Optimizing Operational Parameters for Lithium Hydroxide Production via Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
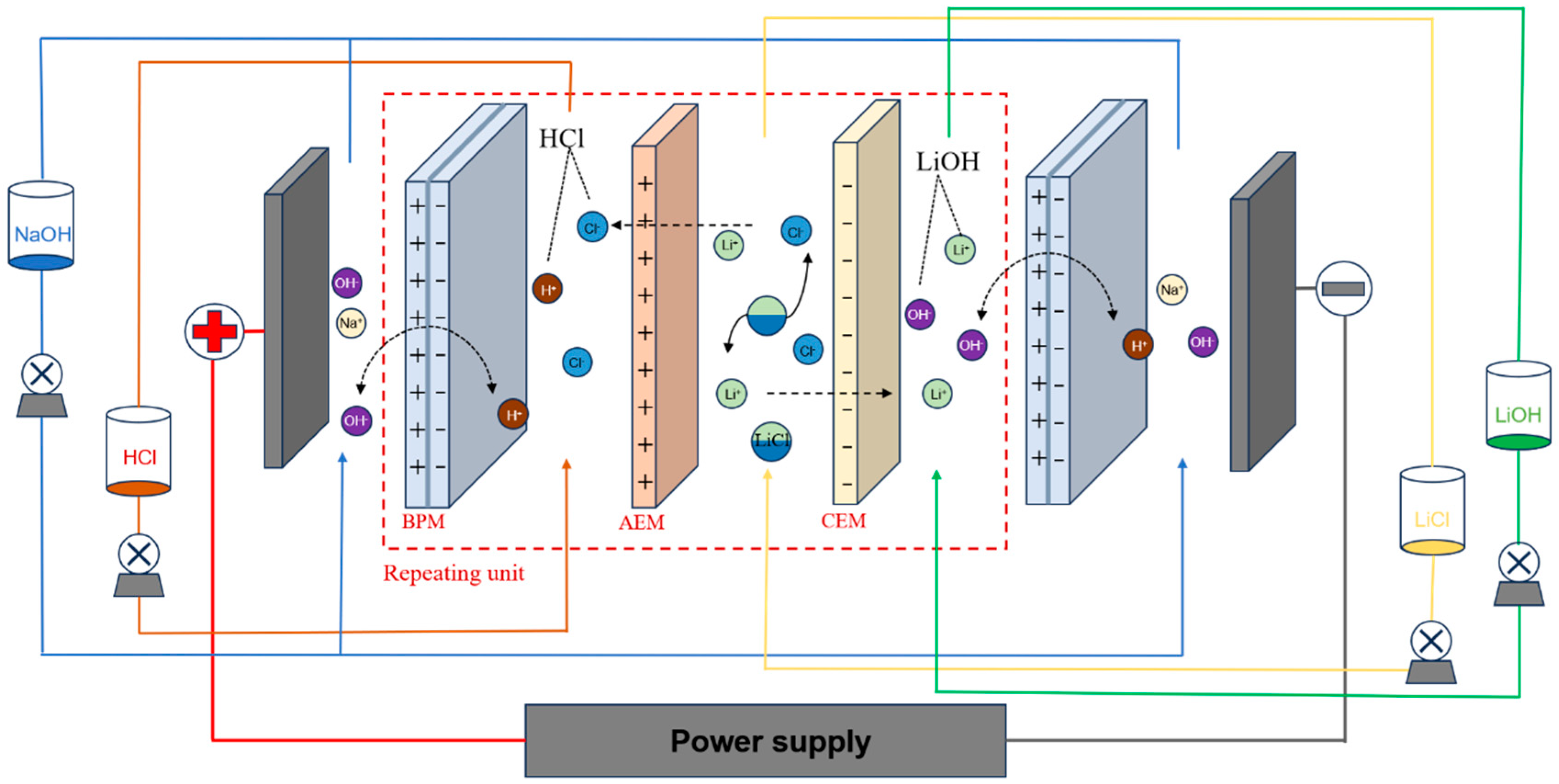
2.2. Measurements of BMED System
2.3. Analyses and Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
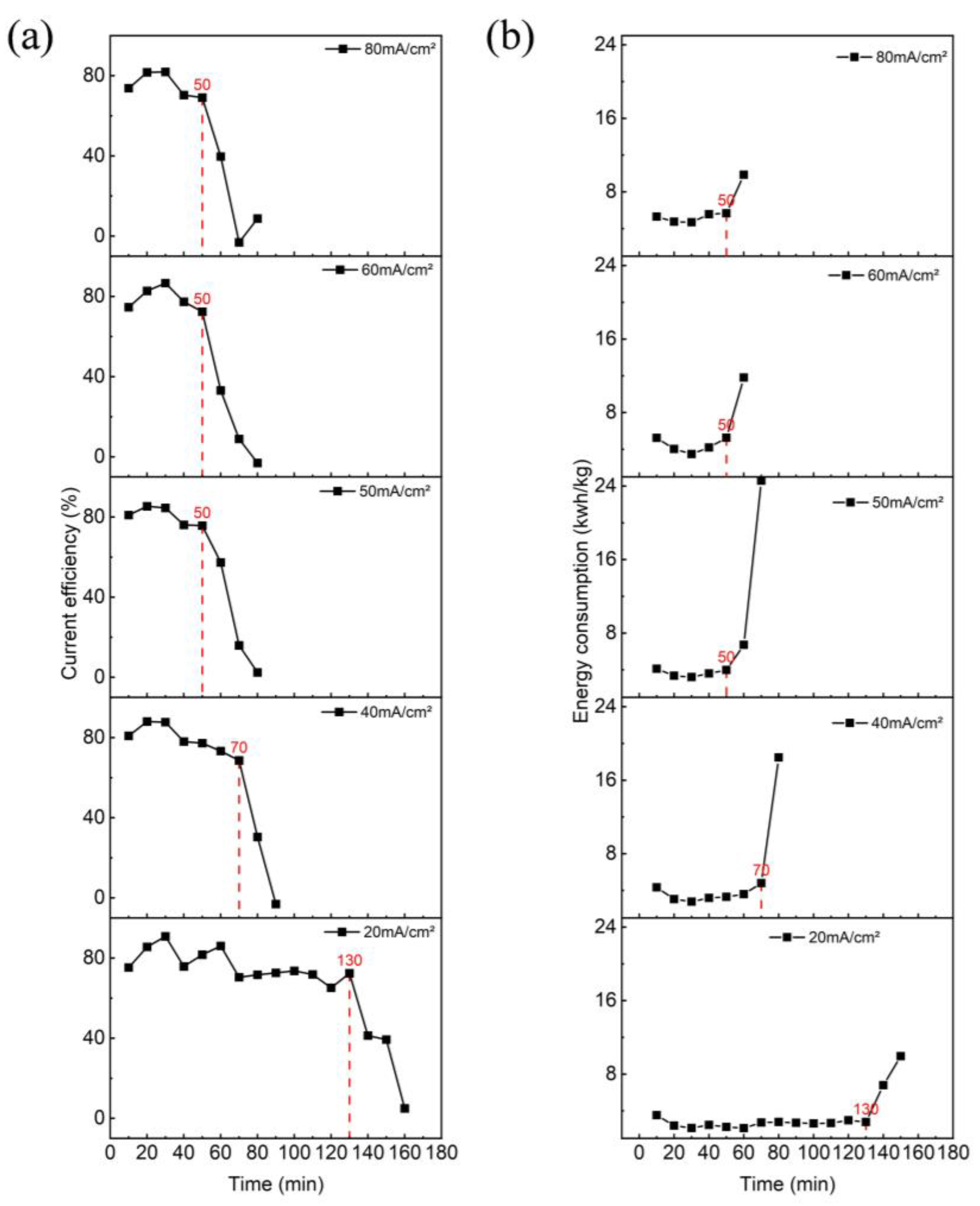
3.1. Effect of Current Density
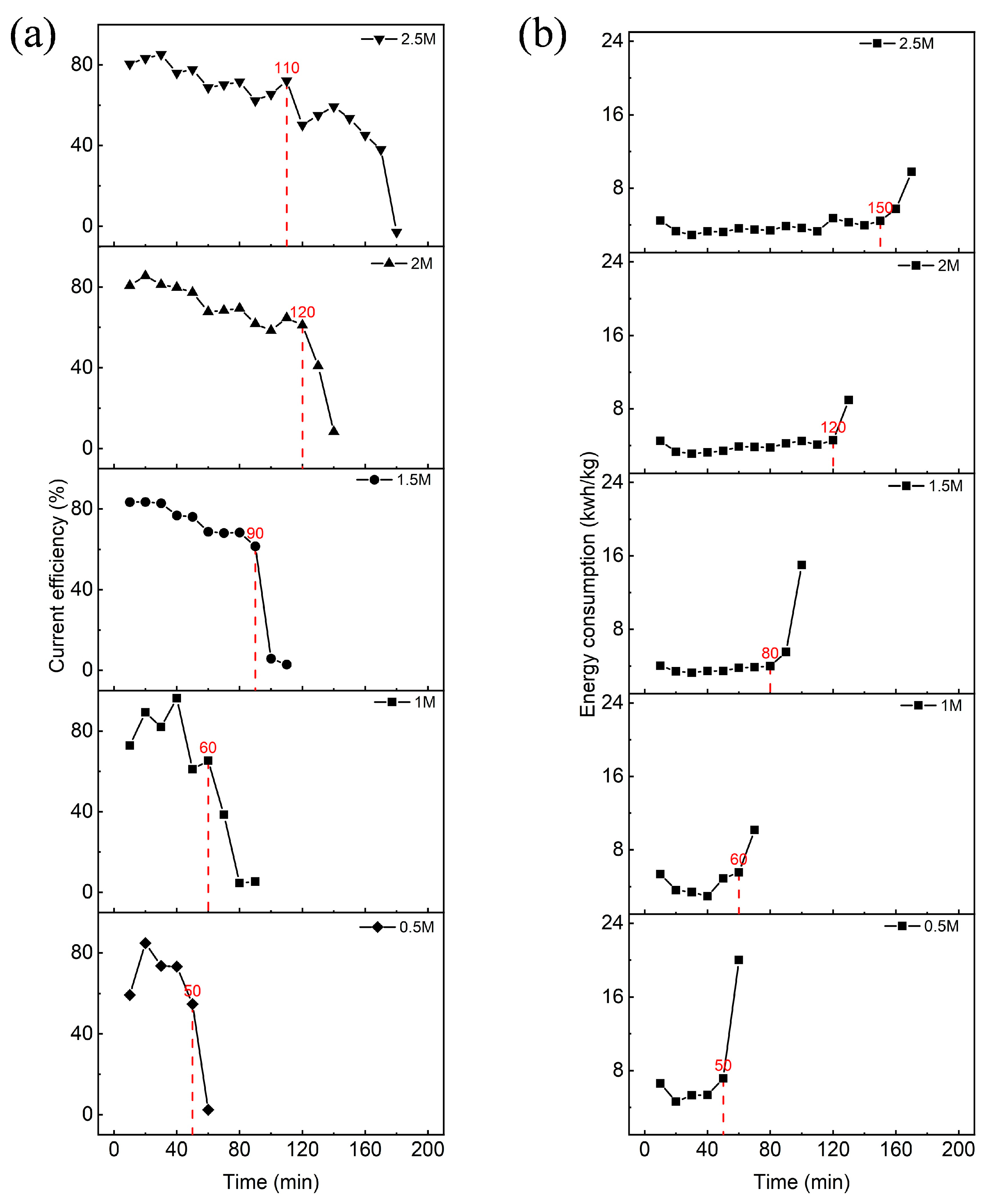
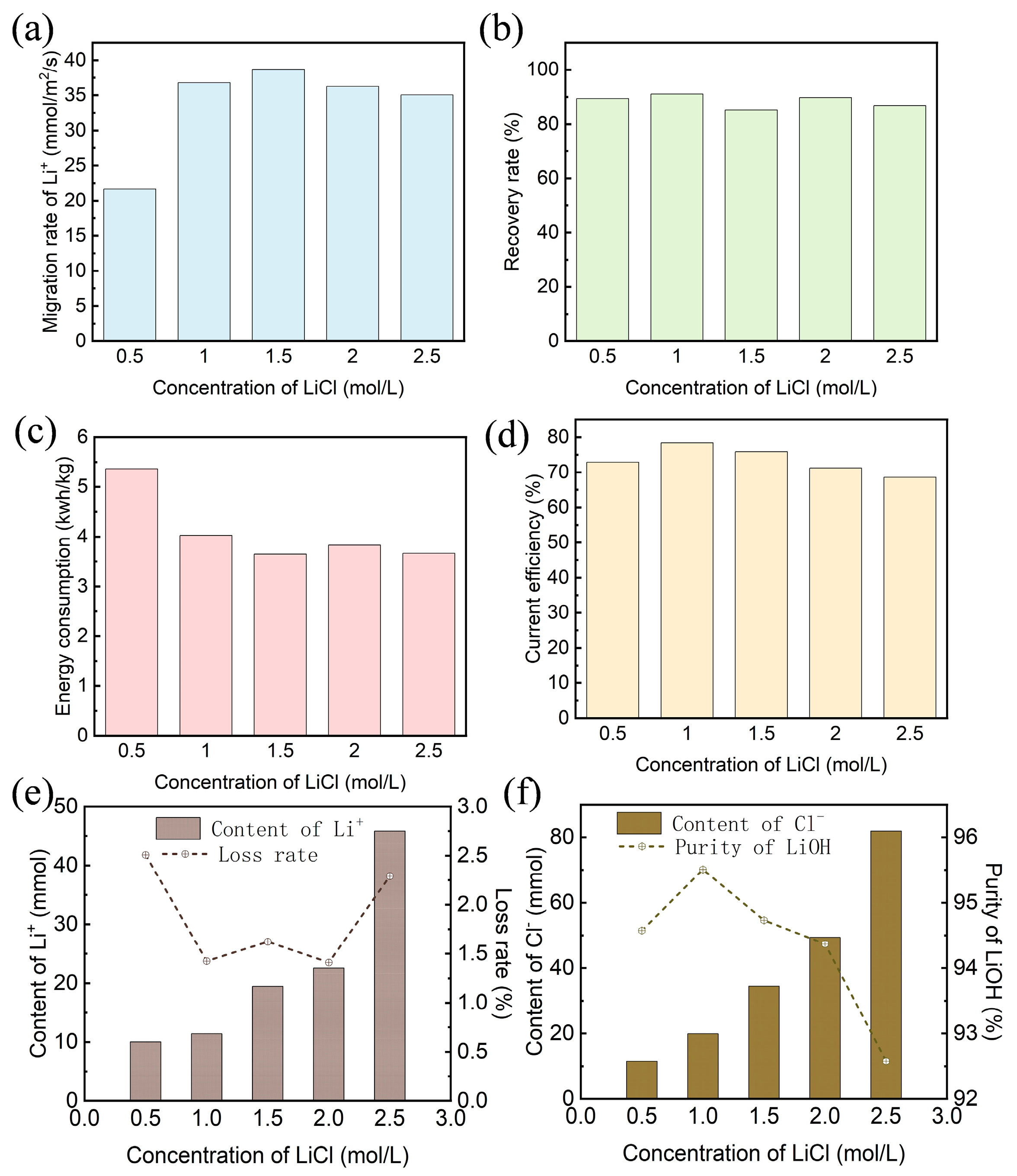
3.2. Effect of Initial Lithium Chloride Concentration
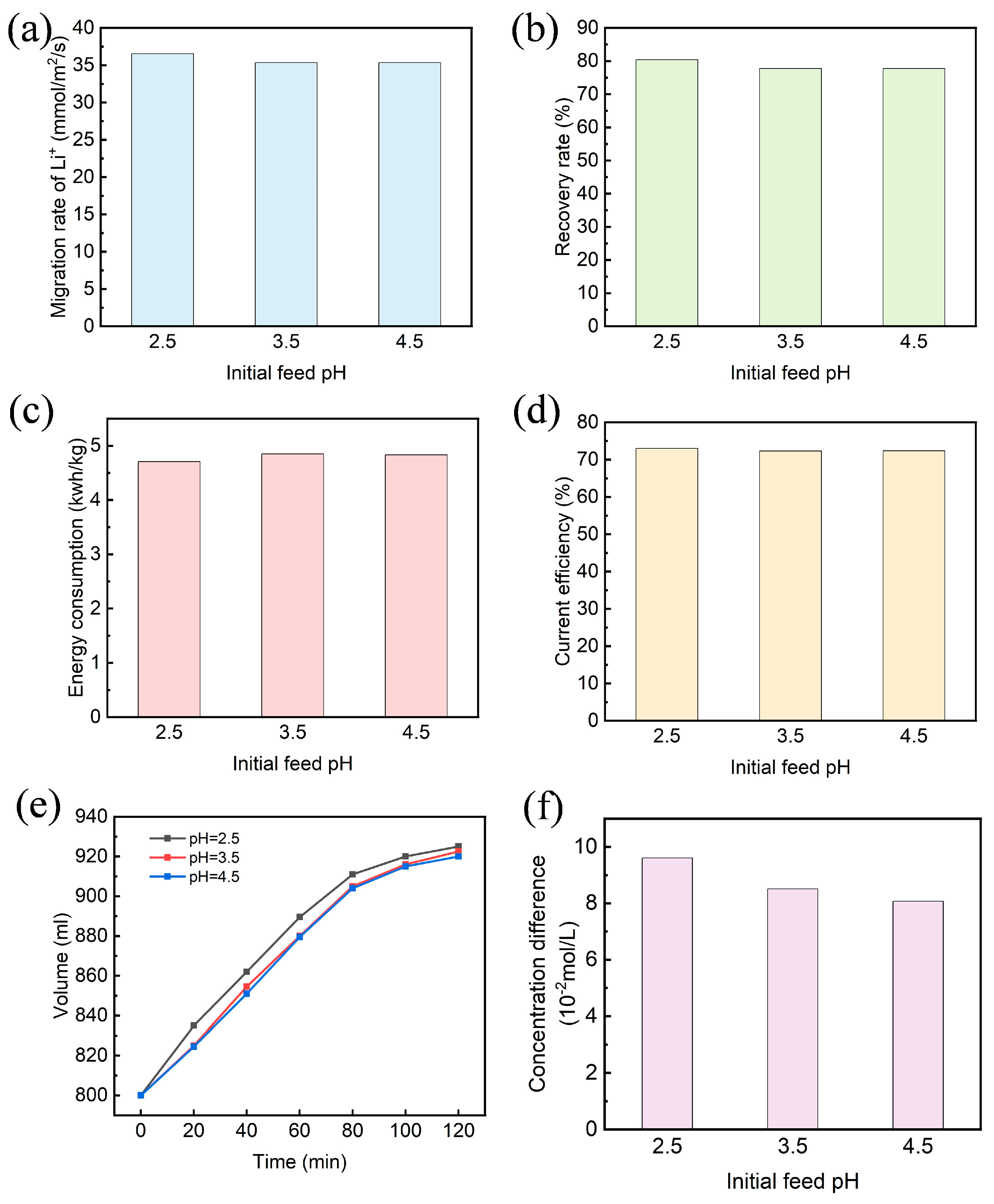
3.3. Effect of Initial Feed pH
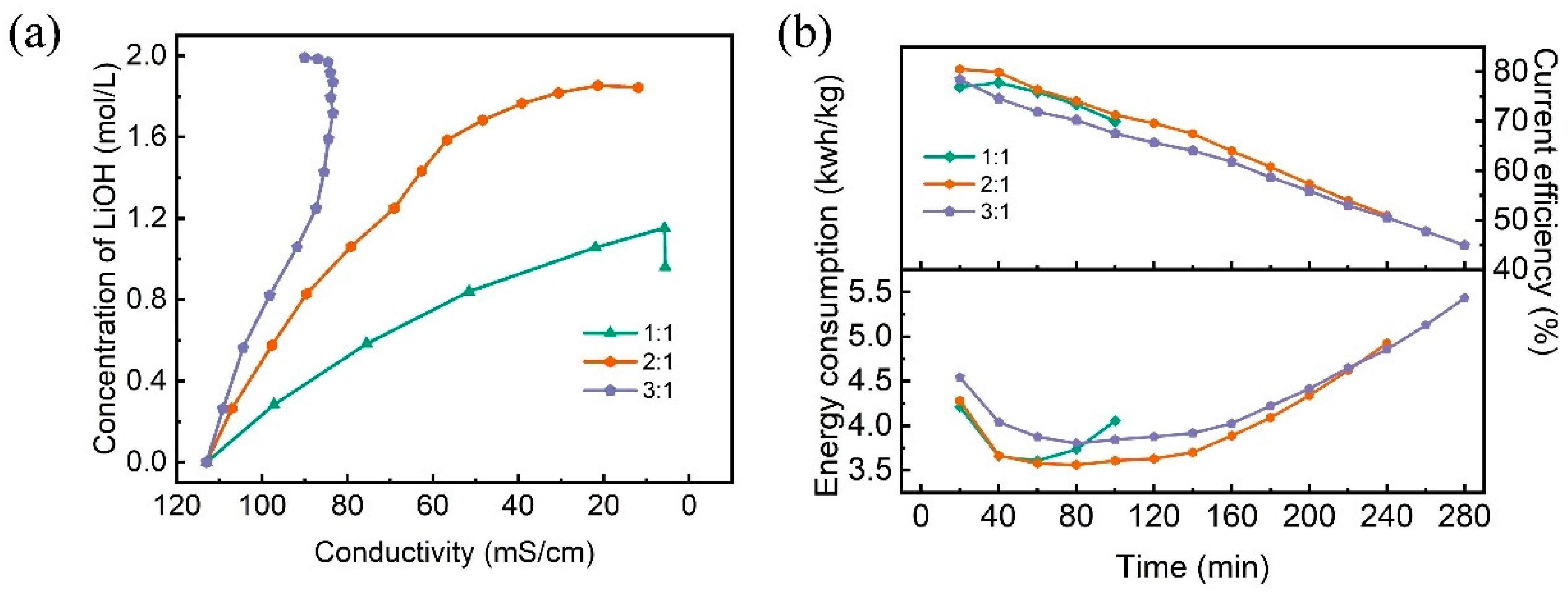
3.4. Effect of the Volume Ratio of the Feed and Base Solution
3.5. Ion Migration
3.6. Economic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoshino, A. The Birth of the Lithium-Ion Battery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5798–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodenough, J.B.; Kim, Y. Challenges for Rechargeable Li Batteries. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Si, W.; Liu, X.; Deng, J.; Xi, L.; Liu, L.; Yan, C.; Schmidt, O.G. Multifunctional Ni/NiO hybrid nanomembranes as anode materials for high-rate Li-ion batteries. Nano Energy 2014, 9, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Zhou, J.; Liang, C.; Pan, A.; Zhang, C.; Tang, Y.; Tan, X.; Liu, J.; Liang, S. MOFs nanosheets derived porous metal oxide-coated