Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Novel Cationic Surfactants as Antibacterial Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis Strategy
2.3. Characterization of QHETA-9 and QHETA-14
2.4. Screening of Antibacterial Activity of QHETA-9 and QHETA-14 against the Tested Pathogens
2.5. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of QHETA-9 and QHETA-14
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of QHETA
3.2. Solubility and Surface Activity of QHETA-9 and QHETA-14 Surfactants at 25 °C
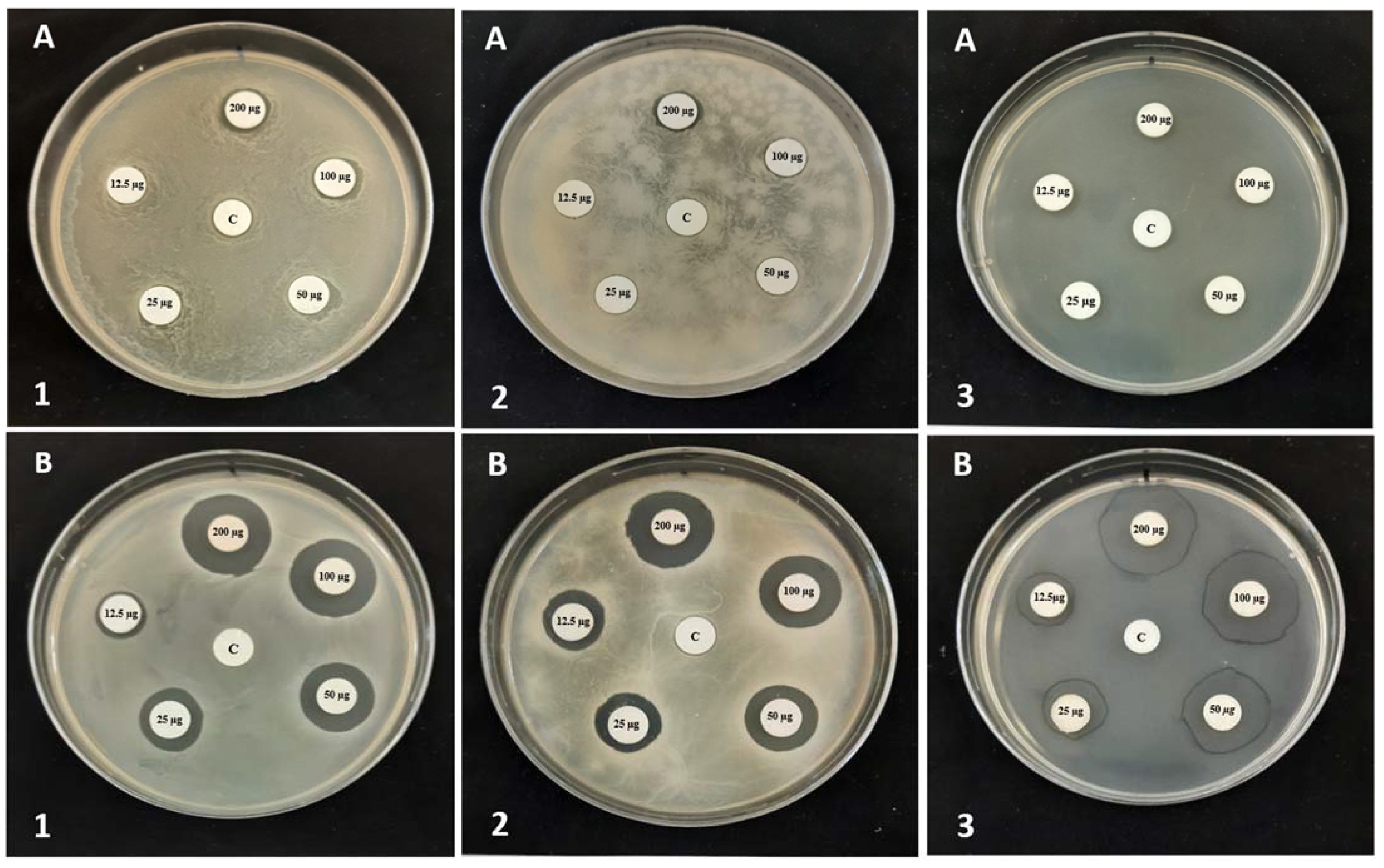
3.3. Screening of Antibacterial Activity of QHETA-9 and QHETA-14
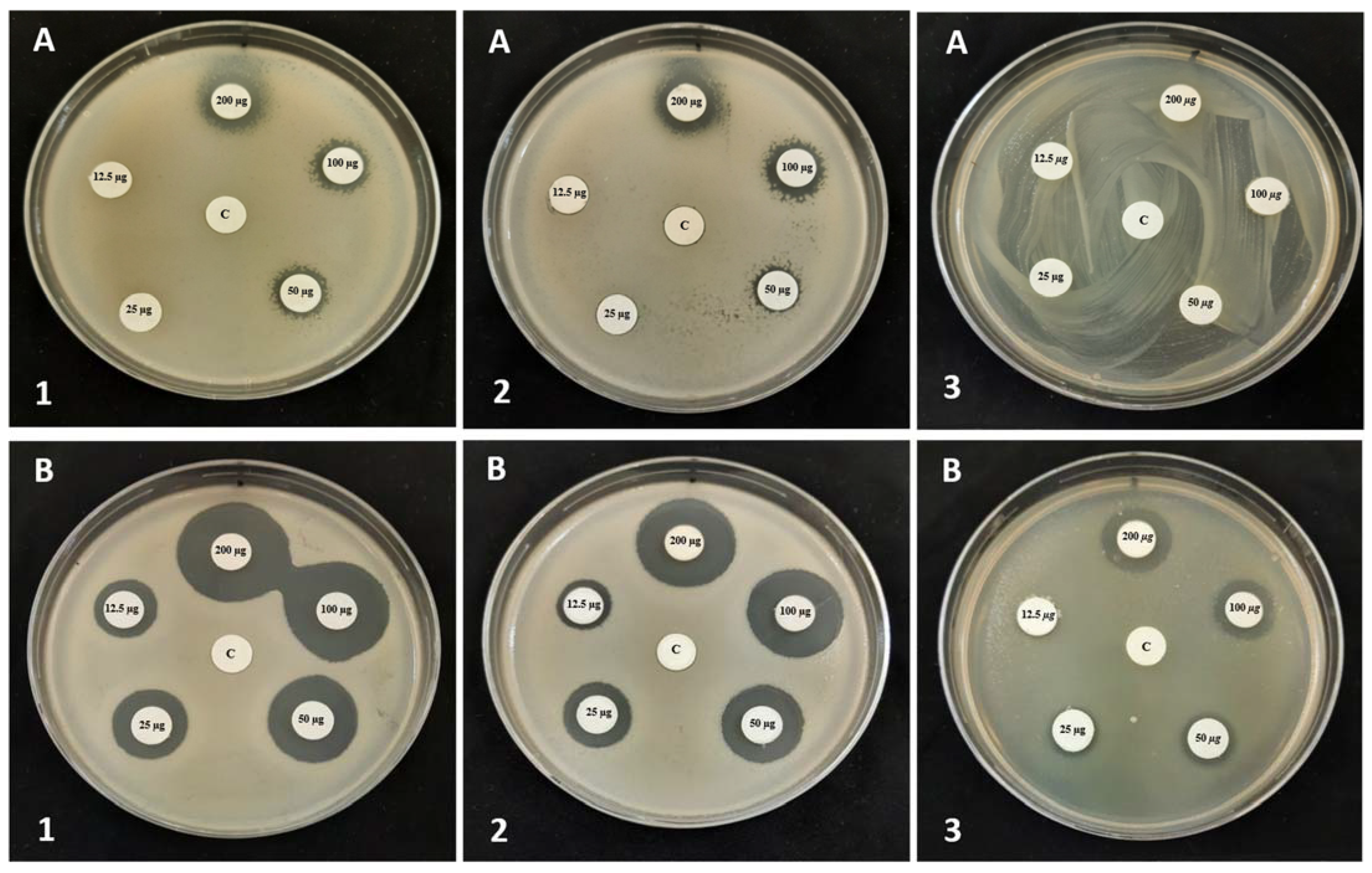
3.4. Minimum Inhibitory and Bactericidal Concentrations (MIC and MBC) of QHETA-9 and QHETA-14
3.5. Structure–Activity Relationship (SAR) Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levy, S.B.; Marshall, B. Antibacterial resistance worldwide: Causes, challenges and responses. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S122–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, S.E.; Sakoulas, G.; Perencevich, E.N.; Schwaber, M.J.; Karchmer, A.W.; Car-meli, Y. Comparison of mortality associated with methicillin-resistant and methicil-lin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: A meta-analysis. Clin. Infec.-Tious Dis. 2003, 36, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirai, A.; Sumitomo, T.; Kurimoto, M.; Maseda, H.; Kourai, H. The mode of the anti-fungal activity of gemini-pyridinium salt against yeast. Biocontrol Sci. 2009, 14, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, J.; Akkapeddi, P.; Yarlagadda, V.; Uppu, D.S.; Kumar, P.; Haldar, J. Cleavable cationic antibacterial amphiphiles: Synthesis, mechanism of action, and cytotoxici-ties. Langmuir 2012, 28, 12225–12234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarron, P.A.; Donnelly, R.F.; Marouf, W.; Calvert, D.E. Anti-adherent and antifungal activities of surfactant-coated poly (ethylcyanoacrylate) nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 340, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lishchynskyi, O.; Shymborska, Y.; Stetsyshyn, Y.; Raczkowska, J.; Skirtach, A.G.; Peretiatko, T.; Budkowski, A. Passive antifouling and active self-disinfecting antiviral surfaces. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klibanov, A.M. Permanently microbicidal materials coatings. