Abstract
PFAS, or per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances, are a broad group of man-made organic compounds that are very persistent, mobile, and tend to bioaccumulate. Their removal from different environmental media is becoming increasingly important because they are associated with a multitude of (eco)toxicological effects on both humans and the environment. PFAS are detected in wastewater, groundwater, drinking water, and surface water, with the subcategories of PFOS and PFOA being the most detected. These organic compounds are divided into polymeric and non-polymeric groups. Non-polymeric PFAS are of great research interest due to their frequent detection in the environment. Numerous methods have been applied for the removal of PFAS and are divided into destructive and non-destructive (separation) techniques. Given the strength of the C–F bond, the destruction of PFAS is challenging, while for most of the separation techniques, the management of isolated PFAS requires further consideration. Most of the techniques have been applied to small-scale applications and show some limitations for larger applications, even though they are promising. Adsorption is an environmentally sustainable, economical, and high-performance technique that is applied to remove several classes of emerging pollutants from water. In this review, the use of various types of adsorbents for PFAS removal from water is reported, as well as the expected adsorption mechanisms. There are several technologies being considered and developed to manage PFAS; however, they are still in the experimental stage, with each showing its appeal for potential larger applications.
1. Introduction
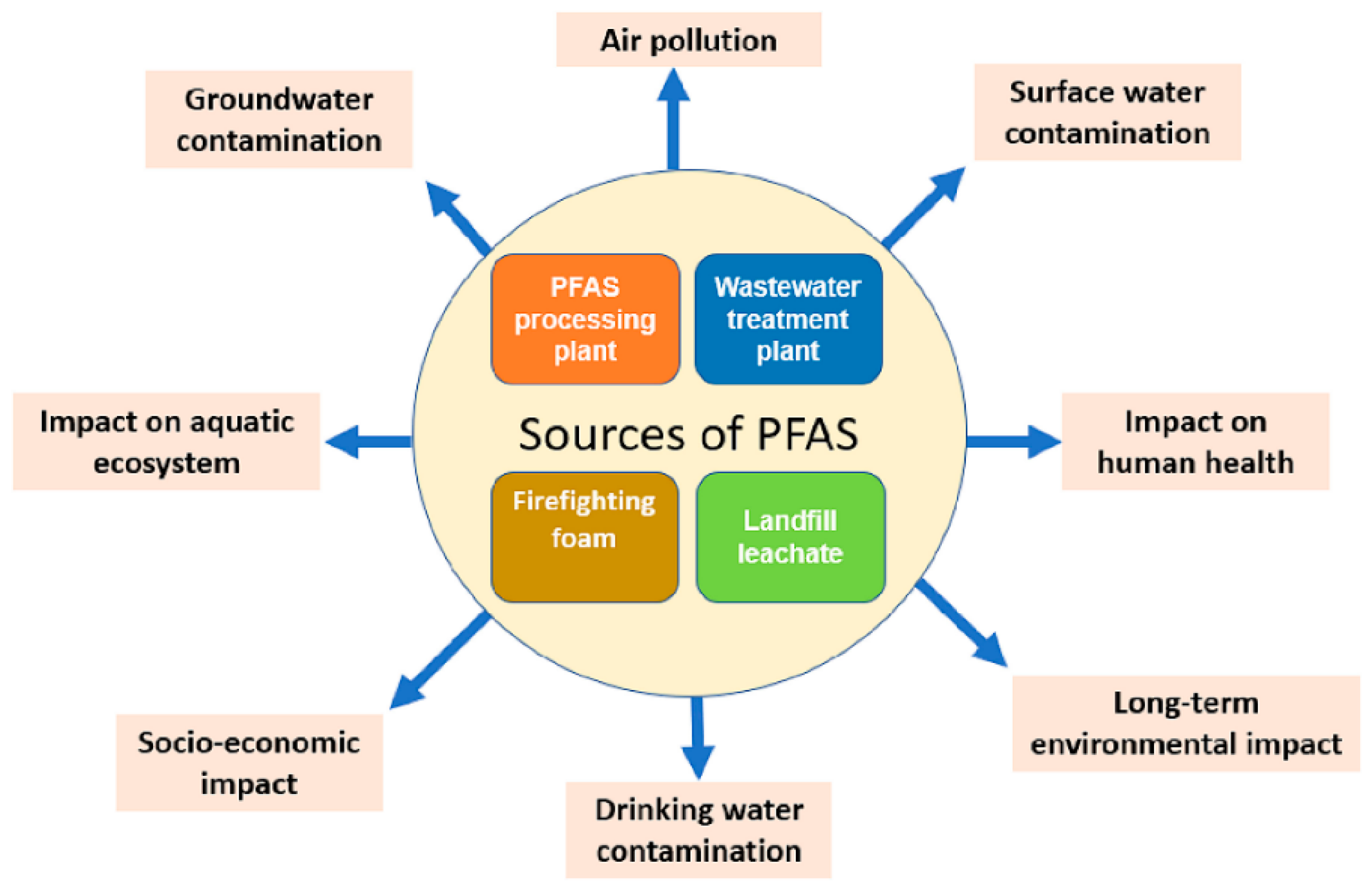
Per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are man-made compounds that constitute a vast family of fluorinated substances. These substances started to gain attention in the early 2000s, when the presence and hazardous properties of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) were reported [1]. The use of these substances dates back to the 1930s–1940s, with a typical example being Teflon, or polytetrafluoroethylene-PTFE, an organic polymer used as a coating for multiple applications, such as cooking utensils or fabrics to make them waterproof [2,3]. As shown in Figure 1, the main sources of PFAS emissions into the environment are processing plants, fire-fighting foam, landfills, and wastewater treatment facilities, and their effects extend to many environmental compartments.
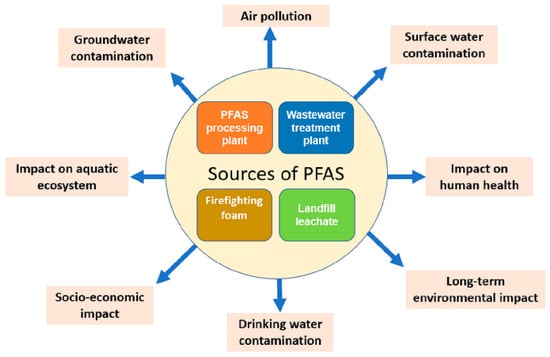
Figure 1.
Sources of PFAS and their impact [4] (reprinted with permission).
In detail, the presence of the carbon–fluorine bond(s) gives these chemicals several characteristics, such as high thermal, chemical, and biological stability and the ability to act as surfactants and waterproofing coatings. In fact, the great persistence and mobility of these substances, alalonga, with their continuous use in industrial and consumer products, lead to their presence and detection worldwide.
Furthermore, these chemicals have also shown the tendency to bioaccumulate, leading to great concern about their possible connection with (eco)toxicological phenomena and, by extension, health effects [5].
2. Classification of PFAS
The first definition of PFAS was introduced by Buck et al. in 2011 as “aliphatic substances containing one or more C atoms on which all the H substituents present in the nonfluorinated analogues from which they are notionally derived have been replaced by F atoms” [6]. However, this definition led to several inconsistences, such as the classification of fully fluorinated aliphatic and aromatic cyclic compounds and of chemicals that have functional groups on both ends of the fully fluorinated carbon moiety [7].
To address these issues, a new definition has been recently suggested by the OECD [1], considering PFAS as “fluorinated substances that contain at least one fully fluorinated methyl or methylene carbon atom (without any H/Cl/Br/I atom attached to it)”.
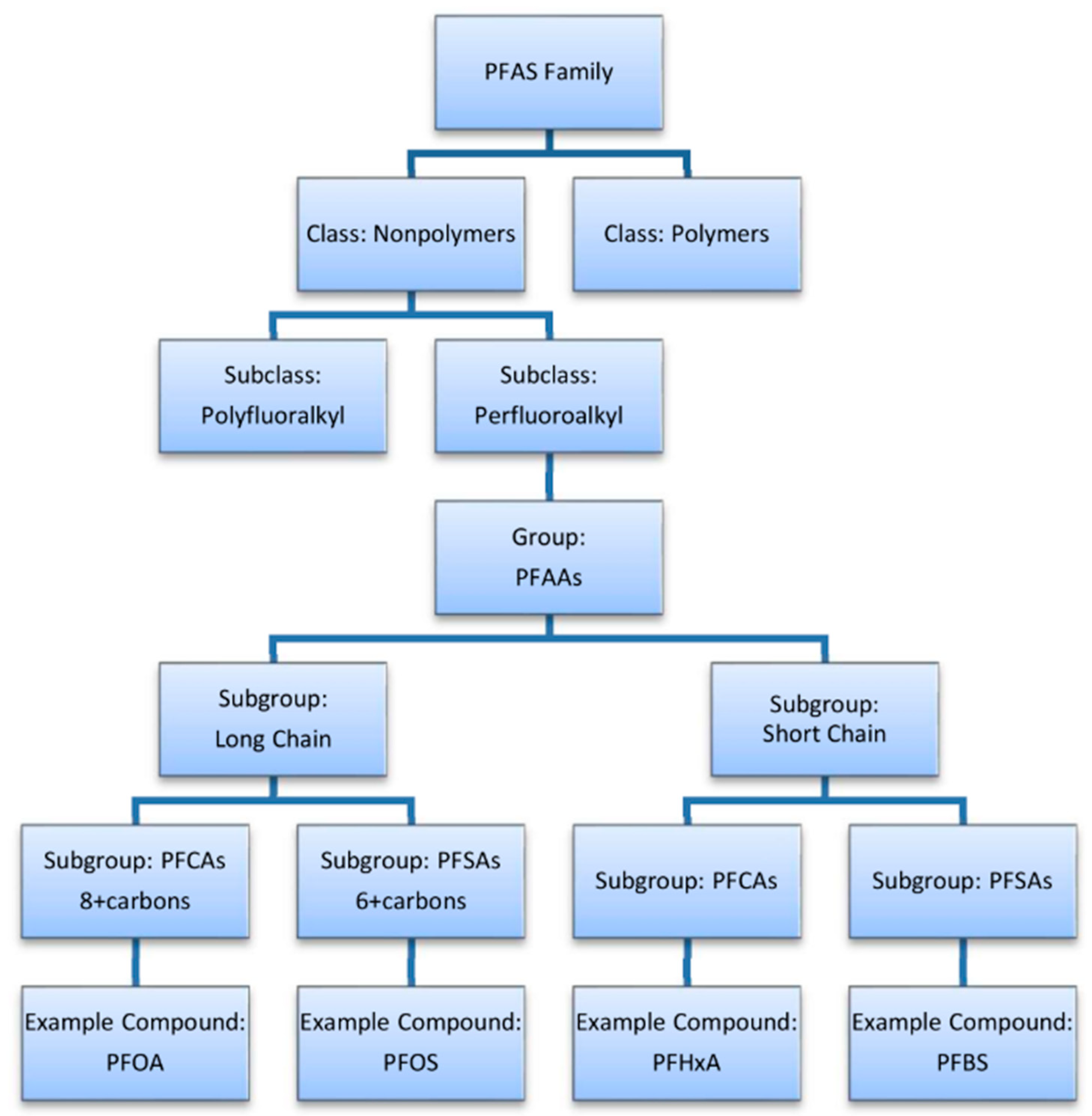
The new definition gives an easily implementable approach that takes into account the broadness of the PFAS universe, starting from small molecules to complex aromatics and polymers. Furthermore, the work from the OECD also highlights the need to also consider user-specific working scopes in the definition of chemicals as PFAS, thus combining the general definition with additional considerations [7]. According to this approach, PFAS can also be further categorized into different classes, as shown in Figure 2 and described in the following paragraphs.
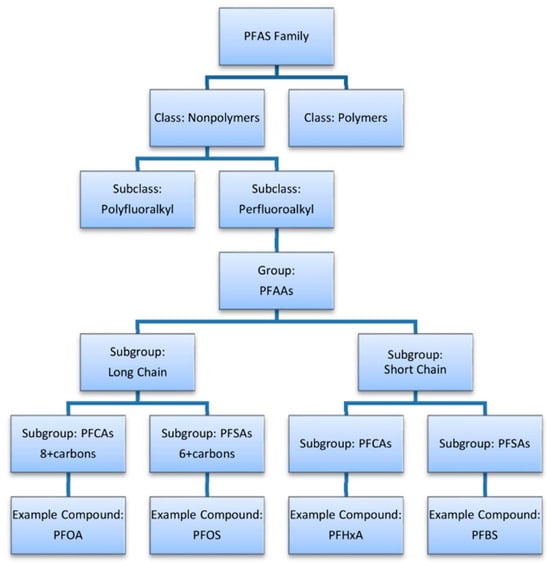
Figure 2.
Classification of PFAS compounds [6].
2.1. Polymeric and Non-Polymeric PFAS
PFAS polymers are divided into three subgroups: (1) fluoropolymers; (2) perfluoropolyether polymers; and (3) side-chain fluorinated polymers. Fluoropolymers comprise a carbon-only polymer chain consisting exclusively of carbon, with fluorine directly bonded to the chain. They include polymers made from perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and salts such as ammonium perfluorooctanoate (APFO), etc. Polymeric perfluoropolyethers (PFPE) are composed of a polymer chain of carbon and oxygen, with the fluorine being directly bonded to carbon. The environmental effects of these chemicals are largely unknown. Fluorinated side-chain polymers have a non-fluorinated polymer chain with fluorinated side chains as branches. Fluorinated urethane polymers, fluorinated acrylic/methacrylate polymers, and fluorinated oxetane polymers fall into this category, whose compounds can be precursors for perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) [3,5].
Non-polymeric PFAS are divided into polyfluoroalkyl and perfluoroalkyl compounds, depending on the degree of the carbon chain’s fluorination. In detail, perfluoroalkyl substances have a fully fluorinated chain (i.e., all H atoms attached to C have been replaced by F atoms), while polyfluoroalkyl substances are only partially fluorinated, (i.e., at least one C atom of the chain is connected to 1 H or O atom and not to F). In general, polyfluoroalkyl substances break down more easily than perfluoroalkyls but are still quite persistent in the environment. Two major subgroups of PFAA within the perfluoroalkyls are PFCA and PFSA, which are perfluorocarboxylic acids and perfluoroalkanesulfonic acids, respectively. They include some of the most commonly found PFAS, such as PFOA and PFOS [2,3].
