Abstract
Edible bird’s nests have a variety of biological activities, the main components of which are sialic acids. Sialic acids are a group of nine-carbon N-acetylated derivatives of neuraminic acid containing a keto group at position C2 and play important roles in many biological processes. To verify whether the oral administration of edible bird’s nests would change the content and distribution of sialic acid components in vivo, a liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry method for the quantitative analysis of sialic acid levels in serum and tissues was developed. In the negative ion mode, the mobile phases consist of 0.1% formic acid in water (A) and acetonitrile (v/v) (B). Isocratic elution was performed with 60% B for 0−15 min. The chromatographic separation was performed on a Morphling HILIC Amide column (2.1 mm × 150 mm, 5 μm) at a flow rate of 0.5 mL min−1. The results showed that the correlation coefficients of the typical calibration curves were all higher than 0.995, exhibiting good linearity. The levels of free and conjugated forms of N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc), N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac), and 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-glycero-D-galactonononic acid (KDN) in the serum and different tissues were simultaneously detected after the oral administration of the edible bird’s nests at a daily dose of 300 and 700 mg Kg−1 for seven days in mice. Our study found that the oral administration of edible bird’s nests can significantly increase the concentration of total sialic acids (Neu5Gc + Neu5Ac + KDN) in serum and spleen and lungs tissues, which may be related to the anti-inflammatory and immune function of edible bird’s nest, but further studies are needed to verify this. Neu5Ac was the dominant sialic acid in brain tissue, and Neu5Gc was the dominant sialic acid in serum and other tissues, including heart, liver, spleen, lungs, and kidney. Moreover, we found that the forms of Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc were mainly conjugated in all groups except liver tissue. In conclusion, the method we established had good linearity and accuracy; it allowed the analytes to be effectively separated from the matrix and endogenous substances in serum or tissues, so it could effectively detect the distribution and concentration of free and conjugated forms of sialic acids in serum and tissues, which was beneficial to the research and exploitation of edible bird’s nests and sialic acids.
1. Introduction
The earliest recorded use of edible bird’s nests as food dates back to the Tang dynasty; today, the consumption of edible bird’s nests represents a culture passed down through the ages [1]. Edible bird’s nests can be categorized as those produced by house and cave swiftlets, which are mainly of Southeast Asian origin [2]. Edible bird’s nests have been an important part of China’s health culture since ancient times, and they have been used for brain development and memory improvement for their antioxidant, anti-viral, anti-ageing, and anti-tumor properties and for their beneficial effects on the immune system, liver protection, and gut flora regulation [3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. The main components of edible bird’s nests are carbohydrates, water-soluble proteins, trace elements such as calcium and phosphorus, and essential amino acids such as phenylalanine, methionine, glycine, lysine, leucine, isoleucine, and valine [10].
Edible bird’s nests are also rich in sialic acids, which are a group of carboxylate monosaccharide acylated derivatives containing nine carbon atoms and systematically named 5-amino-3,5-dideoxy-D-glycero-D-galactononanone sugar. Among the more than 50 sialic acids, the three most common compounds are N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac), N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc), and 2-keto-3-deoxy-D-glycero-D-galactonononic acid (KDN), and Neu5Ac is the most widely distributed one in nature [11]. Sialic acids are important components of glycoproteins, oligosaccharides, and glycolipids, and they are widely distributed in nature, including in the human brain, nervous tissue, blood, and emulsions [12]. Sialic acids exist in both free and conjugated forms in tissues and fluids such as serum, urine, and saliva. Free-form sialic acid refers to the presence of sialic acid in body fluids as a monosaccharide, and conjugated sialic acid refers to the presence of sialic acid as terminal monosaccharides at the ends of free oligosaccharides, glycolipid glycan chains, and glycoprotein glycan chains [13]. Sialic acids exhibit a variety of biological activities, including immune enhancement and anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, and anti-tumor activities, and they can also be used as a brain nutrient, effectively promoting cognitive development, learning, and memory in infants [14,15,16]. They have promising applications in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, the synthesis of drug precursors, the development of health products, and food nutrition. Although sialic acids exhibit many biological activities, it has also been reported that an excess of sialic acids can be harmful to the body. Sialic acid disorders, which are screened out via the quantitative analysis of both total sialic acids and free sialic acids in human serum, show promise in terms of disease monitoring and prognosis [17]. In tumors, especially malignant tumors, the level of sialic acids can be higher than in normal tissue and can thus be used as a marker to identify tumors. Because of the two-sided nature of sialic acids, there is an urgent need to study whether the oral consumption of edible bird’s nests affects the changes in sialic acids content and distribution in the body.
The analytical methods of sialic acid include colorimetry, spectrophotometry, chromatography, and capillary electrophoresis. Colorimetry and capillary electrophoresis are simple to operate but are less sensitive than other methods. High-performance liquid chromatography is the most common method for the detection of sialic acid and is often combined with different detection techniques to detect sialic acid, such as ultraviolet detectors, PAD detectors, fluorescence detectors, and mass spectrometry (MS) [18,19,20]. Among them, LC-MS does not require derivatization of the sample and shows significant advantages with its high sensitivity and accuracy. But mass spectrometers are expensive. In our experiment, a HILIC column was selected, which has a stronger ability to retain polar compounds. Sialic acid is a kind of amino sugar compound containing a carboxyl group, which has a larger polarity and is not retained in the C18 column whose stationary phase is non-polar.
The objective of the present study was to use LC–MS/MS to quantitatively determine the levels of free and conjugated forms of Neu5Gc, Neu5Ac, and KDN in serum and different organ tissues after the oral administration of edible bird’s nests. By measuring the free and conjugated sialic acids in blood and tissues, it is possible to determine whether the oral consumption of edible bird’s nests influences changes in sialic acid levels in the body. Our research provided important information regarding the application and development of edible bird’s nests.
2. Experiments
2.1. Chemicals
The reference standards of Neu5Ac (purity: 98.0%), Neu5Gc (purity: 98.0%), KDN (purity: 98.0%), and the stable isotopically labeled Neu5Ac-13C (isotopic purity: 98.0%) were purchased from Shanghai Zhenzhun Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. The chemical structures of all three compounds are shown in Figure 1. HPLC-grade acetonitrile, methanol, and acetic acid (AA) were purchased from Fisher Scientific (Pittsburgh, PA, USA). Trifluoracetic acid (TFA) was purchased from Energy Chemical (Shanghai, China). Deionized water was generated in-house using a Milli-Q ultrapure water purification system from EMD Millipore (Billerica, MA, USA).
