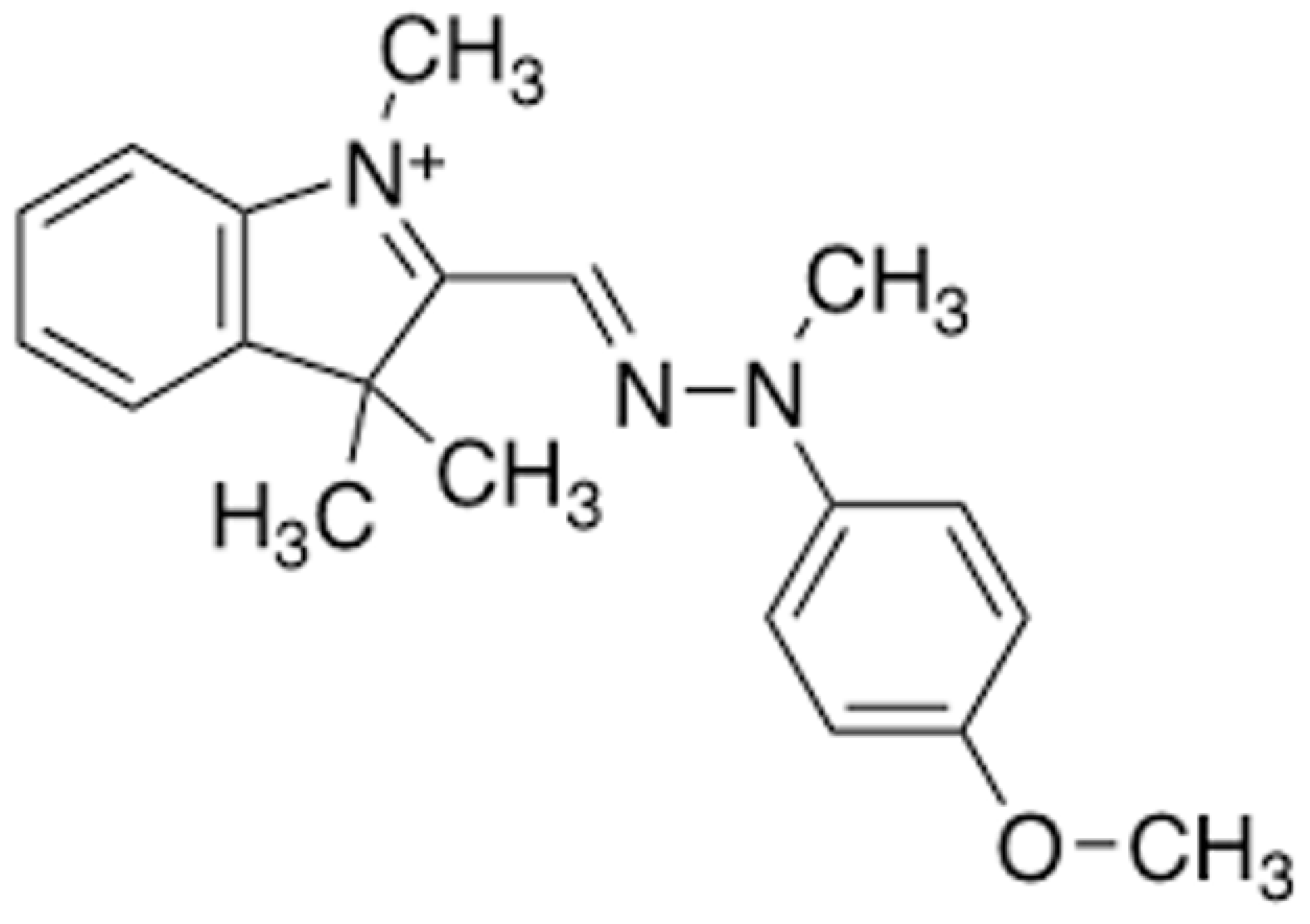
Adsorption, Modeling, Thermodynamic, and Kinetic Studies of Acteray Golden Removal from Polluted Water Using Sindh Clay and Quartz as Low-Cost Adsorbents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
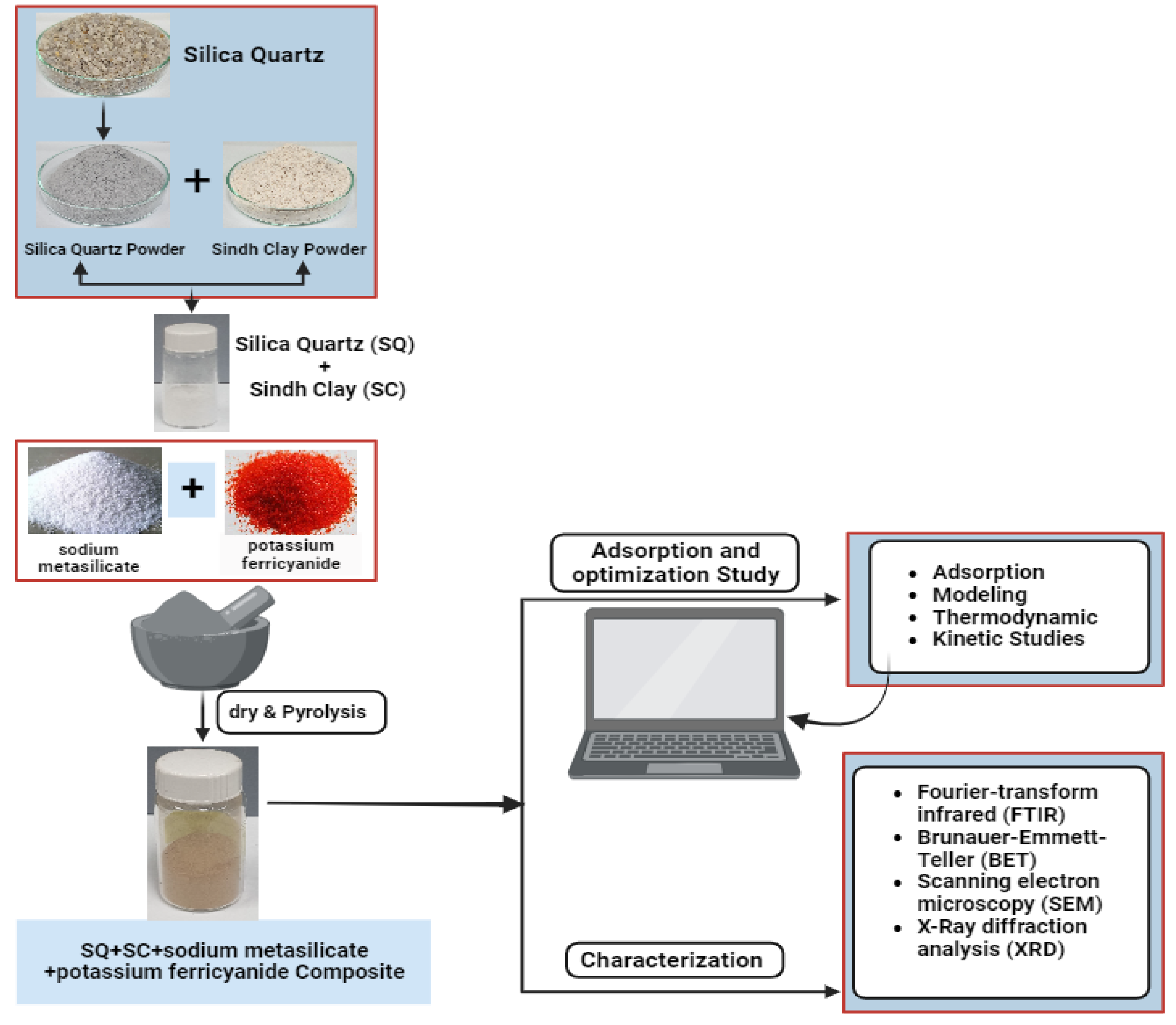
2.2. Preparation of Sample and Composite Materials
2.3. Adsorption Study
2.4. Optimization Experiments
2.4.1. Optimization of Initial Dye Concentration
2.4.2. Optimization of Contact Time
2.4.3. Optimization of Concentration
2.5. Estimation of Absorbance and Spectrophotometric Analysis
2.6. Characterization of Adsorbents
3. Results and Discussion
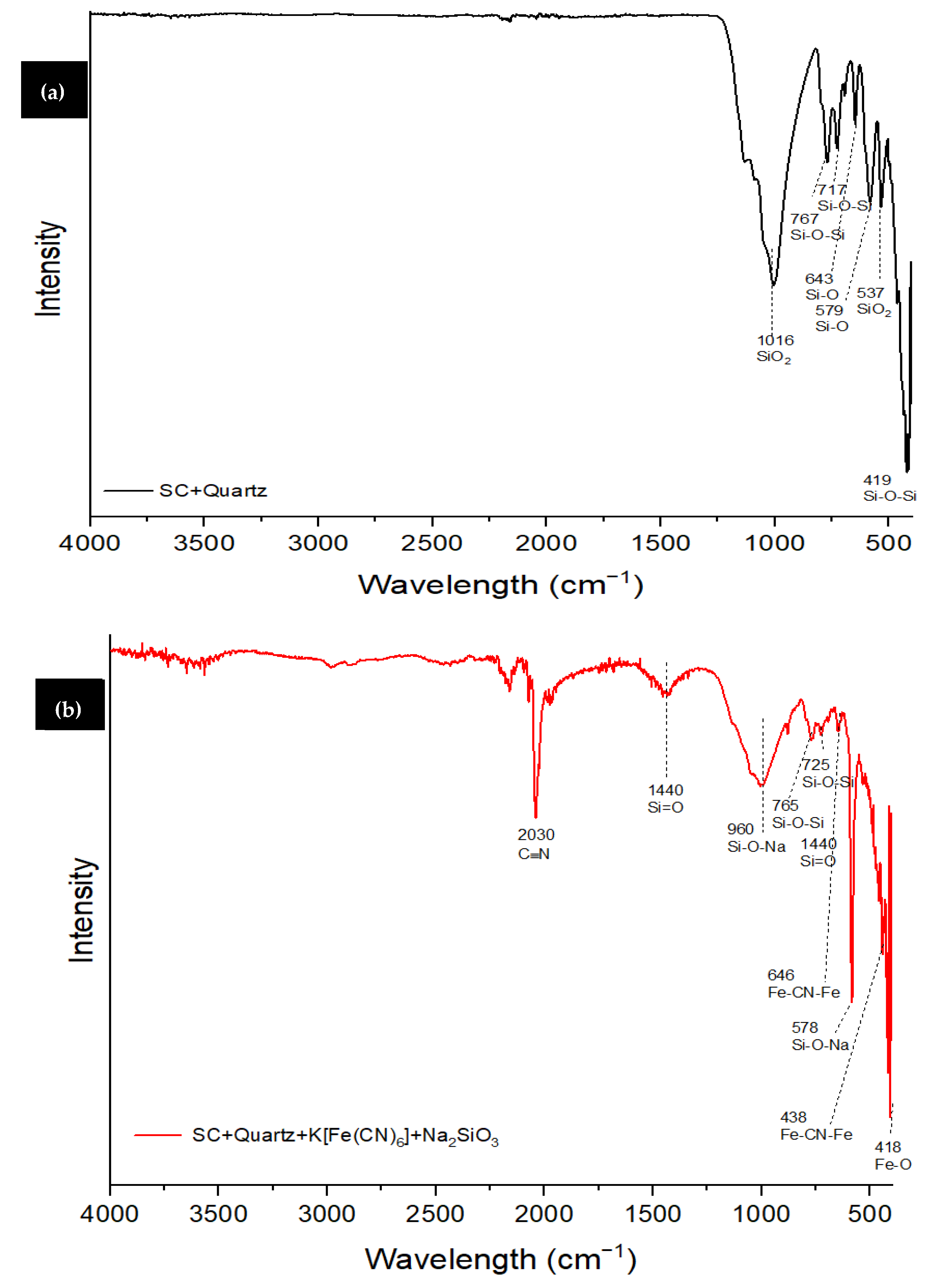
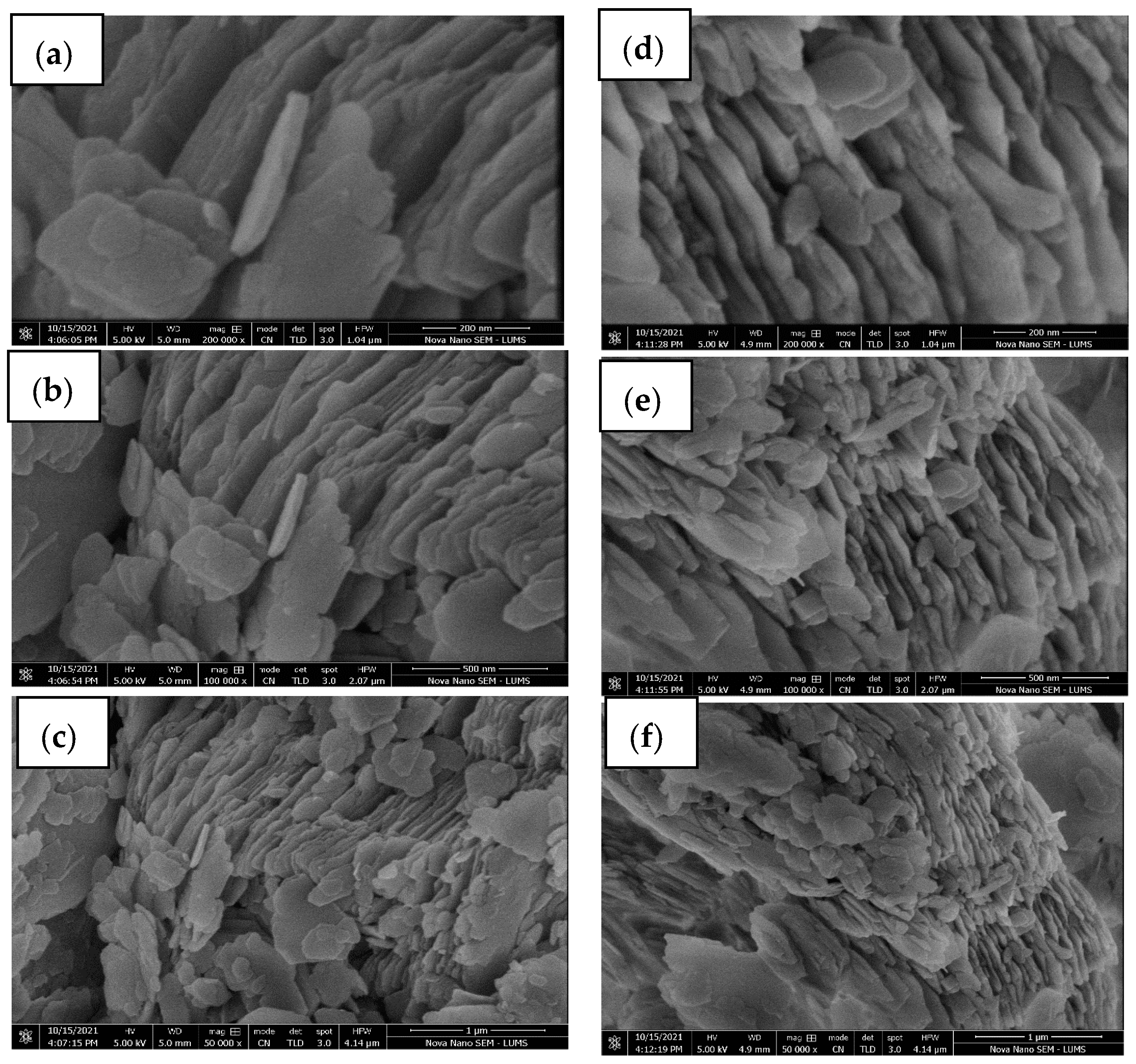
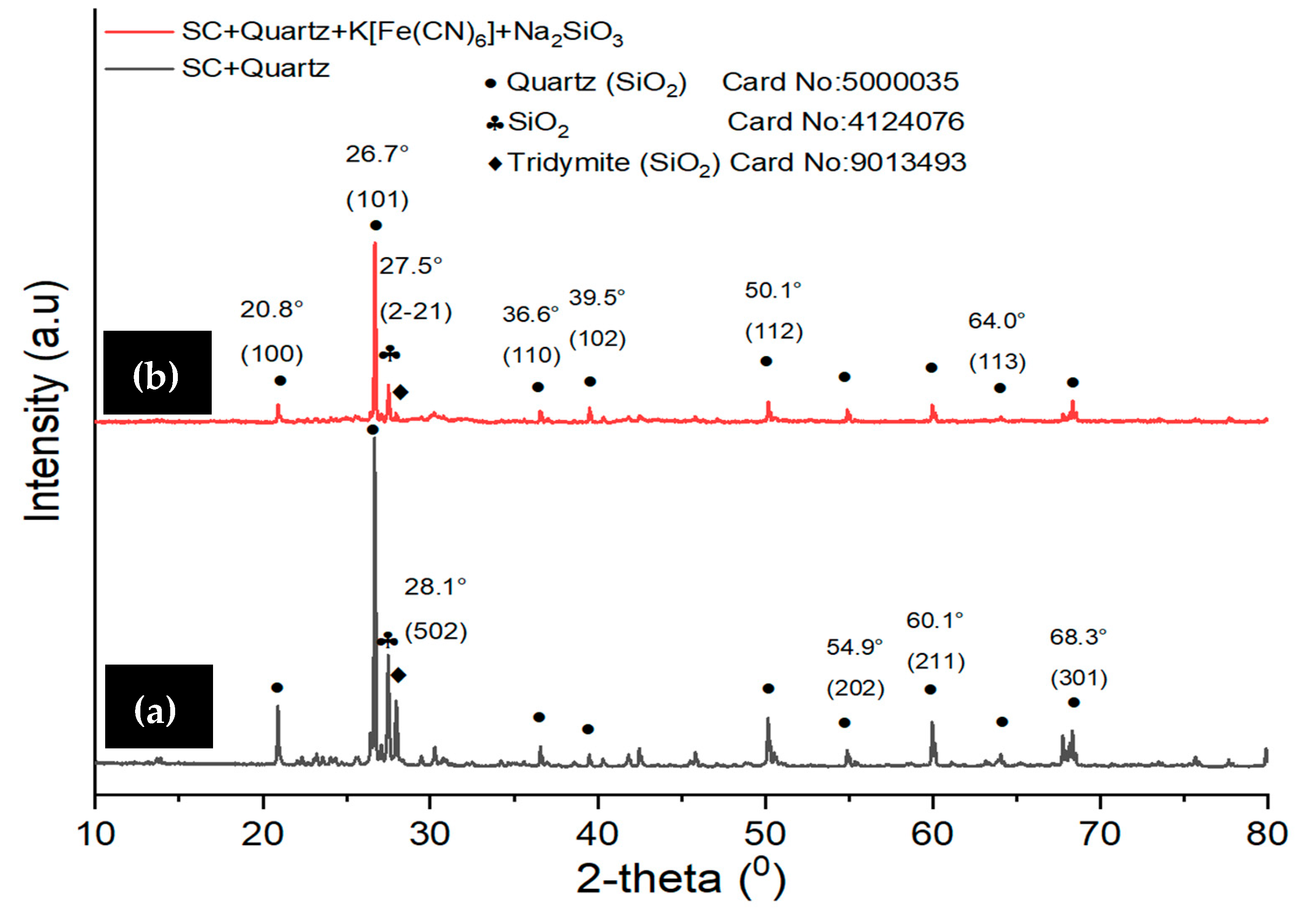
3.1. Characterization of SC + Quartz and SC + Quartz + Potassium Ferricyanide + Sodium Metasilicate
3.2. Determination of Maximum Wavelength (λmax)
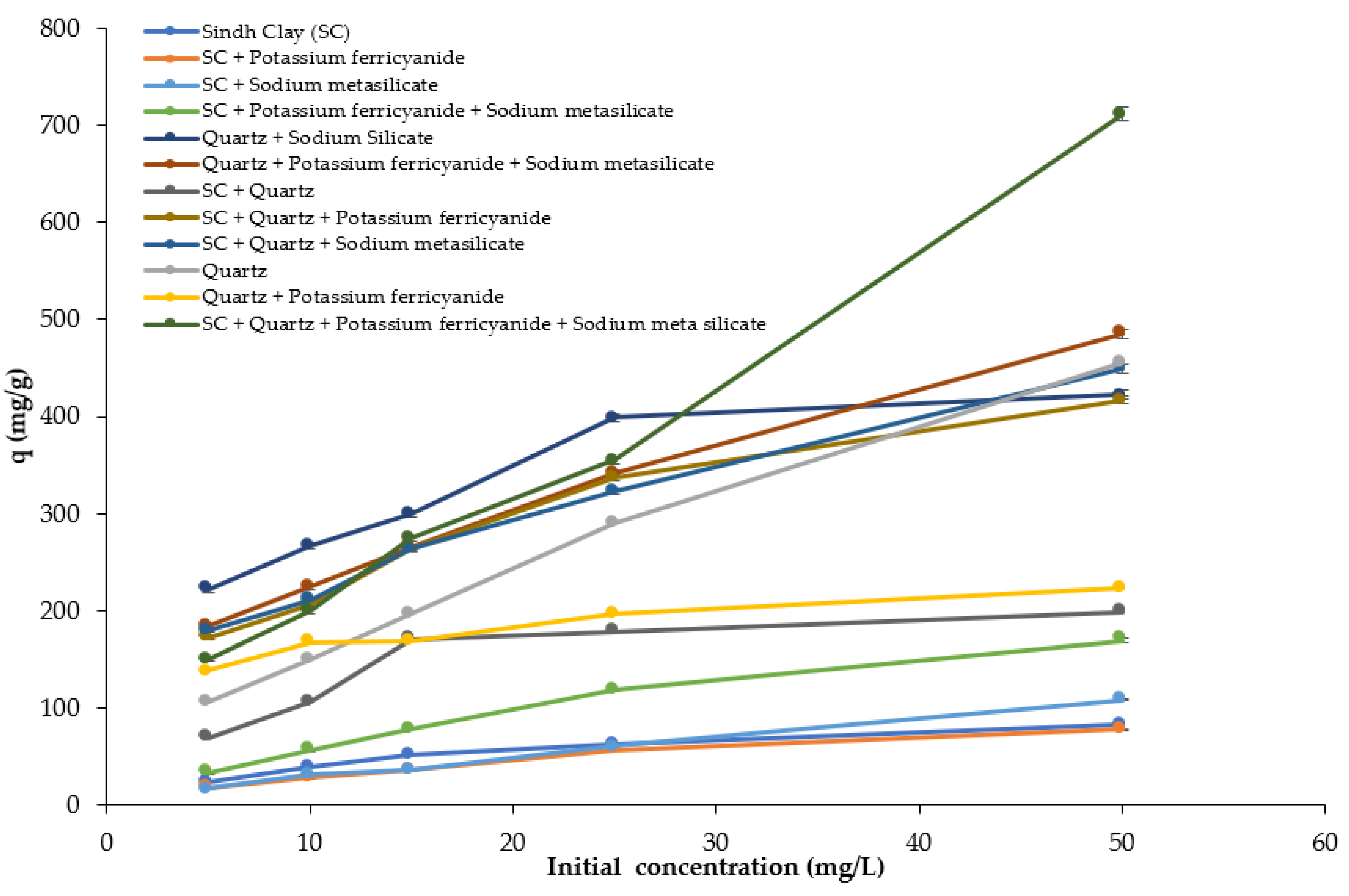
3.3. Effect of Initial Dye Concentration
3.4. Effect of Contact Time
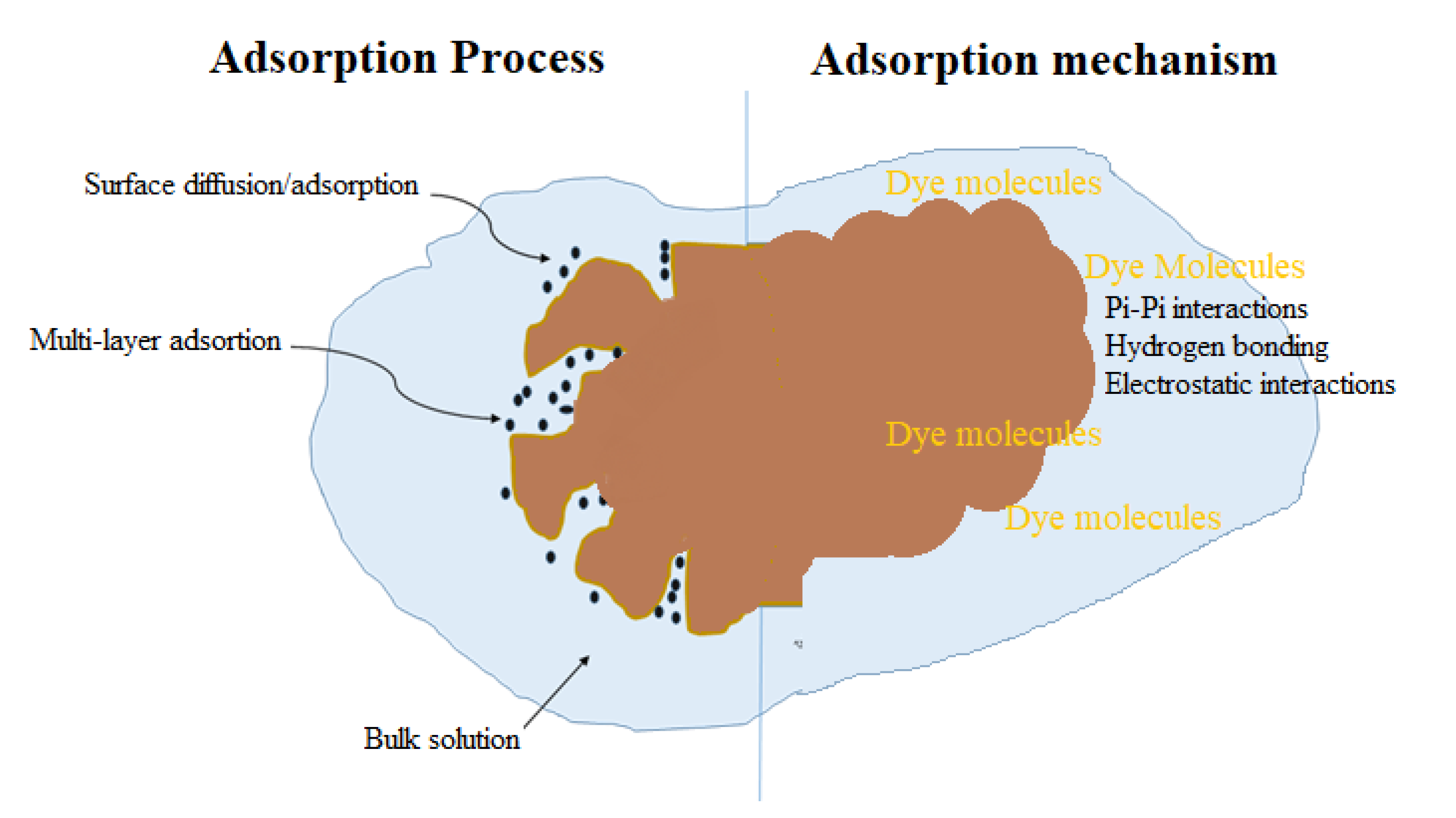
3.5. Plausible Mechanism of Adsorption
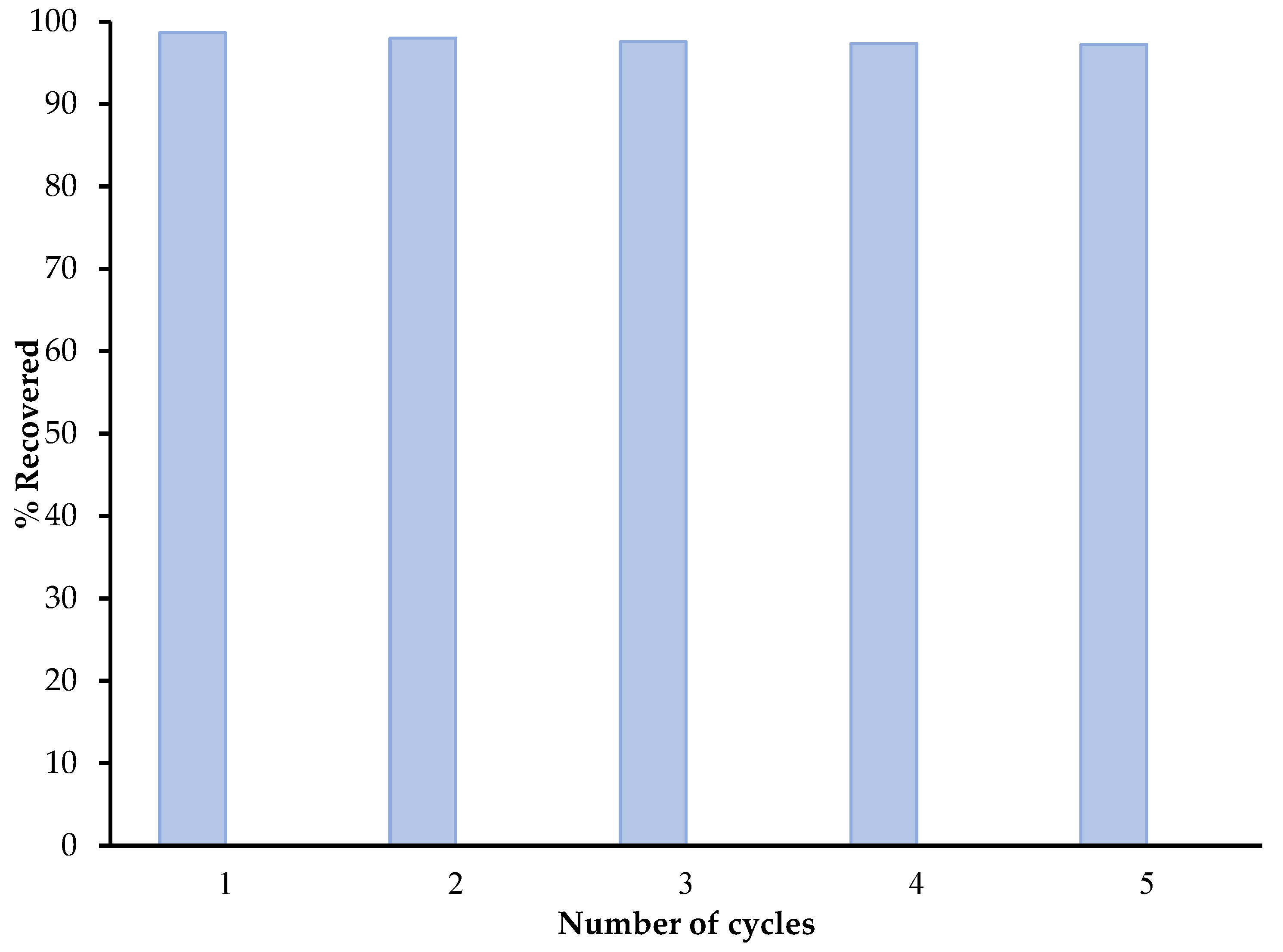
3.6. Reusability of SC + Quartz + Potassium Ferricyanide + Sodium Metasilicate Composite Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zahoor, I.; Mushtaq, A. Water pollution from agricultural activities: A critical global review. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2023, 23, 164–176. [Google Scholar]
- Tariq, A.; Mushtaq, A. Untreated wastewater reasons and causes: A review of most affected areas and cities. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2023, 23, 121–143. [Google Scholar]
- Asghar, F.; Mushtaq, A. The future of nanomaterial in wastewater treatment: A review. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2023, 23, 150–157. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, A.; Mushtaq, A. From pollutant to valuable product: A novel reutilization strategy of wastewater. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2023, 23, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.-Z.; Skrabal, P.; Zollinger, H. A comparison of the absorption spectra of a series of blue disperses dyes with the colorimetric evaluation of their dyeings. Dye. Pigments 1987, 8, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, T.; Mushtaq, A. Efficacy and challenges of carbon-based nanomaterials in water treatment: A review. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2023, 23, 232–248. [Google Scholar]
