Abstract
With the rapid development of China’s zinc-related industries, the grade of zinc concentrate has steadily declined, while the generation of zinc-containing solid waste has shown a significant upward trend. To address this issue, a collaborative smelting process for lead–zinc ores and zinc-containing solid waste has been proposed, aiming to effectively recycle zinc-based solid waste during the processing of lead–zinc ores. This study examined the effects of adding different proportions of electroplating sludge (3%, 6%, 9%, and 12%) to lead–zinc ores on the smelting performance of primary ores. The results indicated that when the addition reached 6% or higher, certain complex compounds were effectively decomposed, while the volatilization rate remained comparable to that of the primary ore. Moreover, increasing the proportion of electroplating sludge not only immobilized part of the lead, reducing its volatilization, but also significantly lowered the melting point of the mixture. The lowest melting point (1199 °C) was observed with a 9% addition; although it slightly increased at 12%, it remained below the melting point of the primary ore. Based on these findings, an optimal addition of approximately 6% electroplating sludge is recommended to maximize the efficiency and benefits of the collaborative smelting process.
1. Introduction
As a pivotal industry underpinning the national economy, lead and zinc smelting plays an irreplaceable role across multiple sectors [1,2]. With the continuous growth of the global economy and the ongoing advancement of technology, zinc, as a versatile strategic material, has seen a persistent rise in market demand. However, the increasing depletion of high-grade zinc ore resources has prompted a shift in focus towards secondary resources—zinc-bearing solid waste [3]. The zinc content in these waste materials is significant, sometimes even exceeding that of raw ores, endowing them with dual characteristics of resource utilization and hazardous solid waste [4,5,6]. However, the overall level of recycling and utilization of zinc-bearing solid waste in China remains relatively low, significantly below the average levels observed in developed countries in Europe and North America [7]. Therefore, efficient management and resource utilization represent a critical pathway for the lead and zinc smelting industry to achieve green and sustainable development, aligning with the industry’s essential needs. Among various types of zinc-bearing solid waste, electroplating sludge has emerged as a critical target for treatment due to its high production volume and significant toxicity. Electroplating sludge [8] contains not only substantial amounts of valuable metals but also toxic metals, which, if not properly managed, can pose severe risks to the environment and human health [9,10]. Currently, the technologies for treating electroplating sludge mainly include solidification/stabilization [11], hydrometallurgical methods [12], and pyrometallurgical methods [13]. Among these, the solidification/stabilization process, despite its simplicity, may lead to the slow release of heavy metals, resulting in secondary pollution and the wastage of valuable metals such as nickel, copper, and zinc [14]. Hydrometallurgical treatment can recover metals with relatively high efficiency [15], but it may cause secondary pollution from waste acid and wastewater containing valuable metals. In contrast, pyrometallurgical treatment technology offers significant advantages in metal recovery and the generation of non-hazardous slag. However, its efficiency still requires improvement, which also presents the possibility of co-processing electroplating sludge with primary zinc ore smelting.
The low-energy pool smelting process used for processing zinc-containing materials typically restricts the zinc content to below 20% at present. This is due to the high melting point of zinc oxide (ZnO) at 1975 °C, which makes it difficult for high-zinc materials to melt and flow at conventional smelting temperatures (1150 –1300 °C). Additionally, the composition and content of metal oxides significantly affect the smelting process. Compared to conventional pyrometallurgical smelting of lead–zinc ores, the co-smelting process of lead–zinc ores and metallic solid waste is more complex, involving multiple challenges such as smelting desulfurization, mineral phase transformation, and the difficulty of achieving molten fluidity under conventional smelting conditions due to the high melting point of high-zinc materials. This complexity makes it difficult to efficiently achieve the co-disposal and resource utilization of lead–zinc heavy metal hazardous waste and industrial solid waste. Therefore, improving fundamental theoretical research and developing key technologies and equipment for the co-smelting of lead and zinc will be an inherent requirement to adapt to the technological advancements in the pyrometallurgical smelting of lead and zinc. Additionally, Zhou et al.’s research on oxygen-enriched side-blown furnaces for direct lead smelting provides further validation. Their successful co-processing of zinc leaching residues and jamesonite lead concentrates confirms the technical feasibility of multi-material synergistic smelting [16]. Currently, both domestically and internationally, the co-processing of primary ores with metal-based solid waste primarily focuses on copper pyrometallurgical smelting with copper-based solid waste [17,18] and lead pyrometallurgical smelting with lead-based solid waste [19,20], while related research on zinc smelting remains relatively limited. Some scholars have conducted theoretical data evaluations on the co-smelting model of solid waste and lead–zinc ores. The results indicate that, compared to traditional models, the total environmental burden is nearly halved. Additionally, the “concentrate + slag” smelting method reduces the consumption of zinc concentrates per unit of zinc product by 26.7% and decreases carbon emissions by 57.3% [21].
Against this backdrop, this study innovatively proposes the application of oxygen-enriched side-blown smelting technology to the co-smelting of lead–zinc ores and various zinc-based solid waste products. Recent advancements by Huang et al. revealed that ZnO concentrations exceeding 25% further exacerbate fluidity challenges, even at 1300 °C. To address this, they optimized the thermodynamic reduction conditions (1250 °C, 5% carbon addition) using high-purity zinc-bearing feedstocks coupled with calcium–silicate regulation, successfully reducing the system’s melting temperature [22]. In comparison, our study extends this direction by proposing the addition of electroplating sludge to reduce the melting point below 1250 °C. The composition of electroplating sludge is complex, containing not only calcium and silicon but also other metal oxides (such as Cu2O). This innovative method reduces the resource consumption caused by the traditional method of adding large amounts of calcium–silicon flux to lower the melting point of lead–zinc ores. We particularly focus on the combination of lead–zinc ores and electroplating sludge, investigating their oxidation reaction characteristics and interaction mechanisms under different temperatures and oxygen partial pressures, especially the melting mechanisms, phase transformations, and flow distribution patterns at low temperatures (around 1250 °C). This research aims to provide theoretical support for the short-process smelting technology for large-scale matching of lead–zinc ores with zinc-based solid waste.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
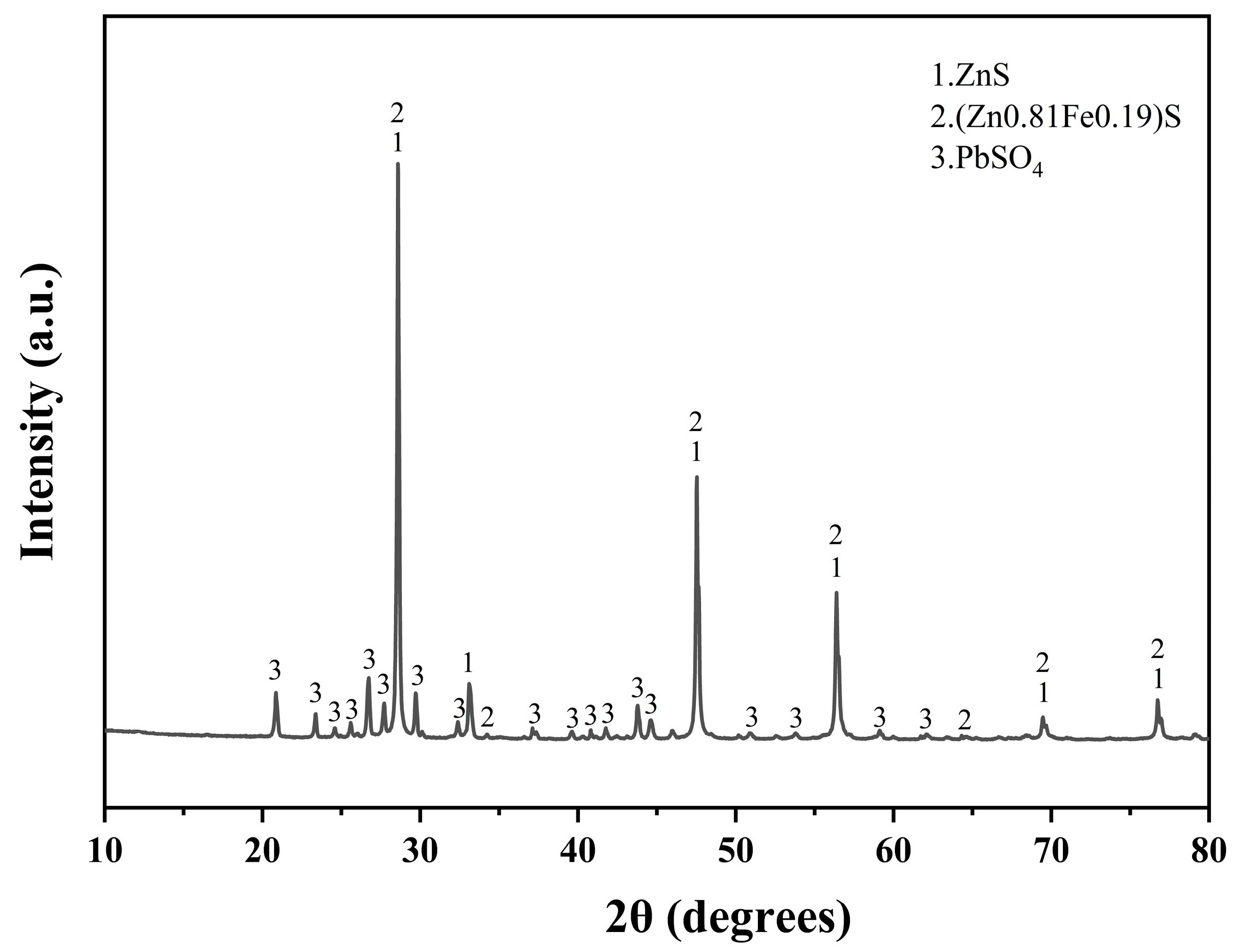
The lead–zinc ore samples used in this experiment were sourced from the lead–zinc concentrate provided by Hong Chi Zinc Germanium Company in Qu Jing City, Yunnan province, a prominent lead–zinc smelting enterprise in Yunnan. The elemental contents of the raw materials, determined by chemical analysis, are shown in Table 1. The zinc content of the ore was 47.3%, qualifying it as a high-grade zinc concentrate. Additionally, the sample contained 9.32% lead, highlighting its potential for the recovery of both zinc and lead. The sample was ground into a powder for XRD detection, and the results were analyzed to obtain the main phases, The ore’s primary mineral components included zinc sulfide (ZnS), marmatite (Zn0.81Fe0.19S) [23], and lead sulfate (PbSO4) (Figure 1).

Table 1.
Main chemical components of samples (mass%).
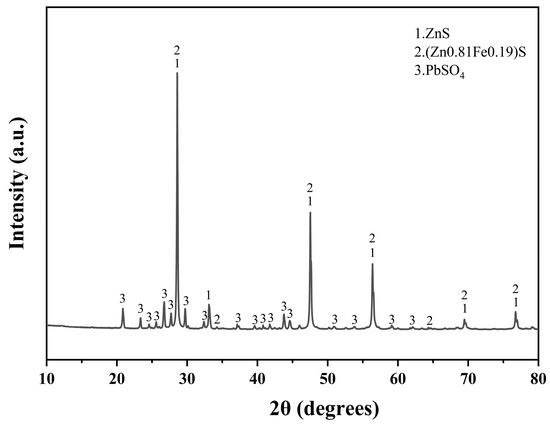
Figure 1.
XRD diffractogram of lead–zinc ore.