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 2479–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domagk, G. Eine neue klasse von desinfektionsmitteln. DMW-Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 1935, 61, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, C. Observations on quaternary ammonium disinfectants. Can. J. Bot. 1951, 29, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.S.; Beech, I.B. The use of biocides to control sulphate-reducing bacteria in biofilms on mild steel surfaces. Biofouling 1996, 9, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Hou, P.; Liu, J.; Fu, S. Design, synthesis, antibacterial, and antitumor activity of linear polyisocyanide quaternary ammonium salts with different structures and chain lengths. Molecules 2021, 26, 5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padnya, P.L.; Terenteva, O.S.; Akhmedov, A.A.; Iksanova, A.G.; Shtyrlin, N.V.; Nikitina, E.V.; Krylova, E.S.; Shtyrlin, Y.G.; Stoikov, I.I. Thiacalixarene based quaternary ammonium salts as promising antibacterial agents. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2021, 29, 115905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frolov, N.; Detusheva, E.; Fursova, N.; Ostashevskaya, I.; Vereshchagin, A. Microbiological Evaluation of Novel Bis-Quaternary Ammonium Compounds: Clinical Strains, Biofilms, and Resistance Study. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rózga-Wijas, K.; Mizerska, U.; Fortuniak, W.; Chojnowski, J.; Hałasa, R.; Werel, W. Quaternary ammonium salts (QAS) modified polysiloxane biocide supported on silica materials. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2007, 17, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merianos, J.J. Disinfection, Sterilization, and Preservation; Block, S.S., Ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001; pp. 63–320. [Google Scholar]
- Zinchenko, A.A.; Sergeyev, V.G.; Yamabe, K.; Murata, S.; Yoshikawa, K. DNA compac-tion by divalent cations: Structural specificity revealed by the potentiality of designed quaternary diammonium salts. ChemBioChem 2004, 5, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, G. Effect of the alkyl chain of quater-nary ammonium cationic surfactants on corrosion inhibition in hydrochloric acid so-lution. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2019, 22, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielska, J.; Sarapuk, J.; Przestalski, S. Investigations of new bis-ammonium salts with potential biological application. Tenside Surfactants Deterg. 