Home Scholarly Culture, Book Selection Reason, and Academic Performance: Pathways to Book Reading Interest among Secondary School Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Individual’s Identities and Traits
2.2. Environmental Characteristics
2.3. The Need for a New Approach
3. Theoretical Foundation
4. Methodology
4.1. Material
4.2. Variables
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Results
5.1. Model 1
5.2. Model 2
5.3. Model 3
6. Discussion
6.1. Book Recommendation or Personal Preference?
6.2. Influence of Parental Book Reading on Source Preference
6.3. How Parental Book Reading Influences Reading Interest
6.4. Implications for Educational Policy
6.4.1. Recommendation Is Important for Students with Low Self-Efficacy
6.4.2. Autonomy Is Important for Students with High Self-Efficacy
6.4.3. Student–Educator Relationship Should Be Considered in Both Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A







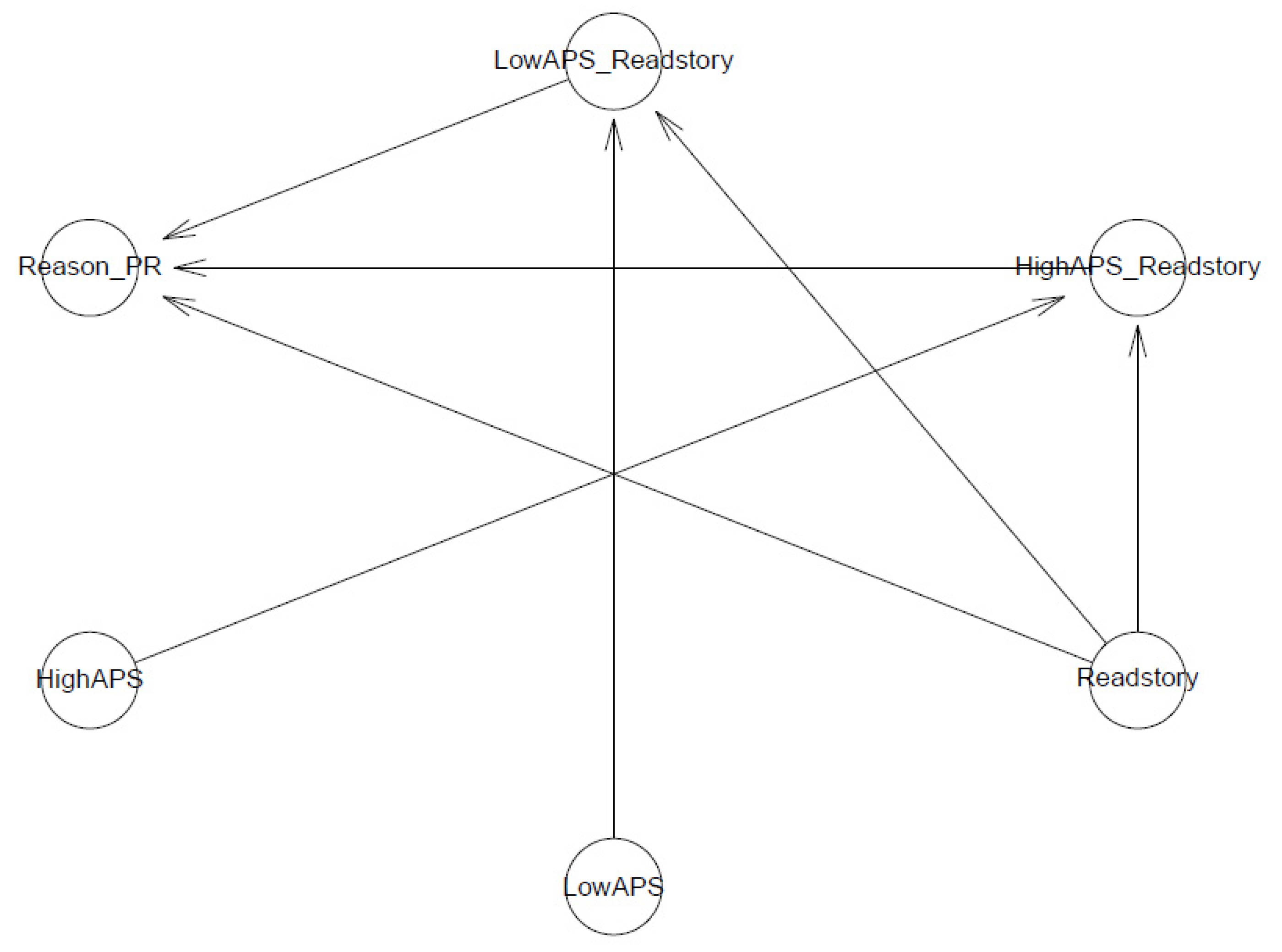













References
- Freire, P. The Importance of the Act of Reading. J. Educ. 1983, 165, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, E.; Puccioni, J. Shared Book Reading and Preschool Children’s Academic Achievement: Evidence from the Early Childhood Longitudinal Study-Birth Cohort. Infant Child Dev. 2017, 26, e2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.; Liu, X.; Bartlett, B.; Ng, C.; Harris, K.R.; Aitken, A.; Barkel, A.; Kavanaugh, C.; Talukdar, J. Reading for Writing: A Meta-Analysis of the Impact of Reading Interventions on Writing. Rev. Educ. Res. 2018, 88, 243–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Wang, H.; Mo, D.; Shi, Y.; Kenny, K.; Rozelle, S. Can Reading Programs Improve Reading Skills and Academic Performance in Rural China? China Econ. Rev. 2018, 52, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO Science Education Programme. Available online: http://www.unesco.org/new/en/natural-sciences/special-themes/science-education/about-the-programme/ (accessed on 9 March 2021).
- Schneps, M.H.; O’Keeffe, J.K.; Heffner-Wong, A.; Sonnert, G. Using Technology to Support STEM Reading. J. Spec. Educ. Technol. 2010, 25, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.-T.-H.; Tran, T.; Trinh, T.-P.-T.; Nguyen, C.-T.; Nguyen, T.-P.-T.; Vuong, T.-T.; Vu, T.-H.; Bui, D.-Q.; Vuong, H.-M.; Hoang, P.-H.; et al. Reading Habits, Socioeconomic Conditions, Occupational Aspiration and Academic Achievement in Vietnamese Junior High School Students. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.-T.; La, V.-P.; Nguyen, M.-H.; Pham, T.-H.; Vuong, T.-T.; Vuong, H.-M.; Pham, H.-H.; Hoang, A.-D.; Vuong, Q.-H. An Analytical View on STEM Education and Outcomes: Examples of the Social Gap and Gender Disparity in Vietnam. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 119, 105650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H. Home Literacy Environments and Children’s Reading Performance: A Comparative Study of 25 Countries. Educ. Res. Eval. 2008, 14, 489–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, J.; Evans, M.D.R.; Kelley, J. Scholarly Culture: How Books in Adolescence Enhance Adult Literacy, Numeracy and Technology Skills in 31 Societies. Soc. Sci. Res. 2019, 77, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.D.R.; Kelley, J.; Sikora, J.; Treiman, D.J. Scholarly Culture and Occupational Success in 31 Societies. Comp. Sociol. 2015, 14, 176–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Le, T.-T.-H.; Nguyen, T.-T.; Pham, A.-G.; Vu, T.-H.; Nguyen, M.-H.; Vuong, H.-M.; Vuong, T.-T.; Hoang, P.-H.; Ho, M.-T.; et al. The Relationship between Birth Order, Sex, Home Scholarly Culture and Youths’ Reading Practices in Promoting Lifelong Learning for Sustainable Development in Vietnam. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.; Wigfield, A. Dimensions of Children’s Motivation for Reading and Their Relations to Reading Activity and Reading Achievement. Read. Res. Q. 1999, 34, 452–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevo, E.; Vaknin-Nusbaum, V.; Brande, S.; Gambrell, L. Oral Reading Fluency, Reading Motivation and Reading Comprehension among Second Graders. Read. Writ. 2020, 33, 1945–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthrie, J.T.; Wigfield, A.; Humenick, N.M.; Perencevich, K.C.; Taboada, A.; Barbosa, P. Influences of Stimulating Tasks on Reading Motivation and Comprehension. J. Educ. Res. 2006, 99, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthrie, J.T.; Hoa, A.L.W.; Wigfield, A.; Tonks, S.M.; Humenick, N.M.; Littles, E. Reading Motivation and Reading Comprehension Growth in the Later Elementary Years. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 2007, 32, 282–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troyer, M.; Kim, J.S.; Hale, E.; Wantchekon, K.A.; Armstrong, C. Relations among Intrinsic and Extrinsic Reading Motivation, Reading Amount, and Comprehension: A Conceptual Replication. Read. Writ. 2019, 32, 1197–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, A.T.; Klauda, S.L. How Reading Motivation and Engagement Enable Reading Achievement: Policy Implications. Policy Insights Behav. Brain Sci. 2020, 7, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbecker, K.; Förster, N.; Souvignier, E. Reciprocal Effects between Reading Achievement and Intrinsic and Extrinsic Reading Motivation. Sci. Stud. Read. 2019, 23, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigfield, A.; Guthrie, J.T. Relations of Children’s Motivation for Reading to the Amount and Breadth or Their Reading. J. Educ. Psychol. 1997, 89, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Badri, M.; Al Rashedi, A.; Almazroui, K. The Role of Reading Motivation, Self-Efficacy, and Home Influence in Students’ Literacy Achievement: A Preliminary Examination of Fourth Graders in Abu Dhabi. Large-Scale Assess Educ. 2018, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, A.M.; Strasser, K. Is Reading a Feminine Domain? The Role of Gender Identity and Stereotypes in Reading Motivation in Chile. Soc. Psychol. Educ. 2020, 23, 861–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, R.A.; Farran, L.K.; Mindrila, D. Reading Motivation in Bi/Multilingual Latinx Adolescents: An Exploratory Structural Equation Model. Read. Psychol. 2020, 41, 856–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, L. Relations between Children’s Reading Motivation, Activity and Performance at the End of Primary School. J. Res. Read. 2019, 42, 562–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steensel, R.; Oostdam, R.; Gelderen, A. Affirming and Undermining Motivations for Reading and Associations with Reading Comprehension, Age and Gender. J. Res. Read. 2019, 42, 504–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, A.; Murayama, K.; Lechner, C.M. The Developmental Trajectory of Intrinsic Reading Motivation: Measurement Invariance, Group Variations, and Implications for Reading Proficiency. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 2020, 63, 101921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, F.; McElvany, N.; Trendtel, M. The School Age Gender Gap in Reading Achievement: Examining the Influences of Item Format and Intrinsic Reading Motivation. Read. Res. Q. 2015, 50, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffner, E.; Schiefele, U.; Ulferts, H. Reading Amount as a Mediator of the Effects of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Reading Motivation on Reading Comprehension. Read. Res. Q. 2013, 48, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diseth, Å.; Mathisen, F.K.S.; Samdal, O. A Comparison of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation among Lower and Upper Secondary School Students. Educ. Psychol. 