- Hamada, M.S.; Jabal, R.A. Doped (Ag) ZnO nanoparticles for removal of azo dyes from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2022, 21, 210–217. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, A.; Mushtaq, A. A critical review of electrocoagulation and other electrochemical methods. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2023, 23, 98–110. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, Z.; Mushtaq, A. Advancements in treatment of high-salinity wastewater: A critical review. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2023, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Aljeboree, A.M.; Alshirifi, A.N.; Alkaim, A.F. Activated carbon (as a waste plant sources)–clay micro/nanocomposite as effective adsorbent: Process optimization for ultrasound-assisted adsorption removal of amoxicillin drug. Plant Arch. 2019, 19, 915–919. [Google Scholar]
- Maqsood, M.; Khalid, T.; Kazerooni, E.G.; Javed, I.; Nadeem, F. Wastewater treatment using soil composites as effective adsorbents–A comprehensive review. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2019, 16, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Nadeem, F.; Khan, F.G.; Bashir, I. Advancements in natural bio-flocculants for water treatment. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2020, 17, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Salleh, M.A.M.; Mahmoud, D.K.; Karim, W.A.W.A.; Idris, A. Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2011, 280, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orucoglu, E.; Grangeon, S.; Gloter, A.; Robinet, J.-C.; Madé, B.; Tournassat, C. Competitive adsorption processes at clay mineral surfaces: A coupled experimental and modeling approach. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2022, 6, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.A.; Najam, T.; Shahzad, K.; Wattoo, M.A.; Hussain, T.; Tufail, M.K.; Shah, S.S.A.; ur Rehman, A. Heterointerface engineering of water stable ZIF-8@ZIF-67: Adsorption of rhodamine B from water. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 34, 102324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.A.; Najam, T.; Jabeen, S.; Wattoo, M.A.; Bashir, M.S.; Shah, S.S.A.; ur Rehman, A. Facile synthesis of Tri-metallic layered double hydroxides (NiZnAl-LDHs): Adsorption of Rhodamine-B and methyl orange from water. Inorg. Chem. Commu. 2022, 145, 110008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshaid, M.; Khan, H.M.; Nazir, M.A.; Wattoo, M.A.; Shahzad, K.; Malik, M.; Rehman, A.U. A novel bentonite–cobalt doped bismuth ferrite nanoparticles with boosted visible light induced photodegradation of methyl orange: Synthesis, characterization and analysis of physiochemical changes. Inter. J. Environ. Analyt. Chem. 2022, 2022, 2032014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshaid, M.; Khan, M.I.; Fernandez, J.; Shanableh, A.; Hussain, T.; ur Rehman, A. Synthesis of Ti4+ doped Ca-BiFO3 for the enhanced photodegradation of moxifloxacin. