Abstract
Owing to the toxicity and widespread use of copper, the pollution caused by copper ions has become a long-standing environmental and industrial challenge. In this study, a new adsorbent was developed to dispose of and remove copper ions from water. The modified chitosan–carboxymethyl starch (MCTS-CMS) polymer was characterised, and FTIR and SEM-EDS confirmed the successful graft modification of the receptor. The adsorption behaviour was investigated through various parameters, and the results showed that the optimal parameters were pH > 4.0, an adsorption time of 30 min, a reaction temperature of 293 K, and an initial concentration of 100–120 mg/L. The experimental data exhibited a good fit with pseudo-second-order models, and the Langmuir isotherm revealed that the polymer was found to be highly suitable for adsorption, with a maximum adsorption capacity of 321.16 mg/g. Thermodynamic analysis revealed that the adsorption process was exothermic and spontaneous. XRD and XPS confirmed the generation of posnjakite after the adsorption and the predominant roles of nitrogen- and sulphur-containing groups in the adsorption. Further analysis confirmed the existence of chemisorption and physical adsorption, with chemisorption mainly facilitating the Cu(II) absorption of the polymer. MCTS-CMS showed an excellent removal efficiency of 98% in acidic solutions. On the basis of these findings, the MCTS-CMS polymer demonstrates excellent performance and high selectivity in the removal of copper ions from industrial wastewater or polluted water bodies. This work recommends expanding the polymer’s practical applications to contribute to water purification efforts.
1. Introduction
Over the past few decades, fast-growing industrialisation has caused severe aquatic environmental issues related to heavy metals. Copper is the third most used metal in the world and widely applied in various industries [1,2,3]. However, its use is often accompanied by water pollution. It is reported that high Cu(II) concentrations above the maximum contamination level goal (1.3 mg/L) have been measured in water resources in various regions around the world, such as the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and China [4,5]. Although copper is an essential element for the proper functioning of human physiological processes, excessive intake of copper ions can overwhelm cells, leading to death [6,7,8]. Different from organic pollutants, copper ions do not break down into less harmful species over time [9]. The amount of Cu(II) pollution in the global water environment has been increasing, and it has been recognised as a major heavy metal contaminant causing significant health risks [10]. Considering water pollution and health problems, minimising and removing Cu from water and wastewater are of paramount importance. Thus, the treatment of wastewater containing copper has attracted much attention in recent years.
Various methods are available for the removal of metal ions, including chemical precipitation, filtration, and adsorption [11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. Among them, adsorption is one of the most popular because of its wider application to sources of raw materials, higher efficiency, higher selectivity, higher recycling rate, and lower secondary pollution levels [18,19]. In this process, the adsorbent is the decisive factor in removing heavy metal ions, and natural polymers are widely used adsorbents because of their characteristics, such as abundant raw materials, high adsorption capacities, and variable product types and functional groups [20,21]. Chitosan has become popular because of its sources and characteristics. Crabs and prawns produce chitin, which is then used to produce chitosan, a linear polyamine obtained through the partial deacetylation of chitin with alkaline solutions, in their shells [22]. Its molecular structure has primary amino and hydroxy groups, which make chitosan an effective chelating agent for transition metals [23]. Chitosan and its derivatives have been widely applied in the adsorption of heavy metal ions because of the hydrogen bonding from intermolecular and intramolecular sources [23,24]. Detailed studies on chitosan-based adsorbent materials for copper ion adsorption have been listed by Mallik [25]. Popuri et al. synthesised a chitosan composite incorporating multi-walled carbon nanotubes and evaluated its adsorption performance in comparison to that of pure chitosan. The results revealed a substantial increase in the adsorption capacity, with the composite achieving 454.55 mg/g compared to 178.6 mg/g for pure chitosan [26]. Comparative analyses demonstrated that the adsorption capacities of chitosan composites surpass that of pure chitosan [26,27]. Among the adsorbents from chitosan-based composites, Fan et al. found the chitosan composite had the highest adsorption capacity, 678.0 mg/g [27]. However, most reported adsorption capacities are concentrated in the range below 200 mg/g [25]. Surface modification appears to be another effective method for enhancing the adsorption capacity and other properties of chitosan, making it suitable for industrial-scale applications. Through graft modification, various functional groups, such as carboxyl, amino, or sulphur groups, can be grafted onto chitosan molecules to improve the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent [28,29]. Li et al. explored the adsorption properties of copper grafted onto porous poly (L-lactic acid)/chitosan nanofibers, achieving an adsorption capacity of 111.66 ± 3.22 mg·g−1 through coordination interactions [30]. Therefore, increasing the adsorption capacity remains the primary concern.
Because of its inherent instability, chitosan easily dissolves in acidic media. Additionally, its adsorption of metal ions is easily affected by the physicochemical properties of the solution and the intermolecular hydrogen bonds within chitosan, which greatly limit its practical applications [31,32]. Therefore, chitosan is often modified through cross-linking reactions to form a stable network structure, making it more suitable for application [33]. Commonly used small-molecule cross-linking agents for chitosan include epichlorohydrin and glutaraldehyde [25]. In this study, the rarely used carboxymethyl starch was chosen as a cross-linking agent, in which condensation reactions between molecules lead to cross-linking. Xanthate, commonly used as a collector in flotation processes, possesses thiol groups that selectively bind to metal ions [34]. Therefore, carbon disulphide was introduced to modify the synthesised compound, enhancing its copper ion adsorption capacity. On this basis, we first prepared the composite and then modified it to further enhance its selectivity. Then, FTIR and SEM-EDS analyses were carried out to characterise the surface and functional groups of the modified polymer. The effects of the pH, contact time, temperature, and initial concentration were also examined. The adsorption mechanism was discussed based on adsorption kinetics, adsorption isotherms, adsorption thermodynamics, XRD, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). This study supports the application of this adsorbent in the removal of copper ions and provides a reference direction for polymer modification.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
A chitosan sample, with a molar mass of approximately 1 million and a deacetylation degree of 95%, was procured from Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. Carboxymethyl starch, with substitution degrees of 0.2–0.3, and 4-(4,6-dimethoxy triazin-2-yl)-4-methyl morpholine hydrochloride (DMT-MM) were acquired from Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. The structures of the chitosan and carboxymethyl starch are shown in Figure 1. The carbon disulphide, copper sulphate pentahydrate, hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide, anhydrous ethanol, and other reagents used in the experiments were analytical grade.
