Application of Selenocysteine Increased Soil Nitrogen Content, Enzyme Activity, and Microbial Quantity in Camellia oleifera Abel. Forests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Material Collection and Design
2.1.1. Experimental Materials
2.1.2. Experimental Design and Treatments
2.2. Test Methods
2.2.1. Determination of the Physical and Chemical Properties of Soil
2.2.2. Soil Enzyme Activity Determination
2.2.3. Measurement of Soil Microbial Quantity
2.2.4. Determination of Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon and Nitrogen
2.2.5. Determination of Selenium and Nitrogen Content in C. oleifera Seedlings
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
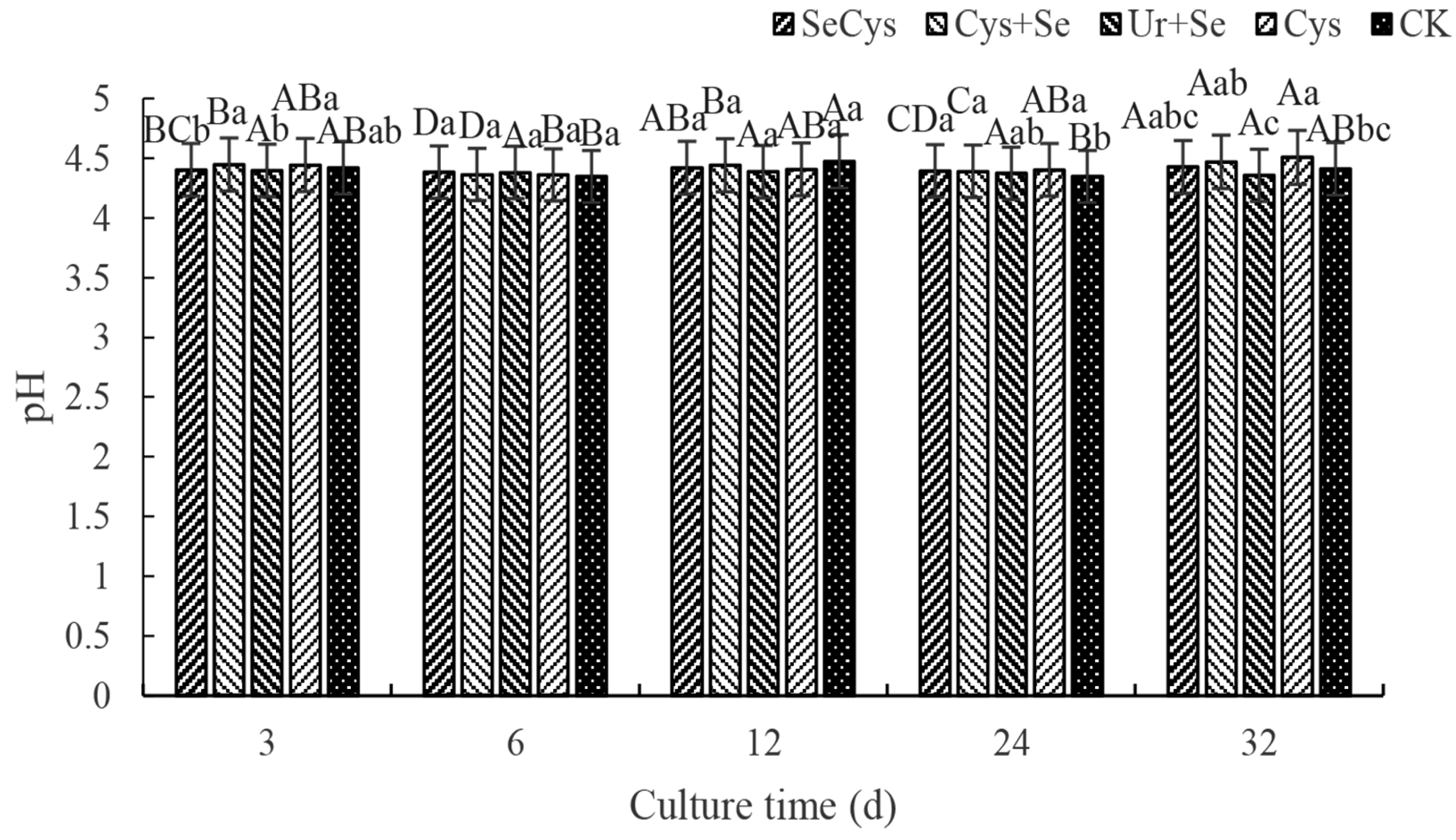
3.1. Soil pH
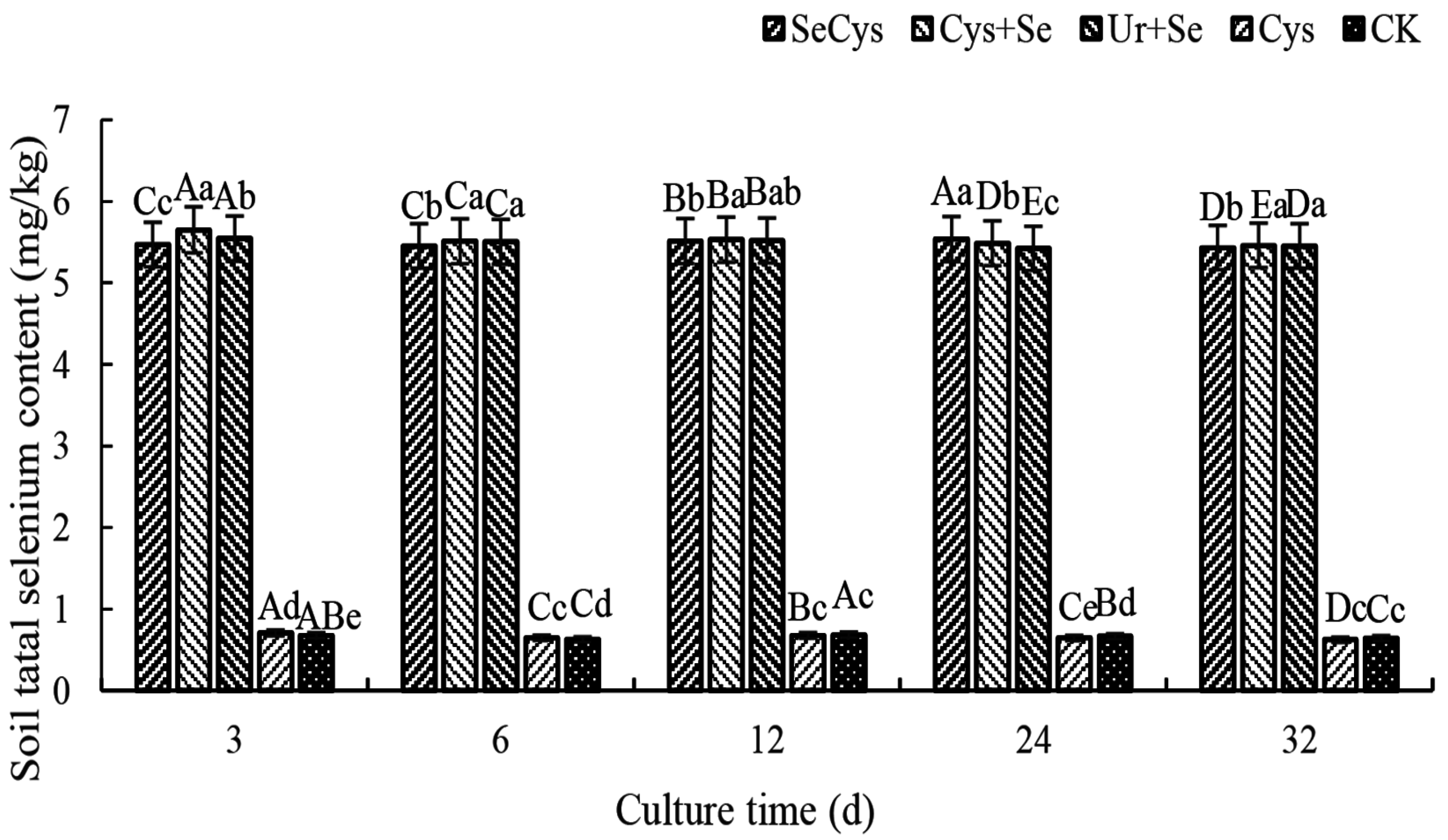
3.2. Soil Total Selenium
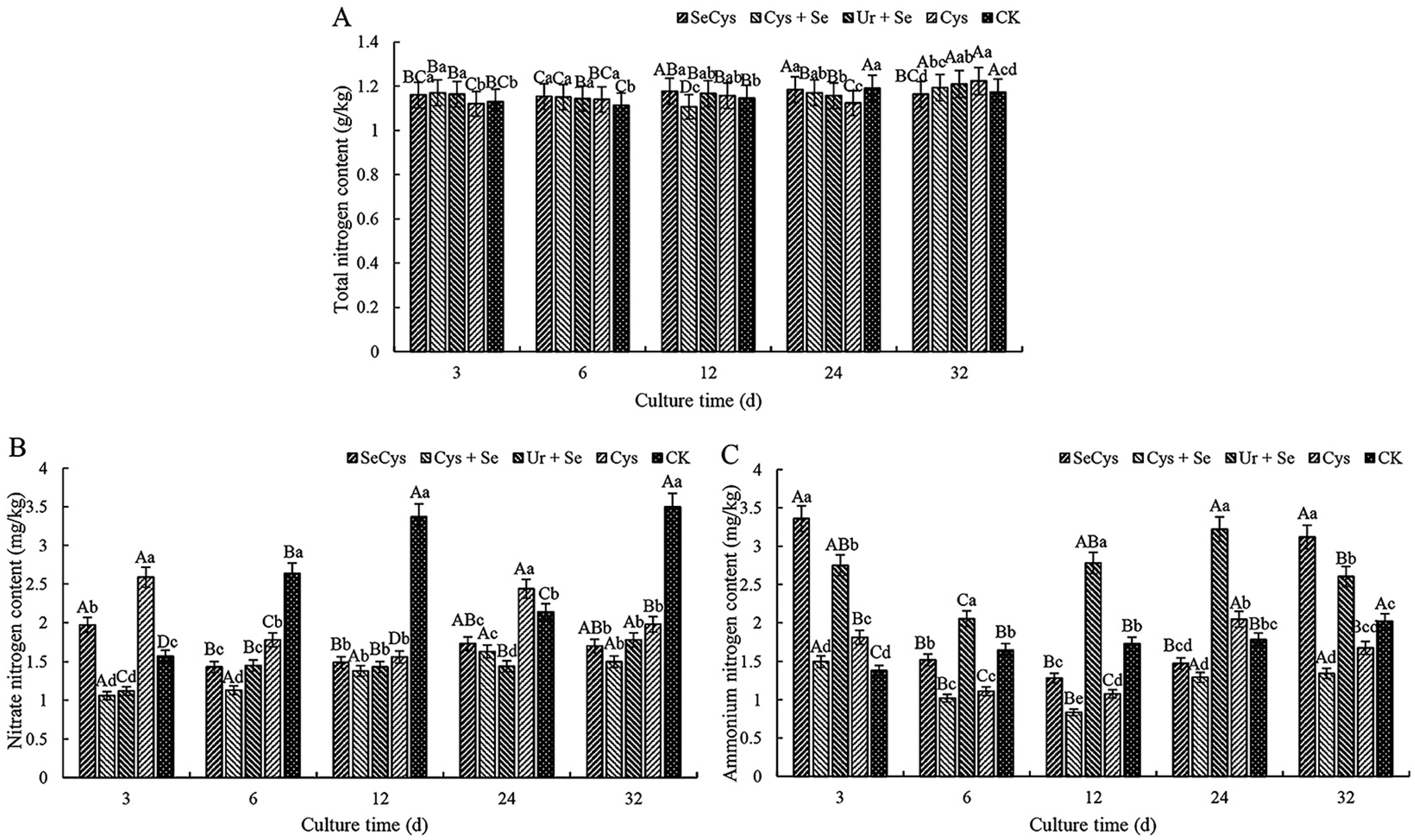
3.3. Soil Nitrogen
3.4. Soil Enzyme Activity
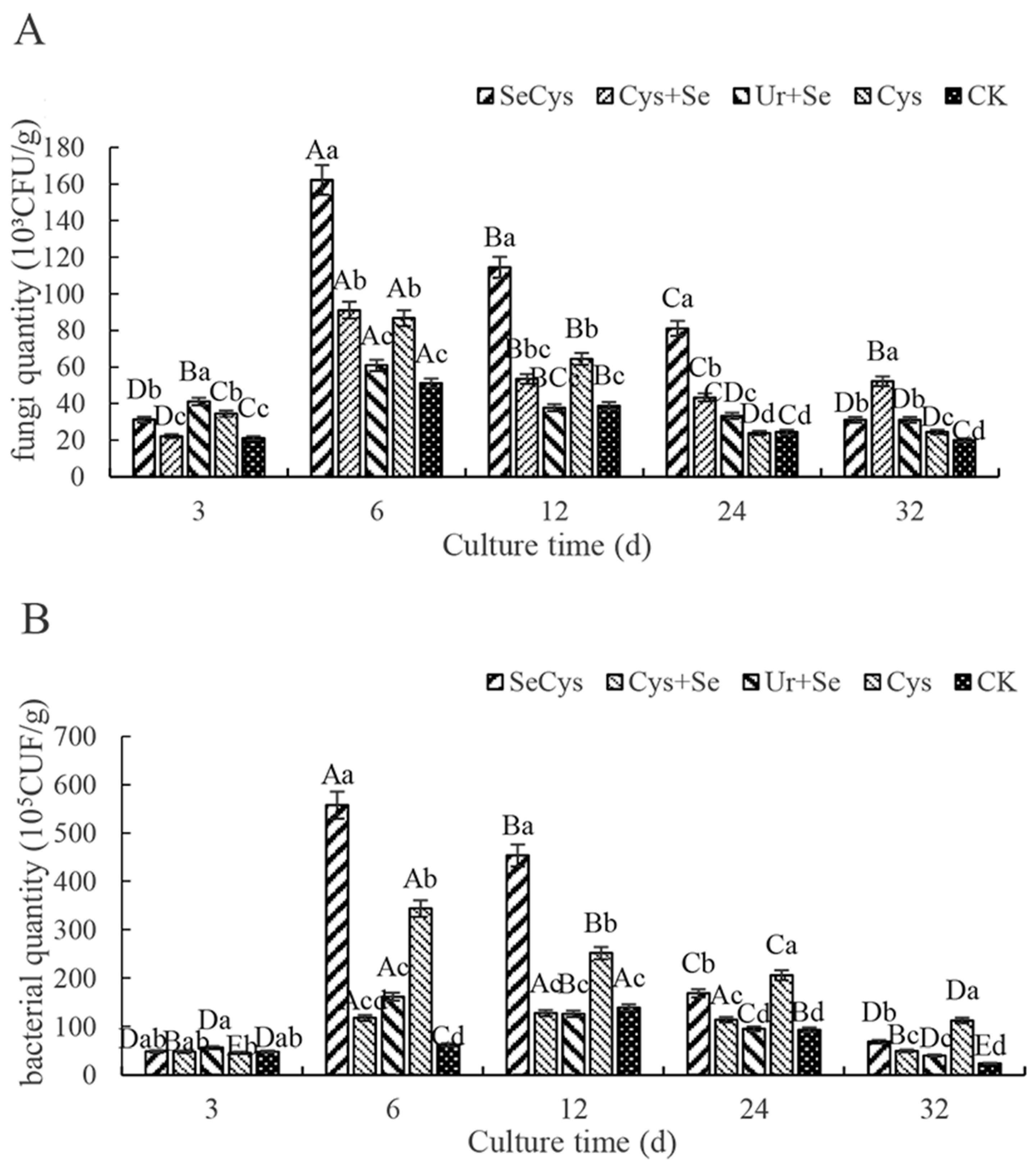
3.5. Soil Fungi and Bacteria Numbers
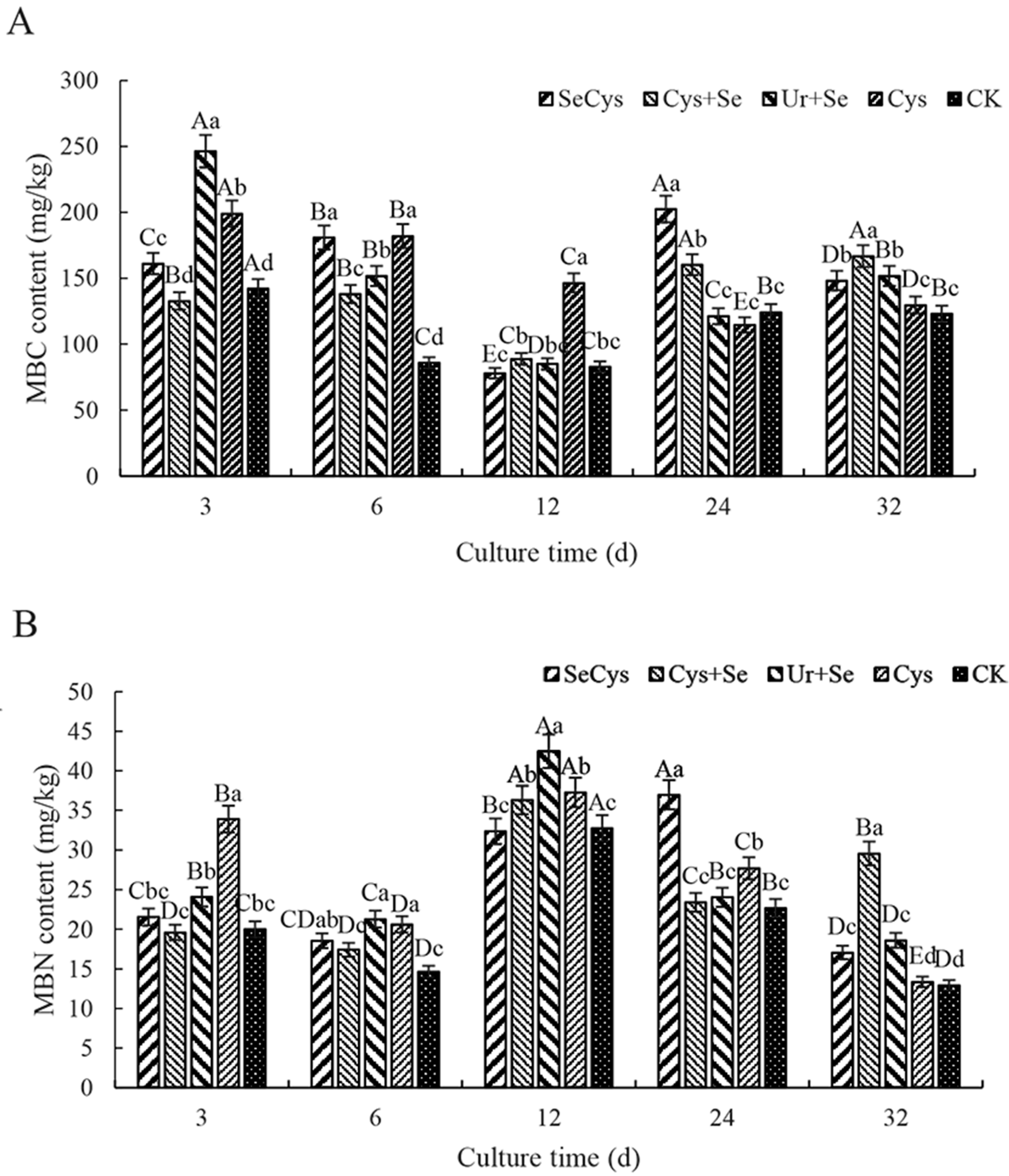
3.6. Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon and Nitrogen Contents
3.7. Selenium and Nitrogen Contents of C. oleifera Seedlings
3.8. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Selenocysteine on Soil Nutrients of C. oleifera Forest
4.2. Effects of Selenocysteine on Soil Enzymes in C. oleifera Forest
4.3. Effects of Selenocysteine on Soil Microbial Characteristics of C. oleifera Forest
4.4. Effects of Selenocysteine on Selenium and Nitrogen Content of Plants and Soils
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsioubri, M.; Gasparatos, D.; Economou-Eliopoulos, M. Selenium Uptake by Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) and Berseem (Trifolium alexandrinum L.) as Affected by the Application of Sodium Selenate, Soil Acidity and Organic Matter Content. Plants 2020, 9, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Hu, C.; Wang, X.; Shi, G.; Li, Y.; Fei, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X. Microbes: A potential tool for selenium biofortification. Metallomics 2021, 13, mfab054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.-H.; Wang, X.-C.; Yao, D.-H.; Zhang, X.-L.; Wong, M.-H. Selenium geochemistry of paddy soils in Yangtze River Delta. Environ. Int. 2001, 26, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiapane, E.; Pessione, A.; Pessione, E. Selenium and selenoproteins: An overview on different biological systems. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2014, 15, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-Q.; Zhu, L.-N.; Li, K.; Wang, Q.; Wang, K.; Guo, Y.-B.; Li, H.-F. Absorption and transportation of selenium nanoparticles in Wheat and Rice. Huan Jing Ke Xue= Huanjing Kexue 2019, 40, 4654–4660. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Dun, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Wu, G. Foliar application of selenium and zinc to alleviate wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cadmium toxicity and uptake from cadmium-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, F.; Wang, L.; Sun, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, W.; Xu, J. Comparative physiological and soil microbial community structural analysis revealed that selenium alleviates cadmium stress in Perilla frutescens. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1022935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Liang, D.; Liu, J.; Xie, J. Ecotoxicological effects of copper and selenium combined pollution on soil enzyme activities in planted and unplanted soils. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ei, H.-H.; Zheng, T.; Farooq, M.-U.; Zeng, R.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Ye, X.; Jia, X.; et al. Impact of selenium, zinc and their interaction on key enzymes, grain yield, selenium, zinc concentrations, and seedling vigor of biofortified rice. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 16940–16949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, W.; Pang, F. Selenium in Soil-Plant-Microbe: A Review. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 108, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavu, R.V.; Du Laing, G.; Van de Wiele, T.; Pratti, V.L.; Willekens, K.; Vandecasteele, B.; Tack, F. Fertilizing soil with selenium fertilizers: Impact on concentration, speciation, and bioaccessibility of selenium in leek (Allium ampeloprasum). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10930–10935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H.; Shang, C.; Luo, L.; Gao, J.; Tang, L. Selenium contamination, consequences and remediation techniques in water and soils: A review. Environ. Res. 2018, 164, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sele, V.; Ørnsrud, R.; Sloth, J.-J.; Berntssen, M.-H.-G.; Amlund, H. Selenium and selenium species in feeds and muscle tissue of Atlantic salmon. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 47, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kil, D.-Y. Comparison of toxic effects of dietary organic or inorganic selenium and prediction of selenium intake and tissue selenium concentrations in broiler chickens using feather selenium concentrations. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 6462–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; He, L.; Du, B.; Pan, S.; Mo, Z.; Duan, M.; Tian, H.; Tang, X. Biofortification with chelating selenium in fragrant rice: Effects on photosynthetic rates, aroma, grain quality and yield formation. Field Crops Res. 2020, 255, 107909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemkemeyer, M.; Schwalb, S.