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 19848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.; McKay, G.; Wase, D.; Forster, C. Study of the sorption of divalent metal ions on to peat. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2000, 18, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, V.F.F.; Mackenzie, K.J.D.; Thaumaturgo, C. Synthesis and characterisation of materials based on inorganic polymers of alumina and silica: Sodium polysialate polymers. Int. J. Inorg. Mater. 2000, 2, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, P.; Peshwe, D.; Pathak, S. FTIR and TGA analysis in relation with the % crystallinity of the SiO2 obtained by burning rice husk at various temperatures. Advan. Mater. Res. 2012, 585, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohilla, S.; Lal, B.; Sunder, S.; Aghamkar, P.; Kumar, S.; Aggarwal, A. Synthesis of Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3·14H2O nanopowder by co-precipitation technique and effect of heat treatment. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2010, 118, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-El-Enein, S.A.; Eissa, M.A.; Diafullah, A.A.; Rizk, M.A.; Mohamed, F.M. Removal of some heavy metals ions from wastewater by copolymer of iron and aluminum impregnated with active silica derived from rice husk ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, S.H.; Islam, A.; Chan, E.S.; Choong, S.Y.T.; Alharthi, N.H.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Awual, M.R. Efficient biodiesel production from Jatropha curcus using CaSO4/Fe2O3-SiO2 core-shell magnetic nanoparticles. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.A.; Jabbari, V.; Islam, M.T.; Turley, R.S.; Dominguez, N.; Kim, H.; Castro, E.; Hernandez-Viezcas, J.A.; Curry, M.L.; Lopez, J.; et al. Sustainable synthesis and remarkable adsorption capacity of MOF/graphene oxide and MOF/CNT based hybrid nanocomposites for the removal of Bisphenol A from water. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, A.; Kaur, D.; Malviya, A.; Mittal, J.; Gupta, V. Adsorption studies on the removal of coloring agent phenol red from wastewater using waste materials as adsorbents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 337, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayakumar, G.; Tamilarasan, R.; Dharmendirakumar, M. Adsorption, kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies on the removal of basic dye Rhodamine-B from aqueous solution by the use of natural adsorbent perlite. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2012, 3, 157–170. [Google Scholar]
