Abstract
Currently, the medical use of food supplements containing Cannabis sativa has attracted the interest of consumers, as well as the medical and scientific community. With the increasing consumption of these products, there is also a risk of their abuse or discrepancy between the actual and declared contents of active substances by the manufacturer in these products. Thus, the development and elaboration of analytical procedures for determination of appropriate phytocannabinoids seems to be important. This work focuses on the development of a simple, fast and environmentally friendly liquid-liquid extraction method combined with fat freezing from an oil sample to isolate two phytocannabinoids: cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabidiolic acid (CBDA). The extraction method was optimized considering efficacy and repeatability of extraction, as well as minimalizing use of organic reagents and sample amount. Under the optimized conditions, extraction recovery for CBD was 97.3–109% and for CBDA was 69.1–69.5% with precision (RSD, %) 5.0–8.4 and 7.1–10.6, respectively. The evaluated main analytical parameters of the developed high pressure liquid chromatography with diode array detector (HPLC-DAD) method for both studied cannabinoids are satisfactory. The usability of the developed method was checked by analysis of real samples of a food supplement–hemp oil enriched with CBD.
1. Introduction
Cannabis sativa, which belongs to botanical family Cannabaceae, is one of the oldest plants known from its therapeutic properties. Since ancient times it was applied for the treatment of neuropsychiatric, ophthalmic, obstetric, and gastrointestinal diseases. However, for the use in Western medicine, cannabis was only introduced in 1833 by Irish physician O’Shaughnessy [1]. At present, it is known that cannabis has a multidirectional and diverse activity; it acts as a painkiller, anxiolytic, and muscle relaxant, as well as possibly having sedative, anti-cancer, or appetite-stimulating effects [2]. Therefore, they are used more and more often for the treatment of multiple sclerosis, neuropathic pain, chronic pain associated with rheumatoid inflammation joints, and migraine, as well as in cancer patients treated with chemotherapy, in mood disorders, and inflammatory diseases [3].
Depending on the contents of certain cannabis ingredients, especially delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (delta 9-THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), cannabis preparations can be divided into recreational cannabis and medical cannabis. A recreational cannabis contains high content of psychoactive delta 9-THC ranging from 1 to 20% (w/w) and relatively small amount of non-psychoactive CBD. A medical cannabis should contain delta 9-THC at very low concentration level, usually at 0.2–0.3% w/w, and its main components are CBD and its precursor CBDA.
CBD is non-psychoactive compound with multitarget action, establishing a high antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity, as well as it possess antimicrobial, neuroprotective, anxiolytic, and anticonvulsant properties [4]. CBD has attracted significant interest due to its beneficial curative effects along with its safety and tolerability profile in humans. This cannabinoid also shows promise in treatment of such diseases as epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, or multiple sclerosis. CBDA belongs to phytocannabinoic acids which are formed enzymatically and are the most abundant cannabinoid in raw plant material [5]. Neutral cannabinoids, such as, CBD are formed from these acids via their decarboxylation as result of heat or light exposure. The study of pharmacological properties on animal models showed that CBDA also may have widespread therapeutic activity, including anxiolytic, anti-inflammatory, antihyperalgesic, antiemetic, neuroprotective, and anticonvulsant effects [5]. The mechanism of action of cannabinoids is related to their binding to cannabinoid receptors CD1 and CD2 [6,7,8].
Considering increasing use of hemp preparations for medical purposes, it is very important to possess appropriate analytical procedures to control quality and safety of the accessible on a market cannabis products. There has been appeared rather small amount of works presenting the separation and determination of certain bioactive ingredients in commercial cannabis products. Currently, most reported methods concern assaying of several active components of cannabis sativa, such as CBD, delta 9-THC, cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), tetrahydrocannabinol acid (THCA), or delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol (delta 8-THC) in plant materials (cannabis leaves, inflorescences) [9,10,11,12]. In turn, relatively rarely compared to other matrices, like oral spray [13], food samples (e.g. butter, margarine, coconut oil, honey, fruit products, and confectionery) [14], cosmetic products (creams, lotions, ointments) [14], or hemp oil [2,14,15,16] were analyzed for determination of some cannabis compounds. As a rule, solid-fluid or liquid-liquid extraction was used to prepare the samples with various amounts of such extraction solvents as mixtures of methanol with three chloromethane, ethyl acetate with isopropanol, mixtures of methanol or acetonitrile with water, 2-propanol, or 95% ethanol. Chromatographic methods, mainly HPLC-UV [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16], and more rarely GC-MS [17,18] or LC-MS/MS [16,19] techniques, were chosen as separation and quantification methods.