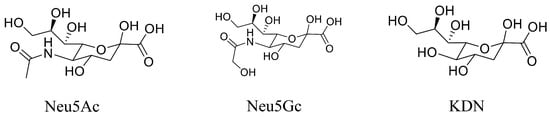
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of the sialic acids Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc, and KDN.
2.2. Calibration Standards
Stock solutions at 1 mg mL−1 of Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc, KDN, and 13C-Neu5Ac were prepared in water and stored at −20 °C until use. The Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc, and KDN working solutions were freshly prepared in water. The concentrations of the calibration standards ranged between 50.0 and 10,000.0 ng mL−1 and were prepared in order to determine the LC–MS/MS parameters for the quantitative analyses of the free and conjugated forms of KDN, Neu5Ac, and Neu5Gc.
2.3. LC–MS/MS System
HPLC-Triple Quadrupole MS (QTRAP6500 LC/MS, AB SCIEX, Foster City, CA, USA) was used to verify the specificity and establish the MRM method. A Morphling HILIC Amide column (2.1 mm × 150 mm, 5 μm) was used for the chromatographic separation. The autosampler temperature was set to 15 °C, and the LC column was maintained at 30 °C. The system was controlled using Analyst version 1.6.2 software.
2.4. LC–MS/MS Conditions
After exploration, the flow rate was 0.5 mL min−1, and the mobile phase A was an aqueous solution containing 0.1% (v/v) formic acid. B was acetonitrile solution, and isocratic elution was performed with 60% B for 0−15 min [21]. The injection volume was 5 μL. The mass spectrometry parameters were set as follows: the mode was set as mass detector, electrospray ionization (ESI) and multiple-reaction monitoring were in the negative ion mode, the sheath gas flow rate was 46 L h−1, the auxiliary gas flow rate was 850 L h−1, the spray voltage was 3.5 kV, the source temperature was 150 °C, and the auxiliary gas temperature was 400 °C. The cone voltage was 30 V, and the collision voltage was 35 V.
2.5. Sample Preparation
2.5.1. Free Sialic Acids in Serum
Before LC-MS analysis, blood samples were removed from a −80 °C refrigerator and thawed to room temperature. For the analysis of free sialic acids, 5 μL IS (5 μg mL−1) was added to 50 μL serum followed by protein precipitation with 200 μL acetonitrile. After mixing and centrifugation (12,000 rpm for 10 min), the supernatant was analyzed [22].
2.5.2. Conjugated Sialic Acids in Serum
For the analysis of conjugated sialic acids, 5 μL IS (5 μg mL−1) was added to 25 μL serum, followed by the addition of 25 μL trifluoroacetic acid (0.15 moL L−1); it was kept at 80 °C for 2 h to obtain all total sialic acids in their free forms. After heating, the samples were cooled to room temperature; this was followed by protein precipitation with 200 μL acetonitrile. The supernatant underwent centrifugation (12,000 rpm for 10 min) prior to the quantitative determination of the sialic acids via LC–MS/MS. The level of conjugated sialic acids was obtained by subtracting the level of free sialic acids in serum [13,23].
2.5.3. Free Sialic Acids in Different Tissues
Before LC-MS analysis, 50–100 mg of frozen tissues was thawed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) on ice before cooling and homogenization in a Polytron homogenizer (IKA, Staufen, Germany) [13,24]. The homogenized samples were filtered through a 0.22 μm membrane filter (Millipore Corporation, Burlington, MA, USA), and the filtrate was used for the determination of free sialic acid concentration. Moreover, 5 μL of IS (5 μg mL−1) was added to 50 μL of the homogenized samples; this was followed by protein precipitation with 200 μL acetonitrile. After mixing and centrifugation (12,000 rpm for 10 min), the supernatant was analyzed.
2.5.4. Conjugated Sialic Acids in Different Tissues
For the determination of the conjugated sialic acids, 5 μL of IS (5 μg mL−1) was added to 25 μL of the homogenized samples; this was followed by the addition of 25 μL of trifluoroacetic acid (0.15 moL L−1), and the samples were kept at 80 °C for 2 h to obtain all the total sialic acids in their free form. After heating, the samples were cooled to room temperature; this was followed by protein precipitation with 200 μL acetonitrile. The supernatant underwent centrifugation (12,000 rpm for 10 min) prior to the quantitative determination of the sialic acids via LC–MS/MS. The level of conjugated sialic acids was obtained by subtracting the level of free sialic acids in tissues [13,23].
2.6. Method Validation
The LC–MS/MS method was validated for linearity, sensitivity, precision, accuracy, and stability according to the currently accepted US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance.
2.6.1. Calibration Curve, Linearity, and Sensitivity
A calibration curve was constructed using six concentrations covering the range 50.0–10,000.0 ng mL−1 derived from the peak area ratio of KDN, Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc, and 13C-Neu5Ac. Concentrations of KDN, Neu5Ac, and Neu5Gc were calculated from these area ratios using the calibration curve established by simple linear regression. The limit of detection (LOD) and the limit of quantification (LOQ) were defined as the lowest concentration with a signal-to-noise ratio of 1/3 and 1/10, respectively.
2.6.2. Precision and Accuracy
The within-assay precision (repeatability) of the method was determined by performing nine consecutive assays on quality control (QC) samples at three different concentration levels: 50.0 (low level), 500.0 (medium level), and 3000.0 (high level) ng mL−1 on the same day. The QC samples were also analyzed on three different days to assess the between-assay precision of the method. Within- and between-assay precision was determined as the %CV, and within- and between-assay accuracy was expressed as the percentage of the theoretical concentration as accuracy (%) = (found concentration/theoretical concentration) × 100.
2.6.3. Stability
The stability of the KDN, Neu5Ac, and Neu5Gc samples was assessed by analyzing the calibration curve samples at the concentrations of 50.0, 500.0, and 3000.0 ng mL−1 for 24 h at room temperature. Short-term stability in the prepared samples was tested by measuring the prepared QCs for 15 days. Moreover, the QC samples were used to test the stability over 3 freeze–thaw cycles.
2.6.4. Recovery
Low, medium, and high concentrations of Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc, and KDN were added to samples with known sialic acids concentrations and analyzed in three replicates for each concentration to calculate the recovery of the method.
