Synthesis and Application of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic Acid) Hydrogels as Sorbent Materials for Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Hydrogels
2.3. Characterization of Hydrogels
2.3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.3. Swelling
2.3.4. Determination of the Point of Zero Charge
2.4. Removal of Heavy Metals from Simulated Wastewater by Hydrogels
2.5. The Effect of Process Parameters on the Sorption Capacity of Hydrogels
2.5.1. Solution pH
2.5.2. Contact Time
2.5.3. Sorbate Initial Concentration
2.5.4. Temperature (Thermodynamics)
2.6. Desorption and Regeneration Studies
2.7. Characterization of Hydrogels with Sorbed Heavy Metals
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization Hydrogels
3.1.1. FTIR Analysis
3.1.2. SEM Analysis
3.1.3. EDX Analysis
3.1.4. Swelling Behavior
3.2. Heavy Metal Ions Adsorption Studies
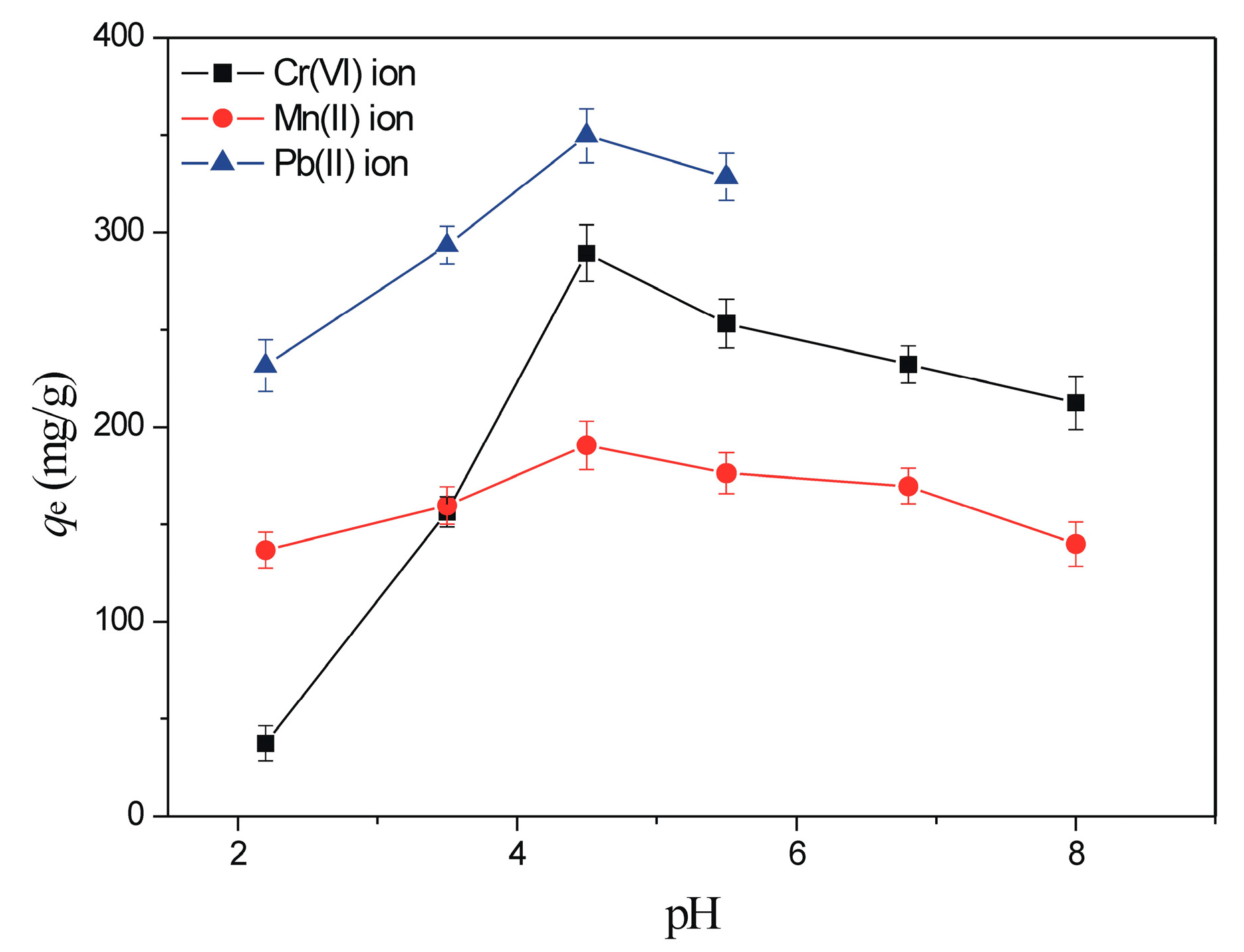
3.2.1. The Effect of pH
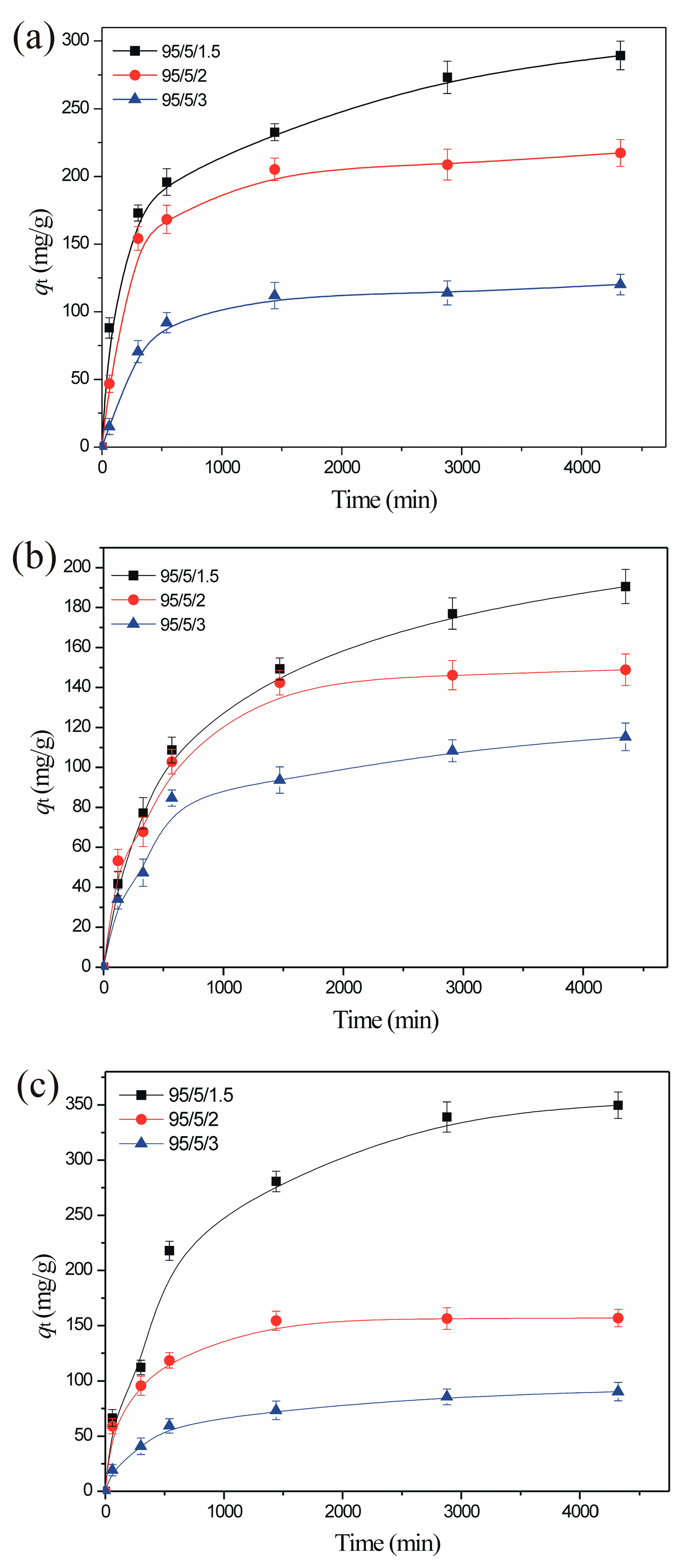
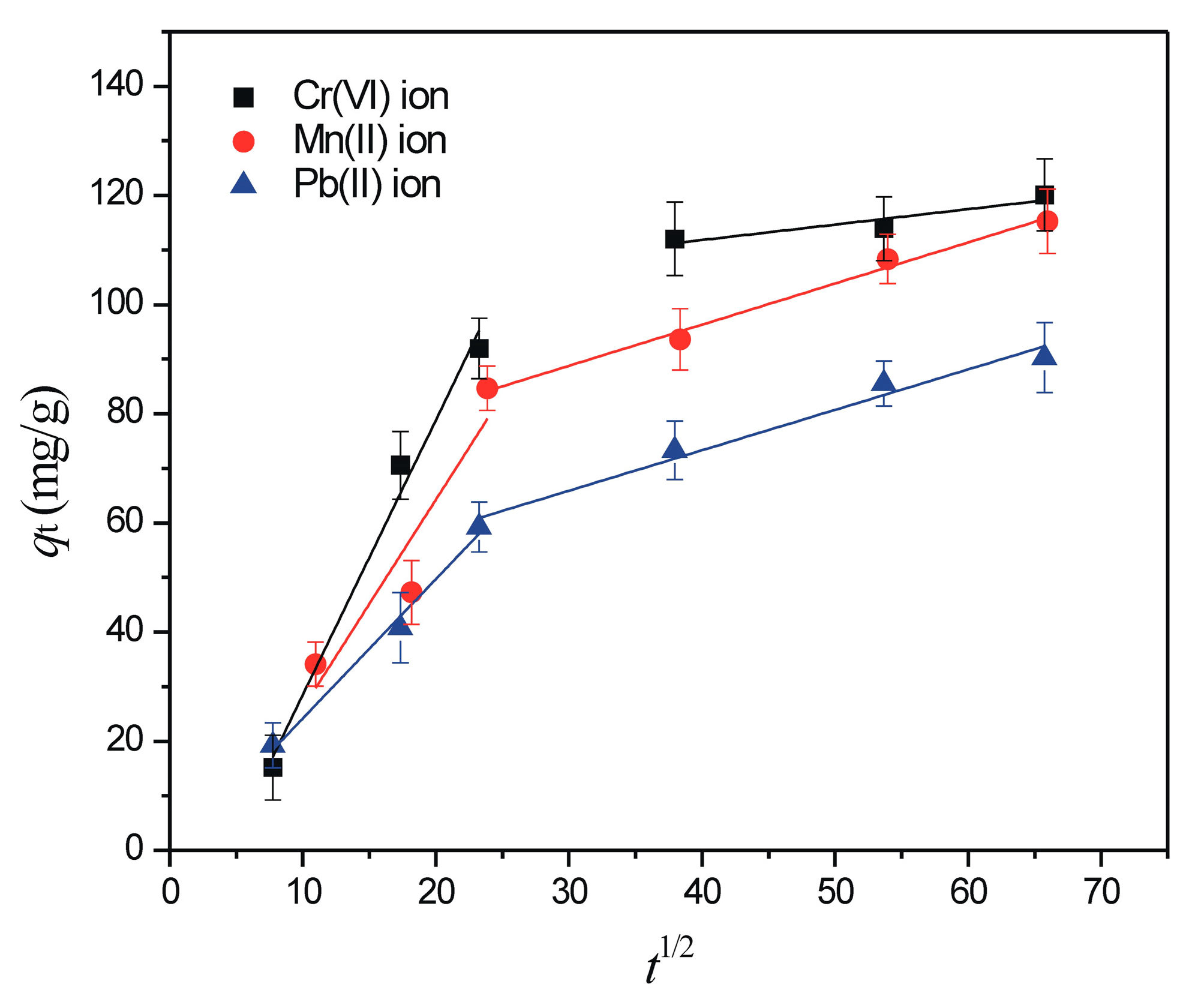
3.2.2. The Effect of Contact Time and Sorption Kinetics
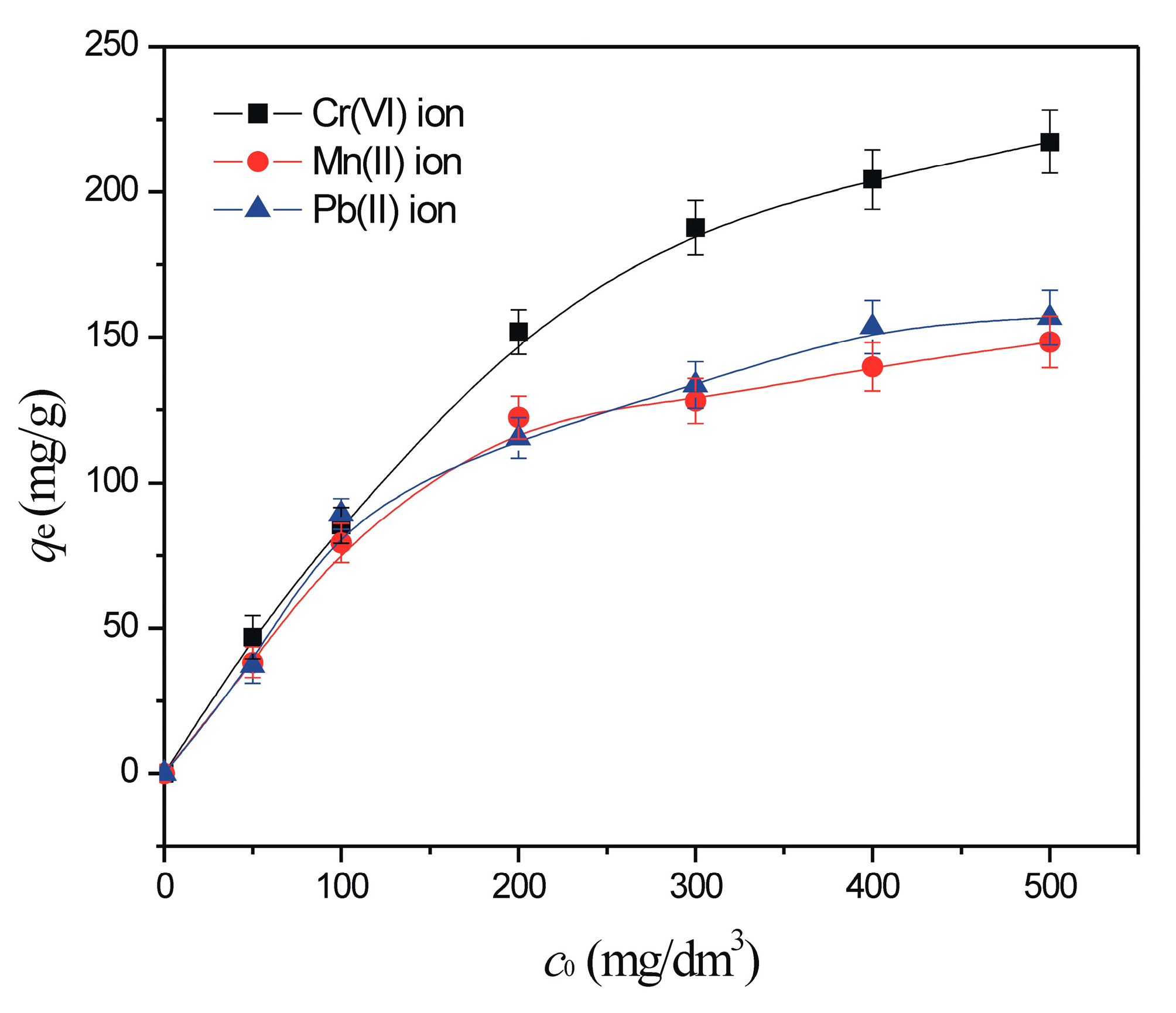
3.2.3. The Effect of Heavy Metal Initial Concentration and Sorption Isotherms
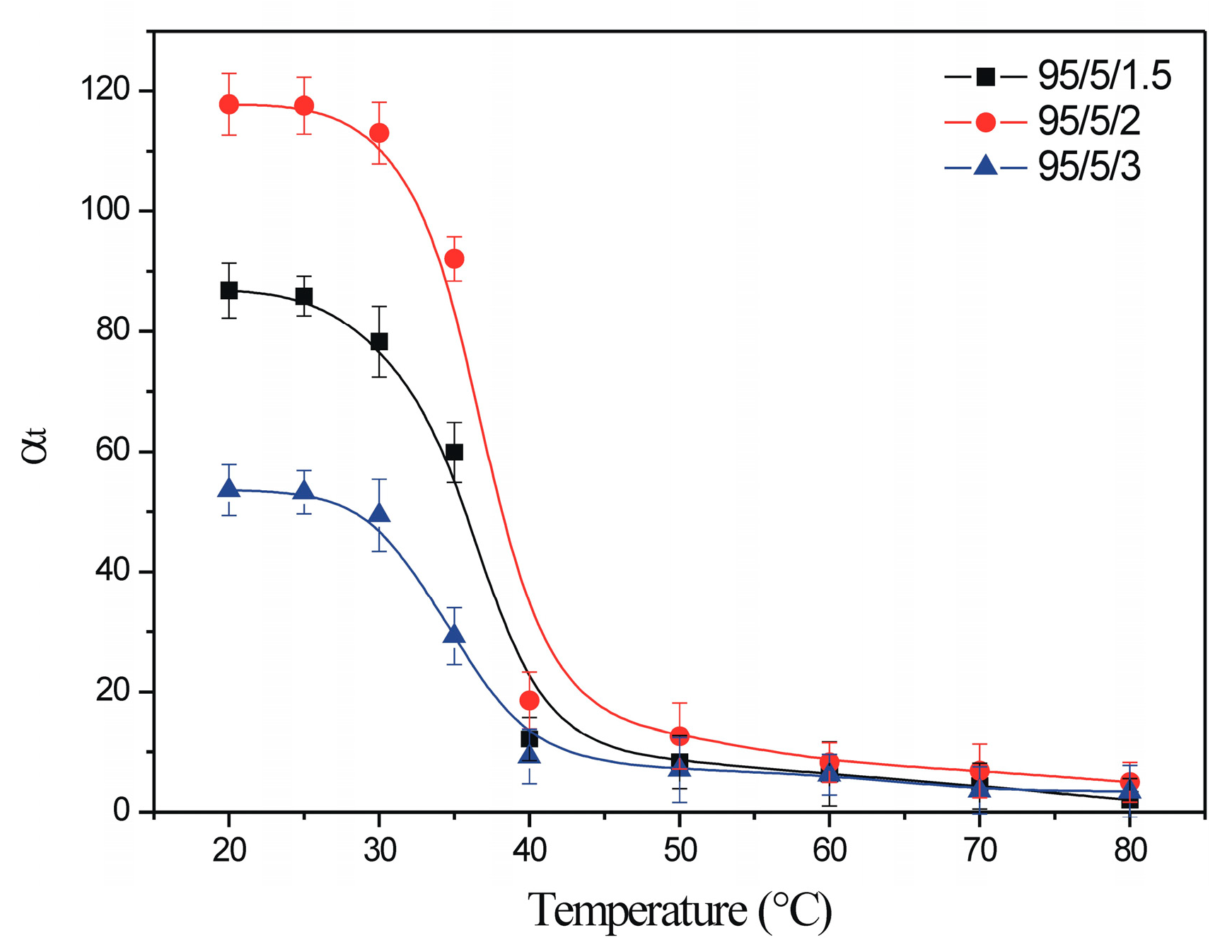
3.2.4. Thermodinamic Studies
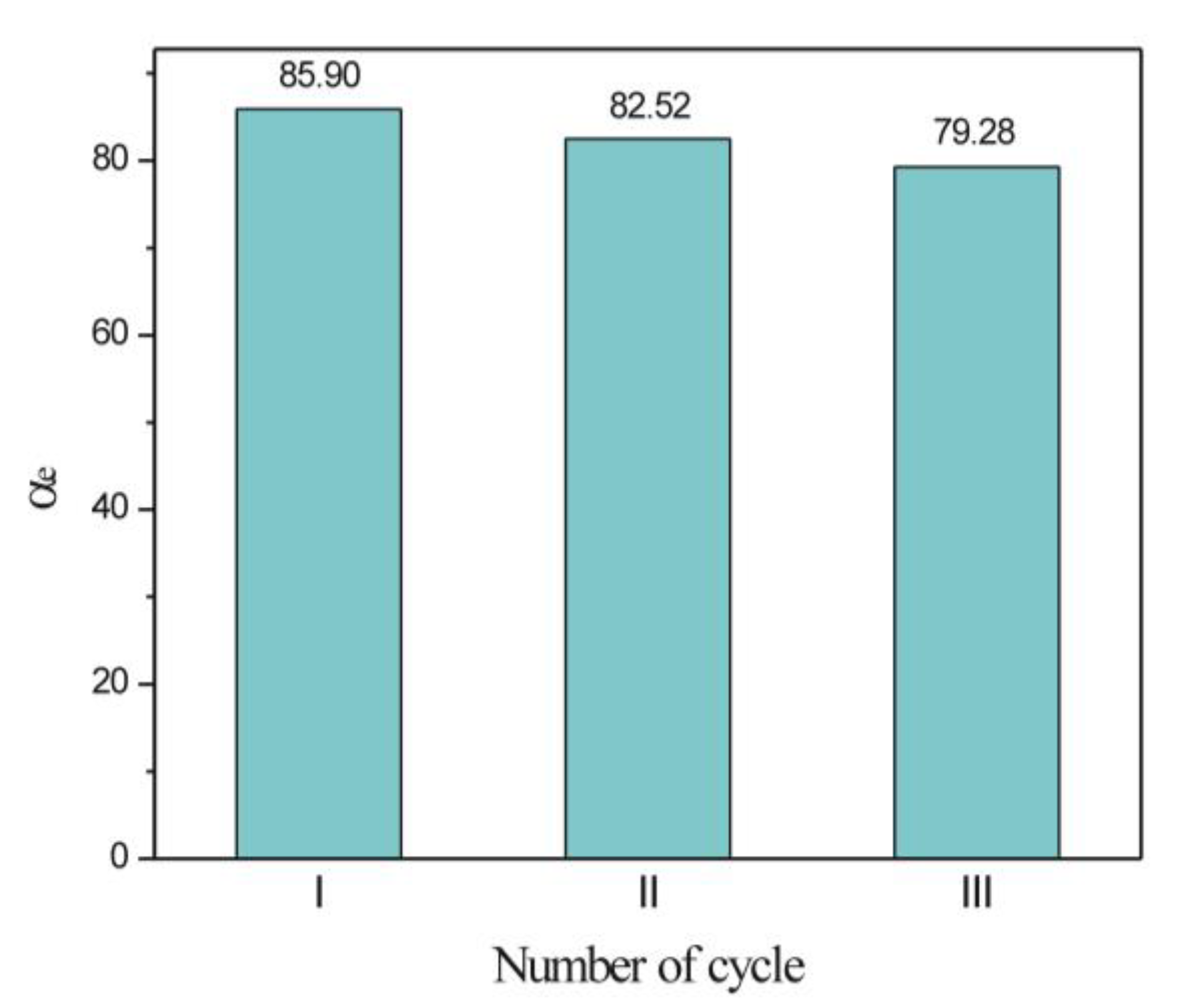
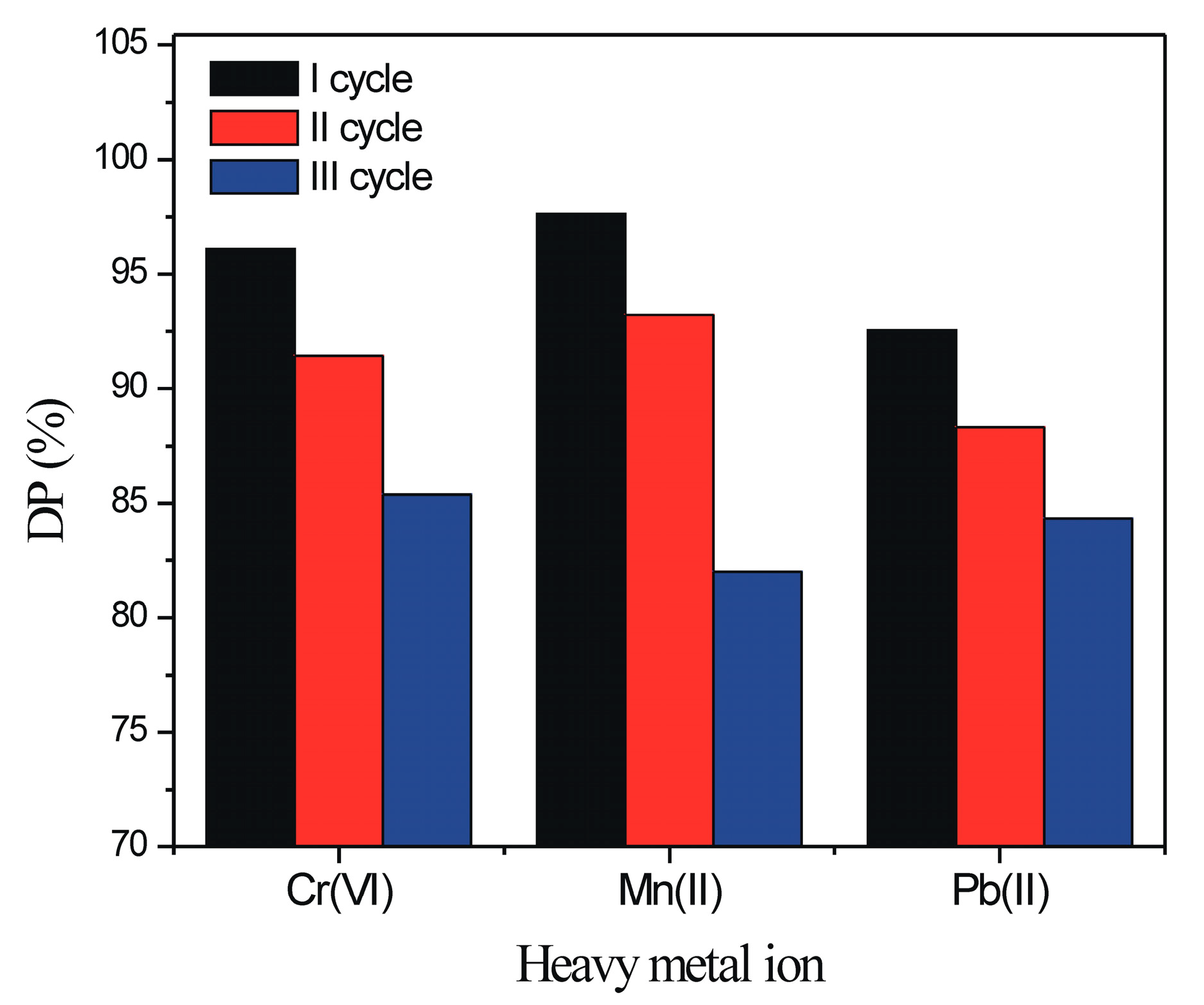
3.2.5. Regeneration and Reuse of Poly(NIPAM-co-MAA) Hydrogel
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NIPAM | N-isopropylacrylamide |
| MAA | Methacrylic acid |
| EGDM | Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate |
| AZDN | 2,2′-azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| DP | Percentage of desorbed metal ions |
References
- Perumal, S.; Atchudan, R.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Babu, R.S.; Karpagavinayagam, P.; Vedhi, C. A short review on recent advances of hydrogel-based adsorbents for heavy metal ions. Metals 2021, 11, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelter, P.B.; Grundman, J.; Hage, D.S.; Carr, J.D.; Castro-Acuña, C.M. A discussion of water pollution in the United States and Mexico; with high school laboratory activities for the analysis of lead, atrazine, and nitrate. J. Chem. Educ. 1997, 74, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivagangi Reddy, N.; Krishna Rao, K.S.V. Polymeric Hydrogels: Recent Advances in Toxic Metal Ion Removal and Anticancer Drug Delivery Applications. Indian J. Adv. Chem. Sci. 2016, 4, 214–234. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.P.; Malik, A.; Sinha, S. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Gomti river (India) using multivariate statistical techniques-a case study. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 538, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranđelović, M.; Jovanović, J. Occupational Medicine; Faculty of Medicine, University of Niš: Niš, Serbia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, J.A.; Testa, S.M. Overview of chromium (VI) in the environment: Background and history. In Chromium (VI) Handbook; Guertin, J., Jacobs, J.A., Avakian, C.P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Oana, P.M. Chromium impact on marine ecosystem. Bull. Univ. Agric. Sci. Vet. Med. Cluj-Napoca 2006, 63, 379–384. [Google Scholar]