2.2. PFAS Chain Length
There have been several studies highlighting significant differences in the environmental behavior, toxicity, and bioaccumulation potential of PFAS depending on their chain length, and Table 1 shows the criteria for classification of the PFCA and PFSA compounds suggested. In detail, a long chain is defined as a series of more than seven (for PFCA) or five (for PFSA) fluorinated C atoms. The different number of fluorinated C atoms considered for the two classes of PFAS is due to the fact that PFAS usually has a higher potential to accumulate in biological systems than a PFCA with the same number of C atoms [8].

Table 1.
Long-chain and short-chain PFCAs and PFSAs [5].
Long-chain and short-chain PFAS have been shown to behave quite differently in the environment due to differences in (i) electrostatic interactions, (ii) hydrophobic interactions, (iii) hydrogen bond and ion exchange, (iv) ligand exchange and surface complexation, and (v) adsorption at the air/soil/water interfaces. In particular, the transport of long-chain PFAS is more influenced by hydrophobic interactions due to the presence of longer fluorinated carbon chains, while short-chain PFAS are more influenced by electrostatic interactions [9]. Furthermore, long-chain PFAS usually form bilayer structures and aggregate more easily in environmental media than short-chain compounds due to a lower critical micelle concentration (CMC) [10].
PFAS have also shown different (eco)toxicological characteristics depending on chain length, starting with a higher tendency to bioaccumulate in adipose tissue and bind to proteins of long-chain compounds, thus leading to higher biomagnification along the food web [11]. Furthermore, chain length has been found to be related to specific modes of action, causing effects on both humans and animals [12].
Regarding biodegradation and metabolization, both long- and short-chain PFAS are considered metabolically inert since any functional derivative (i.e., precursor) will be transformed into the respective acid [11,13].
2.3. Legacy and Emerging PFAS
Another distinction that has been made in the classification of PFAS also considers the start of their use, where the chemicals developed to substitute conventional substances (e.g., PFOA and PFOS) are classified as “emerging PFAS”. In particular, GenX (i.e., hexafluoropropylene oxide dimer acid (HFPO-DA)) has attracted particular interest since 2009, when it was introduced by DuPont to replace PFOA. Table 2 includes some of these emerging PFAS [14]. The physicochemical properties of these newly discovered PFAS have not been fully determined [15].

Table 2.
Examples of legacy and emerging PFAS [14].
3. Effects on Human Health
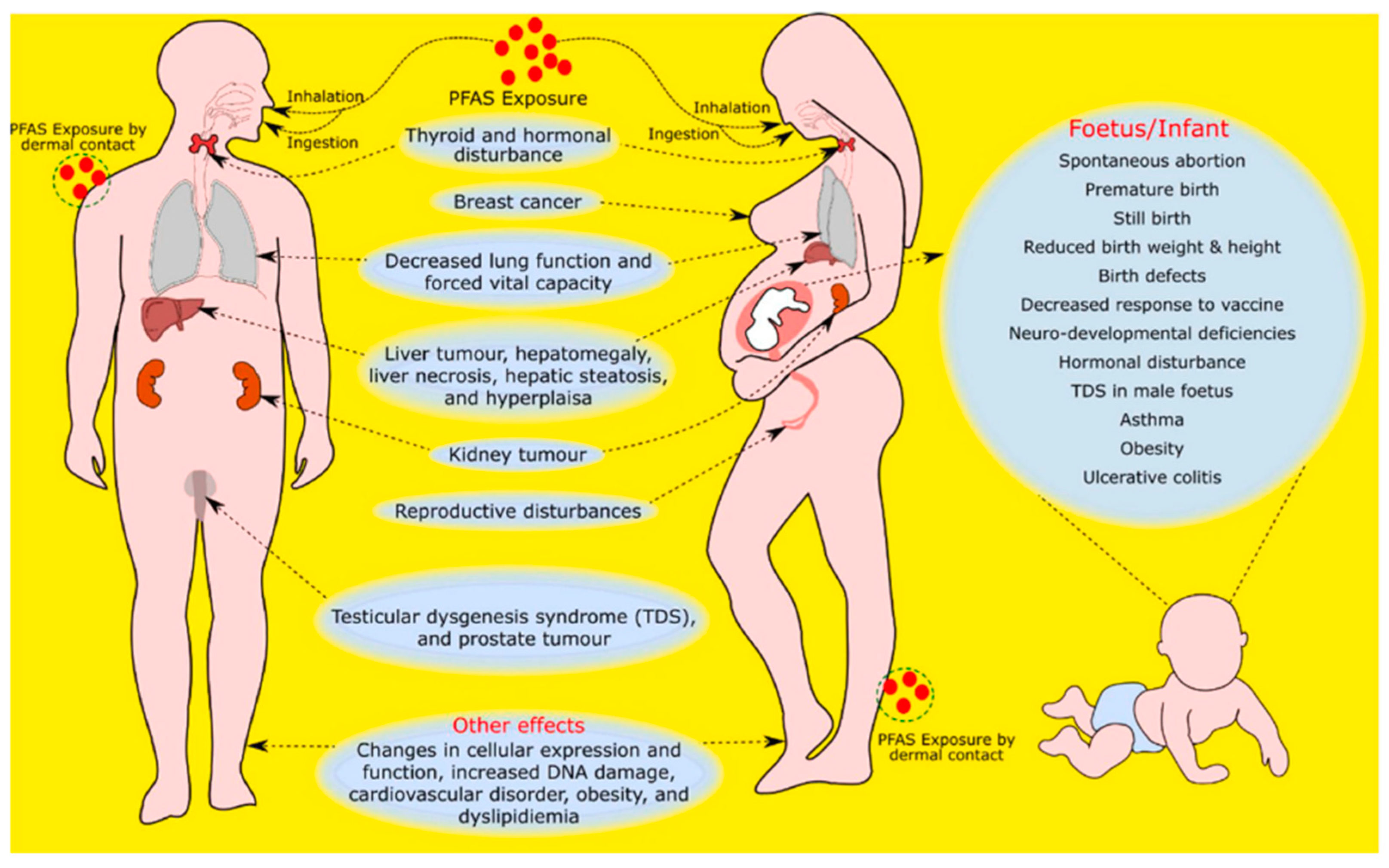
The global utilization of PFAS since the 1950s has caused their extensive dispersion, leading to their detection in water bodies, food webs, animals, and humans [16]. PFAS can make its way into the human body through the consumption of contaminated food, breathing in dust, or skin contact with PFAS-containing items, potentially impacting different bodily organs and systems [17]. However, the main means of human exposure is considered to be drinking water. PFAS is linked to numerous effects on the immune and reproductive systems, hormonal disturbances (for example, thyroid hormone imbalances), kidney and liver cancer, and increased cholesterol levels (dyslipidaemia), both in men and women. These main effects and exposure pathways of humans to PFAS are shown in Figure 3.
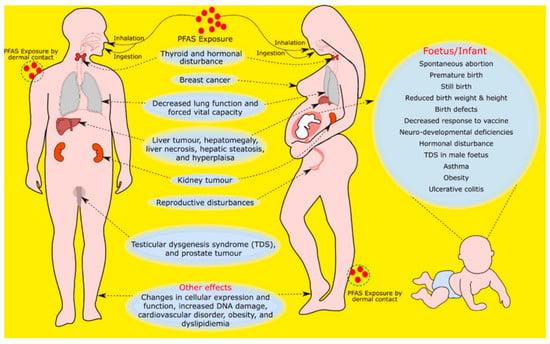
Figure 3.
Impact of PFAS on human health [18] (reprinted with permission).
Due to their widespread use and unique characteristics, PFAS have, through ongoing research, been linked to a variety of effects on the human body. Their mobility allows them to be transported to the ground, water, and atmosphere; however, the main means of human exposure is considered to be drinking water. PFAS is linked to numerous effects on the immune and reproductive systems, hormonal disturbances (for example, thyroid hormone imbalances), kidney and liver cancer, and increased cholesterol levels (dyslipidaemia), both in men and women. These main effects and exposure pathways of humans to PFAS are shown in Figure 3.
In the case of fetuses and later infants, there is particular concern as prenatal exposure to PFAS appears to affect their development, which can cause further problems. According to Post et al., 2017 [19], breastfed infants are more at risk than the elderly (considered a vulnerable group in general), even when their mothers are exposed to low levels. Grandjean et al., 2012 [20], through a survey and biomonitoring campaign conducted on 5- and 7-year-old children in the Faroe Islands, found that high concentrations of PFOS, PFOA, PFHxS, PFNA, and PFDA detected in their blood serum resulted in lower responses to childhood vaccinations. Gallo et al., 2012 [21], demonstrated the indisputable influence of PFOA and PFOS on the levels of ALT (Alanine Transaminase), i.e., an indicator of hepatocellular damage, as well as the increase in total cholesterol, low-density lipoproteins (LDL), and high-density lipoproteins (HDL). Additionally, Zeeshan et al., 2020 [22], highlighted the enhanced risk of vitreous disruption due to exposure to long-chain PFAS.
4. Legislation
Given the concerns and designation of PFAS as emerging pollutants, federal, state, and international authorities are in the process of establishing regulatory values and assessment limits based on health protection.
In the United States, regulations vary at the state and federal levels. In 2016, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) published a healthcare advisory (HA) for drinking water with a limit of 70 ng/L for perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). Seven US states have approved or proposed their own PFOA and PFOS levels for drinking water ranging from 13 to 1000 ng/L, which are derived through research on their effects on the human body. In the Fifth Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule (UCMR 5), published in December 2021, among the 30 chemical pollutants are 29 PFAS, with the lowest reporting restrictions ranging from 2 to 20 ppt [23].
In Europe, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) recommends their universal exclusion. The phasing out of all PFAS is in the European Commission goals, excepting only the uses that their complete reversal is not feasible. The recasting of the Drinking Water Directive, which is valid from 12 January 2021, sets a limit of 0.5 µg/L for all PFAS. Also, Directive (EU) 2020/2184 of the European Parliament and of the Council, of 16 December 2020, on the quality of water for human consumption, determined the limits of PFAS in drinking water. Article 13 (7) sets the technical guidelines for analytical methods for checking per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances under the parameters “Total PFAS” and “Sum of PFAS”. The guidelines (Table 3) include detection limits, parametric values, and sampling frequency.

Table 3.
Guidelines for PFAS limits in drinking water [24].
The research focus is on the presence of PFAS in water matrices, in contrast to their occurrence in both urban and industrial wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), which are important point sources that receive wastewater either through direct discharge from surface and coastal waters or through the application of recycled wastewater, as in the case of groundwater. PFAS emissions and occurrences are expected to be higher in more urbanized and industrialized areas. In terms of regulations, they have mainly focused on soil due to the reuse of biosolids, and only two countries have established limits for PFAS in sludge or biosolids with a maximum of 100 ng/g dw for the main PFAS [25,26,27].
Kunacheva et al., 2011 [28], studied two industrial zones in Central and Eastern Thailand that have biological treatment processes. Ten different PFAS were identified (specifically PFOA, PFOS, PFPA, PFHxA, PFHpA, PFHxS, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnDA, and PFDoA). The concentrations of most PFAS were higher in the effluent samples than in the influent samples, so they were not effectively removed or converted from precursor materials to PFAS. Bossi et al., 2008 [29], in a control survey of six municipal and four industrial WWTPs and landfills in Denmark, found that levels of PFOA and PFOS, which were the main species detected, were higher in effluent samples, except for one municipal WWTP, which yielded complete removal. In respective investigations, Shigei et al., 2020 [30], and Chen et al., 2017b [31], found that the concentrations of short-chain PFAS, such as PFBA, PFPeA, and PFHxA, were higher in the effluent than in the influent, which is most likely due to the degradation of the precursors in shorter-chain PFAS, which are more persistent. However, Zhou et al., 2019 [32], and Sun et al., 2012 [33], reported that longer-chain PFAS (C > 9) as well as precursors in the wastewater were reduced or due to possible sorption into the activated sludge. In conclusion, conventional wastewater treatment processes do not effectively remove PFAS. Also, during the biological treatment of longer-chain PFAS, they create shorter-chain precursors, thus affecting PFAS concentrations in sludge and waste.
