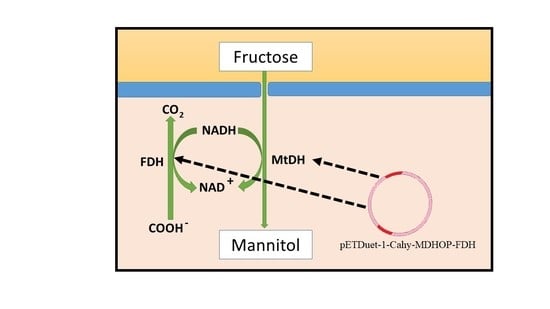
Promising Pathway of Thermostable Mannitol Dehydrogenase (MtDH) from Caldicellulosiruptor hydrothermalis 108 for D-Mannitol Synthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Chemicals Reagents, Plasmids, and Bacteria
2.2. Gene Cloning and Expression
2.3. Purification of CahlyMtDH
2.4. Whole-Cell Biotransformation
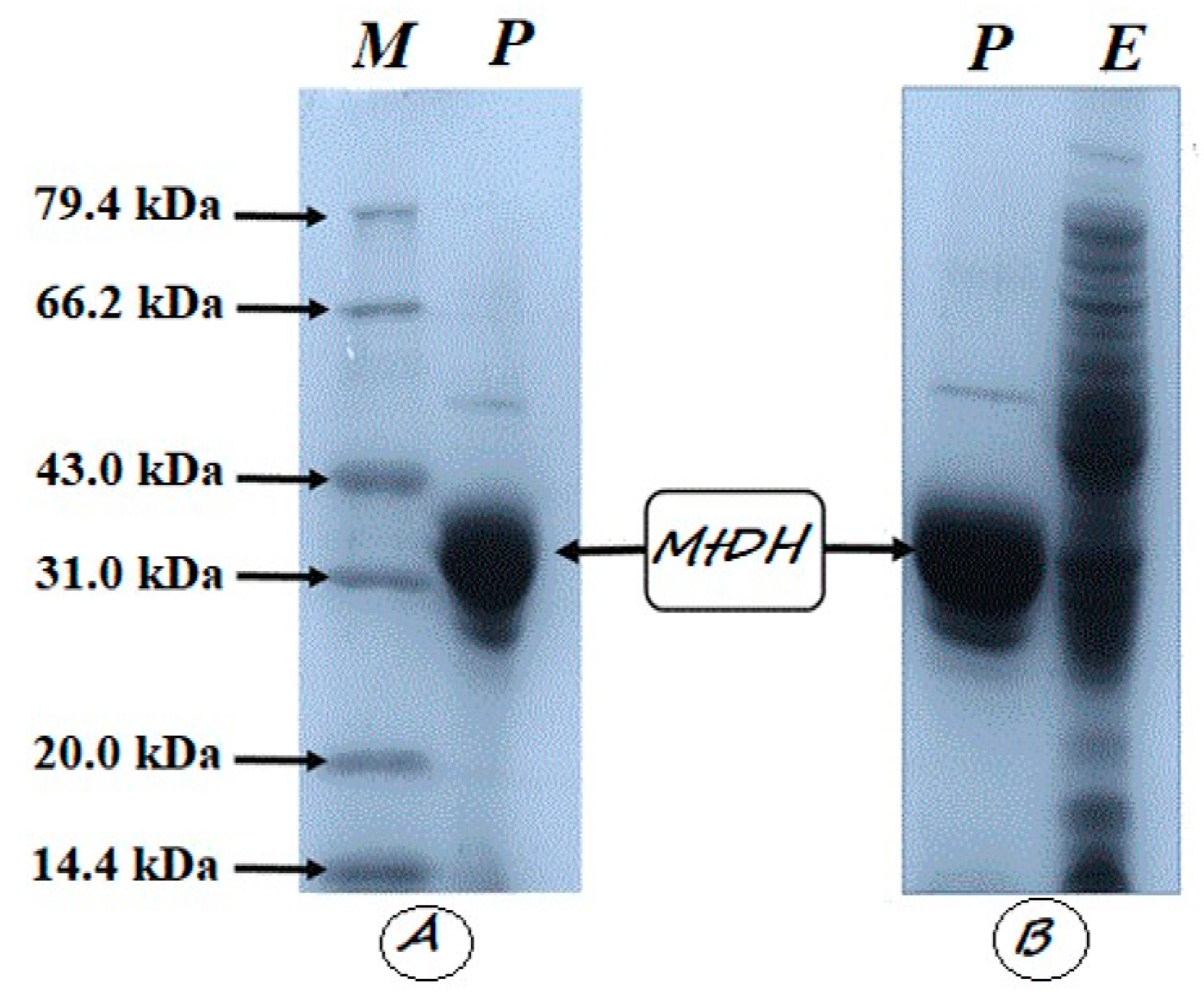
2.5. SDS-PAGE and Molecular Mass Determination
2.6. Enzyme Assay
2.7. The Effects of Temperature and pH
2.8. Temperature, pH, and Biomass Optimization for Biotransformation System
2.9. Effect of Metal Ions
2.10. Determination of Kinetic Parameters
2.11. Substrate Specificity
2.12. Optimization of D-Mannitol Yield from D-Fructose
2.13. 3D Structure and Sequence Alignment
2.14. Analytical Procedure
3. Results
3.1. Cloning, Expression, and Purification of Recombinant CahlyMtDH
3.2. Molecular Weight
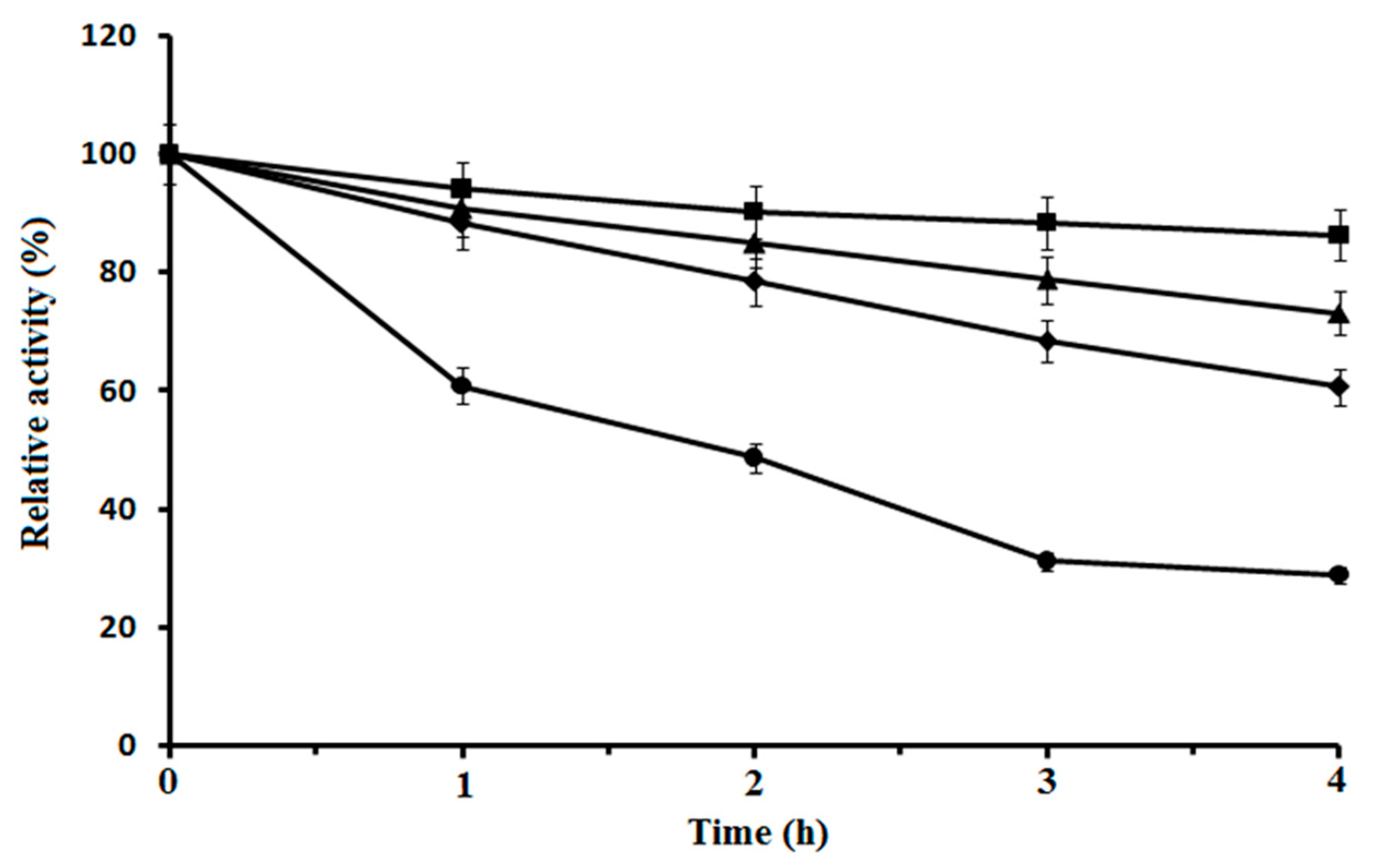
3.3. Effect of Temperature on CahlyMtDH
3.4. Effect of pH Profile on Purified CahlyMtDH and Biotransformation System
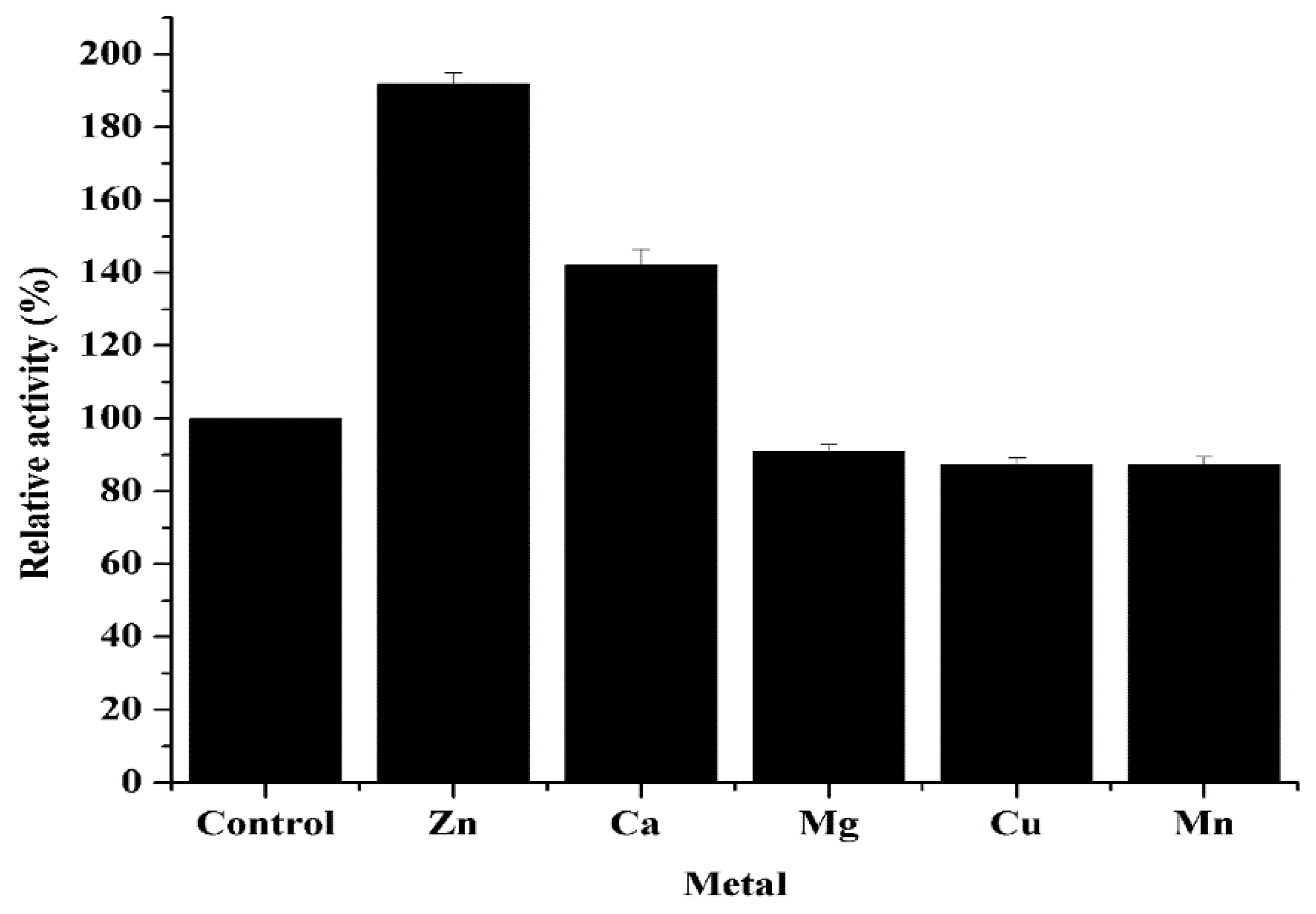
3.5. Effects of Metal Ions on Purified CahlyMtDH Activity
3.6. Kinetic Parameters Determination
3.7. Substrate Specificity
3.8. Sequence Similarity and 3D Structure CahlyMtDH
3.9. Optimization of D-Fructose and D-Mannitol Production
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martău, G.A.; Coman, V.; Vodnar, D.C.; Mart, G.A. Recent advances in the biotechnological production of erythritol and mannitol. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagoub, M.; Koko, F.; Mu, W.; Abdo, H.; Hassanin, M.; Zhang, S.; Lu, H.; Khaleel, J.; Hussain, M.; Baokun, Q.; et al. Archaeal hyperthermostable mannitol dehydrogenases: A promising industrial enzymes for D-mannitol synthesis. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ve, C.; Thalouarn, P.; Delavault, P.; Simier, P. Isolation of mannose 6-phosphate reductase cDNA, changes in enzyme activity and mannitol content in broomrape (Orobanche ramosa) parasitic on tomato roots. Physiol. Plant. 