- Patlolla, A.K.; Barnes, C.; Yedjou, C.; Velma, V.R.; Tchounwou, P.B. Oxidative stress, DNA damage, and antioxidant enzyme activity induced by hexavalent chromium in Sprague-Dawley rats. Environ. Toxicol. 2009, 24, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, A.K.; Cervantes, C.; Loza-Tavera, H.; Avudainayagam, S. Chromium toxicity in plants. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velma, V.; Vutukuru, S.S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Ecotoxicology of hexavalent chromium in freshwater fish: A critical review. Rev. Environ. Health 2009, 24, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrilli, F.L.; De Flora, S. Toxicity and Mutagenicity of Hexavalent Chromium on Salmonella typhimurium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1977, 33, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology; Luch, A., Ed.; Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 101, pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufaman, D.B.; DiNicola, W.; McIntosh, R. Acute potassium dichromate poisoning. Treated by peritoneal dialysis. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1970, 119, 374–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.G. Five of Potential significant. In Metallic Contaminants and Human Health; Lee, D.H.K., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1972; pp. 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Gerber, G.B.; Léonard, A.; Hantson, P. Carcinogenicity, mutagenicity and teratogenicity of manganese compounds. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2002, 42, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, A. Manganese action in brain function. Brain Res. Rev. 2003, 41, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Dubey, R.S. Lead Toxicity in Plants. Braz. J. Plant. Physiol. 2005, 17, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubicki, Z.; Kołodyńsk, D. Selective Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Waters and Waste Waters Using Ion Exchange Methods. In Ion Exchange Technologies; Kilislioğlu, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 193–240. [Google Scholar]
- Flora, G.; Gupta, D.; Tiwari, A. Toxicity of lead: A review with recent updates. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2012, 5, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, Z.; Karim, A.; Karam, A.; Khalloufi, S. Adsorption of Heavy Metals: Mechanisms, Kinetics, and Applications of Various Adsorbents in Wastewater Remediation—A Review. Waste 2023, 1, 775–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muya, F.N.; Sunday, C.E.; Baker, P.; Iwuoha, E. Environmental remediation of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution through hydrogel adsorption: A critical review. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-qudah, Y.H.F.; Mahmoud, G.A.; Abdel Khalek, M.A. Radiation crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol)/acrylic acid copolymer for removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2014, 7, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, C.; Huang, D.; Feng, S.J. Adsorption behavior of amphoteric double-network hydrogel based on poly(acrylic acid) and silica gel. Polym. Res. 2012, 19, 9929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, N.P.; Shah, P.U.; Shah, N.K. Adsorptive removal of nickel(II) ions from aqueous environment: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 179, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volesky, B. Detoxification of metal-bearing effluents: Biosorption for the next century. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 59, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anah, L.; Astrini, N. Influence of pH on Cr(VI) ions removal from aqueous solutions using carboxymethyl cellulose-based hydrogel as adsorbent. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 60, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebara, M.; Kotsuchibashi, Y.; Narain, R.; Idota, N.; Kim, Y.J.; Hoffman, J.M.; Uto, K.; Aoyagi, T. Smart Biomaterials; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Peppas, N.A.; Bures, P.; Leobandung, W.; Ichikawa, H. Hydrogels in pharmaceutical formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaka, L.; Alsaka, L.; Altaee, A.; Zaidi, S.J.; Zhou, J.; Kazwini, T. A Review of Hydrogel Application in Wastewater Purification. Separations 2025, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, G.A.; Mohamed, S.F. Removal of lead ions from aqueous solution using (sodium alginate/itaconic acid) hydrogel prepared by gamma radiation. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2012, 6, 262–273. [Google Scholar]