5. Manufacturing Processes
5.1. Electrochemical Fluorination (EFC)
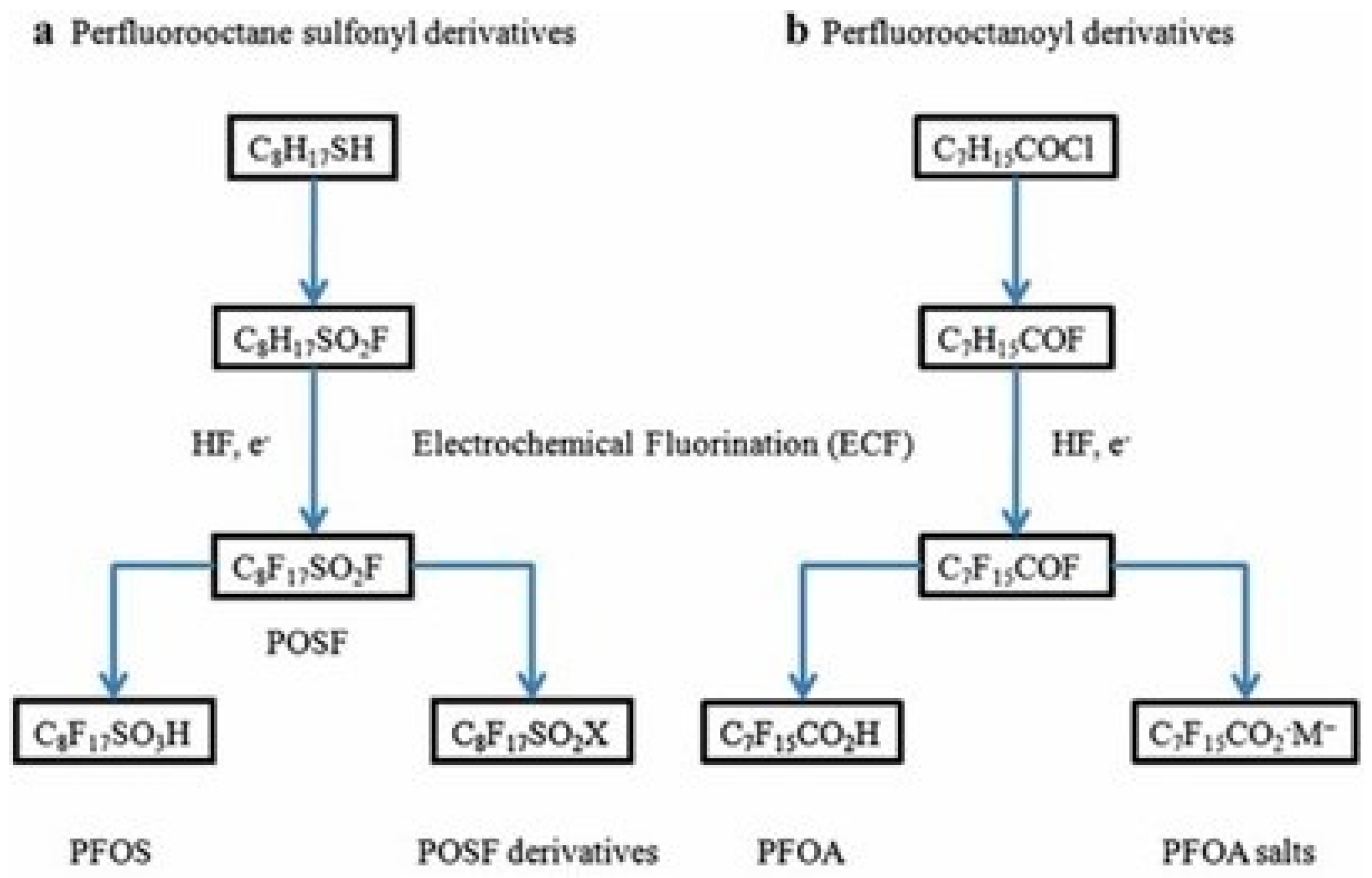
Electrochemical fluorination is a process in which an organic raw material is dissolved in hydrogen fluoride (HF), seeking to counteract the hydrogen atoms with fluorine. Linear and branched chains are produced, the proportion of which depends on the process control, but it usually ranges from 70 to 80% for linear and 20 to 30% for branched, respectively. For example, the electrochemical fluorination of C8H17SO2F that is shown in Figure 4 yields (1) perfluorooctane sulfonyl fluoride (POSF, C8F17SO2F), a primary feedstock used to make PFOS; (2) a range of functional feedstocks such as sulfonamides, sulfonamide monomeric alcohols, and sulfonamidomeric alcohols; and (3) a family of surfactants and polymers derived from them [8].
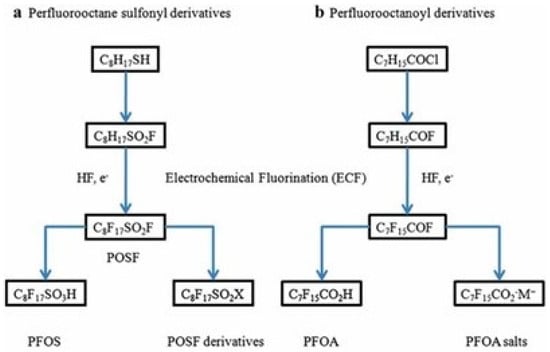
Figure 4.
Synthesis by electrochemical fluorination [8].
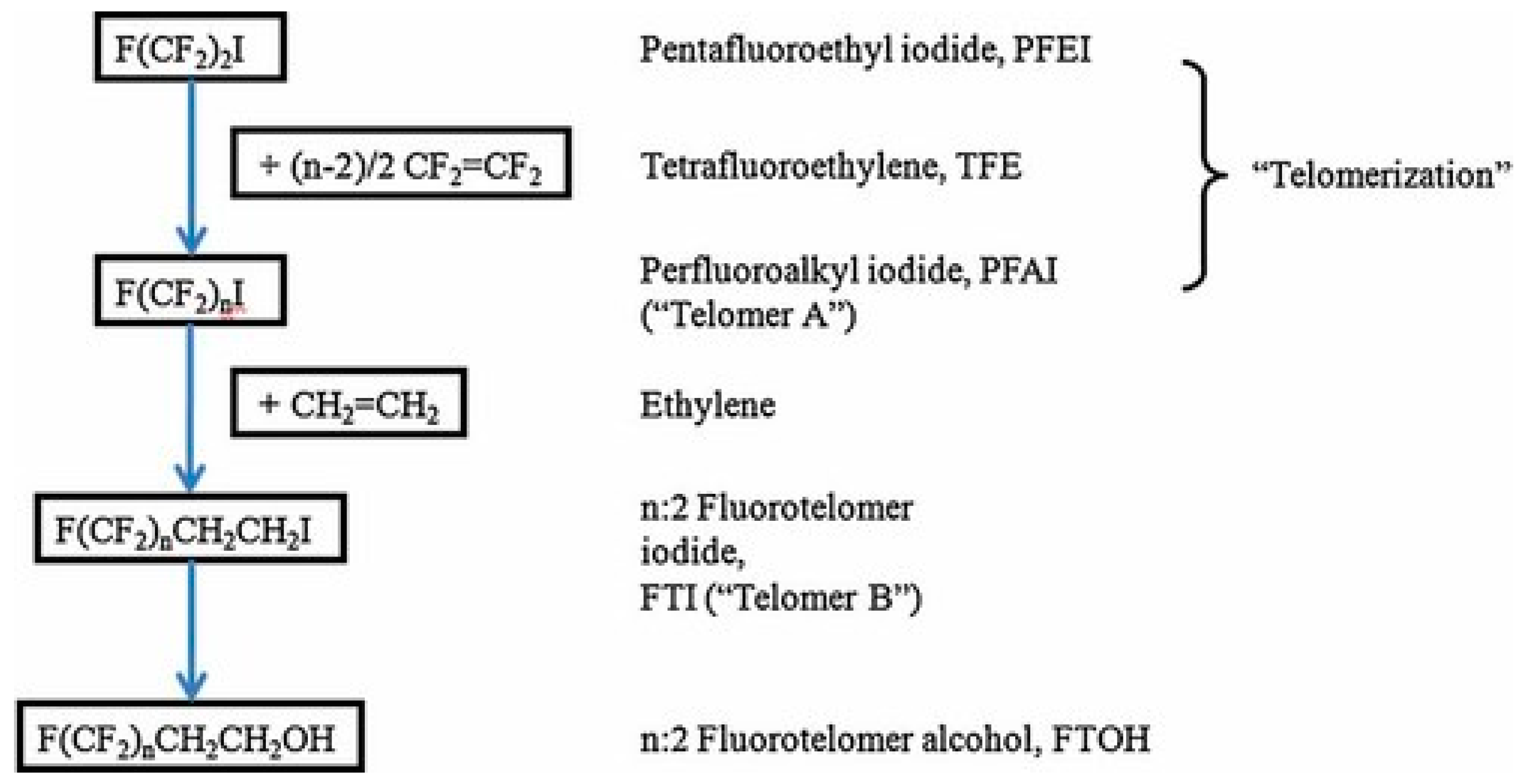
5.2. Telomerization
Telomerization was developed in the 1970s and is the most used procedure nowadays. It involves a two-step method. In the first step, a perfluoroalkyl iodide (CmF2m+1I, PFAI) reacts with tetrafluoroethylene (CF2=CF2, TFE), yielding a longer-chain perfluoroalkyl mixture, CmF2m+1(CF2CF2)nI, which constitutes Telomere A. In the second step, ethylene is added to this mixture to form CmF2m+1(CF2CF2)nCH2CH2I, Telomere B. The two telomeres A and B are intermediate raw materials and are used for the construction of more building blocks, which then react further, producing a variety of surfactants and polymers, based on fluorotelomers [9]. The process is shown in Figure 5.
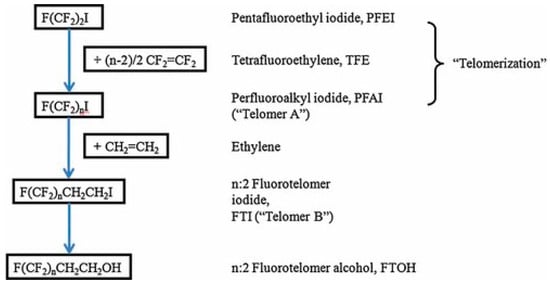
Figure 5.
Synthesis by Telomerization [8].
6. Treatment Technologies
Numerous methods are available for eliminating per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), such as adsorption, ion exchange resin adsorption, photocatalytic processes, and electrochemical oxidation. Innovative approaches like ultrasound and plasma technology are currently under investigation for their potential to extract PFAS. The domain of PFAS removal is evolving, necessitating further study and real-world application to improve its effectiveness and long-term viability [34].
Non-destructive technologies
6.1. Adsorption
Adsorption is a widely applied and highly effective separation process for the elimination of environmental pollutants from water and wastewater. It is environmentally friendly, economically efficient, with high efficiency, simple in design and operation, and less influenced by the presence of toxic substances than biological-based technologies. One of the most important factors in such processes is the choice of a suitable adsorbent, which is determined by its capacity and efficiency. The properties of the sorbent, such as surface functional groups, partial size reduction, or pore structure, are fundamental to determining its adsorption capacity. But the bulk solution chemistry also influences it, which includes the initial contaminant level, pH, temperature, dosage, and mixing rate. Adsorption technology is an established, ex situ technique for removing pollutants from water using various adsorbent materials such as activated carbon, ion exchange resins, polymers, and even natural adsorbents. Essentially, during adsorption, the contaminant is concentrated from the liquid to the solid phase. The used adsorbent needs to be regenerated or disposed of, which is a big disadvantage in adsorption technology because of high operating and maintenance costs, especially high energy consumption for regeneration or replacement and then waste management and off-site waste treatment [35].
Long-chain PFAS have higher hydrophobicity and lower water solubility. They attach to particles in the solution, while short-chain PFAS are mostly in the dissolved phase and have higher mobility. Short-chain compounds can significantly impact the drinking water supply, increasing human exposure to PFAS compounds [36].
6.1.1. Carbonaceous Adsorbents
The most known and used carbonaceous substances for pollutant adsorption are activated carbons (ACs), granular (GAC), and powder form (PAC). The structure of AC consists of carbon atoms in parallel layers of hexagonal shapes. The AC structure has many reactive sites at the dislocations, edges, and discontinuities, which have unpaired carbon atoms and unsaturated valence electrons that can react with different heteroatoms such as oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, and sulfur as surface functional groups. In addition, activated carbon surfaces can include metals like sulfate, calcium, and phosphate ions, which influence adsorption capacities and other surface properties, such as specific surface area and zeta potential. They can be produced from various carbonaceous raw materials, such as wood, coal, walnuts, peat, lignite, and coconut shells [3].
Activated carbons (ACs), such as granular activated carbon (GAC) and powdered activated carbon (PAC), are porous carbonaceous materials with a high specific surface area (SSA). As many studies have shown, ACs can adsorb PFAS. The results show that adding AC to wastewater and drinking water treatment processes is a viable option for PFAS removal. Ross et al., 2018 [37], have shown that GAC can remove long-chain PFAAs well, but not short-chain precursors. Belkouteb et al., 2017 [38], tested a high dose of GAC for the removal of long-chain PFCA (PFOA, PFNA, PFDA, PFUnA, PFDoDA, and PFTeDA) and PFSAs (PFHxS and PFOS). The results ranged from 65–80% [37]. Many studies have concentrated on ex situ treatment methods like ‘Pump and Treat’ for long-chain PFAS; these methods typically involve removing large amounts of polluted water from an affected zone and filtering it through treatment tanks filled with reactive substances or adsorbents. Despite their effectiveness, ‘Pump and Treat’ systems are often costly to set up, operate, and maintain, necessitating ongoing supervision, which raises questions about their long-term viability. On the other hand, in situ sequestration is gaining interest as a potentially more affordable alternative. This method entails stabilizing PFAS directly within the contaminated site, using approaches like permeable reactive barriers or adsorption areas, thereby avoiding the need to extract and treat water off-site [39].
Biochar is a fine-grained, carbon-rich material created by burning biological residues, such as wood, under low oxygen in a controlled environment. Unlike ACs, they are partially carbonized as they may include other amorphous organic matter. They are low-cost materials, with smaller surfaces and pore volumes than conventional AC. They are suitable for adsorption processes to remove both organic and inorganic pollutants from aqueous solutions as they have a high cation exchange capacity. The biochar’s surface area and microporosity, ion exchange capacity, organic matter, and functional groups greatly affect its effectiveness on pollutant removal. Xiao et al., 2017 [40], studied the uptake of PFOA and PFOS in two types of biochar, one derived from pine needle (PN) and the other collected from a garden (MCG), compared to GAC. GAC and MCG biochar had a greater removal efficiency from PN biochar. It was found that biochar with a high surface area could be a possible substitute for GAC. The presence of high organic matter in biochars is an important issue in these materials as it decreases the adsorption capacity of PFAS. Also, Beesley et al., 2011 [41], reported that the organic matter in adsorbents could react with other pollutants in the media and produce toxic pollutants.
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are an exciting nanomaterial that has received a lot of research interest because of their unique electrical, structural, optical, and mechanical properties and thermal stability, characteristics that make them useful for many applications. Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) receive considerable attention as they present a unique one-dimensional hollow tubular structure and strong hydrophobicity; thus, they are studied as suitable adsorbents for many pollutants in the water phase. Multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) have a lower PFAS adsorption capacity due to their smaller SSA. The adsorption capacity of CNT can be improved through functionalization with various covalent and non-covalent methods to modify and attach functional groups to the walls of CNT. In the research of Bei et al., 2014 [42], on the removal of PFOS from aqueous solutions by pristine MWCNTs, MWCNT-COOH, and MWCNT-OH, functionalized MWCNT had better adsorption capacity, with MWCNT-OH exhibiting the highest performance. Regarding non-covalent functionalization, Liu et al., 2018 [43], reinforced MWCNTs with three different nanometals (nano-crystalline iron, copper, and zinc) and compared them for their ability to remove PFOA from aqueous solutions. Modified MWCNTs yielded a higher PFOA uptake. In comparison, Cu/CuO-CNT was the most effective, while pristine-MWCNT had the lowest performance [44].
6.1.2. Polysaccharide-Based Adsorbents
Natural polymers such as cellulose, chitin, starch, chitosan, and cyclodextrins are often applied in wastewater treatment. Ateia et al., 2018 [45], investigated cellulose PEI microcrystals for the removal of 22 different PFAS from water at ambient concentrations. It was observed that they were not effective for short-chain PFAS.