2002, 115, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, G.; Kaup, B. A zinc-containing mannitol-2-dehydrogenase from Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides ATCC 12291: Purification of the enzyme and cloning of the gene. Arch. Microbiol. 2003, 179, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.C.; Oh, E.J.; Jo, J.H.; Jin, Y.S.; Seo, J.H. Recent advances in biological production of sugar alcohols. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 37, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, Y.; Laivenieks, M.; Zeikus, J.G. Lactobacillus reuteri ATCC 53608 mdh gene cloning and recombinant mannitol dehydrogenase characterization. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 68, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brünker, P.; Altenbuchner, J.; Kulbe, K.D.; Mattes, R. Cloning, nucleotide sequence and expression of a mannitol dehydrogenase gene from Pseudomonas fluorescens DSM 50106 in Escherichia coli. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Struct. Expr. 1997, 1351, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.; Stein, M.A.; Schneider, K.H.; Giffhorn, F. Mannitol dehydrogenase from Rhodobacter sphaeroides Si4: Subcloning, overexpression in Escherichia coli and characterization of the recombinant enzyme. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 48, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Koo, B.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Hyun, H.H. Purification and characterization of a novel mannitol dehydrogenase from a newly isolated strain of Candida magnoliae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4438–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.I.; Martinez-Cruz, L.A.; Jancarik, J.; Swanson, R.V.; Robertson, D.E.; Kim, S.H. Crystal structure of the β-glycosidase from the hyperthermophile Thermosphaera aggregans: Insights into its activity and thermostability. FEBS Lett. 1999, 445, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, K.