2020, 40, 961–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Gu, H.; Li, W. Effect of Parents’ Encouragement on Reading Motivation: The Mediating Effect of Reading Self-Concept and the Moderating Effect of Gender. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.E.; Lanza, S.; Osgood, D.W.; Eccles, J.S.; Wigfield, A. Changes in Children’s Self-Competence and Values: Gender and Domain Differences across Grades One through Twelve. Child Dev. 2002, 73, 509–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mucherah, W.; Yoder, A. Motivation for Reading and Middle School Students’ Performance on Standardized Testing in Reading. Read. Psychol. 2008, 29, 214–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, A.; Pfost, M.; Artelt, C. Reciprocal Relations between Intrinsic Reading Motivation and Reading Competence: A Comparison between Native and Immigrant Students in Germany: Reading Motivation and Reading Competence. J. Res. Read. 2018, 41, 176–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toste, J.R.; Didion, L.; Peng, P.; Filderman, M.J.; McClelland, A.M. A Meta-Analytic Review of the Relations between Motivation and Reading Achievement for K–12 Students. Rev. Educ. Res. 2020, 90, 420–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaknin-Nusbaum, V.; Nevo, E.; Brande, S.; Gambrell, L. Developmental Aspects of Reading Motivation and Reading Achievement among Second Grade Low Achievers and Typical Readers: Developmental Aspects of Reading Motivation. J. Res. Read. 2018, 41, 438–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villiger, C.; Niggli, A.; Wandeler, C.; Kutzelmann, S. Does Family Make a Difference? Mid-Term Effects of a School/Home-Based Intervention Program to Enhance Reading Motivation. Learn. Instr. 2012, 22, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lee, C.-K.J.; Yeung, S.S. Predicting Reading Motivation and Achievement: The Role of Family and Classroom Environments in Greater China. Int. J. Educ. Res. 2020, 103, 101642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansor, A.N.; Rasul, M.S.; Rauf, R.A.A.; Koh, B.L. Developing and Sustaining Reading Habit Among Teenagers. Asia-Pac. Educ. Res. 2013, 22, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.M. CHAPTER 1 Influence of Family Factors on Reading Habits and Interest among Level 2 Pupils in National Primary Schools in Malaysia. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2010, 5, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babarinde, E.T.; Babarinde, O.; Dike, V. Reading Habit and Use of Electronic Media by Junior Secondary School Students in Nsukka Local Government of Nigeria. J. Child. Media 2018, 12, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Naeghel, J.; Van Keer, H.; Vansteenkiste, M.; Haerens, L.; Aelterman, N. Promoting Elementary School Students’ Autonomous Reading Motivation: Effects of a Teacher Professional Development Workshop. J. Educ. Res. 2016, 109, 232–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Naeghel, J.; Valcke, M.; De Meyer, I.; Warlop, N.; van Braak, J.; Van Keer, H. The Role of Teacher Behavior in Adolescents’ Intrinsic Reading Motivation. Read. Writ. 2014, 27, 1547–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambrell, L.B. Getting Students Hooked on the Reading Habit. Read. Teach. 2015, 69, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsuddin, S.F.; Mohamed Shaffril, H.A.; Bolong, J.; Mohamed, N.A. Understanding the Reading Habit and Attitudes among the Rural Community in Low Literacy Rate Areas in Malaysia: Rural Library Perspectives. Libr. Manag. 2019, 41, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Mok, S.W.; Cheng, Y.Y.J.; Chu, S.K.W. An Examination of a Gamified E-quiz System in Fostering Students’ Reading Habit, Interest and Ability. Proc. Assoc. Info. Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.H. Global Mindset as the Integration of Emerging Socio-Cultural Values Through Mindsponge Processes: A Transition Economy Perspective. In Global Mindsets: Exploration and Perspectives; Kuada, J., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2016; pp. 109–126. ISBN 978-1-315-73639-6. [Google Scholar]
