Abstract
Fosetyl-aluminum is a widely used ionic fungicide. This pesticide is not amenable to the common multi-residue sample preparation methods. Herein, this paper describes a novel method for the simple and sensitive determination of fosetyl-aluminum residue in wheat flour. The sample preparation method involved extraction with water under ultrasonication and subsequent dilution with six-fold acetonitrile. The fosetyl-aluminum concentration was determined by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. The limit of detection and quantification were only 5 and 10 ng/g, respectively, which meet the requirement of the current European legislation. Matrix-matched linearity (r2 = 0.9999) was established in the range of 10–2000 ng/g. Satisfactory recoveries were achieved in the range of 95.6% to 105.2% for three levels of spiked samples (10, 50, and 100 ng/g). Finally, the method was applied to analyzing 75 wheat flour samples produced in four provinces in China. Two samples were positive with concentrations over the limit of detection. This is the first method focusing on fosetyl-aluminum determination in wheat flour with an extract-dilute-shoot strategy and is very promising for the routine quality control of fosetyl-aluminum in similar cereal matrices.
1. Introduction
Fosetyl-aluminum (fosetyl-Al) is a polar fungicide, and a replacement for the banned sodium arsenite [1]. This fungicide is widely used to control rot in plant roots. Due to its toxic effects, the Joint Meeting on Pesticide Residues recommended set the acceptable daily intake for fosetyl-Al to 0–1 mg/kg bw per day in 2017 [2]. The maximum residue level of fosetyl-Al in food is strictly controlled by Regulation 396/2005 of the European Commission [3], GB 2763-2021 of China [4], and 40CFR180.415 of the USA [5].
Fosetyl-Al is a highly polar compound with an ionic structure. This highly polar pesticide is not amenable to the common multi-residue sample preparation methods because it is difficult to partition into common organic solvents [6] and needs dedicated chromatographic conditions. In addition, it is difficult to retain fosetyl-Al in typical reverse-phase liquid chromatography and the co-eluted salts and polar matrix components seriously interfere with fosetyl-Al determination [7]. Therefore, there is an urgent demand for the development of a simple and general method that could be used to detect this “orphan pesticide”. Until now, few solutions that address this problem have been reported, such as applying a specific column with a polar stationary phase or using an ion-pair reagent within the mobile phase [7]. Because it lacks UV absorption and fluorescence, fosetyl-Al is rather difficult to determine by conventional liquid chromatography detectors such as diode array detectors. In recent years, the use of liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS) for analyte determination has aroused great attention due to its inherent selectivity and sensitivity [8]. Several recent works have described the use of LC-MS for fosetyl-Al determination in different food commodities, such as lettuce [7], tomato [9], grape [1], mango [10], olive oil [11], oat, and soy beans [12]. In these LC-MS methods, polar pesticides are separated with graphitized carbon (Hypercarb) columns [13] or hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) columns [9,14,15]. To the best of our knowledge, no work has reported the determination of fosetyl-Al in wheat flour with the HILIC-MS/MS method.
Wheat flour is a staple food in many countries. It is a typical matrix that is high in carbohydrates and proteins and belongs in category 5 of the AOAC Food Triangle. During its long-term storage, fosetyl-Al may be illegally spiked into wheat flour to avoid fungus growth. Scarce literature is available for the analysis of this polar pesticide in wheat flour. Therefore, the State Administration for Market Regulation of China set up a project and supported us in developing a method for fosetyl-Al determination in wheat flour. Effective removal of the polar, soluble carbohydrates and proteins poses a great challenge in the sample preparation process. For the LC-MS method, sample preparation is necessary prior to analyte detection to eliminate interferences [16] and a lower matrix effect (ME) for MS determination [17,18,19], such as the hydrophilic-lipophilic balance cartridge [1] and the anion-exchange column [20]. One widely adopted sample preparation method was developed by the European Reference Laboratory to determine highly polar pesticides in plant-derived foods such as soy flour, named the Quick Polar Pesticides (QuPPe) method [21]. Although the method is capable of extracting various polar analytes, the extracts probably contain large amounts of matrix interferences that would contaminate the instruments. Furthermore, this QuPPe strategy is tedious and time-consuming. On the contrary, the extract-dilute-shoot procedure is a promising strategy for its simple and fast operation. As an improved method from dilute-and-shoot [22], this method is fit for solid samples. In detail, solid samples are extracted with a suitable extraction solvent to facilitate the migration of analytes into the liquid phase. Then, the liquid extract was diluted with a suitable dilution solvent before the shoot step. The dilution minimizes the ME and thus, reduces the need for an additional clean-up procedure. Recently, this procedure has gained increased attention in food analysis, including rice [23], tomato [24], fruit jam [25], and gingerbread [26]. However, the HILIC-MS/MS method with the extract-dilute-shoot procedure has not yet been applied for fosetyl-Al determination.