-A.; Heinze, S.; Joergensen, R.-G.; Wichern, F. Functions of elements in soil microorganisms. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 252, 126832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.-P.; Singh, K.-R.; Nagpure, G.; Mansoori, A.; Singh, R.-P.; Ghazi, I.-A.; Kumar, A.; Singh, J. Plant-soil-microbes: A tripartite interaction for nutrient acquisition and better plant growth for sustainable agricultural practices. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.-P.; Ren, C.-J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Z.-X.; Fu, S.-Y.; Liu, W.-C.; Yang, G.-H.; Han, X.-H. Responses mechanism of C:N:P stoichiometry of soil microbial biomass and soil enzymes to climate change. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 2445–2454. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.-F.; Pu, L.-J.; Wang, Q.-Q.; Zhu, M.; Wang, X.-H. Response of Soil Enzyme Activities and Their Relationships with Physicochemical Properties to Different Aged Coastal Reclamation Areas, Eastern China. Huanjing Kexue 2018, 39, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Qi, W.-Y.; Chen, H.; Song, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.-G. Selenium Nanoparticles as an Innovative Selenium Fertilizer Exert Less Disturbance to Soil Microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 746046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Hu, C.-X.; Ming, J.-J.; Cai, M.-M.; Liu, K.; Tang, Y.-N.; Zhao, X.-H. Selenium effects on rapeseed rhizosphere microbes. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2021, 38, 104–110. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.-J.; Xiao, K.-C.; Duan, P.-P.; Li, D.-J.; Liu, Y.-X. Effects of selenium fertilization on selenium uptake of pakchoi and soil biological activities. Res. Agric. Mod. 2021, 42, 755–763. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.-J.; Shi, Y.-J.; Wang, Y.-R.; Li, C.-T.; Zhou, B.-C.; Xie, Y.; Xu, F.-Y.; Liang, L.-Y. Dynamic responses of soil enzymes to exogenous sodium selenite and selenomethionine. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2018, 38, 1189–1196. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C. Pollution-free Control Methods for Oil Tea Pests and Diseases. Seed Sci. Technol. 2022, 40, 91–93. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wu, Z.-L.; Yuan, J. Impact of agro-farming activities on microbial diversity of acidic red soils in a Camellia Oleifera Forest. Rev. Bras. Ciência Do Solo 2019, 43, e0190044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-H. Effects of Different Nitrogen Fertilizers on Microbial Communities of Nitrogen Cycling in Rhizosphere Soil of Camellia Oleifera. Master’s Thesis, Central South University of Forestry and Technology, Changsha, China, 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M. Effects of Different Forms of Nitrogen on Seedling Growth and Soil Enzyme Activity of Camellia Oleifera. Master’s Thesis, Jiangxi Agricultural University, Nanchang, China, 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Wang, J.