Technology for Aiding the Cyanide Leaching of Gold Ores
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Grinding Time Test
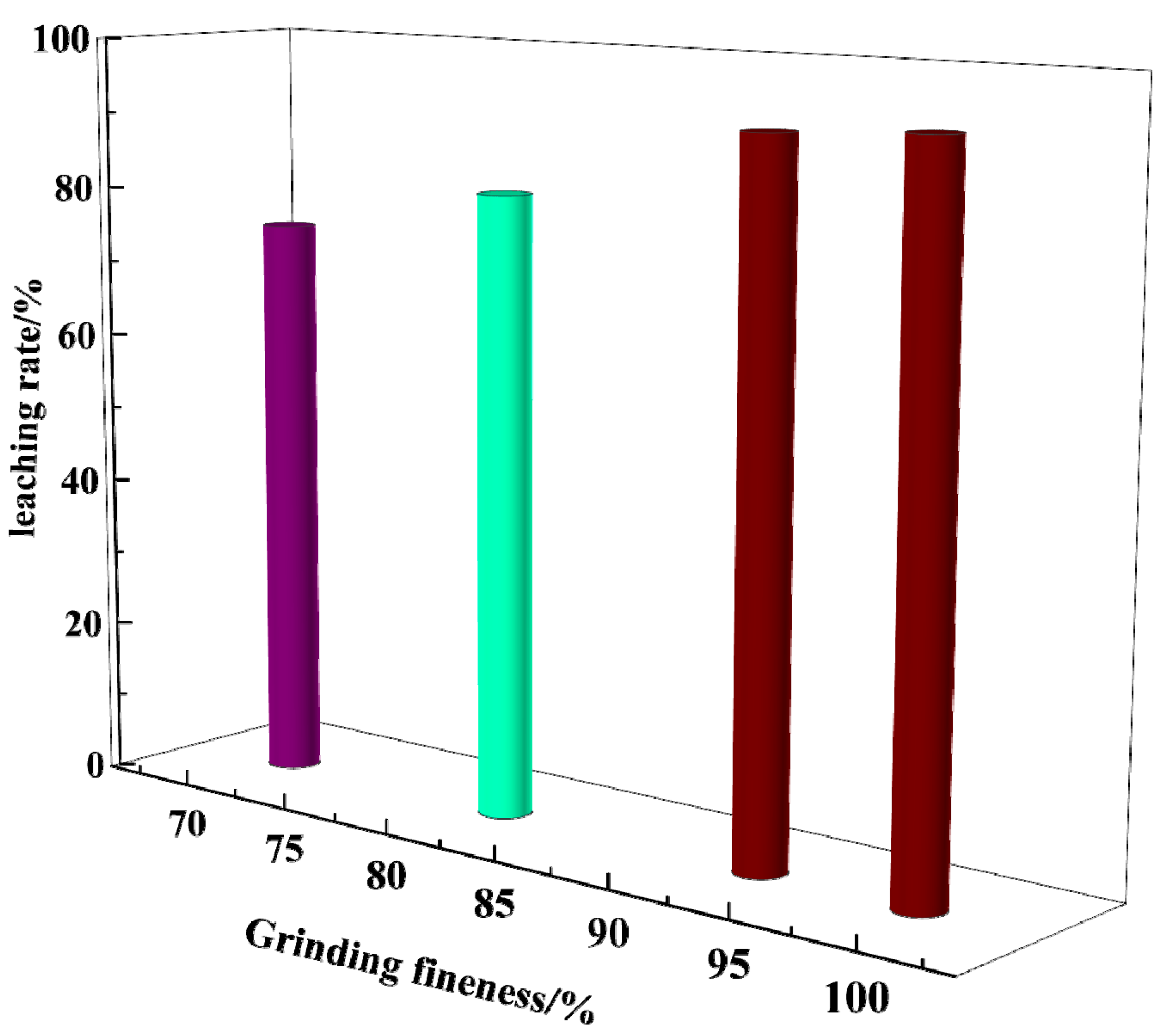
3.2. Effect of Grinding Fineness on Gold Leaching
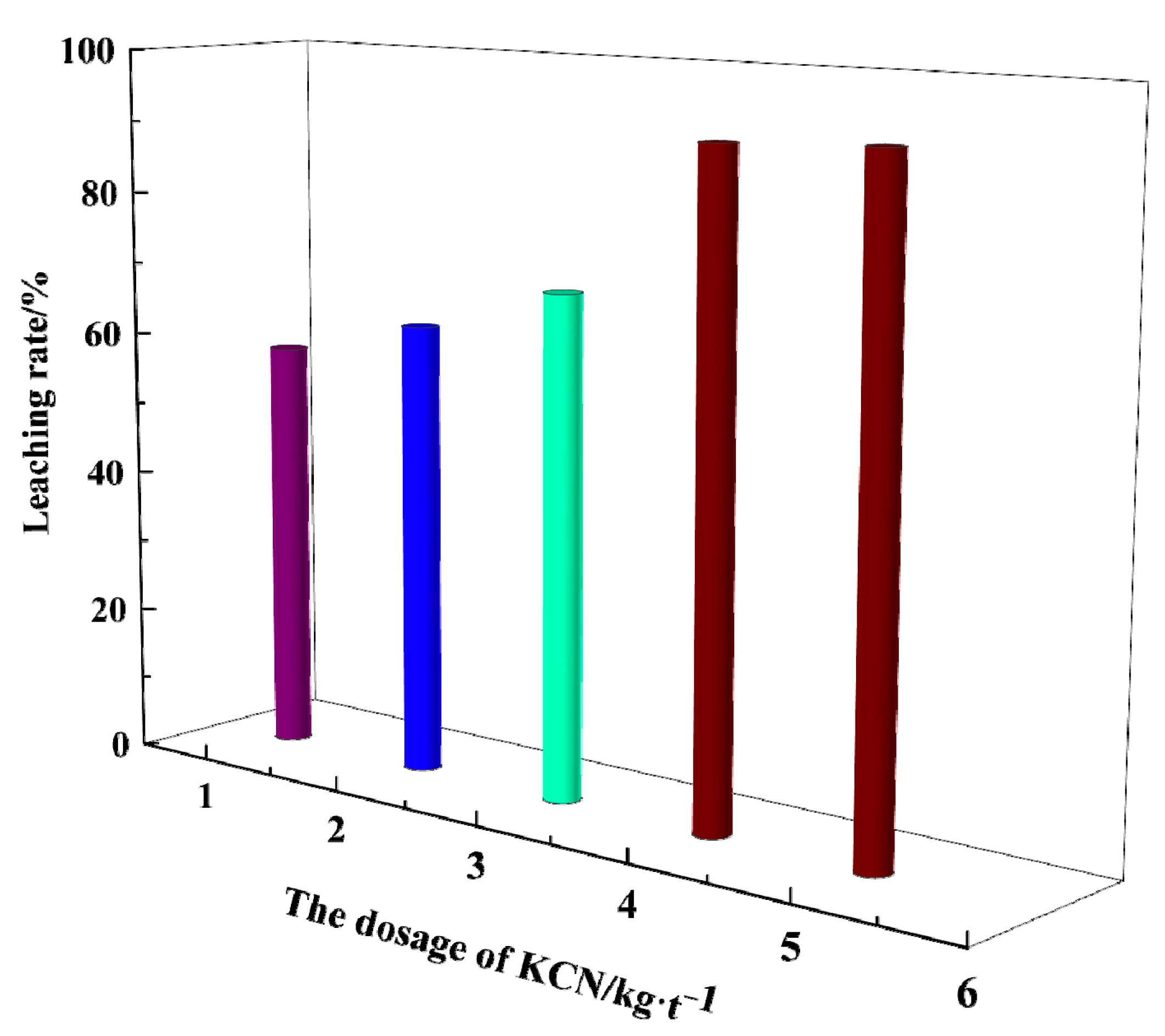
3.3. Effect of Potassium Cyanide Dosage on Gold Leaching
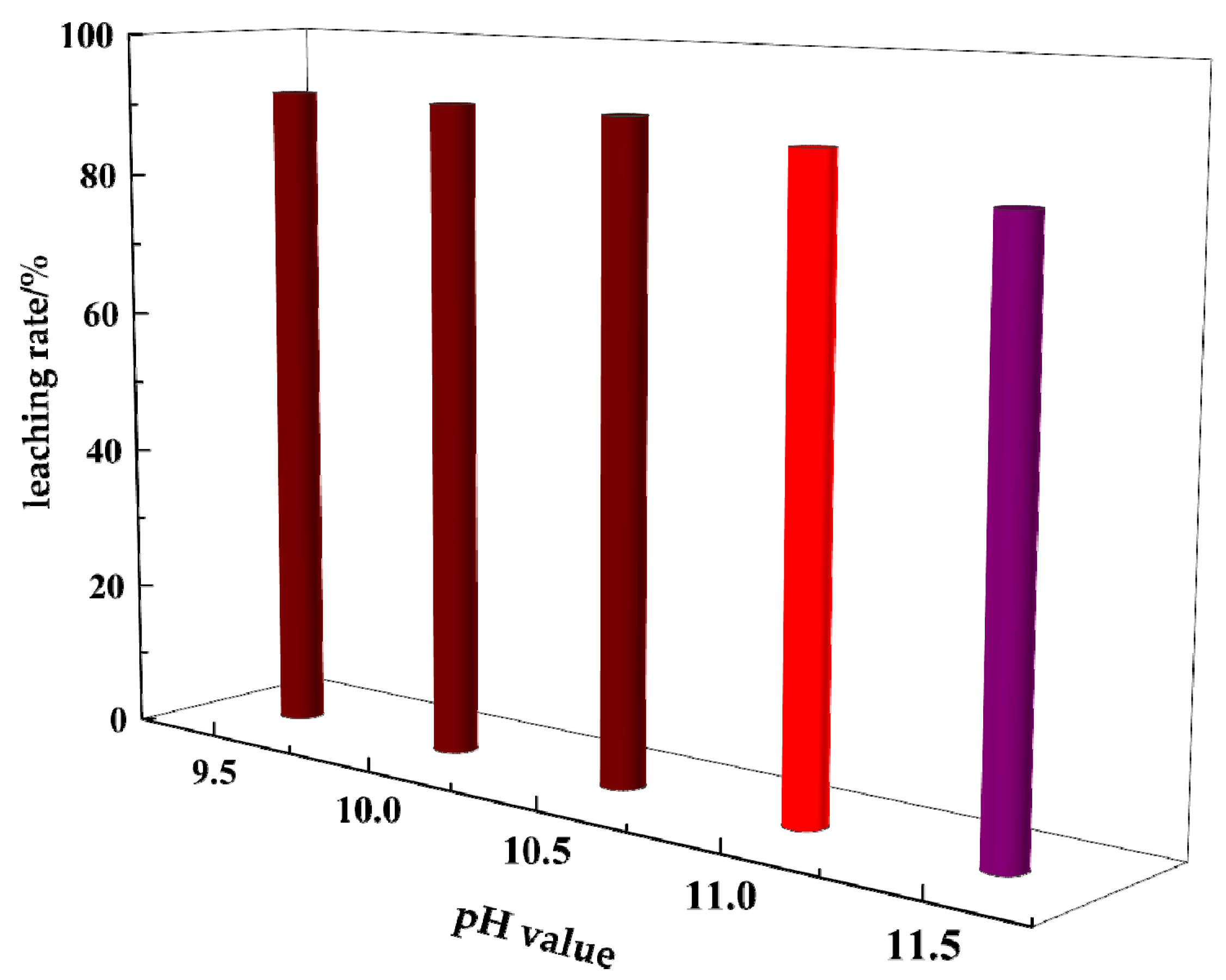
3.4. Effect of pH Value on Gold Leaching
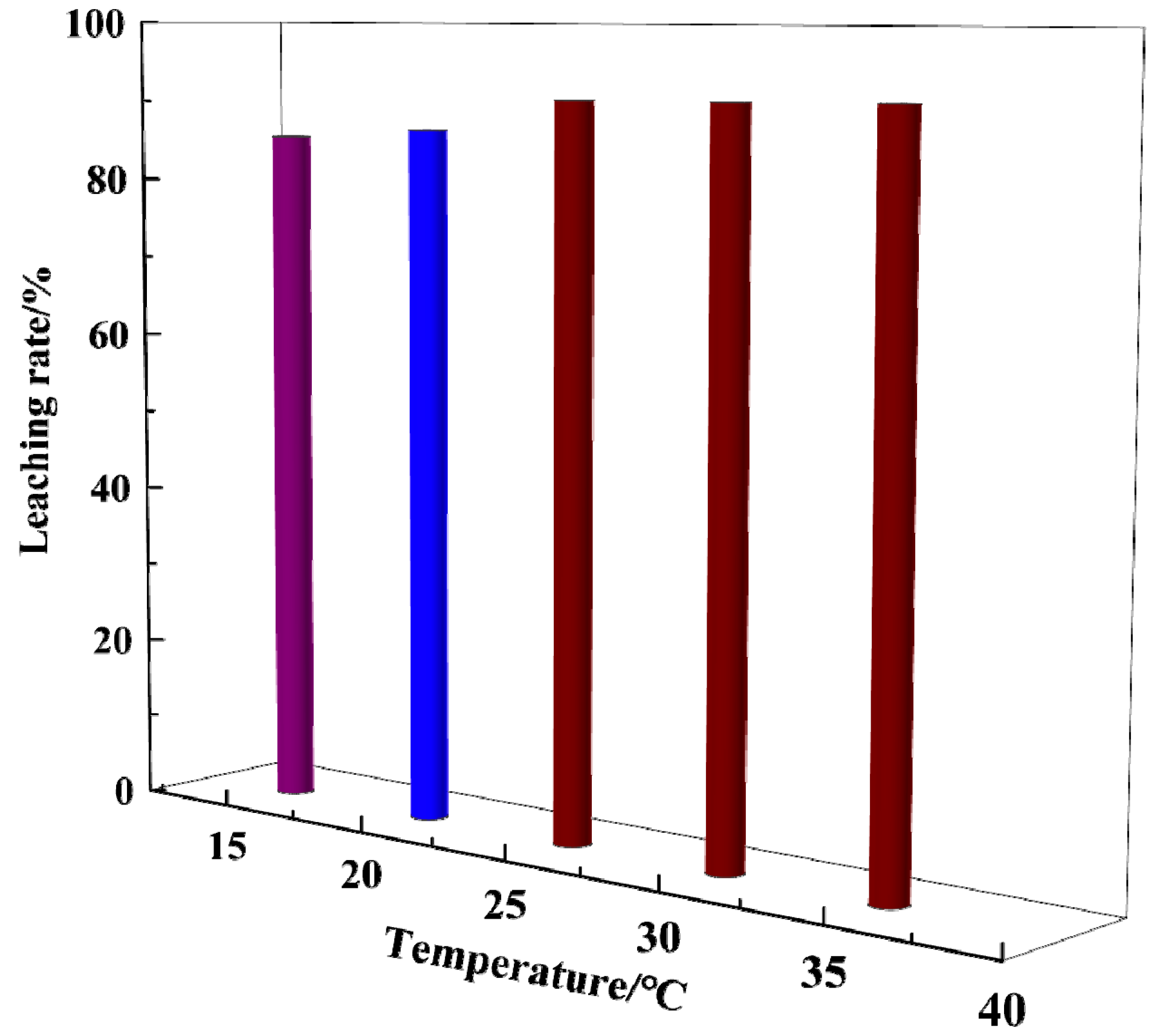
3.5. Effect of Temperature on Gold Dissolution
3.6. Effect of Stirring Speed on Gold Dissolution
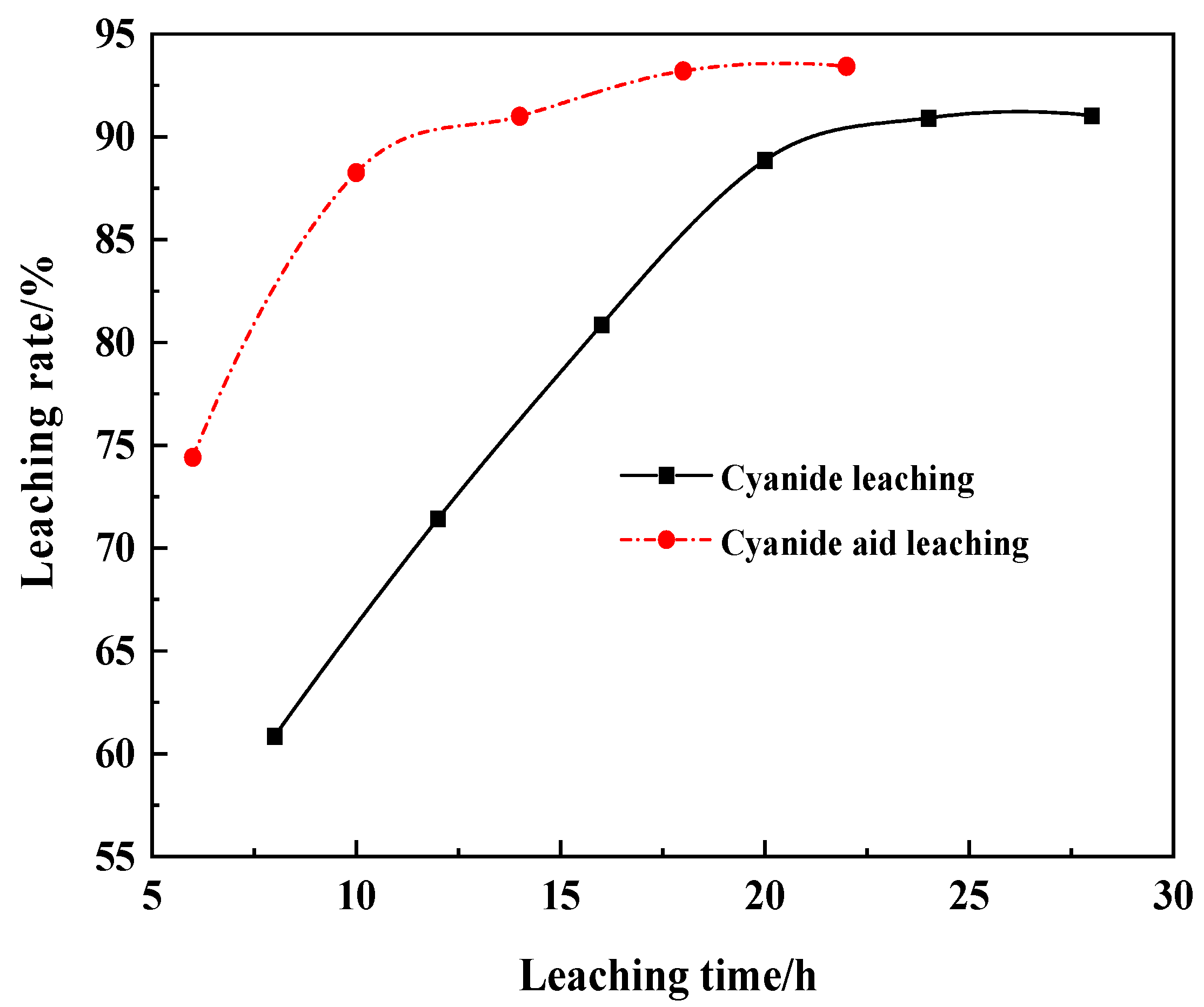
3.7. Effect of Aid-Leaching Agents on Gold Dissolution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Habashi, F. Gold—An historical introduction. In Gold Ore Processing; Project Development and Operations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschênes, G. Advances in the cyanidation of gold. Adv. Gold Ore Process. 2005, 15, 479–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.B.; Li, Q.; Jiang, T.; Jin, Y.S. Cyanide leaching of gold ores by heavy metal ions. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2005, 15, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsner, L. Über das Verhallen verschiedener Metalle in einer wässrigen Lösung von Cyankalium. J. Prakt. Chem. 