- Akl, M.; Youssef, A.; Al-Awadhi, M. Adsorption of acid dyes onto bentonite and surfactant-modified bentonite. J. Anal. Bioanal. Tech. 2013, 4, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Fost, S.D.; Aly, M.O. Adsorption Processes for Water Treatment; Betterworth Publications: Stoneharm, MA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, T.L. Statistical mechanics of multimolecular adsorption II. Localized and mobile adsorption and absorption. J. Chem. Phy. 1946, 14, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayawei, N.; Ekubo, A.T.; Wankasi, D.; Dikio, E.D. Adsorption of congo red by Ni/Al-CO3: Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies. Orient. J. Chem. 2015, 31, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Padmesh, T.V.N.; Palanivelu, K.; Velan, M. Biosorption of nickel(II) ions onto Sargassum wightii: Application of two-parameter and three-parameter isotherm models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 133, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papic, S.; Koprivanac, N.; Metes, A. Optimizing polymer-induced flocculation process to remove reactive dyes from wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2000, 21, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, A.; Loukidou, M.; Matis, K. Biosorption of toxic metals from aqueous solutions by bacteria strains isolated from metal-polluted soils. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimonses, V.; Lei, S.; Jin, B.; Chow, C.W.; Saint, C. Kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analysis of Congo Red adsorption by clay materials. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 148, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerie, E.; Alemu, A. Removal of acid yellow dye 17 from aqueous solutions using an activated bone char. Water Qual. Res. J. 2022, 57, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Mohammadi, L.; Rahdar, A.; Rahdar, S.; Dehghani, R.; Adaobi Igwegbe, C.; Kyzas, G.Z. Acid dye removal from aqueous solution by using neodymium(III) oxide nanoadsorbents. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraei, N.; Khanal, M.; Tizghadam, M. Removing acidic yellow dye from wastewater using Moringa peregrina. Comput. Res. Prog. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Hussain, M.; Mahmood, K.; Wajid, A.; Yusof, M.; Alias, Y.; Yusoff, I. Removal of acid yellow-17 dye from aqueous solution using eco-friendly biosorbent. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 4530–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, A.; Kerie, E. Removal of acid yellow 17 dye from aqueous solutions using activated water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes). Water Pract. Technol. 