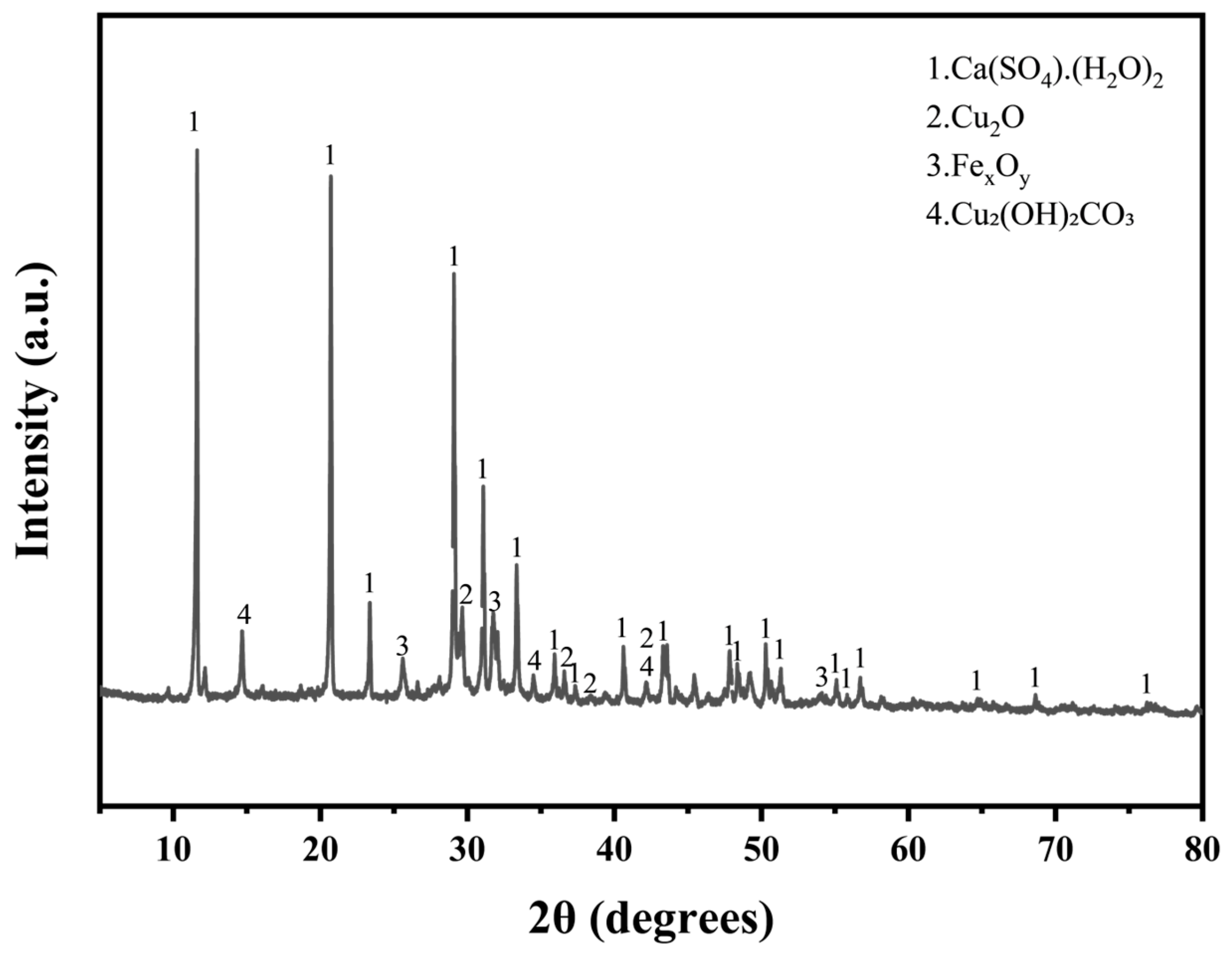
In the experimental process, electroplating sludge was used as an additive to metal-based solid waste. This sludge, a byproduct of the electroplating industry, is rich in metals, particularly copper and calcium, with trace amounts of zinc. As indicated in Table 1, the electroplating sludge contains 29.5% copper, with a calcium content exceeding 24.7%. It also includes a small amount of chlorine. The sludge’s high metal content makes it a valuable resource for metal recovery, while its environmental impact is minimized due to the absence of fluorine, which simplifies subsequent treatment processes. The main chemical constituents of the electroplating sludge include calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO2H2O), cuprous oxide (Cu2O), basic copper carbonate (Cu2 (OH)2 CO3) [24], and iron oxides (FexOy) (Figure 2). The overall blue-green color of the material reflects these compositions. Together, these properties make the electroplating sludge not only a key resource for metal recovery but also an environmentally favorable waste material.
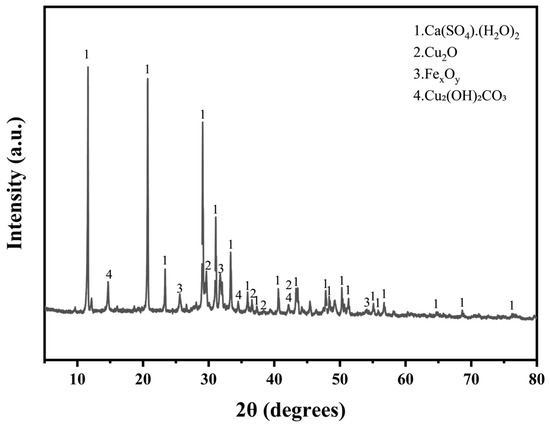
Figure 2.
XRD diffractogram of electroplated sludge.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Experimental Methods
In the experimental procedure described in the process diagram in Figure 3, lead–zinc ore and electroplating sludge were initially placed in an oven and dried at appropriate temperatures to thoroughly remove moisture. The dried samples were then subjected to grinding in a ball mill to obtain a fine, uniform powdered form. In a single-factor experiment, 12 g of either lead–zinc ore or electroplating sludge was compressed into a uniformly round sheet using a tablet press. These discs were subsequently placed in a corundum crucible and heated to different temperatures of 1150 °C, 1250 °C, and 1350 °C to examine the changes in the samples under varying thermal conditions.
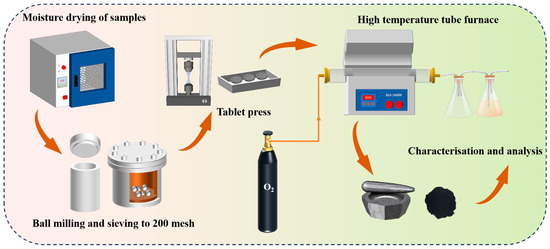
Figure 3.
Experimental process.
In an oxidation section experiment, which simulated the primary processing of lead–zinc ore, 12 g of lead–zinc ore powder was initially weighed, and electroplating sludge was added at varying proportions of 3%, 6%, 9%, and 12%. The resulting mixtures were thoroughly stirred to ensure even distribution of the components and then pressed into discs using a tablet press. The sludge’s high metal content made it a valuable resource for metal recovery, while its environmental impact was minimized due to the absence of Cl, which simplified subsequent treatment processes. To adhere to native processing conditions, all of the experiments were conducted under conditions enriched with 48% oxygen, and in order to ensure the adequacy of roasting, the heating rate of all experiments was maintained at 8.5 °C/min, and the holding time after reaching the established temperature was 90 min.
2.2.2. Detection Methods
XRD: The analysis was performed using an X’ Pert PRO diffractometer (Rigaku Ultima IV, Tokyo, Japan). This instrument employed a Cu target with Kα radiation at a wavelength of λ = 1.5406 Å. The operating conditions were set at 40 kV voltage and 30 mA current, scanning samples over a 10° to 80° range at a speed of 1°/min.
XRF: Elemental contents were measured using a Rigaku ZSX Primus III+ X-ray fluorescence spectrometer in Tokyo, Japan. This device utilized an Rh target X-ray tube with a test diameter of 20 mm and analyzed elements ranging from 11Na to 92U. The detection was achieved using a scintillation counter (SC) and a proportional counter (PC) with 2θ scanning mode.
SEM-EDS: The ZEISS Sigma 300 scanning electron microscope, manufactured by Carl Zeiss, whose headquarters is located in Oberkochen, Germany, was used for capturing sample morphology and conducting EDS mapping. Samples were coated with gold using an Oxford Quorum SC7620 sputter coated. which is a product of Quorum Technologies, a company in Oxfordshire, UK. The microscope was equipped with an SE2 secondary electron detector.
Heating microscope: A melting point apparatus of the German HESSE model (EM301-M17), produced by Hesse Instruments. Hesse Instruments is a company based in Offenbach am Main, Germany, was employed for determining the melting point of the roasted samples. The testing involved sample side-profile projection using LED illumination. The maximum furnace temperature was ≥1650 °C, with PID temperature control ensuring a precision of ±1 °C. Measurement precisions included a sample height accuracy of ≤0.1%, cross-sectional accuracy of ≤0.1%, contact angle accuracy of ±1 degree, apex angle accuracy of ±1 degree, and area accuracy of ≤0.1%.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of Electroplating Sludge on the Phase Transition in Smelting Processes
3.1.1. Physical Phase Transition in Lead–Zinc Ores After Roasting with Electroplating Sludge
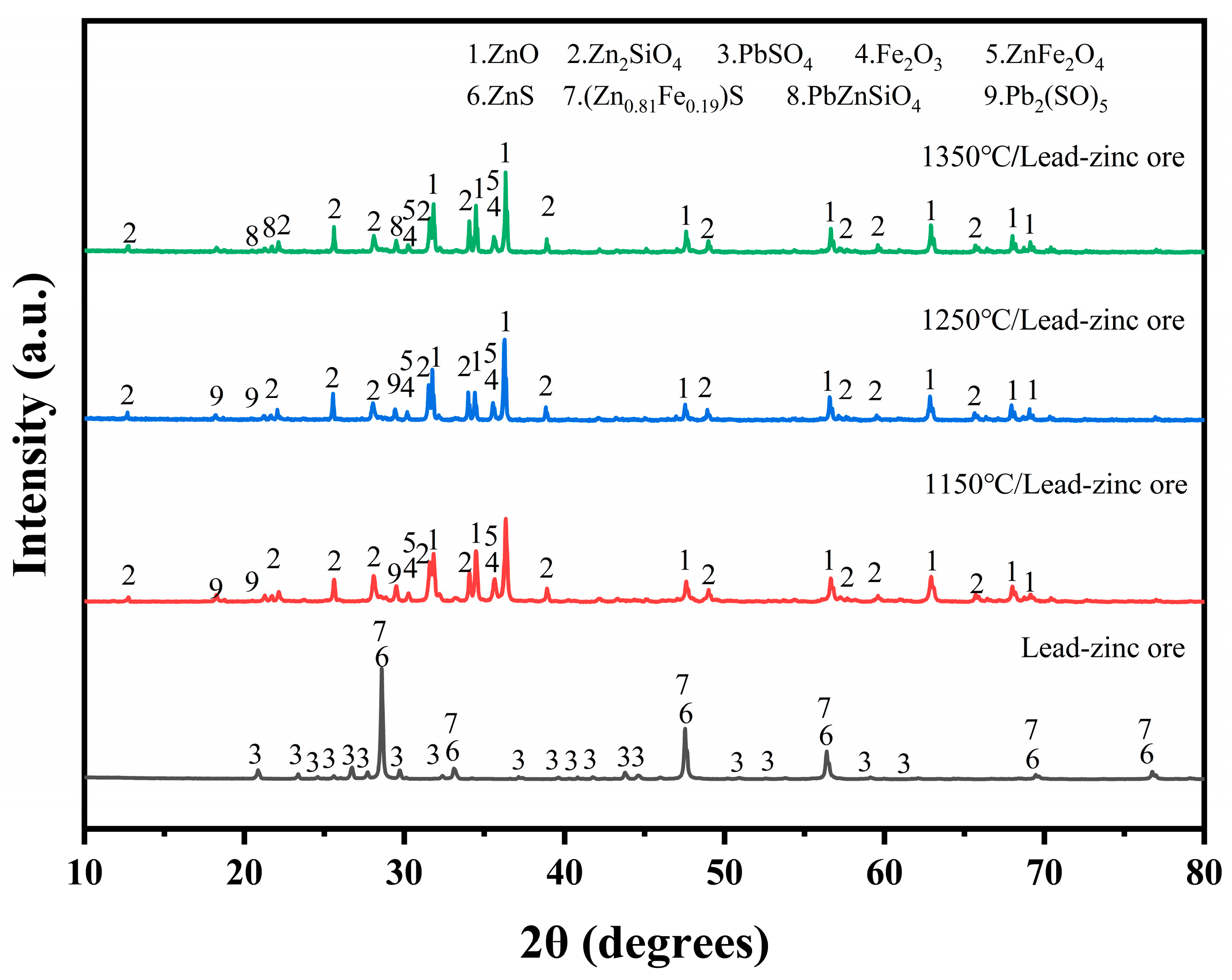
To investigate the effect of electroplating sludge’s addition on the smelting of lead–zinc ore, the lead–zinc ore and electroplating sludge were separately roasted at 1150 °C, 1250 °C, and 1350 °C. The physical phases of the roasted samples were then analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD). As shown in Figure 4, the lead sulfate (PbSO4) in the raw ore was converted to a more complex lead sulfate compound (Pb2SO5) [25] during roasting at 1150 °C and 1250 °C. Simultaneously, zinc sulfide (ZnS) was oxidized in the oxidizing environment to form zinc oxide (ZnO). In this process, zinc not only participated in the generation of ZnO but also reacted with silicates and iron oxides to form new phases, such as zinc silicate (Zn2SiO4) and zinc ferrate (ZnFe2O4) [26]. Additionally, the iron in the raw ore was partially oxidized, producing magnetite (Fe3O4).