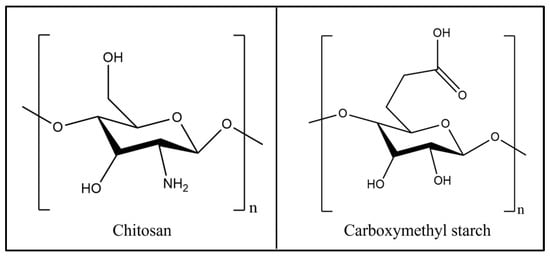
Figure 1.
Structures of chitosan and carboxymethyl starch.
2.2. MCTS-CMS Polymer Preparation
The chitosan–carboxymethyl starch (CTS-CMS) polymer was first prepared by blending and cross-linking and then alkalised with sodium hydroxide for 1 h. After several hours of reaction with a certain amount of CS2, the products were separated from the solution using absolute ethyl alcohol through solvent precipitation. Then, 70% ethanol was used for washing after filtration and soaking in absolute alcohol for 12 h. After vacuum drying, the preparation was completed, and the product was a brown–yellow powder. The preparation reaction of the MCTS-CMS polymer is demonstrated in Figure 2, and the details are listed in the Supplementary Materials. The MCTS-CMS polymer was formed through the xanthate acidification reaction between the CTS-CMS polymer and CS2 in an alkaline environment. Sulphur was introduced to the polymer after the modification to form new groups, such as the C=S group or the thiol group. The new polymer structure is shown in Figure 3.
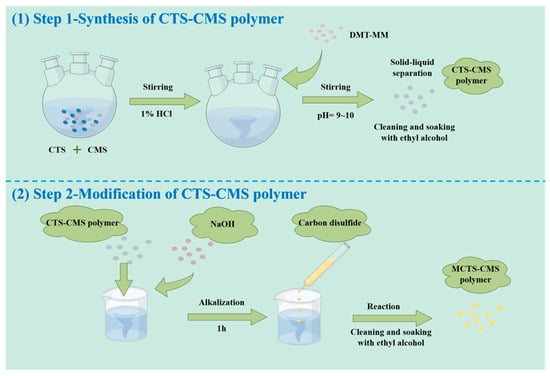
Figure 2.
Synthesis and modification routes of the MCTS-CMS polymer.
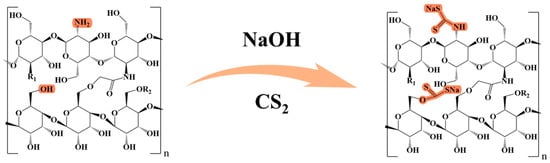
Figure 3.
Polymer structures before and after the modification.
2.3. Characterisation of the MCTS-CMS Polymer
FTIR was used to examine the modification performance of the CTS-CMS polymer. FTIR spectra were carefully recorded using an FTIR IR Affinity-1 instrument from SHIMADZU Corporation, Japan, within the 450–4000 cm−1 range.
Morphological investigation was performed using a JSM-6480 LV, JEOL. The powder samples were tested before and after the adsorption. The relative contents of characteristic elements in the samples were determined using an energy-dispersive spectrometer.
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
Copper sulphate (CuSO4) was used to prepare a standard solution as a source of bivalent copper ions. A sodium hydroxide solution and a diluted hydrochloric acid solution were employed to adjust the pH. The adsorbent amount used in each experiment was 0.05 g. The concentration of the copper in the standard solution was determined using an ultraviolet spectrophotometer from SHIMADZU, Kyoto, Japan. The absorbance was determined, and the complex was stabilised for 30 min under the conditions of the determination. The adsorbent’s adsorption capacity (Q (mg/g)) was calculated as follows:
In this formula, C0 (mg/L) and Ce (mg/L) represent the initial and final concentrations of the copper ions, respectively; V denotes the volume of the solution in litres; and W signifies the weight of the adsorbent in grams.
Adsorption experiments of the Cu(II) in aqueous solutions were conducted by varying the initial adsorbent concentration, solution pH, and temperature at different intervals. The copper adsorption capacity of the MCTS-CMS polymer was determined by measuring the difference between the copper ion concentrations before and after the adsorption. The analysis of the results is presented in Section 3.2, Section 3.3, Section 3.4 and Section 3.5. The reported values were averaged from three repetitions of each adsorption experiment.
2.5. XRD and XPS Measurements
XRD was employed to identify any newly formed compounds resulting from the adsorption. XPS analysis was performed to detect the surface characteristics of the MCTS-CMS polymer before and after Cu(II) adsorption, and the spectral data were recorded using an Al Kα X-ray source at 150 W. The XPS peaks were fitted and analysed using Thermo Avantage 5.96, with all the spectra calibrated to C 1s at 284.8 eV.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the MCTS-CMS Polymer
3.1.1. FTIR Analysis
Figure 4 shows the FTIR spectra of the chitosan, CTS-CMS polymer, and MCTS-CMS polymer.
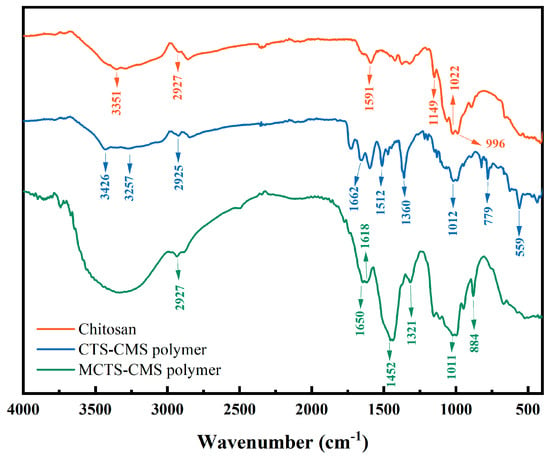
Figure 4.
FTIR spectra of chitosan, chitosan-carboxymethyl starch polymer (CTS-CMS), and modified chitosan-carboxymethyl starch polymer (MCTS-CMS).
The peaks at 3200–3500 cm−1 represent the stretching vibration caused by the overlap of O-H and N-H bonds [35]. The stretching vibration caused by the N-H bond of the CTS-CMS polymer was observed at 3257 cm−1, which shifted to a lower wavenumber compared with the 3351 cm−1 peak of the chitosan. And the peak at 3426 cm−1 typically corresponds to the stretching vibration of O-H groups involved in hydrogen bonding. These variations may be because of the enhanced intramolecular hydrogen bonding [36]. Both the chitosan and CTS-CMS polymers exhibit high-intensity vibration peaks at 2927 cm−1 and 2925 cm−1, respectively, which correspond to the stretching vibration of the C-H in -CH2 [36]. For the CTS-CMS polymer, the secondary amide C=O exhibits a strong stretching vibration peak between 1680 and 1630 cm−1, while the peak at 1662 cm−1 in the spectrum of the CTS-CMS polymer is likely a deformation vibration peak of the primary amide [37]. In the second amide band, primary amides have an N-H peak located between 1640 and 1600 cm−1, while secondary amides exhibit a strong and distinctive characteristic peak between 1500 and 1530 cm−1. Therefore, the presence of the peak at 1512 cm−1 suggests the existence of secondary amide groups [38]. For the MCTS-CMS polymer, new peaks appeared at 1452, 1321, and 884 cm−1, corresponding to the characteristic stretching vibrations of the C-N bond (with a partial double bond characteristic) and the C=S bond from the CS2-NR2 group. These results provide evidence for successful modification with CS2 [39].
