Abstract
Submerged plants and related disturbances can affect both the phosphorus (P) release and the microbial communities in sediments. In this study, a sediment resuspension system was constructed, and P variability characteristics influenced by Vallisneria natans (V. natans) and the response mechanism of the microbial community were studied. The results indicated that the total phosphorus (TP) content increased from 678.875 to 1019.133 mg/kg and from 1126.017 to 1280.679 mg/kg in sediments and suspended solids (SSs) during the sediment resuspension process, respectively. Organic P (OP) increased by 127.344 mg/kg and 302.448 mg/kg in sediments and SSs after the disturbance, respectively. The microbial communities in the sediments and the leaves of V. natans had higher Chao values after the disturbance, while Shannon values decreased after the disturbance compared to the control in SSs. Proteobacteria had the highest abundance with the value of 51.1% after the disturbance in the sediments and SSs, and the abundance values of Proteobacteria in rhizomes and leaves of V. natans could reach 73.2% on average. Chloroflexi, Acidobacteria, and Firmicutes were also the main phyla in the sediment resuspension system. Sodium hydroxide extractable P (NaOH-P) in sediments could reduce the bioavailability of this P fraction under disturbance conditions. The decrease in the abundance of Bacteroidetes and Nitrospirae indicated that they were more sensitive to the disturbance, and the rotational speed changed the survival conditions for the Bacteroidetes and Nitrospirae. The response mechanism of microbial community during the sediment resuspension process could reflect the influence of the microbial community on the changing characteristics of P and could provide a theoretical foundation for P control at the micro level.
1. Introduction
Disturbance is an important factor affecting phosphorus (P) cycling in the sediment–water interface of shallow lakes, and it can affect P transport and transformation in lakes directly [1,2]. The process of sediment resuspension caused by disturbance plays an important role in the P transport, transformation, and cycling in lake water ecosystems. Suspended solids (SSs) produced by disturbance are the main carriers of P transport and sedimentation in the overlying water body [3]. SSs can adsorb P in the overlying water, and different fractions of P can also migrate with most movements of SSs, which are ultimately deposited at the bottom of the lake [4,5]. Related studies have emphasized the important role of SSs as carriers of particulate nutrients in supporting the primary productivity of aquatic systems [6,7]. The physical and chemo-biological properties of SSs reflect the different mechanisms involved in P transport, and the sorption characteristics of SSs are also a key factor influencing P transport [8]. Previous studies have shown that SSs are able to control changes in the P phase in sediments during wind and waves by changing the particle size, source, and flow paths [9]. Phosphorus carried by SSs has significant impacts on aquatic ecosystems, leading to algal growth and eutrophication occurrence in lakes [7,10]. In addition, P in SSs is highly bioavailable, which promotes the transport of sodium hydroxide extractable P (NaOH-P) and enhances the bioavailability of P in the water [11].
Usually, the presence of submerged plants in lake systems will affect the sediment resuspension to some extent, which further influences the P release and uptake characteristics of sediments and SSs [12]. Submerged plants play different roles in the structure and function of lake ecosystems [13]. As the main medium connecting overlying water and sediments in shallow lakes, they can absorb biologically effective P from sediments through the influence of root microorganisms to effectively reduce the diffusion of P from sediments to the overlying water according to the interstitial water [14]. Submerged plants can also use their rhizomes and leaves to effectively intercept and adsorb particulate matter in the water column and adsorb soluble P in the water through the particulate matter, which can effectively reduce the P load in the water [15,16]. In addition, in an aerobic environment, microorganisms in submerged plants can enrich phosphate [17] and excess P is stored as phosphate in plant cells, while in anoxic environments, phosphorus will be released [18].
In the plain river network areas, P release and transformation in shallow lakes is a very complex process due to the interaction between the disturbance from wind or waves and submerged plants [12]. Previous studies only focused on the inhibitory effect of submerged plants on sediment resuspension, such as the decrease in SSs and P concentration in the overlying water or P release from the sediments, and often ignored the participation of the microbial communities of submerged plants on P release and distribution in the process of disturbance [19,20]. In this study, a sediment resuspension system was constructed, and the P variability characteristics influenced by Vallisneria natans (V. natans) during the sediment resuspension process with a rotational speed of 150 rad/min were analyzed. Then, the change in microbial communities before and after the resuspension process was also discussed, which could reveal the response mechanism of the microbial community to the sediment resuspension process. According to the sediment resuspension system, a real simulated environment, such as 150 rad/min, could simulate real wind and wave disturbance, and the results could provide the theoretical foundation of P release control from sediments and SSs.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experiment Design and Sample Collection
A sediment resuspension system was simulated on an experimental apparatus. As shown in Figure 1, in order to simulate the ratio of the water depth and sediment thickness (3:1), the apparatus consisted of two acrylic columns, each with a diameter of 15 cm and a height of 50 cm, and 10 cm deep sediment was placed into each column and covered with 30 cm of overlying water, while plants were planted. The sediment samples were obtained from the plain river network areas, and V. natans was used to structure the sediment resuspension system. The control group was not treated. The treatments of the sediment resuspension system were stirred thoroughly by a stainless-steel stirrer at the speed of 150 rad/min, controlled by a variable-speed motor, for 1 h per day for a total of 21 days.