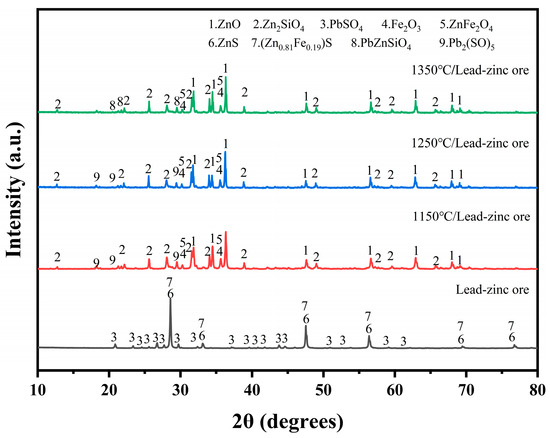
Figure 4.
XRD diffractogram of the phase compositions of lead–zinc ore after roasting at three temperatures: 1150 °C, 1250 °C, and 1350 °C.
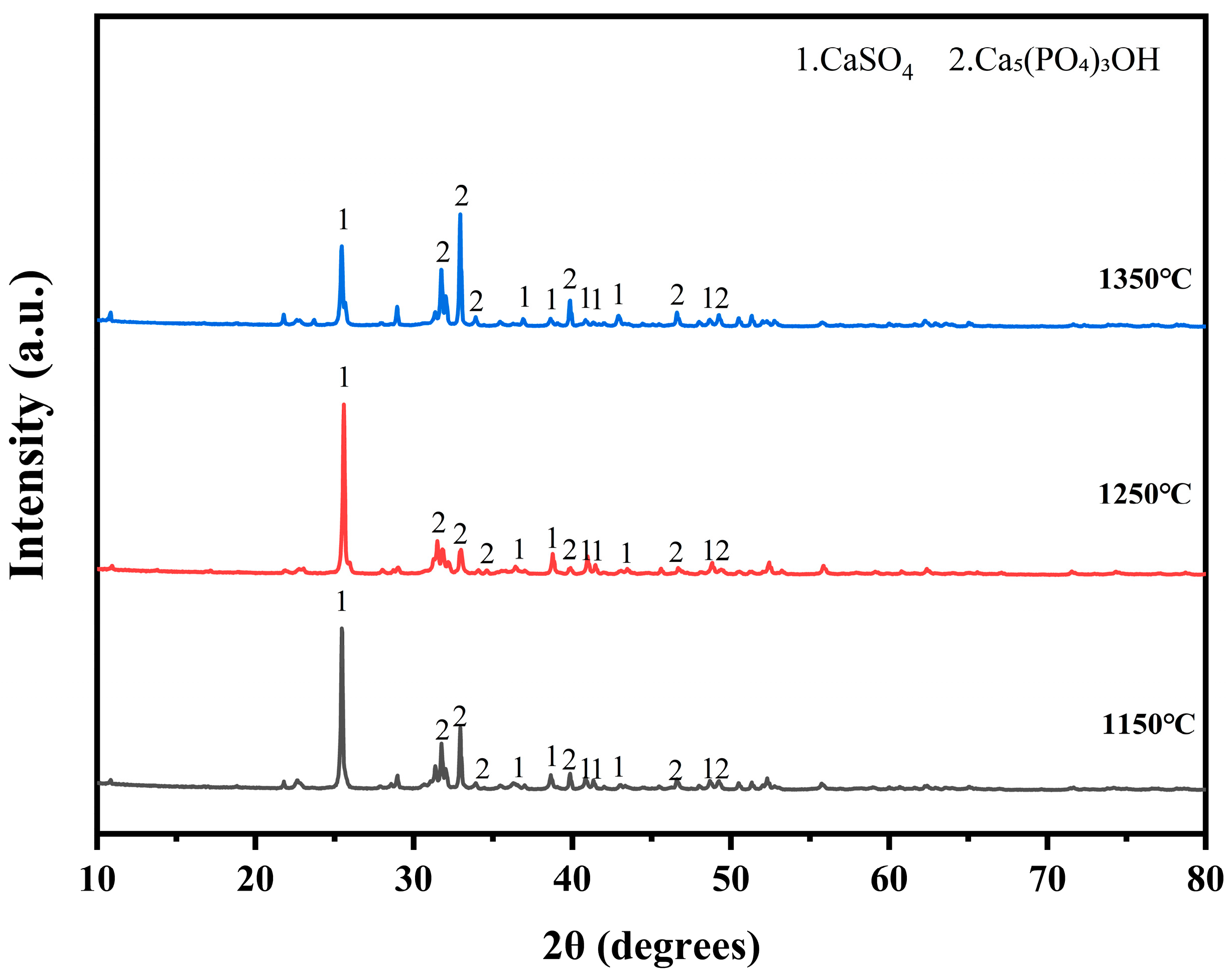
At 1350 °C, significant changes occurred in the physical phases of both zinc and lead. The phase of Pb2SO5 disappeared, and a new refractory phase, PbZnSiO4, appeared. This suggests that, under high-temperature conditions, the compounds of lead and zinc form a more stable structure with silicates. Figure 5 illustrates the physical phases of electroplating sludge after roasting at the three temperatures. Following oxygen-enriched roasting at varying temperatures, the primary components of the electroplating sludge included calcium sulfate, complex apatite phases (Ca5(PO4)3OH) [27], and a small amount of iron oxides. The temperature had minimal impact on the physical phase changes during roasting, but with increasing temperature, the diffraction peak intensity of calcium sulfate gradually decreased, while the intensity of the diffraction peak corresponding to the apatite phase increased. This indicates that higher temperatures facilitate the transformation of calcium sulfate to apatite.
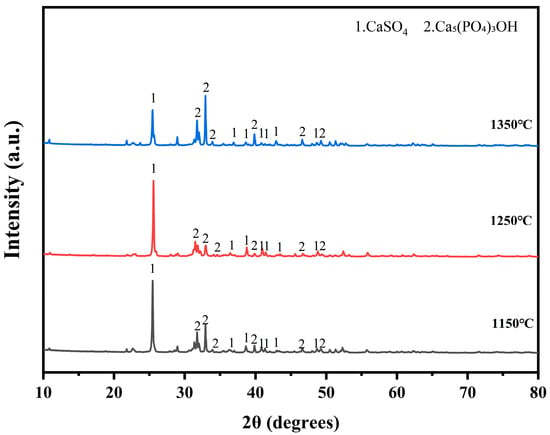
Figure 5.
XRD diffractogram of the phase compositions of electroplated sludge after roasting at three temperatures: 1150 °C, 1250 °C, and 1350 °C.
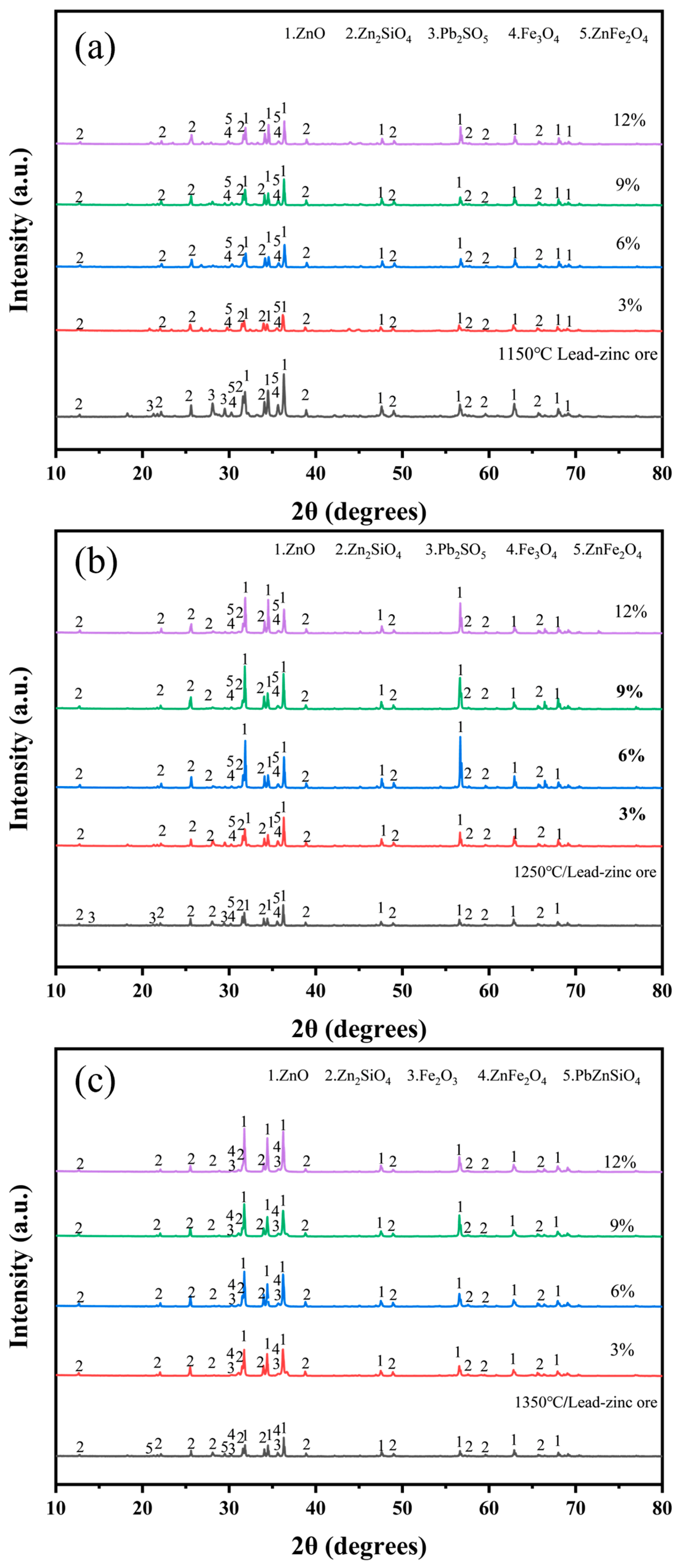
To minimize the influence of external factors in the experiments, electroplating sludge was directly added to lead–zinc ore without the use of any melting agent, to assess its effect on smelting. Figure 6 illustrates the physical phases after mixing and roasting the raw ore with varying proportions of electroplating sludge (3%, 6%, 9%, and 12%) at temperatures of 1150 °C (Figure 6a) and 1250 °C (Figure 6b). The results showed consistent changes in the physical phases post-roasting, with the zinc species remaining relatively stable and primarily forming ZnO, Zn2SiO4, and ZnFe2O4. However, at 1350 °C, the PbZnSiO4 phase decomposed when roasted with electroplating sludge (Figure 6c), and the (Ca5(PO4)3OH) phase, which typically forms during direct roasting of electroplating sludge, disappeared at all three temperatures. Additionally, the diffraction peaks of ZnO were enhanced to varying degrees at all three temperatures, correlating with the increased proportion of electroplating sludge added to the lead–zinc ore. These observations suggest that the addition of electroplating sludge positively impacts the smelting process of lead–zinc ore. From the perspectives of resource utilization and environmental protection, this treatment is viable and holds potential for effectively recovering valuable metals from electroplating sludge.
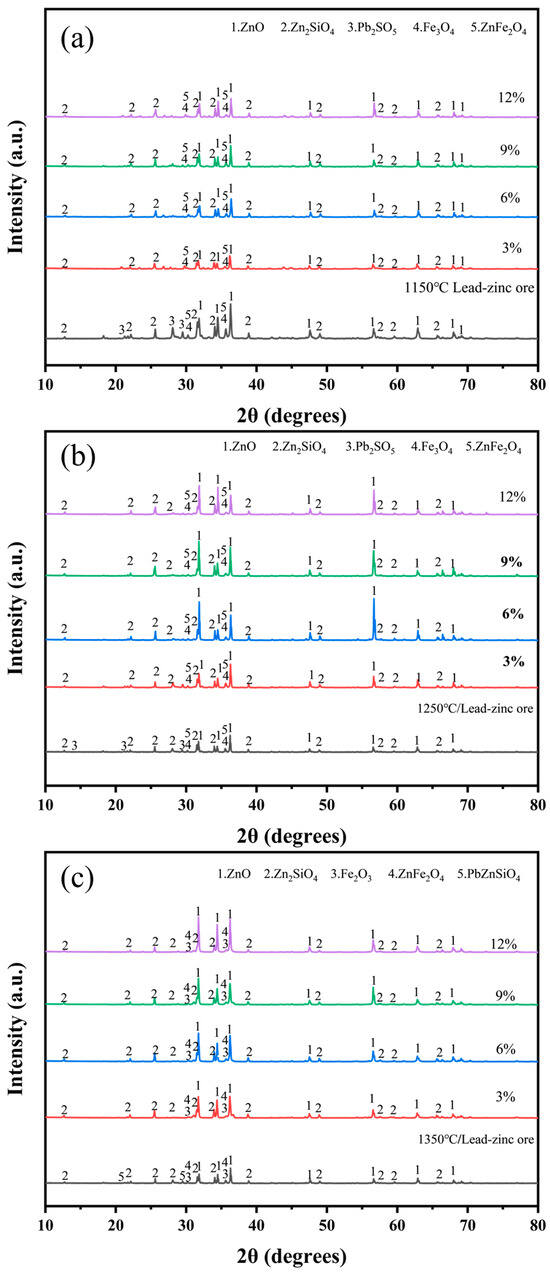
Figure 6.