-P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.-C.; Zhen, Q.; Li, P.-F. Spatial Patterns of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Soil and Their Influencing Factors in a Typical Agro-pastoral Ecotone. Huanjing Kexue 2021, 42, 3010–3017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, D.; Heenan, M.; Xu, Z. Short-term responses of soil nitrogen mineralization, nitrification and denitrification to prescribed burning in a suburban forest ecosystem of subtropical Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, T.; Hu, C.; Kong, Q.; Shi, G.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhai, H.; Xiao, X.; Zhao, X. Chitin combined with selenium reduced nitrogen loss in soil and improved nitrogen uptake efficiency in Guanxi pomelo orchard. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Cai, M.; Hu, C.; Sun, X.; Cheng, Q.; Jia, W.; Yang, T.; Nie, M.; Zhao, X. Selenium (Se) reduces Sclerotinia stem rot disease incidence of oilseed rape by increasing plant Se concentration and shifting soil microbial community and functional profiles. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, L.-S.; Pimenta, T.-M.; Brito, F.-A.L.; Malheiros, R.-S.-P.; Arruda, R.-S.; Araújo, W.-L.; Ribeiro, D.-M. Selenium uptake and grain nutritional quality are affected by nitrogen fertilization in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 40, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadwal, S.; Sharma, S. Selenium alleviates physiological traits, nutrient uptake and nitrogen metabolism in rice under arsenate stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 70862–70881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-P.; Peng, Q.; Liang, D.-L.; Song, W.-W.; Lei, L.-M.; Yu, D.-S. Effects of Nitrogen Application on Selenium Uptake, Translocation and Distribution in Winter Wheat. Huanjing Kexue 2017, 38, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grujcic, D.; Yazici, A.-M.; Tutus, Y.; Cakmak, I.; Singh, B.-R. Biofortification of Silage Maize with Zinc, Iron and Selenium as Affected by Nitrogen Fertilization. Plants 2021, 10, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, F.-C.; Johannes, R.; Philip, C.-B.; Erland, B. Bacterial pH-optima for growth track soil pH, but are higher than expected at low pH. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 7, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, L.; Guo, Q.-S.; Wang, C.