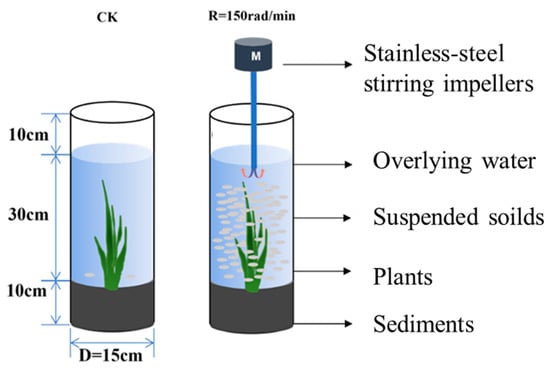
Figure 1.
Sediment resuspension system.
The sediments (Ses), suspended solids (SSs), rhizomes (Gs), and leaves (Ys) of V. natans samples were collected from the sediment resuspension system. The collected samples, sediments, suspended solids, rhizomes, and leaves from the beginning of the experiment were denoted as Se_CK, SS_CK, G_CK, and Y_CK, respectively. The samples collected from the sediment resuspension system on the last day of the experiments were also collected, and were denoted as Se_150, SS_150, G_150, and Y_150 for sediments, suspended solids, rhizomes, and leaves, respectively.
2.2. Experimental Methods
The phosphorus fractions can be divided into total P (TP), sodium hydroxide extractable P (NaOH-P), hydrochloric acid extractable P (HCl-P), inorganic P (IP), and organic P (OP) according to the SMT protocol [21]. The P concentration in the extracted solution or overlying water (soluble active phosphorus, SRP) was determined with the molybdenum blue method after the solution was filtered, and the TP in rhizomes, the leaves of V. natans, and particular P (PP) in water was also measured after digestion [22,23].
DNA was extracted and purified from the sediment and plant samples by a PowerSoil DNA Isolation Kit (Mobio Laboratories Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s manual. The DNA concentration and purity were analyzed using a NanoDrop Spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific NanoDrop Lite, CA USA). The V4–V5 regions of bacterial 16SrRNA genes were amplified with universal primers 515F (GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA) and 926R (CCGTCAATTCMTTTRAGTTT). The PCR mixture (25 μL) contained 1× PCR buffer, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.4 μM each of deoxynucleoside triphosphate, 1.0 μM of each primer, 0.5 U of TaKaRaEx Taq, and 10 mg of template DNA.
2.3. Data and Statistical Analysis
The diversity indices (Simpson and Shannon) and the richness estimator, abundance-based coverage estimator (Chao), of the microbial communities in sediments, plants, or SSs were analyzed using the Usearch [24] and QIIME pipeline [25]. Redundancy analysis (RDA) based on population abundance and P fraction contents was executed using the Canoco version 5.0 software. The relative abundances of the microbial communities on phylum level in sediments or SSs and the contents of P fractions in sediments or SSs were used to analyze their relationship with each other according to IBM SPSS Statistics 21 (Pearson).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in P Characterization during Sediment Resuspension Process
The P contents in the sediments and SSs were measured and the results are shown in Figure 2a. The results showed that the contents of different P fractions increased significantly in the disturbed state, which indicated that sediment resuspension had a significant effect on the release of endogenous P. The content of IP and OP in sediments or SSs had an increasing trend after the disturbance, with the OP content in sediments increasing from 103.345 mg/kg to 127.344 mg/kg, and OP in SSs increasing from 248.552 mg/kg to 302.448 mg/kg. Overall, IP accounted for the major portion of TP, indicating that IP might be more accessible to the water column due to biomineralization and chemical release during the sediment resuspension process, and the increase in TP concentration further confirmed the release of P from the sediments due to the disturbance. In addition, the TP contents of the sediments increased from 678.875 mg/kg to 1019.133 mg/kg, and TP in SSs increased from 1126.017 mg/kg to 1280.679 mg/kg under disturbed condition. The increase in TP suggested that the disturbance enhanced the bioavailability and mobility of P. Disturbance of sediments could result in the P transformation from a fixed form to a more bioavailable form, which would, in turn, affect the nutrient balance and water quality of the water body. P in sediments existed primarily in a chemically precipitated or adsorbed state, and disturbance could destabilize these physical or chemical bonds, releasing P into the water column and leading to an increase in P contents in SSs [26].
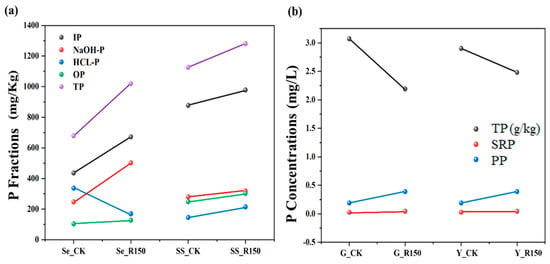
Figure 2.