XRD diffractogram of ore with different proportions of electroplating sludge at different temperatures after roasting: (a) 1150 °C; (b) 1250 °C; (c) 1350 °C.
Subsequently, the chemical composition of the roasted samples was analyzed using XRF, and the results are presented in Table 2. It can be observed that the zinc (Zn) content gradually decreased with the increasing proportion of electroplating sludge, particularly showing a more significant reduction at higher temperatures (such as 1350 °C). However, at a 6% addition level, the Zn content increased across all three temperatures compared to other addition levels. The lead (Pb) content was primarily influenced by temperature, exhibiting a continuous decline as the roasting temperature rose, with a notable reduction at 1350 °C. This trend is closely related to the volatilization characteristics of Pb, as elevated temperatures promote its volatilization. This conclusion was corroborated by XRD analysis, where the characteristic diffraction peaks of Pb completely disappeared at 1350 °C. The copper (Cu) content showed a positive correlation with the addition of electroplating sludge, but due to its relatively low concentration, no corresponding phases were detected in the XRD patterns.

Table 2.
Main elemental contents after roasting with electroplating sludge added (mass%).
The variations in calcium (Ca) and silicon (Si) content were more complex, displaying fluctuations under the combined influence of temperature and addition levels. These fluctuations may be attributed to volatilization or phase transformation processes at high temperatures. Similarly, due to their low concentrations, no distinct phase information was detected in the XRD analysis. The sulfur (S) content exhibited a clear temperature dependence: at 1150 °C, the S content increased with higher addition levels, likely due to the insufficient roasting temperature leading to incomplete desulfurization. When the temperature was raised to 1250 °C, the S content significantly decreased in samples with 3% and 6% addition levels, indicating a more complete desulfurization process. However, as the addition of electroplating sludge further increased, the residual S content rose again. At 1350 °C, the S content nearly disappeared entirely, confirming that high temperatures facilitate the thorough oxidation of minerals.
Although increasing the roasting temperature promotes the oxidation and decomposition of minerals, it also intensifies the volatilization of metallic elements, affecting the phase transformation process. This conclusion aligns well with the XRD diffraction peak analysis, highlighting the critical role of temperature control in optimizing the roasting process.
3.1.2. Physical Phase Transition Analysis of Raw Ore Roasted with Electroplating Sludge After Addition of Melting Agent
In the study of simulating the primary process flow, in order to restore the actual production scenario as much as possible, the frit (CaO/SiO2) was compounded into the lead–zinc ore, making the ratio of calcium oxide to silica in the lead–zinc ore 0.4 [28], and oxygen-enriched roasting was carried out, which gave the experimental results more practical reference value.
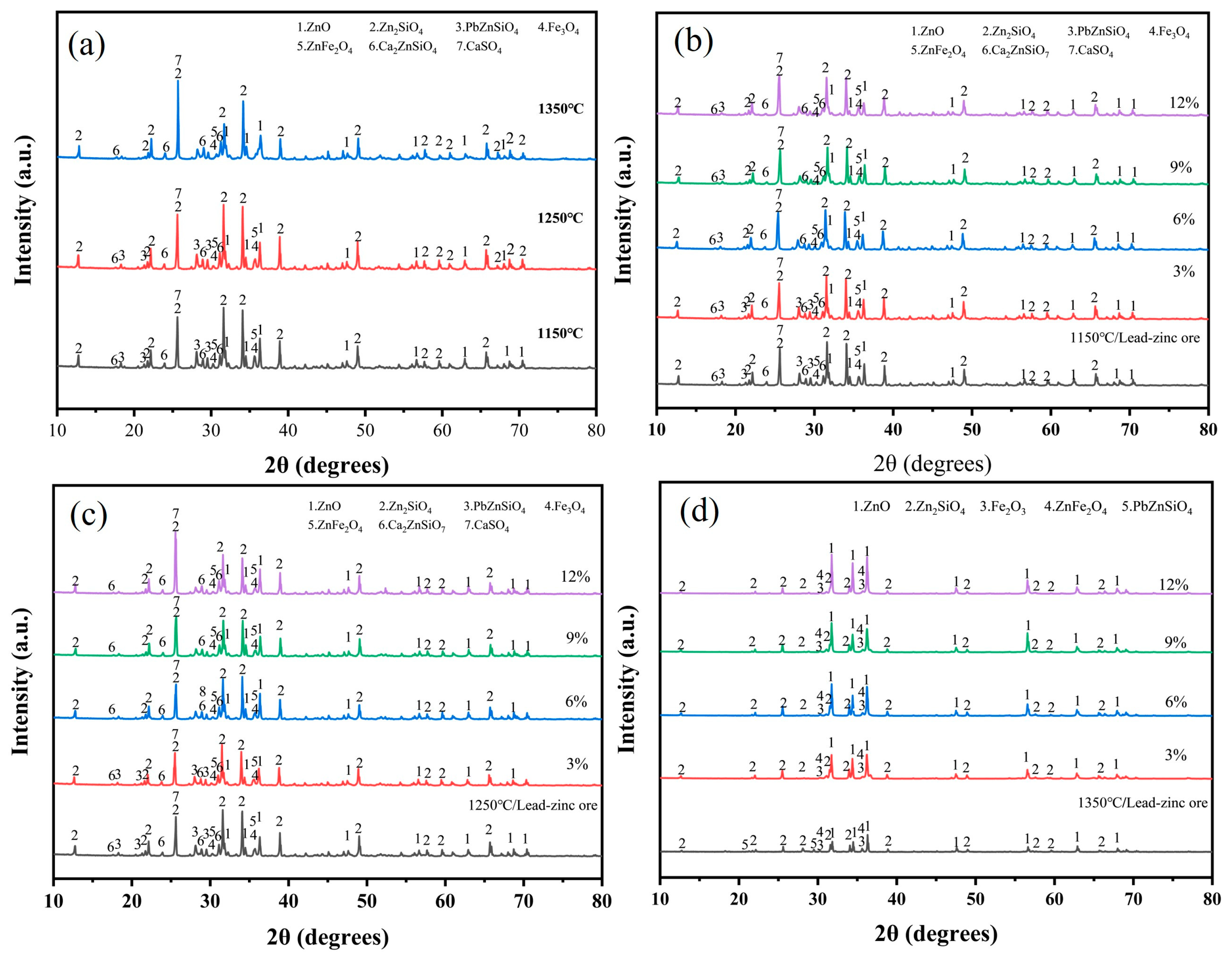
Upon the addition of a melting agent to the lead–zinc ore, without the incorporation of electroplating sludge, a variety of phases were formed under oxygen-enriched roasting conditions at 1150 °C and 1250 °C (Figure 7a). These phases included zinc oxide (ZnO), zinc silicate (Zn2SiO4), zinc–lead silicate (PbZnSiO4), magnetite (Fe3O4), zinc ferrate (ZnFe2O4), calcium zinc silicate (Ca2ZnSiO7) [29,30], and calcium sulfate (CaSO4). The presence of these phases indicates that elements such as zinc, lead, and iron exist in different compound forms within the raw ore at these temperatures. Notably, the formation of PbZnSiO4, a complex compound, suggests that the silicate compounds of zinc and lead remain relatively stable under high-temperature, oxygen-enriched roasting conditions. As the roasting temperature increased to 1350 °C, most phases showed minimal changes, except for the PbZnSiO4 phase. The disappearance of its diffraction peaks indicates that the decomposition of this phase is promoted at this elevated temperature.
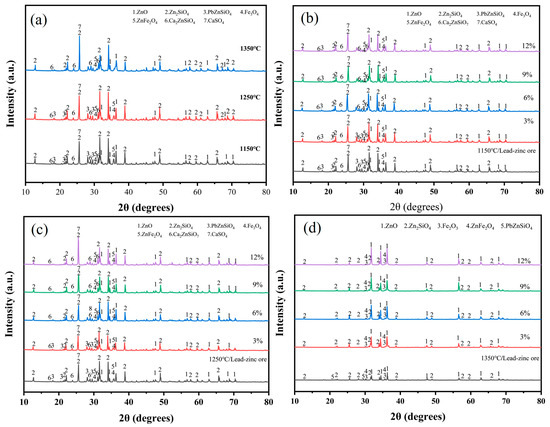
Figure 7.
The lead–zinc ore was blended with a melting accelerator and different proportions of electroplating sludge were added for roasting; XRD diffractograms at different temperatures: (a) lead–zinc ore; (b) 1150 °C; (c) 1250 °C; (d) 1350 °C.
In subsequent experiments, the physical phases after oxygen-enriched roasting changed with the addition of electroplating sludge at varying ratios. Under roasting conditions at 1150 °C (Figure 7b) and 1250 °C (Figure 7c), the PbZnSiO4 phase, a complex compound, disappeared when the electroplating sludge proportion reached 6% or higher. This was accompanied by an enhancement of the diffraction peaks of zinc silicate and lead oxide. These changes suggest that the addition of electroplating sludge significantly lowers the decomposition temperature of PbZnSiO4, enabling its decomposition under conventional melting conditions and, thus, improving smelting efficiency. Lowering the decomposition temperature not only reduces the energy consumption required during the smelting process but also facilitates the more efficient recovery of valuable elements within the smelting temperature range. Consequently, this reduces production costs and increases the recovery of metals such as zinc and lead.
More importantly, the diffraction peaks of Fe3O4 and ZnFe2O4, which were directly generated from the raw ore at a roasting temperature of 1350 °C (Figure 7d), disappeared. Simultaneously, the intensity of the diffraction peaks for ZnO was significantly enhanced. These changes indicate that the addition of electroplating sludge significantly facilitated the disruption of the spinel structure of zinc ferrate. ZnFe2O4 is a stable compound [31], and its spinel structure is usually difficult to decompose. However, in the presence of electroplating sludge, zinc ferrate became destabilized, causing the release of zinc and iron. This promotes higher zinc recovery efficiency and reduces the formation of difficult phases during smelting, thereby enhancing the overall smelting efficiency.
