Chiral Separation and Determination of Enantiomer Elution Order of Novel Ketamine Derivatives Using CE-UV and HPLC-UV-ORD
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Capillary Electrophoresis
2.1.1. Sample Preparation
2.1.2. Instrumentation and Method
2.2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
2.2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2.2. Chromatographic Conditions
2.2.3. Sample Preparation
3. Results and Discussion
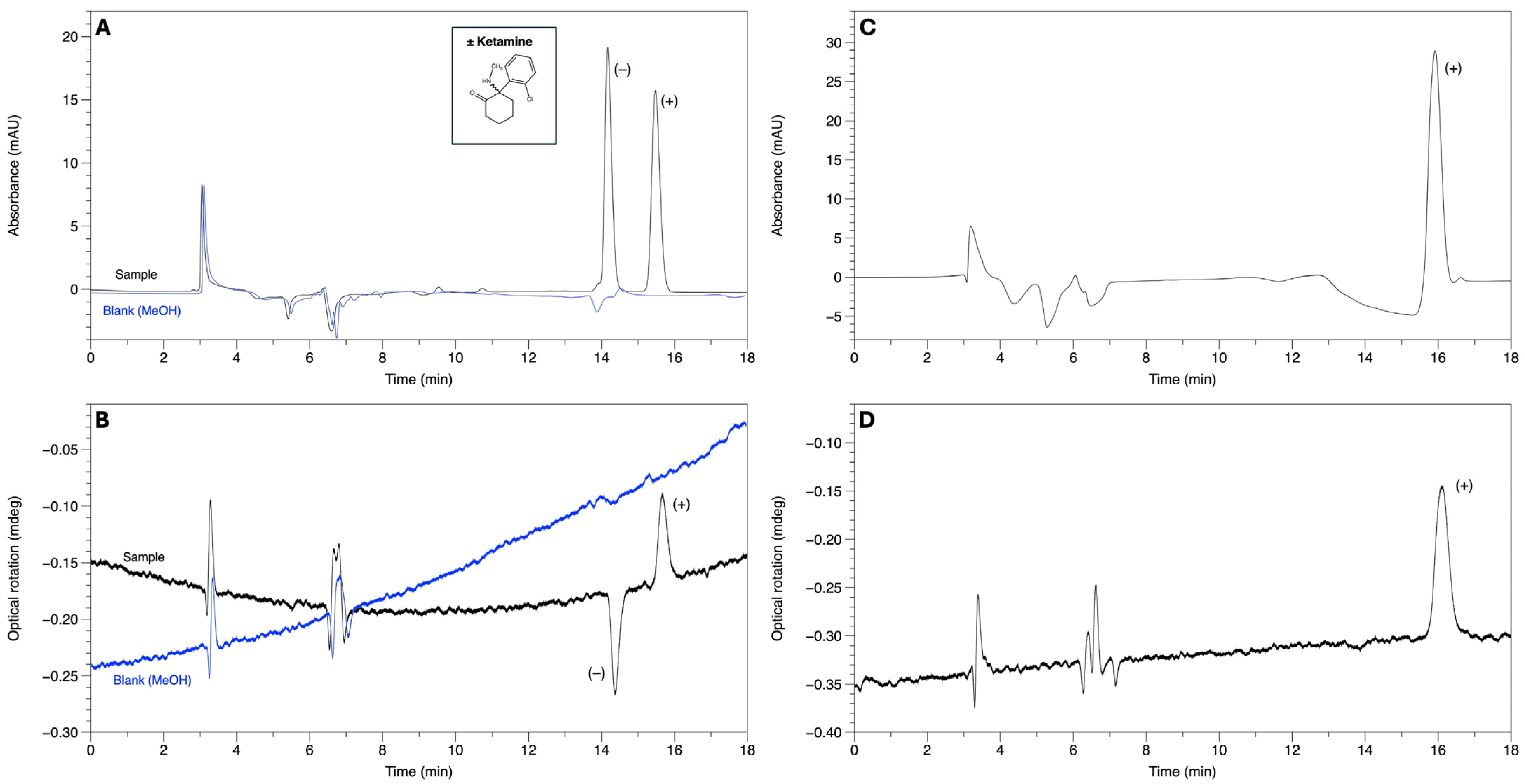
3.1. CE Experiments
3.2. HPLC Experiments
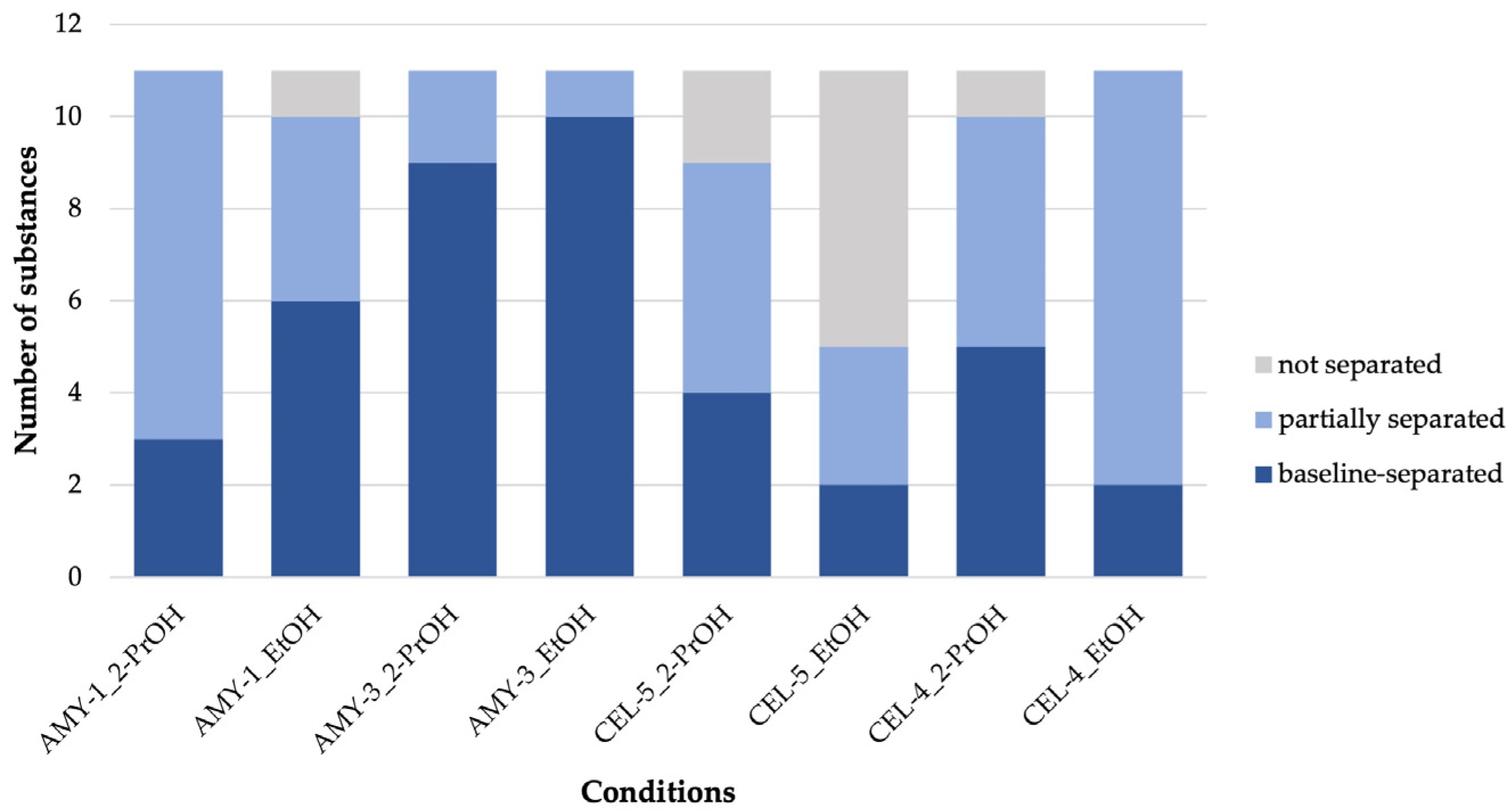
3.2.1. Comparison of Separation Ability of Different CSPs and Mobile Phase Compositions
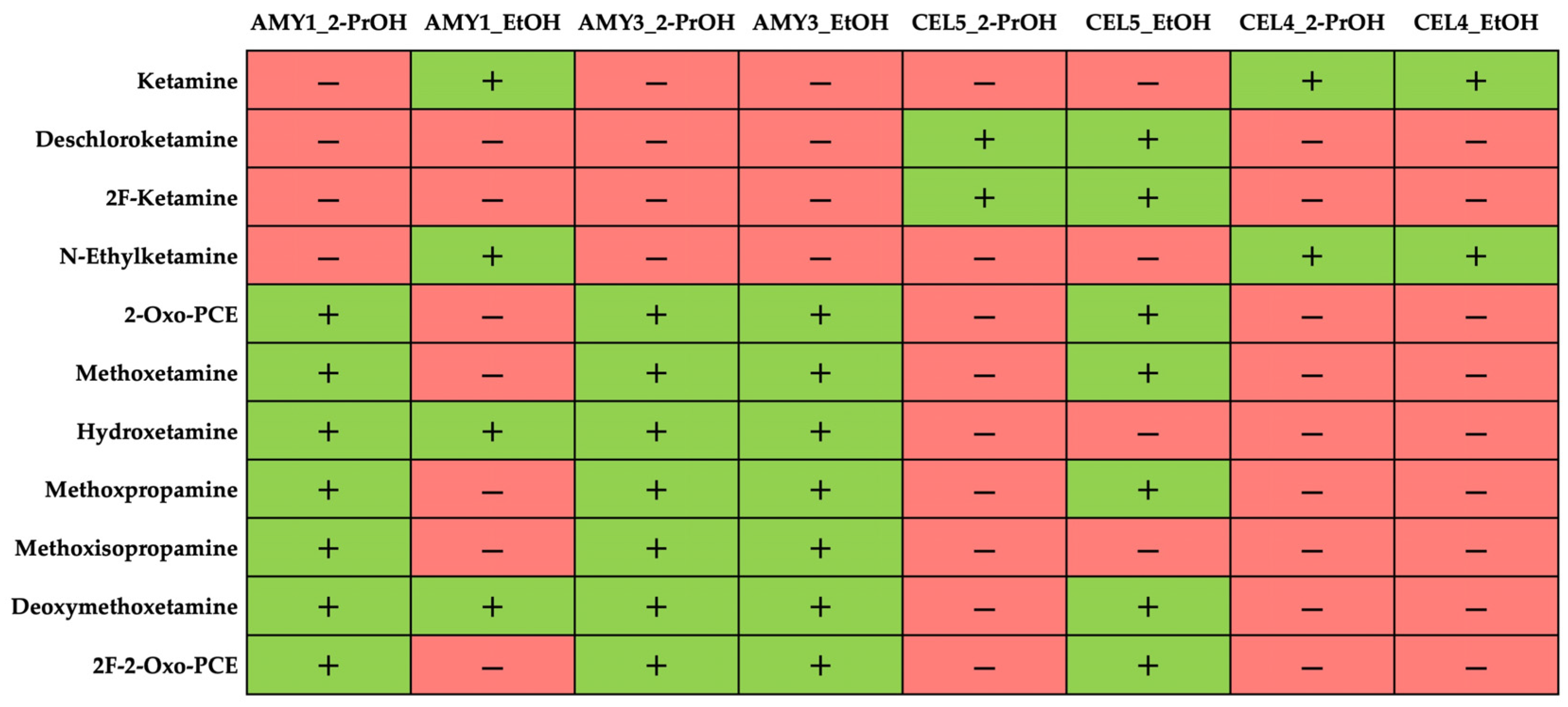
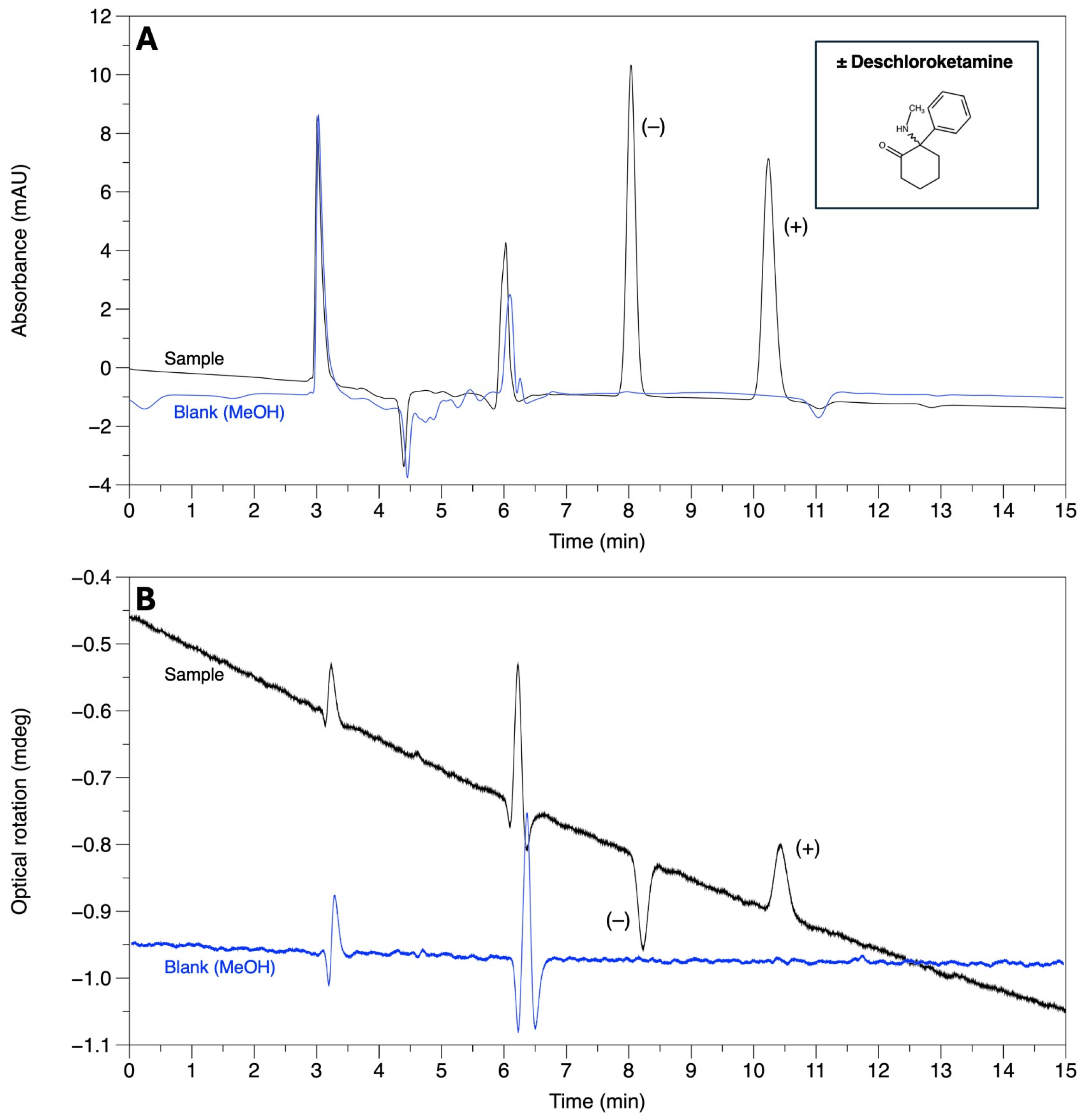
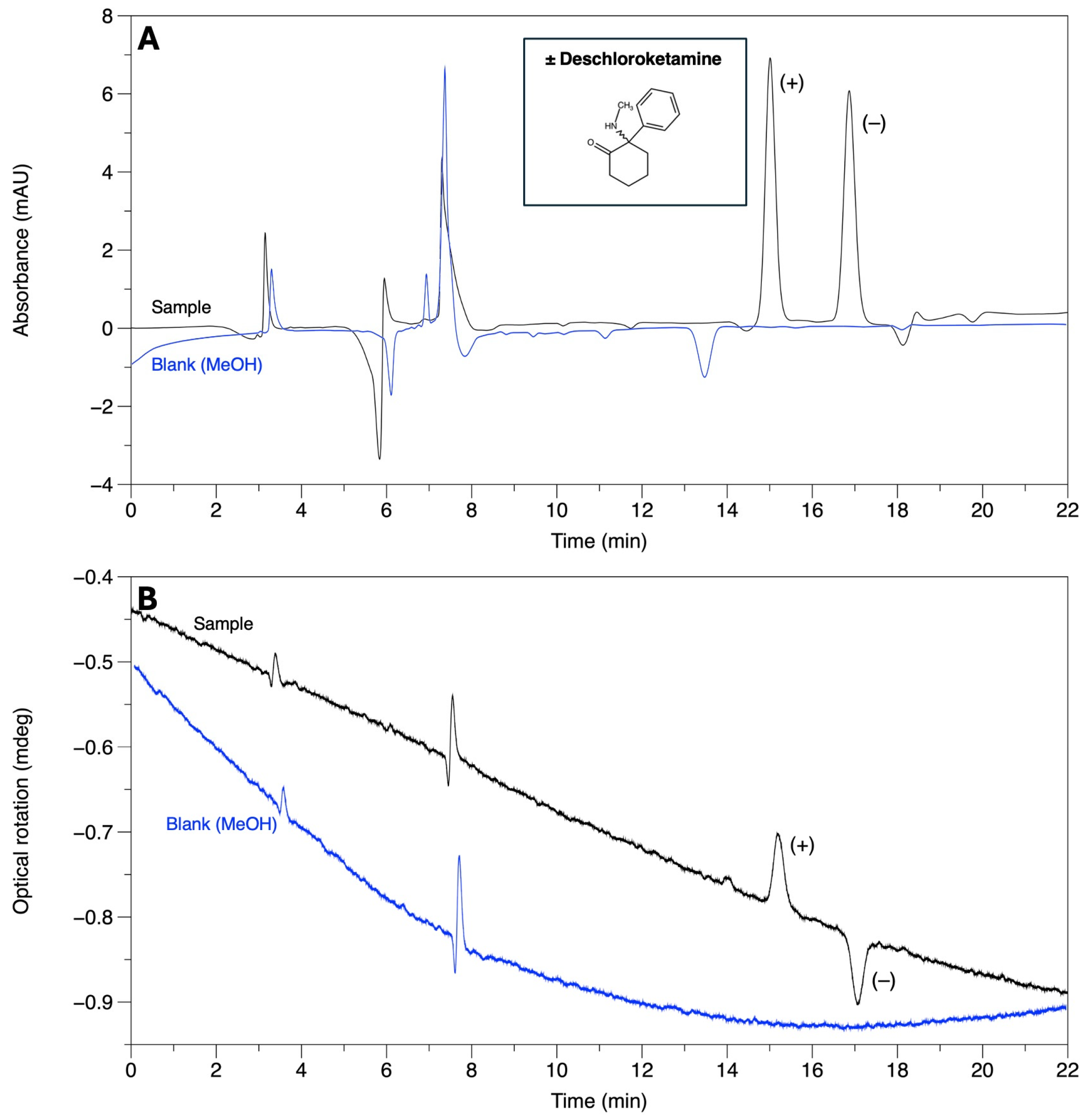
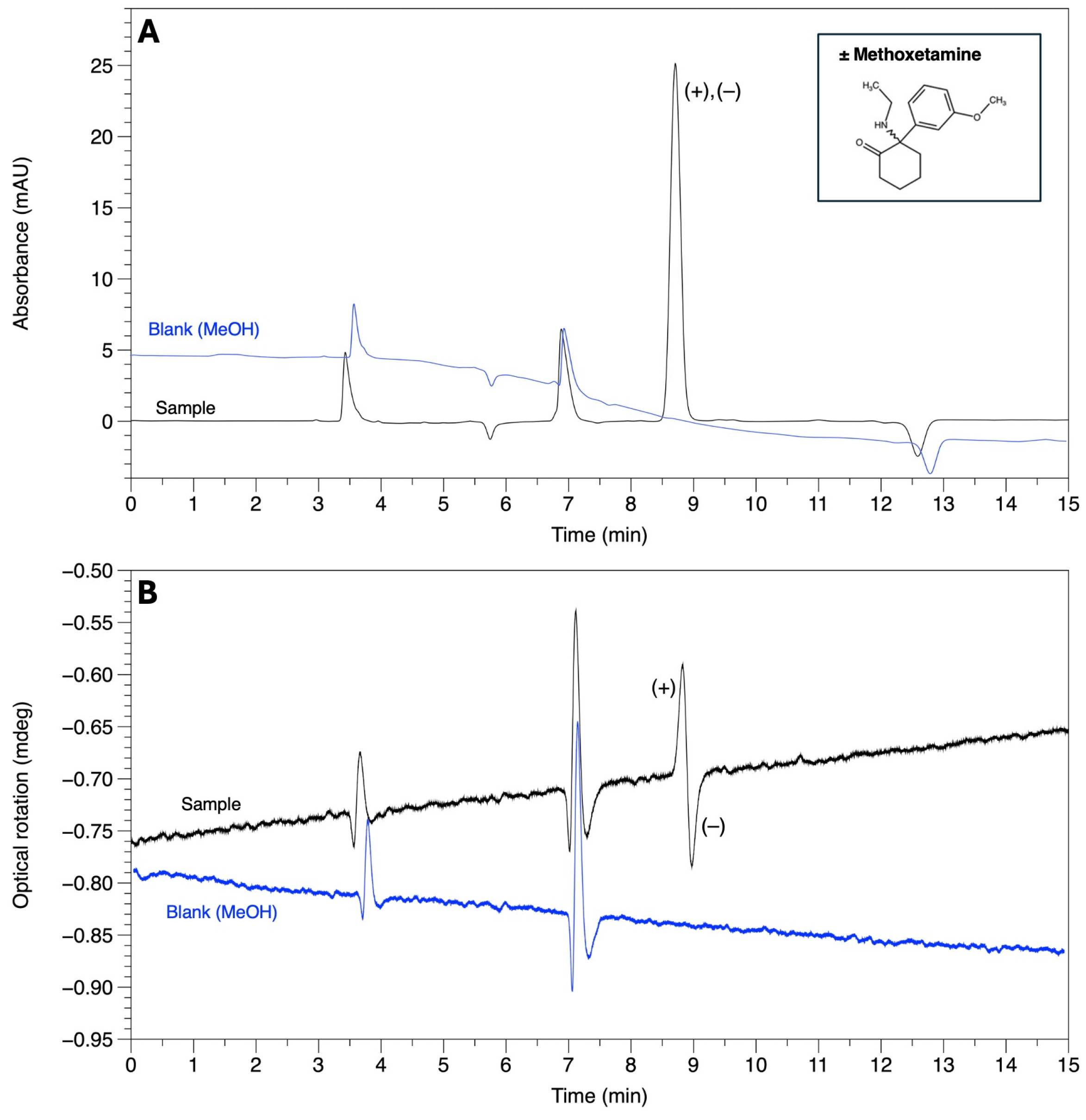