1994, 31, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, N.; Nishiguchi, M. Antibacterial activity of soluble pyridinium-type poly-mers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 2532–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Söderling, E.; Österblad, M.; Vallittu, P.K.; Lassila, L.V. Synthesis of methacry-late monomers with antibacterial effects against S. mutans. Molecules 2011, 16, 9755–9763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, H.F.; Freire, M.G.; Fernandes, A.M.; Lopes-da-Silva, J.A.; Morgado, P.; Shimi-zu, K.; Filipe, E.J.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Santos, L.M.; Coutinho, J.o.A. Cation alkyl side chain length and symmetry effects on the surface tension of ionic liquids. Langmuir 2014, 30, 6408–6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xu, Y.; Dabros, T.; Hamza, H. Development of a method for measurement of relative solubility of nonionic surfactants. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 232, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Peng, H.; Zhu, Y.; Cai, H. Synthesis and surface activity properties of sym-metric double chains alkylbetaine surfactants derived from s-triazine. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 405, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastry, N.V.; Vaghela, N.M.; Aswal, V.K. Effect of alkyl chain length and head group on surface active and aggregation behavior of ionic liquids in water. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2012, 327, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anestopoulos, I.; Kiousi, D.E.; Klavaris, A.; Galanis, A.; Salek, K.; Euston, S.R.; Pappa, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I. Surface active agents and their health-promoting properties: Molecules of multifunctional significance. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, R.; Hiemenz, P.C. Principles of Colloid and Surface Chemistry; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 8247, p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Tolera, M.; Abate, D.; Dheresa, M.; Marami, D. Bacterial nosocomial infections and an-timicrobial susceptibility pattern among patients admitted at Hiwot Fana Specialized University Hospital, Eastern Ethiopia. Adv Med. 2018, 2018, 2127814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdács, M. The continuing threat of methicillin-resistant. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, A.M.; Hennessy, T.; Baggett, H.C.; Bruden, D.; Parks, D.; Klejka, J. Methicil-lin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carriage and risk factors for skin infections, Southwestern Alaska, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.S.; Wang, C.H.; Sun, J.F.; Hou, G.G.; Wang, Y.P.; Qu, R.J. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial properties of dihydroxy quaternary ammonium salts with long chain alkyl bromides. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2015, 85, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusew, R.; Kurteva, V.; Shivachev, B. Novel quaternary ammonium derivatives of 4-pyrrolidino pyridine: Synthesis, structural, thermal, and antibacterial studies. Crystals 2020, 10, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenberg, D.; Opatowski, E.; Kozlov, M.M. Phase boundaries in mixtures of mem-brane-forming amphiphiles and micelle-forming amphiphiles. Biochim. Biophys.-Ica Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2000, 1508, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDonnell, G. Antisepsis, Disinfection, and Sterilization: Types, Action, and Resistance; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Inácio, Â.S.; Costa, G.N.; Domingues, N.S.; Santos, M.S.; Moreno, A.J.; Vaz, W.L.; Vieira, O.V. Mitochondrial dysfunction is the focus of quaternary ammonium surfactant tox-icity to mammalian epithelial cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2631–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, F.; Chen, H.; Li, M.; Qiao, F.; Liu, Z.; Hou, Y.; Wu, C.; Fan, Y.; Liu, L. Se-lective antimicrobial activities and action mechanism of micelles self-assembled by cationic oligomeric surfactants. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4242–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, D.; Dobrowolski, A.; Staszak, K.; Kwaśniewska, D.; Dubyk, P. Synthesis, surface and antimicrobial activity of piperidine-based sulfobetaines. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2017, 20, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, W.; Gao, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, J.; Dai, J. Antibacterial quaternary ammonium agents: Chemical diversity and biological mechanism. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 243, 114765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; He, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y. Adsorption, micellization and antimicrobial activity of formyl-containing cationic surfactant in diluted aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 325, 115168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidy, S.S.; Greenway, G.M.; Paunov, V.N. Enhanced antimicrobial action of chlorhexidine loaded in shellac nanoparticles with cationic surface functionality. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereshchagin, A.N.; Frolov, N.A.; Egorova, K.S.; Seitkalieva, M.M.; Ananikov, V.P. Quaternary ammonium compounds (QACs) and ionic liquids (ILs) as biocides: From simple antiseptics to tunable antimicrobials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

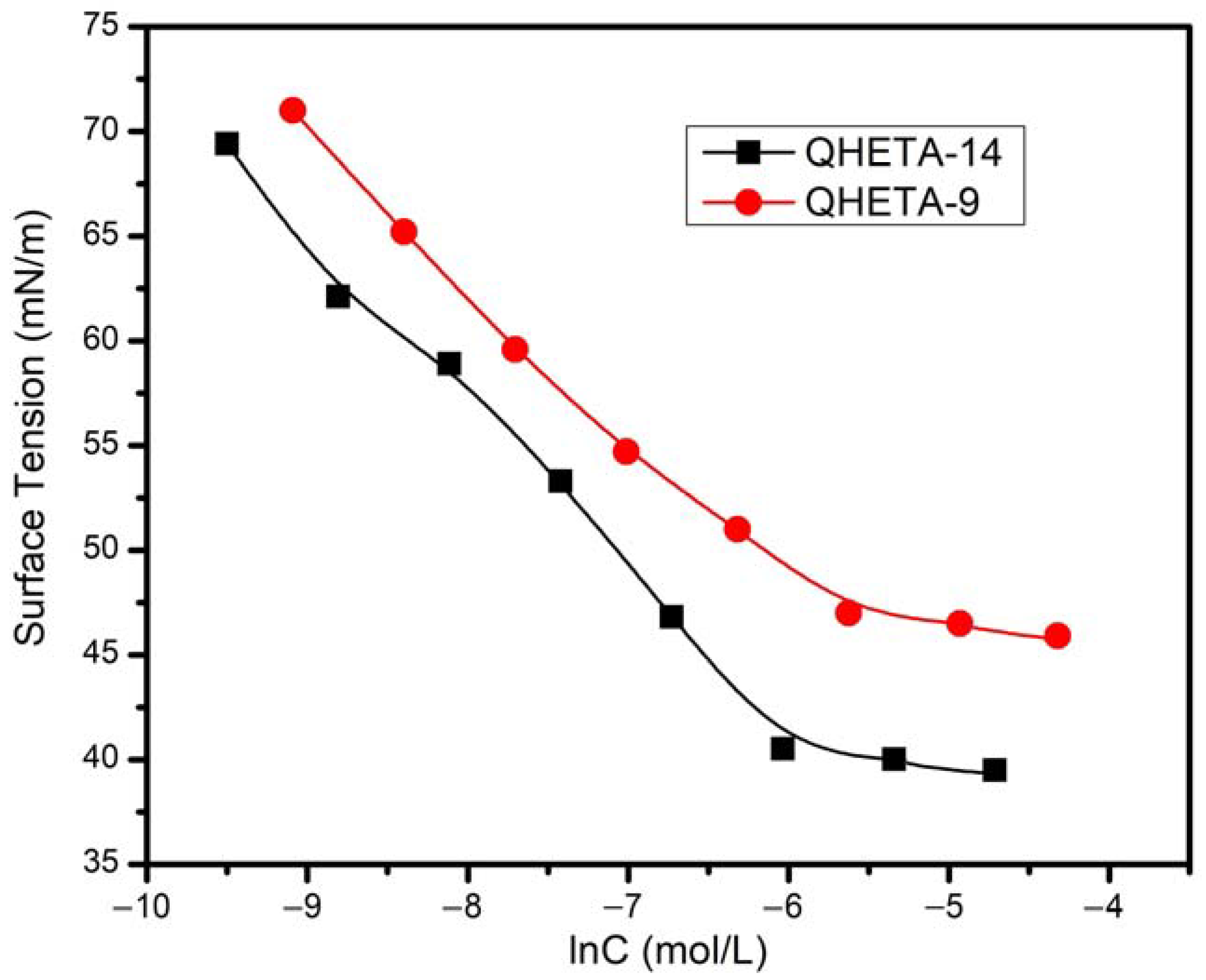
| Surface Activity Properties | QHETA-9 | QHETA-14 |
|---|---|---|
| cmc (mM) | 2.6 | 2.35 |
| (−∂γ/∂ ln c)T | 6.9 | 8.26 |
| γcmc (mN/m) | 47 ± 0.8 | 40 ± 0.5 |
| Δγ (mN/m) | 25 ± 0.8 | 32 ± 0.5 |
| Γmax × 10 −6 (mol/m2) | 2.78 | 3.33 |
| Amin (nm2/molecule) | 0.6 | 0.5 |
| RSN | 21 | 17 |
| Zeta potential (mV) | 18.33 ± 2 | 21.2 ± 3 |
| The Tested Strains | Inhibition Zone Diameter (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QHETA-9 | QHETA-14 | Norfloxacin | Negative Control | |
| S. aureus | 10.03 ± 0.16 | 21.41 ± 0.31 | 18.92 ± 0.15 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| MRSA | 10.53 ± 0.23 | 22.03 ± 0.06 | 21.86 ± 0.11 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| E. faecalis | 10.28 ± 0.02 | 24.54 ± 0.08 | 28.05 ± 0.02 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| A. tumefaciens | 12.82 ± 0.22 | 24.06 ± 0.09 | 25.91 ± 0.03 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| E. carotovora | 13.62 ± 0.24 | 21.57 ± 0.42 | 22.59 ±0.11 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| E. coli | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 18.02 ± 0.13 | 27.86 ± 0.06 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Tested Strains | Inhibition Zone Diameter (mm) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12.5 µg/Disk | 25 µg/Disk | 50 µg/Disk | 100 µg/Disk | 200 µg/Disk | ||||||
| QHETA-9 | QHETA-14 | QHETA-9 | QHETA-14 | QHETA-9 | QHETA-14 | QHETA-9 | QHETA-14 | QHETA-9 | QHETA-14 | |
| S. aureus | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 12.51 ± 0.12 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 16.31± 0.24 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 17.91 ± 0.37 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 20.19 ± 0.42 | 10.43 ± 0.35 | 22.75 ± 0.21 |