2.7. Animals
The animal experiments were approved by the Ethics Committee of Shandong University (No. SYXK2019-0005) and in accordance with the basic principles of animal experiments. Male Babl/c mice were used in testing for the oral administration of the edible bird’s nest effect. Male Babl/c mice (18–20 g) were supplied by the Lab Animal Center of Shandong University (Grade II, Certificate No.SYXK 2022-0006). The animals were housed in a temperature- and humidity-controlled facility (temperature 20–24 °C and 35–75% humidity), maintained on a 12 h light/12 h dark cycle, and given a standard laboratory rodent diet. After overnight fasting, the mice received the oral administration of water or edible bird’s nest. The male Babl/c mice were divided into four groups: one group received distilled water orally for 7 days; two groups received edible bird’s nests orally at 300 mg Kg−1and 700 mg Kg−1 for 7 days; and the last group received oral Neu5Ac 70 mg Kg−1 for 7 days. After seven days of administration, the mice were anesthetized with ether. The blood samples were then taken from the retro-orbital venous plexus and placed in a 1.5 mL EP tube. After 2 h of standing at room temperature, centrifuged at 4 °C, 12,000 rpm for 10 min, the serum samples were obtained and placed in −80 °C. For organ collection, the animals were culled with deep ether, and the hearts, livers, spleens, lungs, kidneys, and brains were harvested separately and stored at −80 °C for further analysis [13,25].
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as the mean ± standard error. GraphPad prism statistical software (version 8.0, Boston, MA, USA) was used to analyze the data. A one-way ANOVA test was used to compare the levels of KDN, Neu5Ac, and Neu5Gc in the different experimental groups. The differences were considered significant at p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of MS and Chromatography Conditions for Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc, and KDN
Mass detection of the analytes was evaluated using full-scan mass spectra in both positive- and negative-ion modes. Greater sensitivity was achieved for Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc, KDN, and IS in the negative mode than in the positive mode. Thus, the negative ESI mode of [M−H]− was used to yield the precursor ions of Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc, KDN, and IS. The product ion scan spectra are shown in Figure S1. To improve the specificity, an MRM scanning type was used in this analysis. The optimized MRM transitions were specific and intense for the analysis of Neu5Ac (m/z 308.1 → 86.9), Neu5Gc (m/z 324.0 → 115.9), KDN (m/z 267.0 → 87.0), and IS (m/z 311.1 → 90.0). A summary of the optimized MRM fragmentation transitions and MS parameters for each analyte is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Summary parameters of the energy values used for the LC–MS/MS quantitative analysis of Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc, KDN, and IS.
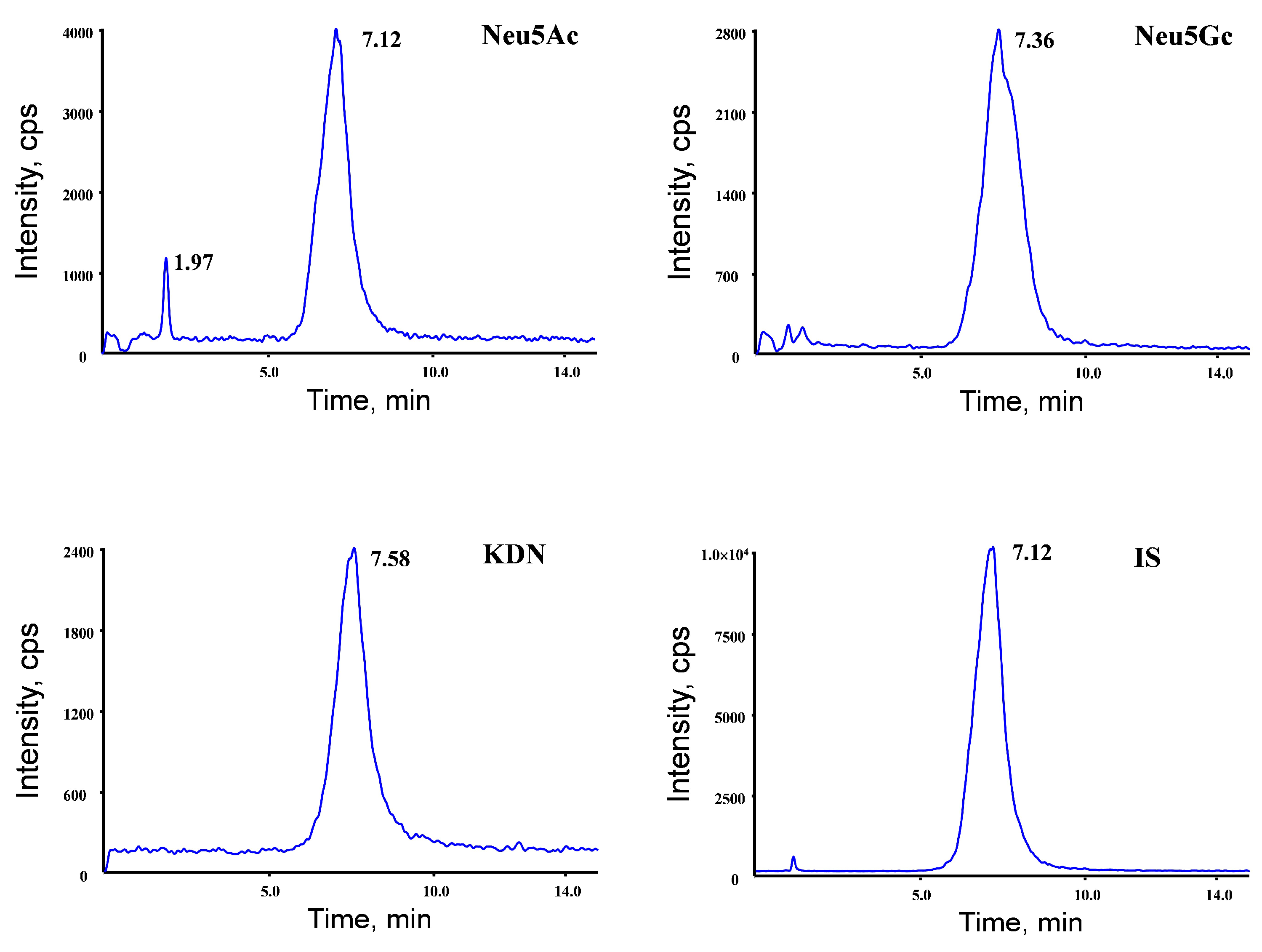
To achieve the efficient chromatographic separation of the analytes with a satisfying response, several kinds of columns were tested and compared. The Morphling HILIC Amide column (2.1 mm × 150 mm, 5 μm) was chosen for this method as it achieved better peak shapes and separation. Different types of mobile-phase systems were tested to obtain the optimal response and good peak shapes for the analytes. Acetonitrile was used as the organic modifier because it provided higher response levels and lower background noises. The isocratic elution was used to obtain satisfactory peak shapes and isolation (Figure 2).
