Advancements in Microextraction by Packed Sorbent: Insights into Sorbent Phases and Automation Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Microextraction by Packed Sorbent (MEPS)
3. Synthetic Strategies: Optimizing MEPS with Tailored Sorbents
| Analyte | Sample | Sorbent | Instrumentation | LOD | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n-propyl gallate | Sesame oil | MIP | Digital image colorimetry (DIC) | 0.03 µg mL−1 | [30] |
| Sulfonylureas herbicides | Corn | MIP | LC-ToF | 2.5 µg kg−1 | [31] |
| Cocaine | Urine | MIP | LC-DAD | 0.025 µg mL−1 | [32] |
| Fipronil and fluazuron | Drinking water and veterinary clinic wastewater | MMIP | LC-DAD | - | [33] |
| Pesticides | Apple juice | Core@mMIP | LC/UV | 0.005 µg mL−1 | [34] |
| Caffeine | Soft and energy drinks | MIP | LC-UV | 1 µg mL−1 | [35] |
| Cannabinoids | Human urine | MIP | LC-MS/MS | 1–5 ng mL−1 | [19] |
| Estrogens | Human urine | MIP | LC-DAD | - | [36] |
| Levofloxacin | Plasma | DES-MIP | LC-DAD | 0.012 µg mL−1 | [37] |
| Dinotefuran | Water and artificial saliva | MIP | LC-DAD | - | [38] |
| Mandelic acid | Urine | MIP | LC-UV | 0.06 µg mL−1 | [39] |
| trans,trans-muconic acid | Urine | MIP | LC-UV | 0.015 µg mL−1 | [40] |
| Dexamethasone, carbamazepine and naproxen | Urine | MI-IPN | LC-UV | 1.3–1.5 µg L−1 | [41] |
| Clenbuterol | Pork | SMIPs | LC-UV | 0.009 µg kg−1 | [42] |
| Fluoroquinolone | Wastewater | MIP | LC-MS/MS | 0.5–3.8 ng L−1 | [43] |
| Estrogenic compounds | Water | MIP | GC-MS | 1.3–22 ng L−1 | [44] |
| Sarcosine | Urine and plasma | DMIP | LC-MS/MS | 1.0 ng mL−1 | [45] |
| Hippuric acid | Urine and plasma | MISM | LC-MS/MS | 0.30 nmol L−1 | [46] |
| Triazines | Corn | MIP | LC-ESI-TOF | 3.3 µg kg−1 | [47] |
| Local anesthetic drugs | Urine and plasma | MIP | LC-MS/MS | 1.0 nmol L−1 | [48] |
| Parabens | Blood | 3D Co3O4/C@HCNFs | LC-MS/MS | 0.1–0.2 ng mL−1 | [49] |
| BTEX biomarkers | Urine | Fe3O4@TbBd nanobeads | LC-UV | 0.02–0.5 µg mL−1 | [50] |
| PAHs | Soil | Amino ethyl-functionalized SBA-15 | LC-UV/Vis | 0.014–0.083 ng g−1 | [51] |
| NSAIDs | Urine | Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) of nickel and iron | LC-UV | 1–10 ng mL−1 | [52] |
| Mandelic acid | Urine | MOF-5@ Fe3O4-NH2 and MOF-5@ SBA-15 | LC-UV/Vis | 0.05 µg mL−1 | [53] |
| Phthalate ester | Water | Nano-hydroxyapatite | GC-FID | 0.02–0.1 ng mL−1 | [54] |
| Antidepressants | Urine | PDA-Ag-Ppy nanocomposite | GC-MS | 0.03–0.05 µg L−1 | [55] |
| Beta-blocker drugs | Saliva, plasma, and urine | Chitosan@MOF-199 | LC-UV | 1.5–4.5 µg L−1 | [56] |
| Nitroimidazoles | Water | MIL-101(Cr)/cellulose aerogel/melamine sponge composite | LC-MS/MS | 8.25–16.33 ng L−1 | [57] |
| Parabens | Vegetable oils | HKUST-1(Cu) | LC-MS/MS | - | [58] |
| Methylhippuric acids | Urine | MIL-53-NH2(Al) | LC-UV | 0.005 µg mL−1 | [59] |
| Opiates | Urine | COF-PPy-CTAB | LC-UV | 0.1–1 µg L−1 | [60] |
| BTEX biomarkers | Urine | Hollow polymer nanospheres and Fe3O4@TFPA-Bd-COF | LC-UV | 0.02–0.5 µg mL−1 | [61] |
| Pesticides | Coffee | ILz/Si@GO | GC-MS/MS | [62] | |
| Isoflavones | Soy-based juice | β-CD@GO@Si | LC-MS/MS | 0.5–1.5 µg L−1 | [63] |
| Local anesthetic drugs and metabolites | Plasma | PAN/GO nanofibers | LC-MS/MS | 0.25–2.5 nmol L−1 | [64] |
| Carbamate pesticides | Juice | RGO–ZnO nanocomposite | LC-UV | 0.23–1.21 ng mL−1 | [65] |
| Organophosphorus pesticides | Water | GO/PA/cellulose paper | GC-FID | 0.2–1 µg L−1 | [66] |
| Local anesthetics | Plasma and saliva | rGO | LC-MS/MS | 2–4 nmol L−1 | [67] |
| Tetracyclines | Milk | G-Si | LC-MS/MS | 0.03–0.21 µg L−1 | [68] |
| Parabens | Breast milk | prGO/Mg-Al LDH | LC-UV | 3–5 µg L−1 | [69] |
| Phthalate esters | Water | CNT/CNF-G | GC-FID | 1–10 ng mL−1 | [70] |
| Parabens | Water | Si-G | LC-MS/MS | 0.06–0.09 µg L−1 | [71] |
| Benzenes and phenols | Water | g-C3N4-IL@HNT | LC-UV | 0.5–1 µg L−1 | [72] |
| Metanephrines | Plasma | Porous graphitic carbon | HILIC-MS/MS | 12.3 pg mL−1 | [73] |
| Antipsychotics | Plasma | Restricted access carbon nanotubes | LC-MS/MS | - | [74] |
| Organochlorine pesticides | Water | Carboxyl-purified multiwalled carbon nanotubes | GC-MS | 0.02–0.19 ng mL−1 | [75] |
| Local anesthetics | Plasma | CarbonX® COA | LC-MS/MS | 1 nmol L−1 | [76] |
| Leukotriene B4 | Urine | Porous graphitic carbon | LC-PDA | 0.37 ng mL−1 | [77] |
| Beta-blockers | Plasma | Carbon-XCOS | LC-MS/MS | - | [78] |
| Rosmarinic acid | Rosmarinus officinalis L. | CMK-3 nanoporous carbon | LC-UV/Vis | 0.059 µg mL−1 | [79] |
| Bisphenols | Rat plasma | CMK-3 nanoporous carbon | LC-UV | 0.25–4.7 µM | [80] |
3.1. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs)
3.2. Nanomaterials
3.3. Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs) and Covalent Organic Frameworks (COFs)
3.4. Graphene-Based Materials (GBMs)
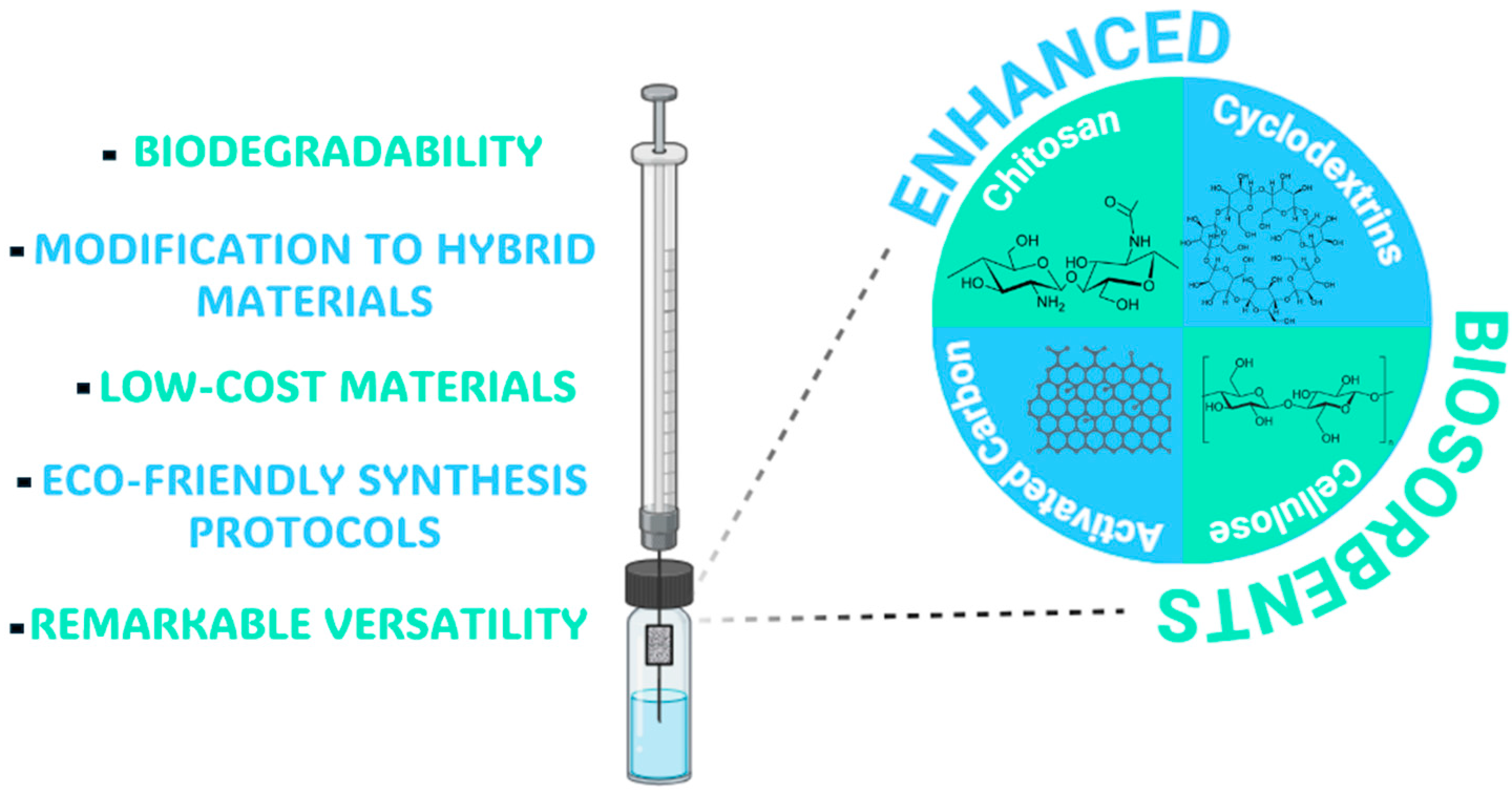
4. Greening Sample Preparation: Natural Biosorbents for MEPS Enhancement
4.1. Cyclodextrins (CDs)
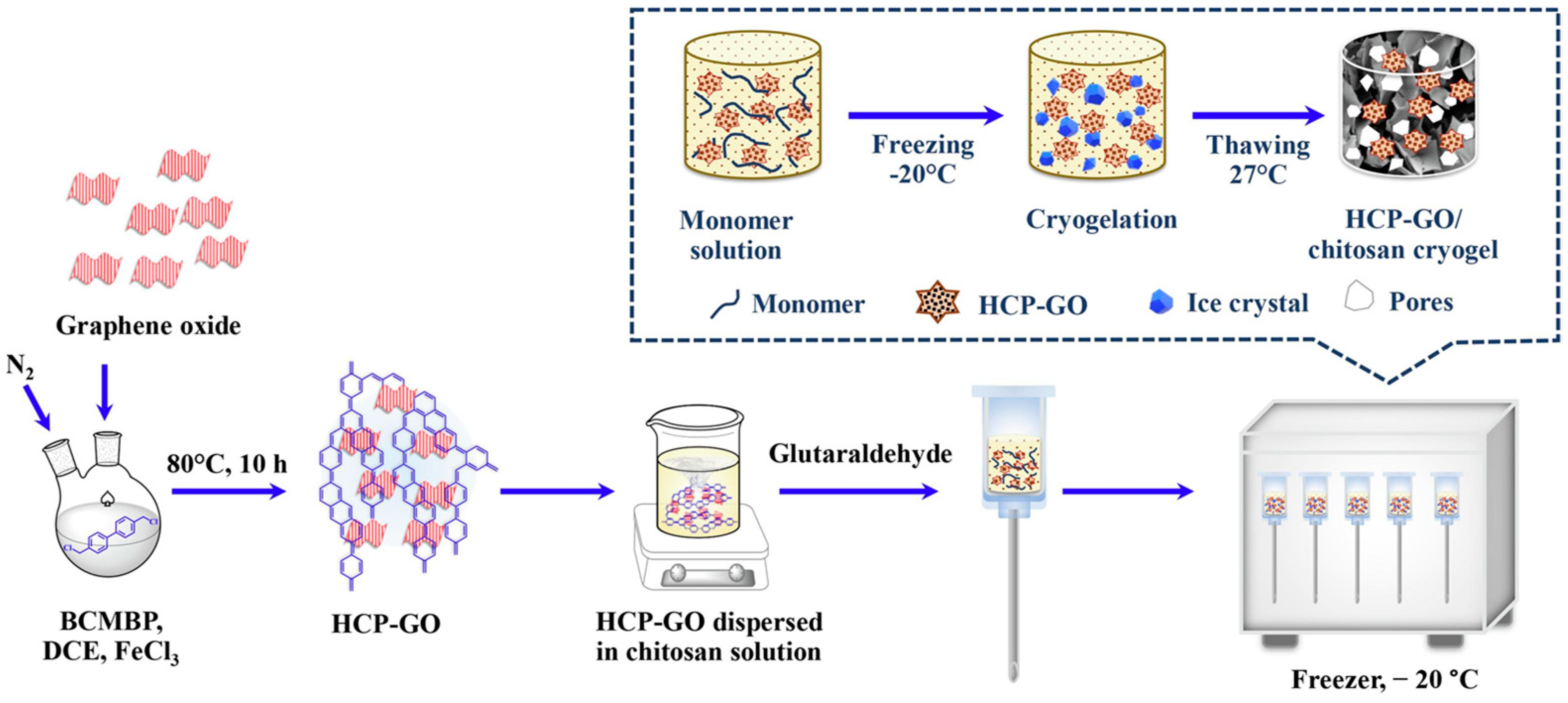
4.2. Chitosan (CS)
4.3. Other Bio-Based Materials
| Biopolymer | Advantages | Drawbacks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan | Biodegradability, non-toxicity, high adsorption capability, easily modified. | Low solubility in neutral and alkaline pH; poor thermal and mechanical stability. | [118,119] |
| Cyclodextrins | Biodegradability, non-toxicity, host–guest chemistry, enhanced selectivity due to e large recognition cavities. | Partial solubility in water. | [118,119,120] |
| Cellulose | Biodegradability, non-toxicity, excellent mechanical proprieties, remarkable porosity, low density, high adsorption capacity, and low-cost material. | Hydrophobic matrix. | [121,122] |
| Natural Activated Carbon | Biodegradability, non-toxicity, high porous material, low-cost material, excellent mechanical proprieties. | Impurities from the biomass, pore size distribution, and the activation process can involve using chemicals and be energy-consuming. | [123] |
| Gelatin | Biodegradability, non-toxicity, low-cost material, and a high abundance of organic functional groups allow its modification and combination with different materials. | Poor thermal stability and chemical resistance, considerable fast degradability in water. | [116,124] |
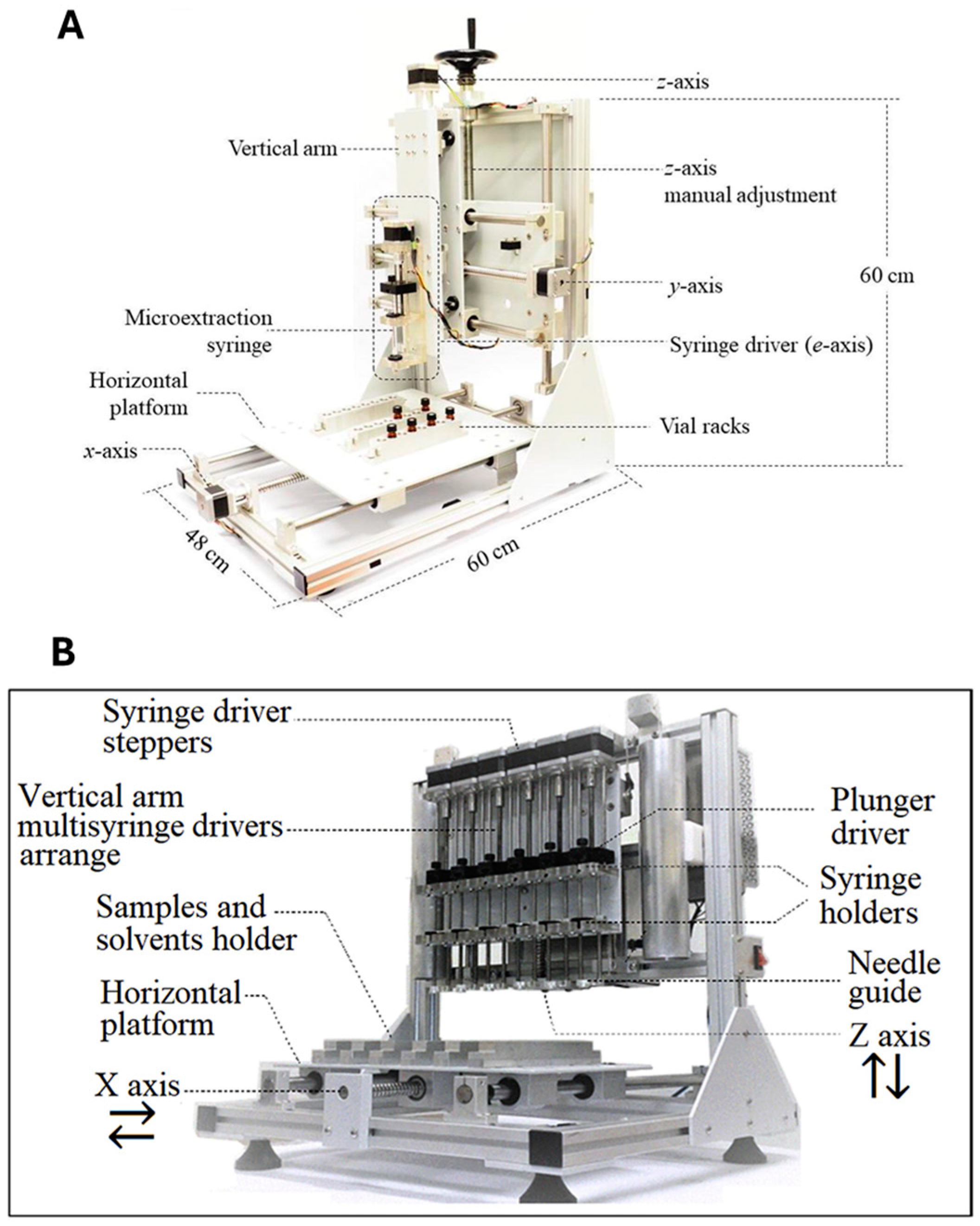
5. Insights into Semi and Automated MEPS Approaches: Current Applications