- Souda, P.; Sreejith, L. Magnetic hydrogel for better adsorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1882–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Wei, J. Enhanced adsorption properties of interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels for heavy metal ion removal. Polym. Bull. 2011, 67, 1709–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Chen, S.; Luo, Y. Adsorption mechanisms of hydrogels for heavy metal and organic dyes removal: A short review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 12, 100552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Li, Z. Synthesis and characterization of poly(HEA/MALA) hydrogel and its application in removal of heavy metal ions from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215–216, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Tian, P. Adsorption of Cu2+ Ions with Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic acid) Micro/Nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 3470–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, H.; Amaral, M.H.; Lobão, P. Temperature and pH stimuli-responsive polymers and their applications in controlled and selfregulated drug delivery. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, K.; Banthia, A.K.; Majumdar, D.K. Polymeric Hydrogels: Characterization and Biomedical Applications. Des. Monomers Polym. 2009, 12, 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hag Ali, A.; Shawky, H.A.; Abd El Rehim, H.A.; Hegazy, E.A. Synthesis and characterization of PVP/AAc copolymer hydrogel and its applications in the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution. Eur. Polym. J. 2003, 39, 2337–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.J.; Zhang, S.B.; Zhou, M.Y.; Xie, R.; Yang, L.; Chu, L.Y. Novel heavy-metal adsorption material: Ion-recognition p(NIPAM-co-BCAm) hydrogels for removal of lead(II) ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.; Solaiman; Roy, C.K.; Firoz, S.H.; Foyez, T.; Imran, A.B. Role of Ionic Moieties in Hydrogel Networks to Remove Heavy Metal Ions from Water. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinfrignini, P.; Boschetti, A.; Ghini, G.; Tenti, A.; Plazanet, M.; Martella, D.; Torre, R. A Gold Rush: Designing Hydrogels for Selective Recovery in Wastewater Containing Mixed Metal Ions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 68368–68378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona-Rivera, M.A.; Ovando-Medina, V.M.; Bernal-Jacome, L.A.; Cervantes-González, E.; Antonio-Carmona, I.D.; Dávila-Guzmán, N.E. Remazol Red Dye Removal Using Poly(Acrylamide-Co-Acrylic Acid) Hydrogels and Water Absorbency Studies. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 2017, 295, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, A. Superadsorbent with three-dimensional networks: From bulk hydrogel to granular hydrogel. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 72, 661–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Chen, Y.; Hu, J.; Xiong, J.; Lu, J.; Liu, J.; Tan, X.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y. A self-supported sodium alginate composite hydrogel membrane and its performance in filtering heavy metal ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 300, 120278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, J.; Lu, J.; Fan, X.; Chen, Y.; Ding, M.; Rong, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y. A novel sodium alginate/cellulose nanofiber self-supported hydrogel membrane and its filtration performance. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 50, 103303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Tan, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Hu, J.; Lu, J.; Ding, M.; Meng, C.; Liu, W.; et al. Self-supported hydrogel loose nanofiltration membrane for dye/salt separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 328, 124982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Peña, E.; Frutos, P.; Frutos, G.; Quijada-Garrido, I.; Barrales-Rienda, J.M. The influence of the copolymer composition on the diltiazem hydrochloride release from a series of pH-sensitive poly[(N-isopropylacrylamide)-co-(methacrylic acid)] hydrogels. AAPS PharmSciTech 2004, 5, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Cao, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, C.; He, C.; Chen, X. pH- and thermo-responsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid derivative) copolymers and hydrogels with LCST dependent on pH and alkyl side groups. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 5578–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velada, J.L.; Liu, Y.; Huglin, M.B. Effect of pH on the swelling behaviour of hydrogels based on Nisopropylacrylamide with acidic comonomers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1998, 199, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, A.K.; Aggarwal, S.; Mandal, U.K. Swelling dynamics of poly(NIPAM-co-AMPS) hydrogels synthesized using PEG as macroinitiator: Effect of AMPS content. J. Polym. Res. 2013, 20, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqi, Z.H.; Butt, Z.; Begum, R.; Khan, S.R.; Sharif, A.; Ahmed, E. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic acid) microgel stabilized copper nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of nitrobenzene. Mater. Sci. Pol. 2015, 33, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, A.; Pathak, D.P.; Majumdar, D.K.; Manchanda, S. Methacrylic Acid-Co-Butylmethacrylate Copolymers: Design, Characterization and Evaluation as Encapsulating Material for Colon Targeted Formulations. Des. Monomers Polym. 2016, 19, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asman, S.; Mohamad, S.; Sarih, N.M. Exploiting β-Cyclodextrin in Molecular Imprinting for Achieving Recognition of Benzylparaben in Aqueous Media. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 3656–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamenković, J.; Cakić, S.; Nikolić, L. Polymer Chemistry; Faculty of Technology, University of Niš: Leskovac, Serbia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, J.B.; Toth, L.M.; Quist, A.S.; Boyd, G.E. Vibrational spectra of crystalline, molten and aqueous potassium dichromate. Spectrochim. Acta A 1973, 29, 1585–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.L.; Bricker, C.E. Comparison of the vibrational spectra of K2Cr2O7, Rb2Cr2O7 and CS2Cr2O7. Spectrochim. Acta A 1973, 29, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfer, S.; Popp, J.; Mayerhöfer, T.G. Dispersion analysis of sodium dichromate dihydrate Na2Cr2O7·2H2O single crystal. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 205, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.M.; Darab, J.G.; Fulton, J.L. An Infrared and X-ray Absorption Study of the Structure and Equilibrium of Chromate, Bichromate, and Dichromate in High-Temperature Aqueous Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 1772–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palopoli, C.M.; Etcheverry, S.B.; Baran, E.J. Vibrational and thermal behaviour of nicotinium dichromate. Thermochim. Acta 1988, 131, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stammreich, H.; Bassi, D.; Sala, O.; Siebert, H. The vibrational spectrum of the dichromate ion. Spectrochim. Acta 1958, 13, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, M.; Ismail, H.; Ahmad, Z.; Fan, M. Synthesis of linear low-density polyethylene-g-poly(acrylic acid)-co-starch/organo-montmorillonite hydrogel composite as an adsorbent for removal of Pb (ΙΙ) from aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 27, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Wei, W.; Li, J.; Zuo, G.