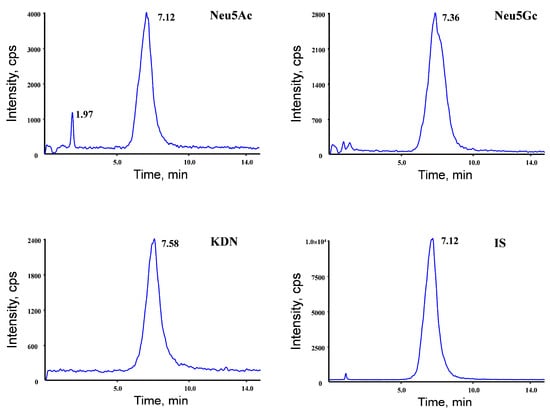
Figure 2.
Representative MRM chromatograms obtained from serum and different tissues.
3.2. Sample Preparation
The pretreatment of biological samples is the key to achieving accurate determinations. Different precipitating reagents (methanol and acetonitrile) were compared, and acetonitrile led to better extractions of all analytes, with no endogenous interference. Therefore, acetonitrile was used for protein precipitation in our method of pretreating the serum samples. Total sialic acids were determined by acid hydrolysis, and, in accordance with the literature, TFA hydrolysis was used. The concentration of TFA and the incubation time were optimized. It was finally determined that the highest concentration of sialic acid was released with only 0.15 moL L−1 TFA and 120 min of incubation. And, the level of conjugated sialic acids was obtained by subtracting the level of free sialic acids in tissues [13,23].
3.3. Method Validation
3.3.1. Linearity and Limits of Quantification
The calibration curves of the analytes exhibited excellent linearity with the concentration range of 50.0–10,000.0 ng mL−1 of Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc, and KDN in the serum. The LOQs were 50.0 ng mL−1 for Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc, and KDN (Table 2). The correlation coefficients (r) of the typical calibration curves were all higher than 0.995, exhibiting good linearity. The method was thus suitable for sialic acids concentration determination studies.

Table 2.
Linear ranges, regression equations, and correlation coefficients of the three analytes.
3.3.2. Precision and Accuracy
In the present study, the precision and accuracy of the LOQs were acceptable, with RSD values ≤ 15% and RE values within ±15% for the analytes, as displayed in Table 3. These results demonstrate that the precision and accuracy values were in the acceptable range.

Table 3.
Precision, accuracy, and recovery for the three analytes.
3.3.3. Extraction Recovery
Extraction recovery for the analytes (at three different QC levels) in the samples with known sialic acids concentrations are shown in Table 3. The mean extraction recoveries were all more than 85.0%, which indicated that the recoveries of the analytes were consistent and reproducible. The results indicated sufficient extraction efficiency [26].
3.4. Effect of Edible Bird’s Nest on Serum Free and Conjugated Sialic Acids Levels after Oral Administration for Seven Days
To investigate the effect of the repeated administration of edible bird’s nests on serum sialic acids levels, LC–MS/MS was used to quantitatively determine the levels of free and conjugated forms of KDN, Neu5Ac, and Neu5Gc in mice serum. The mice were fed a standard diet and were orally administered edible bird’s nests (low and high dose) for seven days. As shown in Table 4, In serum, the level of the conjugated form of Neu5Gc was 2176.75 ± 137.07 µg mL−1 in the control group, whereas the level in the low-dose (300 mg Kg−1) edible bird’s nest group was 2565.40 ± 249.71 µg mL−1, which was significantly higher than that in the control group, and Neu5Gc was the major sialic acid in the serum. The Neu5Ac group was given 70 mg Kg−1 of Neu5Ac, which was consistent with the Neu5Ac content in the high dose (700 mg Kg−1) edible bird’s nest group. And, there was no significant increase in the free and conjugated forms of Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc, and KDN in the high-dose edible bird’s nest group and the Neu5Ac group (Table 4).

Table 4.
Changes in the sialic acids content of serum seven days after administration.
3.5. Effect of Edible Bird’s Nest on the Levels of Free and Conjugated Sialic Acids in Tissues after Oral Administration for Seven Days
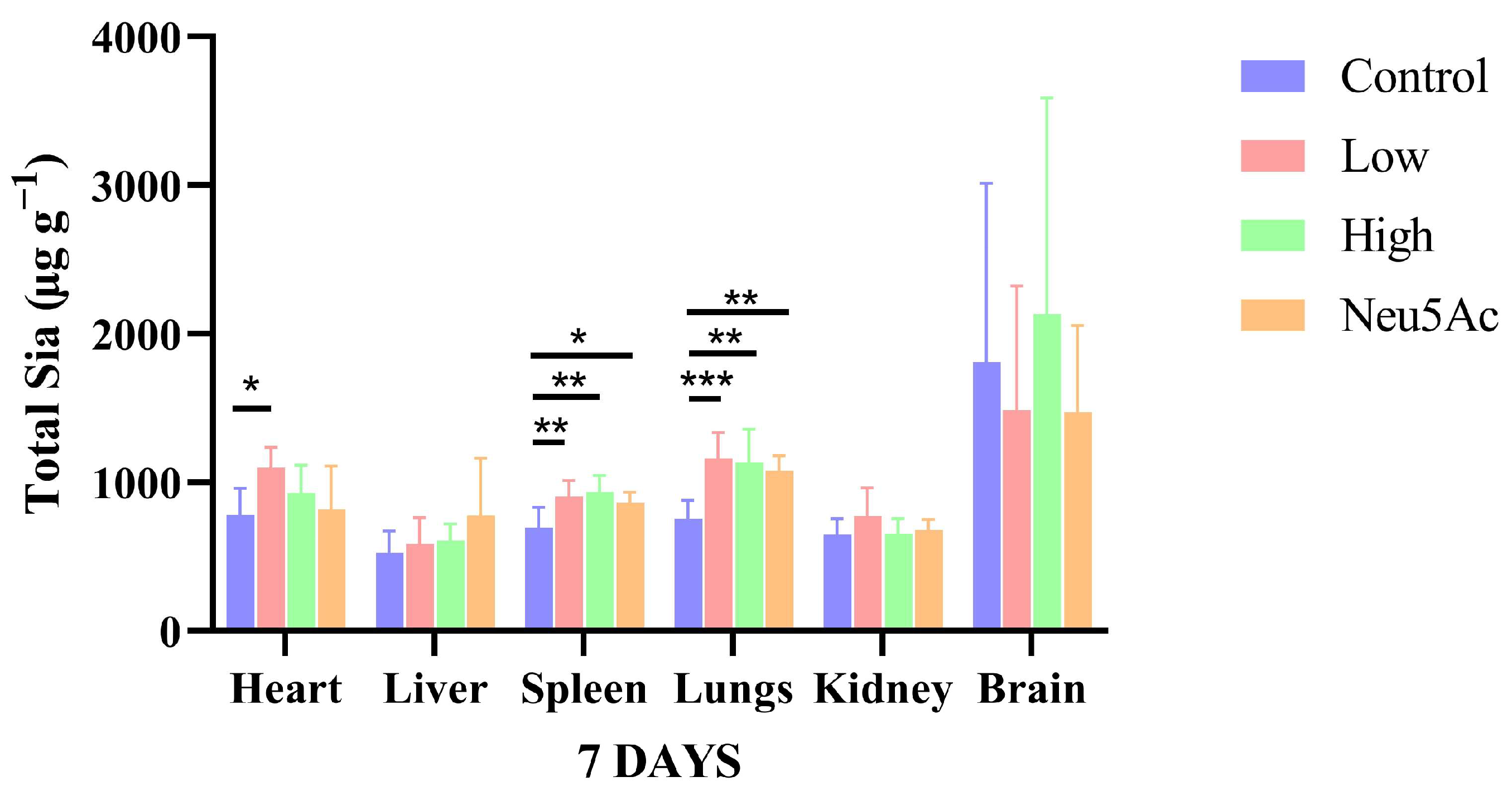
The total sialic acid components (including KDN, Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc) in individual tissues after seven days of oral administration of edible bird’s nests are shown in Figure 3. The results with significant differences have been marked. As shown in Figure 3, after the administration of edible bird’s nest and Neu5Ac, the contents of total sialic acid in liver, kidney, and brain tissues did not significantly increase, but the content of total sialic acids in the brain was about twice that of other tissues, which is consistent previous research that reports that the nervous tissue is the organ with the highest expression level of sialic acids [27].