3.1.2. SEM-EDS Analysis
The surface morphologies of the MCTS-CMS polymer before and after copper ion adsorption were visualised using SEM. Figure 5 shows the SEM micrographs of the MCTS-CMS polymer at various magnifications. The CTS-CMS polymer has a rough and puffy surface, and the MCTS-CMS polymer surface has needle-shaped protuberances and roughness (Figure 5a,b). This finding suggests that the adsorption capacity of the modified polymer may increase; however, further verification through testing or experiments is required. This structure also provides additional adsorption sites on the surface of and inside the adsorbent [40]. The SEM micrograph of the MCTS-CMS polymer after the adsorption of copper ions distinctly differed from Figure 5c. The previous needle-shaped protuberances were completely covered by particles, and the polymer became spherical after the adsorption. According to the EDX spectrum of the MCTS-CMS polymer after the adsorption, carbon, oxygen, sulphur, and copper elements are present in the polymer. This result confirms the existence of copper ions adsorbed by MCTS-CMS and that the polymer has an adsorption effect on copper ions.
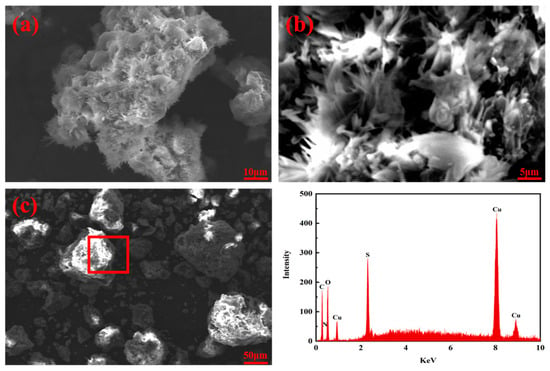
Figure 5.
SEM micrographs of CTS-CMS polymer (a,b) before and after the modification; MCTS-CMS polymer (c) after Cu(II) adsorption and the corresponding EDX plots of the MCTS-CMS polymer.
3.2. Adsorption Experiments
3.2.1. Effect of the pH on Cu(II) Adsorption
The relationship between the adsorption capacity of the MCTS-CMS polymer and the pH (3.0–8.0) is shown in Figure 6. Adsorption experiments were carried out under acidic conditions from pH 3.5 to 8.0. The adsorption time, reaction temperature, and initial concentration were 5 min, 323 K, and 120 mg/L, respectively. According to the results, the Cu(II) adsorption capacity of the MCTS-CMS remarkably increased with increasing pH from 3.0 to 4.0. When the pH increased from 4.0 to 8.0, virtually no change was observed in the polymer’s adsorption capacity. At low pH values, a large number of hydrated hydrogen ions are present in the solution, which may lead to a highly protonated adsorbent surface. This protonation could cause the electrostatic repulsion of the positively charged copper ions. However, as the pH increases, this protonation effect diminishes. This finding indicates that MCTS-CMS is suitable for treating copper-containing wastewater with a pH greater than 4.0.
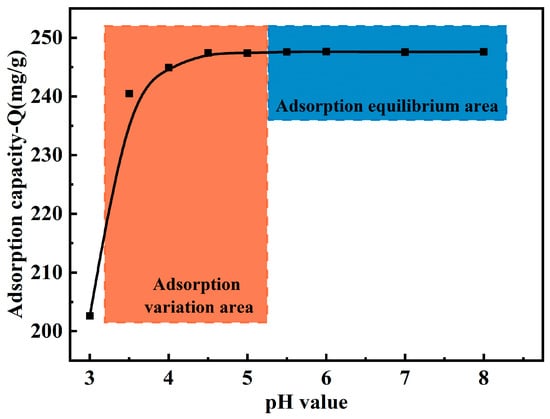
Figure 6.
Effect of the pH on the Cu(II) adsorption capacity of the MCTS-CMS polymer.
3.2.2. Effect of the Adsorption Time
The effect of the contact time on the Cu(II) adsorption capacity of the MCTS-CMS polymer was studied, as shown in Figure 7. The solution pH, reaction temperature, and initial concentration were 5.0, 323 K, and 120 mg/L, respectively. The Cu(II) ion adsorption capacity of the MCTS-CMS polymer increased with increasing adsorption time. Particularly, a rapid increase in the adsorption capacity was observed during the first 5 min. After 30 min, the adsorption equilibrium was reached. The maximum value remained constant, even when the adsorption time was extended beyond 30 min. Therefore, an adsorption time of 30 min was identified as sufficient to reach the adsorption equilibrium.
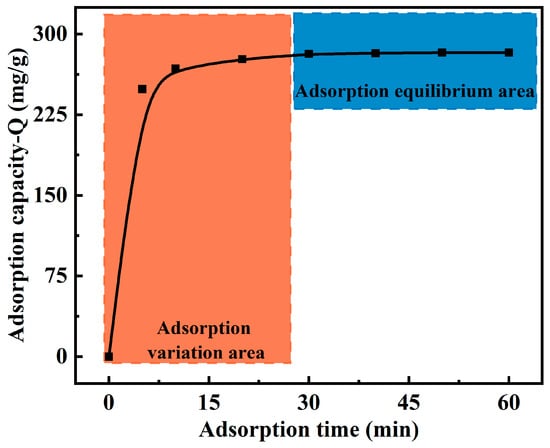
Figure 7.
Effect of the adsorption time on the Cu(II) adsorption capacity of the MCTS-CMS polymer.
3.2.3. Effect of the Reaction Temperature
Figure 8 illustrates the effect of the reaction temperature (293–323 K) on the modified polymer’s Cu(II) adsorption capacity. The solution pH, adsorption time, and initial concentration were 5.0, 30 min, and 120 mg/L, respectively. The Cu(II) adsorption capacity of the MCTS-CMS polymer decreased from 316.65 mg/g to 286.39 mg/g as the temperature increased. These results showed that the adsorption process between Cu(II) and MCTS-CMS was exothermic. On the one hand, according to Le Chatelier’s principle, the system reduced the adsorption to balance the added energy when the temperature increased. On the other hand, as the temperature raised, the kinetic energy of both the adsorbate and adsorbent molecules increased, weakening their interactions and leading to an increase in the desorption rate of the adsorbate, thereby reducing the effective adsorption [41]. In summary, the adsorption capacity decreased as the temperature increased. The optimal temperature chosen was 293 K, at which the MCTS-CMS polymer exhibited a relatively high adsorption capacity and was easily implementable in industrial applications. Future research can further optimise the polymer structure to enhance its adaptability at higher temperatures, thereby expanding its practical application range.