Changes in P fractions in the sediment resuspension system (a) for sediments and suspended solids, and (b) for leaves and roots.
The SRP and PP in overlying water and TP in V. natans were also measured in this study, and the results are shown in Figure 2b. The results indicated that SRP and PP concentrations decreased after the disturbance, SRP increased from 0.025 mg/L to 0.042 mg/L, and PP increased from 0.190 mg/L to 0.390 mg/L. This might be due to the fact that V. natans took up more P under disturbed conditions, or that the disturbance resulted in the transport of P from the plant body to the external water [27,28]. Disturbance promoted the PP transformation in the overlying water, and disturbance could also increase the P bioavailability in the sediments, which could lead to P redistribution in the sediments to the overlying water and SSs. In addition, the P contents in roots and leaves of V. natans decreased from 3.12 to 2.09 g/kg and 2.81 to 2.52 g/kg, respectively. This might be explained by the influence of the disturbance. The above phenomenon was caused by different factors. On the one hand, the algae need mire nutrients (such as P) to support growth, and P bioavailability is one of the most significant factors for algal growth. Therefore, during the sediment resuspension process, the increase in P bioavailability could promote the growth of algae, causing the P content of the whole aquatic system to increase [29,30]. On the other hand, the increase in P in the overlying water might alter the chemistry of the water column, disrupting the environmental P balance, thus increasing the risk of its release in sediments [31].
3.2. Diversity Analysis of Microbial Community in the Sediment Resuspension System
The diversity indexes (Chao, Shannon, and Simpson) were also analyzed to discuss the microbial community structure change during the sediment resuspension, and the results are shown in Figure 3. The Chao index mainly reflected the species richness in the microbial community, and the results indicate that there was a significant increase in the Chao index in sediments and leaves of V. natans after the disturbance (R150). In contrast, the diversity indexes of SSs and the rhizomes changed little. After the disturbance, the values of Chao in sediments increased significantly, indicating an increase in species richness, which might be due to the fact that the disturbance resulted in the release of more microorganisms from the sediments into the overlying water. Therefore, there was also an increase in the number of microbial species in SSs [32,33]. The Chao index values of the rhizomes and leaves in V. natans did not change much after the disturbance, probably because the microorganisms on the surface of V. natans were relatively stable and less susceptible to physical disturbance [34]. The previous study suggested that the conditions of sediment resuspension might have introduced more habitat microenvironments due to the physical disturbance, and that allowed microorganisms and nutrients from the sediments to be stirred up into the upper water column, increasing the microbial diversity. In addition, specific anaerobic microorganisms in sediments might enter the aerobic layer as a result of the disturbance and interact with microorganisms in the new environment [26].
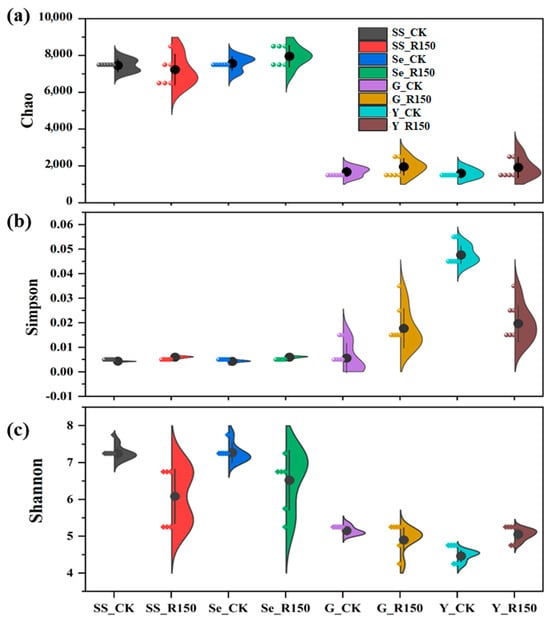
Figure 3.
Diversity indexes of the microbial community in the sediment resuspension system with the speed of 150 rad/min (a) for Chao, (b) for Simpson, and (c) for Shannon.
The values of Shannon put more emphasis on species evenness, while Simpson focuses more on the effect of dominant species. As shown in Figure 3c, the values of Shannon decreased after the disturbance compared to the control in SSs, indicating that the diversity and evenness of the microbial community decreased after the disturbance. The values of Shannon also decreased after the disturbance in sediments, indicating that although the species might have become more abundant, certain species in the community might have begun to dominate, resulting in a decrease in overall diversity [35]. The values of Shannon in rhizomes and leaves of V. natans showed little change or a slight decrease after the disturbance, again suggesting that the microbial community on the surface of the plants was relatively stable and not susceptible to disturbance. The sediments and SSs had relatively higher Simpson values after the disturbance, suggesting that dominant species were beginning to play a more important role in the community and that diversity was actually decreasing [36]. The Simpson values of rhizomes and leaves of V. natans also showed small increases or remained stable after the disturbance, suggesting that the dominant species might have strengthened their position.