2022, 17, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praipipat, P.; Ngamsurach, P.; Prasongdee, V. Comparative reactive blue 4 dye removal by lemon peel bead doping with iron(III) oxide-hydroxide and zinc oxide. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 41744–41758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Sayed, M.; Ali, F.; Khan, H.M. Removal of acid yellow 17 dye by Fenton oxidation process. Z. Für Phys. Chem. 2018, 232, 507–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanis, T.; Hela, D.; Sakellarides, T.; Danis, T. Removal of dyes from aqueous solutions by adsorption on mixtures of fly ash and soil in batch and column techniques. Glob. Nest Int. J. 2000, 2, 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Kabir, S.M.F.; Cueto, R.; Balamurugan, S.; Romeo, L.D.; Kuttruff, J.T.; Marx, B.D.; Negulescu, I.I. Removal of acid dyes from textile wastewaters using fish scales by absorption process. Clean Technol. 2019, 1, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A. Kinetic models and thermodynamics of adsorption processes: Classification. In Interface Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 65–97. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, L.; Kushwaha, A.; Kafle, S.R.; Kim, B.-S. Surface modification of biochar for dye removal from wastewater. Catalysts 2022, 12, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Materials | BET Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SC + Quartz | 4.02 | 0.019 | 3.34 |
| SC + quartz + potassium ferricyanide + sodium metasilicate | 7.20 | 0.025 | 3.27 |
| Models | Adsorbents | R2 | Qe | Qo | K | n | β | E | A | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir Isotherm | Sindh Clay | 0.1564 | 8.293964 | 909.0 | 0.011 | |||||
| SC + K | 0.1195 | 7.816123 | 1250 | 147.87 | ||||||
| SC + Na | 0.0329 | 10.85383 | 5000 | 0.002 | ||||||
| SC + Mix | 0.1217 | 16.96338 | 1000 | 0.0085 | ||||||
| Quartz | 0.3516 | 22.35616 | 1111.1 | 0.073 | ||||||
| Quartz + K | 0.9935 | 42.25485 | 833.3 | 0.235 | ||||||
| Quartz + Na | 0.9812 | 48.50092 | 1666.6 | 0.187 | ||||||
| Quartz + Mix | 0.2991 | 19.83042 | 3333.3 | 0.0256 | ||||||
| SC + Q | 0.9886 | 41.70874 | 769.2 | 0.236 | ||||||
| SC + Q + K | 0.9325 | 44.91711 | 1666.6 | 0.115 | ||||||
| SC + Q + Na | 0.9111 | 19.83042 | 2000 | 0.111 | ||||||
| SC + Q + Mix | 0.964 | 36.04291 | 1428 | 0.166 | ||||||
| Freundlich Isotherm | Sindh Clay | 0.8184 | 8.293964 | 96.82 | 0.917 | 1.089 | ||||
| SC + K | 0.9089 | 7.816123 | 9.783 | 0.246 | 1.0319 | |||||
| SC + Na | 0.9651 | 10.85383 | 11.83 | 0.292 | 1.006 | |||||
| SC + Mix | 0.8285 | 16.96338 | 11.50 | 0.3019 | 0.98 | |||||
| Quartz | 0.9956 | 22.35616 | 22.93 | 4.162 | 1.876 | |||||
| Quartz + K | 0.959 | 42.25485 | 22.02 | 11.12 | 0.1735 | |||||