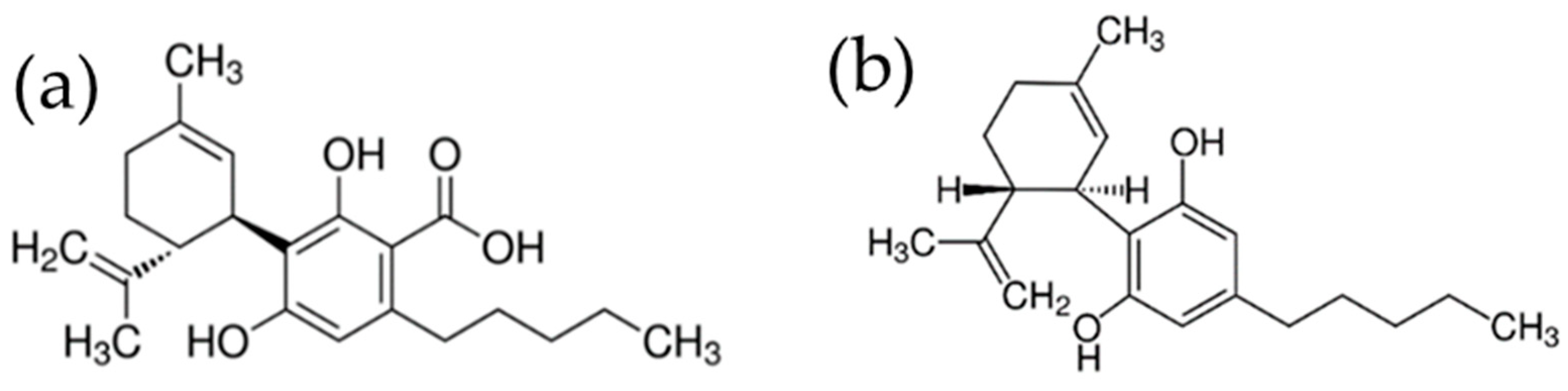
The work presents an alternative approach (to that described in the publications cited above) to the preparation of an oil sample for the determination of two active cannabis compounds (CBDA and CBD, Figure 1) using the HPLC-DAD method. CBD and its precursor CBDA are main constituents of fibrous type hemp, which exhibit significant medical potential. CBD and CBDA are also chief ingredients of often-used diet oil hemp supplements. To obtain more effective treatment effects, these supplements are additionally enriched with CBD, the final content of which is usually 5 or 10% (w/w).
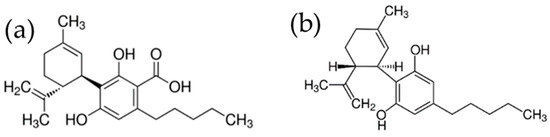
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of CBDA (a) and CBD (b).
The main focus of the work was developing a simple and an environmental friendly sample preparation approach for oil hemp supplements in terms of minimal use of sample amount and toxic reagents without loss of analytical parameters of the method for quantification of the target cannabinoids. According to the authors’ knowledge, acetonitrile was used for the first time as an extraction solvent in combination with the process of freezing fat from oil samples at −41 °C. Due to relatively high content of these two cannabinoids in oil hemp supplements, an easily accessible and moderately sensitive HPLC-DAD method was used.
2. Experimental
2.1. Standards and Reagents
The standard solutions of CBD and CBDA, each at concentration 1 mg per 1 mL of acetonitrile were purchased in LGC Standards (London, UK). Methanol (MeOH) and acetonitrile (ACN), both of HPLC-gradient grade were obtained in Merck (Darmstad, Germany). 98.5% acetic acid and 95% (w/w) ethanol (EtOH), both of analytical grade were bought in Avantor (Gliwice, Poland). Deionized water was obtained from an HLP SUV demineralized water system (Hydrolab, Poznań, Poland).
2.2. Examined Materials
The developed method was validated on samples of olive oil. The standard oil samples that were prepared from “Casa de Azeite” extra virgin olive oil from a local market in Cracow, Poland.
Certified hemp oil supplement “Bio Hemp Complete” (Medihemp, Gols, Austria) was purchased at a local herbal store.