- Vuong, Q.H.; Napier, N.K. Acculturation and Global Mindsponge: An Emerging Market Perspective. Int. J. Intercult. Relat. 2015, 49, 354–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.-H.; Nguyen, H.T.T.; Pham, T.-H.; Ho, M.-T.; Nguyen, M.-H. Assessing the Ideological Homogeneity in Entrepreneurial Finance Research by Highly Cited Publications. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2021, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.-H.; Le, T.-T.; Nguyen, H.-K.T.; Ho, M.-T.; Nguyen, H.T.T.; Vuong, Q.-H. Alice in Suicideland: Exploring the Suicidal Ideation Mechanism through the Sense of Connectedness and Help-Seeking Behaviors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.-H.; La, V.-P.; Ho, M.-T.; Pham, T.-H.; Vuong, T.-T.; Vuong, H.-M.; Nguyen, M.-H. A Data Collection on Secondary School Students’ STEM Performance and Reading Practices in an Emerging Country. Data Intell. 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.-H. The (Ir)Rational Consideration of the Cost of Science in Transition Economies. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2018, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunson, D.B. Commentary: Practical Advantages of Bayesian Analysis of Epidemiologic Data. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 153, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ravenzwaaij, D.; Cassey, P.; Brown, S.D. A Simple Introduction to Markov Chain Monte–Carlo Sampling. Psychon Bull. Rev. 2018, 25, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, P.J.; Łatuszyński, K.; Pereyra, M.; Robert, C.P. Bayesian Computation: A Summary of the Current State, and Samples Backwards and Forwards. Stat. Comput. 2015, 25, 835–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenmakers, E.-J.; Marsman, M.; Jamil, T.; Ly, A.; Verhagen, J.; Love, J.; Selker, R.; Gronau, Q.F.; Šmíra, M.; Epskamp, S.; et al. Bayesian Inference for Psychology. Part I: Theoretical Advantages and Practical Ramifications. Psychon Bull. Rev. 2018, 25, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Open Science Collaboration. Estimating the Reproducibility of Psychological Science. Science 2015, 349, aac4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.H.; La, V.-P. Bayesvl: Visually Learning the Graphical Structure of Bayesian Networks and Performing MCMC with “Stan”; Social Science Research Network: Rochester, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vuong, Q.-H.; La, V.-P.; Nguyen, M.-H.; Ho, M.-T.; Ho, M.-T.; Mantello, P. Improving Bayesian Statistics Understanding in the Age of Big Data with the Bayesvl R Package. Softw. Impacts 2020, 4, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.-H.; La, V.-P.; Nguyen, M.-H.; Ho, M.-T.; Tran, T.; Ho, M.-T. Bayesian Analysis for Social Data: A Step-by-Step Protocol and Interpretation. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehtari, A.; Gelman, A.; Gabry, J. Practical Bayesian Model Evaluation Using Leave-One-out Cross-Validation and WAIC. Stat. Comput 2017, 27, 1413–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElreath, R. Statistical Rethinking: A Bayesian Course with Examples in R and Stan. In CRC Texts in Statistical Science, 2nd ed.; Taylor and Francis, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-0-367-13991-9. [Google Scholar]