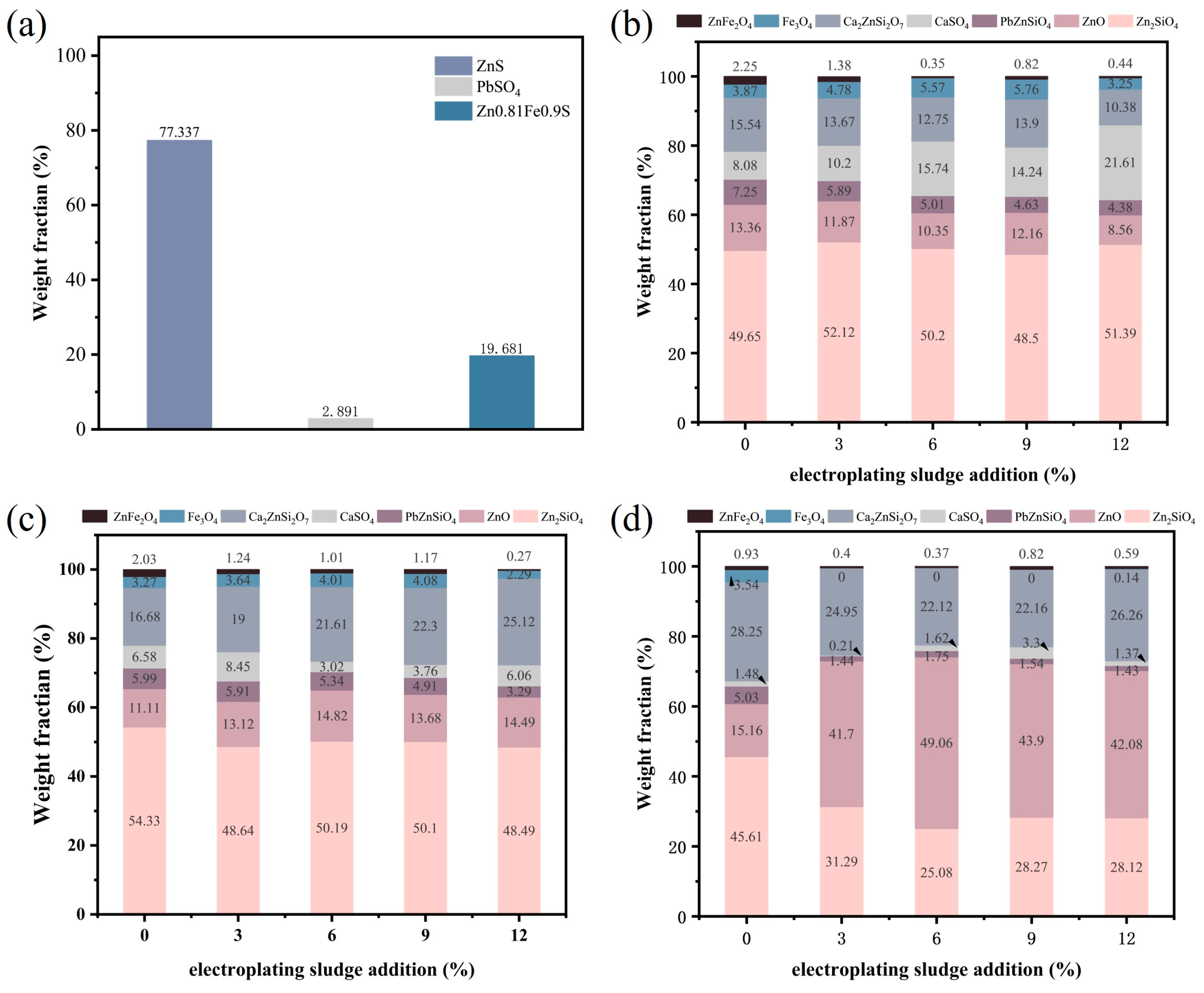
To further investigate the impact of electroplating sludge on the lead–zinc ore smelting process, we conducted semi-quantitative XRD analysis on the lead–zinc ore samples and the samples obtained after the addition of electroplating sludge and flux followed by roasting (Figure 8). Figure 8a illustrates the crystalline phase distribution in the raw ore, with ZnS accounting for 77.337%, PbSO4 for 2.891%, and Zn0.81Fe0.19S for 19.681%. In Figure 8b, we present the semi-quantitative XRD results of the samples after the addition of electroplating sludge and flux at 1150 °C with varying mass fractions (3%, 6%, and 12%). The results show that as the proportion of electroplating sludge increases, the proportion of Zn2SiO4 rises to some extent, while the content of ZnO slightly decreases. However, the contents of PbZnSiO4, Ca2ZnSi4O7, and ZnFe2O4 decrease to varying degrees, indicating that the addition of electroplating sludge promotes the decomposition of complex compounds. The increase in CaSO4 content also suggests the decomposition of Ca2ZnSi4O7. When the sludge addition ratio is 9%, in addition to the decreasing trends of PbZnSiO4, Ca2ZnSi4O7, and ZnFe2O4 observed at 1150 °C, the proportion of Zn2SiO4 also slightly decreases compared to the raw ore, further demonstrating that electroplating sludge facilitates the decomposition of certain refractory compounds.
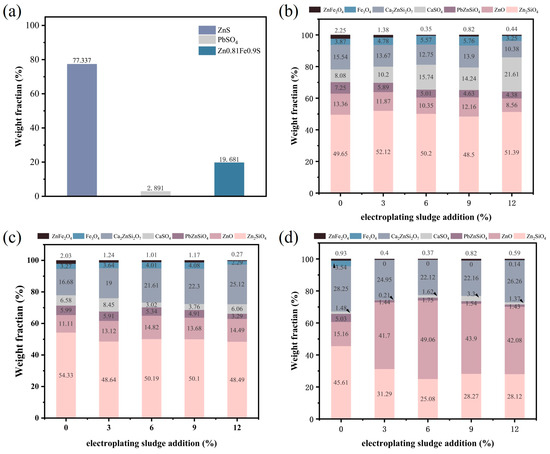
Figure 8.
Semi-quantitative XRD analysis of raw ore and electroplating sludge with flux and different proportions at different temperatures: (a) raw ore; (b) electroplating sludge with flux and different proportions at1150 °C; (c) electroplating sludge with flux and different proportions at1250 °C; (d) electroplating sludge with flux and different proportions at1350 °C.
Figure 8c displays the semi-quantitative XRD analysis results after roasting with the addition of electroplating sludge and flux at 1250 °C. Compared to the results at 1150 °C, the promoting effect of electroplating sludge on the smelting process becomes more pronounced, as evidenced by the significant reduction in the crystalline phase ratios of Zn2SiO4, Ca2ZnSi4O7, and ZnFe2O4, alongside an increase in the proportion of ZnO. This change aligns with the expected smelting outcomes at our target temperature. This innovation is supported by Wang et al.’s findings [32], which identified ZnFe2O4 spinel formation in high-ZnO slags as a critical barrier to metal reduction. Notably, our experiments at 1250 °C demonstrated a marked reduction in ZnFe2O4 content and a concurrent increase in free ZnO, suggesting that metallic oxides within the sludge disrupt spinel structures while lowering the system’s melting temperature. These dual effects synergistically enhance metal reduction efficiency.
Finally, Figure 8d provides the semi-quantitative XRD analysis results for roasting at 1350 °C. At this temperature, following the addition of electroplating sludge, the proportion of Zn2SiO4 significantly decreases to approximately 28%, while the proportion of ZnO surges to over 40%. The contents of other refractory compounds also show varying degrees of reduction compared to the raw ore levels. Although part of this reduction can be attributed to the increase in roasting temperature, more importantly, it confirms the positive role of electroplating sludge, consistent with our earlier conclusions.
To further validate the results obtained from the XRD analysis, XRF elemental analysis was conducted on the slag phase. The results presented in Table 3 indicate that, at temperatures of 1150 °C and 1250 °C, the addition of electroplating sludge results in a slight reduction in Zn content, although the extent of this change is minimal. This observation is consistent with the stability of Zn phases identified in the XRD analysis at these two temperatures. Additionally, the increase in calcium (Ca) content correlates with the enhancement of its diffraction peak intensity. The results from the XRF analysis are generally consistent with the XRD diffraction patterns and quantitative analysis, manifested as an increase in Ca content and a decrease in Si content, corresponding to a reduction in the phases of Ca2ZnSi4O7 and Zn2SiO4, along with an increase in the phase of CaSO4.

Table 3.
Main chemical composition of the sample after roasting with different proportions of electroplating sludge after the raw ore was compounded with the smelter (mass/%).
Regarding lead (Pb), its volatilization at 1150 °C is found to decrease, but the change is not significant. However, at 1250 °C, an increase in Pb content is observed with the addition of 3% and 6% electroplating sludge, while the amount of PbZnSiO4 decreases. At 1350 °C, the high temperature facilitates the volatilization of elements, resulting in a decreased residual content of all elements. Notably, despite the reduction in Pb content, its diffraction peak is completely absent in the XRD spectrum, which warrants further investigation. We hypothesize that the electroplating sludge may exert a certain fixation effect on Pb, transforming it into oxides that subsequently combine with other metal oxides, thereby rendering the associated diffraction peaks undetectable by XRD. Furthermore, the increase in Cu content may be related not only to the higher quantities of electroplating sludge added but also to its potential involvement in the binding processes of such oxides. In light of these observations, we plan to conduct a more in-depth study and discussion of this phenomenon.
3.2. Analysis of the Effects of Electroplating Sludge on the Migration of Major Metal Elements in the Smelting Process
The temperature in the main lead–zinc mining process—specifically, blast furnace zinc refining—is typically maintained at approximately 1250 °C. As the temperature increases and electroplating sludge is added, the volatilization of various substances, particularly lead, zinc, and other volatile elements, significantly intensifies. This results in a greater transfer of volatile elements into the gas phase.
This study therefore focuses on the migration patterns of major elements at 1250 °C. After roasting the samples at this temperature, they were ground into powder and mixed for XRF analysis. The results (Table 4) indicate that the zinc content in the direct roasting of lead–zinc ore is 41.12%. As the electroplating sludge content increases, the zinc content slightly decreases, with values recorded as 40.66%, 40.04%, 38.28%, and 37.88%, respectively. The trends in the remaining contents of calcium (Ca) and silicon (Si) mirror that of zinc, although the changes are relatively minor.

Table 4.
The main chemical composition of the samples after roasting with different proportions of electroplating sludge after adding flux to the raw ore (mass%).
Additionally, the sulfur (S) content increases slightly as the electroplating sludge content rises. This pattern is consistent with the changes in copper (Cu) and sulfur, as electroplating sludge already contains high levels of both elements, making these variations expected. Notably, the lead (Pb) content in the slag phase of the lead–zinc ore after roasting is 7.64%. When 3% and 6% electroplating sludge is added, the lead content increases to 7.96% and 7.80%, respectively. However, further increases in electroplating sludge cause the lead content to decrease again.
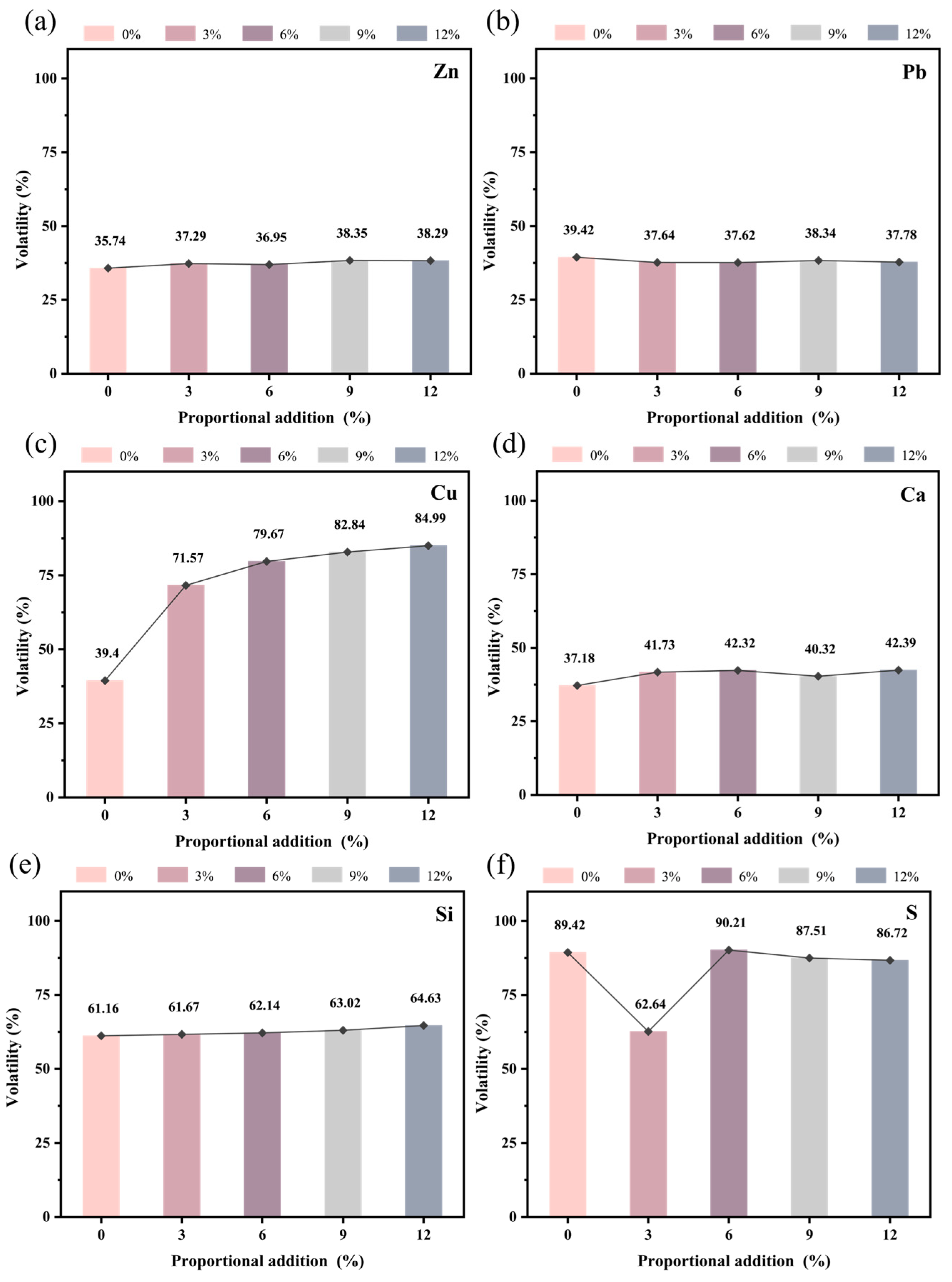
To more accurately assess the migration patterns of elements, the volatilization of major elements was calculated based on the weight loss before and after roasting, utilizing XRF data (Figure 9). As shown in Figure 9, when no electroplating sludge was added, the zinc volatilization was 35.74%, and the lead volatilization was 39.42%. Upon adding varying ratios of electroplating sludge, distinct trends emerged in the volatilization of zinc and lead. Specifically, zinc volatilization increased slightly to 37.29%, 36.95%, 38.35%, and 38.29% with increasing ratios of sludge (Figure 9a), while lead volatilization decreased slightly to 37.64%, 37.62%, 38.34%, and 37.78%, respectively (Figure 9b). Since the electroplating sludge did not contain lead, this indicates that lead volatilization primarily originated from the lead component in the lead–zinc ore. This suggests that the addition of electroplating sludge exerts a certain immobilizing effect on lead volatilization, consistent with the XRF data results.