According to a leaflet, this supplement constituted 100% natural dried hemp leaves oil extract, additionally enriched in CBD. The declared composition of the supplement is: 5% (w/w) CBD and other natural compounds, such as other cannabinoids, flavonoids, terpenes, polyunsaturated fatty acids, minerals, and vitamins.
2.3. Apparatus and Laboratory Equipment
The samples were prepared using the following equipment: analytical balance (Radwag, Radom, Poland), vortex (Kartell, Noviglio, Italy), multifunctional rocker shaker (Grant Instruments Ltd., Cambridge, UK), centrifuge (MPW, Warsaw, Poland), sonic bath (Sonic & Materials Inc., Newtown, CT, USA), as well as low temperature freezer (Pol-Eko, Wodzisław Śląski, Poland) in the temperature regulation range from −80 °C to −40 °C. In optimization study the extracts were filtered using KTL Syringe Filters (4 mm, 0.22 μm) (Taiwan), however, the developed method does not require filtration of the obtained extracts.
Chromatographic analyses were performed with use of liquid chromatography system LaChrom D-7000 (Merck-Hitachy, Japan) equipped with autosampler L-7200, pomp L-7100 and DAD L-7455. Separation of cannabinoids were conducted on a column Spheri-5, type C18 (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 µm). The column was thermostated to 25 °C. The separations were conducted in isocratic condition, using the mixture of acetonitrile with 0.5% acetic acid (66:34, v/v) as the mobile phase. The mobile phase flow was 1 mL/min. The cannabinoids were detected at two waves: 220 and 240 nm and the corresponding to them peaks were additionally confirmed by their spectra analysis (using DAD).
2.4. Development of Sample Preparation Procedure
The best isolation conditions for CBD (main component of most food oil supplements) from oil matrix were studied on the oil supplement samples. The following extraction conditions were taken into account in the optimization study: (1) Volume of extraction solvent; (2) type of solvent; (3) application of sonication energy; (4) time of vortexing and shaking the sample (using a multi-functional rocker shaker); (5) filtration of the obtained extracts; and (6) time to freeze the fat.
In each experiment 100 mg of oil supplement sample was used. As the main optimization criterion, extraction efficacy was assumed. The peak areas of CBD in oil supplement extracts were compared with CBD content declared by the manufacturer. The following main experiments were performed in triplicate for each used conditions.
Experiment 1: Two different volumes of the extraction solvent, 500 and 750 µL, of ACN were used. The samples were vortexed for 1 min, then shaken using rocker shaker for 15 min. After that the samples were kept for 24 h in a freezer at −41 °C. Next, a liquid acetonitrile layer was quickly pipetted into a separate Eppendorf tube and the same volume of acetonitrile was added. The content was vortexed by 30 s and filtrated.
Experiment 2: Two different methods of supporting the extraction process were applied: in one case a sample was vortexed (1 min) with 500 µL of ACN and then sonication energy assisted LLE was applied and in second case multifunctional rocker shaker (15 min) was used followed vortexing (1 min) sample with 500 µL of ACN. In both cases the samples were kept for 24 h at −41 °C, and after freezing liquid acetonitrile layers were quickly pipetted into a separate Eppendorf tubes and the same volume of ACN was added. Next, the diluted extract were vortexed by 30 s and filtrated.
Experiment 3: The same extraction conditions as in experiment 2 were used, with the exception that the extraction solvent (95% EtOH) and no freezing were used.
Experiment 4: Two extraction solvents, ACN and EtOH, (each one 500 µL) were employed. In both cases the samples were vortexed (1 min) and then a multifunctional rocker shaker (15 min) was used. In the case of ACN after fat freezing (for 24 h), the extract was twice diluted with ACN and directly injected onto chromatographic column filtrated, and in the case of EtOH no freezing and no filtration was applied before injection of the obtained extract.
In addition, three freezing times (24 h, 2 h, and 15 min) were tested to determine the minimum time needed to freeze the fat from the acetonitrile phase.