three-dimensional substrates for lithium-ion battery applications. Nano Energy 2016, 26, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitch, B.; Yakovleva, M. Study of the Effect of Lithium Precursor Choice on Performance of Nickel-Rich NMC. In ECS Meeting Abstracts; The Electrochemical Society, Inc.: Pennington, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Y. Influence of Li source on tap density and high rate cycling performance of spherical Li[Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3]O2 for advanced lithium-ion batteries. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2011, 16, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Peng, Z. Technology and development of lithium extraction from salt lake brine. J. Salt Lake Res. 2023, 31, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, S.; Sun, H.; Qin, J.; Yu, M.; Su, J.; Li, L.; Zeng, Y. The Advances in Preparation of Lithium Hydroxide. J. Salt Lake Res. 2019, 27, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Azimi, G. Production of Battery Grade Lithium Hydroxide Monohydrate Using Barium Hydroxide Causticizing Agent. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 179, 106115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Yao, K.; Tu, M.; Dong, H.; Jin, P.; Huo, L.; Huang, C. Method for Preparing Battery-Stage Monohydrate Lithium Hydroxide. CN Patent CN200710051016.5, 9 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Feng, H.; Xu, T. Production of Lithium Hydroxide from Lake Brines through Electro–Electrodialysis with Bipolar Membranes (EEDBM). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 6103–6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Ruan, H.; Tang, C.; Yao, L.; Shen, J.; Sotto, A. Study on Recovering High-Concentration Lithium Salt from Lithium-Containing Wastewater Using a Hybrid Reverse Osmosis (RO)–Electrodialysis (ED) Process. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 13481–13490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhao, H.; Wei, X.; Meng, X.; Wu, K.; Liu, Y. A Green and Economical Method for Preparing Potassium Glutamate through Electrodialysis Metathesis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 1486–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnan, F.G. The Theory of Membrane Equilibria. Chem. Rev. 1924, 1, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuer, K.-D. Ion Conducting Membranes for Fuel Cells and other Electrochemical Devices. Chem. Mater. 2013, 26, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ruan, X.; Kentish, S.E.; Li, G.; Xu, T.; Chen, G.Q. Production of lithium hydroxide by electrodialysis with bipolar membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 274, 119026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; Qiu, Y.; Yao, L.; Wu, Q.; Ruan, H.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Shen, J. Preparation of N,N,N-trimethyl-1-adamantylammonium hydroxide with high purity via bipolar membrane electrodialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 205, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongwen, X. Electrodialysis processes with bipolar membranes (EDBM) in environmental protection—A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2002, 37, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaime-Ferrer, J.S.; Couallier, E.; Viers, P.; Rakib, M. Two-compartment bipolar membrane electrodialysis for splitting of sodium formate into formic acid and sodium hydroxide: Modelling. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 328, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Xu, T. Regenerating sodium hydroxide from the spent caustic by bipolar membrane electrodialysis (BMED). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 86, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Du, J.R.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, F.; Ali, M.E.A.; Feng, X. Treatment of Brackish Water RO Brine via Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 3115–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wei, X.; Chen, J.; Jin, J.; Wu, K.; Meng, W.; Wang, K. Recycling Lithium from Waste Lithium Bromide to Produce Lithium Hydroxide. Membranes 2021, 11, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Yan, X.; Zhou, F.; Xu, C.