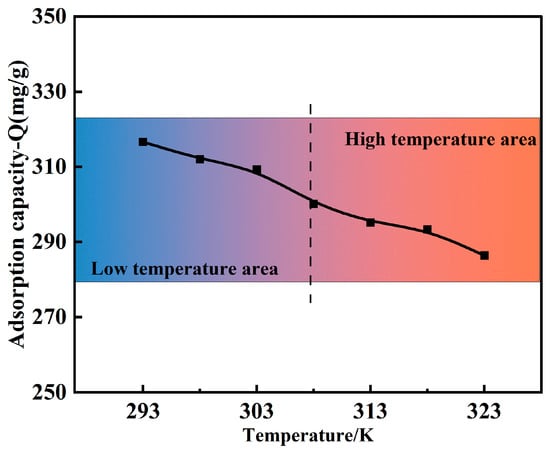
Figure 8.
Effect of the pH on the Cu(II) adsorption capacity of the MCTS-CMS polymer.
3.2.4. Effect of the Initial Concentration
Adsorption tests are highly dependent on the initial concentration. Figure 9 shows how Cu(II) ions affect the MCTS-CMS polymer’s adsorption capacity and removal efficiency. The pH value of the solution, adsorption time, and reaction temperature were 5.0, 30 min, and 293 K, respectively. The adsorption capacity of the polymer increased with increasing initial concentration. When the initial concentration reached 160 mg/L, the adsorption capacity gradually flattened, and the maximum Qe was approximately 317.29 mg/g. Meanwhile, the removal efficiency of Cu(II) ions exhibited an initial increase followed by a subsequent decrease. The maximum removal efficiency reached approximately 98% when the initial concentration ranged from 100 mg/L to 120 mg/L. As the initial concentration continued to increase, the removal efficiency decreased rapidly, which may be because of the adsorbent reaching its maximum adsorption capacity.
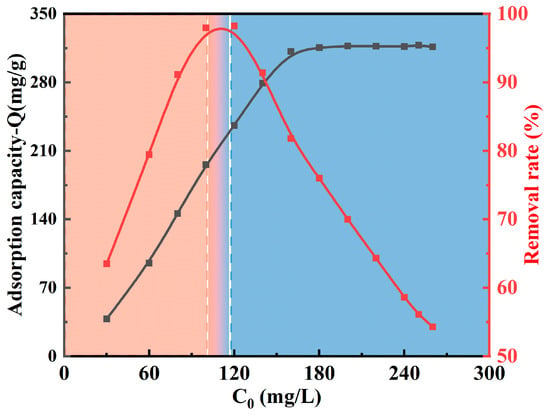
Figure 9.
Effect of the initial concentration on the Cu(II) adsorption capacity and removal of the MCTS-CMS polymer.
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
The following three classical and widely used models were utilised to explicate the kinetic adsorption process: pseudo first order, pseudo second order, and intraparticle diffusion.
The pseudo-first-order model can be expressed as follows:
where k1 (1/min) is the rate constant of the pseudo-first-order adsorption, t (min) denotes the reaction time, Qe (mg/g) represents the equilibrium amount of copper ions adsorbed per gram of the MCTS-CMS polymer, and Qt (mg/g) denotes the quantity of copper ions adsorbed per gram of the MCTS-CMS polymer at any given time (t).
The pseudo-second-order kinetic model can be expressed as follows:
where k2 (g/mg min) represents the rate constant, t (min) denotes the reaction time, Qe (mg/g) represents the equilibrium amount of copper ions adsorbed per gram of the MCTS-CMS polymer, and Qt (mg/g) denotes the quantity of copper ions adsorbed per gram of the MCTS-CMS polymer at any given time (t).
The intraparticle diffusion model can be formulated as follows:
where k (min−1/2 mg/L) is the rate value of the intraparticle diffusion adsorption, t (min) denotes the adsorption time, Qt (mg/g) represents the quantity of copper ions adsorbed per gram of the MCTS-CMS polymer at any given time (t), and C is the kinetic constant of the intraparticle diffusion, as determined by the boundary layer thickness: the higher the boundary layer thickness, the higher the C value.
Different kinetic models were investigated to study the kinetics of the Cu(II) removal. The fitting results are shown in Figure 10, and the kinetic constant (K) and linear correlation coefficient (R2) are presented in Table 1. R2 is often used to measure the predictive effect, and its numerical range is from 0 to 1: the higher its value, the better the prediction. According to the comparison among the three different models, the pseudo-second-order model fitted the data better than the others. As shown in Table 1, the pseudo-second-order model had the maximal correlation coefficients under the same test conditions, and its calculated and experimental Qe values were in agreement. This finding confirms that the pseudo-second-order kinetic model is appropriate for describing the Cu(II) adsorption by the MCTS-CMS polymer. Furthermore, the best fit confirms the dependency of the adsorption mechanism on the amounts of the adsorbate and adsorbent [42]. The interaction rate is proportional to the quadratic power of the reactant concentration. Hence, the chemisorption is explained by the high R2 value and the similar prediction of Qe.
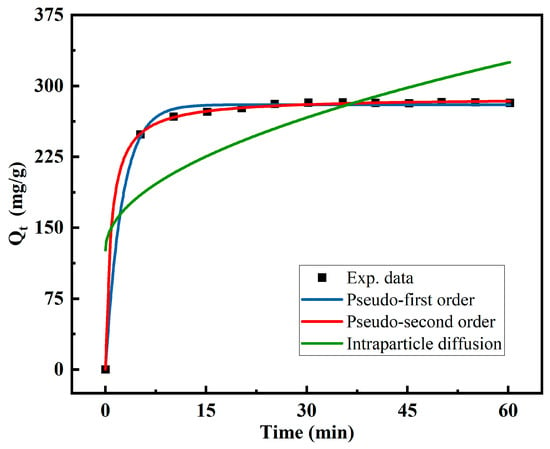
Figure 10.
Adsorption kinetic curves of Cu(II) ions adsorbed on the MCTS-CMS polymer.

Table 1.
Comparison of different kinetic models with parameters.