-L.; Li, X.; An, J. Effect of compound planting on soil physical and chemical properties and soil enzyme activities of Salvia miltiorrhiza. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2018, 43, 2480–2488. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Wang, M.; Zhou, F.; Zhai, H.; Qi, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, N.; Ma, Y.; Huang, J.; et al. Selenium bioavailability in soil-wheat system and its dominant influential factors: A field study in Shaanxi province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 144664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-J.; Wei, Q.-Q.; Xiong, S.-P.; Shi, L.; Ma, X.-M.; Du, P.; Guo, J.-B. A spectral parameter for the estimation of soil total nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen of winter wheat growth period. Soil Use Manag. 2020, 37, 698–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, C. Effects of the herbicide mesotrione on soil enzyme activity and microbial communities. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, B.; Xie, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Lu, H.; Yan, C. Research on the nitrogen cycle in rhizosphere of Kandelia obovata under ammonium and nitrate addition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 76, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walcher, G.; Stessl, B.; Wagner, M.; Eichenseher, F.; Loessner, M.-J.; Hein, I. Evaluation of paramagnetic beads coated with recombinant Listeria phage endolysin-derived cell-wall-binding domain proteins for separation of Listeria monocytogenes from raw milk in combination with culture-based and real-time polymerase chain reaction-based quantification. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2010, 7, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brookes, P.-C.; Landman, A.; Pruden, G.; Jenkinson, D.-S. Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: A rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985, 17, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Song, L.; Hao, S.; Qin, J.; Yang, C.; Yang, W.; Feng, M.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Song, X. Effects of selenium application concentration, period and method on the selenium content and grain yield of Tartary buckwheat of different varieties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 6868–6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Yang, Y.-W.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Kang, L.-Y.; Li, Y.-J.-X.; Miao, Y.-H.; Guo, L.-P.; Liu, D.-H. Moxa nitrogen content determination and it application in moxa floaa grade identification. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2020, 45, 4051–4056. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Ma, Q.; Zhong, C.; Yang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Q.; Wu, L. Elevational Variation in Soil Amino Acid and Inorganic Nitrogen Concentrations in Taibai Mountain, China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrold, D.-D.; Pett-Ridge, J.; Bottomley, P.-J. Nitrogen mineralization and assimilation at millimeter scales. Methods Enzymol. 2011, 496, 91–114. [Google Scholar]