β-Cyclodextrin is a cyclic sugar composed of seven glucose monomers with a truncated cone-like shape. The smallest hole is covered by seven hydroxyl functional groups, and the largest hole is covered by fourteen secondary hydroxyl functional groups, with many C–H bonds inside the cavity. As a result, the interior of the cavity is hydrophobic, while the exterior of β-CD is hydrophilic and thus appropriate for participating in interactions of hydrophobic materials in hydrophilic solutions or water. Yang et al., 2020 [46], studied the role of crosslinking tripods with three amido or amino functional groups and β -CD in the binding capacity and affinity for anionic PFAS components. Amine-containing β -CD polymers yielded more efficient removal for approximately 10 anionic PFAS. Compared to activated carbons, both polymers had higher performance. Cyclodextrin is an economical material; however, the use of a crosslinking agent can increase costs [3].
6.1.3. Mineral Adsorbents
Clays and minerals are small particles that are often found in nature. They include features such as high SSA, positive charge at low pH, suitable pore size, and easy modification that make them appropriate for use in pollutant adsorption from water. Even though their PFAS adsorption affinity is low compared to carbon adsorbents, most clays and minerals are commercially available and non-toxic. Minerals such as silica, kaolinite, alumina, zeolite, montmorillonite, and boehmite are composed of tunable layered structures or tunable mesopores. Modifications are often made with cationic surfactants for more efficient uptake of organic pollutants. Hellsing et al., 2016 [47], studied the adsorption of four PFAS species by silica (SiO2) and alumina (Al2O3). On the positively charged alumina surface, all tested PFAS were adsorbed and formed a hydrated layer, comprising 50% PFAS. The solubility limitation of PFAS decreases with chain length. On the surface of negatively charged silica, no PFOA or PFOS were found. Electrostatic interaction was the dominant mechanism.
Hydrotalcite (HD) is also a positively charged mixed metal oxide adsorbent that can remove anions. It consists of transferrable anions between interlayers that can be swapped by contaminants via anion exchange. Chang et al.’s, 2019 [48], results indicate that the adsorption capacity for PFOA is greater with anionic surfactants compared to GAC, PAC, and resins. Chang et al., 2020 [49], and Yang et al., 2020 [46], tested modified HD, through calcination and decomposition, resulting in improved PFOA and PFOS adsorption capacities from the original HD, demonstrating their potential as adsorbents for the removal of PFAS from wastewater and drinking water.
6.1.4. Regeneration of Adsorbents
Adsorbent regeneration is a key point for adsorption processes for economic and environmental reasons, as it eliminates the need for adsorbent replacement and disposal. Regeneration is a process in which the adsorbed substance, e.g., PFAS, is removed to recover the adsorption capacity. However, this must happen through technologies that are economically viable and environmentally safe. Usually, the regeneration is either chemical or thermal. The chemical regeneration of PFAS saturated adsorbents requires the use of organic solvents, which are harmful. Moreover, thermal reclamation at a high temperature can produce perilous fluorine gases. Therefore, on-site application of either chemical or thermal regeneration is not viable [36,50].
Microwave irradiation is a possible alternative technique to conventional thermal regeneration due to its rapid heating and selectivity. This method converts the energy of the microwave electric field that is adsorbed by a solid adsorbent such as activated carbon into heat at the molecular level. The dielectric properties of the adsorbent, combined with the properties of PFAS, such as their volatility, could make regeneration possible through the interactions between the delocalized π-electrons. However, microwave regeneration is still at a research level [51,52].
The hydrothermal treatment’s high-pressure setting may enhance the defluorination of PFAS. Sühnholz’s research on the hydrothermal method, conducted at moderate temperatures between 200 and 260 °C under high pressure, focused on renewing activated carbon containing organic micropollutants like PFOA and PFOS. The process at 200 °C for 4 h successfully broke down over 99% of PFOAs without generating any shorter-chain by-products. In contrast, more extreme conditions of 260 °C for 16 h were required to partially break down PFOS. The removal efficiency of PFOS during hydrothermal treatment is highly pH-dependent; roughly half of PFOS was removed in acidic conditions (pH = 1), but no degradation occurred in alkaline conditions (pH = 12). Post-treatment analysis showed that the carbon’s properties and mass remained largely unchanged [53].
6.1.5. Adsorption Mechanism
Adsorption of PFAS occurs through electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions. Electrostatic interactions are leading to short-chain PFAS, while longer PFAS are adsorbed through hydrophobic interactions. Electrostatic interactions involve the attraction of oppositely charged ions or molecules. PFAS can interact with charged sites on the surface of the adsorbent as a result of its composition, which includes charged functional groups such as carboxylic acid and sulfonic acid. Alterations in ionic strength can influence the efficiency of the adsorption by introducing electrostatic repulsions; for example, increasing the pH of the solution can reduce the adsorption capacity [3,50].
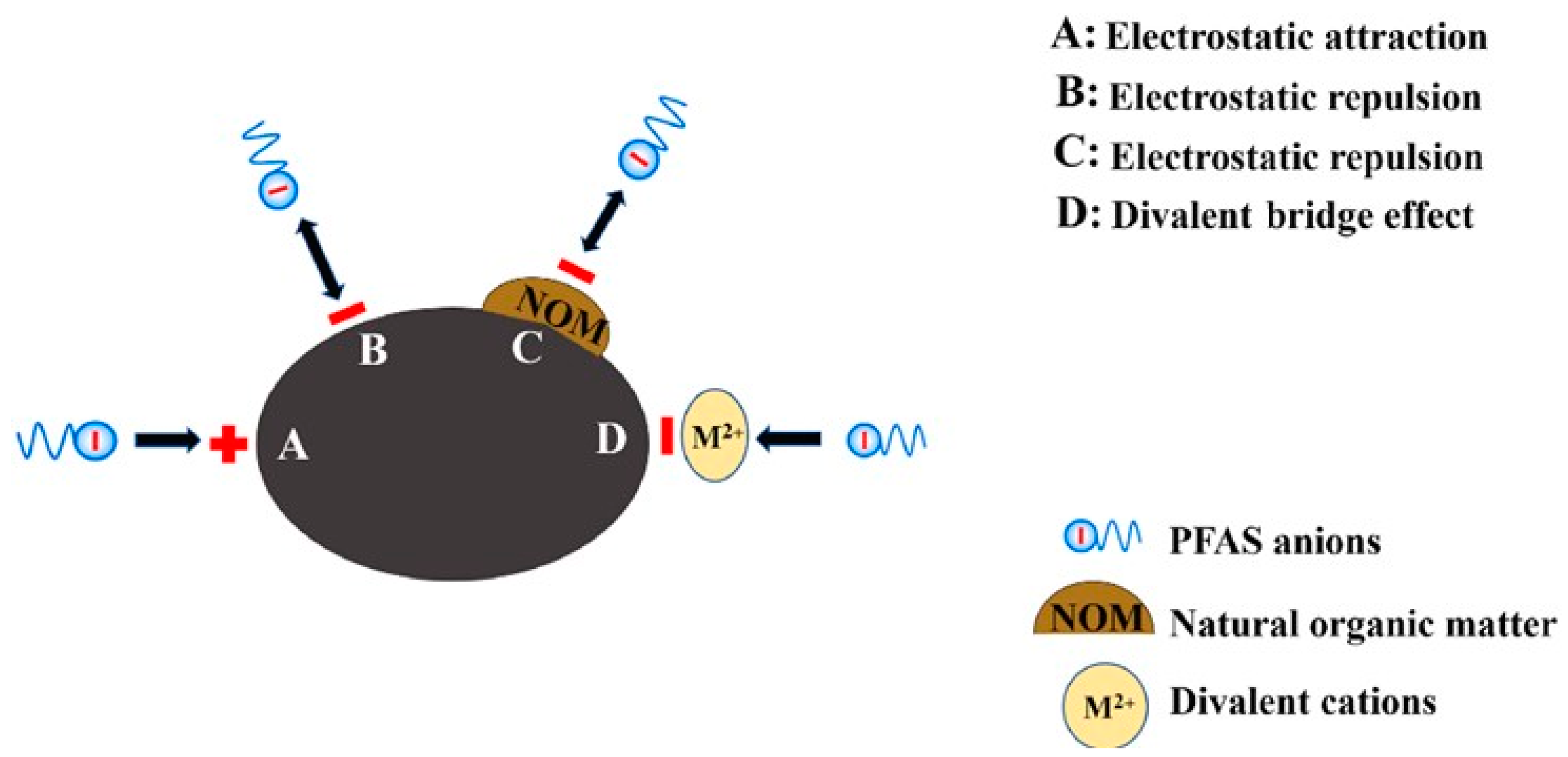
The adsorbed PFAS molecules on the surface of the adsorbents can act repulsively towards the PFAS anions in the bulk solution, reducing the adsorption capacity. Negatively charged NOM molecules are readily adsorbed on positively charged adsorbents, lowering the pHpzc of the adsorbents, which leads to a lower adsorption capacity for PFAS. Increasing the ionic strength of the solution can compress the electrical double layers of the adsorbents, leading to a reduced electrostatic attraction and adsorption capacity. Moreover, monovalent and divalent cations (K+, Na+, Ca2+, and Mg2+) can alternate the charge of the adsorption sites from negative to positive with a cation bridging effect (Figure 6), resulting in the conversion of a negatively to positively charged adsorbent, increasing PFAS adsorption [36,50].
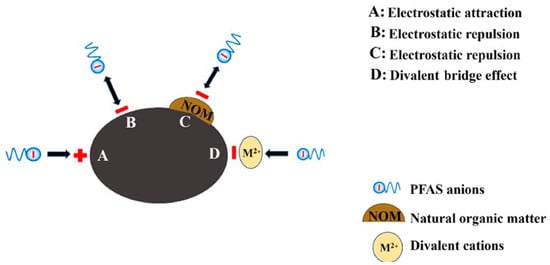
Figure 6.
Electrostatic attraction, repulsion, and divalent bridge effect in PFAS adsorption [50] (reprinted with permission).
The adsorbed PFAS molecules on the surface of the adsorbents can act repulsively towards the PFAS anions in the bulk solution, reducing the adsorption capacity. Negatively charged NOM molecules are readily adsorbed on positively charged adsorbents, lowering the pHpzc of the adsorbents, which leads to a lower adsorption capacity for PFAS (Figure 6). Increasing the ionic strength of the solution can compress the electrical double layers of the adsorbents, leading to a reduced electrostatic attraction and adsorption capacity. Moreover, monovalent and divalent cations (K+, Na+, Ca2+, and Mg2+) can alternate the charge of the adsorption sites from negative to positive with a cation bridging effect (Figure 6), resulting in the conversion of a negatively to positively charged adsorbent, increasing PFAS adsorption [36,50].
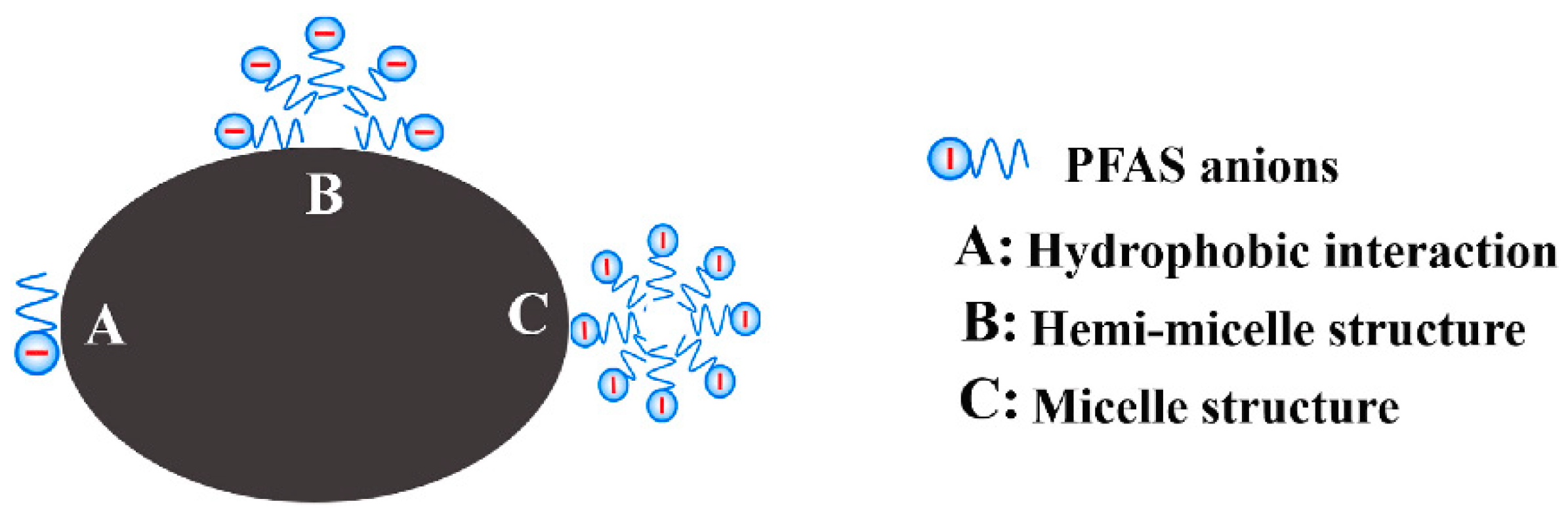
The hydrophobic interactions (Figure 7) are due to the interaction of the hydrophobic fluoroalkyl chains with hydrophobic sites on the surface of the adsorbent. Exceeding the critical micelle concentration (cmc) can result in the formation of multilayered structures, including micelles and hemicells, which can affect adsorption. However, at the environmental level, PFAS micelle formation is rare, and only aggregates have been observed. The PFAS adsorption process may present two distinct phases, i.e., initially, removal occurs via PFAS adsorption on open adsorbent sites, but due to the gradual blocking of pore sites, removal converts to a function of molecular aggregation [36,50].
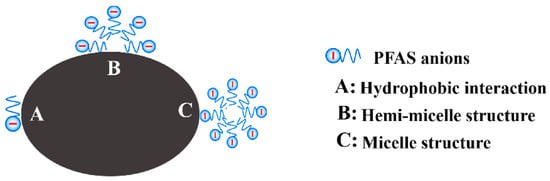
Figure 7.
PFAS adsorption by hydrophobic interactions [50] (reprinted with permission).