3.4. Adsorption Isotherms
Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin models were applied to demonstrate the relationship between the experimental data. The following is the Langmuir isotherm’s equation [43]:
In this formula, Ce (mg/L) denotes the concentration at equilibrium, b denotes the constant of the adsorption equilibrium, and Qe and Qmax (mg/g) represent the adsorption capacity at equilibrium and the maximum theoretical adsorption capacity, respectively.
The Freundlich isotherm is an empirical model that describes the equilibrium on heterogeneous surfaces and does not assume a monolayer capacity [44]. It can be expressed as follows:
where Ce (mg/L) is the concentration at equilibrium, K (mg/g) (L/mg) represents the Freundlich constant, and Qe (mg/g) represents the adsorption capacity at equilibrium. In the − plots, the intercept is denoted as lnKf, and the slope is represented by n−1, where the slope signifies a corresponding increase in the adsorption amount with an increase in the solution concentration, and the intercept denotes the initial adsorption amount.
The Temkin isotherm model can be mathematically formulated as follows [45]:
where A and B have fixed values, Ce (mg/L) denotes the concentration at equilibrium, and Qe (mg/g) represents the adsorption capacity at equilibrium.
The isothermal studies were used to analyse the adsorption mechanism between the adsorbent and the adsorbate. Herein, the adsorption performances of the MCTS-CMS polymer at four different temperatures were characterised using the Langmuir (Equation (5)), Freundlich (Equation (6)), and Temkin (Equation (7)) isotherm models. The fitting curves and isotherm parameters are presented in Figure 11 and Table 2. The comparison of the fits of the three models showed that the Langmuir model explained the adsorption better than the other models in accordance with its higher correlation factor (R2) at different temperatures. This result indicates that the adsorption is a homogenous process in which Cu(II) is adsorbed in the form of a monolayer on the MCTS-CMS polymer, occurring at a fixed number of adsorption sites. Furthermore, the adsorption of the adsorbate on the surface is independent of the presence of other molecules, and there is no interaction between the molecules. This finding aligns with the results presented in Section 3.2.4. The maximum adsorption capacity of 321.16 mg/g, as determined by fitting the Langmuir isotherm model, is close to the experimental value of 317.29 mg/g from the adsorption experiment. Furthermore, the maximum adsorption capacity of the CTS-CMS polymer was 162 mg/g, and that of MCTS-CMS was significantly increased [35]. This result indicates that the modification effectively enhances the polymer’s ability to adsorb copper ions.
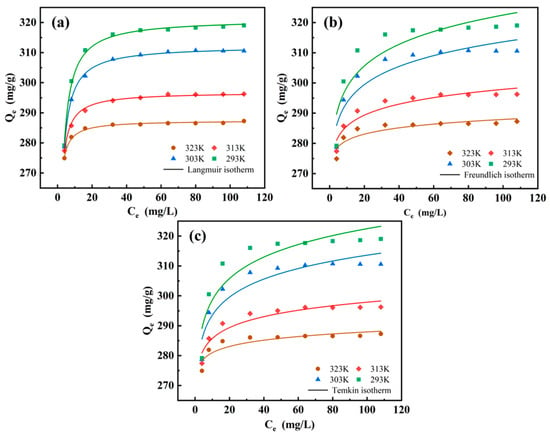
Figure 11.
MCTS-CMS polymer adsorbs Cu(II) nonlinearly at various temperatures: (a) Langmuir; (b) Freundlich; (c) Temkin.

Table 2.
Isotherm constants for the adsorption of Cu(II) on the MCTS-CMS polymer at various temperatures.
RL, from Langmuir isotherms, can be used to identify favourable adsorption. The equation is as follows:
In this formula, KL (L/mg) denotes the adsorption equilibrium value, and Ce (mg/L) denotes the initial concentration of the adsorption process. RL = 0 indicates non-reversible adsorption, and RL = 1 indicates that the adsorption is reversible. If the material is favourable for adsorption, the RL value will range between 0 and 1. Conversely, if the material is unsuitable for adsorption, the RL value will exceed 1. The RL value of the MCTS-CMS polymer was between 0 and 1, indicating that it can easily adsorb Cu(II).
3.5. Adsorption Thermodynamics
The influences of the adsorbent, adsorbate, solvent, and other conditions on the adsorption process can be further analysed. The standard Gibbs free energy can be calculated as follows:
In this formula, the R value is 8.314 J/mol K, T (K) represents the Kelvin temperature of the reaction, and KC (L/mol) represents the equilibrium constant of the Langmuir isotherm. Additionally, the relationship among the enthalpy change (), entropy change (), and Gibbs free energy change (Δ) can be expressed as follows:
Figure 12 shows the results of the linear fitting of the thermodynamic equation. The thermodynamic parameters and can be obtained from the parameters of the equation, and the data are summarised in Table 3.
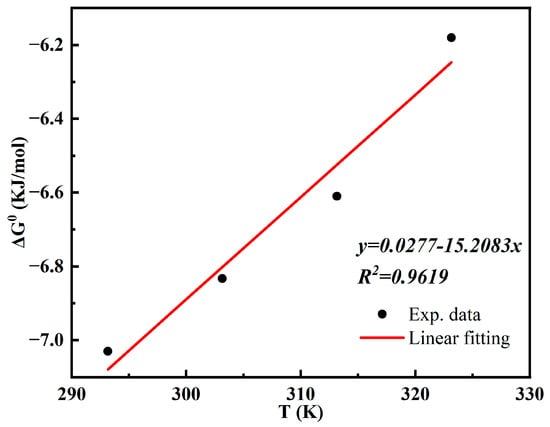
Figure 12.
Linear fitting of the thermodynamic equation.

Table 3.
Thermodynamic constants of the adsorption process.
The negative values of Δ from Table 3 indicate that the MCTS-CMS polymer is adsorbing Cu(II) in a spontaneous manner. The thermodynamic parameters and were calculated at −15.208 kJ·mol−1 and 27.73 kJ·mol−1 K−1, respectively. These values prove that the reaction is an exothermic reaction with an entropically increasing process and an increase in the chaos of the system during the adsorption. Generally, the variation in the physical adsorption’s free energy is less than that in the chemical adsorption’s heat. The physical adsorption’s free energy value generally ranges from several hundreds to several thousands, with a maximum value of 40 kJ·mol−1. Meanwhile, the average experimental value for was −6.66 kJ·mol−1. The adsorption heat of the chemisorption is higher than that of the physical adsorption, with values ranging from 84 kJ·mol−1 to 417 kJ·mol−1. Hence, physical adsorption is present in the Cu(II) adsorption of the MCTS-CMS polymer.