- Hongliang, M.; Guangting, P.; Ren, G.; Yun, F.-Y. Mineralization of amino acids and its signs in nitrogen cycling of forest soil. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 37, 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, M.; Basu, P.; Stolz, J.-F. The physiology and evolution of microbial selenium metabolism. Met. Integr. Biometal Sci. 2021, 13, mfab024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.-Z.; Feng, R.-W.; Wang, R.-G.; Guo, J.-k.; Zheng, X.-Q. A dual effect of Se on Cd toxicity: Evidence from plant growth, root morphology and responses of the antioxidative systems of paddy rice. Plant Soil 2014, 375, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhao, P.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, H.; Ren, S.-C.; Wu, Z.; et al. Underlying mechanisms responsible for restriction of uptake and translocation of heavy metals (metalloids) by selenium via root application in plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-K.; Park, H.-J.; Cha, S.-J.; Kwon, S.-J.; Park, J.-H. Effect of pyroligneous acid on soil urease, amidase, and nitrogen use efficiency by Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris var. Pekinensis). Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Li, T.; Dou, Y.; Qiao, J.; Wang, Y.; An, S.; Chang, S.-X. Nitrogen fertilization weakens the linkage between soil carbon and microbial diversity: A global meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 6446–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, T.; Chang, S.-X.; Jiang, X.; Song, Y. Biochar increases soil microbial biomass but has variable effects on microbial diversity: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukurov, N.; Pen-Mouratov, S.; Steinberger, Y. The influence of soil pollution on soil microbial biomass and nematode community structure in Navoiy Industrial Park, Uzbekistan. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Pan, W.; Tang, S.; Chadwick, D.-R.; Wen, Y.; Hill, P.-W.; Macdonald, A.; Ge, T.; Si, L.; et al. Substrate control of sulphur utilisation and microbial stoichiometry in soil: Results of 13C, 15N, 14C, and 35S quad labelling. ISME J. 2021, 15, 3148–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-Y.; Jiao, Z.-G.; Shi, Z.; Xiao, S.-H.; Wang, C.-Q.; Dong, Y.-M.; Ma, R.-J. Effects of selenium methionine supplementation in soil on physiological characteristics and quality of Muskmelon with thick skin. Plant Nutr. Fertil. J. 2016, 22, 476–485. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Sanchez, L.; Loffredo, N.; Mounier, S.; Martin-Garin, A.; Coppin, F. Kinetics of selenate sorption in soil as influenced by biotic and abiotic conditions: A stirred flow-through reactor study. J. Environ. Radioact. 2014, 138, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Peng, Q.; Wang, D.; Cui, Z.; Huang, J.; Fu, D.; Liang, D. Effects of selenite and selenate application on distribution and transformation of selenium fractions in soil and its bioavailability for wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 8315–8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolu, J.; Thiry, Y.; Bueno, M.; Jolivet, C.; Potin-Gautier, M.; Le Hécho, I. Distribution and speciation of ambient selenium in contrasted soils, from mineral to organic rich. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 479–480, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, J.; Kaklewski, K.; Klódka, D. Influence of various concentrations of selenic acid (IV) on the activity of soil enzymes. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 291, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.-F.; Wu, H.-H.; Weng, B.-Q.; Ye, J.; Zeng, Y.-R.; Wang, Y.-X. Application of biochar to improve microbial characteristics and enzyme activities in acid red soil tea garden. Soil Fertil. China 2019, 7, 68–74. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.-X.; Zhang, Q.-F.; Lin, K.-M.; Zhou, J.-C.; Yuan, X.-C.; Mei, K.-C.; Wu, Y.; Cui, J.-Y.; Xu, J.-G.; Chen, Y.-M. Enzyme stoichiometry evidence revealed that five years nitrogen addition exacerbated the carbon and phosphorus limitation of soil microorganisms in a Phyllostachys pubescens forest. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Gong, L.; Liu, X.; Shao, K.; Li, X.-Z.; Li, R.-X. Soil Enzyme Activity in Picea schrenkiana and Its Relationship with Environmental Factors in the Tianshan Mountains. Huanjing Kexue 2021, 42, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liang, D.-L.; Peng, Q.; Cui, Z.-W.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.-Q. Interaction between selenium and soil organic matter and its impact on soil selenium bioavailability: A review. Geoderma 2017, 295, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, M.; Stolz, J.-F. Microbial selenium metabolism: A brief history, biogeochemistry and ecophysiology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-F.; McGrath, S.-P.; Zhao, F.-J. Selenium uptake, translocation and speciation in wheat supplied with selenate or selenite. New Phytol. 2008, 178, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitterli, C.; Bañuelos, G.-S.; Schulin, R. Use of transfer factors to characterize uptake of selenium by plants. J. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 107, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chu, C. Selenium Uptake, Transport, Metabolism, Reutilization, and Biofortification in Rice. Rice 2022, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, Q.; Zhao, J.; Feng, W.; Zhao, T.; Mao, G.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, L.; et al. Investigation of the uptake and transport of polysaccharide from Se-enriched Grifola frondosa in Caco-2 cells model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Huang, M.-L.; Li, L.-Y.; Geng, C.-Z.; Zhang, F.-K.; Yan, D.-Y. Effects of selenium-rich fertilizer on tea tree and research progress of new selenium-rich fertilizer. Henan Agric. Sci. 2019, 48, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, D.; Bai, E.; Wang, S.; Zong, S.; Liu, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhao, C.; Hagedorn, F. Three-dimensional mapping of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in soil microbial biomass and their stoichiometry at the global scale. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 6728–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Templer, P.; Findlay, S.; Lovett, G. Soil microbial biomass and nitrogen transformations among five tree species of the Catskill Mountains, New York, USA. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Hernandez, J.-C.; Ro, K.-S.; Díaz, F.-J. Biochar and earthworms working in tandem: Research opportunities for soil bioremediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Tang, W.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Yuan, J. Application of Selenocysteine Increased Soil Nitrogen Content, Enzyme Activity, and Microbial Quantity in Camellia oleifera Abel. Forests. Forests 2023, 14, 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050982
Li J, Tang W, Lu S, Wang Y, Kuang Z, Yuan J. Application of Selenocysteine Increased Soil Nitrogen Content, Enzyme Activity, and Microbial Quantity in Camellia oleifera Abel. Forests. Forests. 2023; 14(5):982. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050982
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jian, Wei Tang, Sheng Lu, Ye Wang, Zuoying Kuang, and Jun Yuan. 2023. "Application of Selenocysteine Increased Soil Nitrogen Content, Enzyme Activity, and Microbial Quantity in Camellia oleifera Abel. Forests" Forests 14, no. 5: 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050982
APA StyleLi, J., Tang, W., Lu, S., Wang, Y., Kuang, Z., & Yuan, J. (2023). Application of Selenocysteine Increased Soil Nitrogen Content, Enzyme Activity, and Microbial Quantity in Camellia oleifera Abel. Forests. Forests, 14(5), 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050982





