by membrane technology. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 140, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumay, J.; Radier, S.; Barnathan, G.; Berge, J.P.; Jaouen, P. Recovery of valuable soluble compounds from washing waters generated during small fatty pelagic surimi processing by membrane processes. Environ. Technol. 2008, 29, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, S.K.; Leo, C.P.; Wu, T.Y.; Chai, S.P. A feasibility investigation on ultrafiltration of palm oil and oleic acid removal from glycerin solutions: Flux decline, fouling pattern, rejection and membrane characterisations. J. Memb. Sci. 2012, 389, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Diniz da Costa, J.; Duke, M.; Giessler, S.; Socolow, R.; Williams, R.; Kreutz, T. Inorganic membranes for hydrogen production and purification: A critical review and perspective. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 314, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, M.C.S.; Arroyo, P.A.; Pereira, N.C. Influence of acidified water addition on the biodiesel and glycerol separation through membrane technology. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 431, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daramola, M.; Aransiola, E.; Ojumu, T. Potential applications of zeolite membranes in reaction coupling separation processes. Materials 2012, 5, 2101–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, J.; Dubé, M.A.; Tremblay, A.Y. Separation of glycerol from FAME using ceramic membranes. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Ou, S.; Tan, Y.; Tang, S. Refining of biodiesel by ceramic membrane separation. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayvani Fard, A.; McKay, G.; Buekenhoudt, A.; Al Sulaiti, H.; Motmans, F.; Khraisheh, M.; Atieh, M. Inorganic membranes: Preparation and application for water treatment and desalination. Materials 2018, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusworo, T.D.; Kumoro, A.C.; Yaqin, M.A.; Fatiyah, N.; Utomo, D. Modification of nano hybrid PES-ZnO membrane using UV irradiation for biodiesel purification. Jurnal Teknologi 2020, 82, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, E.; Villafán-Cáceres, S.M.; Rodríguez-Mejía, Y.; García-Loyola, J.A.; Masera, O.; Sandoval, G. Biodiesel dry purification using unconventional bioadsorbents. Processes 2021, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostojčić, M.; Brkić, S.; Tišma, M.; Zelić, B.; Budžaki, S. Membrane filtration as an environmentally friendly method for crude biodiesel purification. Kemija u Industriji 2020, 69, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandouqa, A.; Al-Shannag, M.; Al-Hamamre, Z. Biodiesel purification using biomass-based adsorbent manufactured from delignified olive cake residues. Renew. Energy 2020, 151, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Source of Crude Glycerol | Purification Method | Result | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Used-oil waste |
|
| [21] |
| Glycerol residue from palm kernel oil methyl ester plant |
|
| [22] |
| Transesterification of used cooking oil |
|
| [23] |
| Raw glycerol phase |
|
| [24] |
| Transesterification of waste cooking oil |
|
| [25] |
| Reactants Used in Biodiesel Production | Purification Method | Operating Condition | Finding | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunflower oil, methanol, NaOH | Natural adsorbents (corn, potato, cassava and rice) | Sugarcane bagasse as adsorbents | Acidity index, combined alkalinity, free glycerine and turbidity decreased | [43] |
| Waste frying oil, methanol, KOH | Rice husk ash (RHA) as adsorbents | By varying the concentration of RHA adsorbents (1%, 2%, 3%, 4%, 5% w/w) at 65 °C for 20 min of stirring | At 4% rice husk ash, an efficient removal of glycerine and glycerides, potassium were achieved | [45] |
| Soybean oil | Sugarcane bagasse as adsorbents | Adsorbent loading ranged from 0.1 to 3 wt%, and stirred at 120 rpm at 30 °C for two hours | 3 wt% of sugarcane bagasse adsorbents were able to remove 82% of glycerine from crude biodiesel, thus yielding 87% | [46] |
| Waste cooking oil | Sawdust, coconut coir, nutshell, rice husk and water hyacinth fiber | 5% of bioadsorbents was stirred for 20 min at 700 rpm | 5% of sawdust decreased the acid number, water content and free glycerine content of biodiesel with values below the ASTM standard | [38] |
| Types of Silica-Based Adsorbent | Function | References |
|---|---|---|
| Silica | To remove glycerides and free fatty acid | [49] |
| Silica hydrogel | To remove unreacted methanol, monoglycerides, diglycerides and moisture | [50] |
| Fixed silica beds | To remove glycerol from a mixture of glycerol and purified biodiesel | [51] |
| Organic | Inorganic | References | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advantage | Cheap | Autoclavable | [34,70,71] |
| Easy processing | Long lifetime | ||
| Requires low energy in operation | Withstand high temperature (>200 °C) | ||
| Inertness to microbiological degradation | |||
| pH fluctuation resistance | |||
| Disadvantage | Short lifetime | Fragile | [70,71] |
| Structurally weak, unstable, temperature constrained | Rigid High capital cost |
| Method | Advantage | Disadvantage | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water washing |
|
| [73,74] |
| Dry washing by adsorption and ion exchange process |
|
| [73,75] |
| Membrane filtration |
|
| [72,74] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jariah, N.F.; Hassan, M.A.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Roslan, A.M. Technological Advancement for Efficiency Enhancement of Biodiesel and Residual Glycerol Refining: A Mini Review. Processes 2021, 9, 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071198
Jariah NF, Hassan MA, Taufiq-Yap YH, Roslan AM. Technological Advancement for Efficiency Enhancement of Biodiesel and Residual Glycerol Refining: A Mini Review. Processes. 2021; 9(7):1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071198
Chicago/Turabian StyleJariah, Nurhani Fatihah, Mohd Ali Hassan, Yun Hin Taufiq-Yap, and Ahmad Muhaimin Roslan. 2021. "Technological Advancement for Efficiency Enhancement of Biodiesel and Residual Glycerol Refining: A Mini Review" Processes 9, no. 7: 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071198
APA StyleJariah, N. F., Hassan, M. A., Taufiq-Yap, Y. H., & Roslan, A. M. (2021). Technological Advancement for Efficiency Enhancement of Biodiesel and Residual Glycerol Refining: A Mini Review. Processes, 9(7), 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071198