3.2.2. Influence of Chiral Selector and Mobile Phase Composition on Enantiomer Elution Order
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corssen, G.; Domino, E.F. Dissociative Anesthesia: Further Pharmacologic Studies and First Clinical Experience with the Phencyclidine Derivative CI-581. Anesth. Analg. 1966, 45, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketalar-FDA Approval. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm?event=overview.process&ApplNo=016812 (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Savić Vujović, K.; Jotić, A.; Medić, B.; Srebro, D.; Vujović, A.; Žujović, J.; Opanković, A.; Vučković, S. Ketamine, an Old–New Drug: Uses and Abuses. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 17, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation List of Essential Medicines—23rd List, 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-MHP-HPS-EML-2023.02 (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Vekhova, K.A.; Namiot, E.D.; Jonsson, J.; Schiöth, H.B. Ketamine and Esketamine in Clinical Trials: FDA-Approved and Emerging Indications, Trial Trends with Putative Mechanistic Explanations. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 117, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, R.M.; Cappiello, A.; Anand, A.; Oren, D.A.; Heninger, G.R.; Charney, D.S.; Krystal, J.H. Antidepressant Effects of Ketamine in Depressed Patients. Biol. Psychiatry 2000, 47, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency Spravato. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/spravato (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- White, P.F.; Ham, J.; Way, W.L.; Trevor, A. Pharmacology of Ketamine Isomers in Surgical Patients. Anesthesiology 1980, 52, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.F.; Schüttler, J.; Shafer, A.; Stanski, D.R.; Horai, Y.; Trevor, A.J. Comparative Pharmacology of the Ketamine Isomers. Br. J. Anaesth. 1985, 57, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union Drugs Agency (EUDA). Europol EU Drug Market: New Psychoactive Substances—Distribution and Supply in Europe: Ketamine. Available online: https://www.euda.europa.eu/publications/eu-drug-markets/new-psychoactive-substances/distribution-and-supply/ketamine_en (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- European Union Drugs Agency. Other Drugs—The Current Situation in Europe. In European Drug Report. 2024: Trends and Developments; EUDA: Lisbon, Portugal, 2024; Available online: https://www.euda.europa.eu/publications/european-drug-report/2024/other-drugs_en (accessed on 18 December 2024)ISBN 978-92-9497-975-9.