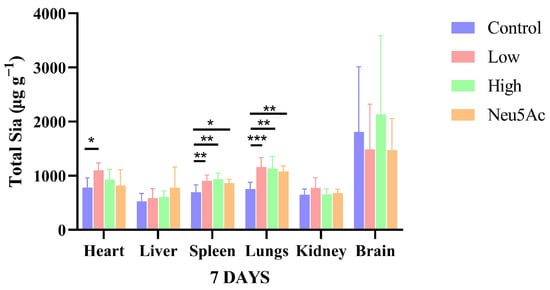
Figure 3.
Comparison of total sialic acids contents in different tissues after the oral administration of edible bird’s nests. The results shown are means ± SD; n = 6. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
Our previous study revealed the immunomodulatory function of stewed edible bird’s nests at low temperature. According to the results of animal experiments, it was found that cooking edible bird’s nests at low temperature can significantly increase the number of antibody-producing cells in mice (Table S3). These results suggest that edible bird’s nests cooked at low temperatures can be used as a functional food to enhance immunity (see Supplementary Materials Tables S1–S3). The spleen is the largest peripheral immune organ in the human body and plays an important role in the body’s performance of immune functions, which can be enhanced by sialic acids [28]. In our study, the levels of total sialic acid components (including KDN, Neu5Ac, and Neu5Gc) in the spleen were significantly increased after the administration of edible bird’s nests and Neu5Ac, with the levels in the low-dose group, high-dose group, and control group being 905.26 ± 105.05, 935.90 ± 108.75, 862.97 ± 69.81, and 695.54 ± 137.66 µg g−1 (Figure 3). In more details, the conjugated Neu5Ac contents were significantly increased in the low-dose edible bird’s nest group, high-dose edible bird’s nest group, and Neu5Ac group. Both free and conjugated Neu5Gc contents were significantly increased in the high-dose edible bird’s nest group, and the conjugated KDN contents were significantly higher in the low-dose edible bird’s nest, high-dose edible bird’s nest, and Neu5Ac groups than in the control group (Table 5).

Table 5.
Changes in the sialic acid content of individual tissues seven day after administration.