Overall, the sediment resuspension caused by disturbance could change the diversity and richness of the microbial communities in sediments, SSs, and plants; the diversity and richness increased, especially the microbial diversity in the sediments, as it increased significantly. This might be due to the fact that the sediment resuspension brought microorganisms and nutrients from the bottom layer into the overlying water, providing new growth environments and resources for microorganisms. Comparatively, the microbial community on the rhizomes and surface of the plants’ leaves was less affected by the disturbance and showed greater stability [37].
3.3. Distribution of the Microbial Community in Sediments and Suspended Solids at Phylum and Genus Levels
The microbial community distribution at phylum and genus levels in sediments and SSs is shown in Figure 4. The microbial community structure in SSs showed relatively small changes before and after the disturbance, which suggested that the microbial community might be relatively stable under this environmental condition. The microbial community structure in sediments showed a difference before and after the disturbance. The abundance of Proteobacteria increased from 46.1% to 51.1%, while the abundance of Chloroflexi decreased from 10.1% to 8.6%. Proteobacteria are usually one of the most common microbial phyla in aquatic environments, and they play an important role in redox processes [38]. The increase in their relative abundance after the disturbance might indicate an increase in the oxidative environment or the availability of organic matter. Chloroflexi are commonly found in anaerobic or microaerobic environments, and their decrease might be indicative of improved oxidative conditions following sediment disturbance [39,40]. After sediment resuspension, Bacteroidetes and Acidobacteria also showed some proportional variations, which might be related to their role in organic matter decomposition and nutrient cycling. The disturbances could increase the level of oxidation in the surface sediment layer and affect the structure and function of the microbial community, especially the microorganisms, which are redox-sensitive. Then, the disturbances could lead to the reorganization of microbial communities in sediments, which could cause significant changes to the microbial community abundance in sediments [41,42]. At the same time, disturbance induced the resuspension of nutrients in the sediments, providing an additional source of nutrients for microorganisms in overlying water, which in turn affected the ecosystem of the entire water body.
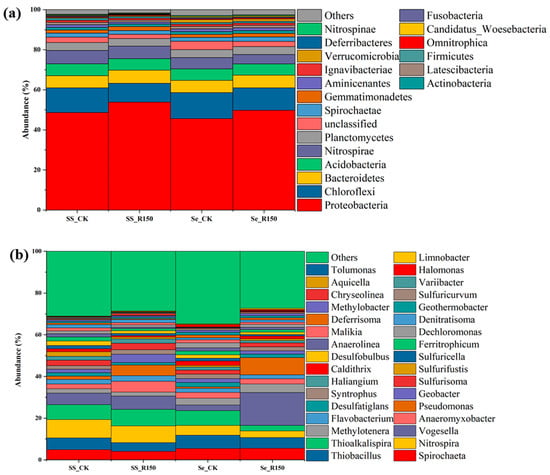
Figure 4.
Microbial community distribution at different levels in sediments and suspended solids (a) for phylum level and (b) for genus level.
Figure 4b shows the microbial community distribution at genus level in sediments and SSs. The relative abundance of most of the microbial genera remained stable, showing that the microorganisms in SSs were highly adaptive to the disturbance. In sediments, the disturbance caused changes in the relative abundance of some microbial genera, such as Desulfobulbus and Desulfatiglans. Desulfobulbus and Desulfatiglans are sulphate-reducing bacteria, and changes in abundance are more pronounced, especially in sediments [43]. Disturbance led to an increase in the abundance of these microorganisms, which implied an increase in the production of sulphide, and in turn might affect the reactions associated with P. Sulphides could react with metal ions to form insoluble metal sulphides, reducing the opportunity for P to bind to metal ions, potentially leading to more P in a dissolved form and increasing its bioavailability. Geobacter plays a key role in the iron cycle, particularly through iron reduction and influencing P release. The abundance of Geobacter increased in sediments, as well as in SSs after the disturbance, promoting more iron reduction in sediments, which in turn released iron-bound P and increased P bioavailability [44].
3.4. Distribution of Microbial Community of the Plants at Phylum and Genus Levels
The relative abundance change in each microbial phylum in the rhizomes and leaves of V. natans under disturbance conditions is shown in Figure 5a. The results showed that the disturbance had little effect on the abundance of the microbial community in rhizomes and leaves, indicating that these microbial communities were relatively stable after the disturbance. Proteobacteria dominated (73.2% in average) and their relative abundance did not change significantly after the disturbance, and the phenomenon was different from sediments and SSs. Actinobacteria and Firmicutes are microorganisms that also play important roles in decomposing organic matters and nutrient cycling [45]. Their abundance did not change significantly after the disturbance in rhizomes, suggesting that their role in the P cycle might not have been significantly affected. In the leaves, the abundance of Firmicutes decreased from 5.2% to 1.1%, which indicated that the leaves might participate in the P sorption during the sediment resuspension [46]. These phyla caused P release during organic matter decomposition, which had a direct impact on P bioavailability. The abundance of Chloroflexi and Acidobacteria in rhizomes and leaves also changed during the disturbance, and they had more specific roles in the environment, including involvement in the decomposition of complex organic matter and P transformations in the sediments. Although changes in their abundance were not significant in rhizomes and leaves, their activities had potential effects on P morphology and availability, particularly in the rhizomes of the plants, which might affect P uptake and storage. Disturbance might alter sediment properties around roots, such as pH and redox state, affecting P release and fixation mediated by microorganisms [47,48]. Disturbance might also result in the redistribution of nutrients in roots, influencing plants’ P uptake efficiency. Overall, the relative stability of the microbial community suggested that the rhizomes and leaves of V. natans were resistant to environmental perturbations.