-H.; Giffhorn, F. Purification and properties of a polyol dehydrogenase from the phototrophic bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989, 184, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.H.; Ahluwalia, N.; Leduc, Y.; Delbaere, L.T.J.; Vieille, C. Thermotoga maritima TM0298 is a highly thermostable mannitol dehydrogenase. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 81, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koko, M.Y.F.; Hassanin, H.A.M.; Letsididi, R.; Zhang, T.; Mu, W. Characterization of a thermostable mannitol dehydrogenase from hyperthermophilic Thermotoga neapolitana DSM 4359 with potential application in mannitol production. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2016, 134, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsworth, L.D.; Van Der Oost, J.; Koutsopoulos, S. Hyperthermophilic enzymes—Stability, activity and implementation strategies for high temperature applications. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 4044–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainey, F.A.; Donnison, A.M.; Janssen, P.H.; Saul, D.; Rodrigo, A.; Bergquist, P.L. Description of Caldicellulosiruptor saccharolyticus gen. nov., sp. nov: An obligately anaerobic, extremely thermophilic, cellulolytic bacterium. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1994, 120, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, P. Construction of allitol synthesis pathway by multi—Enzyme coexpression in Escherichia coli and its application in allitol production. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Du, G.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for (2S)-pinocembrin production from glucose by a modular metabolic strategy. Metab. Eng. 2013, 16, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.C. Purification and characterization of novel mannitol dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus intermedius. Biotechnol. Prog. 2004, 20, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäumchen, C.; Roth, A.H.F.J.; Biedendieck, R.; Malten, M.; Follman, M.; Sahm, H.; Bringer-Meyer, S.; Jahn, D. D-Mannitol production by resting state whole cell biotransformation of D-fructose by heterologous mannitol and