Terminal sialic acid is an important determinant of the integrity of the lung endothelial barrier [29]. As shown in Figure 3, in lungs tissue, the total sialic acids content in the control group was 753.64 ± 123.90 µg g−1, and that of the low-dose edible bird’s nest group, high-dose edible bird’s nest group, and Neu5Ac group was 1160.68 ± 174.91, 1135.45 ± 224.34, and 1079.51 ± 97.79 µg g−1, respectively, which were significantly higher than content of the control group. More specifically, conjugated forms of Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc were significantly higher in low-dose edible bird’s nest group and high-dose edible bird’s nest group than in control group (Table 5).
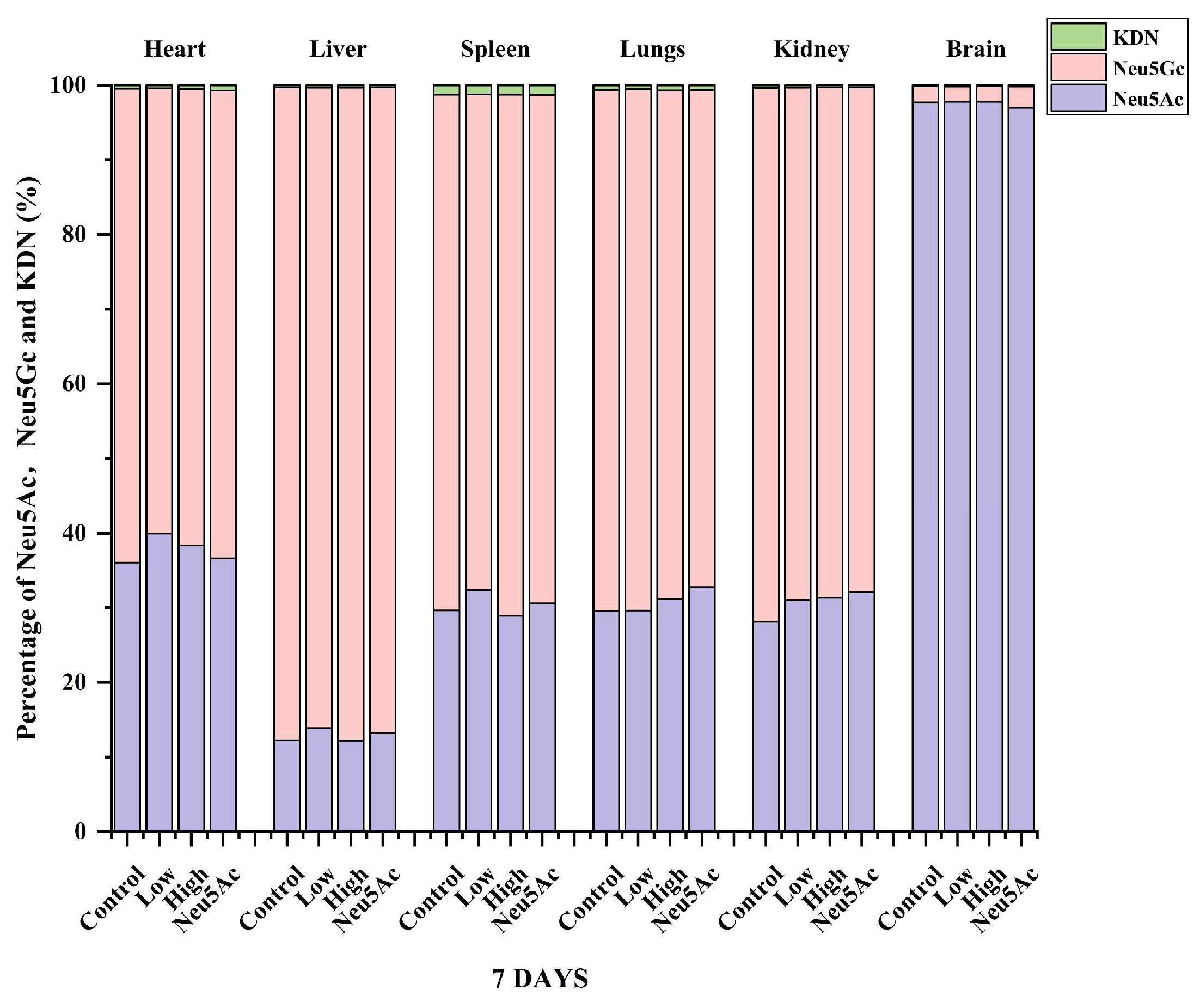
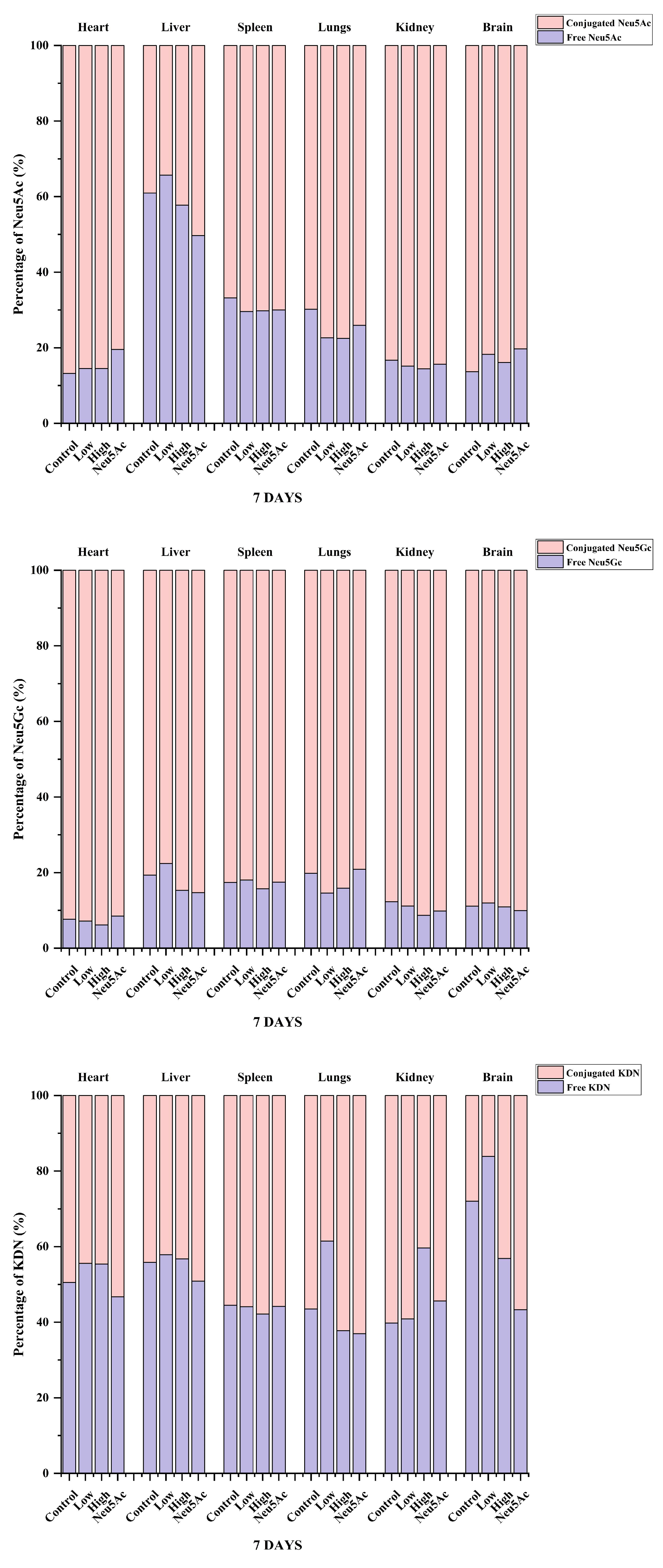
We also analyzed the proportions of the three sialic acids in different tissues after 7 days of administration and found that even after seven days of administration, the highest proportion of Neu5Ac content was found in brain tissue, higher than 97% (Figure 4). The study by Huang et al. [30] showed that the proportion of Neu5Ac in mouse pups was 91%, which was slightly different from our study, indicating that the proportion of sialic acid may be related to the strain and age of mice, and further research is needed to verify this. The content of Neu5Gc was the highest in other tissues, and the proportion was higher than 60% (Figure 4). Figure 5 shows the percentage distribution of free and conjugated forms of Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc, and KDN after administration. The form of sialic acid in pigs has been studied previously, and it was reported that the majority of Neu5Ac (76–100%) and Neu5Gc (70–100%) were conjugated in five organ tissues and skeletal tissues in 3-day-old pigs or adult pigs (180 days of age) [13]. Our study showed that the majority of Neu5Ac (67–87%) and Neu5Gc (78–94%) in different tissues of mice in the administration and control groups were conjugated (Figure 5). The only exception was that the level of free Neu5Ac in the liver accounted for 34–50% of the total Neu5Ac level (Figure 5). In contrast, the proportion of free and conjugated KDN was similar in the six tissues (Figure 5).