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; He, X. Effect of process conditions on generation of hydrochloric acid and lithium hydroxide from simulated lithium chloride solution using bipolar membrane electrodialysis. SN Appl. Sci. 2022, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhao, Z. Recovery of lithium from spent lithium-ion batteries using precipitation and electrodialysis techniques. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 206, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Tian, B.; Luo, S.; Chi, Y.; Aishajiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M. High-value conversion of waste Na2SO4 by a bipolar membrane electrodialysis metathesis system. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 186, 106556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Pan, J.; Zhou, M.; Xu, Y.; Lin, J.; Shen, J.; Gao, C.; Van der Bruggen, B. Extraction of Amphoteric Amino Acid by Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis: Methionine Acid as a Case Study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 2813–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Gao, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, K.; Xu, T. A green and economical method for preparing lithium hydroxide from lithium phosphate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 280, 119909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xiang, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, H. Preparation of LiOH through BMED process from lithium-containing solutions: Effects of coexisting ions and competition between Na+ and Li+. Desalination 2021, 512, 115126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathmann, H.; Krol, J.J.; Rapp, H.J.; Eigenberger, G. Limiting current density and water dissociation in bipolar membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 125, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Yao, L.; Tang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Shen, J. Integration of selectrodialysis and selectrodialysis with bipolar membrane to salt lake treatment for the production of lithium hydroxide. Desalination 2019, 465, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Fang, Q.; Yan, H.; Wei, X.; Wu, K. Recovery of Acid and Base from Sodium Sulfate Containing Lithium Carbonate Using Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis. Membranes 2021, 11, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, H.; Jiang, C.; Xu, T. A sustainable valorization of neopentyl glycol salt waste containing sodium formate via bipolar membrane electrodialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 254, 117563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T. Simultaneous CO2 capture and amino acid production using bipolar membrane electrodialysis (BMED). J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 542, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson; Elizabeth, K. Gearing up for Genomics Protein Avalanche. (cover story). Chem. Eng. News 2000, 78, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, Z.; Luo, N. Domestic production process and cost analysis of lithium hydroxide. China Met. Bull. 2020, 5, 9–10. [Google Scholar]





| Characteristics | CT-4 | ATD | BP-2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.28 |
| Bursting intensity (MPa) | >0.5 | >1.0 | >0.5 |
| Resistance (0.5 N HCl) (Ω·cm2) | 3.6 | 4.3 | \ |
| Operating temperature (°C) | 25–40 | 25–40 | 25–40 |
| Water dissociation voltage (V) | \ | \ | 0.9–1.3 |
| Operating pH | 0–14 | 0–4 | 0–14 |
| \ | Unit Consumption of Auxiliary Materials (t/t LiOH) | Unit Price of Auxiliary Materials (USD/t LiOH) | Total (USD/t LiOH) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfuric acid | 1.52 | 34.58 | 52.56 |
| Sodium Carbonate | 0.025 | 193.64 | 4.841 |
| Sodium hydroxide | 1.18 | 262.79 | 310.1 |
| Calcium carbonate | 0.6 | 89.9 | 53.94 |
| \ | Unit specific energy consumption | Unit price of energy | Total (USD/t LiOH) |
| Electrical | 3500 (KWh/t LiOH) | 0.1007 (USD/KWh) | 352.45 |
| Coal | 3.15 (t/t LiOH) | 6.92 (USD/t LiOH) | 21.798 |
| Current Density | Concentration of LiCl | Feed pH |
|---|---|---|
| 50 mA/cm2 | 1.5 M | 2.5 or 3.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, G.; Wang, M.; Lin, C.; Xu, C.; Gao, J. Optimizing Operational Parameters for Lithium Hydroxide Production via Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis. Separations 2024, 11, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050146
Wei G, Wang M, Lin C, Xu C, Gao J. Optimizing Operational Parameters for Lithium Hydroxide Production via Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis. Separations. 2024; 11(5):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050146
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Guoxiang, Mengmeng Wang, Chenxiao Lin, Chuan Xu, and Jie Gao. 2024. "Optimizing Operational Parameters for Lithium Hydroxide Production via Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis" Separations 11, no. 5: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050146
APA StyleWei, G., Wang, M., Lin, C., Xu, C., & Gao, J. (2024). Optimizing Operational Parameters for Lithium Hydroxide Production via Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis. Separations, 11(5), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11050146