formate dehydrogenase gene expression in Bacillus megaterium. Biotechnol. J. 2007, 2, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korakli, M.; Rossmann, A.; Gänzle, M.G.; Vogel, R.F. Sucrose metabolism and exopolysaccharide production in wheat and rye sourdoughs by Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5194–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaup, B.; Bringer-Meyer, S.; Sahm, H. D-mannitol formation from D-glucose in whole-cell biotransformation with recombinant Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 69, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slatner, M.; Nagl, G.; Haltrich, D.; Kulbe, K.D.; Nidetzky, B. Enzymatic production of pure D-mannitol at high productivity. Biocatal. Biotransformation 1998, 16, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, S.M.; Mohan, A.; Srivastava, S.K. Challenges in enzymatic route of mannitol production. Int. Sch. Res. Notices 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäumchen, C.; Bringer-Meyer, S. Expression of glf Zm increases D-mannitol formation in whole cell biotransformation with resting cells of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 7, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Strain and Plasmid | Function | Source |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli BL21 Star (DE3) | For gene expression | Invitrogen |
| pETDuet-1-Cahy-MDHOP-FDH | MtDH and FDH regeneration | Novagen (Darmstadt, Germany) |
| pET-Op-FDH | FDH gene carrier | This study |
| pET-Cahly-MtDH | MtDH gene carrier | This study |
| Escherichia coli DH5α | For gene cloning | Invitrogen |
| MtDH Source | Molecular Mass (kDa) | Coenzyme | Native Form | Km (mM) | Catalytic Efficiency | Opt pH | Opt Temp (°C) | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subunit | Native | Reduction | Oxidation | |||||||
| CahlyMtDH | 38 | 76.6 | NADH | Dimer | 6.0 | 6.2 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 60 °C | This study |
| Candida magnoliae | 35 | 142 | NADH/NADPH | Tetramer | 28.0 | 29.4 | 7.5 | 10 | 37 °C | [1] |