- European Pharmacopoeia Department. Esketamini Hydrochloridum 11.0/1742. In Europäisches Arzneibuch; Verlag Österreich: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Volume 11.0, ISBN 978-3-7046-9177-4. [Google Scholar]
- European Pharmacopoeia Department. Ketamini Hydrochloridum 11.0/1020. In Europäisches Arzneibuch; Verlag Österreich: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Volume 11.0, ISBN 978-3-7046-9177-4. [Google Scholar]
- Amini, A.; Sörman, U.P.; Lindgren, B.H.; Westerlund, D. Enantioseparation of Anaestethic Drugs by Capillary Zone Electrophoresis Using Cyclodextrin-containing Background Electrolytes. Electrophoresis 1998, 19, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandbaumhüter, F.A.; Aerts, J.T.; Theurillat, R.; Andrén, P.E.; Thormann, W.; Jansson, E.T. Enantioselective CE–MS Analysis of Ketamine Metabolites in Urine. Electrophoresis 2023, 44, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwaterczak, A.; Duszczyk, K.; Bielejewska, A. Comparison of Chiral Separation of Basic Drugs in Capillary Electrophoresis and Liquid Chromatography Using Neutral and Negatively Charged Cyclodextrins. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 645, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theurillat, R.; Knobloch, M.; Schmitz, A.; Lassahn, P.; Mevissen, M.; Thormann, W. Enantioselective Analysis of Ketamine and Its Metabolites in Equine Plasma and Urine by CE with Multiple Isomer Sulfated Β-CD. Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 2748–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theurillat, R.; Sandbaumhüter, F.A.; Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R.; Thormann, W. Microassay for Ketamine and Metabolites in Plasma and Serum Based on Enantioselective Capillary Electrophoresis with Highly Sulfated γ-Cyclodextrin and Electrokinetic Analyte Injection. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porpiglia, N.; Musile, G.; Bortolotti, F.; De Palo, E.F.; Tagliaro, F. Chiral Separation and Determination of Ketamine and Norketamine in Hair by Capillary Electrophoresis. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 266, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Cole, R.B. Determination of Chiral Pharmaceutical Compounds, Terbutaline, Ketamine and Propranolol, by on-Line Capillary Electrophoresis–Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1998, 714, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkaoui, S.; Veuthey, J.-L. Use of Negatively Charged Cyclodextrins for the Simultaneous Enantioseparation of Selected Anesthetic Drugs by Capillary Electrophoresis–Mass Spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 27, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägele, J.S.; Hubner, E.; Schmid, M.G. Determination of the Chiral Status of Different Novel Psychoactive Substance Classes by Capillary Electrophoresis and Β-cyclodextrin Derivatives. Chirality 2020, 32, 1191–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chankvetadze, B.; Scriba, G.K.E. Cyclodextrins as Chiral Selectors in Capillary Electrophoresis: Recent Trends in Mechanistic Studies. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 160, 116987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scriba, G.K.E.; Konjaria, M.; Krait, S. Cyclodextrins. In Chiral Separations and Stereochemical Elucidation; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 273–323. [Google Scholar]
- Kadkhodaei, K.; Forcher, L.; Schmid, M.G. Separation of Enantiomers of New Psychoactive Substances by High-performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 1274–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadkhodaei, K.; Kadisch, M.; Schmid, M.G. Successful Use of a Novel Lux® I-Amylose-1 Chiral Column for Enantioseparation of “Legal Highs” by HPLC. Chirality 2020, 32, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägele, J.S.; Basrak, M.; Schmid, M.G. Enantioselective Separation of Novel Psychoactive Substances Using a Lux® AMP 3 μm Column and HPLC-UV. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 179, 112967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergely, A.; Zsila, F.; Horváth, P.; Szász, G. Determination of Absolute Configuration of Ketamine Enantiomers by HPLC-CD-UV Technique. Chirality 1999, 11, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toki, H.; Ichikawa, T.; Mizuno-Yasuhira, A.; Yamaguchi, J. A Rapid and Sensitive Chiral LC–MS/MS Method for the Determination of Ketamine and Norketamine in Mouse Plasma, Brain and Cerebrospinal Fluid Applicable to the Stereoselective Pharmacokinetic Study of Ketamine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 148, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toki, H.; Yamaguchi, J.; Mizuno-Yasuhira, A.; Endo, H. Chiral LC-MS/MS Method for the Simultaneous Determination of (R,S)-Ketamine, (R,S)-Norketamine, and (2R,6R;2S,6S)-Hydroxynorketamine in Mouse Plasma and Brain. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 224, 115168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Hofstetter, R.; Fassauer, G.M.; Link, A.; Siegmund, W.; Oswald, S. Quantitative Chiral and Achiral Determination of Ketamine and Its Metabolites by LC–MS/MS in Human Serum, Urine and Fecal Samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 139, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.G.; Hägele, J.S. Separation of Enantiomers and Positional Isomers of Novel Psychoactive Substances in Solid Samples by Chromatographic and Electrophoretic Techniques—A Selective Review. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1624, 461256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moaddel, R.; Venkata, S.L.V.; Tanga, M.J.; Bupp, J.E.; Green, C.E.; Iyer, L.; Furimsky, A.; Goldberg, M.E.; Torjman, M.C.; Wainer, I.W. A Parallel Chiral–Achiral Liquid Chromatographic Method for the Determination of the Stereoisomers of Ketamine and Ketamine Metabolites in the Plasma and Urine of Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Talanta 2010, 82, 1892–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Rosas, M.E.; Patel, S.; Wainer, I.W. Determination of the Enantiomers of Ketamine and Norketamine in Human Plasma by Enantioselective Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 794, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, J.-O.; Gustafsson, L.L. Determination of Ketamine and Norketamine Enantiomers in Plasma by Solid-Phase Extraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1996, 678, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhong, K.; Jiang, J.; Zhan, Y.; Chen, X. Enantioselective Determination of Ketamine in Dog Plasma by Chiral Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarossa, A.; Bardhi, A.; Gazzotti, T.; Pagliuca, G. A Critical Point in Chiral Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Ketamine Metabolites. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.E.; Torjman, M.C.; Schwartzman, R.J.; Mager, D.E.; Wainer, I.W. Enantioselective Pharmacokinetics of (R)- and (S)-ketamine after a 5-day Infusion in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Chirality 2011, 23, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaňkátová, P.; Kubíčková, A.; Kalíková, K. How Mobile Phase Composition and Column Temperature Affect Enantiomer Elution Order of Liquid Crystals on Amylose Tris(3-chloro-5-methylphenylcarbamate) as Chiral Selector. Electrophoresis 2021, 42, 1844–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chankvetadze, L.; Ghibradze, N.; Karchkhadze, M.; Peng, L.; Farkas, T.; Chankvetadze, B. Enantiomer Elution Order Reversal of Fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl-Isoleucine in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography by Changing the Mobile Phase Temperature and Composition. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 6554–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, H.-W.; Wang, Y.-J.; Wu, P.-J. Conformational Changes in Polysaccharide-Based Chiral Selectors Induced by Mobile Phase Composition: Effects on Enantioselective Retention and Enantiomer Elution Order Reversal. J. Chromatogr. A 2025, 1742, 465660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyllenhaal, O.; Stefansson, M. Reversal of Elution Order for Profen Acid Enantiomers in Normal Phase LC on Chiralpak AD. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 46, 860–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanács, D.; Orosz, T.; Szakonyi, Z.; Le, T.M.; Fülöp, F.; Lindner, W.; Ilisz, I.; Péter, A. High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Enantioseparation of Isopulegol-Based ß-Amino Lactone and ß-Amino Amide Analogs on Polysaccharide-Based Chiral Stationary Phases Focusing on the Change of the Enantiomer Elution Order. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1621, 461054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Shen, S.; Lee, H.; Eriksson, M.; Zeng, X.; Xu, J.; Fandrick, K.; Yee, N.; Senanayake, C.; Grinberg, N. Mechanistic Studies on the Chiral Recognition of Polysaccharide-Based Chiral Stationary Phases Using Liquid Chromatography and Vibrational Circular Dichroism. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 3784–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ketamine 2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)cyclohexan-1-one 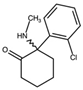 | Deschloroketamine 2-Phenyl-2-(methylamino)cyclohexan-1-one 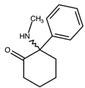 | 2F-Ketamine 2-(2-Fluorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)cyclohexan-1-one  | N-Ethylketamine 2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-2-(ethylamino)cyclohexan-1-one  |
| 2-Oxo-PCE 2-(Ethylamino)-2-phenylcyclohexan-1-one 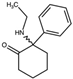 | Methoxetamine 2-(Ethylamino)-2-(3-methoxyphenyl)cyclohexan-1-one 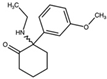 | Hydroxetamine (3-HO-2-Oxo-PCE) 2-(Ethylamino)-2-(3-hydroxyphenyl)cyclohexan-1-one 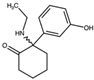 | Methoxpropamine (MXPr) 2-(3-Methoxyphenyl)-2-(propylamino)cyclohexan-1-one 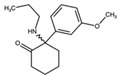 |
| Methoxisopropamine (MXiPr) 2-(Isopropylamino)-2-(3-methoxyphenyl)cyclohexan-1-one 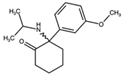 | Deoxymethoxetamine (DMXE) 2-(Ethylamino)-2-(3-methylphenyl)cyclohexan-1-one 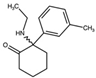 | 2F-2-Oxo-PCE 2-(Ethylamino)-2-(2-fluorophenyl)cyclohexan-1-one 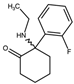 |
| Abbreviation | Trade Name | Chiral Selector | Column Dimensions and Particle Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMY-1 | Lux® i-Amylose-1 | Amylose tris(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate | 250 × 4.6 mm I.D.; 5 μm |
| AMY-3 | Lux® i-Amylose-3 | Amylose tris(3-chloro-5-methylphenylcarbamate | 250 × 4.6 mm I.D.; 3 μm |
| CEL-5 | Lux® i-Cellulose-5 | Cellulose tris(3,5-dichlorophenylcarbamate | 250 × 4.6 mm I.D.; 3 μm |
| CEL-4 | Lux® Cellulose-4 | Cellulose tris(4-chloro-3-methylphenylcarbamate | 250 × 4.6 mm I.D.; 3 μm |
| (a) | ||||
| Compound | t1 (min) | t2 (min) | αapp (t2/t1) | Rs |
| Ketamine | 14.13 | 14.26 | 1.009 | 0.50 |
| Deschloroketamine | 12.53 | 13.21 | 1.054 | 2.70 |
| 2F-Ketamine | 12.80 | 13.05 | 1.020 | 1.35 |
| N-Ethylketamine | 14.44 | 14.58 | 1.010 | 0.63 |
| 2-Oxo-PCE | 13.94 | 14.68 | 1.053 | 3.17 |
| Methoxetamine | 14.19 | 15.20 | 1.072 | 3.34 |
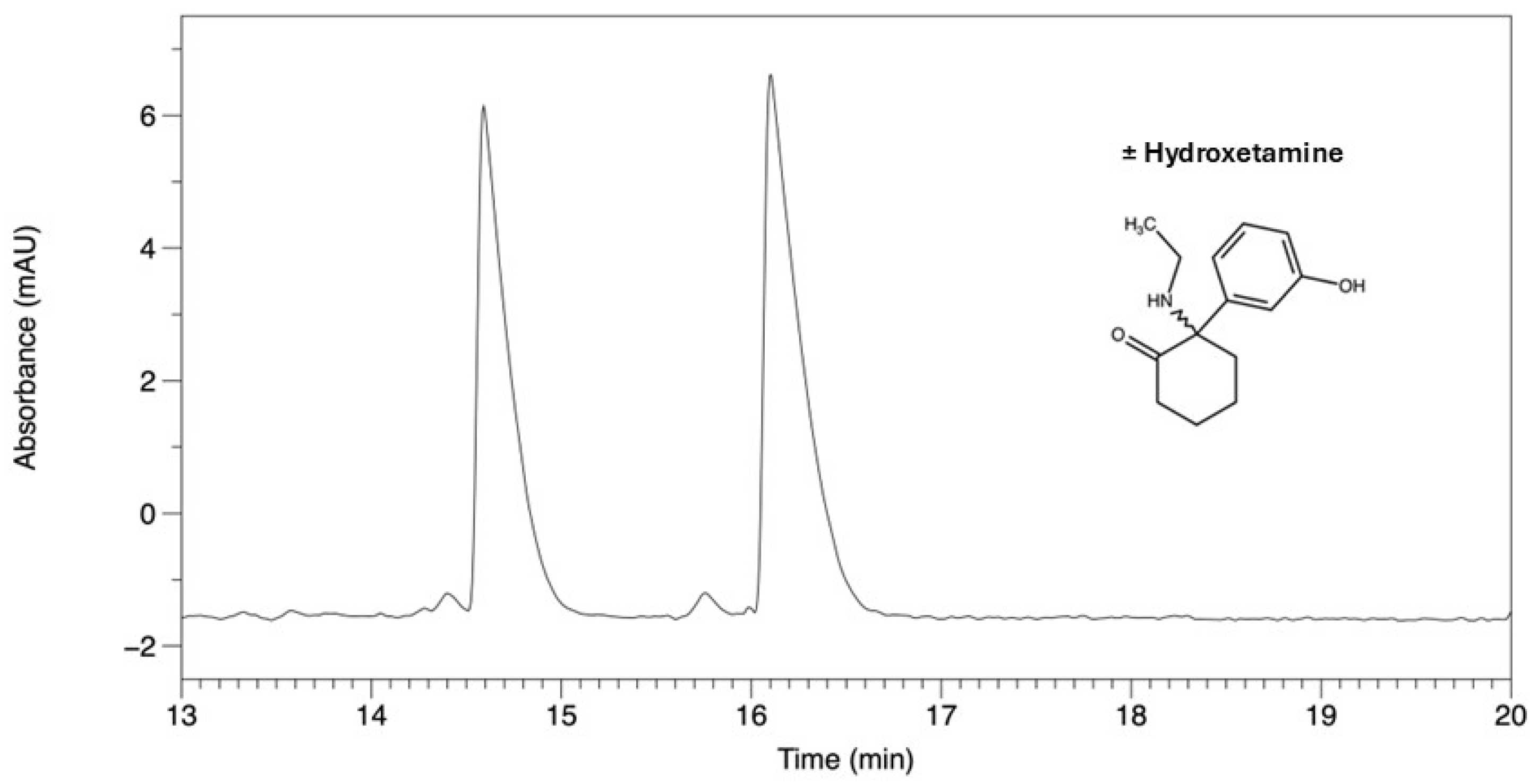
| Hydroxetamine (3-HO-2-oxo-PCE) | 14.59 | 16.10 | 1.103 | 5.41 |
| Methoxpropamine (MXPr) | 13.78 | 14.27 | 1.035 | 1.96 |
| Methoxisopropamine (MXiPr) | 15.45 | 15.98 | 1.034 | 1.82 |
| Deoxymethoxetamine (DMXE) | 13.24 | 13.54 | 1.023 | 1.24 |
| 2F-2-Oxo-PCE | 13.68 | 13.78 | 1.007 | 0.47 |
| (b) | ||||
| Compound | t1 (min) | t2 (min) | αapp (t2/t1) | Rs |
| Ketamine | 16.77 | - | - | - |
| Deschloroketamine | 15.06 | 15.31 | 1.016 | 1.08 |
| 2F-Ketamine | 15.41 | 15.46 | 1.003 | 0.21 |
| N-Ethylketamine | 18.04 | 18.38 | 1.019 | 1.28 |
| 2-Oxo-PCE | 15.35 | 15.44 | 1.006 | 0.42 |
| Methoxetamine | 18.93 | 19.37 | 1.023 | 1.28 |
| Hydroxetamine (3-HO-2-oxo-PCE) | 18.32 | 18.93 | 1.033 | 2.10 |
| Methoxpropamine (MXPr) | 16.64 | - | - | - |
| Methoxisopropamine (MXiPr) | 19.65 | 19.74 | 1.005 | 0.34 |
| Deoxymethoxetamine (DMXE) | 18.31 | - | - | - |
| 2F-2-Oxo-PCE | 16.34 | 16.59 | 1.015 | 1.07 |
| (a) | |||||
| Compound | t1 (min) | t2 (min) | α | Rs | CSP |
| Ketamine | 8.31 | 8.62 | 1.06 | 1.11 | AMY-1 |
| 14.40 | 15.80 | 1.12 | 3.60 | AMY-3 | |
| 21.67 | 21.94 | 1.01 | 0.48 | CEL-5 | |
| 12.50 | 13.16 | 1.07 | 1.64 | CEL-4 | |
| Deschloroketamine | 8.04 | 10.24 | 1.44 | 6.96 | AMY-1 |
| 13.82 | 14.17 | 1.03 | 0.94 | AMY-3 | |
| 15.01 | 16.87 | 1.16 | 3.91 | CEL-5 | |
| 10.49 | 11.77 | 1.17 | 3.66 | CEL-4 | |
| 2F-Ketamine | 8.57 | 9.47 | 1.16 | 3.00 | AMY-1 |
| 16.34 | 16.91 | 1.04 | 1.35 | AMY-3 | |
| 22.08 | 23.50 | 1.08 | 2.12 | CEL-5 | |
| 13.13 | 15.62 | 1.25 | 5.64 | CEL-4 | |
| N-Ethylketamine | 5.72 | 5.77 | 1.02 | 0.31 | AMY-1 |
| 8.72 | 9.56 | 1.15 | 3.49 | AMY-3 | |
| 12.06 | n.d. | - | - | CEL-5 | |