6.1.6. Factors Affecting Adsorption
- Particle size
Particle size is one of the main influencing factors in PFAS adsorption. For example, activated carbons with diverse particle sizes yield different adsorption capacities for PFAS; even with similar SSA, PAC has a higher adsorption capacity than GAC. However, activated carbons with larger particle sizes are associated with slower adsorption kinetics due to diffusion limitations within the particles, as the diffusion of PFAS anions into the internal micropores requires more time [50].
- 2.
- pH
The pH of the solution is one of the main parameters for PFAS adsorption. The PFAS adsorption capacity is inversely proportional to the solution pH because, at a low pH, protonation is easier. The adsorption sites become positively charged, making it easier for negatively charged PFAS anions to be attracted through electrostatic interaction. Conversely, at a higher pH, hydrogen ions are lost, resulting in deprotonation and, by extension, the reduction of attractive interactions [50].
- 3.
- Co-existing ions
PFAS absorption capacity is enhanced by the presence of divalent cations, such as Ca2+, Cu2+, and Pb2+, that increase the PFAS adsorption capacity through electrostatic attraction via the cation bridging effect, as they bond with negatively charged hydroxyl or carboxyl groups on adsorbent surfaces and convert them into positively charged ions. Conversely, the presence of anions, e.g., anions often found in water, such as Cl−, SO42−, and HCrO4−, act competitively with PFAS for adsorption sites on the surface of the adsorbent, reducing the efficiency of adsorption [50,51].
- 4.
- Co-existing organic matter
The main organic compounds that exist in surface water or groundwater are humic acid (HA) and fulvic acid. The abundant carboxyl groups in NOM act competitively for the limited adsorbent sites on the adsorbents, consequently reducing the sorption capacity of PFAS. In addition, due to the presence of NOM, the surface charge of the adsorbents decreases, thus affecting the electrostatic interactions. In fact, possible electrostatic repulsions can further reduce the adsorption capacity [50]. DOM has an important influence on the fate, adsorption, and degradation behavior of PFAS in soil and water. When DOM co-precipitates directly with PFAS, it leads to a higher concentration of PFAS in sediment layers. Additionally, DOM can compete with PFAS on adsorbents’ surfaces, potentially decreasing the efficiency of PFAS adsorption and subsequent removal [52].
6.2. Anion Exchange Resins
The ion exchange process is a viable alternative with many possibilities for effective PFAS removal. Ion exchange exhibits high PFAS removal while simultaneously removing inorganic and organic anions in a single-step treatment. Resins are classified into ion-exchange and non-ion-exchange resins. Ion exchange resins are polystyrene or polyacrylate beads with charged functional groups saturated with a counterion, usually chloride, which can be exchanged with PFAS, that exist mainly as anions. Polystyrene is characterized by a slightly higher adsorption capacity, while polyacrylic has significantly faster kinetics. Non-ion exchange resins are synthetic polymer structures with no charge that do not contain exchangeable ionic sites, basing their action on non-ionic interactions, i.e., hydrophobic interactions. In recent years, industries such as Purolite, DuPont, Calgon Carbon Corporation, and many others have initiated the manufacturing of PFAS-specific resins that typically operate in a use-and-dispose manner [3,15].
Since PFAS are considered anions, anion exchange resins seem favorable for their removal. The main PFAS removal mechanism by anion exchange resins is ionic interaction, with alternative mechanisms including hydrophobic interactions and interactions between PFAS functional groups and resin functional groups. As stated above, besides PFAS, ion exchange resins also remove other pollutants, such as natural organic matter (NOM), and inorganic substances, such as sulfate, nitrate, and phosphate ions. In general, sulfates are the most competitive inorganic ions, followed by phosphates and nitrates. Regarding the organic fractions, the humic fraction with a higher molecular weight has the most unfavorable effect on PFAS removal. This fraction can block the exchange pores, limiting, in that way, the exchange capacity of microporous resins. As with other adsorbents, regeneration is an important challenge for ion exchange resins. The disposal of single-use resins involves thermal destruction and is preferred in small-scale systems due to its simplicity. Therefore, the regeneration and reuse of resins are highly recommended, given the environmental burden of their manufacture. Renewable resins require a longer contact time with the resin compared to disposable resins, so a larger amount of resin is required. Also, the management of PFAS brine remains an important problem. In conclusion, it is recommended that improvements in resin regeneration and management of waste streams that will enable the multiple use of resins are necessary, thereby reducing both the cost and environmental impact [15].
Wang et al., 2019 [54], revealed the mechanisms by which six emerging and traditional PFAS were adsorbed on IRA67 anion exchange resin. The adsorption equilibrium for long-chain PFAS was at least 96 h, while for short-chain PFAS, it was 48 h. At higher concentrations (0.07666 mmol/L), PFBS and PFBA adsorptions were reduced by 72.09% and 77.78%, respectively. The polyamine groups in the IRA67 resin were altered to the base forms when the solution pH increased from 3 to 7, leading to a decrease in the effective adsorption sites and a more competitive substitution. The results showed that long-chain PFAS were removed more efficiently, while short-chain PFAS were adsorbed on high amounts of resins or at a lower pH. Park et al., 2020 [55], used MIEX ion exchange resin to remove three PFAS sulfonates and six carboxylates from groundwater with low organic content. MIEX was highly effective in removing long-chain carboxylated PFAS, with >80% efficiency.
6.3. High-Pressure Membranes
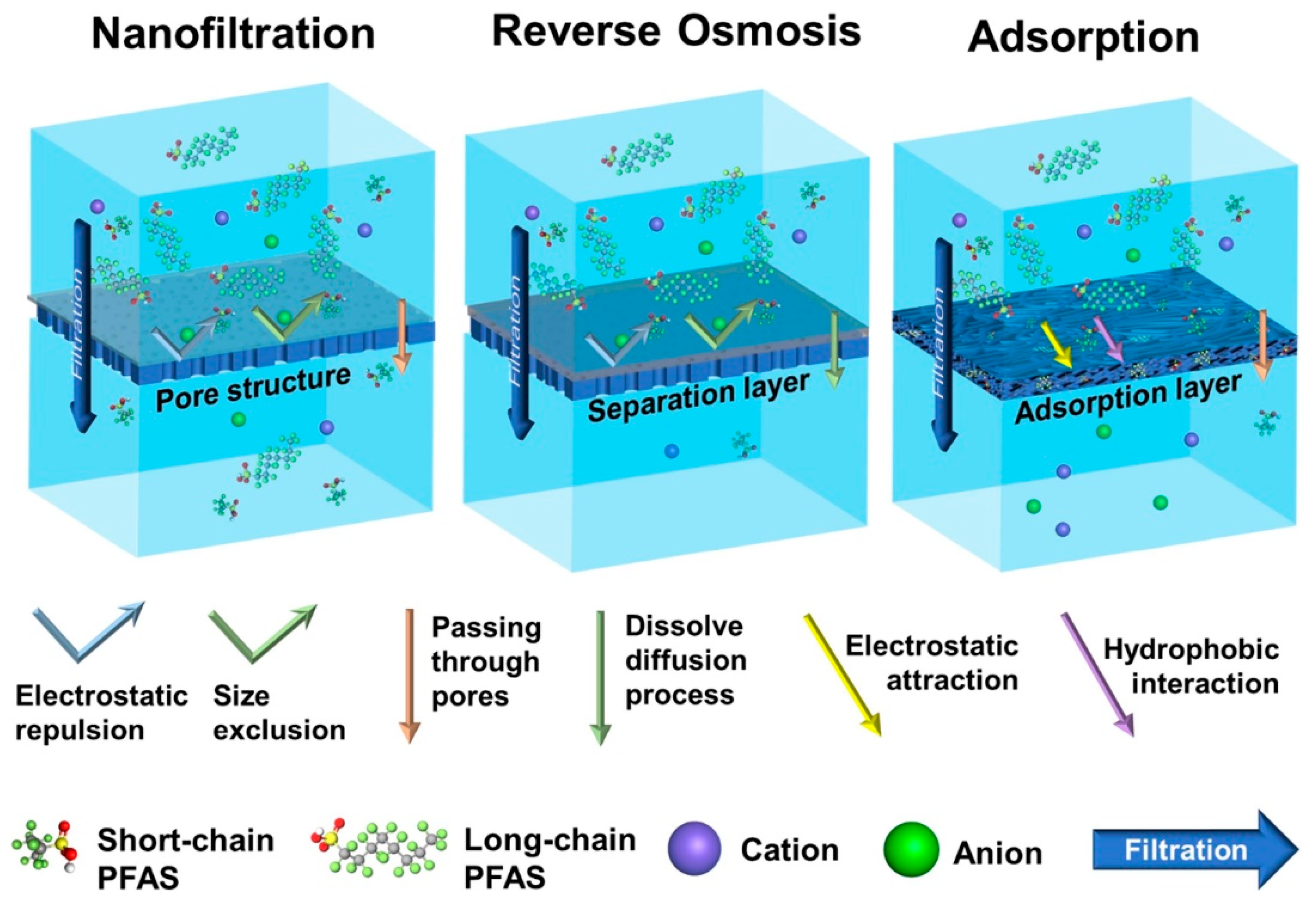
Membrane technology has been developed and used with proven effectiveness in the field of water treatment. Membranes are categorized as low and high pressure. According to the literature, PFOA and PFOS removal by low-pressure membranes, such as microfiltration and ultrafiltration, reaches values between 0 and 23%. High-pressure membranes, such as nanofiltration and reverse osmosis, have higher efficiency at removing substances such as PFAS [56].
Nanofiltration (NF) is a membrane technique based on pressure that involves membranes with a pore size between 1 and 10 nm, which is smaller than that of PFAS molecules. Typically, they comprise negatively charged and hydrophilic surfaces along with a rather low molecular weight cut-off (MWCO). Reverse osmosis (RO) is a process in which the transfer of water through the semi-permeable membrane occurs due to compression, increasing the pressure of the feed water above its equilibrium point, or osmotic pressure. When the RO membrane feed solution is subjected to such a higher pressure, the water will infiltrate the pores of the membrane, while 95–99% of the molecules bigger than the membrane pores will be blocked, creating a concentration difference on the feed solution side, which is known as brine or brine rejection. The pore size of reverse osmosis membranes is less than 1 nm, while the size of PFAS molecules is significantly bigger. The removal of long-chain PFAS for NF is estimated to be around 85–99%, while for short-chain PFAS, the removal rate is lower, in the range of 20–70%. RO, in general, is more effective in treating both long- and short-chain PFAS. RO membranes generally have a denser structure than NF membranes, which makes RO more effective in removal techniques. The main pathways to remove PFAS from NF and RO membranes are steric (size) exclusion, solution diffusion, and electrostatic interaction. Electrostatic interaction is the dominant mechanism for the treatment of short-chain PFAS, while the effect of size exclusion is not efficient when dealing with membranes possessing a similar or greater MWCO [57]. The different mechanisms of nanofiltration, reverse osmosis, and adsorption are shown in Figure 8.
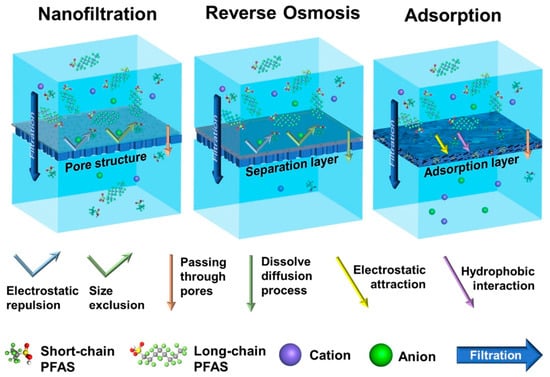
Figure 8.
Membrane processes and removal mechanisms for PFAS [57].
Appleman et al., 2013 [58], examined the pathways by which nine perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) with different sizes (molecular weight: 214–500 g/mol) were removed from water by an NF270 membrane. All of the PFAS rejection rates were above 93% for all PFAAs studied. Higher rejection rates corresponded to higher molecular weight PFAAs. Steinle-Darling and Reinhard [59] investigated the removal of fifteen PFAS (molecular weight: 263–713 g/mol) from four different NF membranes (NF270, NF200, DK, and DL). Anionic species had rejections >95% for MW > 300 g/mol, with size exclusion being the main mechanism, while the charge interaction between the solute and membrane was also crucial for removing these pollutants. Furthermore, Thompson et al., 2011 [60], investigated the role of RO in a drinking water treatment plant for PFOS removal in south-east Queensland, Australia. The PFOS concentration was reduced by several ng/L, highlighting the significance of RO for PFAS removal.
Each removal technology holds its own advantages and disadvantages. A challenge for the application of the membranes is the management of the retainer, the substances that were rejected in our case, the PFAS. Therefore, further processing is required, as membrane technology does not “destroy” PFAS; it simply separates and retains them. Another problem is related to the by-products that are likely to be produced during the degradation process, resulting in the presence of more short-chain compounds. Membrane fouling is a typical problem during their application, resulting in increased operating costs and reduced processing efficiency, including instability after the membrane has operated for a long period. Furthermore, the high capital and operating costs of membrane plants remain important problems for their widespread application [56].