2.5. Preparation of Standard Oil Solutions for the Method Validation
One-hundred milligrams (100 mg) of olive oil in an Eppendorf tube (2 mL) was weighed and then enriched with appropriate amounts of CBD and CBDA standard solutions. To establish the calibration curves, the standard solutions of CBD and CBDA were prepared, at six concentration levels for each cannabinoid, i.e., at 50, 25, 12.5, 6.25, 3.125, 1.563 µg/mL for CBD and at 25, 12.5, 6.25, 3.125, 1.563, 0.782 µg/mL for CBDA. The oil spiked with both cannabinoids in the tube was vortexed by 1 min and equilibrated for one hour. Next, 460 µL acetonitrile was added and the sample was shaken by 15 min using a rocker shaker. To freeze the oil layer, the sample was kept in a freezer at −41 °C for 15 min. After that time, a liquid acetonitrile layer was quickly pipetted into a separate Eppendorf tube and twice diluted with acetonitrile. The content was vortexed for 30 s.
2.6. Final Procedure for Hemp Oil Supplement Preparation
In an Eppendorf tube 10 mg of the supplement was weighed and diluted with 2490 mg of olive oil and vortexed for 1 min. In a separate Eppendorf tube, 100 mg of the obtained solution was weighed and mixed with 500 µL acetonitrile using vortex (1 min) and then shaken in a multifunctional rocker shaker (15 min). To freeze the oil layer, the prepared sample was kept at −41 °C for 15 min. After freezing, a liquid acetonitrile layer was quickly pipetted into a flask (5 mL), diluted with water to the mark, and accurately mixed. Next, 500 µL of the solution was mixed by vortex (30 s) with the same volume of acetonitrile.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Study of Sample Preparation Conditions
The obtained results from four step-experiments are given in Table 1.

Table 1.
Study of extraction conditions for CBD from a food oil supplement.
On the basis of the performed experiments the following conclusions may be drawn: (i) The smaller volume (500 µL) of acetonitrile extraction solvent was enough to reach the same extraction yield as using 750 µL ACN; (ii) sonication energy and shaking with a rocker shaker as the methods of supporting the extraction process may be used alternatively; (iii) application of the same methods with ethanol as the extraction solvent gave better recovery results, however, injecting the final acetonitrile extracts without filtration results in a comparable extraction yield to that obtained for 99% ethanol using sonication energy; and (iv) in the situation when filtration of the final ethanol extract was not used, the extraction efficiency decreased drastically. This can be explained by the fact that small amounts of fat dissolved in the ethanol extracts can form an emulsion under increased pressure during filtration (after filtration the extracts turned whitish). In turn, the use of a 15-minute fat freezing from acetonitrile oil extracts turned out to be sufficient. As the optimal procedure alternative to the one with 95% EtOH found in literature [14], the sample preparation procedure as it was described (in Section 2) for preparation of standard oil solutions was assumed.
Under optimal conditions, extraction recovery and repeatability for CBD and CBDA were determined. Extraction efficiency for two concentration levels of the cannabinoids tested was from 97.3 to 109.5% for CBD and from 69.1 to 69.5% for CBDA. In turn, the repeatability of the extraction ranged from 5.0 to 8.4% for CBD and from 7.1 to 10.6% for CBDA. As predicted on the base of chemical structure, CBDA was confirmed to be more polar than CBD and, thus, CBDA is extracted from the oil matrix into ACN with less yield but the developed for it extraction conditions are satisfactory enough to be used for determination of CBDA in this matrix. The calculated extraction parameters for both studied cannabinoids are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Extraction recovery and repeatability for CBD and CBDA from olive oil samples.
3.2. Estimation of Main Analytical Parameters of HPLC Method for CBD and CBDA Determination
Under the optimized extraction conditions the main analytical parameters of the proposed analytical method were determined: linearity range, limits of detection, and quantification and precision at two concentration levels of CBD and CBDA.
3.2.1. Linearity Range
The calibration graphs of CBD and CBDA were established on the basis of triplicate measurements (peak areas) corresponding to the above-mentioned (in Section 2) six concentrations for each cannabinoid.
After removing one point, corresponding to the lowest CBD concentration (1.563 µg/mL), both calibration curves display good linearity, ranging from 3.12 to 50 µg/mL for CBD and from 0.78 to 25 µg/mL for CBDA, with determination coefficient R2 higher than 0.997.
3.2.2. Limits of Detection (LOD) and Quantification (LOQ)
The method is more sensitive for CBDA than CBD due to the absorption coefficient, at two used waves (220 and 240 nm), which is higher for CBDA.