The aim of this work was to develop a simple and sensitive analytical method for fosetyl-Al determination in wheat flour. Therefore, we adopted an extract-dilute-shoot strategy for sample preparation, and combined it with HILIC separation and tandem mass spectrometry determination. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report that focuses on fosetyl-Al determination in wheat flour with extract-dilute-shoot sample preparation and HILIC-MS/MS determination.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
HPLC-grade acetonitrile and methanol were bought from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Water was supplied by Hangzhou Wahaha Group Co., Ltd. (Hangzhou, China). Ammonium formate and formic acid (FA) were provided by Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Analyte-grade fosetyl-Al standard was purchased from Dr. Ehrenstorfer (Augsburg, Germany). All wheat flour samples were commercial products from the local market.
For the syringe filter (0.22 μm), GHP was from PALL Life Sciences (Ann Arbor, MI, USA), nylon was from UA Filter & Chrom (Taibei, Taiwan, China), PTFE PVDF and PP were from Jinteng Experimental Equipment (Tianjin, China). The syringe (2 mL) was from Jiangsu Yuzhi Medical instrument (Taixing, China).
Chromatography columns were Hypercarb columns (2.1 × 100 mm, 5 μm) from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Bellefonte, PA, USA); BEH C18 column (2.1 mm × 50 mm, 1.7 μm) and BEH amide column (2.1 × 50 mm, 1.7 μm) were obtained from Waters (Milford, CT, USA). Guard columns of the same stationary phase were connected in front of the separation columns. All the columns were preconditioned according to the manufacturer’s instructions before use.
2.2. Preparation of Calibration Solutions
A stock solution of fosetyl-Al was prepared by dissolving an accurately weighed portion of the pure standard compound in acetonitrile at a concentration of 250 μg/g. Blank wheat flour samples were spiked with the fosetyl-Al stock solution to prepare matrix-matched external calibration solutions. The concentrations of fosetyl-Al varied between 5 and 2000 ng/g. Then, the spiked samples were extracted by water, and the extracts were diluted with 6-fold acetonitrile. After centrifugation and filtration, the matrix-matched standards were ready for further use. All solutions were stored at −20 °C in the dark.
2.3. Instruments
Samples were centrifuged by a Hettich universal 320R centrifuge to separate the supernatant (Tuttlingen, Germany). Samples and solutions were mixed by a Vortex Genie-2 from Scientific Industries Inc. (New York, NY, USA). Samples were sonicated with a Branson 8510 Ultrasonic Cleaner (Danbury, CT, USA).
HILIC-MS/MS experiments were performed using a Waters instrument. An ACQUITY UPLC® system was used for LC separation. The LC system was connected to a triple quadrupole MS (TQ-S, Manchester, UK) with a Z-spray electrospray ionization interface. MassLynxTM 4.1 software (Milford, CT, USA) was used for instrument control and data acquisition. Nitrogen was used as the nebulizer gas and was supplied by the generator NM31LA of Peak Scientific (Scotland, UK).
2.4. Optimization of Extract-Dilute-Shoot Parameters
To accurately quantify fosetyl-Al concentration in wheat flour, it was important to extract fosetyl-Al and remove matrix interference by efficient sample preparation. To obtain optimal extraction efficiency for fosetyl-Al, several important parameters influencing the extraction efficiency were evaluated in this study, such as type and volume of extraction solvent, dilution factor of the extract, and type of filter. To obtain a reliable result, all the optimizations were carried out in fosetyl-Al-spiked wheat flour at a concentration of 50 ng/g in triplicate.
2.5. Sample Pretreatment
A 2.00 g portion of wheat flour was accurately weighed into a 50 mL polypropylene centrifuge tube, and mixed with 12 mL water using an automatic pipette. The tube was capped tightly and vortexed for 2 min to form a homogeneous paste. Then, the paste was extracted under sonication for 15 min at room temperature. Afterward, the mixture was vortexed again for 1 min. Then, the tube was centrifuged at 9000 rpm for 3 min, and 1 mL supernatant was collected and diluted with 6-fold acetonitrile. Finally, the extract was filtered with a 0.22 μm GHP syringe filter before analysis by HILIC-MS/MS.
2.6. Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Three different columns were tested for the retention of fosetyl-Al, including BEH C18, BEH amide, and Hypercarb. Afterward, the mobile phase and additive were also optimized to achieve better separation and peak shape in liquid chromatography.
The ion source parameters were optimized automatically by a TQ-S system (Waters, Manchester, UK) with the direct infusion of fosetyl-Al solution at a flow rate of 10 μL/min, source temperature of 150 °C, desolvation temperature of 500 °C, capillary voltage of −2.3 kV, corn voltage of 30 V, source offset voltage of 50 V, desolvation gas at 700 L/h, cone gas at 150 L/h, and collision gas at 0.13 mL/min. The detection of fosetyl-Al was performed in multiple reactions monitoring mode with a collision energy of 10. The precursor ion with m/z 109 corresponded to the fosetyl anion. The product ion with m/z 81 was the product of the McLaffery rearrangement with the loss of ethene, and the product ion with m/z 63 was PO2− [7]. Therefore, the most intense transition of m/z 109 > m/z 81 was selected for quantification and the transition of m/z 109 > m/z 63 was used for qualification. Two transitions were selected to qualitatively and quantitatively detect fosetyl-Al in the validation study.