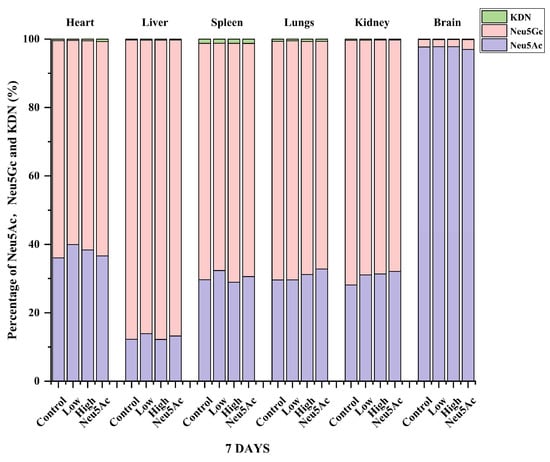
Figure 4.
Summary analysis of the percentage distribution of the total levels of Neu5Gc, Neu5Ac, and KDN in different tissues after the oral administration of edible bird’s nests and Neu5Ac for seven days.
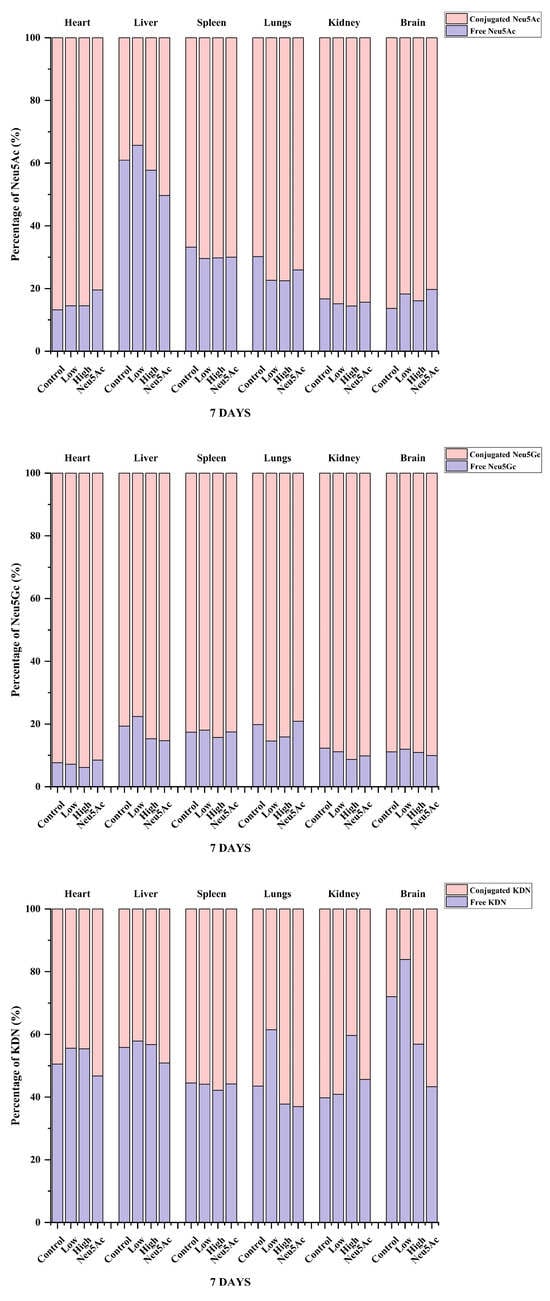
Figure 5.
Summary analysis of the percentage distribution of free and conjugated forms of Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc, and KDN in different tissues after the oral administration of edible bird’s nests for seven days.
In conclusion, we used an LC-MS method combined with a HILIC column to determine the distribution of and changes in sialic acids contents in serum and tissues of mice after the oral administration of edible bird’s nests. The method had good linearity and high accuracy. The results showed that the oral administration of edible bird’s nests can significantly increase the contents of sialic acids in serum, spleen, and lungs, which was conducive to the study of the mechanism of action of edible bird’s nest.
4. Concluding Remarks
An edible bird’s nest has anti-aging and anti-virus effects and enhances memory and immunity. And, in our previous studies, we revealed the immunomodulatory function of low-temperature edible bird’s nest stew. Sialic acid has many functions, such as immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and neurodevelopmental effects. The change in sialic acid content caused by the oral administration of bird’s nests is helpful to reveal the molecular basis of the effect of edible bird’s nest. In our study, we used LC-MS combined with a HILIC column to determine the contents of three different sialic acids in free and conjugated forms in mice serum and tissues with high sensitivity and accuracy. Analytes could be efficiently separated from the matrix and endogenous substances in serum or tissues. However, due to the nature of the column, the peak width became larger and the sensitivity decreased. Our results suggested that the oral administration of edible bird’s nests could significantly increase the contents of sialic acid components in the serum and some tissues in the body, such as the spleen and lungs. Moreover, we found that Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc were mainly conjugated in all groups except liver tissue. Unlike other tissues, Neu5Ac had the highest proportion in the brain, which was also consistent with a previous study [30]. But, the effect of oral administration of edible bird’s nests on different forms of sialic acids in other animals or humans remains to be studied. In conclusion, our study revealed the distribution and contents of free and conjugated forms of Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc, and KDN in serum and body tissues of normal mice and oral edible bird’s nest mice. It was beneficial to further study the mechanism of action of Neu5Ac and edible bird’s nest and to promote the development and utilization of edible bird’s nests as a functional food.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/separations11040107/s1, Table S1: Effect of stewed edible bird’s nest on organ/body weight ratio in mice ( ± SD, n = 12); Table S2: Effect of stewed edible bird’s nest on DTH and CONA-induced lymphocyte transformation in mice ( ± SD, n = 12); Table S3: Effect of fresh stewed edible bird’s nest on the number of antibody-producing cells and HC 50 ( ± SD, n = 12). Figure S1: Product ion mass spectra of the [M−H]− ions of Neu5Gc, Neu5Ac, KDN, and IS.
Author Contributions
M.-H.W., Z.-F.W. and M.Y.: laboratory work, analysis of data, and writing—original draft preparation; C.-G.Y.: analysis of data and writing—original draft preparation; D.-L.W.: supervision and writing—reviewing and editing. S.-Q.W.: funding acquisition, analysis of data, writing, and project administration. All authors contributed to the writing and review of the article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81773807), the Shandong Province Major Scientific and Technological Innovation Project (2021CXGC010511), and the National Key R&D Program of China (2023YFC3504102); it was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China (ZR2022MH224), the Program of Shandong University (2018WLJH93), and the Instrument Improvement Funds of the Shandong University Public Technology Platform (TS20220206).