LOD was determined as 3.3s/a (where s is the standard deviation of regression line and a is the directional coefficient of calibration curve) and LOQ was estimated as the lower concentration range of the calibration curves. LOD/LOQ are 0.17/0.78 µL/mL for CBDA and 1.94/3.12 µL/mL for CBD. It should be also stressed that the quoted LOD and LOQ values does not considered the possibility of achieving lower detection limits by preconcentration of the obtained extracts.
3.2.3. Precision
The precision (inter-day) was evaluated as %, RSD from five repeatable measurements, at two concentration levels of both cannabinoids.
At lower concentration level (2 µg/mL) this parameter (%, RSD 8.07) was calculated only for CBDA because this concentration of CBD was below the linearity range of the calibration curve for this compound. In turn, at the higher concentration level (at 20 µg/mL) the precision was higher for CBD (%, RSD 5.38) than for CBDA (%, RSD 10.47).
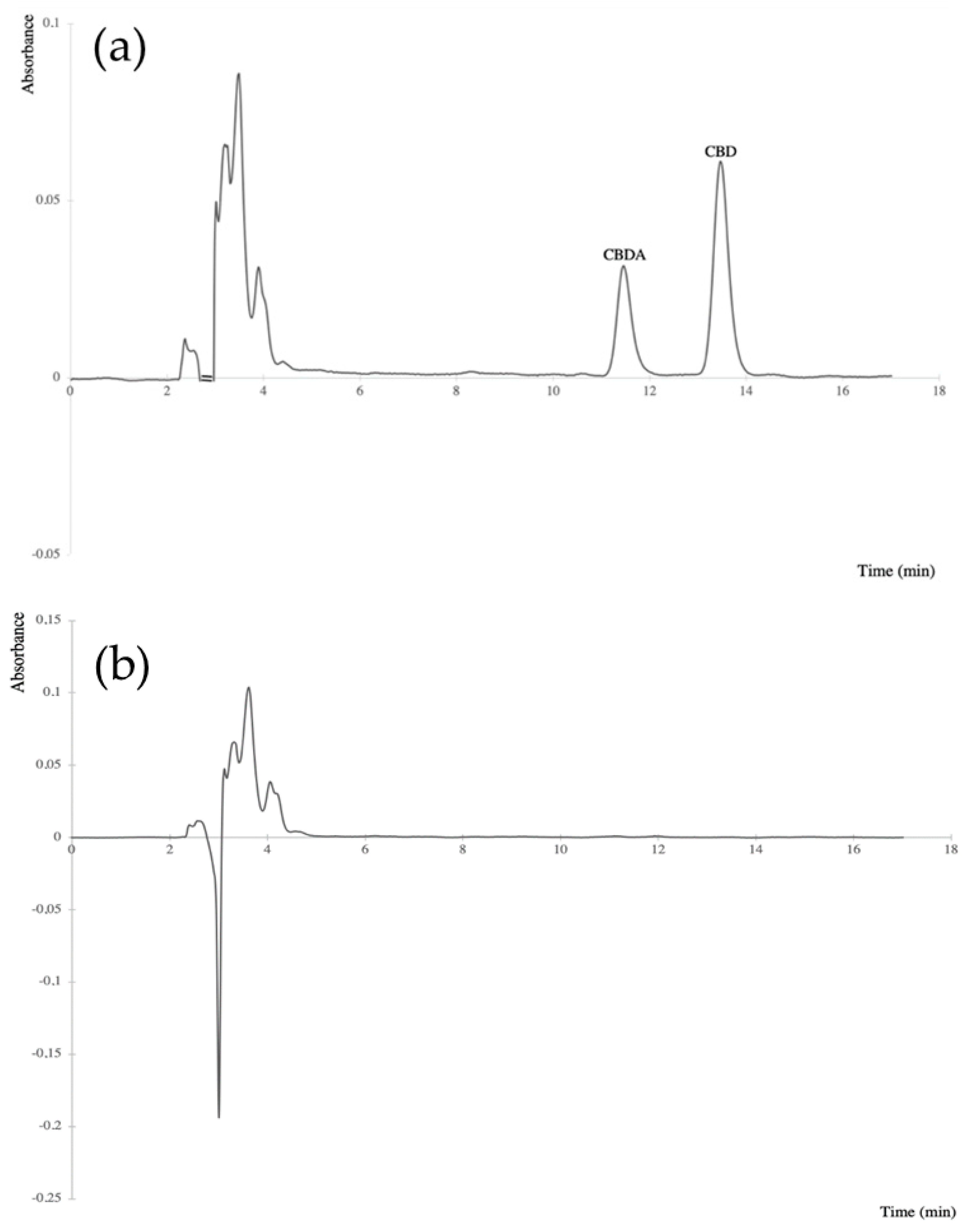
The validation results, given in Table 3, appeared to be satisfactory. The exemplified chromatograms of extracts of: a blank olive oil sample spiked with CBDA and CBD and a blank olive oil sample were shown in Figure 2.