2.7. Method Validation
To validate the applicability of the developed method for fosetyl-Al determination, the linearity, linear range, limit of detection (LOD), limit of quantification (LOQ), ME, recovery, and precision were investigated. A calibration curve for the quantitative analysis was established using the matrix-matched standard of spiked wheat flour samples. The standards were produced using the developed extract-dilute-shoot method. The spike concentrations were in the range of 5–2000 ng/g. The linearity of the method was evaluated by using a linear regression curve fit with the areas obtained for the matrix-matched standard. The LOD and LOQ were calculated from chromatograms of fortified samples according to SANTE/2020/12830, defined as the concentration of signal-to-noise ratios larger than 3 and 10, respectively. To quantitively evaluate the ME (suppression or enhancement), standard solutions of both solvent and matrix were shot into the HILIC-MS/MS. The ME was assessed by the slope of the calibration curve between the matrix and solvent standards by the below equation [27]. An ME of less than 100% indicates matrix suppression; an ME greater than 100% indicates matrix enhancement. To establish the reliability and validity of the analytical method, recovery and precision tests of fosetyl-Al were carried out in blank samples fortified with three different levels (10, 50, and 100 ng/g) with five replicates.
where bm and bs are the angular coefficients of the curve in the matrix and in the solvent, respectively.
ME = bm/bs × 100%
2.8. Real Sample Analysis
Seventy-five commercial wheat flour samples were collected from four provinces of China, including Shandong (25 samples), Henan (15 samples), Hebei (3 samples), and Jiangsu (32 samples). Two replicates were tested from each sample to ensure that reliable results were collected. Retention time and intensity of product ions were used to identify positive samples. Quantification was achieved using an external matrix-matched calibration curve that was produced from the peak area of fosetyl-Al versus the corresponding concentration of the spiked wheat flour samples.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Extract-Dilute-Shoot Optimization
3.1.1. Type of Extraction Solvent
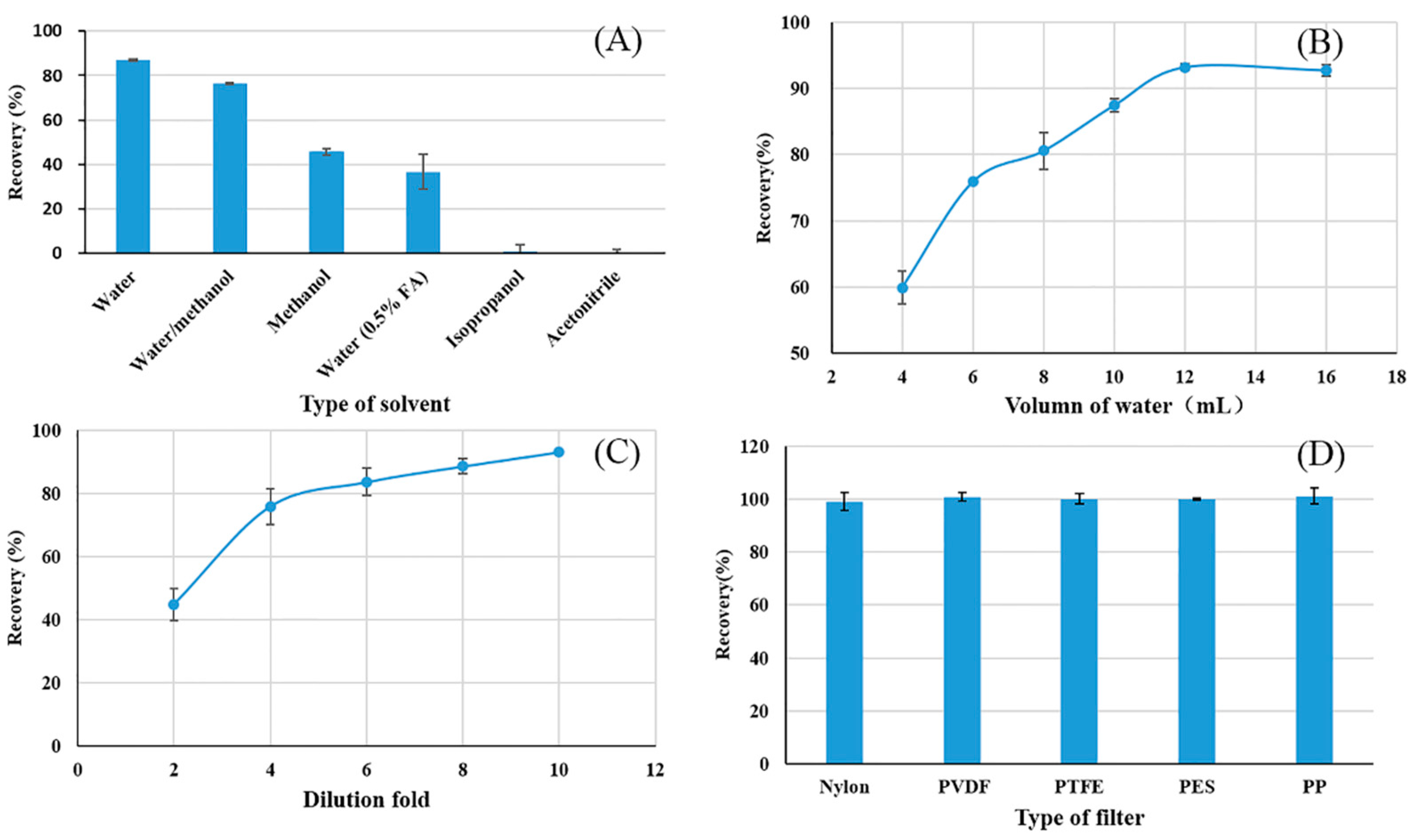
The choice of extraction solvent directly impacted the extraction efficiency of fosetyl-Al for further analysis. Initially, acidified methanol, described by the QuPPe method, was used for the extraction of the fosetyl-Al. However, this extraction method was not suitable to the wheat flour matrix, because a doughy mixture was inevitably generated when the acidified methanol was added. The doughy substance was difficult to remove from the solution via high-speed centrifugation or syringe filter. This finding is consistent with a previous study about the analysis of fosetyl-Al in soy nutraceuticals [28]. To achieve a satisfactory extraction efficiency, five kinds of polar extraction solvents were tested in this study. The extraction was evaluated by recoveries of spiked fosetyl-Al. From the results in Figure 1A, polarity played a dominated role in the extraction; therefore, recoveries were in the following order: water > water/methanol (50%) > methanol > water (0.5% FA) > isopropanol > acetonitrile. This indicated that water had excellent performance for the extraction of fosetyl-Al. In water, fosetyl-Al transforms into fosetyl anions. The addition of FA would turn the negative ion to neutral molecular and lower extraction efficiency. Therefore, water was used in the following extractions, consistent with a previous report [29].
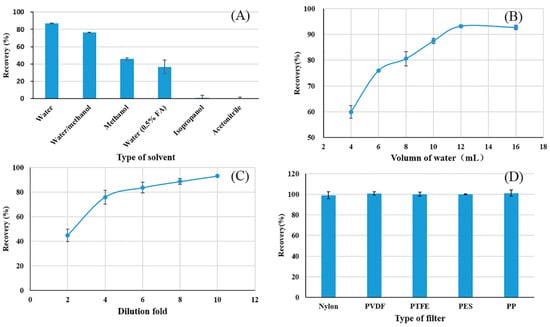
Figure 1.
Optimization of the (A) type and (B) volume of extraction solvent; (C) effect of dilution fold; (D) type of filter (n = 3).
3.1.2. Volume of Extraction Solvent
The volume of water can directly influence the extraction efficiency of wheat flour. A larger volume of extraction solvent would extract more fosetyl-Al in theory, while signal intensity may decrease remarkably because of the dilution effect. On the other hand, a smaller volume would not provide enough quantity of the sample for LC-MS analysis and the reproducibility would be poor. Herein, the volume of water was optimized from 4 L to 16 mL for 2.00 g wheat flour to find the optimal volume. From Figure 1B, the recovery increased with water volume from 4 to 12 mL, and no significant signal enhancement was observed with increasing water volume. Better recovery would provide better accuracy and that was very important for the real samples test. Moreover, larger volume led to less variation. As a result, 12 mL was chosen for following experiment.
3.1.3. Effect of Dilution Fold
In wheat flour, the main compositions were 71.2% carbohydrate, 15.1% protein, 2.7% lipid, and 9.4% water [30]. During the water extraction, some soluble carbohydrates and proteins are extracted simultaneously. Therefore, acetonitrile was chosen to dilute the extract solution to precipitate these compounds and minimize the ME. Acetonitrile is widely used for protein precipitation [31] and it can lower the solubility of carbohydrates [32]. Once acetonitrile was added, the extract turned cloudy immediately. The employed dilution factors usually range from 2 to 50 according the matrix [22]. Thus, dilution fold was optimized from 2 to 10, as exhibited in Figure 1C. Recoveries increased with higher dilution and relative standard deviations (RSDs) decreased. This indicated that lower ME and better repeatability were achieved with acetonitrile dilution. Conversely, large dilution factors would subsequently reduce the sensitivity of the method in terms of LOD. In conclusion, a six-fold dilution factor was selected as a compromise between sensitivity and repeatability.