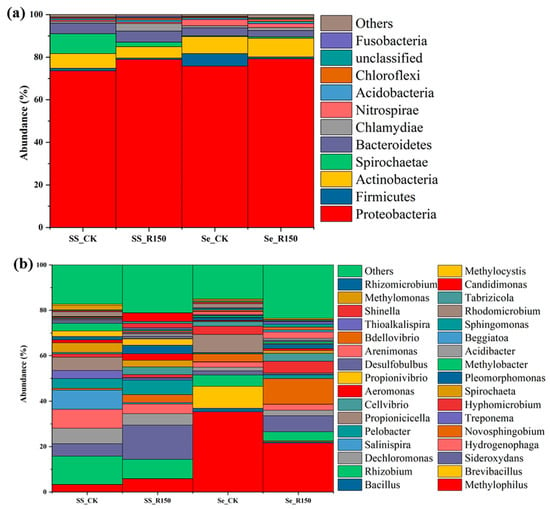
Figure 5.
Microbial community distribution at different levels of the plants (a) for phylum level, and (b) for genus level.
The change in genus abundance in rhizomes and leaves had a similar trend to the phylum abundance (Figure 5b), and the relative abundance of most of the microbial genera did not change significantly after the disturbance, suggesting that these microorganisms were relatively stable in plants. However, Spirochaeta and Propionivibrio showed significant changes in plant leaves, with an increase (from 1.8% to 9.7%) in the abundance of Spirochaeta in leaves after the disturbance, possibly because of the change in environmental conditions (e.g., increases in organic matter and nitrogen sources), while the disturbance provided favourable conditions for these bacteria in anaerobic environments [49]. Although Spirochaeta had no direct connection to the P cycle, their metabolic activities might indirectly affect P availability. Related studies suggested that the P released during the decomposition of organic matter might increase P concentrations, thereby affecting P uptake and utilization in plants. The decreased abundance (from 8.9% to 0.1%) of Propionivibrio in leaves might be attributed to disturbance-induced environmental changes, such as changes in pH and increases in the concentration of organic matter, which provided more substrate for the fermenting bacteria. After the disturbace, the decrease in Propionivibrio might affect the pH of the surrounding environment through their metabolites (e.g., propionic acid), which affected P solubility and P uptake by plant roots [50]. In addition, these bacteria might release P directly during the decomposition of organic matter, increasing the form of P available for plant uptake.
3.5. Response Mechanism of Microbial Community during Sediment Resuspension Process
The correlation analysis between microbial communities and P fractions in sediments/SSs and the RDAs of microbial communities and P contents in the sediment resuspension system are shown in Figure 6(a1, a2). The results indicate that the rotational speed influenced the activity of P, as well as its capacity to handle the microbial community. An increase in rotational speed might lead to enhanced disturbance at the sediment–water interface, altering the microbial growth environment and P morphology. Proteobacteria showed a positive correlation with IP (p < 0.1), suggesting that Proteobacteria might play an active role in P cycling and availability, especially under disturbance conditions, where they might be more effective in facilitating P release or transformation [19]. Chloroflexi showed a negative correlation with NaOH-P (p < 0.1), suggesting that it might reduce the bioavailability of this P fraction under disturbance conditions by some mechanism [51]. The negative correlation of Bacteroidetes and OP indicated that Bacteroidetes might play a role in the mineralization or transformation of OP, and this process could be accelerated or intensified under increased rotational speed. Although OP was not the main P fraction during the release of P from the sediments, during the sediment resuspension process, the P concentration (such as SRP or PP) still increased due to the participation of OP according to the microbial function. Nitrospirae and Planctomycete had less influence on P morphology with the low negative correlations with P fractions, which indicated that they had a more complex influence on P dynamics under specific environmental conditions. This might be due to their metabolic pathways or environmental adaptations. Disturbance increased nutrient resuspension and oxygen diffusion, providing better conditions for microbial activity, which could increase the diversity or richness of the microbial communities. Disturbance might lead to P resuspension in bottom sediments, changing its chemical form and increasing the amount of P available for microbial utilization [52,53].
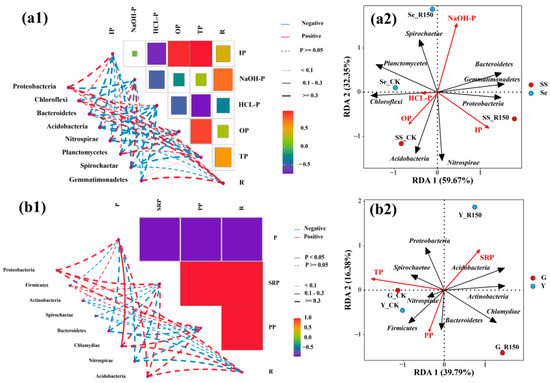
Figure 6.