- Vuong, Q.-H. Reform Retractions to Make Them More Transparent. Nature 2020, 582, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.; Anderson, J. The Book Whisperer Awakening the Inner Reader in Every Child; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-470-62339-8. [Google Scholar]
- Grimes, M.L. When Children Choose Their Own Books. Child. Educ. 1945, 21, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaria, T.; Alay, A. Effects of Self-Efficacy on Students’ Academic Performance. J. Educ. Health Community Psychol. 2013, 2, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitzmann, T.; Yeo, G. A Meta-Analytic Investigation of the Within-Person Self-Efficacy Domain: Is Self-Efficacy a Product of Past Performance or a Driver of Future Performance? Pers. Psychol. 2013, 66, 531–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cera, R.; Mancini, M.; Antonietti, A. Relationships between Metacognition, Self-Efficacy and Self-Regulation in Learning. J. Educ. Cult. Psychol. Stud. (ECPS J.) 2013, 4, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilfarlioglu, F.Y.; Ciftci, F.S. Supporting Self-Efficacy and Learner Autonomy in Relation to Academic Success in EFL Classrooms (A Case Study). Theory Pract. Lang. Stud. 2011, 1, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.M.; Fults, B.A. Self-Concept and the Gifted Classroom: The Role of Social Comparisons. Gift. Child. Q. 1982, 26, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk, D.H.; Pajares, F. The Development of Academic Self-Efficacy. In Development of Achievement Motivation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 15–31. ISBN 978-0-12-750053-9. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, V.D. Predicting the Attitudes and Self-Esteem of the Grade 9th Lower Secondary School Students towards Mathematics from Their Perceptions of the Classroom Learning Environment. World J. Educ. 2012, 2, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, B.; Lee, Y. A Model for Academic Success: The School and Home Environment of East Asian Students. Anthropol. Educ. Q. 1990, 21, 358–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kleeck, A.; Stahl, S.A.; Bauer, E.B. On Reading Books to Children: Parents and Teachers; L. Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-1-4106-0735-5. [Google Scholar]
- Holdaway, D. Shared Book Experience: Teaching Reading Using Favorite Books. Theory Pract. 1982, 21, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, S.B.; Dickinson, D.K. (Eds.) Handbook of Early Literacy Research; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-1-57230-653-0. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, J. Choosing Books for Young Children. Child. Educ. 1959, 35, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiu-Kai, N. CBRec: A Book Recommendation System for Children Using the Matrix Factorisation and Content-Based Filtering Approaches. IJBIDM 2020, 16, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, S.H.; Nellis, L.M.; Martínez, R.S.; Kirk, M. Supporting the Students Most in Need: Academic Self-Efficacy and Perceived Teacher Support in Relation to within-Year Academic Growth. J. Sch. Psychol. 2011, 49, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J. Universals and Specifics of Math Self-Concept, Math Self-Efficacy, and Math Anxiety across 41 PISA 2003 Participating Countries. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2009, 19, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, K.M. Fostering Middle School Students’ Autonomy to Support Motivation and Engagement. Middle Sch. J. 2019, 50, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchotte, J.A.; Suhr, D.; Alfurayh, N.F.; Graefe, A.K. An Exploration of the Psychosocial Characteristics of High Achieving Students and Identified Gifted Students: Implications for Practice. J. Adv. Acad. 2016, 27, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.