3.1.4. Type of Filter
To remove the cloudy particles in solution and prolong the lifetime of the column, filtration is necessary before LC separation. Sometimes, pesticides can be adsorbed by the membrane filters and lead to analyte loss and low recovery [33]. As a result, filter adsorption of fosetyl-Al was evaluated among five widely used filters (GHP, nylon, PTFE, PVDF, and PP). From the results in Figure 1D, there was no significant difference between the tested filters. So, any kind of the tested filter was feasible for further tests.
3.2. Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry
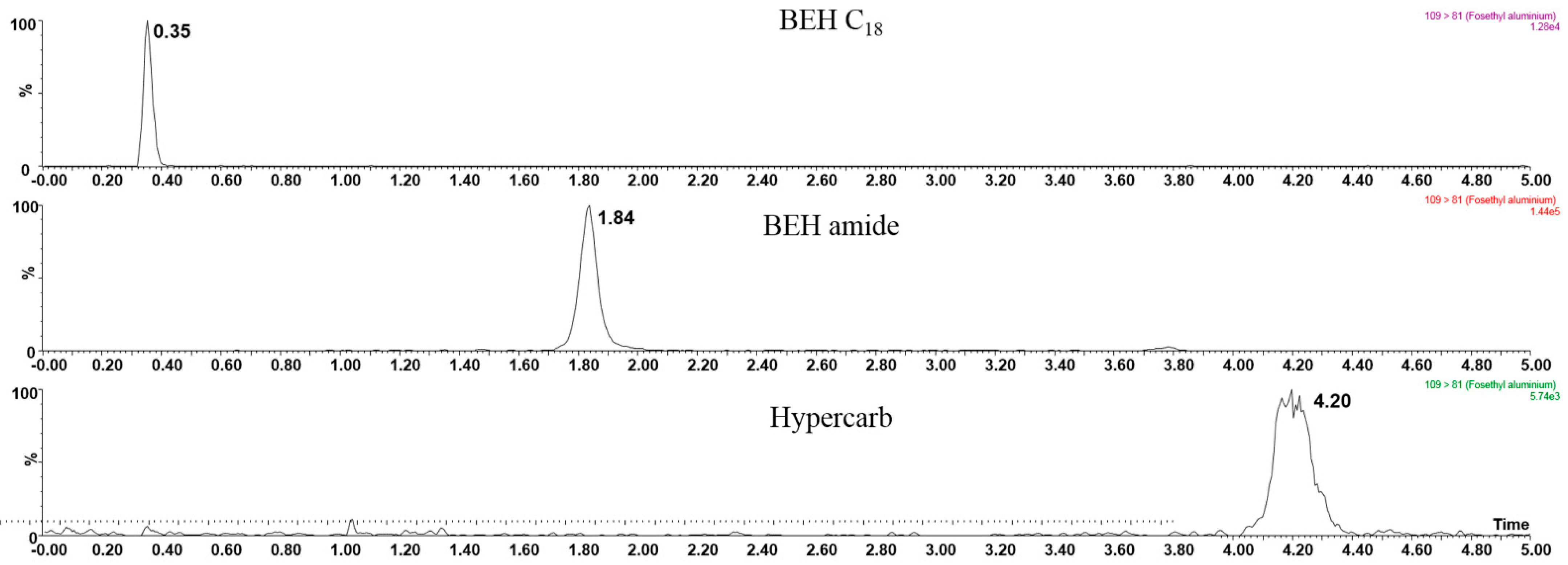
The column was selected on the basis of the polarity of fosetyl-Al. As shown in Figure 2, preliminary testing with the BEH C18 column demonstrated its low retention capability with fosetyl-Al, which appeared in the peak void with a retention time of 0.35 min. Due to the highly polar nature of fosetyl-Al, it was difficult to obtain enough retention on a C18 column. Conversely, the Hypercarb column exhibited such a strong retention for fosetyl-Al that it resulted in an increased elution time. The BEH amide column had better retention behavior toward fosetyl-Al, with 17 times higher sensitivity than the Hypercarb column. With regard to the optimization of the mobile phase, acetonitrile/water showed better elution performance than methanol/water on the BEH amide column. Moreover, to keep the pH value and the retention time of fosetyl anion constant throughout the run, the buffer concentration was further optimized with gradient elution. Referring to previous research on polar pesticides [34], mobile phase A was chosen as water with 5.0 mmol/L ammonium formate and B was acetonitrile. The gradient started at 90% of phase B to elute non-polar compounds while fosetyl-Al was still retained. Afterward, phase B decreased linearly to 50% over 3 min and the polar compounds eluted gradually. Then, the mobile phase composition returned to the initial condition in 0.1 min and was held for 1.9 min for re-equilibration. The separation was operated at a flow rate of 0.3 mL/min and the column temperature was kept at 35 °C. The total chromatographic run time was 5 min. The retention time of fosetyl-Al was 1.86 min under this condition.