1846, 37, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodländer, G. Die Chemie des Cyanidverfahrens. Z. Angew. Chem. 1896, 9, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameda, M. Fundamental Studies on Dissolution of Gold in Cyanide Solutions. II: On Equations of Reactions and Effects of Cyanide Strength and Other Variables on Dissolution Rate. Ph.D. Thesis, Tohoku University, Miyagi, Japan, 1949; pp. 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Monhemius, A.J. Recent applications of peroxygen reagents in hydrometallurgy. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 1992, 8, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, A.D.; Safizadeh, F.; Zhang, W.; Ghali, E.; Choi, Y. Active and passive behaviors of gold in cyanide solutions. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 3442–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, D.B.; Nichols, O.; Possingham, H.; Moore, M.; Ricci, P.F.; Noller, B.N. A critical review of the effects of gold cyanide-bearing tailings solutions on wildlife. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, A.; Ghaedrahmati, R. Optimizing and evaluating the operational factors affecting the cyanide leaching circuit of the Aghdareh gold processing plant using a CCD model. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2015, 471, 20150681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, A.D.; Zhang, W.; Ghali, E.; Choi, Y. A study of the electrochemical dissolution and passivation phenomenon of roasted gold ore in cyanide solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 158, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Yang, Y.B.; Huang, Z.C. Influence of copper minerals on cyanide leaching of gold. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2001, 8, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, G. A review of effects of silver, lead, sulfide and carbonaceous matter on gold cyanidation and mechanistic interpretation. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 90, 46–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Breuer, P.L. Leaching and electrochemistry of gold, silver, and gold-silver alloys in cyanide solutions: Effect of oxidant and lead (II) ions. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 133, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, R.G.; Jayaweera, L.D. Arsenic in gold processing. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 1992, 9, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, P.; Abdollahi, H.; Amini, A.; Noaparast, M.; Shafaei, S.Z.; Habashi, F. Cyanidation of gold ores containing copper, silver, lead, arsenic and antimony. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2010, 95, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, Q.; Xu, B.; Jiang, T. Intensification Behavior of Mercury Ions on Gold Cyanide Leaching. Metals 2018, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, M.I.; Breuer, P.L. The cyanide leaching of gold in solutions containing sulfide. Miner. Eng. 2000, 13, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, J.; Shen, Z. [Au(CN)2]— Adsorption on a Graphite (0001) Surface: A First Principles Study. Minerals 2018, 8, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choma, J.; Dziura, A.; Jamioła, D.; Nyga, P.; Jaroniec, M. Preparation and properties of silica–gold core–shell particles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 373, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadnejad, S.; Provis, J.L.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Computational modelling of interactions between gold complexes and silicates. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2017, 1101, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondos, P.D.; Deschênes, G.; Morrison, R.M. Process optimization studies in gold cyanidation. Hydrometallurgy 1995, 39, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Deng, Z.; Dong, P. Study on the Intensification Cyanide Leaching of High Arsenic Bearing Gold Concentrate. Nonferrous Met. Eng. 2018, 8, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Oraby, E.A.; Eksteen, J.J.; Tanda, B.C. Gold and copper leaching from gold-copper ores and concentrates using a synergistic lixiviant mixture of glycine and cyanide. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 169, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eksteen, J.J.; Oraby, E.A. The leaching and adsorption of gold using low concentration amino acids and hydrogen peroxide: Effect of catalytic ions, sulphide minerals and amino acid type. Miner. Eng. 2015, 70, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphulu, M.C.; Scurrell, M.S. Cyanide leaching of gold catalysts. Catal. Commun. 2015, 67, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, L.; Chimenos, J.M.; Fernandez, M.A.; Segarra, M.; Espiell, F. Gold cyanidation with potassium persulfate in the presence of a thallium (I) salt. Hydrometallurgy 2000, 54, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Yin, W.; Huang, S.; Xue, J.; Zuo, W. Enhancement of gold agitation leaching by HPGR comminution via microstructural modification