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Dong, W. Development of novel hydrogels based on Salecan and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic acid) for controlled doxorubicin release. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 69869–69881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganji, F.; Vasheghani-Farahani, S.; Vasheghani-Farahani, E. Theoretical description of hydrogel swelling: A review. Iran. Polym. J. 2010, 19, 375–398. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.; Chen, J.; Park, H. Hydrogel Composites and Superporous Hydrogel Composites Having Fast Swelling, High Mechanical Strength, and Superabsorbent Properties. U.S. Patent US6271278 B1, 7 August 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Antić, K.M.; Babić, M.M.; Jovašević-Vuković, J.J.; Vasiljević-Radović, D.G.; Onjiac, A.E.; Filipović, J.M.; Tomić, S.L. Preparation and characterization of novel P(HEA/IA) hydrogels for Cd2+ ion removal from aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 338, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosavljević, N.; Debeljković, A.; Kalagasidis-Krušić, M.; Milašinović, N.; Üzüm, Ö.B.; Karadağ, E. Application of poly(acrlymide-co-sodium methacrylate) hydrogels in copper and cadmium removal from aqueous solution. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2014, 33, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, A.K.; Sharma, M. Preparation and characterization of novel pH-sensitive binary grafted polymeric blends of gelatin and poly(vinyl alcohol): Water sorption and blood compatibility study. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 100, 599–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, S.K. Swelling–deswelling behavior of poly(acrylamide-co-maleic acid) hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 80, 2782–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wang, F.J.; Chung, T.S. Thermosensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels with expanded network structures and improved oscillating swelling-deswelling properties. Langmuir 2002, 18, 2013–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazel, C.S.; Peppas, N.A. Pulsatile local delivery of thrombolytic and antithrombotic agents using poly(Nisopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic acid) hydrogels. J. Control. Release 1996, 39, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Montaño, E.L.; Rodríguez-Laguna, N.; Sánchez-Hernández, A.; Rojas-Hernández, A. Determination of pKa Values for Acrylic, Methacrylic and Itaconic Acids by 1H and 13C NMR in Deuterated Water. J. Appl. Sol. Chem. Model. 2015, 4, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Ahmad, A.L.; Ooi, B.S. Thermo-responsive properties of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogel and its effect on copper ion removal and fouling of polymer-enhanced ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 469, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Hu, J.; Tang, H.; Wu, P. Spectral interpretation of thermally irreversible recovery of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogel. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 5061–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.K.; Swami, V.; Kumar, D.; Rajagopal, C. Removal of toxic metals using superabsorbent polyelectrolytic hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 122, 2415–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, R.; Li, Z. Sulfhydryl functionalized hydrogel with magnetism: Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption behavior study for heavy metal removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 249, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, P.J.; Shao, L.M.; Li, X.J. Leaching behavior of heavy metals from municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash and its geochemical modeling. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2008, 10, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Yu, J.; Gao, J.; Yang, W.; Li, Y. A promising absorbent of acrylic acid/poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel prepared by glow-discharge electrolysis plasma. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2012, 10, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrikhpour, H.; Jalali, M. Waste calcite sludge as an adsorbent for the removal of cadmium, copper, lead, and zinc from aqueous solutions. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2012, 14, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Lin, M.S.; Hsu, K.R. Recovery of Cu(II) and Cd(II) by a chelating resin containing aspartate groups. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayan, G.Ö.; Kayan, A. Composite of Natural Polymers and Their Adsorbent Properties on the Dyes and Heavy Metal Ions. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 3477–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrygiannia, M.; Lada, Z.G.; Manousoua, A.; Aggelopoulos, C.A.; Deimede, V. Removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solution by novel pyrrolidiniumbased Polymeric Ionic Liquid (PIL) as adsorbent: Investigation of the adsorption kinetics, equilibrium isotherms and the adsorption mechanisms involved. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.S.; Musharraf, S.G.; Bhanger, M.I.; Malik, M.I. Salicylaldehyde derivative of nano-chitosan as an efficient adsorbent for lead (II), copper (II), and cadmium (II) ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessa, E.F.; Medina, A.L.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Fajardo, A.R. Removal of multi-metals from water using reusable pectin/cellulose microfibers composite beads. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, H.N.; Safa, Y.; Yakout, S.M.; Shair, O.H.; Iqbal, M.; Nazir, A. Efficient removal of dyes using carboxymethyl cellulose/ alginate/polyvinyl alcohol/rice husk composite: Adsorption/ desorption, kinetics and recycling studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.; Ahmad, R. An efficient sequestration of toxic crystal violet dye from aqueous solution by Alginate/Pectin nanocomposite: A novel and ecofriendly adsorbent. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worch, E. Adsorption Technology in Water Treatment: Fundamentals, Processes, and Modeling; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lagergren, S. About the Theory of So-Called Adsorption of Soluble Substances. K. Sven. Vetensk. Akad. Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. A Comparison of Chemisorption Kinetic Models Applied to Pollutant Removal on Various Sorbents. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 1998, 76, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of Adsorption on Carbon from Solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. ASCE. 1963, 89, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil Kumar, P.; Ramalingam, S.; Senthamarai, C.; Niranjanaa, M.; Vijayalakshmi, P.; Sivanesan, S. Adsorption of dye from aqueous solution by cashew nut shell: Studies on equilibrium isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics of interactions. Desalination 2010, 261, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Ahmad, A.L.; Ooi, B.S. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels for copper ion adsorption: Equilibrium isotherms, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdravković, A.; Nikolić, L.; Ilić-Stojanović, S.; Nikolić, V.; Najman, S.; Mitić, Ž.; Ćirić, A.; Petrović, S. The removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by hydrogels based on N-isopropylacrylamide and acrylic acid. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 4797–4821. [Google Scholar]