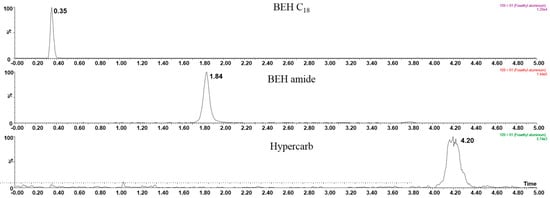
Figure 2.
Performance comparison between three types of columns.
3.3. Method Validation
As listed in Table 1, the linear range of the developed method covered from 10 to 2000 ng/g with eight concentration levels in the matrix-matched standards. Simultaneously, correlation coefficient (r2) of the matrix-matched calibration curve equaled 0.9999, which is very satisfactory for accurate quantification. The LOD and LOQ of the developed method were 5 and 10 ng/g, respectively, using the signal-to-noise ratio of the qualifier transition signal. This is sufficiently low to meet the maximum residue limits for many regulations, including the European Commission, China, and the USA. The proposed method showed satisfactory accuracy with recoveries of 95.6%, 105.2%, and 104.6%, respectively. Method precision was evaluated by the RSDs of five repetitions. The result was lower than 6.2%, indicating that this method is quite fit for routine analysis. The ME was calculated by comparing the slopes of standards prepared in wheat flour extract and water/acetonitrile solvent. The ME evaluation (88.33%) showed that the residual matrix could suppress the fosetyl-Al signal. Therefore, a matrix-matched calibration solution was used for accurate quantitation during the real sample analysis.

Table 1.
Validation data of the developed method for the detection of fosetyl-Al.
From the above, a simple and sensitive extract-dilute-shoot HILIC-MS/MS method was established. This proposed method is easy to operate and has excellent sensitivity (Table 2), which is promising for the analysis of fosetyl-Al in wheat flour samples.

Table 2.
Method comparison of fosetyl-Al in different matrices.
3.4. Real Sample Analysis
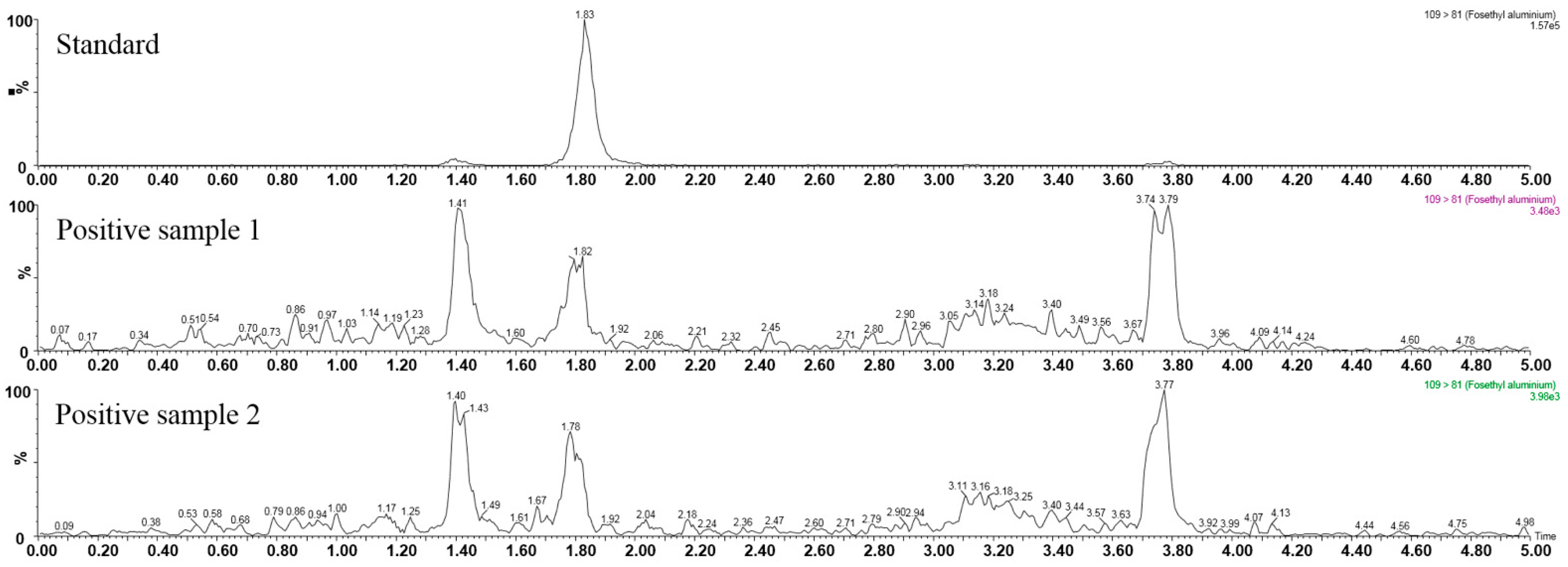
In order to study the applicability of the proposed method, the developed method was applied to analyze the fosetyl-Al residual in commercial wheat flour samples. In total, 75 samples were collected from four provinces that covered China’s main wheat flour production areas. For each kind of sample, the determination was repeated two times. Matrix-matched calibrations were injected in every sequence of samples in order to explore the carry-over effect and to ensure that a reagent blank was injected immediately after the highest standard. As a result, two samples were positive for fosetyl-Al, as shown in Figure 3. The signal intensity reflected that their concentrations were higher than the LOD and lower than the LOQ. One sample was produced in Shandong Province, the other was from Henan Province. All samples were below the maximum residue limits, suggesting that it is generally safe to consume wheat flour in China.