Data Availability Statement
All data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Man Yuan was employed by the company Beijing Rongshutang Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Author Chun-Guo Yang was employed by the company Shandong Yifang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Lee, T.H.; Wani, W.A.; Lee, C.H.; Cheng, K.K.; Shreaz, S.; Wong, S.; Hamdan, N.; Azmi, N.A. Edible bird’s nest: The functional values of the prized animal-based bioproduct from Southeast Asia—A review. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 626233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quek, M.C.; Chin, N.L.; Yusof, Y.A.; Law, C.L.; Tan, S.W. Characterization of edible bird’s nest of different production, species and geographical origins using nutritional composition, physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, K.H.; Lee, T.H.; Nagandran, K.; Md Yahaya, N.H.; Lee, C.T.; Tjih, E.T.T.; Aziz, R.A. Edible bird’s nest extract as a chondro-protective agent for human chondrocytes isolated from osteoarthritic knee: In vitro study. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, S.P.; Cheng, S.H.; Mohamed, W. Edible bird’s nest as a potential cognitive enhancer. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 865671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Careena, S.; Sani, D.; Tan, S.N.; Lim, C.W.; Hassan, S.; Norhafizah, M.; Kirby, B.P.; Ideris, A.; Stanslas, J.; Basri, H.B.; et al. Effect of edible bird’s nest extract on lipopolysaccharide-induced impairment of learning and memory in wistar rats. Evid.-Based Complement Altern. Med. Evid. 2018, 2018, 9318789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khaldi, K.; Yimer, N.; Sadiq, M.B.; Abdullah, F.F.J.B.; Salam Babji, A.; Al-Bulushi, S. Edible bird’s nest supplementation in chilled and cryopreserved Arabian stallion semen. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghani, A.; Mehrbod, P.; Safi, N.; Kadir, F.A.A.; Omar, A.R.; Ideris, A. Edible bird’s nest modulate intracellular molecular pathways of influenza a virus infected cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, I.S.; Park, S.Y.; Seo, S.A.; Yang, J.E.; Hwang, E. The protective effect of edible bird’s nest against the immune-senescence process of UVB-irradiated hairless mice. Photochem. Photobiol. 2022, 98, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Fan, Y.; Liu, K.; Lonan, P.; Liao, F.; Huo, Y.; Zhong, X.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hou, S.; et al. Edible bird’s nest ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in C57BL/6J mice by restoring the Th17/Treg cell balance. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 632602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sheikha, A.F. Why the importance of geo-origin tracing of edible bird nests is arising? Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, A.J.W.; Chang, L.S.; Babji, A.S.; Latip, J.; Koketsu, M.; Lim, S.J. Review of sialic acid’s biochemistry, sources, extraction and functions with special reference to edible bird’s nest. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, A.; Severi, E.; Owen, C.D.; Latousakis, D.; Juge, N. Biochemical and structural basis of sialic acid utilization by gut microbes. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 102989. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Troy, F.A., 2nd; Wang, B. Developmental changes in the level of free and conjugated sialic acids, Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc and KDN in different organs of pig: A LC-MS/MS quantitative analyses. Glycoconjugate J. 2017, 34, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, P.; Adeniji, O.S.; Abdel-Mohsen, M. Inhibitory Siglec-sialic acid interactions in balancing immunological activation and tolerance during viral infections. EBioMedicine 2022, 86, 104354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, D.; Li, C.; Tang, X.; Meng, X.; Ding, J.; Yang, Q.; Qi, Z.; Liu, X.; Deng, Y.; Song, Y. Sialic acid-mediated photochemotherapy enhances infiltration of CD8+ T cells from tumor-draining lymph nodes into tumors of immunosenescent mice. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveros, E.; Vázquez, E.; Barranco, A.; Ramírez, M.; Gruart, A.; Delgado-García, J.M.; Buck, R.; Rueda, R.; Martín, M.J. Sialic acid and sialylated oligosaccharide supplementation during lactation improves learning and memory in rats. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruszewska, E.; Cylwik, B.; Panasiuk, A.; Szmitkowski, M.; Flisiak, R.; Chrostek, L. Total and free serum sialic acid concentration in liver diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 876096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, T.T.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Fan, Y.; Huang, F.Q.; Cai, Y.Y.; Ma, G.; Liu, J.F.; Chen, Q.Q.; et al. Functional metabolomics characterizes a key role for N -acetylneuraminic acid in coronary artery diseases. Circulation 2018, 137, 1374–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.L.; Conway, L.P.; Wang, M.M.; Huang, K.; Liu, L.; Voglmeir, J. Quantification of sialic acids in red meat by UPLC-FLD using indoxylsialosides as internal standards. Glycoconjugate J. 2016, 33, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, Y.; Sakakibara, L.; Toyoda, H. Microdetermination of sialic acids in blood samples by hydrophilic interaction chromatography coupled to post-column derivatization and fluorometric detection. Anal. Sci. 2019, 35, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Mu, L.; Li, G.; Bao, Y. Assessing sialic acid content in food by hydrophilic chromatography-high performance liquid chromatography. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 87, 103393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, T.; Zhang, X.; Du, Y.; Wei, B.; Wang, J. Clinical application of liver diseases diagnosis using ultrahigh-sensitive liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for sialic acids detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1666, 462837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylie, A.D.; Zandberg, W.F. Quantitation of sialic acids in infant formulas by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry: An assessment of different protein sources and discovery of new analogues. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 8114–8123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Xie, B.; Wang, B.; Troy, F.A., 2nd. LC-MS/MS glycomic analyses of free and conjugated forms of the sialic acids, Neu5Ac, Neu5Gc and KDN in human throat cancers. Glycobiology 2015, 25, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.F.; Kong, W.R.; Wang, N.; You, Y.L.; Wang, J.F.; Wang, S.Q. A serum metabolomics study based on LC-MS: Chemosensitization effects of Rauvolfia vomitoria Afzel. combined with 5- fluorouracil on colorectal cancer mice. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 221, 115074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, D.; Xin, B.; Cechner, K.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, A. Quantification of monosialogangliosides in human plasma through chemical derivatization for signal enhancement in LC-ESI-MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 929, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.; Klaus, C.; Neumann, H. Control of innate immunity by sialic acids in the nervous tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva-Cabello, T.M.; Gutiérrez-Valenzuela, L.D.; Salinas-Marín, R.; López-Guerrero, D.V.; Martínez-Duncker, I. Polysialic acid in the immune system. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 823637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioffi, D.L.; Pandey, S.; Alvarez, D.F.; Cioffi, E.A. Terminal sialic acids are an important determinant of pulmonary endothelial barrier integrity. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2012, 302, L1067–L1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Tol, A.J.C.; Kuipers, F.; Oosterveer, M.H.; van der Beek, E.M.; van Leeuwen, S.S. Characterization of milk oligosaccharide and sialic acid content and their influence on brain sialic acid in a lean mouse model for gestational diabetes. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).