| Type | Sorbent | Analytes | Matrix | LOQ | LOD | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semi-automated | C18 | Catecholamines, metanephrines | Urine | 0.167–1.53 ng mL−1 | 0.0800–0.440 ng mL−1 | 2020 | [133] |
| Semi-automated | AX | Vanillylmandelic acid | Urine | 0.5 μg mL−1 | - | 2020 | [134] |
| Semi-automated | C18 | Parabens | Cosmetics | 0.05 µg mL−1 | 2–5 ng mL−1 | 2021 | [135] |
| Semi-automated | C8, C18, and M1 mixed-mode sorbent containing 80% C8 and 20% SCX strong cationic exchange | Forty-one compounds from brain-derived cell cultures | Cell cultures | 0.1–10 ng mL−1 | - | 2023 | [136] |
| Fully automated (commercial) | C18 | Monohydroxy polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons | Urine | 1.5–65.6 µg L−1 | 0.6–19.4 µg L−1 | 2022 | [137] |
| Fully automated (commercial) | C18 | Polyamines and related compounds | Saliva | 8.68–23.8 µg L−1 | 1.83–33.8 µg L−1 | 2019 | [138] |
| Lab-made fully automated | MIP | Cannabinoids | Urine | 5.0–20 g mL−1 | 1.0–5.0 ng mL−1 | 2020 | [19] |
| Lab-made fully automated | Strata-X | Parabens, benzophenones, synthetic phenolic antioxidants | Wastewater | 0.15–0.6 ng L−1 | 0.15–0.30 ng L−1 | 2023 | [144] |
| Lab-made fully automated | Carboxylic acid-modified polystyrene divinylbenzene copolymer | N-nitrosamines | Drug tablets | 80 ng g−1 | 50 ng g−1 | 2023 | [145] |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alampanos, V.; Samanidou, V. An Overview of Sample Preparation Approaches Prior to Liquid Chromatography Methods for the Determination of Parabens in Biological Matrices. Microchem. J. 2021, 164, 105995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.T.; Martins, R.O.; Lanças, F.M.; Chaves, A.R. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Online Extraction Liquid Chromatography Methods: Current Advances and Recent Applications. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1284, 341952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, X.; Zheng, Y.; Qin, Q.; Chen, D. Recent Advances in Sample Preparation and Chromatographic/Mass Spectrometric Techniques for Detecting Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Edible Oils: 2010 to Present. Foods 2024, 13, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peris-Pastor, G.; Azorín, C.; Grau, J.; Benedé, J.L.; Chisvert, A. Miniaturization as a Smart Strategy to Achieve Greener Sample Preparation Approaches: A View through Greenness Assessment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 170, 117434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.R.; Meireles, A.N.; Marques, S.S.; Silva, L.; Barreiros, L.; Sampaio-Maia, B.; Miró, M.; Segundo, M.A. Sample Preparation and Chromatographic Methods for the Determination of Protein-Bound Uremic Retention Solutes in Human Biological Samples: An Overview. J. Chromatogr. B 2023, 1215, 123578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Li, A. Trends in Sample Preparation and Analysis of Current Use Pesticides in Abiotic Environmental Matrices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 172, 117605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis, R.S.; Silva, U.N.; Santos, L.B.; Silva Melo, A.; Coutinho, J.J.; Cerqueira, U.M.F.M.; Lemos, V.A.; Bezerra, M.A. Sample Preparation Strategies Alternative to Mineralization for Elemental Analysis in Foods by Spectroanalytical Techniques—A Review. Microchem. J. 2024, 199, 110059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavijalal, M.; Petio, C.; Staffilano, G.; Mandrioli, R.; Protti, M. Innovative Solid-Phase Extraction Strategies for Improving the Advanced Chromatographic Determination of Drugs in Challenging Biological Samples. Molecules 2024, 29, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, M.E.I.; El-Nouby, M.A.M.; Kimani, P.K.; Lim, L.W.; Rabea, E.I. A Review of the Modern Principles and Applications of Solid-Phase Extraction Techniques in Chromatographic Analysis. Anal. Sci. 2022, 38, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosendo, L.M.; Brinca, A.T.; Pires, B.; Catarro, G.; Rosado, T.; Guiné, R.P.F.; Araújo, A.R.T.S.; Anjos, O.; Gallardo, E. Miniaturized Solid Phase Extraction Techniques Applied to Natural Products. Processes 2023, 11, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, C.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid Phase Microextraction with Thermal Desorption Using Fused Silica Optical Fibers. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 2145–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rehim, M. New Trend in Sample Preparation: On-Line Microextraction in Packed Syringe for Liquid and Gas Chromatography Applications: I. Determination of Local Anaesthetics in Human Plasma Samples Using Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 801, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andruch, V.; Kalyniukova, A.; Yordanova, T.; Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Vojteková, V.; Zengin, G. Microextraction by Packed Sorbent: Uncommon Detection Techniques, Sorbents, Samples and Analytes. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 176, 117769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Said, R.; Abdel-Rehim, M. Sorbent, Device, Matrix and Application in Microextraction by Packed Sorbent (MEPS): A Review. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1043, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granados-Guzmán, G.; Díaz-Hernández, M.; Alvarez-Román, R.; Cavazos-Rocha, N.; Portillo-Castillo, O.J. A Brief Review of the Application of Microextraction by Packed Sorbent for Antibiotics Analysis from Biological, Food, and Environmental Samples. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2023, 42, 20230057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moein, M.M.; Abdel-Rehim, A.; Abdel-Rehim, M. Microextraction by Packed Sorbent (MEPS). TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 67, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartore, D.M.; Vargas Medina, D.A.; Bocelli, M.D.; Jordan-Sinisterra, M.; Santos-Neto, Á.J.; Lanças, F.M. Modern Automated Microextraction Procedures for Bioanalytical, Environmental, and Food Analyses. J. Sep. Sci. 2023, 46, 2300215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadifar, M.; Yamini, Y.; Khataei, M.M.; Shirani, M. Automated and Semi-Automated Packed Sorbent Solid Phase (Micro) Extraction Methods for Extraction of Organic and Inorganic Pollutants. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1706, 464227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartore, D.M.; Vargas Medina, D.A.; Costa, J.L.; Lanças, F.M.; Santos-Neto, Á.J. Automated Microextraction by Packed Sorbent of Cannabinoids from Human Urine Using a Lab-Made Device Packed with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. Talanta 2020, 219, 121185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torabi, E.; Abdar, A.; Lotfian, N.; Bazargan, M.; Simms, C.; Moussawi, M.A.; Amiri, A.; Mirzaei, M.; Parac-Vogt, T.N. Advanced Materials in Sorbent-Based Analytical Sample Preparation. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 506, 215680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagirani, M.S.; Soylak, M. Green Sorbents for the Solid Phase Extraction of Trace Species. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2024, 47, 100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, J.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A.; Grześkowiak, T.; Frankowski, R. Biopolymers-Based Sorbents as a Future Green Direction for Solid Phase (Micro)Extraction Techniques. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 173, 117659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Tang, S.; Shen, W.; Yang, F.; Lee, H.K. Recent Progress of Graphene Aerogel as Sorbent in Solid-Phase Extraction: A Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 168, 117352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.O.; de Araújo, G.L.; de Freitas, C.S.; Silva, A.R.; Simas, R.C.; Vaz, B.G.; Chaves, A.R. Miniaturized Sample Preparation Techniques and Ambient Mass Spectrometry as Approaches for Food Residue Analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1640, 461949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.A.M.; Gonçalves, J.; Porto-Figueira, P.; Figueira, J.A.; Alves, V.; Perestrelo, R.; Medina, S.; Câmara, J.S. Current Trends on Microextraction by Packed Sorbent—Fundamentals, Application Fields, Innovative Improvements and Future Applications. Analyst 2019, 144, 5048–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, A.R.; Martins, R.O.; de Oliveira Júnior, C.I.; Maciel, L.I.L.; Bernardo, R.A.; Machado, L.S. Sample Treatment Based on Solid Miniaturized Techniques: An Effective Approach for Biological Samples Evaluation. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, G.; Rodrigues, M.; Fortuna, A.; Falcão, A.; Queiroz, J. A Critical Review of Microextraction by Packed Sorbent as A Sample Preparation Approach in Drug Bioanalysis. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 1409–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.; Câmara, J.S.; Colmsjö, A.; Abdel-Rehim, M. Microextraction by Packed Sorbent: An Emerging, Selective and High-Throughput Extraction Technique in Bioanalysis. BMC 2014, 28, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoś-Chełstowska, P.; Gębicki, J. Sorbents Modified by Deep Eutectic Solvents in Microextraction Techniques. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 172, 117577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashayi Sarnaghi, S.; Ayazi, Z. Synthesis of a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Thin Film as a Smart Sorbent for Microextraction by Packed Syringe of n-Propyl Gallate in Vegetable Edible Oils Followed by Its Colorimetric Detection Applying a Smartphone. Microchem. J. 2024, 203, 110772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, F.N.; Santos-Neto, A.J.; Medina, D.A.V.; Lanças, F.M. A Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Microextraction by Packed Sorbent of Sulfonylureas Herbicides from Corn Samples. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 121, 105388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.B.; Dos Santos, N.A.; Borges, K.B.; Conceição, N.S.; Baptista, C.S.D.; França, H.S.; Romão, W. Synthesis and Characterization of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for the Determination of Cocaine in Urine Using Microextraction in Packed Sorvent. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2023, 34, 1677–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, R.A.; Dinali, L.A.F.; Silva, C.F.; de Oliveira, H.L.; da Silva, A.T.M.; Nascimento, C.S.; Borges, K.B. Microextraction by Packed Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Followed by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography for Determination of Fipronil and Fluazuron Residues in Drinking Water and Veterinary Clinic Wastewater. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinali, L.A.F.; de Oliveira, H.L.; Teixeira, L.S.; de Souza Borges, W.; Borges, K.B. Mesoporous Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Core@shell Hybrid Silica Nanoparticles as Adsorbent in Microextraction by Packed Sorbent for Multiresidue Determination of Pesticides in Apple Juice. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, L.S.; Silva, C.F.; de Oliveira, H.L.; Dinali, L.A.F.; Nascimento, C.S.; Borges, K.B. Microextraction by Packed Molecularly Imprinted Polymer to Selectively Determine Caffeine in Soft and Energy Drinks. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, H.L.; Teixeira, L.S.; Dinali, L.A.F.; Pires, B.C.; Simões, N.S.; Borges, K.B. Microextraction by Packed Sorbent Using a New Restricted Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for the Determination of Estrogens from Human Urine Samples. Microchem. J. 2019, 150, 104162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Wang, X. Microextraction by Packed Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Combined Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography for the Determination of Levofloxacin in Human Plasma. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 4783432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.F.; Borges, K.B.; Do Nascimento, C.S. Rational Design of a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Dinotefuran: Theoretical and Experimental Studies Aimed at the Development of an Efficient Adsorbent for Microextraction by Packed Sorbent. Analyst 2017, 143, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleimani, E.; Bahrami, A.; Afkhami, A.; Shahna, F.G. Selective Determination of Mandelic Acid in Urine Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer in Microextraction by Packed Sorbent. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, E.; Bahrami, A.; Afkhami, A.; Shahna, F.G. Determination of Urinary Trans,Trans-Muconic Acid Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer in Microextraction by Packed Sorbent Followed by Liquid Chromatography with Ultraviolet Detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1061–1062, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgari, S.; Bagheri, H.; Es-haghi, A.; AminiTabrizi, R. An Imprinted Interpenetrating Polymer Network for Microextraction in Packed Syringe of Carbamazepine. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1491, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; Lei, C.; Zhang, S.; Bai, G.; Zhou, H.; Sun, M.; Fu, Q.; Chang, C. Determination of Clenbuterol from Pork Samples Using Surface Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as the Selective Sorbents for Microextraction in Packed Syringe. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 91, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, A.; Schrader, S.; Bauer, C.; Möder, M. Synthesis of a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer and Its Application for Microextraction by Packed Sorbent for the Determination of Fluoroquinolone Related Compounds in Water. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 685, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, A.; Vallejo, A.; Zuloaga, O.; Paschke, A.; Sellergen, B.; Schillinger, E.; Schrader, S.; Möder, M. Selective Determination of Estrogenic Compounds in Water by Microextraction by Packed Sorbents and a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Coupled with Large Volume Injection-in-Port-Derivatization Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 703, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moein, M.M.; Abdel-Rehim, A.; Abdel-Rehim, M. On-Line Determination of Sarcosine in Biological Fluids Utilizing Dummy Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Microextraction by Packed Sorbent. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moein, M.M.; El-Beqqali, A.; Javanbakht, M.; Karimi, M.; Akbari-adergani, B.; Abdel-Rehim, M. On-Line Detection of Hippuric Acid by Microextraction with a Molecularly-Imprinted Polysulfone Membrane Sorbent and Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1372, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, F.; Andradé, A.; José, A.; José, J.; Fernando, S.-N.; Lanças, M. Microextraction by Packed Sorbent Liquid Chromatography with Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry of Triazines Employing a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 3150–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryanavard, S.M.; Jeppsson-Dadoun, A.; Andersson, L.I.; Hashemi, M.; Colmsjö, A.; Abdel-Rehim, M. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer in Microextraction by Packed Sorbent for the Simultaneous Determination of Local Anesthetics: Lidocaine, Ropivacaine, Mepivacaine and Bupivacaine in Plasma and Urine Samples. BMC 2013, 27, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari, S.; Seidi, S. Fabrication of Porous Cobalt Oxide/Carbon Nanopolks on Electrospun Hollow Carbon Nanofibers for Microextraction by Packed Sorbent of Parabens from Human Blood. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1702, 464080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurd, N.; Bahrami, A.; Afkhami, A.; Shahna, F.G.; Assari, M.J.; Farhadian, M. Application of Fe3O4@TbBd Nanobeads in Microextraction by Packed Sorbent (MEPS) for Determination of BTEXs Biomarkers by HPLC–UV in Urine Samples. J. Chromatogr. B 2022, 1197, 123197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serenjeh, F.N.; Hashemi, P.; Ghiasvand, A.R.; Rasolzadeh, F.; Heydari, N.; Badiei, A. Cooling Assisted Headspace Microextraction by Packed Sorbent Coupled to HPLC for the Determination of Volatile Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Soil. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1125, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidi, S.; Sanàti, S.E. Nickel-Iron Layered Double Hydroxide Nanostructures for Micro Solid Phase Extraction of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs, Followed by Quantitation by HPLC-UV. Mckrochem. Acta 2019, 186, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimpoor, R.; Bahrami, A.; Nematollahi, D.; Shahna, F.G.; Farhadian, M. Facile and Sensitive Determination of Urinary Mandelic Acid by Combination of Metal Organic Frameworks with Microextraction by Packed Sorbents. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1114–1115, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, A.; Chahkandi, M.; Targhoo, A. Synthesis of Nano-Hydroxyapatite Sorbent for Microextraction in Packed Syringe of Phthalate Esters in Water Samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 950, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, H.; Banihashemi, S.; Zandian, F.K. Microextraction of Antidepressant Drugs into Syringes Packed with a Nanocomposite Consisting of Polydopamine, Silver Nanoparticles and Polypyrrole. Microchem. Acta 2016, 183, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadifar, M.; Yamini, Y. Microextraction by Packed Sorbent of Some β-Blocker Drugs with Chitosan@mof-199 Bio-Composite in Human Saliva, Plasma, and Urine Samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 234, 115520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, T.; Hou, X. Monolithic and Compressible MIL-101(Cr)/Cellulose Aerogel/Melamine Sponge Based Microextraction in Packed Syringe towards Trace Nitroimidazoles in Water Samples Prior to UPLC-MS/MS Analysis. Talanta 2023, 253, 123935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Qin, Z.; Song, X.; Piao, H.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Song, D.; Ma, P.; Sun, Y. Facile Preparation of Metal Organic Framework-Based Laboratory Semi-Automatic Micro-Extraction Syringe Packed Column for Analysis of Parabens in Vegetable Oil Samples. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirmohammadi, Z.; Bahrami, A.; Nematollahi, D.; Alizadeh, S.; Ghorbani Shahna, F.; Rahimpoor, R. Determination of Urinary Methylhippuric Acids Using MIL-53-NH2 (Al) Metal–Organic Framework in Microextraction by Packed Sorbent Followed by HPLC–UV Analysis. BMC 2020, 34, e4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanganeh, F.; Yamini, Y.; Khataei, M.M.; Shirani, M. Determination of Opiates in Urine Samples Using a Composite of Covalent Organic Framework and Polypyrrole as a Sorbent for Microextraction in a Packed Syringe Combined with HPLC/UV. Talanta Open 2023, 7, 100183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurd, N.; Bahrami, A.; Afkhami, A.; Shahna, G.; Assari, M.J.; Farhadian, M. Hollow Polymer Nanospheres and Fe3O4@TFPA-Bd-COF as a Mixture Adsorbent in Microextraction by Packed Sorbent for Extraction of BTEX Biomarkers in Urine. Iran. Chem. Soc. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. Res. 2023, 10, 237–250. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan-Sinisterra, M.; Lanças, F.M. Microextraction by Packed Sorbent of Selected Pesticides in Coffee Samples Employing Ionic Liquids Supported on Graphene Nanosheets as Extraction Phase. Microchem. Acta 2022, 414, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, L.F.; Lanças, F.M. β-Cyclodextrin Coupled to Graphene Oxide Supported on Aminopropyl Silica as a Sorbent Material for Determination of Isoflavones. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 4347–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimiyan, H.; Uheida, A.; Hadjmohammadi, M.; Moein, M.M.; Abdel-Rehim, M. Polyacrylonitrile/Graphene Oxide Nanofibers for Packed Sorbent Microextraction of Drugs and Their Metabolites from Human Plasma Samples. Talanta 2019, 201, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Fan, Y.; Fan, P.; Geng, F.; Chen, P.; Zhao, F. Use of Graphene Coated with ZnO Nanocomposites for Microextraction in Packed Syringe of Carbamate Pesticides from Juice Samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 2131–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayazi, Z.; Shekari Esfahlan, F.; Matin, P. Graphene Oxide Reinforced Polyamide Nanocomposite Coated on Paper as a Novel Layered Sorbent for Microextraction by Packed Sorbent. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 1118–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Moein, M.M.; Madrakian, T.; Afkhami, A.; Bahar, S.; Abdel-Rehim, M. Reduced Graphene Oxide as an Efficient Sorbent in Microextraction by Packed Sorbent: Determination of Local Anesthetics in Human Plasma and Saliva Samples Utilizing Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1095, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos Soares Maciel, E.; Henrique Fumes, B.; Lúcia de Toffoli, A.; Mauro Lanças, F. Graphene Particles Supported on Silica as Sorbent for Residue Analysis of Tetracyclines in Milk Employing Microextraction by Packed Sorbent. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manouchehri, M.; Seidi, S.; Rouhollahi, A.; Noormohammadi, H.; Shanehsaz, M. Micro Solid Phase Extraction of Parabens from Breast Milk Samples Using Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxide Functionalized Partially Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite. Food Chem. 2020, 314, 126223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, A.; Ghaemi, F. Microextraction in Packed Syringe by Using a Three-Dimensional Carbon Nanotube/Carbon Nanofiber-Graphene Nanostructure Coupled to Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction for the Determination of Phthalate Esters in Water Samples. Microchem. Acta 2017, 184, 3851–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumes, B.H.; Lanças, F.M. Use of Graphene Supported on Aminopropyl Silica for Microextraction of Parabens from Water Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1487, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishnejad, M.; Ebrahimzadeh, H. Graphitic Carbon Nitride-Reinforced Polymer Ionic Liquid Nanocomposite: A Novel Mixed-Mode Sorbent for Microextraction in Packed Syringe. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 3471–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, R. Quantitative Measurement of Plasma Free Metanephrines by a Simple and Cost-Effective Microextraction Packed Sorbent with Porous Graphitic Carbon and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2021, 2021, 8821276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro Cruz, J.; Dipe De Faria, H.; Figueiredo, E.C.; Eugênia Costa Queiroz, M. Restricted Access Carbon Nanotube for Microextraction by Packed Sorbent to Determine Antipsychotics in Plasma Samples by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2465–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghani, A.; Goudarzi, N.; Bagherian, G. Application of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes for the Preconcentration and Determination of Organochlorine Pesticides in Water Samples by Gas Chromatography with Mass Spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 4219–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadaresta, F.; Crescenzi, C.; Amini, A.; Colmsjö, A.; Koyi, H.; Abdel-Rehim, M. Application of Graphitic Sorbent for Online Microextraction of Drugs in Human Plasma Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1422, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perestrelo, R.; Silva, C.L.; Câmara, J.S. Determination of Urinary Levels of Leukotriene B4 Using Ad Highly Specific and Sensitive Methodology Based on Automatic MEPS Combined with UHPLC-PDA Analysis. Talanta 2015, 144, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuzooda, T.; Amini, A.; Abdel-Rehim, M. Graphite-Based Microextraction by Packed Sorbent for Online Extraction of β-Blockers from Human Plasma Samples. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 992, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, A.; Hashemi, P.; Badiei, A.; Safdarian, M.; Rashidipour, M. Microextraction of Rosmarinic acid Using CMK-3 Nanoporous Carbon in a Packed Syringe. Chromatographia 2013, 76, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshdel, Z.; Hashemi, P.; Safdaryan, M.; Delfan, B.; RashidipouR, M.; Badiei, A. Microextraction in a Packed Syringe for the Analysis of Olive Biophenols in Rat Plasma Using CMK-3 Nanoporous Sorbent. Anal. Sci. 2013, 29, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Bagheri, A.R.; Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Chen, L. Strategies of Molecular Imprinting-Based Solid-Phase Extraction Prior to Chromatographic Analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 128, 115923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapacz, D.; Smolinska-Kempisty, K.; Wolska, J. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers toward Herbicides—Progress in Development and the Current State of the Art Depending on the Polymerization Environment—Short Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Fernández, L.; San Andrés, M.P.; Díez-Pascual, A.M. Nanomaterials As Sorbents in Solid-Phase Extraction for Bioactive Compounds. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2024, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Tao, H.; Tao, H.; Shuai, Q.; Huang, L. Recent Progress of Covalent Organic Frameworks as Attractive Materials for Solid-Phase Microextraction: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1287, 341953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duo, H.; Yue, J.; Wan, X.; Sha, L.; Hou, X.; Zhu, Q. Recent Advances in Synthesis and Applications of Metal–Organic Frameworks for Sample Preparation in Antibiotic Analysis. Microchem. J. 2023, 193, 109053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Keshavarzi, M.; Pakseresht, M.; Mohammadi, P.; Ojaghzadeh Khalil Abad, M.; Mehraban, A. Advancements, Applications, and Prospects of Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Derivatives as Distinct Sorbents in Exhaustive and Non-Exhaustive Extraction Strategies. Microchem. J. 2024, 198, 110158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, M.A.; Sajid, M.; Nazal, M.K.; Islam, M.A. Carbon-Based Materials as Promising Sorbents for Analytical Sample Preparation: Recent Advances and Trends in Extraction of Toxic Metal Pollutants from Various Media. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 167, 117265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, E.V.S.; de Toffoli, A.L.; Neto, E.S.; Nazario, C.E.D.; Lanças, F.M. New Materials in Sample Preparation: Recent Advances and Future Trends. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunkoed, O.; Orachorn, N.; Jullakan, S.; Nurerk, P. Composite Solid Phase Adsorbents: Carbon-Based and Framework-Based Materials for Micro-Extraction of Trace Organic Compounds. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 177, 117808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delińska, K.; Rakowska, P.W.; Kloskowski, A. Porous Material-Based Sorbent Coatings in Solid-Phase Microextraction Technique: Recent Trends and Future Perspectives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Chabowska, A.; Pantanit, S.; Bunkoed, O.; Fares, M.Y.; Sajid, M.; Lambropoulou, D.; Kurowska-Susdorf, A.; Jatkowska, N. Natural/Bio-Based Sorbents as Greener Extractive Materials for Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Samples of Different Matrix Composition. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 176, 117773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Ammar Haeri, S. Biodegradable Materials and Their Applications in Sample Preparation Techniques–A Review. Microchem. J. 2021, 171, 106831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouladi, M.; Kavousi Heidari, M.; Tavakoli, O. Development of Porous Biodegradable Sorbents for Oil/Water Separation: A Critical Review. J. Porous Mater. 2022, 30, 1037–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogiouri, N.P.; Papatheocharidou, C.; Samanidou, V.F. Recent Advances towards the Use of Deep Eutectic Solvents and Cyclodextrins in the Extraction of Food Contaminants: From Traditional Sample Pretreatment Techniques to Green Microextraction and Beyond. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 173, 117649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, E.V.S.; dos Santos, N.G.P.; Medina, D.A.V.; Lanças, F.M. Cyclodextrins-Based Sorbents for Sustainable Sample Preparation Focusing on Food Analysis. Green Anal. Chem. 2023, 7, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaraj, M.; Suresh Babu, P.; Shyamalagowri, S.; Pavithra, M.K.S.; Aravind, J.; Kim, W.; Govarthanan, M. β-Cyclodextrin Polymer Composites for the Removal of Pharmaceutical Substances, Endocrine Disruptor Chemicals, and Dyes from Aqueous Solution- A Review of Recent Trends. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Abdiryim, T.; Liu, X. Cyclodextrin-Derived Materials: From Design to Promising Applications in Water Treatment. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 502, 215613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Valverde, M.T.; Soriano, M.L.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S. Cotton Fibers Functionalized with β-Cyclodextrins as Selectivity Enhancer for the Direct Infusion Mass Spectrometric Determination of Cocaine and Methamphetamine in Saliva Samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1126, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, S.G.; Peters, L.; Mucalo, M. Chitosan: A Review of Molecular Structure, Bioactivities and Interactions with the Human Body and Micro-Organisms. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 282, 119132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, N.H.; Borhan, A.; Saadon, S.Z.A.H. Biosorption of Wastewater Pollutants by Chitosan-Based Porous Carbons: A Sustainable Approach for Advanced Wastewater Treatment. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2024, 25, 101705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saheed, I.O.; Da Oh, W.; Suah, F.B.M. Chitosan Modifications for Adsorption of Pollutants—A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benettayeb, A.; Seihoub, F.Z.; Pal, P.; Ghosh, S.; Usman, M.; Chia, C.H.; Usman, M.; Sillanpää, M. Chitosan Nanoparticles as Potential Nano-Sorbent for Removal of Toxic Environmental Pollutants. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, A.R.; Aramesh, N.; Lee, H.K. Chitosan- and/or Cellulose-Based Materials in Analytical Extraction Processes: A Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.T.; Hu, X.L.; He, S.; He, X.M.; Zhu, S.K.; Feng, Y.Q. Hydrothermally Tailor-Made Chitosan Fiber for Micro-Solid Phase Extraction of Petroleum Acids in Crude Oils. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1564, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurerk, P.; Sillapawisut, S.; Bunkoed, O.; Rongwong, W.; Llompart, M. A Monolith Adsorbent of Hyper-Crosslinked Polymer, Graphene Oxide Composite Chitosan Cryogel for in-Syringe Solid Phase Extraction of Furfural Derivatives from Cellulosic Biomass Hydrolysate. Microchem. J. 2022, 183, 108056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Nazir, G.; Heo, K.; Hussain, S.; Ikram, M.; Akhter, Z.; Algaradah, M.M.; Mahmood, Q.; Fouda, A.M. A Focused Review on Lignocellulosic Biomass-Derived Porous Carbons for Effective Pharmaceuticals Removal: Current Trends, Challenges and Future Prospects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Fu, J.; Deng, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhong, G.; Xu, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhou, J. Valorization of Biomass Hydrolysis Waste: Activated Carbon from Humins as Exceptional Sorbent for Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, T.W.; H’Ng, P.S.; Luqman Chuah Abdullah, B.C.T.G.; Chin, K.L.; Lee, C.L.; Mohd Nor Hafizuddin, B.M.S.; TaungMai, L. A Review of Bio-Based Activated Carbon Properties Produced from Different Activating Chemicals during Chemicals Activation Process on Biomass and Its Potential for Malaysia. Materials 2023, 16, 7365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ani, J.U.; Akpomie, K.G.; Okoro, U.C.; Aneke, L.E.; Onukwuli, O.D.; Ujam, O.T. Potentials of Activated Carbon Produced from Biomass Materials for Sequestration of Dyes, Heavy Metals, and Crude Oil Components from Aqueous Environment. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashile, G.P.; Mpupa, A.; Nomngongo, P.N. In-Syringe Micro Solid-Phase Extraction Method for the Separation and Preconcentration of Parabens in Environmental Water Samples. Molecules 2018, 23, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasolzadeh, F.; Hashemi, P.; Madadkar Haghjou, M.; Safdarian, M. Chlorella Vulgaris Microalgae as a Green Packing for the Microextraction by Packed Sorbent of Nitrofurantoin in Urine. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. Res. 2019, 6, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukčević, M.; Maletić, M.; Pejić, B.; Kalijadis, A.; Kostić, M.; Trivunac, K.; Perić Grujić, A. Cellulose-Based Waste in a Close Loop as an Adsorbent for Removing Dyes from Textile Industry Wastewater. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, J.; Frankowski, R.; Grześkowiak, T.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A. Green Sorbents in Sample Preparation Techniques—Naturally Occurring Materials and Biowastes. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 176, 117772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, P.; Ayazi, Z.; Jamshidi-Ghaleh, K. Montmorillonite Reinforced Polystyrene Nanocomposite Supported on Cellulose as a Novel Layered Sorbent for Microextraction by Packed Sorbent for Determination of Fluoxetine Followed by Spectrofluorimetry Based on Multivariate Optimisation. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 5150–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigueto, C.V.T.; Nazari, M.T.; Massuda, L.Á.; Ostwald, B.E.P.; Piccin, J.S.; Dettmer, A. Production and Environmental Applications of Gelatin-Based Composite Adsorbents for Contaminants Removal: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2465–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Elella, M.H.; Aamer, N.; Abdallah, H.M.; López-Maldonado, E.A.; Mohamed, Y.M.A.; El Nazer, H.A.; Mohamed, R.R. Novel High-Efficient Adsorbent Based on Modified Gelatin/Montmorillonite Nanocomposite for Removal of Malachite Green Dye. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, E.; Mehrani, Z.; Ebrahimzadeh, H. Gelatin/Sodium Triphosphate Hydrogel Electrospun Nanofiber Mat as a Novel Nanosorbent for Microextraction in Packed Syringe of La3+ and Tb3+ Ions Prior to Their Determination by ICP-OES. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 153, 104627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Kaushik, B.; Rao, G.K.; Srivastava, C.M.; Vaya, D. Advances and Challenges in the Use of Chitosan and Its Derivatives in Biomedical Fields: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2023, 5, 100323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindihama, G.K.; Gitari, M.W.; Mudzielwana, R.; Madala, N.E. Evaluating the Application of Chitosan-Based Sorbents for the Solid-Phase Adsorption Toxin Tracking of Microcystins in Irrigation Water. Water 2023, 16, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okasha, A.T.; Abdel-Khalek, A.A.; Alenazi, N.A.; AlHammadi, A.A.; Al Zoubi, W.; Alhammadi, S.; Ko, Y.G.; Abukhadra, M.R. Progress of Synthetic Cyclodextrins-Based Materials as Effective Adsorbents of the Common Water Pollutants: Comprehensive Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Wang, Y.-Z. Cellulose-Based Absorbents for Oil Contaminant Removal; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 951–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, T.; Haq, F.; Farid, A.; Kiran, M.; Faisal, S.; Ullah, A.; Ullah, N.; Bokhari, A.; Mubashir, M.; Chuah, L.F.; et al. Challenges Associated with Cellulose Composite Material: Facet Engineering and Prospective. Environ. Res. 2023, 223, 115429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Azmi, N.Z.; Buthiyappan, A.; Abdul Raman, A.A.; Abdul Patah, M.F.; Sufian, S. Recent Advances in Biomass Based Activated Carbon for Carbon Dioxide Capture—A Review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 116, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint Zaw, M.; Poorahong, S.; Kanatharana, P.; Thavarungkul, P.; Thammakhet-Buranachai, C. A Simple Gelatin Aerogel Tablet Sorbent for the Effective Vortex Assisted Solid Phase Extraction of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Tea Samples. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciel, E.V.S.; Vargas Medina, D.A.; Borsatto, J.V.B.; Lanças, F.M. Towards a Universal Automated and Miniaturized Sample Preparation Approach. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 21, 100427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technical Analytical Methods Committee Briefs. What Causes Most Errors in Chemical Analysis? Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 2914–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Cid, G.; Cárdenas, S.; Simonet, B.M.; Valcárcel, M. Fully Automatic Sample Treatment by Integration of Microextraction by Packed Sorbents into Commercial Capillary Electrophoresis−Mass Spectrometry Equipment: Application to the Determination of Fluoroquinolones in Urine. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 3188–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Cid, G.; Cárdenas, S.; Simonet, B.M.; Valcárcel, M. Direct Automatic Determination of Free and Total Anesthetic Drugs in Human Plasma by Use of a Dual (Microdialysis–Microextraction by Packed Sorbent) Sample Treatment Coupled At-line to NACE–MS. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 1684–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Rehim, M.; Dahlgren, M.; Blomberg, L. Quantification of Ropivacaine and Its Major Metabolites in Human Urine Samples Utilizing Microextraction in a Packed Syringe Automated with Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (MEPS-LC-MS/MS). J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 1658–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Neto, A.J.; Rodrigues, J.C.; Fernandes, C.; Titato, G.M.; Alves, C.; Lanças, F.M. Automated Microcolumn-Switching System for Drug Analysis by Direct Injection of Human Plasma. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1105, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, H. Automated Sample Preparation Using In-Tube Solid-Phase Microextraction and Its Application—A Review. Anal Bioanal. Chem. 2002, 373, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Cui, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Q.; Sui, X.; He, A.; Zhang, X.; Xu, R.; Tian, R. Combination of Automated Sample Preparation and Micro-Flow LC–MS for High-Throughput Plasma Proteomics. Clin. Proteom. 2023, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Zhang, Y. Simple, Rapid, and Cost-Effective Microextraction by the Packed Sorbent Method for Quantifying of Urinary Free Catecholamines and Metanephrines Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry and Its Application in Clinical Analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2763–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Zhang, Y. A New Approach for Urinary Vanillylmandelic Acid Determination Using EVol Microextraction by Packed Sorbent Coupled to Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khesina, Z.B.; Iartsev, S.D.; Revelsky, A.I.; Buryak, A.K. Microextraction by Packed Sorbent Optimized by Statistical Design of Experiment as an Approach to Increase the Sensitivity and Selectivity of HPLC-UV Determination of Parabens in Cosmetics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 195, 113843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protti, M.; Cirrincione, M.; Palano, S.; Poeta, E.; Babini, G.; Magnifico, M.C.; Barile, S.N.; Balboni, N.; Massenzio, F.; Mahdavijalal, M.; et al. Targeted Quantitative Metabolic Profiling of Brain-Derived Cell Cultures by Semi-Automated MEPS and LC-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 236, 115757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-García, S.; Matilla-González, H.; Peña, J.; Sánchez, M.d.N.; Casas-Ferreira, A.M.; Pérez Pavón, J.L. Determination of Hydroxy Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Human Urine Using Automated Microextraction by Packed Sorbent and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, J.; Casas-Ferreira, A.M.; Morales-Tenorio, M.; Moreno-Cordero, B.; Pérez-Pavón, J.L. Determination of Polyamines and Related Compounds in Saliva via in Situ Derivatization and Microextraction by Packed Sorbents Coupled to GC-MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1129, 121821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, D.A.V.; Rodriguez Cabal, L.F.; Lanças, F.M.; Santos-Neto, Á.J. Sample Treatment Platform for Automated Integration of Microextraction Techniques and Liquid Chromatography Analysis. HardwareX 2019, 5, e00056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.F.; Vargas Medina, D.A.; Lanças, F.M. Automated Needle-Sleeve Based Online Hyphenation of Solid-Phase Microextraction and Liquid Chromatography. Talanta 2021, 221, 121608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabal, L.F.R.; Medina, D.A.V.; Costa, J.L.; Lanças, F.M.; Santos-Neto, Á.J. Determination of Ring-Substituted Amphetamines through Automated Online Hollow Fiber Liquid-Phase Microextraction-Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 7889–7897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Cabal, L.F.; Vargas Medina, D.A.; Martins Lima, A.; Lanças, F.M.; Santos-Neto, Á.J. Robotic-Assisted Dynamic Large Drop Microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1608, 460416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, D.A.V.; Rodríguez Cabal, L.F.; Titato, G.M.; Lanças, F.M.; Santos-Neto, Á.J. Automated Online Coupling of Robot-Assisted Single Drop Microextraction and Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1595, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocelli, M.D.; Medina, D.A.V.; Lanças, F.M.; dos Santos-Neto, Á.J. Automated Microextraction by Packed Sorbent of Endocrine Disruptors in Wastewater Using a High-Throughput Robotic Platform Followed by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 6165–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira dos Santos, N.G.; Medina, D.A.V.; Lanças, F.M. Microextraction by Packed Sorbent of N—Nitrosamines from Losartan Tablets Using a High-throughput Robot Platform Followed by Liquid Chromatography-tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2023, 46, e2300214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martins, R.O.; Borsatto, J.V.B.; Will, C.; Lanças, F.M. Advancements in Microextraction by Packed Sorbent: Insights into Sorbent Phases and Automation Strategies. Separations 2025, 12, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12010011
Martins RO, Borsatto JVB, Will C, Lanças FM. Advancements in Microextraction by Packed Sorbent: Insights into Sorbent Phases and Automation Strategies. Separations. 2025; 12(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins, Rafael Oliveira, João Victor Basolli Borsatto, Camila Will, and Fernando Mauro Lanças. 2025. "Advancements in Microextraction by Packed Sorbent: Insights into Sorbent Phases and Automation Strategies" Separations 12, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12010011
APA StyleMartins, R. O., Borsatto, J. V. B., Will, C., & Lanças, F. M. (2025). Advancements in Microextraction by Packed Sorbent: Insights into Sorbent Phases and Automation Strategies. Separations, 12(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12010011