-H. Breaking Barriers in Publishing Demands a Proactive Attitude. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2019, 3, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.S. Student Influence on Teacher Behavior. Am. Educ. Res. J. 1971, 8, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, M. Student-Teacher Connection: A Place of Possibility. J. Adv. Nurs. 2005, 52, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamre, B.K.; Pianta, R.C. Student-Teacher Relationships. In Children’s Needs III: Development, Prevention, and Intervention; National Association of School Psychologists: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; pp. 59–71. ISBN 978-0-932955-79-1. [Google Scholar]




| Name | Variable | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reading Interest | Readbook | Binary | Whether the student likes reading books or not. “Yes” is coded as 1 and “No” as 0. |
| Students with high APS | HighAPS | Binary | Students with an average score of STEM-related subjects “APS45” ≥ 8, coded as 1, others are coded as 0. |
| Students with low APS | LowAPS | Binary | Students with an average score of STEM-related subjects “APS45” < 5, coded as 1, others are coded as 0. |
| Reason for choosing a preferred type of book | Reason_PR | Binary | Whether the reason is a recommendation or personal preference. “Personal preference” is coded as 1; “Recommendation” is coded as 0. |
| Parental book reading | Readstory | Binary | Whether a student’s parents read stories for him/her. “Yes” is coded as 1 and “No’ as 0. |
| Parameters | Mean | SD | n_eff | Rhat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 2.66 | 0.19 | 5986 | 1 |
| Reason_PR | −0.26 | 0.20 | 5853 | 1 |
| Reason_PR*HighAPS | 0.70 | 0.18 | 8140 | 1 |
| Reason_PR*LowAPS | −0.18 | 0.16 | 8140 | 1 |
| Parameters | Mean | SD | n_eff | Rhat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 2.17 | 0.06 | 9511 | 1 |
| Readstory | −0.51 | 0.13 | 7583 | 1 |
| Readstory*HighAPS | 0.39 | 0.21 | 8664 | 1 |
| Readstory*LowAPS | 0.04 | 0.24 | 9172 | 1 |
| Parameters | Mean | SD | n_eff | Rhat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 2.34 | 0.06 | 10,555 | 1 |
| Readstory | 0.83 | 0.22 | 9247 | 1 |
| Readstory*HighAPS | 0.65 | 0.44 | 9856 | 1 |
| Readstory*LowAPS | 0.23 | 0.48 | 8741 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vuong, Q.-H.; Nguyen, M.-H.; Le, T.-T. Home Scholarly Culture, Book Selection Reason, and Academic Performance: Pathways to Book Reading Interest among Secondary School Students. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2021, 11, 468-495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe11020034
Vuong Q-H, Nguyen M-H, Le T-T. Home Scholarly Culture, Book Selection Reason, and Academic Performance: Pathways to Book Reading Interest among Secondary School Students. European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education. 2021; 11(2):468-495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe11020034
Chicago/Turabian StyleVuong, Quan-Hoang, Minh-Hoang Nguyen, and Tam-Tri Le. 2021. "Home Scholarly Culture, Book Selection Reason, and Academic Performance: Pathways to Book Reading Interest among Secondary School Students" European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education 11, no. 2: 468-495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe11020034
APA StyleVuong, Q.-H., Nguyen, M.-H., & Le, T.-T. (2021). Home Scholarly Culture, Book Selection Reason, and Academic Performance: Pathways to Book Reading Interest among Secondary School Students. European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education, 11(2), 468-495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe11020034