- Bayramoglu, G.; Altintas, B.; Arica, M.Y. Adsorption kinetics and thermodynamic parameters of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions by using a new strong cation-exchange resin. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 152, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Halim, E.S.; Al-Deyab, S.S. Preparation of poly (acrylic acid)/starch hydrogel and its application for cadmium ion removal from aqueous solutions. React. Funct. Polym. 2014, 75, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Králik, M. Adsorption, chemisorption, and catalysis. Chem. Pap. 2014, 68, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–471. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, K.R.; Eagleton, L.C.; Acrivos, A.; Vermeulen, T. Pore- and solid-diffusion kinetics in fixedbed adsorption under constant-pattern conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1966, 5, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R. Studies on adsorption of crystal violet dye from aqueous solution onto coniferous pinus bark powder (CPBP). J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Mirza, A. Synthesis of Guar gum/bentonite a novel bionanocomposite: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic studies for the removal of Pb (II) and crystal violet dye. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yue, Q.Y.; Su, Y.; Gao, B.Y.; Sun, H.J. Equilibrium, thermodynamics and process design to minimize adsorbent amount for the adsorption of acid dyes onto cationic polymer-loaded bentonite. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 158, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.J. Biosorption isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 61, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
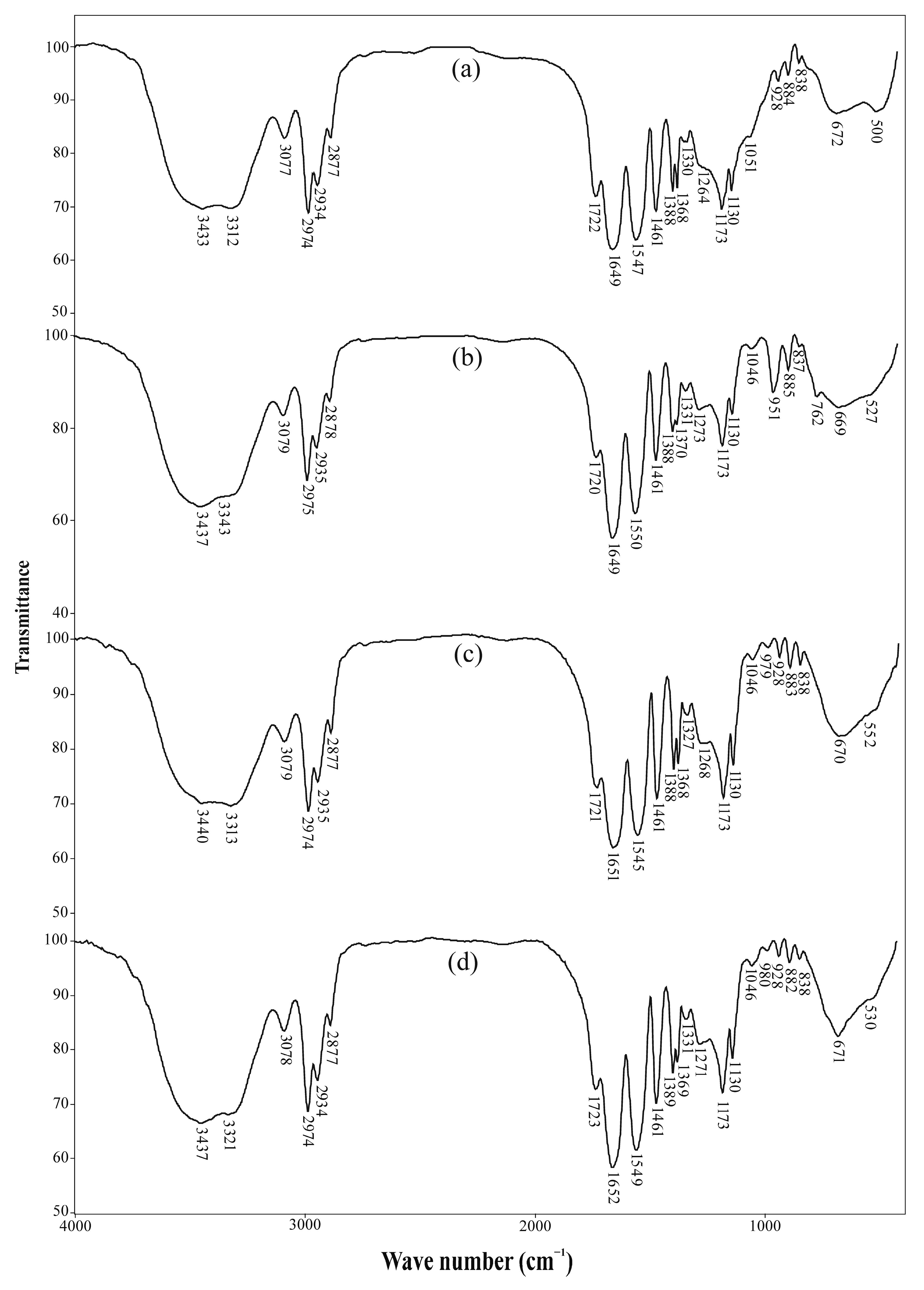
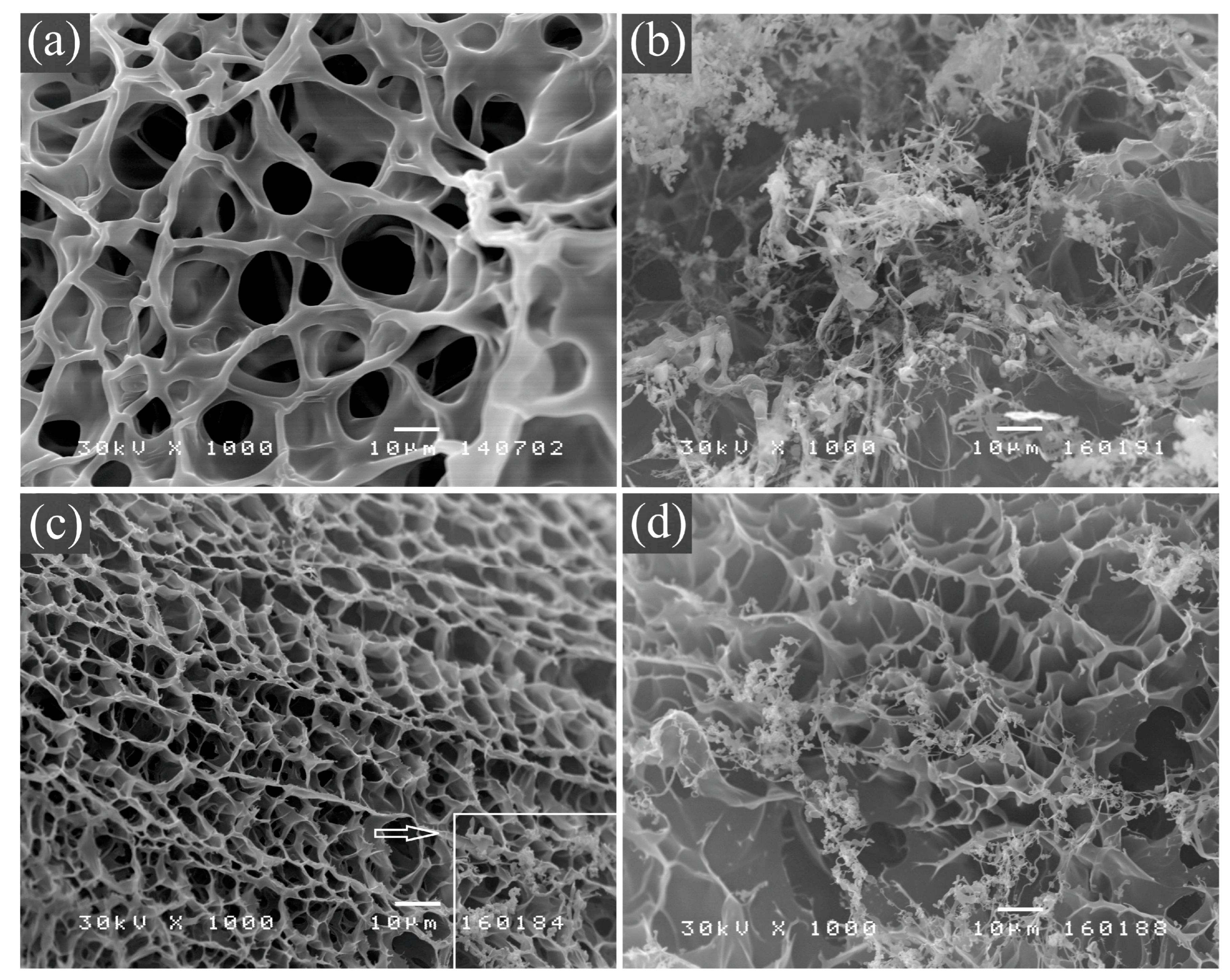
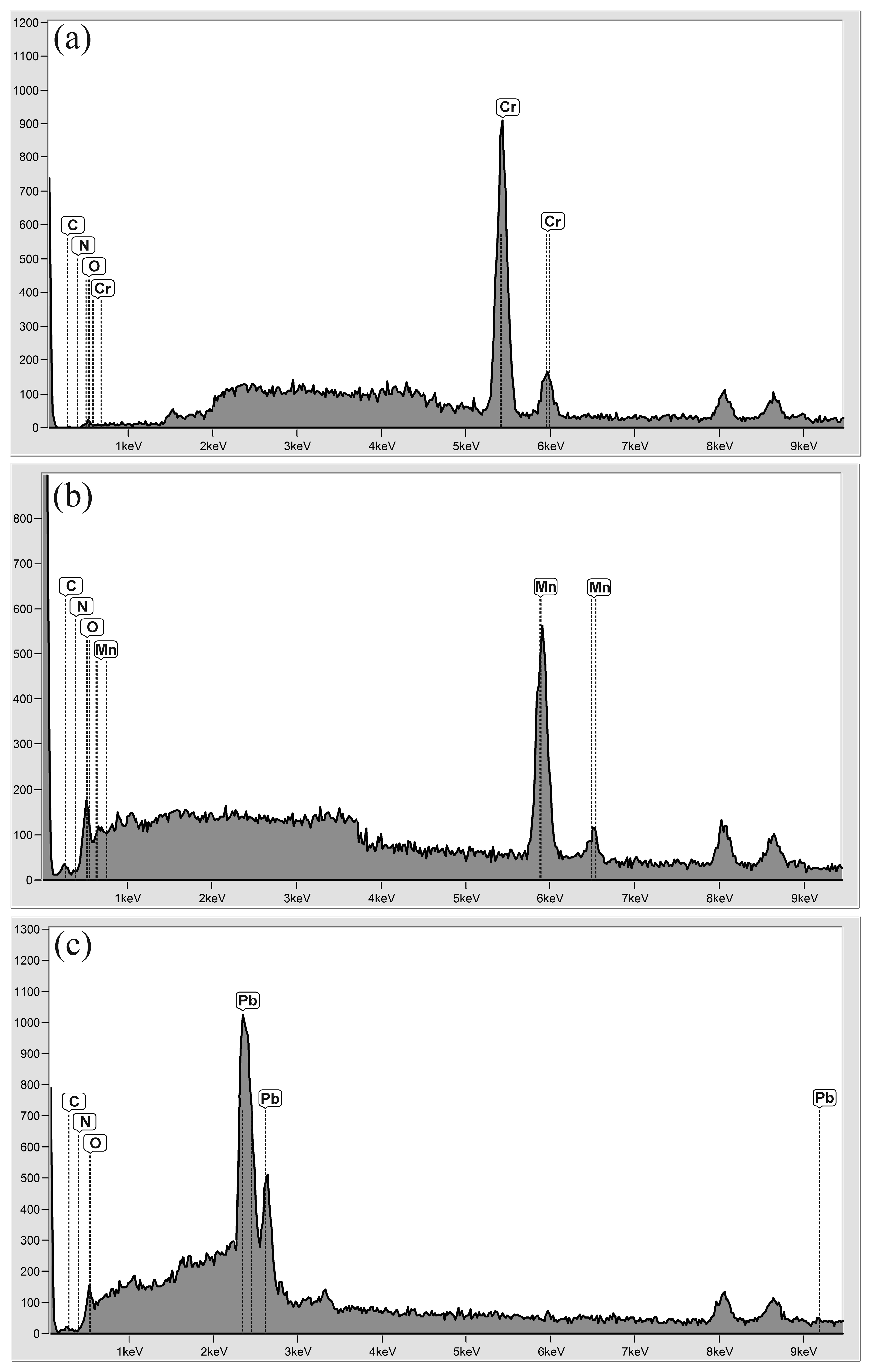

| Vibration Assignment | Pure Hydrogel | Hydrogel After Sorption of Heavy Metal Ions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr(VI) | Mn(II) | Pb(II) | ||
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | ||||
| ν(OH) | 3433 | 3437 (+4) | 3440 (+7) | 3437 (+4) |
| ν(N-H) | 3312 | 3343 (+31) | 3313 (+1) | 3321 (+9) |
| νas(=C-H) | 3077 | 3079 (+2) | 3079 (+2) | 3078 (+1) |
| νas(C-H) | 2974 | 2975 (+1) | 2974 (0) | 2974 (0) |
| νs(C-H) | 2877 | 2878 (+1) | 2877 (0) | 2877 (0) |
| ν(C=O) | 1722 | 1720 (−2) | 1721 (−1) | 1723 (+1) |
| Amide band I, ν(C=O) | 1649 | 1649 (0) | 1651 (+2) | 1652 (+3) |
| Amide band II, coupling of δ(N-H) and ν(C-N) | 1547 | 1550 (+3) | 1545 (−2) | 1549 (+2) |
| δas(C-H) | 1461 | 1461 (0) | 1461 (0) | 1461 (0) |
| Heavy Metal Ion | Hydrogel Sample | qm (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|
| Cr(VI) | 90/10/1.5 | 225.12 |
| 90/10/2 | 165.54 | |
| 90/10/3 | 62.04 | |
| Mn(II) | 90/10/1.5 | 131.92 |
| 90/10/2 | 34.90 | |
| 90/10/3 | 29.58 | |
| Pb(II) | 90/10/1.5 | 449.90 |
| 90/10/2 | 77.32 | |
| 90/10/3 | 33.03 |
| Sorbent | Sorbat | Sorption Capacity (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) | Au(III) | up to 124 | [41] |
| poly(NIPAM) | Pb(II) | 120 | [39] |
| poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) | Fe(III), Cr(III) | 276 for Fe(III), and 139 for Cr(III) | [40] |
| poly(NIPAM-co-MAA) | Cu(II) | 0.765 mmol/g | [35] |