of gold ore particles. Miner. Eng. 2020, 159, 106639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, S. Process development metallurgical studies for gold cyanidation process, Miner. Metall. Process. 2016, 33, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Dai, S.J.; Zhang, Z.J.; Li, J.H. Study on grinding effects while steel forging as grinding medium. Min. Process. Equip. 2017, 3, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Hu, X.; Zi, F.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Rapid gold cyanidation from a sulfur-high and arsenic-high micro-fine concentrate via facile two-stage roasting pre-treatment. Miner. Eng. 2022, 190, 107938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evdokimov, S.I.; Golikov, N.S.; Pryalukhin, A.F. Studying Flotation of Gold Microdispersions with Carrier Minerals and Pulp Aeration with a Steam–Air Mixture. Minerals 2024, 14, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ren, Y.; Qu, G.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ning, P. A review of environmental functional materials for cyanide removal by adsorption and catalysis. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 157, 111298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzila, A.N.; Moyo, T.; Petersen, J. A Study on the Applicability of Agitated Cyanide Leaching and Thiosulphate Leaching for Gold Extraction in Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining. Minerals 2005, 2022, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dove, P.M.; Han, N.; De Yoreo, J.J. Mechanisms of classical crystal growth theory explain quartz and silicate dissolution behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15357–15362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.H.; Li, X.A.; Dai, S.J. Electrochemical Influence of Quartz on Cyanide Leaching of Gold. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 739, 136997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
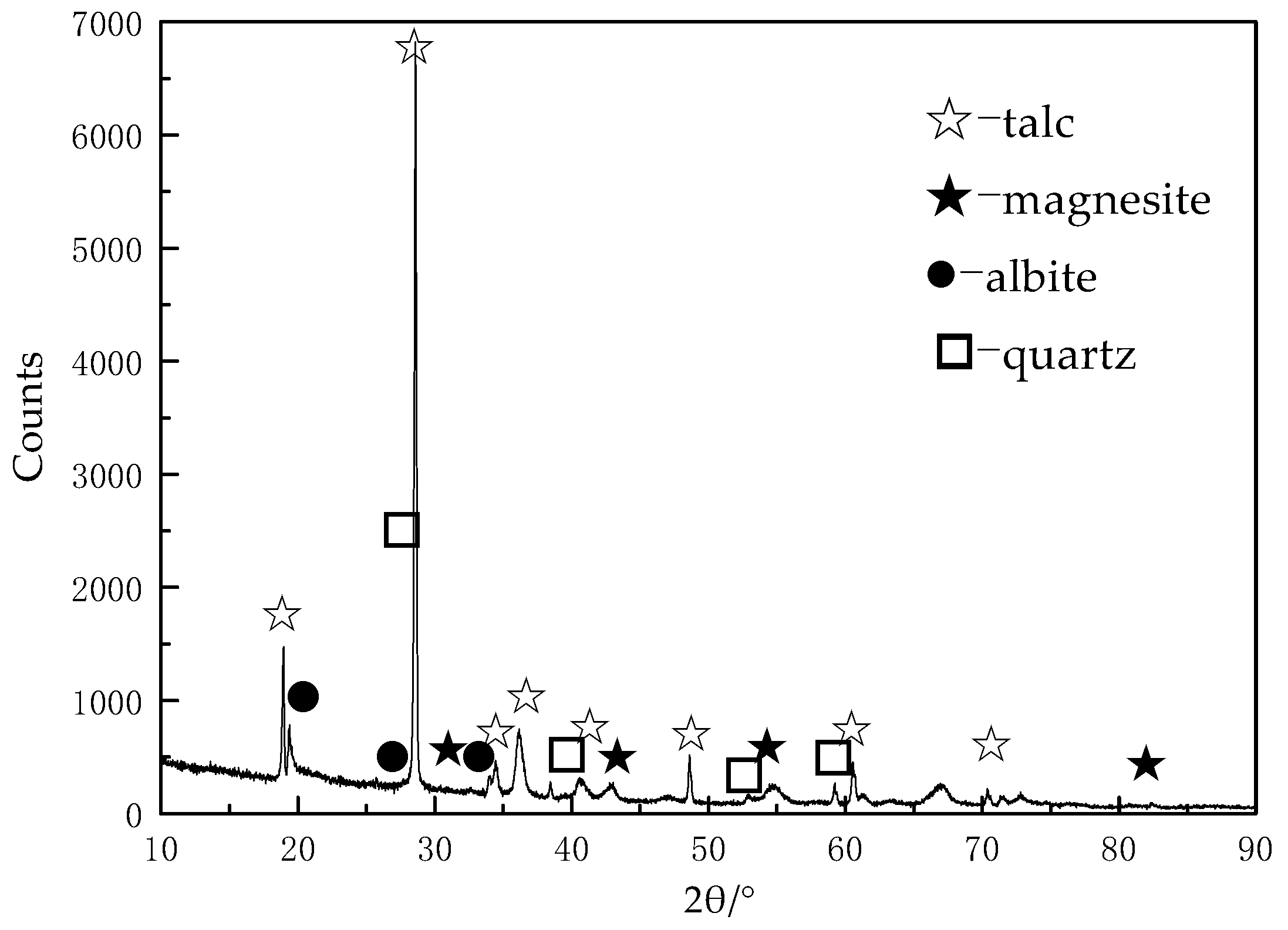
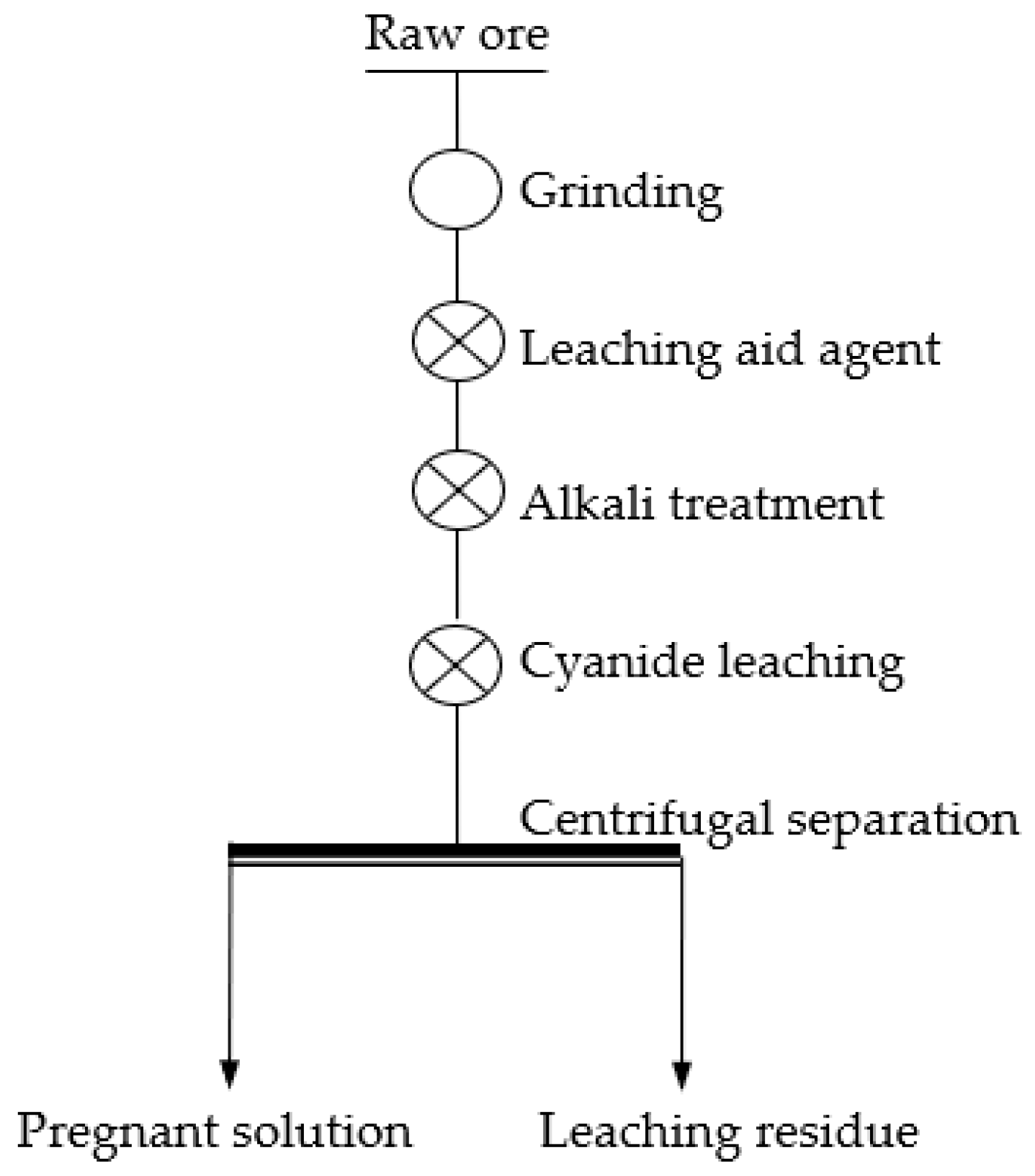


| Name | Conical Ball Mill |
|---|---|
| Model | XMQ Φ-240 × 90 |
| Feeding size/mm | ≤3 |
| Discharge/mesh | 200 |
| Reference grinding capacity/kg | ≤1 |
| Cylinder volume/L | 6.25 |
| Motor power/kW | 0.55 |
| Composition | Na2O | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | P2O5 | SO3 | K2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| content/% | 0.035 | 0.193 | 6.872 | 90.222 | 0.022 | 0.194 | 0.683 |
| Composition | CaO | TiO2 | Cr2O3 | MnO | Fe2O3 | CuO | ZnO |