Correlation analyses between different indexes. (a1,b1) for the correlation analysis between microbial communities and P fractions in sediments/SSs or P content in rhizomes and leaves, respectively. (a2,b2) for the RDA of microbial communities and P contents in sediment resuspension system.
Figure 6(b1,b2) show the correlation analysis between microbial communities and P content in overlying water and plants, and an RDA was also conducted. The results indicated that Proteobacteria were positively correlated with TP in the rhizomes and leaves of V. natans, suggesting that microorganisms directly affected P content in plants by promoting P uptake and metabolism and participated in the inter-root P conversion process [54]. The SRP concentration in the overlying water was significantly positively correlated with Proteobacteria (p < 0.05), which increased the SRP concentration in the overlying water through the decomposition of organic matters or other pathways of P releasing into the water. IP was the main P fraction in the sediments or SSs and was the significant P source of the overlying water during the sediment resuspension process. The transformation or immigration of IP occurred frequently to increase the SRP concentration in the overlying water. The results also showed that the rotational speed led to greater release of P from the sediments to the overlying water, especially through physical disturbance with the expansion of bacterial activity to increase the opportunities for contact with P in the sediments [55]. The positive correlation of Proteobacteria was significant across all P fractions in rhizomes and leaves, and they could accelerate P cycling when activity increased. In addition, Bacteroidetes and Nitrospirae in rhizomes and leaves of V. natans were negatively correlated with the rotational speed, and the abundance of Bacteroidetes and Nitrospirae decreased. This indicated that microorganisms were more sensitive to disturbance while the rotational speed changed the environmental conditions for their survival [56]. Thus, the function of Proteobacteria was more active during the disturbance with the facilitating of P cycling, whereas Bacteroidetes and Nitrospirae might be more sensitive when responding to the disturbance.
4. Conclusions
Phosphorus content in sediments and SSs increased significantly in response to disturbance, showing the significant effect of sediment resuspension on endogenous P release. Both IP and OP content in sediments increased significantly after the disturbance. IP accounted for the major fraction of TP, indicating that IP was more likely to enter the overlying water. The SRP and PP concentration increased from 0.025 mg/L to 0.042 mg/L, and from 0.190 mg/L to 0.390 mg/L, respectively, which suggested that the disturbance enhanced the P bioavailability and mobility and facilitated the P transformation from a fixed to a bioavailable form to affect the nutrient balance and water quality in overlying water. In addition, significant increases in Chao values in sediments and leaves indicated increased species richness. Although Shannon values decreased after the disturbance, indicating a decrease in diversity due to the dominance of certain species, the increase in Simpson values indicated an increase in the status of dominant species in the SSs and sediments after the disturbance. The composition of microbial communities in sediments and SSs changed significantly before and after the disturbance, especially the increased proportion of Proteobacteria (from 46.1% to 51.1%) and the decreased proportion of Chloroflexi (from 10.1% to 8.6%). In contrast, the microbial community in rhizomes and leaves of V. natans was relatively stable and less affected by the disturbance. Proteobacteria were positively correlated with IP contents (p < 0.1), suggesting that they might play an active role in P release or transformation. Chloroflexi and Bacteroidetes were negatively correlated with NaOH-P and OP (p < 0.1), respectively, which indicated that the mineralization or transformation of OP could be accelerated or intensified under the sediment resuspension process.