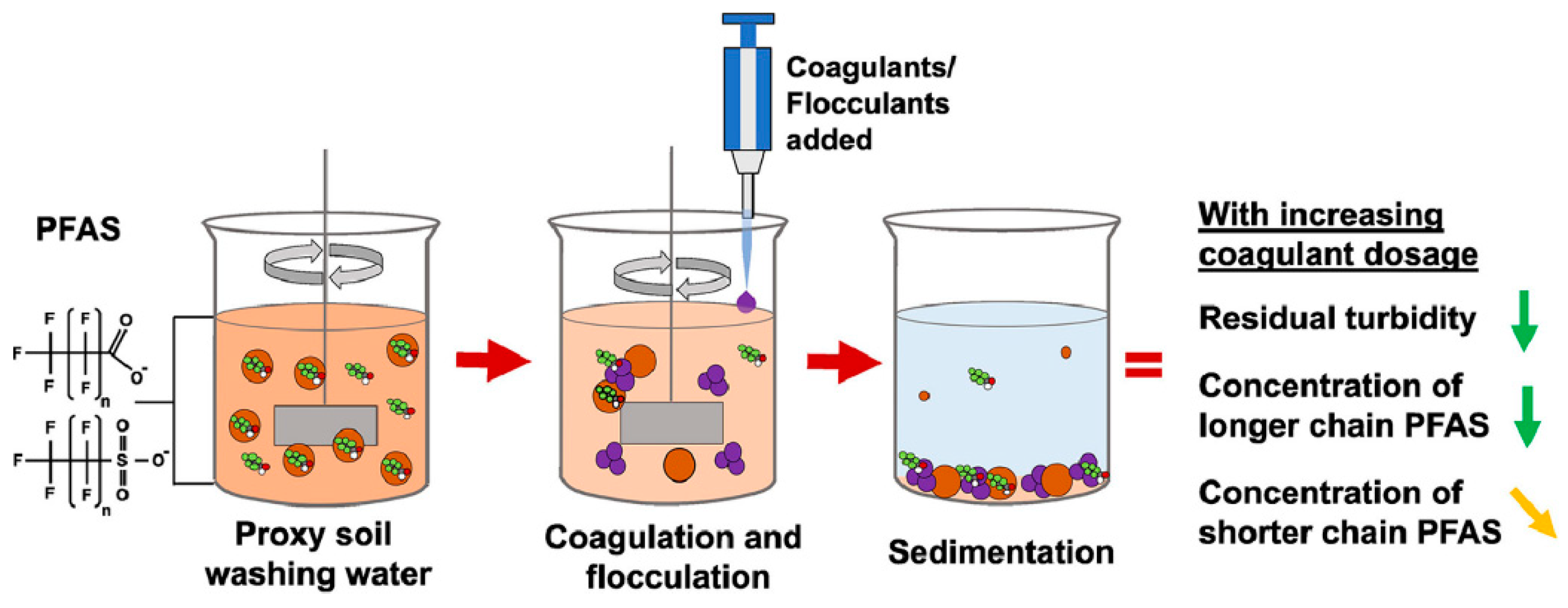
6.4. Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is a very effective method of removing contaminants from water, in which metal hydroxide flakes are formed that absorb and remove these contaminants. The formed amorphous metal hydroxide flocs, such as aluminum and iron, are highly porous aggregates with large surface areas, which enhance the rapid adsorption of soluble organic compounds and the capture of colloidal particles. Regarding the removal of PFAS by electrocoagulation (Figure 9), it is characterized as a non-destructive method because the removal is achieved through metal hydroxide flocs produced through the use of sacrificial (usually iron or aluminum) electrodes. The adsorption mechanism in this case is mainly ascribed to hydrophobic interactions, a result of the hydrophobic sorption of the PFAS tail to the flocs via multilayer sorption. Studies showcase that electrocoagulation of waters that contain high levels of PFAS, with iron and aluminum, can achieve high removal efficiency (e.g., 90%) [61,62,63].
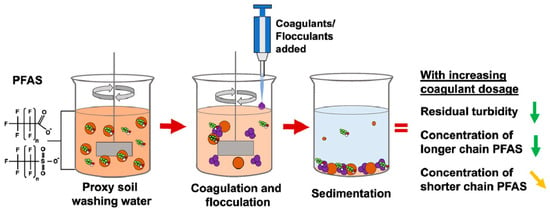
Figure 9.
Coagulation process for PFAS removal [63].
In a study from Lin et al., 2015 [64], a stainless steel cathode was used along with a zinc anode, achieving the highest PFOS and PFOA removal efficiency of 99.7% compared to other cell materials that were tested, including iron, magnesium, or aluminum. Wang et al., 2016 [64], concluded that, for PFOA removal, the efficiency of stainless steel rods as cathodes was greater than that of aluminum rods as cathodes. Specifically, for the stainless steel rod, the removal capacity for PFOA was 99.7%, 98.1%, 96.2%, and 4.1% in the presence of Cl−, NO3−, SO42−, and CO32−/HCO3−, respectively. For the aluminum rod, they were 98.9%, 97.3%, 7.4%, and 4.6% in the presence of Cl−, NO3−, SO42−, and CO32−/HCO3−, respectively. Yang et al., 2016 [65], used an iron anode and stainless steel cathode in a 600 mL cell and achieved over 99% PFOS removal. In a laboratory-scale study of cleaning firewater containing perfluorinated surfactant, Baudequin et al., 2011 [66], were able to remove 71–77% of perfluorinated compounds, while the flocs were then removed by the reverse osmosis process.
6.5. Foam/Ozon Fractionation
Foam fractionation is a separation technique based on adsorption that does not require solid adsorbents. Foam fractionation works by releasing air bubbles from the bottom of a container, creating many air–liquid interfaces in the solution. When the surface energy of the adsorbed compounds is low enough, the bubble film stabilizes, and thus the bubbles accumulate on the surface, creating foam. The excess foam can then be separated and collapsed to form a concentrated liquid (foam) of the surfactant, which can then be used in destructive or recycling processes [61].
Burns et al., 2021 [67], reported on a field study at Oakey Air Force Base in Australia where a water treatment plant consisting of a foam flotation system combined with anion exchange resin was constructed and used as the final step to treat groundwater and is currently in a trial phase, able to treat 250 m 3/d of PFAS-contaminated groundwater. Only the foam flotation process removes at least 99.5% of the urgent PFAS (PFOS, PFOA, and PFHxS). Anion exchange resins are useful when there is a great amount of short-chain PFAS in the influent because foam fractionation does not remove them efficiently. Dai et al., 2019 [68], evaluated the efficiency of foam fractionation with air and ozone for PFAS removal. For a residence time of 20 min, foam fractionation removes 80% of PFAS, while ozone fractionation removes 95%, the difference being due to the high affinity of hydroxyl radicals to the negatively charged hydrophilic ends of PFAA.
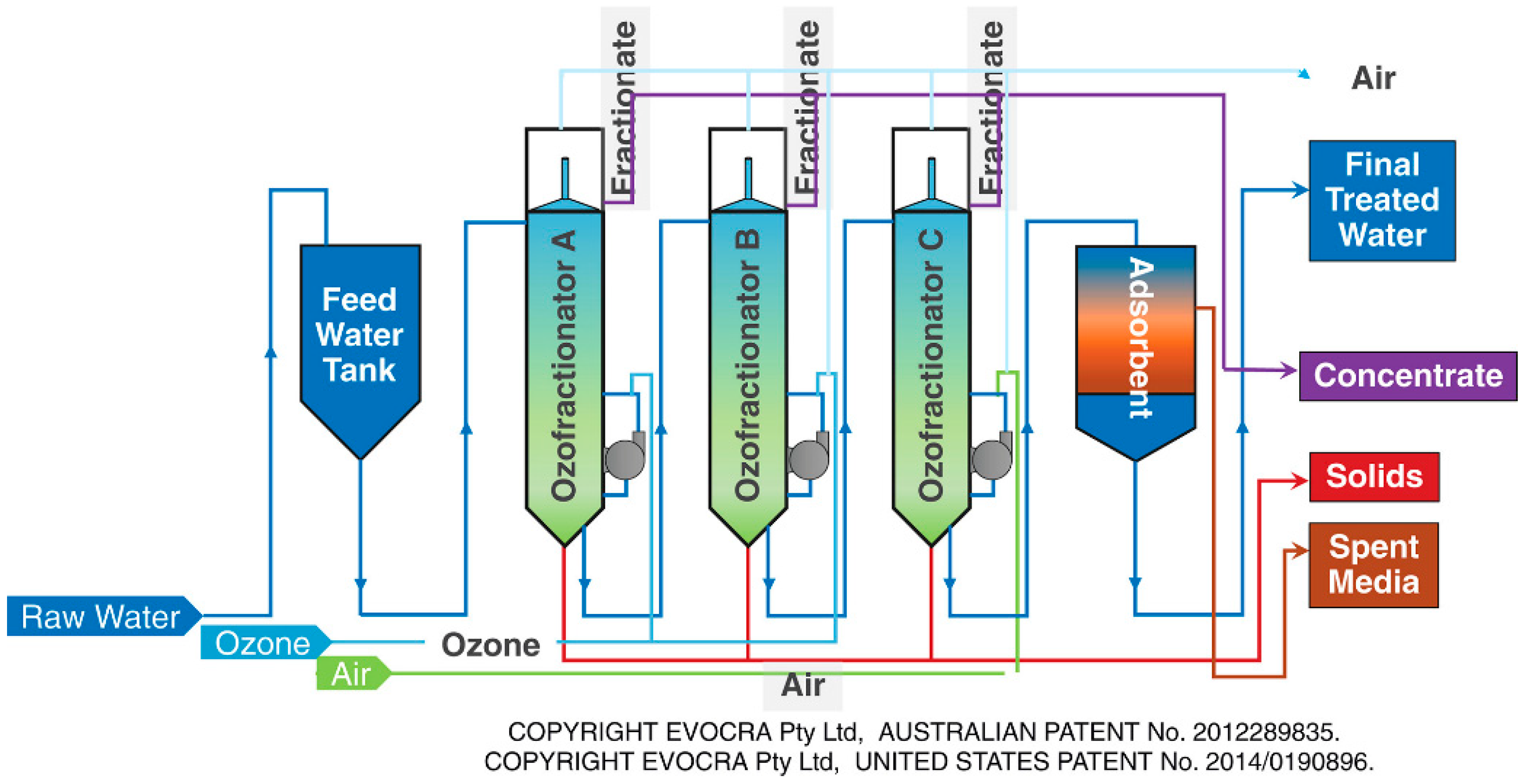
According to the Dickson patent (2014), ozofractionation is a technique that combines foam fractionation with ozone. Ozofractionation is considered a suitable separation technique due to the surface-active nature of PFAS, making the interface of a bubble appropriate for PFAS aggregation. Ozofractionation technology is a trademarked process by EVOCRA and is marketed as Ozofractionation Catalytic Addition of Reagents (OCRA), a three-chamber process in series where ozone bubbles with a diameter less than 200 µm are dispersed, able to treat PFAS by 99.9%. The process is shown in Figure 10. EVOCRA noted that there is solid evidence for oxidative change and the elimination of short-chain intermediates [35,36,61].
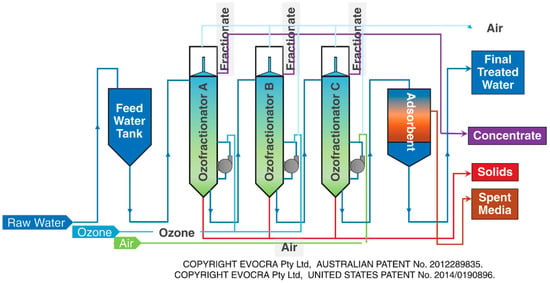
Figure 10.
ORCA process [69] (reprinted with permission).
Fractionation processes have many advantages, as they are fast, efficient, and do not require the construction and subsequent replacement of adsorbents. However, the foam generated is considered waste and therefore needs further treatment and management. It is also not as effective, typically, on short-chain PFAS, so polishing steps such as anion exchange resins will be required. In ozofractionation, the formation of short-chain PFAS is possible [61].
Destructive technologies
6.6. Biodegradation
In general, PFAS compounds are resistant to biodegradation, and existing research presents mixed findings. The challenges in breaking down PFAS by microbes stem from their molecular structure, which includes robust carbon–fluorine (C–F) bonds, a hydrophobic protective layer around the carbon–carbon (C–C) bonds, and a carbon chain fully saturated with fluorine, making them unsuitable as an energy source for microorganisms [70]. Because of the durability of the C–F bond and the electronegativity of fluorine, the biodegradation of PFAS is of particular interest. Similarities between dechlorination and defluorination reactions, as well as other biologically degradable halogenated compounds, suggest the possibility of biological treatment [61].
Vo et al., 2020 [71], used enzymes, derived from Cannabis sativa L. that were judged capable of rapid degradation of PFAS compared to other microorganisms that require more than 100 days. Taken together, it was found that the enzyme could degrade 98% of PFOS and PFHxS in 1 h, a result that motivates further study in this area. Beškoski et al., 2018 [72], examined how PFOA and PFOS, with initial concentrations of 1 μg/mL, were defluorinated by two different microbial groups from two river sediments in Saitama and Osaka, Japan, a region impacted by long-term PFAA pollution. The results showed, after 28 days of incubation, a reduction of 46–69% for PFOS and 16–36% for PFOA. Moreover, new unsaturated monofluorinated fatty acids and hydrocarbons with multiple unsaturated bonds or ring structures were detected. Furthermore, the results showed that PFAA defluorination occurred, but no fluoride ions were detected due to possible adsorption on or within the microbial cells. Huang and Jaffe, 2019 [73], investigated enrichment cultures of Acidimicrobium sp. strain A6, an autotroph that reduces ferric ions while oxidizing ammonium to nitrate, for PFAA degradation. After 100 days, PFOS and PFOA removals were observed. The researchers detected fluoride, shorter-chain perfluorinated products, and acetate, along with the consumption of one Fe(III) reduced per oxidized ammonium. In addition, incubation with hydrogen, the only electron donor, also led to defluorination.
6.7. AOPs and ARPs
Advanced Oxidation/Reduction Processes (AOPs/ARPs) are in situ treatment processes that include a chain of reactions assisted either by a catalyst or by an external energy source, with the aim of generating reactive radicals for pollutant degradation. AOPs and ARPs are particularly useful for degrading organic compounds of human origin, especially when they are resistant to natural degradation or degradation by simple chemical processes. AOPs and ARPs combine activation methods and chemical agents to generate reactive radicals. AOPs rely on the production of highly reactive radicals, mainly hydroxyl radicals, OH, to oxidize organic pollutants in a solution. Activation processes include a variety of processes such as UV photolysis, Fenton processes, electrochemical oxidation, sonochemical processes, microwaves, etc., often in combination with oxidants (e.g., O3, H2O2) and/or catalysts (e.g., TiO2). A hydroxyl radical is one of the strongest oxidants applied in processes [61,74,75].
Ross et al., 2018 [37], reported that some oxidants could degrade perfluoroalkyl carboxylates, but perfluoroalkylsulfonates remain a challenge. The advanced oxidation process with O3/H2O2 and O3/UV failed to treat PFOS at the ppm level. Dichromate (Cr2O72−) and permanganate (MnO42−) had no impact on a variety of PFAAs, including PFOS. The electronegativity of the fluorine atoms on the carbon chain protects the atoms from oxidation by hydroxyl radicals. However, they seemed to be more prone to reduction. Park et al., 2016 [76], examined the oxidation of PFOA, 6:2 fluorotelomer sulfonate (6:2 FTSA), and PFOS by heat-activated persulfate. PFOA oxidation produced shorter-chain-length compounds and fluoride, while 6:2 FTSA was oxidized to PFHpA and PFHxA. Jin et al., 2014 [77], researched the photochemical degradation of PFOS in the presence of Fe3+ and achieved treatment below the detection limit of PFOS. Thus, numerous photolytic oxidation/reduction methods, including UV light combined with iodide, iron, aqueous periodide, and titanium-mediated photochemical decomposition, were tested, with PFOA removal ranging from 9–70% [78].