| content/% | 0.195 | 0.085 | 0.019 | 0.013 | 1.356 | 0.008 | 0.021 |
| Composition | As2O3 | Rb2O | SrO | ZrO2 | BaO | Ag | PbO |
| content/% | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.003 | 0.023 | 0.028 | 0.016 |
| Composition | Au * | Zn | TFe | MgO | Al2O3 | CaO | S | SiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| content/% | 1.32 | 0.008 | 1.597 | 0.185 | 6.876 | 0.172 | 0.112 | 91.050 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.; Dai, S.; Deng, J.; Que, S.; Zhou, Y. Technology for Aiding the Cyanide Leaching of Gold Ores. Separations 2024, 11, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11080228
Han J, Dai S, Deng J, Que S, Zhou Y. Technology for Aiding the Cyanide Leaching of Gold Ores. Separations. 2024; 11(8):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11080228
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Jiahong, Shujuan Dai, Jiushuai Deng, Shandong Que, and Yugao Zhou. 2024. "Technology for Aiding the Cyanide Leaching of Gold Ores" Separations 11, no. 8: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11080228
APA StyleHan, J., Dai, S., Deng, J., Que, S., & Zhou, Y. (2024). Technology for Aiding the Cyanide Leaching of Gold Ores. Separations, 11(8), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11080228