3.6. Adsorption Mechanism of Cu(II)
3.6.1. XRD Analysis
The crystal state of the copper adsorbed on the surface of the MCTS-CMS polymer was investigated. According to the peak data from the No. 83-1410 PDF, the adsorbed material is posnjakite (Cu4(SO4) (OH)6 (H2O)), as shown in Figure 13. The specific XRD data of the MCTS-CMS polymer after Cu(II) adsorption are listed in Table 4. The interplanar spacing and average crystal diameter were 73.76 and 0.32 nm, respectively.
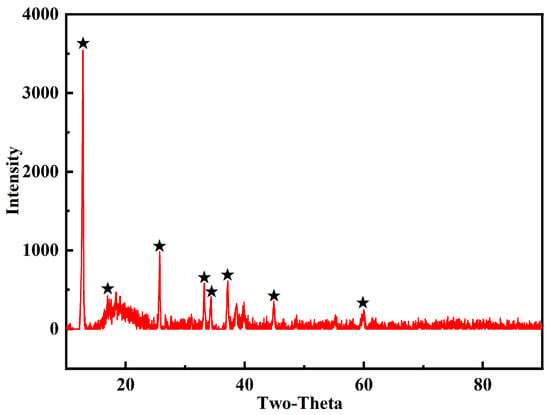
Figure 13.
XRD pattern of the MCTS-CMS polymer with adsorbed Cu(II).

Table 4.
Specific XRD data of the MCTS-CMS polymer after Cu(II) adsorption.
3.6.2. XPS Analysis
The modified polymer was subjected to XPS analysis before and after adsorbing Cu(II) to further study the adsorption process. The elements of the functional groups playing the main role in the adsorption were determined by analysing the changes in the binding energies of the elements after the adsorption.
The comparison of the XPS spectra of the MCTS-CMS polymer before and after Cu(II) adsorption is shown in Table 5. The binding energies of N 1s and S 2p changed, and those of the spectra of C 1s and O 1s showed no distinct change. This finding suggests that the functional groups containing nitrogen and sulphur play a crucial role in the adsorption.

Table 5.
The XPS total spectra of the MCTS-CMS polymer before and after adsorbing Cu(II).
As shown in Figure 14a,b, the N 1s spectra of the MCTS-CMS polymer before and after adsorbing Cu(II) can be divided into three peaks. Before the adsorption, the binding energies of the amino group (-NH2), proto-amino group (-NH2/NH3+), and amide group (NHC=O) were 399.1, 400.2, and 400.9 eV, respectively. These values are consistent with previous research [46,47]. After Cu(II) adsorption, the binding energies of -NH2 and -NH3+ changed to 399.7 and 401.8 eV, respectively. Meanwhile, the binding energy of the amide group remained at 400.2 eV. This finding indicates that the amide group is not involved in bonding or in reactions, and the -NH2 and -NH2/NH3+ groups have adsorbed copper ions.
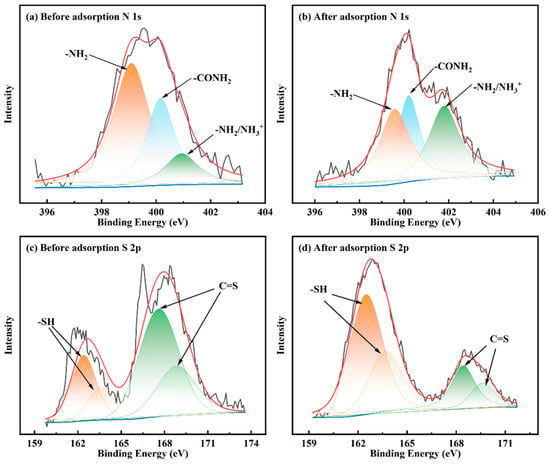
Figure 14.
N and S spectra of the MCTS-CMS polymer before and after Cu(II) adsorption.
As shown in Figure 14c,d, the peaks with binding energies at 161.9 and 163.1 eV were attributed to the thiol group without adsorption, and those with binding energies at 167.5 and 168.7 eV were ascribed to the C=S group [48,49]. The binding energies of the original peaks changed after the reaction with copper ions. The binding energies of the thiol group changed to 162.5 and 163.7 eV and those of the C=S group to 168.42 and 169.6 eV. Therefore, the thiol group and C=S group are involved in the adsorption of copper ions.
By observing the narrow-scan spectra of Cu and noting that there is only a weak satellite peak at around 945.0 eV, it can be inferred that copper ions mainly exist in the form of Cu(I). During fitting, the G-L values of Cu(I) and Cu(II) ions should differ, with the former being around 20% and the latter generally exceeding 70%. Additionally, the FWHM of Cu(I) is 1.62 eV, while that of Cu(II) is broader, at 3.15 eV. The Cu 2p spectra are shown in Figure 15. Each spectrum consists of two Gaussian–Lorentzian bands separated by 19.75 eV and comprises two sets of peaks and a satellite peak. The peaks with binding energies at 932.4 and 952.2 eV were attributed to Cu(I), and those with binding energies at 933.9 and 953.7 eV were attributed to Cu(II) [50]. The satellite peak at 944.4 eV exhibited a relatively low intensity. It was also identified as the Cu(I) satellite peak and indicates the existence of Cu(I) [46]. The Auger spectrum of the copper cannot be analysed using the conventional Gaussian–Lorentzian peak-fitting method; instead, the nonlinear least square (NLS) method should be employed for peak deconvolution and identification of chemical states to enable the accurate determination of the proportions of copper in different valence states. According to the Auger peak of the copper, the peak area ratios of monovalent copper (Cu(I)) and bivalent copper (Cu(II)) ions are 81.21% and 18.79%, respectively. The copper ions, primarily existing in a monovalent form, are mainly adsorbed through chemical adsorption because physical adsorption does not alter the valence state. Therefore, the high area ratio of Cu(I) illustrates that chemisorption and physical adsorption exist, but chemisorption predominates in the Cu(II) adsorption of the MCTS-CMS polymer.
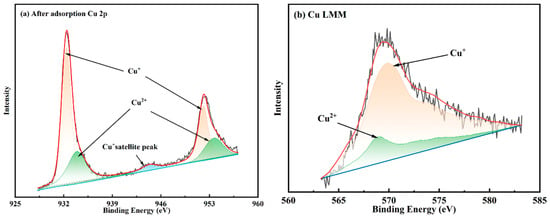
Figure 15.
Cu spectra of the MCTS-CMS polymer after Cu(II) adsorption.
4. Conclusions
In this work, an MCTS-CMS polymer was successfully synthesised and demonstrated high efficiency in removing Cu(II) from aqueous solutions. The optimal adsorption conditions were pH > 4.0, an adsorption time of 30 min, a reaction temperature of 293 K, and an initial Cu(II) concentration of 100–120 mg/L. The kinetic data fitted the pseudo-second-order model, and the Langmuir isotherm revealed a maximum adsorption capacity of 321.16 mg/g at 293 K. Thermodynamic analysis confirmed that the process was exothermic and spontaneous.