ARPs are a new class of technologies that combat emerging pollutants by combining reducing agents, such as ferrous, sulfide, iodide, and dithionite, with numerous activation methods, such as ultrasound, ultraviolet, microwave, and electron beam, with the goal of forming highly reactive species, like hydrated electrons, hydrogen, and sulfite radicals. Unlike AOPs, they can easily degrade oxidized pollutants. The selection of reductant depends on the ability of the activation method to produce reducing radicals or other effective reducing agents [76].
Park et al., 2011 [79], studied the pathways of PFOA and PFOS degradation by iodine photolysis at 254 nm and concluded that the degradation rate was influenced by parameters such as iodine concentration, initial PFAS concentration, head group type, and chain length, but not by pH. Qu et al., 2010 [80], achieved almost complete degradation and defluorination of PFOA in a UV-KI pH 9.0 system under anaerobic conditions. Primarily, it was observed that PFOA removal increased with increasing KI concentration, but then with further increases, it decreased because of the formation of hydrated electrons and triiodide (I3−), which also acts as an oxidant. Zhang et al., 2015 [81], examined the effect of temperature and ionic strength on the reductive degradation of PFOA with a UV-KI system, under a nitrogen atmosphere. As the temperature rose, the breakdown of PFOA was enhanced, but the amount of PFAS and shorter-chain intermediates was reduced. Therefore, a positive correlation was observed between the PFOA degradation rate and ionic strength.
In brief, both AOPs and ARPs can degrade PFAS. Thus, the reaction conditions, efficiency, and products are different. Hydrated electron-based ARPs can degrade and defluorinate PFAS more efficiently and possibly at higher defluorination rates, compared to AOPs. In AOPs, the hydroxyl radical cannot deal with PFAS, while SO4− effectively fights PFAS. However, complete defluorination is not possible, and some F-containing intermediates accumulate. In AOPs, PFAS are degraded to short-chain PFCA. Additionally, in both AOPs and ARPs, the main degradation pathways of long-chain PFAS are through rapid degradation to short-chain intermediates, with simultaneous defluorination.
6.8. Sonolysis-Ultrasonication
Ultrasonic treatment, or sonication, is a process in which sound waves, at frequencies of 20 kHz–1100 kHz, create microbubbles. An ultrasonic wave in an aqueous solution usually has two main effects: compression and rarefaction. Compression applies positive pressure by pushing particles together, while rarefaction applies negative pressure by pushing particles apart. Microbubbles grow and shrink in size, burst, and produce shock waves. During this process, which is called cavitation, pressures on the order of hundreds of atmospheric temperatures between 4000 and 10,000 K and bubble interface temperatures in the range of 1000–1500 K prevail [82].
According to a study by Rodriguez-Freire et al. [83], different frequencies suit different chain lengths, although higher frequencies favor PFAS degradation. Lei et al., 2020 [84], investigated a combination of dual frequencies with activated persulfate, which yielded 100% degradation for PFOA but only 46.5% for PFOS in a 1-L setup. Also, the system could simultaneously degrade PFAS in soil, leaving a small amount of residue in the liquid phase. Application to larger-scale facilities is affected by many parameters, such as density and size or converter, frequency, and reaction geometry, as well as the physicochemical properties of environmental matrices, etc., and it remains a big challenge [61,85].
Kucharzyk et al., 2017 [86], mention that the application of higher-frequency ultrasound is favorable with moderate operating costs; however, for larger-scale applications, the capital cost is high. Babu et al., 2016 [87], proposed the coexistence of ultrasonic treatment with AOPs, i.e., the application of hybrid technology, such as sono-ozone, sonophotocatalysis, sonoFenton, and sonophoto-Fenton techniques. It is operationally simple, efficient, and has no obvious environmental issues; therefore, as well as for larger-scale applications, it is economically viable. The combination of ozone and ultrasound enhances the degradation of toxic organic pollutants, such as PFAS, through hydroxyl radical reactions, breaking them down into smaller molecules and fully mineralizing them into F−, SO42−, CO2, and H2O. More generally, hybrid AOPs are more efficient in most environmental restorations [35].
6.9. Electrochemical Oxidation
Electrochemical oxidation is a water treatment technique that has received increasing interest in recent years in water treatment because it can degrade numerous persistent organic compounds through direct and indirect oxidation. In the direct method, the electrode directly adsorbed and degraded the impurities, while in the indirect method, the degradation takes place in the solution, due to reactions with oxidizing agents formed at the electrode. Several materials can be used as electrodes, such as boron diamond doped (BDD) due to its mechanical, chemical, and thermal stability, lead dioxide (PbO2), titanium oxide (TiO2), and tin oxide (SnO2), all of which are capable of PFAS degradation. Electrochemical oxidation is affected by multiple parameters, such as pH, current density, electrolyte type, electrode spacing, initial PFAS concentration, and temperature. In relation to other oxidation processes, it has the duality of producing zero waste, eliminating the need for chemicals, and operating at ambient temperature [76].
Schaefer et al., 2015 [88], achieved enhanced PFOA degradation as a result of increased current density using a titanium electrode coated with ruthenium (IV) oxide (Ti/RuO2). Nevertheless, no fluorine or shorter-chain PFCAs were detected, possibly due to their decomposition into volatile PFCAs and transport to the gas phase. The degradation of PFOS decreased after some time because the reactive anode sites were saturated. Trautmann et al., 2015 [89], examined the electrochemical degradation from groundwater of a past fire training site, which contained high amounts of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and synthetic groundwater. The results showed that PFSAs were degraded and defluoridated in the synthetic groundwater with a greater degradation yield for PFOS than PFBS and PFHxS, indicating that the degradation rate rose with the chain length. PFBA was completely degraded, unlike PFBS, because the degradation of PFSA with the same carbon number is not as feasible because the functional group of PFSAs is more electrophilic than the carboxyl functional group of PFCAs, limiting mass transfer to the electrode.
Therefore, the electrochemical degradation and defluorination of PFAS, at least at an experimental level, are feasible. However, its application on a larger scale is still limited due to various issues related to energy consumption, the cost of manufacturing efficient electrodes, and the formation of toxic by-products [76].
6.10. Non-Thermal Plasma
Plasma, the fourth state of matter, is a gas that is partly or fully ionized and contains reactive particles, such as electrons, ions, free radicals, and neutral particles. Non-thermal plasma is a novel technique that generates highly reactive particles, mainly from the impact of a high-voltage discharged electron with gas atoms or molecules. Then, reactive species are produced by radical recombination reactions or metastable deexcitation species. The most abundant and active species are the hydroxyl radicals H2O2 and O3, which are used to degrade pollutants [54,61].
Singh et al., 2019 [90], reported that basic plasma water treatment of PFAS produced various PFAA byproducts with linear chains (C4–C7) from PFOA and PFOS, along with 43 PFOA-related by-products and 35 PFOS-related by-products. Some were first reported in PFAS degradation experiments, such as cyclic PFAS. The results of the study showed that 90% of PFOA was removed in 60 min, but the increased concentration of other by-products is a significant drawback.
Alam et al. [91] utilized bubbles to elevate PFAS to the surface, where they were then degraded by an argon plasma discharge. This technique was particularly effective for long-chain PFAS (with more than 6 carbons) in both prepared solutions and polluted surface water. The degradation process took advantage of the surface-active properties of PFCAs and PFSAs with longer chains, which were more prone to degradation. The concentration of PFAS was a critical factor affecting the rate of degradation; as the concentration fell below 5 µg/L, the elimination rate diminished over the course of the plasma treatment. The research indicated that the rate-determining step in the decomposition process is the presence of PFAS molecules at the liquid surface, which interact with the plasma.
The main limitations of the plasma process so far are high energy requirements, high cost, and safety issues. Contaminant removal from water occurs initially at the liquid plasma interface, resulting in reduced susceptibility to both organic and inorganic co-contaminants. It is safe to conclude that plasma technology is a potential solution for PFAS removal, as it has advantages over other treatment methods. However, more research is needed to address byproduct formation. Plasma technology is a new method for removing PFAS and is still in the experimental stage [82].
7. Conclusions
The choice of the appropriate treatment technology to remove PFAS mixtures from water depends on several parameters, such as the mixture composition, the site-specific conditions, and the treatment objectives. The efficiency of most treatment processes can be influenced by physicochemical factors such as pH and temperature, while the presence of dissolved organic matter, other organic pollutants, and metal ions can also significantly influence the adsorption and regeneration processes. In particular, regardless of the adsorbent used, short-chain PFAS were shown to be harder to remove than long-chain compounds, while the regeneration of adsorbent materials by in situ application of either chemical or thermal processes is not yet viable at full-scale installations.
So far, most of the experimental work that has been published has been performed under unrealistic operating conditions that are not equivalent to either full-scale treatment plants or real environmental contamination. for example, with high dosages of adsorbents and high concentrations of PFAS. Foam and ozone fractionation are quite promising technologies for full-scale applications, as they have already been tested in conditions greater than those of the laboratory. Also, the application of sonolysis seems quite attractive; however, in larger-scale applications it is recommended to apply hybrid technologies, such as the combination of sonolysis and AOPs. According to our knowledge, there is no literature on large-scale installations; all applications are at the pilot-laboratory level. In destructive technologies, such as electrochemical oxidation and non-thermal plasma, the risk of toxic by-products has been reported. In order to deal with such cases, the combined application of treatment technologies, such as AOPs, and subsequent treatment with activated carbon is recommended. For large-scale applications, a combination of treatment techniques may provide the optimal solution for sustainable PFAS removal.
Moreover, further research is needed to better understand the properties (e.g., solubility, hydrophobicity, bioaccumulation, and toxicity) and the adsorption mechanisms (e.g., van der Waals vs. electrostatic interactions) of short-chain PFAS to improve current removal technologies.
Based on the information reported, the integration of different treatment technologies for PFAS removal will be the most cost-effective and energy-efficient method, but each treatment train should be carefully evaluated based on the nature of the stream being treated and on the further use and destination of the reclaimed water.