| N-methyl pyrrolidinium-based Polymeric Ionic Liquid | Orange G, Orange II, Sunset Yellow | 198.4 for Orange G, 279.3 for Orange II, and 316.5 for Sunset Yellow | [81] |
| Chitosan/salicylaldehyde composite | Pb(II) | 123.67 | [82] |
| Cellulose/pectin composite | Fe(II) | 98 | [83] |
| Alginate/rice husk composite | Direct Blue 67 | 0.63 | [84] |
| Alginate/pectin | Crystal Violet | 619.22 | [85] |
| Hydrogel | qe, exp 1 (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | Intra-Particle Diffusion | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 × 104 (1/min) | qe, cal 2 (mg/g) | R2 | k2 × 106 (g/mg min) | qe, cal (mg/g) | R2 | kid (mg/g min1/2) | C (mg/g) | R2 | ||
| Cr(VI) ion | ||||||||||
| 95/5/1.5 | 289.35 | 8.19 | 170.47 | 0.965 | 12.73 | 301.20 | 0.996 | 3.14 | 101.04 | 0.877 |
| 95/5/2 | 217.34 | 9.72 | 97.67 | 0.771 | 24.36 | 225.73 | 0.999 | 2.38 | 85.22 | 0.616 |
| 95/5/3 | 120.12 | 9.41 | 63.01 | 0.756 | 26.58 | 128.20 | 0.996 | 1.52 | 35.24 | 0.659 |
| Mn(II) ion | ||||||||||
| 95/5/1.5 | 190.59 | 8.33 | 147.43 | 0.989 | 8.37 | 213.22 | 0.999 | 2.63 | 31.52 | 0.922 |
| 95/5/2 | 148.87 | 13.46 | 97.99 | 0.904 | 20.27 | 160.77 | 0.996 | 1.79 | 47.08 | 0.793 |
| 95/5/3 | 115.28 | 8.37 | 74.67 | 0.917 | 19.94 | 124.67 | 0.995 | 1.42 | 30.71 | 0.818 |
| Pb(II) ion | ||||||||||
| 95/5/1.5 | 349.71 | 11.42 | 302.82 | 0.983 | 5.17 | 390.62 | 0.990 | 5.03 | 55.23 | 0.884 |
| 95/5/2 | 156.86 | 20.08 | 96.22 | 0.945 | 39.95 | 163.40 | 0.999 | 1.62 | 67.91 | 0.758 |
| 95/5/3 | 90.30 | 9.16 | 63.62 | 0.976 | 29.00 | 96.71 | 0.997 | 1.17 | 21.35 | 0.879 |
| Heavy Metal Ion | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg/g) | KL × 103 (dm3/mg) | R2 | KF | n | R2 | |
| Cr(VI) | 309.60 | 6.14 | 0.988 | 6.58 | 1.66 | 0.954 |
| Mn(II) | 184.16 | 9.63 | 0.982 | 8.13 | 2.01 | 0.866 |
| Pb(II) | 202.43 | 8.38 | 0.970 | 7.84 | 1.95 | 0.842 |
| Heavy Metal Ion | Temperature (C°) | ΔG° (kJ/mol) | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔS° (J/mol K) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr(VI) | 25 | 2.978 | −9.116 | 40.607 | 0.984 |
| 35 | 3.429 | ||||
| 45 | 3.788 | ||||
| Mn(II) | 25 | 4.254 | −5.947 | 34.183 | 0.991 |
| 35 | 4.574 | ||||
| 45 | 4.939 | ||||
| Pb(II) | 25 | 2.345 | −8.936 | 37.788 | 0.984 |
| 35 | 2.679 | ||||
| 45 | 3.103 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zdravković, A.; Nikolić, V.; Ilić-Stojanović, S.; Stojanović, S.; Dinić, A.; Urošević, M.; Gajić, I.; Nikolić, L. Synthesis and Application of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic Acid) Hydrogels as Sorbent Materials for Wastewater Treatment. Separations 2025, 12, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12040100
Zdravković A, Nikolić V, Ilić-Stojanović S, Stojanović S, Dinić A, Urošević M, Gajić I, Nikolić L. Synthesis and Application of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic Acid) Hydrogels as Sorbent Materials for Wastewater Treatment. Separations. 2025; 12(4):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12040100
Chicago/Turabian StyleZdravković, Aleksandar, Vesna Nikolić, Snežana Ilić-Stojanović, Sanja Stojanović, Ana Dinić, Maja Urošević, Ivana Gajić, and Ljubiša Nikolić. 2025. "Synthesis and Application of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic Acid) Hydrogels as Sorbent Materials for Wastewater Treatment" Separations 12, no. 4: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12040100
APA StyleZdravković, A., Nikolić, V., Ilić-Stojanović, S., Stojanović, S., Dinić, A., Urošević, M., Gajić, I., & Nikolić, L. (2025). Synthesis and Application of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic Acid) Hydrogels as Sorbent Materials for Wastewater Treatment. Separations, 12(4), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12040100