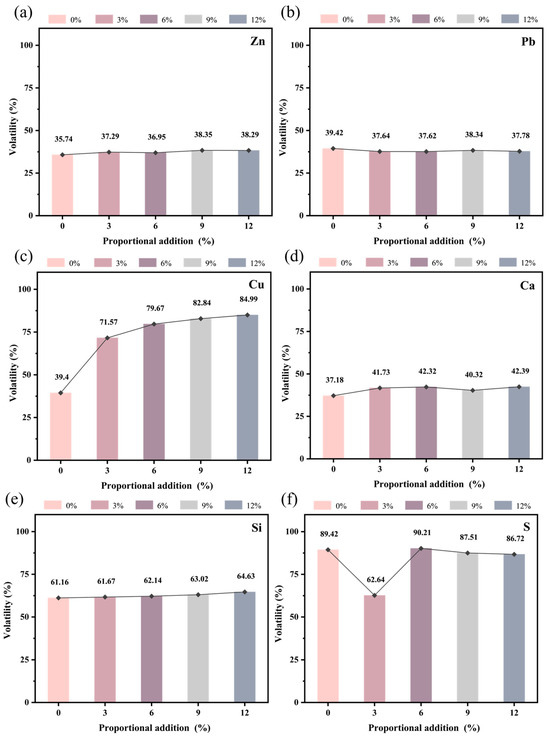
Figure 9.
Migration of major elements at 1250 °C: (a) Zn; (b) Pb; (c) Cu; (d) Ca; (e) Si; (f) S.
Furthermore, the volatilization of copper (Cu) (Figure 9c) and silicon (Si) (Figure 9e) increased with a higher proportion of electroplating sludge, with copper showing a more pronounced increase. However, the copper volatilization data were somewhat biased due to blue copper sulfate residue on the crucible surface, which was difficult to entirely remove by conventional means. In contrast, calcium (Ca) volatilization (Figure 9d) was observed, but it fluctuated minimally. Sulfur (S), on the other hand, consistently volatilized into the gas phase (Figure 9f), with its volatilization decreasing as the proportion of sludge increased. Chlorine (Cl) was almost entirely volatilized into the gas phase throughout the process.
By comparing volatilization under various conditions, it can be concluded that the addition of electroplating sludge facilitates the incorporation of metal elements such as lead and zinc into the liquid slag phase, while chlorine is almost entirely volatilized into the gas phase. Elements like sulfur, copper, calcium, and silicon are distributed between both phases, with their degrees of volatilization varying as the proportion of electroplating sludge increases.
3.3. Analysis of the Effect of Electroplating Sludge on the Melting Point of the Smelting Process
To deeply investigate the effect of the addition of electroplating sludge on the melt flow characteristics of lead–zinc ore, in this study, for the primary ore samples with added melting agent [33], different ratios of electroplating sludge were added for roasting. The relationship between the electroplating sludge content and the melting point of the lead–zinc ore was analyzed using a melting point assay. The objective was to elucidate how the addition of electroplating sludge influences the melting characteristics of the primary ore to optimize the smelting process.
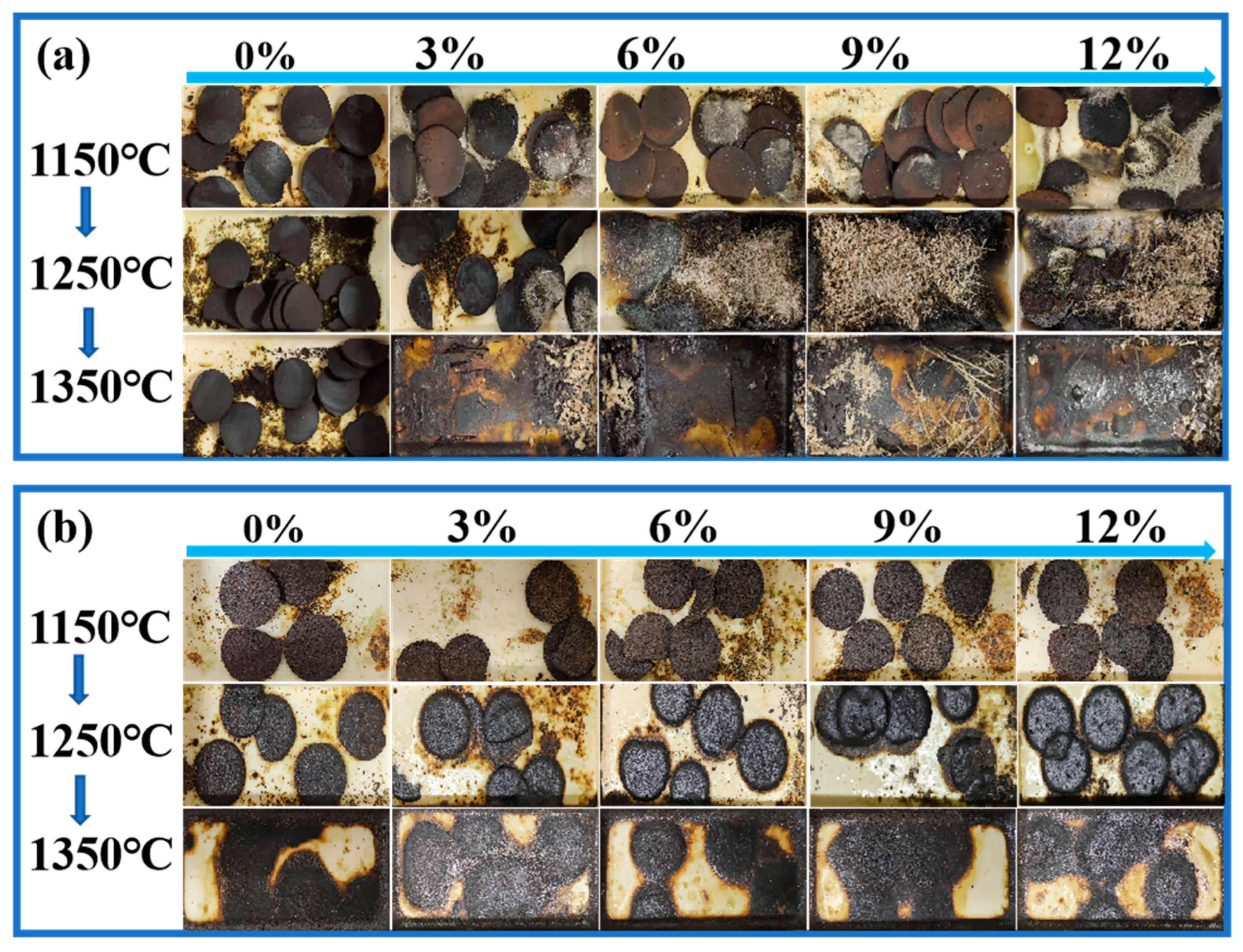
According to the graphical representation of the experimental results (the diagram was taken out of the tube furnace and photographed for retention after roasting), without the addition of the melting agent (CaO/SiO2) (Figure 10a), the system was able to produce relatively pure zinc oxide (ZnO) at 1150 °C. The amount of precipitated ZnO increased with greater additions of electroplating sludge; however, the overall melting phenomenon remained limited. When the roasting temperature was increased to 1250 °C and the electroplating sludge content exceeded 6%, the slag exhibited a favorable melting state, and the crystallinity of ZnO improved, resulting in a significant reduction in the melting point. This change facilitated the formation and flow of liquid slag during the smelting process, thereby enhancing the smelting efficiency.
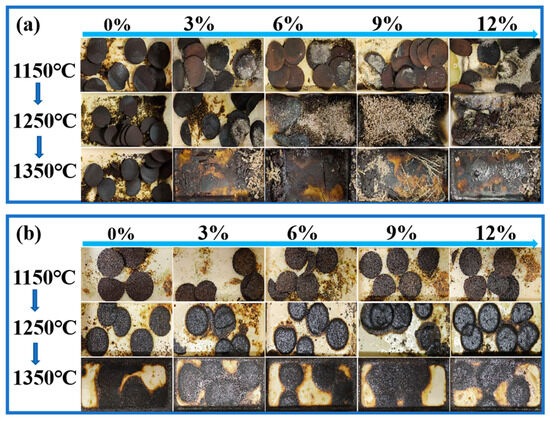
Figure 10.
Experimental phenomenon diagrams: (a) lead–zinc ore mixed with electroplating sludge without flux added; (b) lead–zinc ore mixed with electroplating sludge with flux added.
The experimental results with the addition of the melting agent (CaO/SiO2) showed (Figure 10b) that the melting point of the raw ore itself had been lowered by the addition of the melting agent without the addition of the electroplating sludge, but the zinc phase of the roasted slag changed again after the addition of the electroplating sludge. Specifically, at 1150 °C, the addition of electroplating sludge in different proportions failed to cause an obvious melting trend. However, when the temperature was raised to 1250 °C, the slag phase began to show a partially molten state as the proportion of electroplating sludge addition was increased from 3% to 12%, indicating that the melting point of the slag phase was lowered by the addition of the electroplating sludge. When the temperature was further increased to 1350 °C, all of the samples were completely melted.
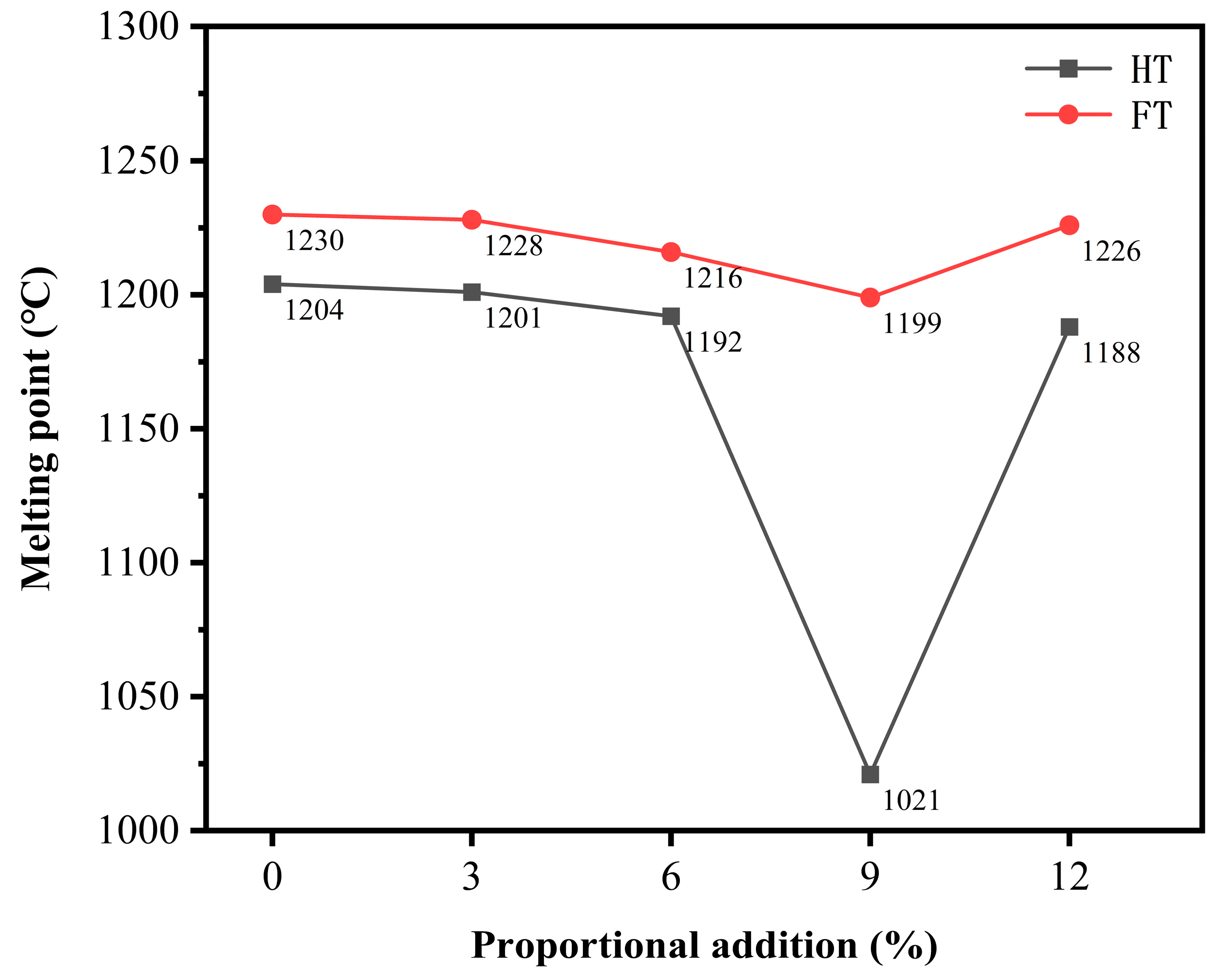
To verify this conclusion, the roasted samples were subjected to melting point testing (by using a heating microscope). The experimental results (Figure 11) revealed that the flow temperature (FT) of the virgin ore was 1230 °C. When 3% electroplating sludge was added to the primary ore, the melting point slightly decreased to 1228 °C, which was not a significant change. As the electroplating sludge content increased, the melting point further decreased to 1206 °C with a 6% addition, where the reduction became more noticeable. Increasing the electroplating sludge content to 9% caused the melting point to decrease further to 1199 °C. However, when the electroplating sludge addition reached 12%, the melting point increased slightly to 1226 °C. Despite this increase, the melting point remained lower than that of both the primary ore and the 3% electroplating sludge addition. This indicates that the effect of electroplating sludge addition on the melting point follows a nonlinear pattern. The hemispherical temperature (HT) and flow temperature exhibited a similar trend.