| Quartz + Na | 0.6528 | 48.50092 | 43.28 | 17.30 | 0.246 | |||||
| Quartz + Mix | 0.5672 | 19.83042 | 43.16 | 5.84 | 1.750 | |||||
| SC + Q | 0.6682 | 41.70874 | 22.96 | 6.429 | 2.994 | |||||
| SC + Q + K | 0.5958 | 44.91711 | 42.86 | 11.06 | 2.64 | |||||
| SC + Q + Na | 0.5562 | 19.83042 | 44.66 | 13.18 | 2.90 | |||||
| SC + Q + Mix | 0.6054 | 36.04291 | 39.76 | 10.19 | 2.812 | |||||
| Dubinin Isotherm | Sindh Clay | 0.9828 | 8.293964 | 7.314 | 9 × 10−6 | 238.09 | ||||
| SC + K | 0.9444 | 7.816123 | 6.025 | 9 × 10−6 | 238.09 | |||||
| SC + Na | 0.853 | 10.85383 | 6.855 | 7 × 10−6 | 267.37 | |||||
| SC + Mix | 0.4022 | 16.96338 | 6.269 | 5 × 10−6 | 316.45 | |||||
| Quartz | 0.3029 | 22.35616 | 20.32 | 3 ×10−6 | 409.83 | |||||
| Quartz + K | 0.7136 | 42.25485 | 19.51 | 1 × 10−6 | 709.21 | |||||
| Quartz + Na | 0.4137 | 48.50092 | 37.22 | 2 × 10−6 | 500 | |||||
| Quartz + Mix | 0.3579 | 19.83042 | 37.95 | 9 × 10−6 | 238.09 | |||||
| SC + Q | 0.9407 | 41.70874 | 20.05 | 2 × 10−6 | 500 | |||||
| SC + Q + K | 0.5248 | 44.91711 | 38.47 | 4 × 10−6 | 354.60 | |||||
| SC + Q + Na | 0.413 | 19.83042 | 39.30 | 3 × 10−6 | 413.223 | |||||
| SC + Q + Mix | 0.7582 | 36.04291 | 37.49 | 3 × 10−6 | 409.83 | |||||
| Temkin Isotherm | Sindh Clay | 0.9844 | 8.293964 | 3.1855 | 0.384 | |||||
| SC + K | 0.9891 | 7.816123 | 3.0841 | 0.268 | ||||||
| SC + Na | 0.9267 | 10.85383 | 4.1606 | 0.252 | ||||||
| SC + Mix | 0.6611 | 16.96338 | 6.2149 | 0.199 | ||||||
| Quartz | 0.3413 | 22.35616 | 11.05 | 0.443 | ||||||
| Quartz + K | 0.9507 | 42.25485 | 3.084 | 22.78 | ||||||
| Quartz + Na | 0.7107 | 48.50092 | 10.84 | 1.708 | ||||||
| Quartz + Mix | 0.2931 | 19.83042 | 9.516 | 1.110 | ||||||
| SC + Q | 0.7739 | 41.70874 | 4.204 | 3.485 | ||||||
| SC + Q + K | 0.694 | 44.91711 | 10.802 | 1.329 | ||||||
| SC + Q + Na | 0.6778 | 19.83042 | 10.846 | 1.708 | ||||||
| SC + Q + Mix | 0.7072 | 36.04291 | 8.7758 | 2.011 | ||||||
| Herkin–Jura Isotherm | Sindh Clay | 0.5243 | 8.293964 | −0.876 | −1.411 | |||||
| SC + K | 0.5856 | 7.816123 | −0.688 | −1.384 | ||||||
| SC + Na | 0.6404 | 10.85383 | −1.177 | −1.401 | ||||||
| SC + Mix | 0.9513 | 16.96338 | −2.878 | −1.505 | ||||||
| Quartz | 0.8391 | 22.35616 | −104.16 | −1.666 | ||||||
| Quartz + K | 0.9396 | 42.25485 | −370.3 | −2.407 | ||||||
| Quartz + Na | 0.5115 | 48.50092 | −833.3 | −2 | ||||||
| Quartz + Mix | 0.276 | 19.83042 | −277.7 | −1.66 | ||||||
| SC + Q | 0.4635 | 41.70874 | −75.18 | −1.593 | ||||||
| SC + Q + K | 0.417 | 44.91711 | −0.0026 | −1.629 | ||||||
| SC + Q + Na | 0.3289 | 19.83042 | −526.3 | −1.789 | ||||||
| SC + Q + Mix | 0.4175 | 36.04291 | −0.0034 | −1.617 |
| Temperature | Adsorbents | R2 | Qe | QO | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 °C | Sindh Clay | 0.9132 | 47.37458 | 51.70 | 0.0156 |