Author Contributions
B.Z. and Y.G.: preparation, creation and/or presentation of the published work, specifically writing the initial draft (including substantive translation). Y.L.: application of statistical, mathematical, computational, or other formal techniques to analyze or synthesize study data. H.Y.: provision of study materials, reagents, materials, laboratory samples, instrumentation, computing resources, or other analysis tools. P.J.: preparation, creation and/or presentation of the published work by those from the original research group, specifically critical review, commentary or revision—including pre- or post-publication stages. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (23ZR1400700).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Bo Zhang, Yujia Liu, Peng Ji and Yunyan Guo were employed by the company Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences Environmental Technology & Engineering Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Sondergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Jeppesen, E. Internal phosphorus loading in shallow Danish lakes. Hydrobiologia 1999, 408, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D. Effects of seasonal variation and resuspension on microplastics in river sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabholkar, N.; Gorantla, S.; Waghule, T.; Rapalli, V.K.; Kothuru, A.; Goel, S.; Singhvi, G. Biodegradable microneedles fabricated with carbohydrates and proteins: Revolutionary approach for transdermal drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 170, 602–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Fang, H.; Fazeli, M.; Chen, Y.; He, G.; Chen, D. Mobility of phosphorus induced by sediment resuspension in the Three Gorges Reservoir by flume experiment. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Du, Y.; Kong, M.; Liu, C. Interactions of riverine suspended particulate matter with phosphorus inactivation agents across sediment-water interface and the implications for eutrophic lake restoration. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Appan, A.; Gulliver, J.S. Modeling of phosphorus dynamics in aquatic sediments: I—Model development. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3928–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Sun, Z.; Fang, W.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Lv, C. Release of phosphorus from sediments under wave-induced liquefaction. Water Res. 2018, 144, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xue, B.; Bi, C.; Ren, X.; Liu, Y. Influence mechanisms of macro-infrastructure on micro-environments in the recirculating aquaculture system and biofloc technology system. Rev. Aquacult. 2023, 15, 991–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, D.L. The role of phosphorus in the eutrophication of receiving waters: A review. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbeck, L.S.; Unger, D.; Krumme, U.; Liu, S.M.; Jennerjahn, T.C. Typhoon-induced precipitation impact on nutrient and suspended matter dynamics of a tropical estuary affected by human activities in Hainan, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 93, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerhoff, M.; Mazzeo, N.; Moss, B.; Rodríguez-Gallego, L. The structuring role of free-floating versus submerged plants in a subtropical shallow lake. Aquat. Ecol. 2003, 37, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chang, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, S.; Che, F.; Huang, W. The coupled effect of sediment resuspension and microbiota on phosphorus release and transformation in a simulated aquatic ecosystem. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 57, 104653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Sun, C.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y. Adsorption of Arsenite by Six Submerged Plants from Nansi Lake, China. J. Chem. 2014, 2014, 450790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Ge, X.; Yu, Z.; Gu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhang, F. Influence of Submerged Plants on Phosphorus Fractions and Profiles of Sediments in Gucheng Lake. Soil Sediment Contam. 2012, 21, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Grift, B.; Oste, L.; Schot, P.; Kratz, A.; van Popta, E.; Wassen, M.; Griffioen, J. Forms of phosphorus in suspended particulate matter in agriculture-dominated lowland catchments: Iron as phosphorus carrier. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Day, P.A.; Nwosu, U.G.; Barnes, M.E.; Hart, S.C.; Berhe, A.A.; Christensen, J.N.; Williams, K.H. Phosphorus Speciation in Atmospherically Deposited Particulate Matter and Implications for Terrestrial Ecosystem Productivity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4984–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hupfer, M.; Gloess, S.; Grossart, H.-P. Polyphosphate-accumulating microorganisms in aquatic sediments. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 47, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 380, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yang, H.; Chang, Y.; Huang, W.; Jiang, X. Phosphorus release and distribution in sediment resuspension systems under disturbing conditions. Chemosphere 2024, 359, 142386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yi, Q.; Buyang, S.; Cui, H.; Zhang, S. Enrichment of bioavailable phosphorus in fine particles when sediment resuspension hinders the ecological restoration of shallow eutrophic lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 135672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruban, V.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.F.; Pardo, P.; Rauret, G.; Muntau, H.; Quevauviller, P. Harmonized protocol and certified reference material for the determination of extractable contents of phosphorus in freshwater sediments—A synthesis of recent works. Fresen. J. Anal. Chem. 2001, 370, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Curr. Contents/Agric. Biol. Environ. Sci. 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Dong, X.; Tu, C.; Yang, H.; Chang, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, H.; Che, F. Response mechanism of sediment endogenous phosphorus release to functional microorganisms and its cyanobacterial growth and disappearance effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, C.; Jin, Z.; Che, F.; Cao, X.; Song, X.; Lu, C.; Huang, W. Characterization of phosphorus sorption and microbial community in lake sediments during overwinter and recruitment periods of cyanobacteria. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhou, C.; Ma, T.; Guo, W.; Percival, L.; Baeyens, W.; Gao, Y. Anthropogenic activities influence the mobilization of trace metals and oxyanions in coastal sediment porewaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 156353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Xing, X.; Ding, S. Enhancing the retention of phosphorus through bacterial oxidation of iron or sulfide in the eutrophic sediments of Lake Taihu. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Cao, X.; Huang, D.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J. Phosphorus characteristics and microbial community in the sediment-water-algal system during algal growth. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 31414–31421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, C.J.; Mohd, M.H.; Teh, S.Y.; Koh, H.L. Internal phosphorus recycling promotes rich and complex dynamics in an algae-phosphorus model: Implications for eutrophication management. J. Theor. Biol. 2022, 532, 110913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Dong, X.; Yang, H.; Chang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Che, F.; Wang, S.; Huang, W. Characterization of phosphate solubilizing bacteria in the sediments of eutrophic lakes and their potential for cyanobacterial recruitment. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibeid, S.; Elektorowicz, M.; Oleszkiewicz, J.A. Impact of electrocoagulation of soluble microbial products on membrane fouling at different volatile suspended solids’ concentrations. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Zhao, Z.; Yao, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L. Suspended solids induce increasing microbial ammonium recycling along the river-estuary continuum of the Yangtze River. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-h.; Liu, Q.-z.; Chen, P. Effect of long-term continuous cropping of strawberry on soil bacterial community structure and diversity. J. Integr. Agr. 2018, 17, 2570–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wu, B.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, L.; Zhou, M.; Deng, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, L. Effect of suspended solids from anaerobic digested wastewater on performance and microbial community of autotrophic nitrogen removal process. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 450, 141973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Qi, W.; Cao, X.; Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Peng, J.; Hu, C.; Qu, J. Microplastic residues in wetland ecosystems: Do they truly threaten the plant-microbe-soil system? Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Song, P.; Jiang, Y.; Fan, J.; Khan, A.; Liu, P.; Masek, O.; Li, X. Biochar immobilized hydrolase degrades PET microplastics and alleviates the disturbance of soil microbial function via modulating nitrogen and phosphorus cycles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 474, 134838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Dong, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, H.; Yang, H.; Huang, W. Temporal and Spatial Characterization of Sediment Bacterial Communities from Lake Wetlands in a Plain River Network Region. Separations 2023, 10, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagervold, S.K.; Watts, J.E.M.; May, H.D.; Sowers, K.R. Sequential reductive dechlorination of meta-chlorinated polychlorinated biphenyl congeners in sediment microcosms by two different Chloroflexi phylotypes. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2005, 71, 8085–8090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Du, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, L.; Wei, H.; Fang, J.; Liu, R. Biogeographic distribution, ecotype partitioning and controlling factors of Chloroflexi in the sediments of six hadal trenches of the Paciflc Ocean. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, A.; Folster, J.; Kyllmar, K. Determining suspended solids and total phosphorus from turbidity: Comparison of high-frequency sampling with conventional monitoring methods. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandstrom, S.; Futter, M.N.; Kyllmar, K.; Bishop, K.; O’Connell, D.W.; Djodjic, F. Particulate phosphorus and suspended solids losses from small agricultural catchments: Links to stream and catchment characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharrat, H.; Karray, F.; Bartoli, M.; Ben Hnia, W.; Mhiri, N.; Fardeau, M.-L.; Bennour, F.; Kamoun, L.; Alazard, D.; Sayadi, S. Desulfobulbus aggregans sp nov., a Novel Sulfate Reducing Bacterium Isolated from Marine Sediment from the Gulf of Gabes. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, D.E.; O’Neil, R.A.; Chavan, M.A.; N’Guessan, L.A.; Vrionis, H.A.; Perpetua, L.A.; Larrahondo, M.J.; DiDonato, R.; Liu, A.; Lovley, D.R. Transcriptome of Geobacter uraniireducens growing in uranium-contaminated subsurface sediments. Isme J. 2009, 3, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, P.A.; Jha, B. Intertidal marine sediment harbours Actinobacteria with promising bioactive and biosynthetic potential. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlin, T.; Junier, T.; Roussel-Delif, L.; Jeanneret, N.; Junier, P. Endospore-enriched sequencing approach reveals unprecedented diversity of Firmicutes in sediments. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 6, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, B.; Sleimi, N.; Cacador, I. Sediment phosphorus speciation changes by extracellular enzymatic activity (EEA) of three phosphatase pH-dependent isoforms. Mar. Chem. 2022, 246, 104162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yi, Q.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, X. Quantifying phosphorus levels in water columns equilibrated with sediment particles in shallow lakes: From algae/cyanobacteria-available phosphorus pools to pH response. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 868, 161694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertsen, M.; McIlroy, S.J.; Stokholm-Bjerregaard, M.; Karst, S.M.; Nielsen, P.H. “Candidatus Propionivibrio aalborgensis”: A Novel Glycogen Accumulating Organism Abundant in Full-Scale Enhanced Biological Phosphorus Removal Plants. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.T.K.; Watts-Williams, S.J.; Smernik, R.J.; Cavagnaro, T.R. Effects of plant roots and arbuscular mycorrhizas on soil phosphorus leaching. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.H.; Zhao, L.; Jin, Z.H.; Yang, H.R.; Tu, C.Q.; Che, F.F.; Russel, M.; Song, X.S.; Huang, W. Study on the management efficiency of lanthanum/iron co-modified attapulgite on sediment phosphorus load. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.R.; Warnemuende, E.A.; Haggard, B.E.; Huang, C. Changes in sediment-water column phosphorus interactions following sediment disturbance. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 27, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Hong, Z.; Wei, J.; Liao, Y.; You, S.; Wang, Y.; Lv, J.; Feng, H.; Kolencik, M.; Chang, X.; et al. Phosphorus fractionation and adsorption characteristics in drinking water reservoir inlet river sediments under human disturbance. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 2530–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Ha, H.K.; Woo, S.B. Dynamics of sediment disturbance by periodic artificial discharges from the world’s largest tidal power plant. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 190, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breshears, D.D.; Whicker, J.J.; Zou, C.B.; Field, J.P.; Allen, C.D. A conceptual framework for dryland aeolian sediment transport along the grassland-forest continuum: Effects of woody plant canopy cover and disturbance. Geomorphology 2009, 105, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Liu, M.; Hou, L.; Zhao, M.; Tang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Li, J.; Han, P. Community structure and abundance of comammox Nitrospira in Chongming eastern intertidal sediments. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 3213–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).