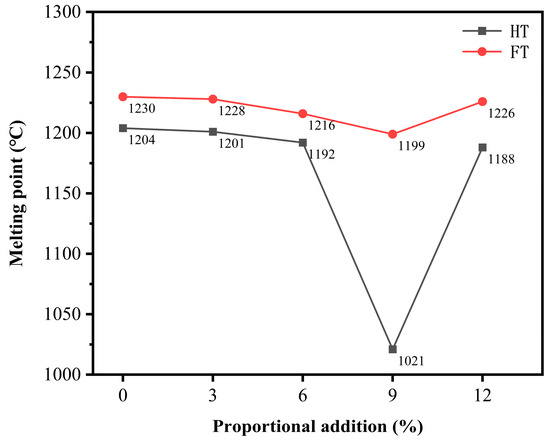
Figure 11.
Melting points of slag phases with different proportions of electroplating sludge.
These experimental data suggest that adding moderate amounts of electroplating sludge can lower the melting point of the primary ore during smelting. This reduction in melting point facilitates the flow of the melt, allowing the lead–zinc ore to transition into the liquid phase more easily at lower temperatures, thereby enhancing the smelting efficiency. This effect can be attributed to certain components in the electroplating sludge, particularly metal oxides, which can alter the internal structure and chemical composition of the primary ore, thus lowering the melting point.
However, when the addition of electroplating sludge exceeds a certain threshold, some metal elements within the sludge may counteract the reduction in melting point, resulting in an increase instead. For instance, in some complex sulfide ore systems, iron may interact with other elements, such as zinc, forming solid solutions of iron and zinc sulfides. The formation of these solid solutions can alter the melting point, potentially raising it above the original melting point of the primary ore. In this study, excessive addition of electroplating sludge may have led to similar complex reactions, causing the melting point to rise.
Considering the previously discussed changes in physical phase, volatilization of key elements, and current melting point data, it can be concluded that an electroplating sludge addition of approximately 6% is optimal. This ratio effectively lowers the melting point of the primary ore, facilitating easier melting and flow during smelting. Simultaneously, it ensures that the volatilization of metal elements is comparable to that observed without the addition of sludge, thus improving the smelting efficiency. Moreover, it maintains the stability of the material composition during the smelting process, avoiding potential negative impacts associated with excessive sludge addition.
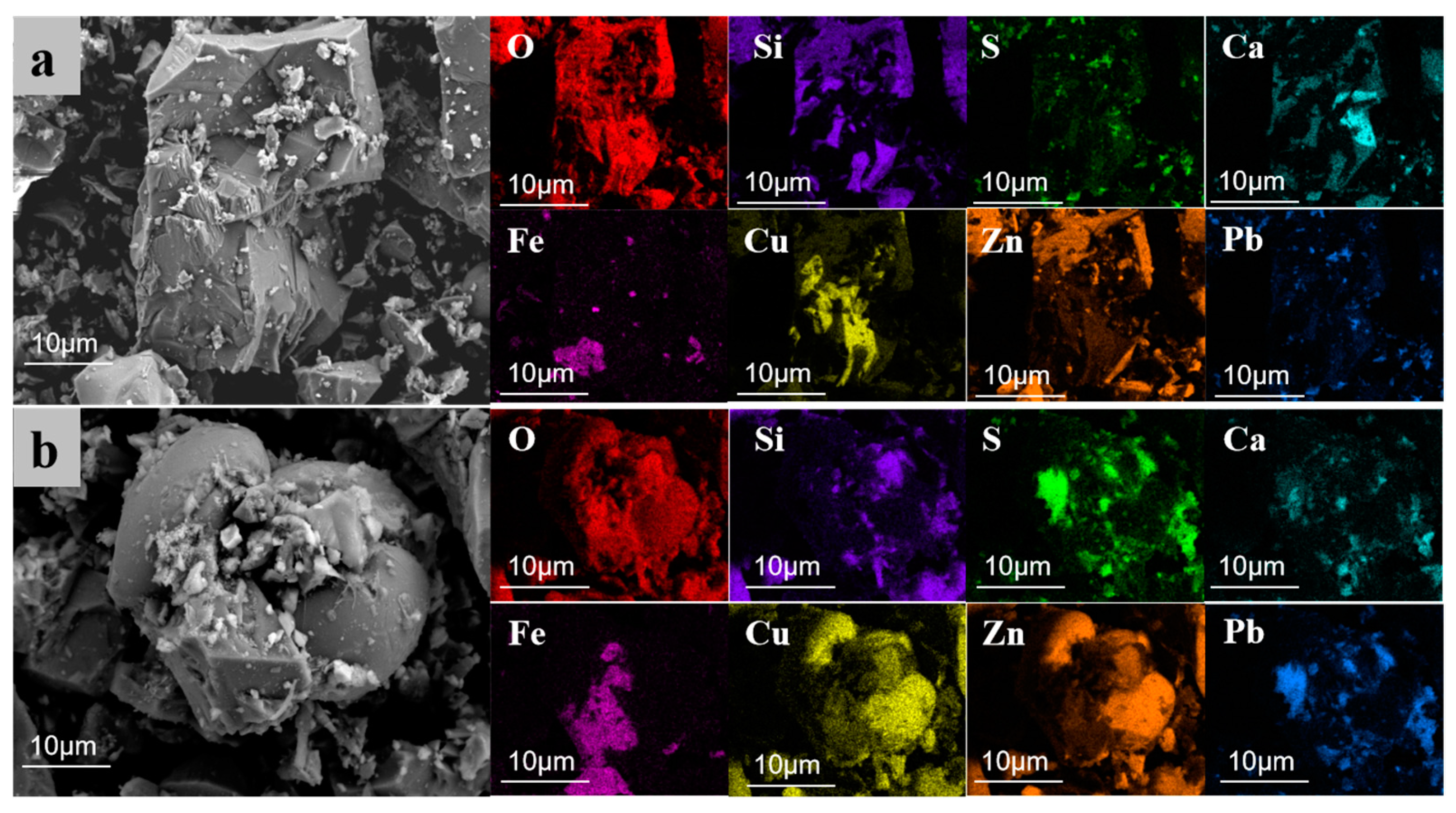
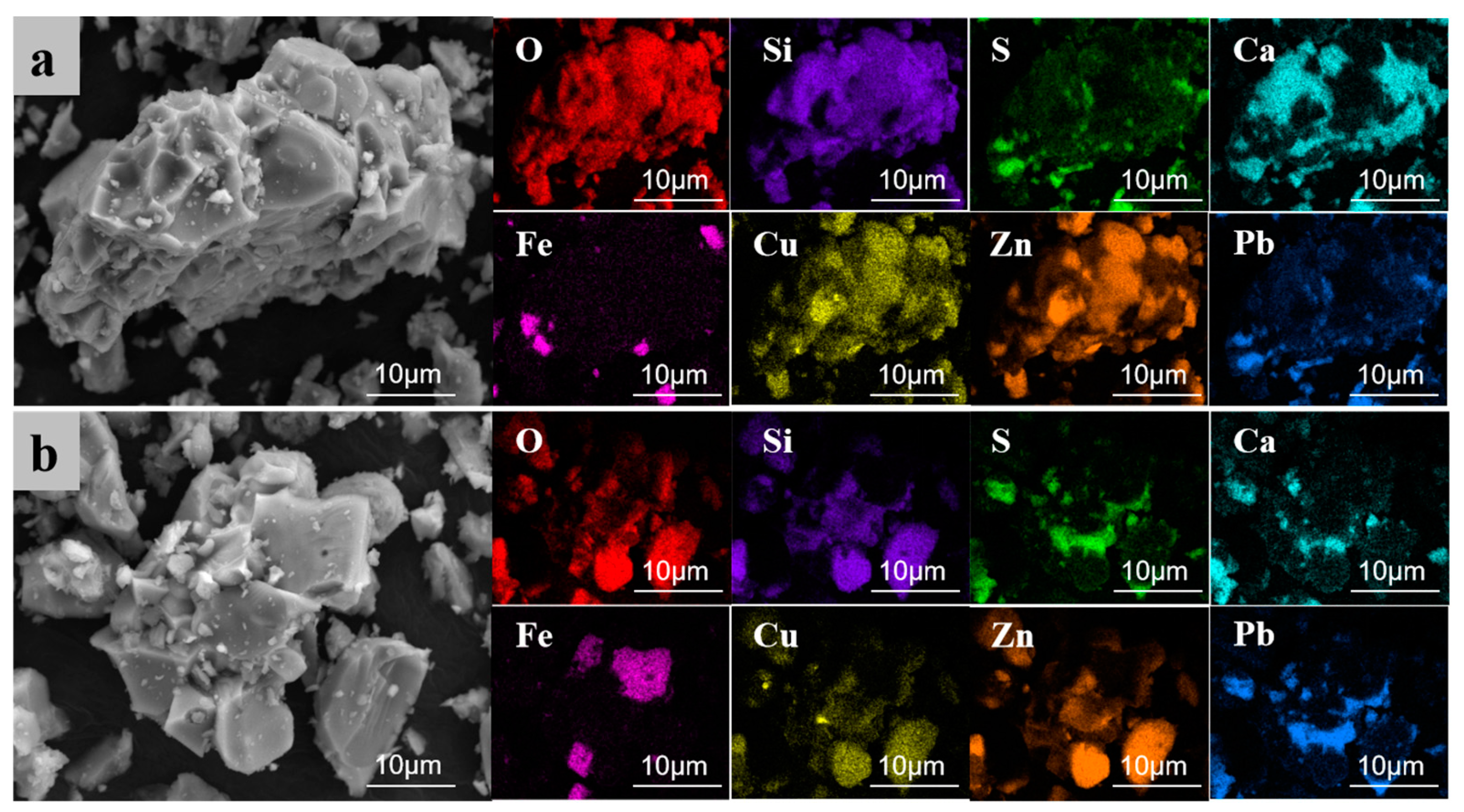
To thoroughly analyze the microscopic effects of electroplating sludge in promoting the melting of raw ore, this study utilized scanning electron microscope (SEM) analysis on two samples after roasting at 1250 °C. One sample contained 6% electroplating sludge without an added melting agent (Figure 12), while the other included 6% electroplating sludge and a melting agent (Figure 13). The analysis revealed the impact of electroplating sludge’s addition on the raw ore’s microstructure and elucidated the reasons that it promotes melting. Figure 12a,b display electron micrographs of samples with 6% electroplating sludge and no melting agent. Figure 12a shows an irregular mass containing elements such as oxygen (O), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), iron (Fe), silicon (Si), calcium (Ca), lead (Pb), and sulfur (S). These elements coexist within the same crystal structure, indicating their presence in the form of complex compounds. Conversely, Figure 12b reveals distinct structures bonded into a single mass. According to energy spectral mapping analysis, the spherical structures on the left and right are primarily composed of Cu-Zn-Pb oxides, while the middle part is an orthorhombic crystal of ZnFe2O4. This suggests that metal elements like Cu, Zn, and Pb form symbiotic complexes within the ore through their interactions, resulting in stable compounds such as ZnFe2O4 that are resistant to decomposition. Figure 13a,b present electron micrographs of samples with 6% electroplating sludge and an added melting agent. Figure 13a resembles Figure 12a, consisting of a complex compound of multiple elements forming a complete crystal without a specific morphology. In contrast, Figure 13b, similar to Figure 12b, features multiple substances assembled into a block with an orthorhombic ZnFe2O4 crystal in the center. This indicates that the microstructure of the ore changed with the addition of electroplating sludge and the melting agent, further facilitating interactions between metallic elements and the compounding process.