| MRSA | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 14.76 ± 0.36 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 15.83 ± 0.31 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 17.15 ± 0.29 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 19.22 ± 0.18 | 10.65 ± 0.24 | 21.52 ± 0.08 |
| E. faecalis | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 14.34 ± 0.28 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 16.76 ± 0.17 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 21.34 ± 0.15 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 24.25 ± 026 | 10.39 ± 0.14 | 25.96 ± 0.43 |
| A. tumefaciens | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 14.38 ± 0.19 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 18.23 ± 0.38 | 11.41 ± 0.23 | 21.26 ± 0.09 | 12.67 ± 0.38 | 24.37 ± 0.32 | 13.71 ± 0.34 | 25.23 ± 0.23 |
| E. carotovora | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 13.27 ± 0.41 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 16.71 ± 0.24 | 10.83 ± 0.14 | 19.32 ± 0.36 | 13.21 ± 0.21 | 22.53 ± 0.43 | 14.26 ± 0.19 | 23.86 ± 0.51 |
| E. coli | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 10.15 ± 0.41 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 11.63 ± 0.31 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 15.13 ± 0.17 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 17.54 ± 0.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sayed, S.R.M.; Ezzat, A.O.; Yassin, M.T.; Abdelbacki, A.M.M. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Novel Cationic Surfactants as Antibacterial Agents. Separations 2023, 10, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10020097
Sayed SRM, Ezzat AO, Yassin MT, Abdelbacki AMM. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Novel Cationic Surfactants as Antibacterial Agents. Separations. 2023; 10(2):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10020097
Chicago/Turabian StyleSayed, Shaban R. M., Abdelrahman O. Ezzat, Mohamed Taha Yassin, and Ashraf M. M. Abdelbacki. 2023. "Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Novel Cationic Surfactants as Antibacterial Agents" Separations 10, no. 2: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10020097
APA StyleSayed, S. R. M., Ezzat, A. O., Yassin, M. T., & Abdelbacki, A. M. M. (2023). Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Novel Cationic Surfactants as Antibacterial Agents. Separations, 10(2), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10020097