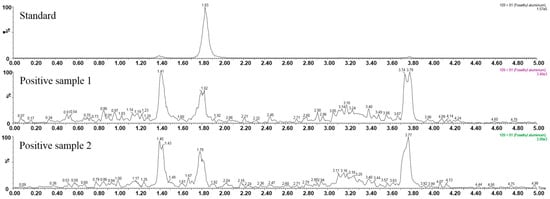
Figure 3.
Chromatograms of the positive samples.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we developed and validated a method by combining an extract-dilute-shoot strategy for sample preparation with HILIC-MS/MS for fosetyl-Al determination in wheat flour. This simple and fast dilution procedure effectively lowered the ME and improved the repeatability. Moreover, HILIC column provided both sufficient retention of fosetyl-Al and removal of the matrix, and MS/MS measurement demonstrated excellent sensitivity and selectivity. This approach offers simple operation, minimal consumption of chemicals, wide linear range, and high sensitivity. Satisfactory results were obtained as evidenced by matrix-matched standards. The observed LOQ was 10 ng/g in wheat flour. The satisfactory precisions and recoveries achieved with the spiked samples demonstrated the reliability and practicability of the developed method. The proposed method was applied to the quantitation of fosetyl-Al in 75 wheat flour samples, which overall showed low levels of contamination. These results showed that our proposed method is very promising for routine analysis and could find more applications in quality control of fosetyl-Al in high-carbohydrate food matrices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, validation, and writing—original draft preparation, X.L. (Xianjiang Li); data curation and writing—review and editing, S.W.; investigation, Z.G.; supervision, X.L. (Xiuqin Li); project administration, Q.Z.; funding acquisition, H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China, grant number 2019YFC1604801.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chamkasem, N. Determination of Glyphosate, Maleic Hydrazide, Fosetyl Aluminum, and Ethephon in Grapes by Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2017, 65, 7535–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesticide Residues in Food; Joint FAO/WHO Meeting on Pesticide Residues: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/agphome/documents/Pests_Pesticides/JMPR/Report2017/web_2017_JMPR_Report_Final.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- European Food Safety Authority. Modification of the existing maximum residue level for fosetyl in blackberry, celeriac and Florence fennel. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- NHC; MoA; SAMR of China. National Food Safety Standard—Maximum Residue Limits for Pesticides in Food; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Aluminum Tris (O-ethylphosphonate); Tolerances for Residues. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/cgi-bin/text-idx?SID=c30d88a8176fe20021d927e53e9422c7&mc=true&node=se40.26.180_1415&rgn=div8 (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Buiarelli, F.; Di Filippo, P.; Riccardi, C.; Pomata, D.; Marsiglia, R.; Console, C.; Puri, D. Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Fosetyl-Aluminum in Airborne Particulate Matter. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2018, 2018, 8792085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, F.; Sancho, J.V.; Pozo, Ó.J.; Villaplana, C.; Ibáñez, M.; Grimalt, S. Rapid Determination of Fosetyl-Aluminum Residues in Lettuce by Liquid Chromatography/Electrospray Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Zeng, X.; Du, Z.; Cao, J.; Jiang, W. Metal–organic framework for the extraction and detection of pesticides from food commodities. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. F. 2021, 20, 1009–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano-Sanchez, L.; Martinez-Martinez, J.A.; Dominguez, I.; Martinez Vidal, J.L.; Frenich, A.G.; Romero-Gonzalez, R. Development and Application of a Novel Pluri-Residue Method to Determine Polar Pesticides in Fruits and Vegetables through Liquid Chromatography High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Foods 2020, 9, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho Pereira da Silva, H.C.; Galindo Bedor, D.C.; Cunha, A.N.; dos Santos Rodrigues, H.O.; Telles, D.L.; Pessoa Araujo, A.C.; de Santana, D.P. Ethephon and fosetyl residues in fruits from São Francisco Valley, Brazil. Food Addit. Contam. B 2019, 13, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nortes-Mendez, R.; Robles-Molina, J.; Lopez-Blanco, R.; Vass, A.; Molina-Diaz, A.; Garcia-Reyes, J.F. Determination of polar pesticides in olive oil and olives by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry and high resolution mass spectrometry. Talanta 2016, 158, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, S.H.; Scholten, J.; Kiedrowska, B.; de Kok, A. Method validation and application of a selective multiresidue analysis of highly polar pesticides in food matrices using hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1594, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savini, S.; Bandini, M.; Sannino, A. An Improved, Rapid, and Sensitive Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-High-Resolution Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry Analysis for the Determination of Highly Polar Pesticides and Contaminants in Processed Fruits and Vegetables. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2019, 67, 2716–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, J.; López, S.H.; Mol, H.; de Kok, A. Influence of different hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography stationary phases on method performance for the determination of highly polar anionic pesticides in complex feed matrices. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 2165–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, F.-Q.; Ge, L.; Hu, Y.-J.; Xia, Z.-N. Recent applications of hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography in pharmaceutical analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 49–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, S.M.; Makarem, S.; Alexovič, M.; Tabani, H. Simultaneous separation and quantification of acidic and basic dye specimens via a dual gel electro-membrane extraction from real environmental samples. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2021, 18, 2091–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; Guo, Z.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. Determination of patulin in apple juice by single-drop liquid-liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2018, 257, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ma, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, Z. Determination of residual fipronil and its metabolites in food samples: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wu, G.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z. Determination of Triazine Herbicides in Environmental Water Samples by Acetonitrile Inorganic Salt Aqueous Two-Phase Microextraction System. J. Anal. Test. 2018, 2, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajski, L.; Diaz Galiano, F.J.; Cutillas, V.; Fernandez-Alba, A.R. Coupling Ion Chromatography to Q-Orbitrap for the Fast and Robust Analysis of Anionic Pesticides in Fruits and Vegetables. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastassiades, M.; Kolberg, D.I.; Wachtler, E.E.A.-K.; Benkenstein, A.; Zechmann, S.; Mack, D.; Wildgrube, C.; Barth, A.; Sigalov, I.; Görlich, S.; et al. Quick Method for the Analysis of Numerous Highly Polar Pesticides in Food Involving Extraction with Acidified Methanol and LC-MS/MS Measurement I. Food of Plant Origin (QuPPe-PO-Method), 11th ed.; EU Reference Laboratory for Pesticides: Stuttgart, Germany, 2020; Available online: https://www.eurl-pesticides.eu/userfiles/file/EurlSRM/meth_QuPPe_PO_V11(1).pdf (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Greer, B.; Chevallier, O.; Quinn, B.; Botana, L.M.; Elliott, C.T. Redefining dilute and shoot: The evolution of the technique and its application in the analysis of foods and biological matrices by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 141, 116284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.P.; Madureira, F.; de Azevedo Vargas, E.; Faria, A.F.; Augusti, R. Development and validation of a multianalyte method for quantification of mycotoxins and pesticides in rice using a simple dilute and shoot procedure and UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebrehiwot, W.H.; Erkmen, C.; Uslu, B. A novel HPLC-DAD method with dilute-and-shoot sample preparation technique for the determination of buprofezin, dinobuton and chlorothalonil in food, environmental and biological samples. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrarca, M.H.; Meinhart, A.D.; Godoy, H.T. Dilute-and-Shoot Liquid Chromatography Approach for Simple and High-throughput Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural in Fruit-based Baby Foods. Food Anal. Methods 2020, 13, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tölgyesi, Á.; Sharma, V.K. Determination of acrylamide in gingerbread and other food samples by HILIC-MS/MS: A dilute-and-shoot method. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1136, 121933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Xiao, W.; Wan, Y.; Li, Z.; Luo, D.; Yang, H. Dispersive solid-phase extraction using microporous metal-organic framework UiO-66: Improving the matrix compounds removal for assaying pesticide residues in organic and conventional vegetables. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.D.; Romero-González, R.; López-Ruiz, R.; Jiménez-Medina, M.L.; Frenich, A.G. Fast determination of four polar contaminants in soy nutraceutical products by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 8089–8098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mol, H.G.J.; van Dam, R.C.J. Rapid detection of pesticides not amenable to multi-residue methods by flow injection–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 6817–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flour, Whole Wheat, Unenriched. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/790085/nutrients (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Li, X.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; Guo, Z.; Li, X.; Song, S.; Tang, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. Development of precise GC-EI-MS method to determine the residual fipronil and its metabolites in chicken egg. Food Chem. 2019, 281, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlik, P.; Molnarova, K.; Jecmen, T.; Krizek, T.; Goldman, R. Glycan-specific precipitation of glycopeptides in high organic content sample solvents used in HILIC. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1150, 122196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulia, D.S.; Anagnos, E.K.; Liapis, K.S.; Klimentzos, D.A. Removal of pesticides from white and red wines by microfiltration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkasem, N.; Harmon, T. Direct determination of glyphosate, glufosinate, and AMPA in soybean and corn by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 4995–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).