XRD results revealed the presence of posnjakite after the adsorption. XPS analysis showed that nitrogen- and sulphur-containing groups, particularly sulphur, played a key role in the adsorption process. Chemisorption and physical adsorption were both observed, with chemisorption being the dominant mechanism. In conclusion, the distinctive advantages of the MCTS-CMS polymer render it as an efficacious adsorbent to eliminate excessive Cu(II) from aqueous media. However, this study does not explore the material’s performance in selective adsorption or during repeated use, which indicates a lack of research in these areas. Future studies will concentrate on enhancing the polymer’s structure to optimise its performance under higher-temperature conditions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/separations11100283/s1, Table S1: Factors and levels in the orthogonal experiments, Table S2: Design of orthogonal experiments and results, Table S3: Analysis results of copper ion adsorbed in orthogonal experiments, Table S4: Analysis results of sulfur content in orthogonal experiments, Figure S1: Linear fitting results of sulfur content and adsorption capacity of modified polymer, Figure S2: Effect of dosage of carbon disulfide on the sulfur content of modified polymer, Figure S3: Effect of sulfur content on the adsorption capacity of MCTS-CMS polymer.
Author Contributions
Z.H., conceptualisation, methodology, data curation, validation, and writing—original draft; Y.D., validation and investigation; L.C., validation and investigation; F.J., validation and investigation; H.T., conceptualisation, methodology, investigation, writing—review and editing, and supervision; D.F., supervision and investigation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province (grant number 2023RC3067); the National Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (grant number 2023JJ20071); the Technology Research Center of Hunan Province for Comprehensive Utilization of Associated Fluorite and Fluorine Chemical Engineering (grant number CF-SZX-2023002); and the Yunnan Science and Technology Talents and Platform Program (Academician and Expert Workstation) (grant number 202205AF150048).
Data Availability Statement
The authors will supply the relevant data in response to reasonable requests.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Liang Chen was employed by the company Jiangsu Vilory Advanced Materials Technology Co., Ltd, Xuzhou 22100, China. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Fulke, A.B.; Ratanpal, S.; Sonker, S. Understanding Heavy Metal Toxicity: Implications on Human Health, Marine Ecosystems and Bioremediation Strategies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 206, 116707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Wu, L.; Su, Q.; Ji, X.; Zhou, J.; Wu, S.; Tang, Y.; Li, H. Neurotoxic Effects of Heavy Metal Pollutants in the Environment: Focusing on Epigenetic Mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 345, 123563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, P.; Saravanan, V.; Rajeshkannan, R.; Arnica, G.; Rajasimman, M.; Baskar, G.; Pugazhendhi, A. Comprehensive Review on Toxic Heavy Metals in the Aquatic System: Sources, Identification, Treatment Strategies, and Health Risk Assessment. Environ. Res. 2024, 258, 119440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utilization of Organic-Rich Materials for the Adsorption of Copper Ions from Aqueous Environments. Results Eng. 2024, 22, 102216. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Cui, Y.; Chen, N. Removal of Copper Ions from Wastewater: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barceloux, D.G.; Barceloux, D. Copper. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlson, M.A.; Dixon, S.J. Copper-Induced Cell Death. Science 2022, 375, 1231–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiber, I.; Dringen, R.; Mercer, J.F.B. Copper: Effects of Deficiency and Overload. In Interrelations between Essential Metal Ions and Human Diseases; Sigel, A., Sigel, H., Sigel, R.K.O., Eds.; Metal Ions in Life Sciences; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 359–387. ISBN 978-94-007-7500-8. [Google Scholar]
- Thorgersen, M.P.; Lancaster, W.A.; Ge, X.; Zane, G.M.; Wetmore, K.M.; Vaccaro, B.J.; Poole, F.L.; Younkin, A.D.; Deutschbauer, A.M.; Arkin, A.P.; et al. Mechanisms of Chromium and Uranium Toxicity in Pseudomonas Stutzeri RCH2 Grown under Anaerobic Nitrate-Reducing Conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incorporation of Copper Ion Promoted Adsorption of Anionic Dye (Acid Yellow 36) by Acrolein-Crosslinked Polyethyleneimine/Chitosan Hydrogel: Adsorption, Dynamics, and Mechanisms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 274, 133281. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yoon, S.; Choi, M.; Min, K.J.; Park, K.Y.; Chon, K.; Bae, S. Metal Ion Recovery from Electrodialysis-Concentrated Plating Wastewater via Pilot-Scale Sequential Electrowinning/Chemical Precipitation. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, M.S.; Rahul, A.K.; Shekhar, S.; Kumar, S. Removal of Heavy Metal from Wastewater Using Ion Exchange with Membrane Filtration from Swarnamukhi River in Tirupati. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 78, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampalanonwat, P.; Supaphol, P. Preparation and Adsorption Behavior of Aminated Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile Nanofiber Mats for Heavy Metal Ion Removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 3619–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, G.; Thakur, B.; Naushad, M.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Kumar, A.; Sillanpaa, M.; Mola, G.T. Fabrication and Characterization of Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate@ironsilicophosphate Nanocomposite: Ion Exchange Properties and Selectivity for Binary Metal Ions. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 193, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X. Molecular Simulation of Reverse Osmosis for Heavy Metal Ions Using Functionalized Nanoporous Graphenes. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2017, 139, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuya, L.; Yang, C.; Xuefeng, C.; Wei, S.; Yaqing, W.; Yue, Y. Separation of Lithium and Transition Metals from Leachate of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries by Solvent Extraction Method with Versatic 10. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allioux, F.-M.; Kapruwan, P.; Milne, N.; Kong, L.; Fattaccioli, J.; Chen, Y.; Dumée, L.F. Electro-Capture of Heavy Metal Ions with Carbon Cloth Integrated Microfluidic Devices. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 194, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Mondal, S.; Bhaumik, A. Thioether-Functionalized Covalent Triazine Nanospheres: A Robust Adsorbent for Mercury Removal. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 7353–7361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Du, R. Carboxyl Functional Poly(Ionic Liquid)s Confined in Metal–Organic Frameworks with Enhanced Adsorption of Metal Ions from Water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 299, 121790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-J.; Cui, W.-R.; Jiang, W.; Yan, R.-H.; Liang, R.-P.; Qiu, J.-D. Bi-Functional Natural Polymers for Highly Efficient Adsorption and Reduction of Gold. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 422, 130577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.; Rokicka, J.; Janik, J.; Wilpiszewska, K. Preparation and Characterization of Potato Starch Copolymers with a High Natural Polymer Content for the Removal of Cu(II) and Fe(III) from Solutions. Polymers 2020, 12, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and Chitosan: Properties and Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, P.S.; Selvakumar, D.; Kadirvelu, K.; Kumar, N.S. Chitosan as an Environment Friendly Biomaterial—A Review on Recent Modifications and Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croisier, F.; Jérôme, C. Chitosan-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, A.K.; Kabir, S.F.; Bin Abdur Rahman, F.; Sakib, M.N.; Efty, S.S.; Rahman, M.M. Cu(II) Removal from Wastewater Using Chitosan-Based Adsorbents: A Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popuri, S.R.; Frederick, R.; Chang, C.-Y.; Fang, S.-S.; Wang, C.-C.; Lee, L.-C. Removal of Copper (II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions onto Chitosan/Carbon Nanotubes Composite Sorbent. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 52, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wang, X.; Cai, Y.; Xie, H.; Han, S.; Hao, C. Functionalized Cotton Charcoal/Chitosan Biomass-Based Hydrogel for Capturing Pb2+, Cu2+ and MB. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Gou, S.; Zhou, L.; Tang, L.; Liu, T.; Liu, L.; Duan, M. Amidoxime-Functionalized Polyacrylamide-Modified Chitosan Containing Imidazoline Groups for Effective Removal of Cu2+ and Ni2+. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 252, 117160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.B.; Vitali, L.; Tavares, A.; Germano, C.A.; Amorim, S.M.; Moreira, R.F.P.M.; Peralta, R.A.; Neves, A. Chitosan Functionalized with Heptadentate Dinucleating Ligand Applied to Removal of Nickel, Copper and Zinc. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 256, 117589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, Q.; Tabassum, M.; Lu, Z.; Khawar, M.T.; Song, J.; Gong, H.; Meng, J.; Li, Z.; Li, J. Porous Poly(L–Lactic Acid)/Chitosan Nanofibres for Copper Ion Adsorption. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 115343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, D.; Lu, X.; Sheng, J.; Zheng, X.; Xiao, X. Flocculation of Combined Contaminants of Dye and Heavy Metal by Nano-Chitosan Flocculants. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humelnicu, D.; Dragan, E.S.; Ignat, M.; Dinu, M.V. A Comparative Study on Cu2+, Zn2+, Ni2+, Fe3+, and Cr3+ Metal Ions Removal from Industrial Wastewaters by Chitosan-Based Composite Cryogels. Molecules 2020, 25, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.A.R.; Sousa, K.S.; Cavalcanti, G.R.S.; Fonseca, M.G.; de Souza, A.G.; Alves, A.P.M. Chitosan-Montmorillonite Biocomposite as an Adsorbent for Copper (II) Cations from Aqueous Solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 61, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Wang, C.; He, J.; Hua, Z.; Cheng, K.; Wu, X.; Sun, W.; Wang, L.; Hu, J.; Tang, H. Selective Depressing Mechanism of H-Acid Monosodium Salt on Flotation Separation of Graphite and Sphalerite. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2023, 33, 3812–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hao, H.; Zhang, W.; Shao, Z. Adsorption Mechanism of Copper Ions in Aqueous Solution by Chitosan–Carboxymethyl Starch Composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Lee, I.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, V.; Kim, H. Simultaneous Removal of Heavy Metals and Ciprofloxacin Micropollutants from Wastewater Using Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid-Functionalized β-Cyclodextrin-Chitosan Adsorbent. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 34624–34634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.N.; Khan, M.N.; Mallik, A.K.; Rahman, M.M. Preparation of Bio-Inspired Trimethoxysilyl Group Terminated Poly(1-Vinylimidazole)-Modified-Chitosan Composite for Adsorption of Chromium (VI) Ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 379, 120792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radosavljević, S.A.; Stojanović, J.N.; Radosavljević-Mihajlović, A.S.; Vuković, N.S. (Pb–Sb)-Bearing Sphalerite from the Čumavići Polymetallic Ore Deposit, Podrinje Metallogenic District, East Bosnia and Herzegovina. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 72, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.-J.; Niu, C.-G.; Wang, X.-Y.; Wen, X.-J.; Zeng, G.-M. DTC-GO as Effective Adsorbent for the Removal of Cu2+ and Cd2+ from Aqueous Solution. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, A.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, H.; Sun, P.; Yao, B.; Zang, Y.; Du, X.; Dong, L. Xanthate-Modified Magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2-Based Polyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan Composite Material for Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water. Polymers 2022, 14, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, E.; Silvi, B.; Raybaud, P. Mixed Sites and Promoter Segregation: A DFT Study of the Manifestation of Le Chatelier’s Principle for the Co(Ni)MoS Active Phase in Reaction Conditions. Catal. Today 2008, 130, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Das, R. Strong Adsorption of CV Dye by Ni Ferrite Nanoparticles for Waste Water Purification: Fits Well the Pseudo Second Order Kinetic and Freundlich Isotherm Model. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 16199–16215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The Constitution and Fundamental Properties of Solids and Liquids. J. Frankl. Inst. 1917, 183, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Über die Adsorption in Lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1907, 57U, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temkin, M.; Pyzhev, V. Recent Modifications to Langmuir Isotherms. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 1940, 12, 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Graf, N.; Yegen, E.; Gross, T.; Lippitz, A.; Weigel, W.; Krakert, S.; Terfort, A.; Unger, W.E.S. XPS and NEXAFS Studies of Aliphatic and Aromatic Amine Species on Functionalized Surfaces. Surf. Sci. 2009, 603, 2849–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.; Girard-Lauriault, P.-L.; Gross, T.; Lippitz, A.; Dietrich, P.; Unger, W.E.S. Ambient-Ageing Processes in Amine Self-Assembled Monolayers on Microarray Slides as Studied by ToF-SIMS with Principal Component Analysis, XPS, and NEXAFS Spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, S.D.; Singamsetty, C.S.K.; Booth, G.L.; He, G.-R.; Pittman, C.U. Surface Characterization of Carbon Fibers Using Angle-Resolved XPS and ISS. Carbon 1995, 33, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Wei, Z.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Spinney, R.; Hu, W.-P.; Chai, L.; Yang, Z.; Ye, T.; Xiao, R. Mechanistic Insight into Reactivity of Sulfate Radical with Aromatic Contaminants through Single-Electron Transfer Pathway. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodselahi, T.; Vesaghi, M.A.; Shafiekhani, A.; Baghizadeh, A.; Lameii, M. XPS Study of the Cu@Cu2O Core-Shell Nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 2730–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).