Table 3.
Validation parameters of HPLC method for determination of CBDA and CBD in oil matrix.
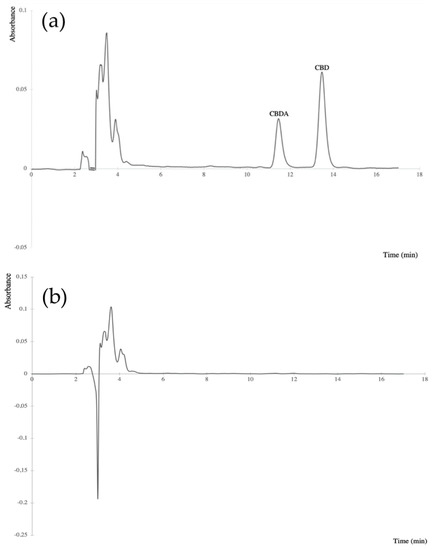
Figure 2.
Chromatograms of: (a) extract of an olive oil sample (100 mg) spiked with CBDA (12.5 µg/mL) and CBD (25 µg/mL) standards, (b) blank olive oil sample extract. The cannabinoids were detected at 220 nm.
3.3. Analysis of the Oil Hemp Supplement
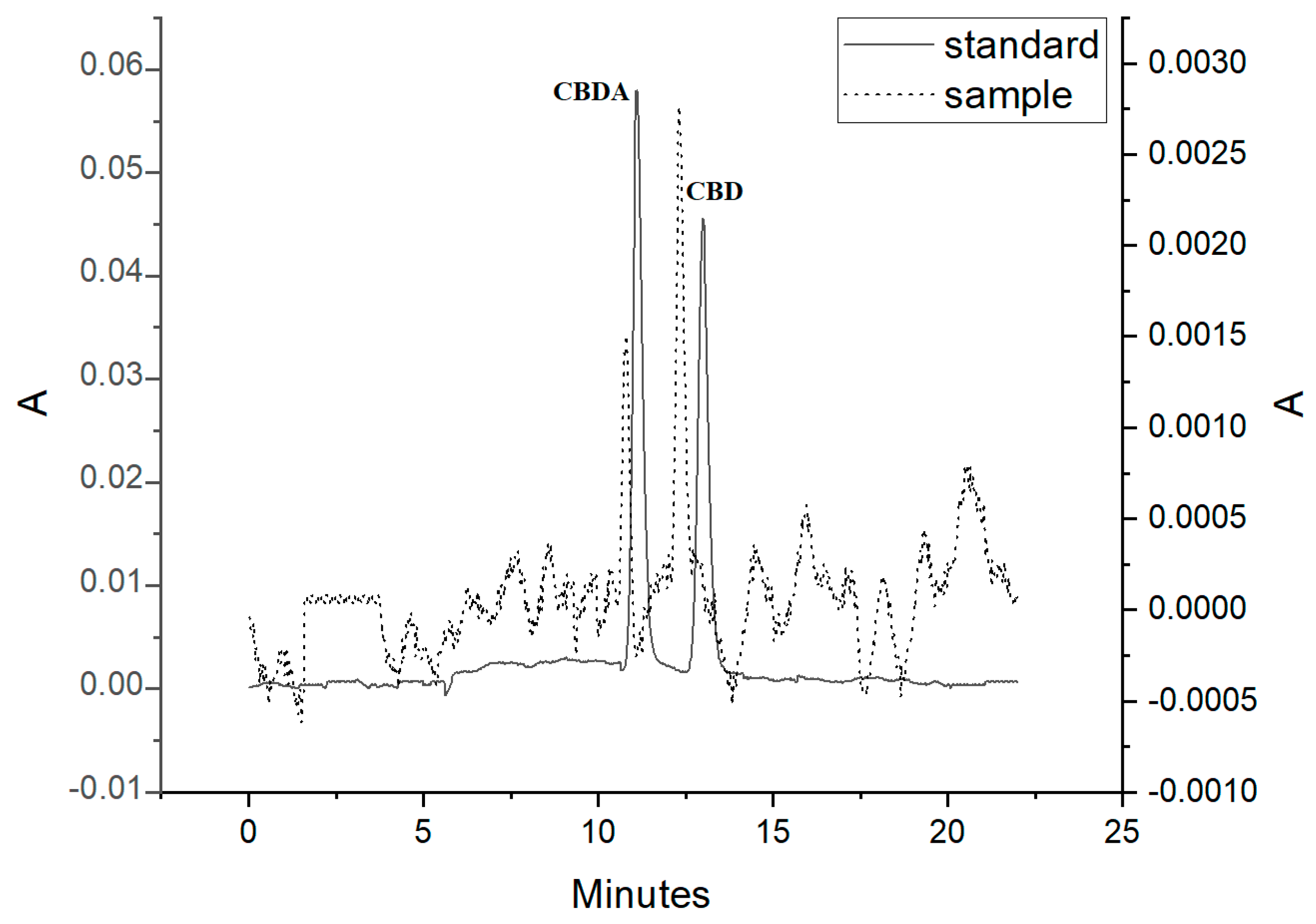
Considering general high concentrations of CBD in oil supplements and taking minimal sample volume for analysis, 10 mg sample of the supplement was subjected to final preparation procedure as it was described in Section 2. The chromatogram representing analysis of this supplement was presented in Figure 3. After recalculation of the determined CBD and CBDA in a hemp oil supplement, CBD accounted for 4.75% of the sample mass, and CBDA, for 2.34%.
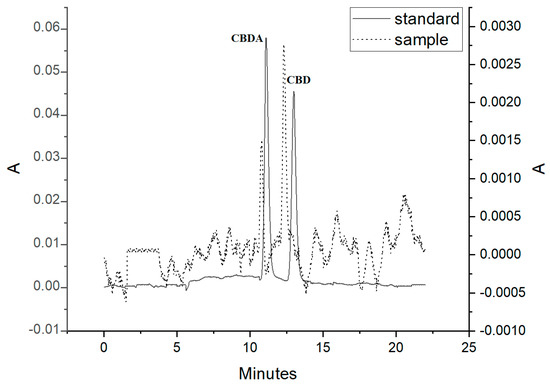
Figure 3.
Chromatogram of an oil hemp supplement. The cannabinoids were detected at 220 nm.
3.4. Comparison of the Proposed Method with HPLC-UV Methods of Other Authors
As it was mentioned above there is a relatively small number of methods dealing with the determination of cannabinoids in an oil matrix. The more details of extraction procedures and analytical parameters of the found HPLC-UV/DAD methods were placed in Table 4. In general, the reported methods are not described in detail and are strongly validated, with some exceptions [15]. Comparing extraction methods in cited works with our sample preparation method, extraction recovery for more polar CBDA (than CBD) was lower (over 69%) than this reported by other authors. This fact results from the use of more polar extraction solvents (95% ethanol, methanol, or 2-propanol) by other authors than the one (acetonitrile) used in our work. However, the achieved extraction recovery