Separation of D-Amino Acid-Containing Tripeptide L-Asn-D-Trp-L-Phe-NH2 and Its Diastereomer Using Crown–Ether-Type Chiral Stationary Phase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
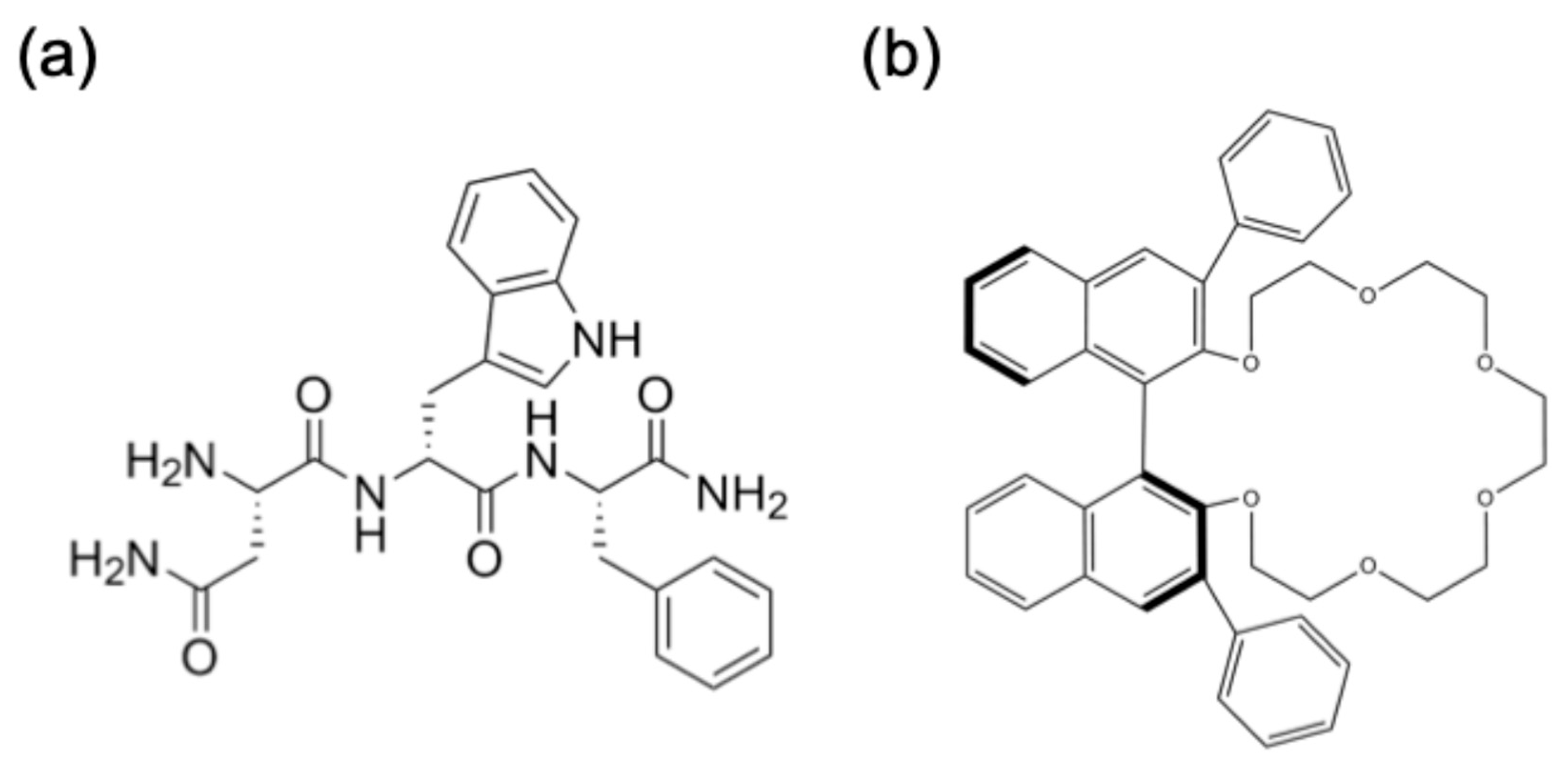
2.1. Synthesis of N(dW)F and NWF Peptide
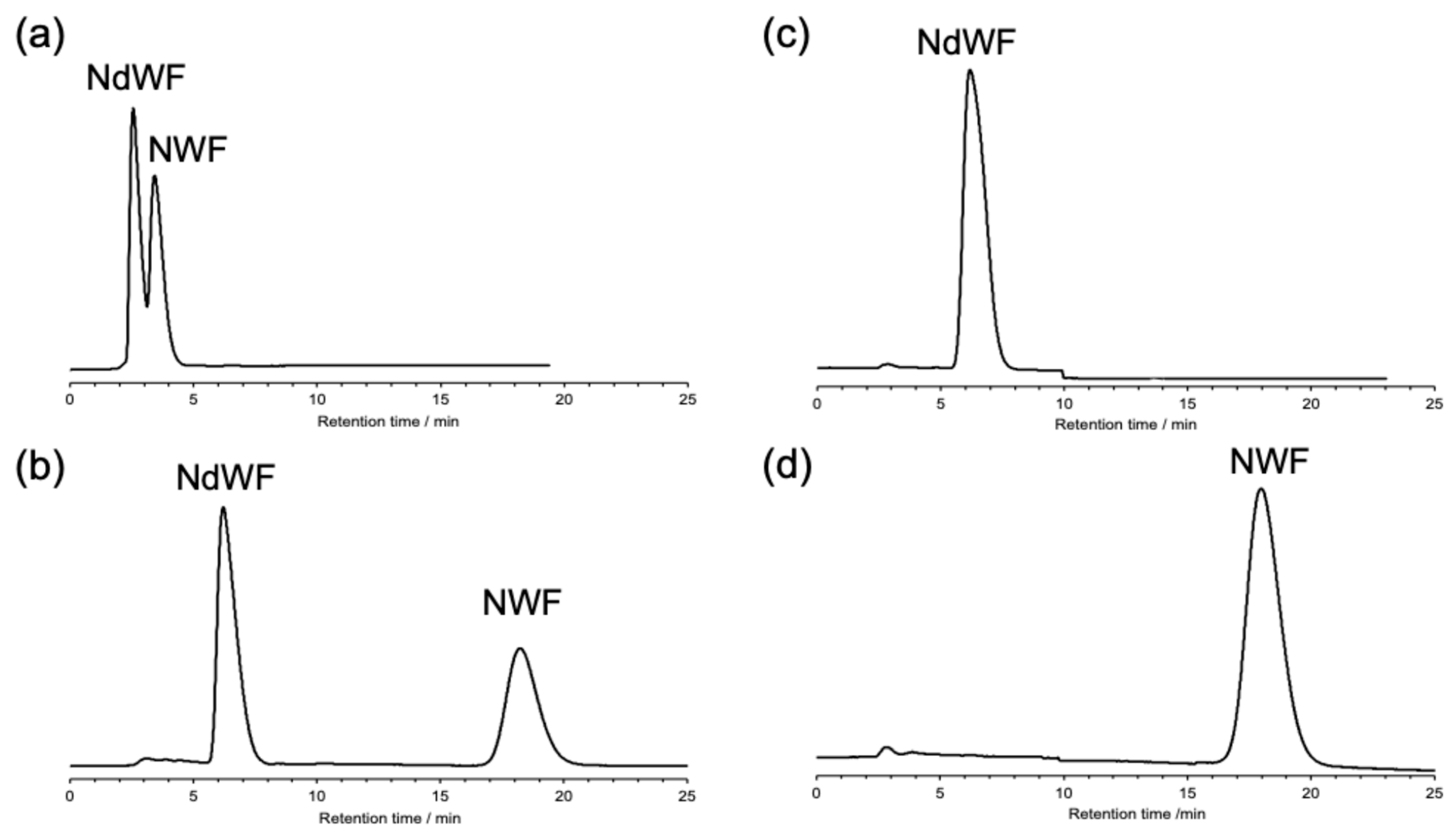
2.2. Separation by CR-I Column
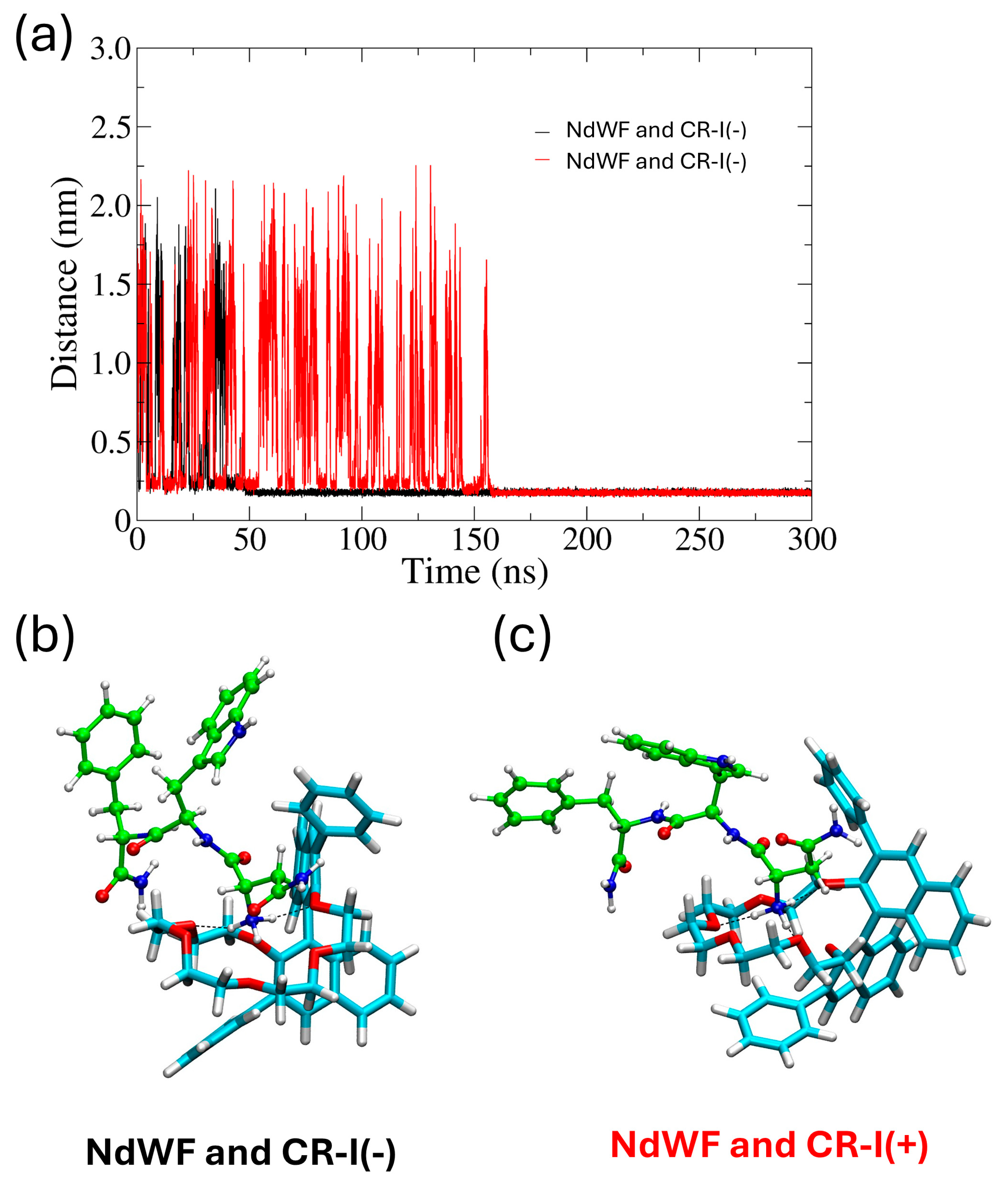
2.3. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fujii, N.; Takata, T.; Fujii, N.; Aki, K.; Sakaue, H. D-amino acids in protein: The mirror of life as a molecular index of aging. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2018, 1866, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ollivaux, C.; Soyez, D.; Toullec, J.Y. Biogenesis of D-amino acid containing peptides/proteins: Where, when and how? J. Pept. Sci. 2014, 20, 595–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreil, G. D-amino acids in animal peptides. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997, 66, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mast, D.H.; Checco, J.W.; Sweedler, J.V. Advancing D-amino acid-containing peptide discovery in the metazoan. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2021, 1869, 140553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulbagi, M.; Wang, L.; Siddig, O.; Di, B.; Li, B. D-amino acids and D-amino acid-containing peptides: Potential disease biomarkers and therapeutic targets? Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreil, G. Conversion of L- to D-amino acids: A posttranslational reaction. Science 1994, 266, 996–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehmayr, G.; Mollay, C.; Reith, L.; Muller, N.; Jilek, A. Tight binding of transition-state analogues to a peptidyl-aminoacyl-l/d-isomerase from frog skin. ChemBioChem 2011, 12, 1996–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.M. Post-translational modifications of protein backbones: Unique functions, mechanisms, and challenges. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilek, A.; Mollay, C.; Lohner, K.; Kreil, G. Substrate specificity of a peptidyl-aminoacyl-l/d-isomerase from frog skin. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecucchi, P.C.; De Castiglione, R.; Piani, S.; Gozzini, L.; Erspamer, V. Amino acid composition and sequence of dermorphin, a novel opiate-like peptide from the skin of Phyllomedusa sauvagei. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1981, 17, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janecka, A.; Fichna, J.; Janecki, T. Opioid receptors and their ligands. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishita, F.; Nakanishi, Y.; Kaku, S.; Furukawa, Y.; Ohta, S.; Hirata, T.; Ohtani, M.; Fujisawa, Y.; Muneoka, Y.; Matsushima, O. A novel D-amin-acid-containing peptide isolated from Aplysia heart. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 240, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mignogna, G.; Simmaco, M.; Kreil, G.; Barra, D. Antibacterial and haemolytic peptides containing D-alloisoleucine from the skin of Bombina variegate. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 4829–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangoni, M.L. A lesson from Bombinin H, mildly cationic diastereomeric antimicrobial peptides from Bombina skin. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2013, 14, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Magalhães, M.T.Q.; Barbosa, E.A.; Prates, M.V.; Verly, R.M.; Munhoz, V.H.O.; de Araújo, I.E.; Bloch, C. Conformational and functional effects induced by d- and l-amino acid epimerization on a single gene encoded peptide from the skin secretion of Hypsiboas punctatus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsaikhan, M.; Matsuo, Y.; Sato, H.; Ueda, K.; Kawamura, I. A comparative study of interactions of antimicrobial peptides L- and D-phenylseptin with 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, Y.; Sato, H.; Kayano, Y.; Yamaki, N.; Izato, Y.; Miyake, A.; Naito, A.; Kawamura, I. Self-assembly of tripeptides into γ-turn nanostructures. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 10879–10883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, A.; Shibata, T.; Imase, T.; Shinkura, S.; Nagai, K. Achiral molecular recognition of substituted aniline position isomers by crown ether type chiral stationary phase. Molecules 2021, 26, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cram, D.J. The design of molecular hosts, guests, and their complexes. Science 1988, 240, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konya, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Furuno, M.; Nakano, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Fukusaki, E. Mechanistic study on the high-selectivity enantioseparation of amino acids using a chiral crown ether-bonded stationary phase and acidic, highly organic mobile phase by liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1578, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, U.; Chankvetadze, B.; Scriba, G.K.E. High performance liquid chromatographic separation of dipeptide and tripeptide enantiomers using a chiral crown ether stationary phase. J. Sep. Sci. 2005, 28, 2275–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konya, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Fukusaki, E. Novel high throughput and widely targeted liquid chromatography-time of flight mass spectrometry method for D-amino acids in foods. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 123, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upmanis, T.; Kažoka, H.; Arsenyan, P. A study of tetrapeptide enantiomeric separation on crown ether based chiral stationary phases. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1622, 461152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, I.; Mijiddorj, B.; Kayano, Y.; Matsuo, Y.; Ozawa, Y.; Ueda, K.; Sato, H. Separation of D-amino acid-containing peptide phenylseptin using 3,3′-phenyl-1,1′-binaphthyl-18-crown-6-ether columns. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2020, 1868, 140429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijiddorj, B.; Kaneda, S.; Sato, H.; Kitahashi, Y.; Javkhlantugs, N.; Naito, A.; Ueda, K.; Kawamura, I. The role of D-allo-isoleucine in the deposition of the anti-Leishmania peptide bombinin H4 as revealed by 31P solid-state NMR, VCD spectroscopy and MD simulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2018, 