| SC + K | 0.6434 | 32.62975 | 17.98 | 0.0092 | |
| SC + Na | 0.9227 | 33.92675 | 22.94 | 0.0131 | |
| SC + Mix | 0.6068 | 39.11474 | 29.88 | 0.011 | |
| Quartz | 0.8335 | 64.98645 | 89.92 | 0.0165 | |
| Quartz + K | 0.2439 | 66.96608 | 16.83 | 0.0096 | |
| Quartz + Na | 0.9447 | 55.77094 | 46.53 | 0.015 | |
| Quartz + Mix | 0.8362 | 42.66442 | 30.98 | 0.0126 | |
| SC + Q | 0.8656 | 38.56864 | 35.05 | 0.0133 | |
| SC + Q + K | 0.8961 | 47.71589 | 36.46 | 0.0138 | |
| SC + Q + Na | 0.7554 | 40.13869 | 26.28 | 0.0156 | |
| SC + Q + Mix | 0.8192 | 37.06685 | 23.78 | 0.0117 | |
| 40 °C | Sindh Clay | 0.9559 | 48.67158 | 49.78 | 0.0163 |
| SC + K | 0.9065 | 50.71947 | 76.45 | 0.0165 | |
| SC + Na | 0.9158 | 40.34348 | 46.31 | 0.0147 | |
| SC + Mix | 0.8813 | 42.80095 | 54.50 | 0.0151 | |
| Quartz | 0.9081 | 53.79131 | 67.76 | 0.00016 | |
| Quartz + K | 0.912 | 57.27272 | 92.00 | 0.0172 | |
| Quartz + Na | 0.8696 | 64.78166 | 111.17 | 0.0175 | |
| Quartz + Mix | 0.9251 | 53.65478 | 65.32 | 0.0161 | |
| SC + Q | 0.8748 | 53.31346 | 80.35 | 0.163 | |
| SC + Q + K | 0.9562 | 35.70159 | 38.12 | 0.0142 | |
| SC + Q + Na | 0.8473 | 48.12547 | 52.50 | 0.0147 | |
| SC + Q + Mix | 0.8551 | 51.33384 | 61.84 | 0.0154 | |
| 50 °C | Sindh Clay | 0.9521 | 48.19373 | 38.77 | 0.0142 |
| SC + K | 0.9407 | 40.00216 | 31.85 | 0.0135 | |
| SC + Na | 0.9116 | 41.98179 | 37.11 | 0.0138 | |
| SC + Mix | 0.9189 | 45.1219 | 54.52 | 0.015 | |
| Quartz | 0.8451 | 46.965 | 55.11 | 0.014 | |
| Quartz + K | 0.9249 | 49.90031 | 37.32 | 0.0138 | |
| Quartz + Na | 0.8523 | 54.26915 | 60.10 | 0.0151 | |
| Quartz + Mix | 0.8716 | 43.8249 | 35.39 | 0.0133 | |
| SC + Q | 0.8694 | 45.80453 | 35.90 | 0.0133 | |
| SC + Q + K | 0.8759 | 44.02969 | 35.25 | 0.0135 | |
| SC + Q + Na | 0.8595 | 48.60331 | 41.83 | 0.013 | |
| SC + Q + Mix | 0.9051 | 55.0883 | 64.61 | 0.0158 | |
| 60 °C | Sindh Clay | 0.9646 | 67.78524 | 90.24 | 0.0165 |
| SC + K | 0.8231 | 41.36743 | 35.90 | 0.013 | |
| SC + Na | 0.8319 | 41.29916 | 38.55 | 0.013 | |
| SC + Mix | 0.8816 | 44.43926 | 48.71 | 0.014 | |
| Quartz | 0.7746 | 36.86206 | 28.99 | 0.012 | |
| Quartz + K | 0.855 | 62.59724 | 71.26 | 0.015 | |
| Quartz + Na | 0.8334 | 40.41174 | 38.66 | 0.013 | |
| Quartz + Mix | 0.7571 | 38.02254 | 21.03 | 0.010 | |
| SC + Q | 0.8127 | 38.6369 | 29.84 | 0.0124 | |
| SC + Q + K | 0.8055 | 43.89316 | 37.71 | 0.0131 | |
| SC + Q + Na | 0.8111 | 38.0908 | 21.38 | 0.0115 | |
| SC + Q + Mix | 0.7497 | 38.43211 | 28.75 | 0.012 | |
| 70 °C | Sindh Clay | 0.2085 | 29.08007 | 2.955 | −0.0014 |
| SC + K | 0.1164 | 20.47892 | 2.293 | −0.0034 | |
| SC + Na | 0.2867 | 26.96392 | 7.48 | 0.0055 | |
| SC + Mix | 0.915 | 25.80344 | 12.72 | 0.010 | |