seems to be satisfactory for quantification of this cannabinoid in oil matrix. Moreover, our method consumes the lower volume of extracting solvent (500 µL) and sample amount (10 mg), as well as it does not require filtration of the obtained extracts. In one case [15] the authors used a smaller amount of extracting solvent (400 µL) and only mixing an oil sample with the solvent was applied, however, no more sample preparation procedure details were provided (e.g., time of mixing). As for the analytical parameters in the proposed method, they are comparable to those obtained by other authors, except for a slightly lower precision of CBDA determination.

Table 4.
Comparison of the proposed method with HPLC-UV/DAD methods of other authors.
4. Conclusions
The simple, relatively quick, and consuming small amounts of sample and toxic reagents method for separation of two important non-psychoactive cannabinoids (CBD and CBDA) from oil matrix was developed. These cannabinoids are chief constituents of commercially accessible hemp oil supplements. The proposed sample preparation method is based on liquid-liquid extraction with acetonitrile in combination with freezing out of fat phase from an oil sample. Only 500 µL of acetonitrile per 10 mg of an oil supplement sample was used, so the developed sample preparation method fulfills requirements of ‘green method’. The estimated validation parameters of the HPLC method used for determination of CBD and CBDA are satisfactory. The usefulness of the proposed method was check by analysis of an oil supplement containing CBD as main component (5% w/w) and its precursor–CBDA. The method shows potential to be developed and extended to simultaneous determination of CBD and CBDA with such other significant cannabinoids as 9-delta THC, cannabinol (CBN), or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA).