| 7.60 | 8.05 | 1.10 | 1.71 | CEL-4 | |
| 2-Oxo-PCE | 5.19 | 5.45 | 1.12 | 1.46 | AMY-1 |
| 7.50 | 8.79 | 1.29 | 6.19 | AMY-3 | |
| 7.90 | n.d. | - | - | CEL-5 | |
| 6.30 | 6.59 | 1.09 | 1.50 | CEL-4 | |
| Methoxetamine | 6.41 | 6.59 | 1.05 | 0.87 | AMY-1 |
| 10.67 | 12.47 | 1.24 | 5.71 | AMY-3 | |
| 10.07 | 10.50 | 1.06 | 1.38 | CEL-5 | |
| 7.47 | 7.89 | 1.10 | 1.74 | CEL-4 | |
| Hydroxetamine | 11.17 | 13.69 | 1.31 | 4.95 | AMY-1 |
| 18.19 | 22.21 | 1.27 | 7.22 | AMY-3 | |
| 11.95 | 14.09 | 1.24 | 4.58 | CEL-5 | |
| 12.88 | n.d. | - | - | CEL-4 | |
| Methoxpropamine | 6.04 | 6.12 | 1.03 | 0.80 | AMY-1 |
| 8.73 | 10.48 | 1.31 | 6.73 | AMY-3 | |
| 8.55 | 8.90 | 1.06 | 1.23 | CEL-5 | |
| 6.43 | 6.72 | 1.09 | 1.42 | CEL-4 | |
| Methoxisopropamine | 4.93 | 5.05 | 1.06 | 0.59 | AMY-1 |
| 6.84 | 8.16 | 1.35 | 7.06 | AMY-3 | |
| 6.59 | 7.09 | 1.15 | 1.98 | CEL-5 | |
| 5.33 | 5.88 | 1.25 | 3.10 | CEL-4 | |
| Deoxymethoxetamine | 4.56 | 4.81 | 1.16 | 1.36 | AMY-1 |
| 6.71 | 7.71 | 1.28 | 6.19 | AMY-3 | |
| 8.03 | 8.10 | 1.02 | 0.39 | CEL-5 | |
| 5.85 | 6.11 | 1.09 | 1.29 | CEL-4 | |
| 2F-2-Oxo-PCE | 4.91 | 5.08 | 1.09 | 0.75 | AMY-1 |
| 9.83 | 10.29 | 1.07 | 1.76 | AMY-3 | |
| 10.90 | 11.04 | 1.02 | 0.49 | CEL-5 | |
| 7.61 | 8.02 | 1.09 | 1.66 | CEL-4 | |
| (b) | |||||
| Compound | t1 (min) | t2 (min) | α | Rs | CSP |
| Ketamine | 8.35 | 9.14 | 1.15 | 2.72 | AMY-1 |
| 13.88 | 14.32 | 1.04 | 1.16 | AMY-3 | |
| 13.95 | 14.36 | 1.04 | 0.95 | CEL-5 | |
| 9.76 | 10.16 | 1.06 | 1.30 | CEL-4 | |
| Deschloroketamine | 8.79 | 16.51 | 2.37 | 17.38 | AMY-1 |
| 14.88 | 32.36 | 2.49 | 27.65 | AMY-3 | |
| 11.68 | 12.76 | 1.13 | 3.13 | CEL-5 | |
| 8.53 | 9.15 | 1.12 | 2.45 | CEL-4 | |
| 2F-Ketamine | 8.81 | 10.81 | 1.36 | 6.15 | AMY-1 |
| 16.09 | 18.52 | 1.19 | 5.37 | AMY-3 | |
| 14.69 | 15.84 | 1.10 | 2.62 | CEL-5 | |
| 10.13 | 11.06 | 1.14 | 2.92 | CEL-4 | |
| N-Ethylketamine | 5.72 | 6.23 | 1.20 | 2.67 | AMY-1 |
| 7.54 | 8.18 | 1.15 | 3.14 | AMY-3 | |
| 8.57 | n.d. | - | - | CEL-5 | |
| 6.50 | 6.78 | 1.09 | 1.31 | CEL-4 | |
| 2-Oxo-PCE | 5.72 | n.d. | - | - | AMY-1 |
| 8.05 | 8.78 | 1.15 | 3.28 | AMY-3 | |
| 7.17 | n.d. | - | - | CEL-5 | |
| 5.60 | 5.79 | 1.08 | 0.92 | CEL-4 | |
| Methoxetamine | 6.69 | 7.16 | 1.14 | 1.99 | AMY-1 |
| 12.63 | 13.28 | 1.07 | 1.76 | AMY-3 | |
| 8.71 | n.d. | - | - | CEL-5 | |
| 6.51 | 6.69 | 1.05 | 0.97 | CEL-4 | |
| Hydroxetamine | 9.56 | 9.94 | 1.06 | 1.07 | AMY-1 |
| 15.75 | 16.85 | 1.09 | 2.39 | AMY-3 | |
| 9.43 | 9.62 | 1.03 | 0.73 | CEL-5 | |
| 9.13 | 9.40 | 1.05 | 0.86 | CEL-4 | |
| Methoxpropamine | 5.80 | 5.99 | 1.07 | 0.95 | AMY-1 |
| 9.19 | 10.12 | 1.16 | 3.59 | AMY-3 | |
| 7.22 | n.d. | - | - | CEL-5 | |
| 5.61 | 5.65 | 1.01 | 0.23 | CEL-4 | |
| Methoxisopropamine | 5.10 | 5.27 | 1.09 | 0.87 | AMY-1 |
| 7.10 | 8.47 | 1.35 | 6.34 | AMY-3 | |
| 5.92 | 6.08 | 1.06 | 0.90 | CEL-5 | |
| 5.02 | 5.23 | 1.12 | 1.29 | CEL-4 | |
| Deoxymethoxetamine | 4.60 | 4.76 | 1.11 | 0.94 | AMY-1 |
| 5.65 | 6.93 | 1.52 | 7.30 | AMY-3 | |
| 6.91 | n.d. | - | - | CEL-5 | |
| 5.30 | 5.44 | 1.07 | 0.79 | CEL-4 | |
| 2F-2-Oxo-PCE | 5.78 | 6.33 | 1.21 | 3.06 | AMY-1 |
| 8.21 | 9.01 | 1.16 | 3.55 | AMY-3 | |
| 8.43 | n.d. | - | CEL-5 | ||
| 6.48 | 6.68 | 1.06 | 1.00 | CEL-4 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seibert, E.; Hubner, E.-M.; Schmid, M.G. Chiral Separation and Determination of Enantiomer Elution Order of Novel Ketamine Derivatives Using CE-UV and HPLC-UV-ORD. Separations 2025, 12, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12020044
Seibert E, Hubner E-M, Schmid MG. Chiral Separation and Determination of Enantiomer Elution Order of Novel Ketamine Derivatives Using CE-UV and HPLC-UV-ORD. Separations. 2025; 12(2):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12020044
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeibert, Elisabeth, Eva-Maria Hubner, and Martin G. Schmid. 2025. "Chiral Separation and Determination of Enantiomer Elution Order of Novel Ketamine Derivatives Using CE-UV and HPLC-UV-ORD" Separations 12, no. 2: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12020044
APA StyleSeibert, E., Hubner, E.-M., & Schmid, M. G. (2025). Chiral Separation and Determination of Enantiomer Elution Order of Novel Ketamine Derivatives Using CE-UV and HPLC-UV-ORD. Separations, 12(2), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12020044