| Quartz | 0.9214 | 33.03933 | 27.46 | 0.0126 | |
| Quartz + K | 0.7976 | 51.12905 | 42.83 | 0.013 | |
| Quartz + Na | 0.1689 | 31.0597 | 3.21 | −0.003 | |
| Quartz + Mix | 0.7758 | 28.53397 | 8.02 | 0.0089 | |
| SC + Q | 0.7493 | 33.24412 | 14.34 | 0.0096 | |
| SC + Q + K | 0.9337 | 26.00823 | 7.70 | 0.0080 | |
| SC + Q + Na | 0.7341 | 35.15549 | 17.33 | 0.010 | |
| SC + Q + Mix | 0.8143 | 31.87886 | 19.15 | 0.010 |
| Material | Dye | % Removed | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| SC + Quartz + Potassium ferricyanide + Sodium metasilicate | Acetary Golden | 96.26 | The present study |
| Activated bone char | Acid Yellow-17 | 91.43 | [37] |
| Neodymium(III) Oxide Nanoadsorbents | Acid Blue 92 | 90.70 | [38] |
| Moringa peregrina seeds | Acid Yellow | 80.00 | [39] |
| Typha angustata L. | Acid Yellow-17 | 89.98 | [40] |
| Activated water hyacinth | Acid Yellow-17 | 92.26 | [41] |
| Lemon peel beads-doped iron(III) oxide-hydroxide (LBF) | Reactive Blue 4 | 83.55 | [42] |
| Lemon peel beads-doped zinc oxide (LBZ) | Reactive Blue 4 | 66.64 | [42] |
| H2O2/Fe2+ | Acid Yellow-17 | 89.00 | [43] |
| Fly ash mixtures with a sandy clay loam soil | Acid Yellow-7 | 53.00 | [44] |
| Fly ash mixtures with a sandy clay loam soil | Acid Yellow-23 | 44.90 | [44] |
| Fish scales | Acid Yellow-127 | 93.00 | [45] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fatima, A.; Hanif, M.A.; Rashid, U.; Jilani, M.I.; Alharthi, F.A.; Han, J. Adsorption, Modeling, Thermodynamic, and Kinetic Studies of Acteray Golden Removal from Polluted Water Using Sindh Clay and Quartz as Low-Cost Adsorbents. Separations 2023, 10, 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10100538
Fatima A, Hanif MA, Rashid U, Jilani MI, Alharthi FA, Han J. Adsorption, Modeling, Thermodynamic, and Kinetic Studies of Acteray Golden Removal from Polluted Water Using Sindh Clay and Quartz as Low-Cost Adsorbents. Separations. 2023; 10(10):538. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10100538
Chicago/Turabian StyleFatima, Aqsa, Muhammad Asif Hanif, Umer Rashid, Muhammad Idrees Jilani, Fahad A. Alharthi, and Jeehoon Han. 2023. "Adsorption, Modeling, Thermodynamic, and Kinetic Studies of Acteray Golden Removal from Polluted Water Using Sindh Clay and Quartz as Low-Cost Adsorbents" Separations 10, no. 10: 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10100538
APA StyleFatima, A., Hanif, M. A., Rashid, U., Jilani, M. I., Alharthi, F. A., & Han, J. (2023). Adsorption, Modeling, Thermodynamic, and Kinetic Studies of Acteray Golden Removal from Polluted Water Using Sindh Clay and Quartz as Low-Cost Adsorbents. Separations, 10(10), 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10100538