1866, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, F.; Matsushima, O.; Furukawa, Y.; Minakata, H. Deamidase inactivates a D-amino acid-containing Aplysia neuropeptide. Peptides 2003, 24, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, F.; Furukata, Y.; Matsushima, O. N(dW)Famide: A D-amino acid containing neuropeptide of an opistobranch gastropod, Aplysia kurodai. Comp. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 28, 308–316. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.; Sheeley, S.; Sweedler, J.V. Analysis of endogenous d-amino acid-containing peptides in Metazoa. Bioanal. Rev. 2009, 1, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, N.; Kubota, I.; Takao, T.; Shimonishi, Y.; Yasuda-Kamatani, Y.; Minakata, H.; Nomoto, K.; Muneoka, Y.; Kobayashi, M. Fulicin, a novel neuropeptide containing a d-amino acid residue isolated from the ganglia of Achatina fulica. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 178, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda-Kamatani, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Yasuda, A.; Fujita, T.; Minakata, H.; Nomoto, K.; Nakamura, M.; Sakiyama, F. A novel d-amino acid-containing peptide, fulyal, coexists with fulicin gene-related peptides in Achatina atria. Peptides 1997, 18, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, H.; Sato, H.; Kawamura, I. Vibrational circular dichroism of D-amino acid-containing peptide N(dW)Famide in the crystal form. Chirality 2021, 33, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, M.J.; van der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; The GROMACSS development team. GROMACS User Manual Version 2018; GROMACS: Uppsala, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vanommeslaeghe, K.; Hatcher, E.; Acharya, C.; Kundu, S.; Zhong, S.; Shim, J.; Darian, E.; Guvench, O.; Lopes, P.; Vorobyov, I.; et al. CHARMM general force field: A force field for drug-like molecules compatible with the CHARMM all-atom additive biological force fields. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 671–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; MacKerell, A.D. CHARMM36 all-atom additive protein force field: Validation based on comparison to NMR data. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussi, G.; Donadio, D.; Parrinello, M. Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrinello, M.; Rahman, A. Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: A new molecular dynamics method. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 7182–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N⋅log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.L.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, L.G. A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 8577–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.J.C.; Fraaije, J.G.E.M. Lincs: A linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 1997, 18, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaught, A. Graphing with Gnuplot and Xmgr: Two graphing packages available under Linux. Linux J. 1996, 1996, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mijiddorj, B.; Kayano, Y.; Yamagishi, H.; Nakajima, H.; Kawamura, I. Separation of D-Amino Acid-Containing Tripeptide L-Asn-D-Trp-L-Phe-NH2 and Its Diastereomer Using Crown–Ether-Type Chiral Stationary Phase. Separations 2025, 12, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12030067
Mijiddorj B, Kayano Y, Yamagishi H, Nakajima H, Kawamura I. Separation of D-Amino Acid-Containing Tripeptide L-Asn-D-Trp-L-Phe-NH2 and Its Diastereomer Using Crown–Ether-Type Chiral Stationary Phase. Separations. 2025; 12(3):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12030067
Chicago/Turabian StyleMijiddorj, Batsaikhan, Yohei Kayano, Hiroki Yamagishi, Haruto Nakajima, and Izuru Kawamura. 2025. "Separation of D-Amino Acid-Containing Tripeptide L-Asn-D-Trp-L-Phe-NH2 and Its Diastereomer Using Crown–Ether-Type Chiral Stationary Phase" Separations 12, no. 3: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12030067
APA StyleMijiddorj, B., Kayano, Y., Yamagishi, H., Nakajima, H., & Kawamura, I. (2025). Separation of D-Amino Acid-Containing Tripeptide L-Asn-D-Trp-L-Phe-NH2 and Its Diastereomer Using Crown–Ether-Type Chiral Stationary Phase. Separations, 12(3), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12030067