| Rhodobacter sphaeroides | 51.4 | NR | NADH | Monomer | NR | NR | 6.5 | 9.0 | NR | [10] |
| Thermotoga neapolitana | 36 | 135 | NADH | Tetramer | 20.0 | 9.0 | 6.5 | 8.0 | 90 | [12] |
| Agaricus bisporus | 29 | 116 | NADPH | Tetramer | 190 | 13 | 6.5–7.5 | 8.8–9.0 | NR | [2] |
| Thermotoga maritima | 34 | NR | NADH/NADPH | Homodimer, tetramer, andoctamer | 50.97 | 1.15 | 5.5–6.0 | NR | 95 | [11] |
| Lactobacillus intermedius | 43, 34.5 | 170 | NADPH | Heterotetramer | 25 | 19.8 | 5.5 | 4.7 | 35 | [18] |
| Factor | E. coli BL21 Star (This Study) | E. coli BL21 (DE3) [23] | C. glutamicum ATCC 13,032 [24] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 60 | 30 | 30 |
| Cofactor | Formate/formate dehydrogenase | Formate/formate dehydrogenase | Formate/formate dehydrogenase |
| Byproducts | None | None | None |
| D-mannitol yield | 41 mg/mL | 178 g−1 | 1.55 g/L |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koko, M.Y.F.; Sami, R.; Muhoza, B.; Khojah, E.; Mansour, A.M.A. Promising Pathway of Thermostable Mannitol Dehydrogenase (MtDH) from Caldicellulosiruptor hydrothermalis 108 for D-Mannitol Synthesis. Separations 2021, 8, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8060076
Koko MYF, Sami R, Muhoza B, Khojah E, Mansour AMA. Promising Pathway of Thermostable Mannitol Dehydrogenase (MtDH) from Caldicellulosiruptor hydrothermalis 108 for D-Mannitol Synthesis. Separations. 2021; 8(6):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8060076
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoko, Marwa Y. F., Rokayya Sami, Bertrand Muhoza, Ebtihal Khojah, and Ahmed M. A. Mansour. 2021. "Promising Pathway of Thermostable Mannitol Dehydrogenase (MtDH) from Caldicellulosiruptor hydrothermalis 108 for D-Mannitol Synthesis" Separations 8, no. 6: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8060076
APA StyleKoko, M. Y. F., Sami, R., Muhoza, B., Khojah, E., & Mansour, A. M. A. (2021). Promising Pathway of Thermostable Mannitol Dehydrogenase (MtDH) from Caldicellulosiruptor hydrothermalis 108 for D-Mannitol Synthesis. Separations, 8(6), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8060076