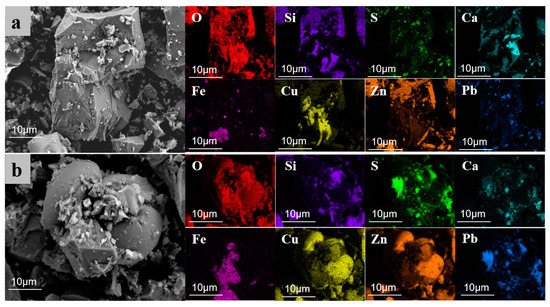
Figure 12.
SEM images of the sample roasted at 1250 °C with 6% electroplating sludge added, and without flux addition. (a) SEM image 1 of sample roasted at 1250 °C with 6% electroplating sludge and without flux addition; (b) SEM image 2 of sample roasted at 1250 °C with 6% electroplating sludge and without flux addition.

Figure 13.
SEM of the sample after roasting at 1250 °C with 6% electroplating sludge added and flux added. (a) SEM image 1 of sample roasted at 1250 °C with 6% electroplating sludge and flux added; (b) SEM image 2 of sample roasted at 1250 °C with 6% electroplating sludge and flux added.
Based on the analysis of the SEM images, the following conclusions can be reasonably drawn: On the one hand, copper elements in the electroplating sludge form complex symbiotic crystal structures with metal elements such as zinc, lead, and iron in the lead–zinc ore [34,35]. These metal elements interact by doping, replacing, or filling gaps in the crystal lattice, causing a distortion in the lattice structure. This distortion facilitates the formation of solid solutions between copper oxides and other metal oxides, such as CuO-ZnO-PbO [36,37]. The solid solution not only stabilizes a portion of the lead that would otherwise volatilize but also lowers the melting point of the metal oxides, thereby enhancing the melt flow of the lead–zinc ore. On the other hand, the interaction between copper oxides and other metal oxides promotes the formation of new polymeric systems. These systems combine several high-melting-point substances to form a composite structure that is difficult to decompose. Since the eutectic point temperature of this composite system is lower than the melting point of any individual substance [38], the overall melting point of the system is reduced. This lowers both the energy consumption and temperature requirements for the smelting process, thus improving the meltability and smelting efficiency of the lead–zinc ore.
4. Conclusions
This study compared volatilization behaviors under different conditions and found that the addition of electroplating sludge promotes the incorporation of metallic elements such as lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn) into the liquid slag phase, while chlorine almost completely volatilizes into the gas phase. Elements such as sulfur, copper, calcium, and silicon are distributed between both phases, and their volatilization behaviors change with the sludge addition ratio. The addition of electroplating sludge can lower the melting point of the ore, with a 9% addition reducing the melting point from 1230 °C to 1199 °C. Considering the volatilization of key metallic elements (Pb and Zn) at a roasting temperature of 1250 °C, the optimal addition of electroplating sludge was found to be approximately 6%. At this ratio, the melting point is 1216 °C, and this addition not only stabilizes part of the lead, reducing its volatilization to 37.62%, but also effectively decomposes PbZnSiO4 and Ca2ZnSi4O7. This optimal addition improves the metal recovery and smelting efficiency. Furthermore, the reduced melting point decreases energy consumption during the smelting process, thereby enhancing both the smelting process and resource recovery. These findings provide a theoretical basis for the resource utilization of electroplating sludge and the optimization of lead–zinc ore smelting processes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.S. and C.W.; methodology, L.S.; software, L.S. and C.P.; validation, L.S., M.W. and C.W.; formal analysis, L.S. and M.W.; investigation, C.W. and M.W.; resources, C.P.; data curation, M.W.; writing—original draft preparation, M.W.; writing—review and editing, L.S., C.W. and M.W.; visualization, C.W. and K.L.; supervision, K.L.; project administration, K.L.; funding acquisition, C.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program, China (grant No. 2022YFC3901603) and received additional funding from the Yunnan Provincial Key Laboratory of Energy Saving in Phosphorus Chemical Engineering and New Phosphorus Materials (grant No. 202205AG070067) and the Yunnan Technological Innovation Center of Phosphorus Resources (grant No. 202305AK340002).
Data Availability Statement
Due to the ongoing use of the data in further research, the data supporting this study are not publicly available at this time to avoid compromising the research progress. Researchers who require access to the raw data may contact the corresponding author to request it. We will provide the data on a case-by-case basis, ensuring compliance with all relevant regulations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cauvin, L.; Raghavan, B.; Bouvier, S.; Wang, X.; Meraghni, F. Multi-scale investigation of highly anisotropic zinc alloys using crystal plasticity and inverse analysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 729, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pola, A.; Tocci, M.; Goodwin, F. Review of Microstructures and Properties of Zinc Alloys. Metals 2020, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.S.; Head, I.; Premier, G.C.; Scott, K.; Yu, E.; Lloyd, J. A multilevel sustainability analysis of zinc recovery from wastes. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 113, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, J.L.; Peng, C.; Liu, Z.; Wilson, B.P.; Lundström, M. Recovery and separation of silver and mercury from hazardous zinc refinery residues produced by zinc oxygen pressure leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 185, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Huang, R.; Lv, X. Separation and recovery of metallic zinc and iron concentrate from blast furnace dust by vacuum carbothermal reduction. Transactions of The Institution of Chemical Engineers. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. Part B. 2022, 162, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihoglu, G.; Pinarli, V. Steel foundry electric arc furnace dust management: Stabilization by using lime and Portland cement. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Guo, Z.Q.; Zhu, D.Q.; Pan, J.; Yang, C.; Li, S. Application of coal-based direct reduction-magnetic separation process for recycling of high-iron-content non-ferrous metallurgical wastes: Challenges and opportunities. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng. Part B 2024, 183, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Wu, Y.Q.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Q.Q. The reuse of waste glass for enhancement of heavy metals immobilization during the introduction of galvanized sludge in brick manufacturing. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.Y.; Sammon, W.J. Enhancement of in-plant recycling of integrated steel mill offgas solid wastes by reallocating crucial zinc-bearing materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Wu, Y.Y. Effective self-purification of polynary metal electroplating wastewaters through formation of layered double hydroxides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8884–8890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yuan, H.H.; Mao, L.Q.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Xu, F.N.; Tang, X.J. Stabilization/solidification of chromium-bearing electroplating sludge with alkali-activated slag binders. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124885.1–124885.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Wang, H.M.; Liu, X.M.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Liu, Y. Approaches for the Treatment and Resource Utilization of Electroplating Sludge. Materials 2024, 17, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocellin, J.; Mercier, G.; Morel, J.L.; Charbonnier, P.; Blais, J.F.; Simonnot, M.O. Recovery of zinc and manganese from pyrometallurgy sludge by hydrometallurgical processing. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.Q. Approaches for electroplating sludge treatment and disposal technology: Reduction, pretreatment and reuse. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, F.M.; Pereira, R.A.; Souza, T.M.; Saczk, A.A.; Magriotis, Z.M. Treatment, reuse, leaching characteristics and genotoxicity evaluation of electroplating sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.B.; Wu, X.S.; Xia, L.G.; Liu, Z.H. Co-Smelting Process of Pb Concentrate and Zn Leaching Residues with Oxygen-Rich Side Blowing Furnaces: Industrial Application and Material Balance. JOM 2023, 75, 5833–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Q.; Pan, J.; Zhu, D.Q.; Zhang, F. Green and efficient utilization of waste ferric-oxide desulfurizer to clean waste copper slag by the smelting reduction-sulfurizing process. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 199, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.L.; Feng, Y.; Dong, X.J.; Luo, S.; Ren, D.D.; Zhang, W.W.; Lin, H.; Lin, X.Q. Energy absorption characteristics and kinetics of carbonaceous solid waste gasification with copper slag as heat carrier. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 20076–20086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Yang, H.F.; Gao, Y.L. Synchronous stabilization of Pb, Zn, Cd, and As in lead smelting slag by industrial solid waste. Chemosphere 2023, 339, 139755.1–139755.11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Tang, C.B.; Xiao, J.; Zeng, P.; Tang, M.T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.H. A cleaner process for lead recovery from lead-containing hazardous solid waste and zinc leaching residue via reducing-matting smelting-ScienceDirect. J. Clean. Production. 2019, 241, 118328. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.N.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, C.M.; Liu, L.M.; Li, H.Q.; Lu, B.; Xie, Y.B.; Zhuang, C.B.; Sun, T.Y.; Liu, W.P. Environmental impact of typical zinc that implements solid waste collaborative utilization in China. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2022, 27, 1316–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Min, X.; Chai, L.Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Ke, Y.; Peng, C.; Lu, H.; Lu, J.W.; Wang, X. Melting Properties and Bath Reduction of High-Zn Materials for Zinc and Lead Recovery. SSRN 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, L.Z. Enhanced marmatite activation by copper with ammonium sulfate: An experimental and DFT investigation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 679, 161229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebernegg, S.; Tsirlin, A.A.; Janson, O.; Rosner, H. The spin gap in malachite Cu2(OH)2CO3 and its evolution under pressure. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 5647–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.F.; Ke, C.M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.S. Methods of recovering lead and lead compounds from spend lead paste. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 2014, 46, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Yao, H.; Qiu, D.; Omran, M.; Wei, S.Y.; Ren, J.; Lu, C.Y.; Cao, S.; Wei, T.D.; Yu, Y.W. Influence of localized thermal effect of microwave heating on the carbothermic reduction process of ZnFe2O4. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 477, 143887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Du Jiaheng, W.Z.; Yan, J.; He, K.; Duan, K.; Yin, Y.; Li, Z. Antibacterial magnesium oxide-calcium phosphate composite coating prepared by combining electrodeposition and sol-gel impregnation. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 2024, 28, 4663. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, J.W.; Huang, L.Y.; Yu, M.X.; Ke, Y.; Peng, C.; Min, X.B. Research selection of slag property of high-zinc materials bath reduction smelting for co-recovery of zinc, lead and copper. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2023, 54, 538–547. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, R.; Lui Wei, C.K.; Wollentin, R.W. Calcium Zinc Silicate Phosphor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 99, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, H.H.A.; Hamzaey, E.M.A.; El Zawawi, I.K.; Kenawy, S.H.; El Bassyouni, G.T.; Mahdy, M.A. Novel nanocomposite made of calcium zinc silicate/NiO2 for biomedical applications. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 12459–12471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tan, J.; Liu, C.Q.; Yin, Z.L.; Chen, Q.Y.; Zhang, P.M.; Liao, Z. Thermodynamic analysis on iron-making process of zinc leaching residue by carbon reduction. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2015, 25, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Xu, K.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Yu, Z.; Ma, K.; Wu, K.T.; Xia, L. The transformation behaviour of ZnFe2O4 spinel particles in the CaO-FexO-SiO2-ZnO slag system. J. Phys. Conf. Series. 2024, 2738, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, T.; Schmuecker, M. Metal oxides for thermochemical energy storage: A comparison of several metal oxide systems. Sol. Energy 2016, 126, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Chen, H.; Chen, F.; Chen, Q.S.; Ying, Z.B.; Wu, X.L.; Wang, J.E. Silicon Control and Heat Balance Calculation in Roasting Process of High Silicon Zinc Sulfide Concentrate. Nonferrous Met. Eng. 2024, 14, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Shevchenko, M.; Jak, E. Experimental liquidus study of the binary PbO-ZnO and ternary PbO-ZnO-SiO2 systems. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 6795–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.A.; Qiu, G.X.; Wang, X.M. Effect of CaO on zinc migration mechanism and kinetics during zinc ferrite reduction. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2023, 33, 2832–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C. Thermodynamic Calculation of Phosphorus Distribution Ratio and Components activityof CaO-SiO2-FeO-MnO-MgO-P2O5Converter Slag; Chongqing Universit: Chongqing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rincent, C.; Castillo-Sánchez, J.R.; Gheribi, A.E.; Harvey, J.P. On the exploration of the melting behavior of metallic compounds and solid solutions via multiple classical molecular dynamics approaches: Application to Al-based systems. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. PCCP 2023, 25, 10866–10884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).