Author Contributions
K.M. and W.P. conceived and designed the experiments; G.K. and M.W. performed the experiments and analyzed the data; K.M. wrote the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
References
- Ehrenkranz, J.; Levine, M.A. Bones and joints: The effects of cannabinoids on the skeleton. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 4683–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudge, E.M.; Murch, S.J.; Brown, P.N. Leaner and greener analysis of cannabinoids. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 3153–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, N.; Velmurugan, B.K. Therapeutic applications of cannabinoids. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 293, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protti, M.; Brighenti, V.; Battaglia, M.R.; Anceschi, L.; Pellati, F.; Mercolini, L. Cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa L.: A new tool based on HPLC− DAD−MS/MS for a rational use in medicinal chemistry. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.L.; Low, I.K.; Samuel, D.; Banister, S.D.; McGregor, I.S.; Arnold, J.C. Pharmacokinetics of phytocannabinoid acids and anticonvulsant effect of cannabidiolic acid in a mouse model of Dravet Syndrome. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 3047–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Garcíaa, C.; Torresa, I.M.; García-Hernándeza, R.; Campos-Ruíza, L.; Esparragozaa, L.R.; Coronadob, M.J.; Grandec, A.G.; García-Merinoa, A.; López, A.J.S. Mechanisms of action of cannabidiol in adoptively transferred experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 298, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackie, K. Cannabinoid receptors: Where they are and what they do. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 20, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisanti, S.; Malfitano, A.M.; Ciaglia, E.; Lamber, A.; Ranieri, R.; Cuomo, G.; Abate, M.; Faggiana, G.; Proto, M.C.; Fiore, D.; et al. Cannabinoid receptors: Where they are and what they do. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 175, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandrioli, M.; Tura, M.; Scott, S.; Toschi, T.G. Fast detection of 10 cannabinoids by RP-HPLC-UV method in Cannabis Savita L. Molecules 2019, 24, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivovinovic, S.; Alder, R.; Allenspach, M.D.; Steuer, C. Determination of cannabinoids in Cannabis sativa L. samples for recreational, medical, and forensic purposes by reversed-phase liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detection. JAST 2018, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Backer, B.; Debrus, B.; Lebrun, P.; Theunis, L.; Dubois, N.; Decock, L.; Verstraete, A.; Hubert, P.; Charlier, C. Innovative development and validation of an HPLC/DAD method for the qualitative and quantitative determination of major cannabinoids in cannabis plant material. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 411524. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, B.; Wene, D.; Fan, Z.T. Qualitative and quantitative measurement of cannabinoids in cannabis using modified HPLC/DAD. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 146, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saingam, W.; Sakunpak, A. Development and validation of reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography method for the determination of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol in oromucosal spray from cannabis extract. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2018, 28, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciolino, L.A.; Ranieri, T.L.; Taylor, A.M. Commercial cannabis consumer products part 2: HPLC-DAD quantitave analysis of cannabis cannabinoids. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 289, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citti, C.; Pacchetti, B.; Vandelli, M.A.; Forni, F.; Cannazza, G. Analysis of cannabinoids in commercial hemp seed oil and decarboxylation kinetics studies of cannabidiolic acid (CBDA). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 149, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeškalová, A.; Hájková, K.; Mikulů, L.; Sýkora, D.; Kuchař, M. Combination of UV and MS/MS detection for the LC analysis of cannabidiolrich products. Talanta 2020, 219, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciolino, L.A.; Ranieri, T.L.; Taylor, A.M. Commercial cannabis consumer products part 1: GC-MS quantitave analysis of cannabis cannabinoids. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 289, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmeier, D.W.; Kroener, L.; Musshoff, F.; Madea, B. Determination of cannabinoids in hemp food products by use of headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Buchanan, B.; Zuccolo, J.; Poulin, M.-M.; Gabriele, J.; Baranowski, D.C. A reliable and validated LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of 4 cannabinoids in 40 consumer products. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).