However, all applications described so far are at the pilot-laboratory scale. For large-scale applications, several critical aspects need to be addressed, such as (i) high variability in the behavior of different PFAS that co-occur in water (e.g., long- and short-chain) with respect to different removal technologies; (ii) the presence of other organic compounds that may compete with PFAS removal; (iii) the lack of regulatory standardized procedures for identifying all PFAS of concern whose removal from water resources should be prioritized; and (iv) the lack of information on the presence and behavior of PFAS precursors whose degradation may produce further PFAS. A combination of treatment techniques (e.g., removal followed by destruction) may provide the optimal solution for sustainable PFAS management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K.T., G.Z.K., A.M. and I.A.K.; methodology, N.M., S.C., N.M., A.K.T., G.Z.K., L.C., A.M. and I.A.K.; validation, A.K.T., G.Z.K., A.M. and I.A.K.; formal analysis, N.M., S.C., A.K.T., G.Z.K., A.M. and I.A.K.; investigation, N.M., S.C., A.K.T. and I.A.K.; resources, N.M., S.C., A.K.T., and I.A.K.; data curation, N.M., S.C. and A.K.T.; writing—original draft preparation, N.M., S.C. and A.K.T.; writing—review and editing, N.M., S.C., A.K.T., G.Z.K., L.C., A.M. and I.A.K.; supervision, G.Z.K., A.M. and I.A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All data analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- OECD. Reconciling Terminology of the Universe of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Recommendations and Practical Guidance; OECD Series on Risk Management—No. 61; OECD: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Meegoda, J.N.; Kewalramani, J.A.; Li, B.; Marsh, R.W. A Review of the Applications, Environmental Release, and Remediation Technologies of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymourian, T.; Teymoorian, T.; Kowsari, E.; Ramakrishna, S. A review of emerging PFAS contaminants: Sources, fate, health risks, and a comprehensive assortment of recent sorbents for PFAS treatment by evaluating their mechanism. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2021, 47, 4879–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsan, M.N.; Riza, M.; Pervez, N.; Khyum, M.M.O.; Liang, Y.; Naddeo, V. Environmental and health impacts of PFAS: Sources, distribution and sustainable management in North Carolina (USA). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, R.; Yingling, V. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Fact Sheets; Interstate Technology Regulatory Council Sheets: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Brennan, N.M.; Evans, A.T.; Fritz, M.K.; Peak, S.A.; von Holst, H.E. Trends in the Regulation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Buser, A.M.; Cousins, I.T.; Demattio, S.; Drost, W.; Johansson, O.; Ohno, K.; Patlewicz, G.; Richard, A.M.; Walker, G.W.; et al. A New OECD Definition for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15575–15578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; De Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, S.A.; Van Leeuwen, S.P.J. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: Terminology, classification, and origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, M.; Gong, T.; Zan, R.; Wang, W. Transport behavior difference and transport model of long- and short-chain per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in underground environmental media: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y. Adsorption of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) from aqueous solution—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjølholt, J.; Jensen, A.A.; Warmning, M. Short-Chain Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). A Literature Review on Human Health Effects and Environmental Fate and Effect Aspects of Short-Chain PFAS; Environmental Project No. 1707; Danish Environmental Protection Agency: Odense, Denmark, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fenton, S.E.; Ducatman, A.; Boobis, A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Lau, C.; Ng, C.; Smith, J.S.; Roberts, S.M. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Toxicity and Human Health Review: Current State of Knowledge and Strategies for Informing Future Research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 40, 606–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calore, F.; Badetti, E.; Bonetto, A.; Pozzobon, A.; Marcomini, A. Non-conventional sorption materials for the removal of legacy and emerging PFAS from water: A review. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, H.; Xie, Y.; Brinkmann, M.; Giesy, J.P. Next generation per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances: Status and trends, aquatic toxicity, and risk assessment. Eco-Environ. Health 2022, 1, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, F.; Dutta, R.; Barbeau, B.; Berube, P.; Mohseni, M. PFAS removal by ion exchange resins: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, D.J.; Sinclair, G.M.; Shah, R.; Paten, A.M.; Kumar, A.; Long, S.M.; Vardy, S.; Jones, O.A. A review of omics-based PFAS exposure studies reveals common biochemical response pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorakova, D.; Jurikova, M.; Svobodova, V.; Parizek, O.; Kozisek, F.; Kotal, F.; Jeligova, H.; Mayerova, L.; Pulkrabova, J. Complex monitoring of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from tap drinking water in the Czech Republic. Water Res. 2023, 247, 120764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Kumar, P.; Mishra, V.; Guijt, R.; Singh, P.; Dumée, L.F.; Sharma, R.S. A review on the sources, occurrence and health risks of per-/poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) arising from the manufacture and disposal of electric and electronic products. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 38, 101683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, G.B.; Gleason, J.A.; Cooper, K.R. Key scientific issues in developing drinking water guidelines for perfluoroalkyl acids: Contaminants of emerging concern. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2002855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandjean, P.; Andersen, E.W.; Budtz-Jørgensen, E.; Nielsen, F.; Mølbak, K.; Weihe, P.; Heilmann, C. Serum Vaccine Antibody Concentrations in Children Exposed to Perfluorinated Compounds. JAMA 2012, 307, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, V.; Leonardi, G.; Genser, B.; Lopez-Espinosa, M.-J.; Frisbee, S.J.; Karlsson, L.; Ducatman, A.M.; Fletcher, T. Serum Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) Concentrations and Liver Function Biomarkers in a Population with Elevated PFOA Exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeeshan, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, R.-Q.; Yang, B.-Y.; Hu, L.-W.; Zeng, X.-W.; Sun, X.; et al. Incidence of ocular conditions associated with perfluoroalkyl substances exposure: Isomers of C8 Health Project in China. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Fifth Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- EU Parliament. Directive (EU) 2020/2184 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2020 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption; The European Parliament and of The Council: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Barisci, S.; Suri, R. Occurrence and removal of poly/perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 3442–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenka, S.P.; Kah, M.; Padhye, L.P. A review of the occurrence, transformation, and removal of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2021, 199, 117187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Dong, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Nghiem, L.D.; Khan, S.J.; Wang, Q. Occurrence, fate, and remediation for per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in sewage sludge: A comprehensive review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunacheva, C.; Tanaka, S.; Fujii, S.; Boontanon, S.K.; Musirat, C.; Wongwattana, T.; Shivakoti, B.R. Mass flows of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in central wastewater treatment plants of industrial zones in Thailand. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossi, R.; Strand, J.; Sortkjær, O.; Larsen, M. Perfluoroalkyl compounds in Danish wastewater treatment plants and aquatic environments. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigei, M.; Ahrens, L.; Hazaymeh, A.; Dalahmeh, S.S. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water and soil in wastewater-irrigated farmland in Jordan. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Peng, H.; Yang, M.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y. Detection, Occurrence, and Fate of Fluorotelomer Alcohols in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8953–8961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Meng, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; He, B.; Zhao, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.; Wang, T. Which type of pollutants need to be controlled with priority in wastewater treatment plants: Traditional or emerging pollutants? Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 104982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; Li, F.; He, N.; Alder, A.C. Perfluoroalkyl compounds in municipal WWTPs in Tianjin, China—Concentrations, distribution and mass flow. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Lu, H.; Liang, D.; Feng, S.; Li, Y.; Li, J. A review of the occurrence, monitoring, and removal technologies for the remediation of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from landfill leachate. Chemosphere 2023, 332, 138824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanninayake, D.M. Comparison of currently available PFAS remediation technologies in water: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 283, 111977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliano, E.; Sgroi, M.; Falciglia, P.P.; Vagliasindi, F.G.A.; Roccaro, P. Removal of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from water by adsorption: Role of PFAS chain length, effect of organic matter and challenges in adsorbent regeneration. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, I.; McDonough, J.; Miles, J.; Storch, P.; Kochunarayanan, P.T.; Kalve, E.; Hurst, J.; Dasgupta, S.S.; Burdick, J. A review of emerging technologies for remediation of PFASs. Remediat. J. 2018, 28, 101–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkouteb, N.; Franke, V.; McCleaf, P.; Köhler, S.; Ahrens, L. Removal of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in a full-scale drinking water treatment plant: Long-term performance of granular activated carbon (GAC) and influence of flow-rate. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umeh, A.C.; Hassan, M.; Egbuatu, M.; Zeng, Z.; Amin, A.; Samarasinghe, C.; Naidu, R. Multicomponent PFAS sorption and desorption in common commercial adsorbents: Kinetics, isotherm, adsorbent dose, pH, and index ion and ionic strength effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Ulrich, B.A.; Chen, B.; Higgins, C.P. Sorption of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) Relevant to Aqueous Film-Forming Foam (AFFF)-Impacted Groundwater by Biochars and Activated Carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6342–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beesley, L.; Moreno-Jiménez, E.; Gomez-Eyles, J.L.; Harris, E.; Robinson, B.; Sizmur, T. A review of biochars’ potential role in the remediation, revegetation and restoration of contaminated soils. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3269–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, Y.; Deng, S.; Du, Z.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Adsorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate on carbon nanotubes: Influence of pH and competitive ions. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Li, D.; Li, C.; Ji, R.; Tian, X. Metal nanoparticles by doping carbon nanotubes improved the sorption of perfluorooctanoic acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 351, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyetade, O.A.; Varadwaj, G.B.B.; Nyamori, V.O.; Jonnalagadda, S.B.; Martincigh, B.S. A critical review of the occurrence of perfluoroalkyl acids in aqueous environments and their removal by adsorption onto carbon nanotubes. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 17, 603–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateia, M.; Attia, M.F.; Maroli, A.S.; Tharayil, N.; Alexis, F.; Whitehead, D.C.; Karanfil, T. Rapid Removal of Poly- and Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances by Poly(ethylenimine)-Functionalized Cellulose Microcrystals at Environmentally Relevant Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, X. Highly effective adsorption removal of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) from aqueous solution using calcined layer-like Mg-Al hydrotalcites nanosheets. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 13396–13408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellsing, M.S.; Josefsson, S.; Hughes, A.V.; Ahrens, L. Sorption of perfluoroalkyl substances to two types of minerals. Chemosphere 2016, 159, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.-H.; Jiang, W.-T.; Li, Z. Removal of perfluorooctanoic acid from water using calcined hydrotalcite—A mechanistic study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 368, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.-H.; Li, Z.; Jiang, W.-T. Calcination of hydrotalcite to enhance the removal of perfluorooctane sulfonate from water. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 190, 105563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Lian, Q.; Zhang, X.; Karsili, T.K.; Holmes, W.; Chen, Y.; Zappi, M.E.; Gang, D.D. A review of PFAS adsorption from aqueous solutions: Current approaches, engineering applications, challenges, and opportunities. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 321, 121138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauletto, P.S.; Bandosz, T.J. Activated carbon versus metal-organic frameworks: A review of their PFAS adsorption performance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Cao, H.; Pan, W.; Wang, C.; Liang, Y. The role of dissolved organic matter during Per- and Polyfluorinated Substance (PFAS) adsorption, degradation, and plant uptake: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falciglia, P.P.; Malarbì, D.; Maddalena, R.; Greco, V.; Vagliasindi, F.G. Remediation of Hg-contaminated marine sediments by simultaneous application of enhancing agents and microwave heating (MWH). Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 321, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Mi, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, S.; Li, C.; Hu, X.; Qi, D.; Deng, S. Novel insights into the competitive adsorption behavior and mechanism of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances on the anion-exchange resin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 557, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Daniels, K.D.; Wu, S.; Ziska, A.D.; Snyder, S.A. Magnetic ion-exchange (MIEX) resin for perfluorinated alkylsubstance (PFAS) removal in groundwater: Roles of atomic charges for adsorption. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crone, B.C.; Speth, T.F.; Wahman, D.G.; Smith, S.J.; Abulikemu, G.; Kleiner, E.J.; Pressman, J.G. Occurrence of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in source water and their treatment in drinking water. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 2359–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Peydayesh, M.; Mezzenga, R. Membrane-based technologies for per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) removal from water: Removal mechanisms, applications, challenges and perspectives. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleman, T.D.; Dickenson, E.R.; Bellona, C.; Higgins, C.P. Nanofiltration and granular activated carbon treatment of perfluoroalkyl acids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinle-Darling, E.; Reinhard, M. Nanofiltration for trace organic contaminant removal: Structure, solution, and membrane fouling effects on the rejection of perfluorochemicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5292–5297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Eaglesham, G.; Reungoat, J.; Poussade, Y.; Bartkow, M.; Lawrence, M.; Mueller, J.F. Removal of PFOS, PFOA and other perfluoroalkyl acids at water reclamation plants in South East Queensland Australia. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, S.C.E.; Shukla, P.; Chen, D.; Eftekhari, E.; An, H.; Zare, F.; Ghasemi, N.; Zhang, D.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Li, Q. Emerging technologies for PFOS/PFOA degradation and removal: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 153669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, Y.; Niu, J.; Yue, Z.; Huang, Q. Efficient Sorption and Removal of Perfluoroalkyl Acids (PFAAs) from Aqueous Solution by Metal Hydroxides Generated in Situ by Electrocoagulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10562–10569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, M.; Meyn, T.; Hansen, M.C.; Hale, S.E.; Arp, H.P.H. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) removal from soil washing water by coagulation and flocculation. Water Res. 2024, 249, 120888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Jin, F.; Niu, J.; Zhao, J.; Bi, Y.; Li, Y. Electrocoagulation mechanism of perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) on a zinc anode: Influence of cathodes and anions. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557–558, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Han, Y.; Yu, G.; Zhuo, Q.; Deng, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, P. Efficient removal of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) from aqueous solution by electrocoagulation using iron electrode. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 303, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudequin, C.; Couallier, E.; Rakib, M.; Deguerry, I.; Severac, R.; Pabon, M. Purification of firefighting water containing a fluorinated surfactant by reverse osmosis coupled to electrocoagulation–filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 76, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, D.J.; Stevenson, P.; Murphy, P.J.C. PFAS removal from groundwaters using Surface-Active Foam Fractionation. Remediat. J. 2021, 31, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Xie, Z.; Dorian, B.; Gray, S.; Zhang, J. Comparative study of PFAS treatment by UV, UV/ozone, and fractionations with air and ozonated air. Environ. Sci. 2019, 5, 1897–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horst, J.; McDonough, J.; Ross, I.; Dickson, M.; Miles, J.; Hurst, J.; Storch, P. Water Treatment Technologies for PFAS: The Next Generation. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 2018, 38, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Munir, U.; Huang, Q. Occurrence of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in soil: Sources, fate, and remediation. Soil Environ. Health 2023, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, H.N.P.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Nguyen, T.M.H.; Li, J.; Liang, H.; Deng, L.; Chen, Z.; Nguyen, T.A.H. Poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances in water and wastewater: A comprehensive review from sources to remediation. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 36, 101393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beškoski, V.P.; Yamamoto, A.; Nakano, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Matsumura, C.; Motegi, M.; Beškoski, L.S.; Inui, H. Defluorination of perfluoroalkyl acids is followed by production of monofluorinated fatty acids. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Jaffé, P.R. Defluorination of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) by Acidimicrobium sp. Strain A6. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11410–11419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodaglio, A.G. Critical Perspective on Advanced Treatment Processes for Water and Wastewater: AOPs, ARPs, and AORPs. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatankhah, H.; Anderson, R.H.; Ghosh, R.; Willey, J.; Leeson, A. A review of innovative approaches for onsite management of PFAS-impacted investigation derived waste. Water Res. 2023, 247, 120769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, L.S.; Medina, V.F.; Zull, A.; Waisner, S. Heat-activated persulfate oxidation of PFOA, 6:2 fluorotelomer sulfonate, and PFOS under conditions suitable for in-situ groundwater remediation. Chemosphere 2016, 145, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zhang, P.; Shao, T.; Zhao, S. Ferric ion mediated photodecomposition of aqueous perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) under UV irradiation and its mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 271, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzeribe, B.N.; Crimi, M.; Thagard, S.M.; Holsen, T.M. Physico-Chemical Processes for the Treatment of Per- And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 866–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Vecitis, C.D.; Cheng, J.; Dalleska, N.F.; Mader, B.T.; Hoffmann, M.R. Reductive degradation of perfluoroalkyl compounds with aquated electrons generated from iodide photolysis at 254 nm. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2011, 10, 1945–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, F.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Q. Photo-reductive defluorination of perfluorooctanoic acid in water. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2939–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Qu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Q. Photoinduced Reductive Decomposition of Perflurooctanoic Acid in Water: Effect of Temperature and Ionic Strength. Clean 2015, 43, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambaye, T.G.; Vaccari, M.; Prasad, S.; Rtimi, S. Recent progress and challenges on the removal of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from contaminated soil and water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 58405–58428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Freire, L.; Balachandran, R.; Sierra-Alvarez, R.; Keswani, M. Effect of sound frequency and initial concentration on the sonochemical degradation of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.-J.; Tian, Y.; Sobhani, Z.; Naidu, R.; Fang, C. Synergistic degradation of PFAS in water and soil by dual-frequency ultrasonic activated persulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Liang, Y. Sonochemical degradation of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances—A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 69, 105245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharzyk, K.H.; Darlington, R.; Benotti, M.; Deeb, R.; Hawley, E. Novel treatment technologies for PFAS compounds: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 204, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, S.G.; Ashokkumar, M.; Neppolian, B. The role of ultrasound on advanced oxidation processes. Top. Curr. Chem. 2016, 374, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, C.E.; Andaya, C.; Urtiaga, A.; McKenzie, E.R.; Higgins, C.P. Electrochemical treatment of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) in groundwater impacted by aqueous film forming foams (AFFFs). J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 295, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trautmann, A.M.; Schell, H.; Schmidt, K.R.; Mangold, K.-M.; Tiehm, A. Electrochemical degradation of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in groundwater. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 71, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.K.; Fernando, S.; Baygi, S.F.; Multari, N.; Thagard, S.M.; Holsen, T.M. Breakdown Products from Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances (PFAS) Degradation in a Plasma-Based Water Treatment Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, D.; Lee, S.; Hong, J.; Fletcher, D.F.; McClure, D.; Cook, D.; Cullen, P.; Kavanagh, J.M. Experimental investigations of Per- and Poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) degradation by non-thermal plasma in aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).