Difference in Biological Oxidation Between High-Sulfur Coal and Pure Pyrite at Different pH Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of High-Sulfur Coal and Pyrite Samples
2.2. Preparation of Bacterial Suspension
2.3. Coal Biological Desulfurization and Pyrite Bio-Oxidation by A. ferrooxidans LX5
2.3.1. Coal Biological Desulfurization by A. ferrooxidans LX5
2.3.2. Pyrite Bio-Oxidation by A. ferrooxidans LX5
2.4. Analytical Procedures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Initial pH on pH and ORP in the Coal Desulfurization and Pyrite Bio-Oxidation Systems
3.2. Effect of Initial pH on Fe and SO42− Concentrations in the Coal Desulfurization and Pyrite Bio-Oxidation Systems
3.2.1. Effect of Initial pH on Total Fe, Fe3+, and Fe2+ Concentrations in the Coal Desulfurization and Pyrite Bio-Oxidation Systems
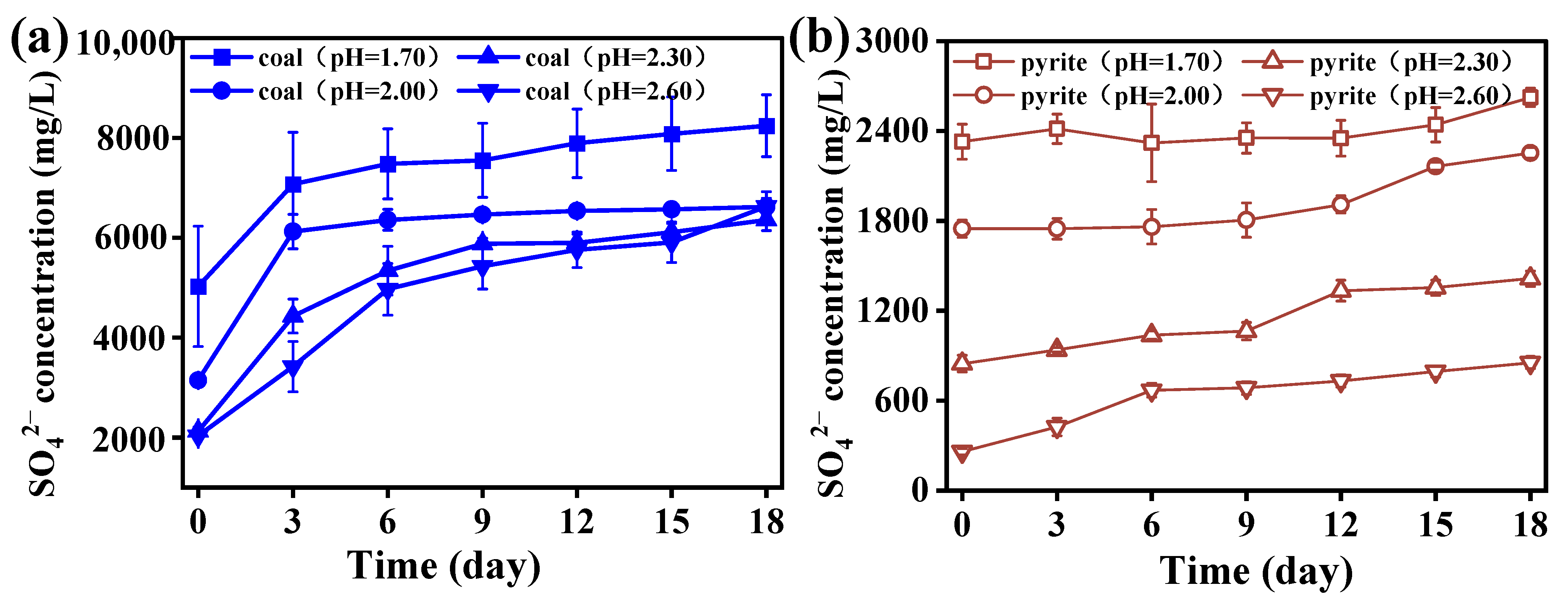
3.2.2. Effect of Initial pH on SO42− Concentration in the Coal Desulfurization and Pyrite Bio-Oxidation Systems
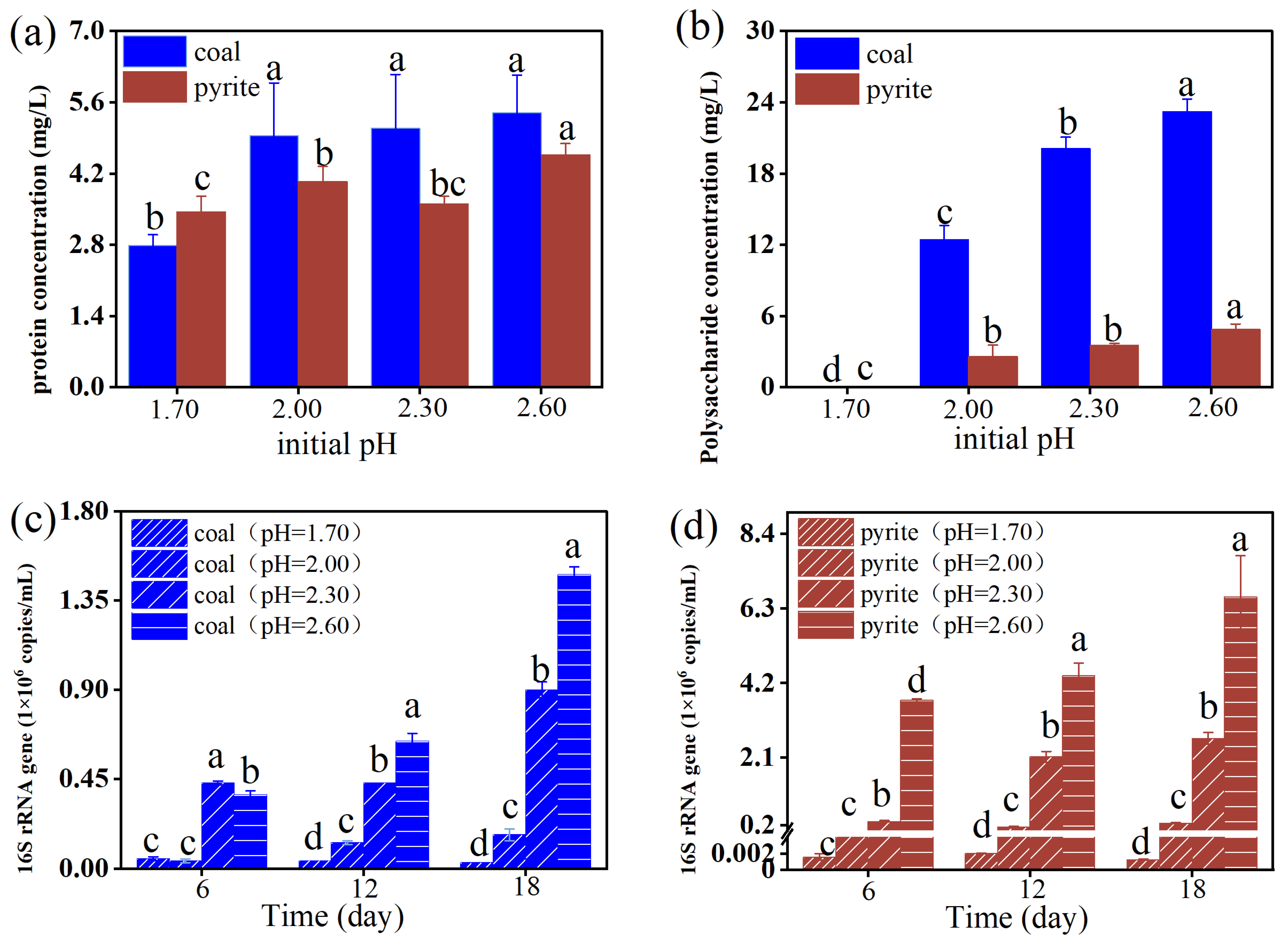
3.3. Effect of Initial pH on Bacterial Density and EPS in the Coal Desulfurization and Pyrite Bio-Oxidation Systems
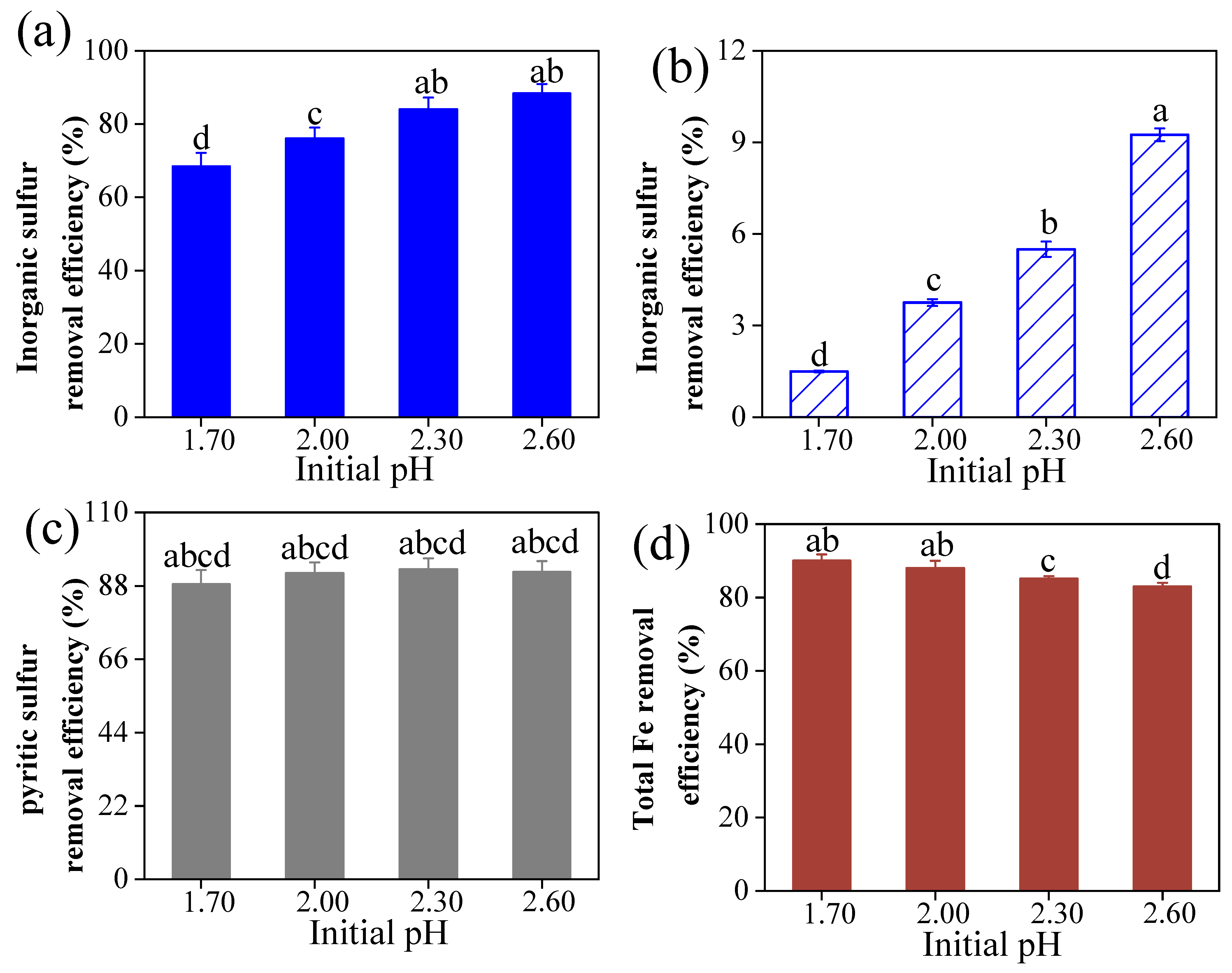
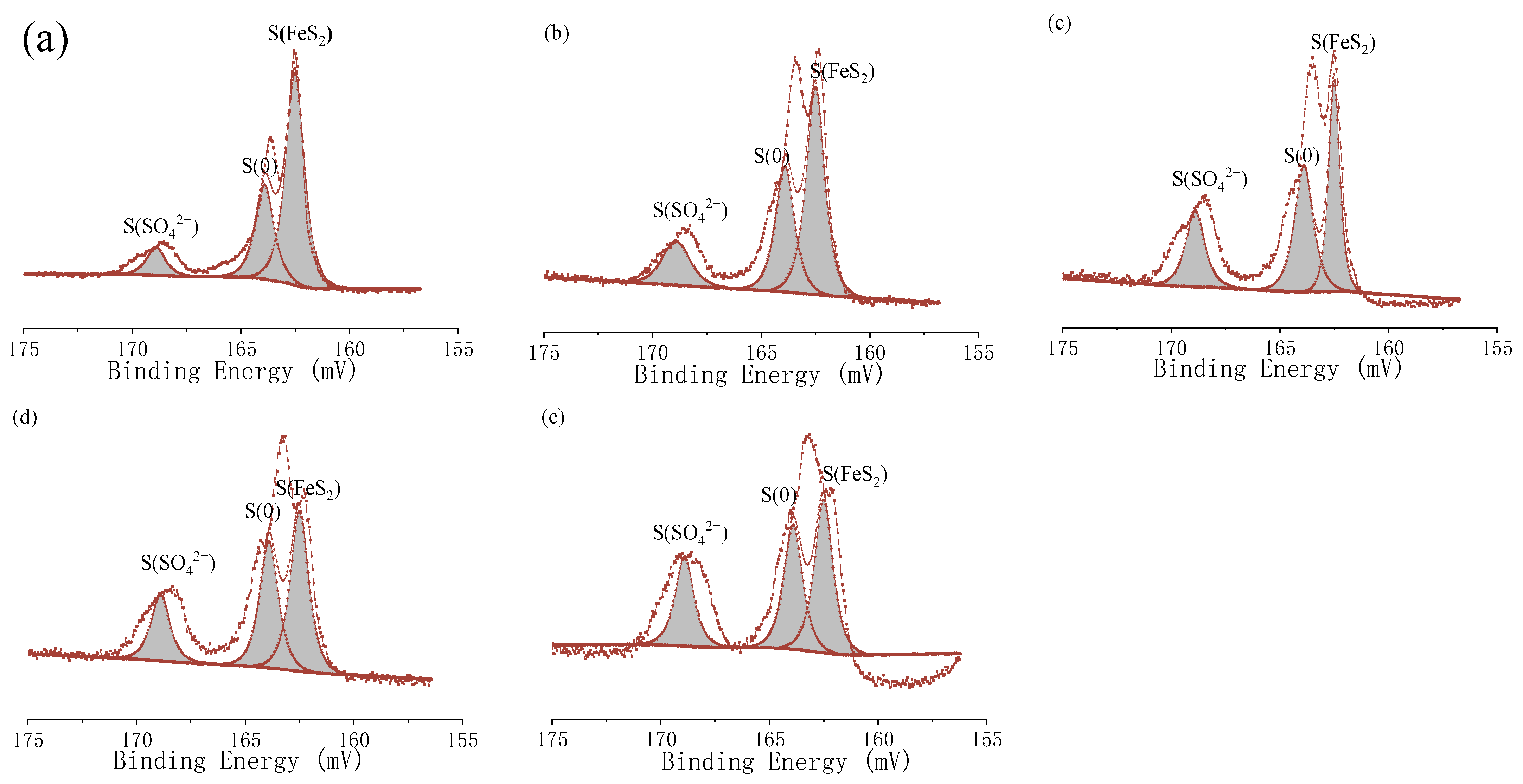
3.4. Analysis of Inorganic Sulfur and Pyritic Sulfur Removal in the Coal Desulfurization and Pyrite Bio-Oxidation Systems
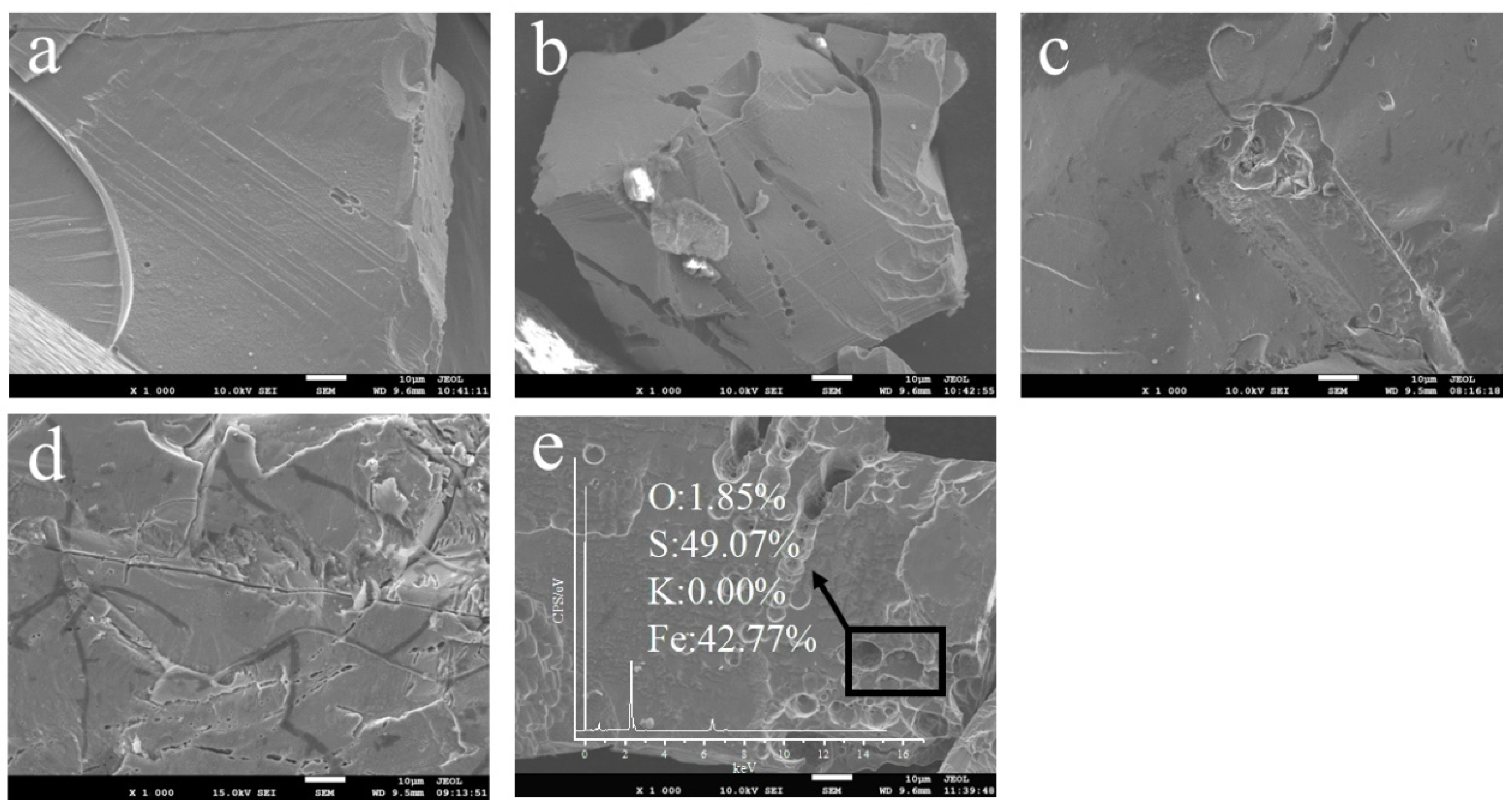
3.5. Effect of Initial pH on the Morphology and Chemical Composition of Bio-Oxidized Pyrite
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, M.; Hu, T.; Ren, G.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, Y. Research on the Effect of Surfactants on the Biodesulfurization of Coal. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 8116–8119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. Statistical Communique of People’s Republic of China on the 2018 National Economic and Social Development; National Bureau of Statistics of China: Beijing, China, 2019; Volume 3, pp. 8–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, T.; Cai, C.C.; Min, F.F.; Zhang, M. Effects of temperature and frequency on the dielectric properties of thiophene compounds and its application in coal microwave-assisted desulfurization. Fuel 2021, 301, 121089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Cen, X.W.; Xing, Y.W.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Gui, X. Depression Mechanisms of Sodium Humate and 3-Mercaptopropionic Acid on Pyrite in Fine Coal Flotation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 613, 156151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, S.G.; Shang, K.Z. Progress in Research of Acid Rain in China. Arid Eteorol. 2006, 2, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Nuhu, A.A. Bio-catalytic desulfurization of fossil fuels: A mini review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2013, 12, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.H.; Kasim, S.; Ahmed, O.H.; Rakib, M.R.M.; Hasbullah, N.A.; Shajib, T.I. Impact of simulated acid rain on chemical properties of Nyalau series soil and its leachate. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jigyasa, P.; Bhushan, A.S.; Madhoolika, A. Global Trends of Acidity in Rainfall and Its Impact on Plants and Soil. J. Soil. Sci. Plant. Nutr. 2023, 23, 398419. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.; Yousaf, M.; Han, J.C.; Rahman, S.U.; Sharif, H.M.A.; Wang, L.; Tang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Y. State-of-the-art analysis of the fuel desulphurization processes: Perspective of CO2 utilization in coal biodesulphurization. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 478, 147517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Ali, M.I.; Achakzai, J.K.; Jamal, A.; Ahmed, I.; Kakar, A.M.; Uddin, S. Sequential Chemical and Biological Desulphurization of High Sulfur Containing Pakistani Coal. Geomicrobiol. J. 2024, 41, 959965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.F.; Chen, S.J.; Gui, D.J.; Zhu, X.; He, H.; Tao, X. Effect of Removal Organic Sulfur from Coal Macromolecular on the Properties of High Organic Sulfur Coal. Fuel 2020, 259, 116264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.W.; Lei, Y.S.; Shi, J.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Bi, W. Effect of microbial nutrients supply on coal bio-desulfurization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.Y.; Li, Y.T.; Zhang, L.J.; He, W.J.; Han, Y.; Xu, D. Study on the effect of organic sulfur on coal spontaneous combustion based on model compounds. Fuel 2021, 289, 119846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Hong, F.F.; Tao, X.X.; Li, L.; Ma, C.Y.; Zhao, Y.D. Biodesulfurization of coal with Acidithiobacillus caldus and analysis of the interfacial interaction between cells and pyrite. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 101, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahraki, S.; Karamoozian, M.; Azizi, A. Desulfurization of coal by HNO3 leaching: Optimization of influential factors using Box-Behnken design. J. Min. Environ. 2018, 9, 657–665. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, P.P.; Wang, W.F.; Liu, X.H.; Qian, F.; Sang, S.; Xu, S. Distribution of As, Hg and other trace elements in different size and density fractions of the reshuihe high-sulfur coal. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2017, 173, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, M.N.; Cao, Y.; Von Lau, E. Advances in depressants used for pyrite flotation separation from coal/minerals. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2022, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.D.; Luo, Z.F. Upgrading of Low-Grade High Sulfur Lignite Using Differential Dynamic Field Dry Cascade Cleaning Apparatus. Fuel 2022, 324, 124485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, P.A.; Aksoy, D.Ö.; Koca, S.; Koca, H.; Çabuk, A. The approach of biodesulfurization for clean coal technologies: A review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 2115–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, M.; Ma, C.Y. Review of Coal-Fired Electrification and Magnetic Separation Desulfurization Technology. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.P.; Zhang, P.Y.; Zhang, G.M.; Wang, S.; Nabi, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H. Biodesulfurization of High Sulfur Fat Coal with Indigenous and Exotic Microorganisms. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.L.; Liu, Y.; Bu, Y.C.; Chen, M.; Wang, L. Review on the Ionic Liquids Affecting the Desulfurization of Coal by Chemical Agents. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Yang, L.G.; Jin, H.M.; Yi, R.; Liao, Z. Experimental study on microbial desulphurization of sulfide ores and self-heating simulation of ore heaps under ultrasonic and microwave. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 164, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Hou, J.H.; Peng, Y.L. Biodesulfurization from the High Sulfur Coal with a Newly Isolated Native Bacterium, Aspergillus sp. DP06. Environ. Prog. 2017, 36, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Li, Y.L.; Cao, Y.J.; Zhang, Z. A novel method for the desulfurization of medium high sulfur coking coal. Fuel 2023, 335, 126988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, A.S.; Bridgwood, E.W.; Davis, A.J.; Pooley, F.D. A Study of the Suppression of Pyritic Sulphur in Coal Froth Flotation by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Coal Prep. 1987, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 15224.2-2021; Coal Quality Classification—Part 2: Sulphur Content. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China, Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Liu, F.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, J.; Song, X.; Wang, D. Improvement of sludge dewaterability and removal of sludge borne metals by bioleaching at optimum pH. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 221–222, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, J.; Zhang, S.S.; Zhou, L.X.; Xu, J.M.; Ge, Y.; Fan, W.; Liu, F. Schwertmannite Adherence to the Reactor Wall during the Bio-Synthesis Process and Deterioration of Its Structural Characteristics and Arsenic(III) Removal Efficiency. Minerals 2017, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkin, B.P.; Somerfield, C. The determination of total sulphur in geological materials by coulometric titration. Chem. Geol. 1994, 111, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.W.; Qiao, X.; Zhou, L.X.; Zhang, J. Migration and Fate of Acid Mine Drainage Pollutants in Calcareous Soil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.Y.; Liang, J.L.; Liao, X.J.; Li, L.; Feng, X.; Qian, W.; Zhou, S.; Sun, S. Bioleaching for Detoxification of Waste Flotation Tailings: Relationship Between EPS Substances and Bioleaching Behavior. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.X.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, H.P.; Tan, Q.; Sun, H.; Jiang, C.; Ruan, R. Evidence of weak interaction between ferric iron and extracellular polymeric substances of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 209, 105817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, C.J.; Liu, H.; Ding, G.C.; Sun, Y.; Yu, X.; Chen, J.; Ren, J.; Gong, X. Impact of Direct Application of Biogas Slurry and Residue in Fields: In Situ Analysis of Antibiotic Resistance Genes from Pig Manure to Fields. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, M.; Li, M.M.; Zeng, J.; Liu, X.-X.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Hu, Y.-H.; Qiu, G.-Z. Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans enhanced heavy metals immobilization efficiency in acidic aqueous system through bio-mediated coprecipitation. Trans. Nonferrous Metals Soc. China 2017, 27, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouhi, E.; Ahmadi, A. Application of acid mine drainage for the biooxidation of a high-grade refractory sulfide gold ore. Environ. Earth. Sci. 2025, 84, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.Y.; Wang, H.M.; Wu, J.J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, X. Metatranscriptomics reveals microbial adaptation and resistance to extreme environment coupling with bioleaching performance. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 280, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastidar, M.G.; Malik, A.; Roychoudhury, P.K. Biodesulphurization of Indian (Assam) coal using Thiobacillus ferrooxidans (ATCC 13984). Energy Convers. 2000, 41, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinn, J.H. From Coal to Single-Stage and Two-Stage Products: A Reactive Model of Coal Structure. Fuel 1984, 63, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Vars, S.M.; Newton, K.; Quinton, J.S.; Cheng, P.-Y.; Wei, D.-H.; Chan, Y.-L.; Harmer, S.L. Surface Chemical Characterisation of Pyrite Exposed to Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Associated Extracellular Polymeric Substances. Minerals 2018, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muravyov, M.; Panyushkina, A. Distinct Roles of Acidophiles in Complete Oxidation of High Sulfur Ferric Leach Product of Zinc Sulfide Concentrate. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.P.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhong, C.; Li, Y.; Hao, W.; Zhu, J. The effect of quorum sensing and extracellular proteins on the microbial attachment of aerobic granular activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, I. The Biofilm Matrix—An Immobilized but Dynamic Microbial Environment. Trends Microbiol. 2001, 9, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Yang, H.Y.; Tong, L.L.; Ma, P.; Luan, Z.; Sun, Q. Applying bio-oxidation waste solution into two-stage oxidation process to enhance the bio-oxidation of pyrite: Insight on enhanced mechanism. J. Water Process. Eng. 2024, 59, 104939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, D.; Wei, Y.; Fan, X.; Liu, F. Difference in Biological Oxidation Between High-Sulfur Coal and Pure Pyrite at Different pH Levels. Separations 2025, 12, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12030066
Yuan D, Wei Y, Fan X, Liu F. Difference in Biological Oxidation Between High-Sulfur Coal and Pure Pyrite at Different pH Levels. Separations. 2025; 12(3):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12030066
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Dongxu, Yiyang Wei, Xinyu Fan, and Fenwu Liu. 2025. "Difference in Biological Oxidation Between High-Sulfur Coal and Pure Pyrite at Different pH Levels" Separations 12, no. 3: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12030066
APA StyleYuan, D., Wei, Y., Fan, X., & Liu, F. (2025). Difference in Biological Oxidation Between High-Sulfur Coal and Pure Pyrite at Different pH Levels. Separations, 12(3), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12030066




