Reaeration Coefficient Empirical Equation Selection for Water Quality Modeling in Surface Waterbodies: An Integrated Numerical-Modeling-Based Technique with Field Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Conceptual Framework of the Study
| Equation of Ka | Equation Reference | Equation No. |
|---|---|---|
| Downing and Truesdale (1955) | (1) | |
| Smith (1978) | (2) | |
| Gelda et al. (1996) | (3) | |
| Kanwisher (1963) | (4) | |
| Banks (1975) | (5) | |
| Cole and Buchak (1995) | (6) | |
| Liss (1973) | (7) | |
| Yu et al. (1977) | (8) | |
| Weiler (1974) | (9) | |
| Broecker et al. (1978) | (10) | |
| Wanninkhof et al. (1991) | (11) | |
| Banks and Herrera (1977) | (12) |
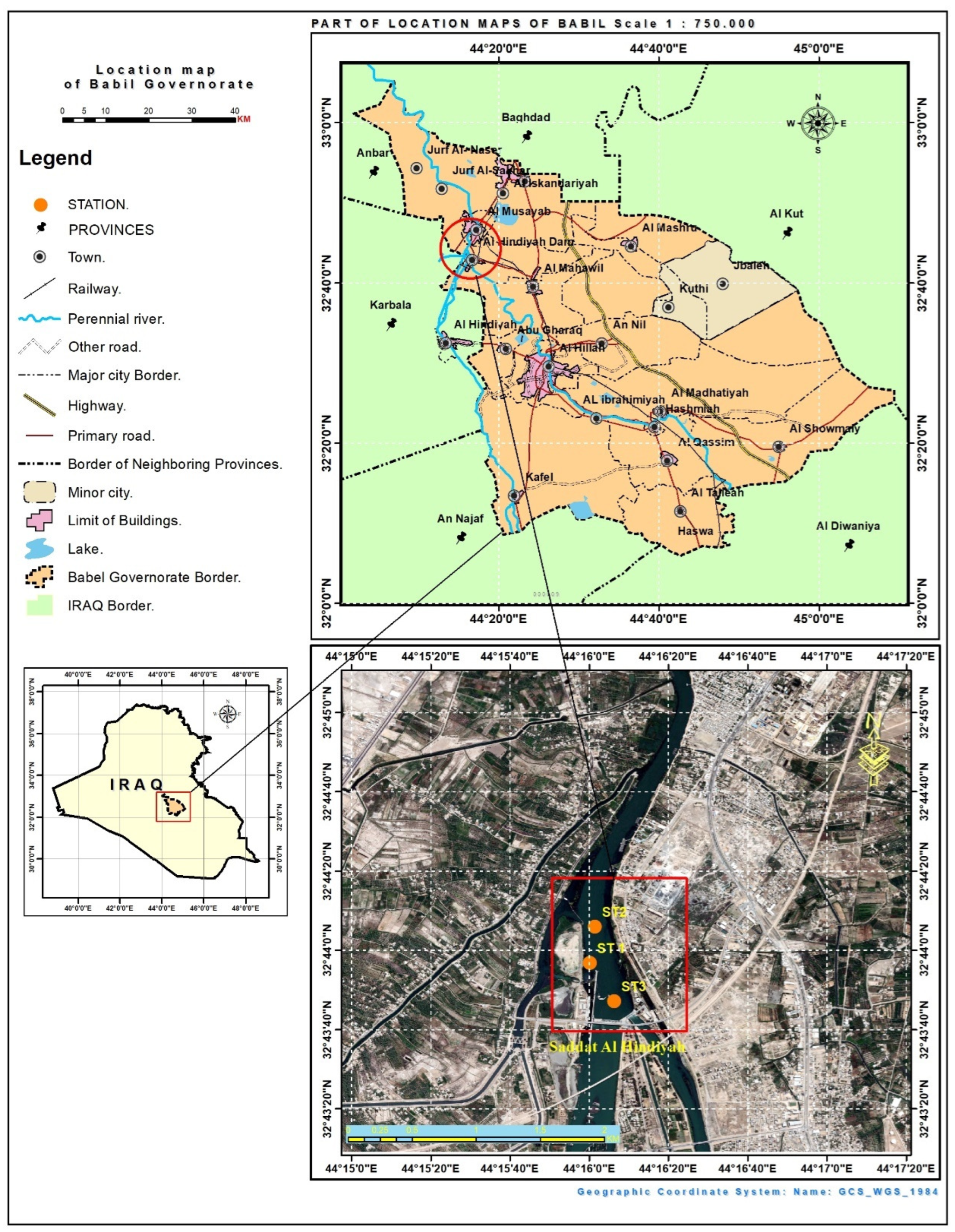
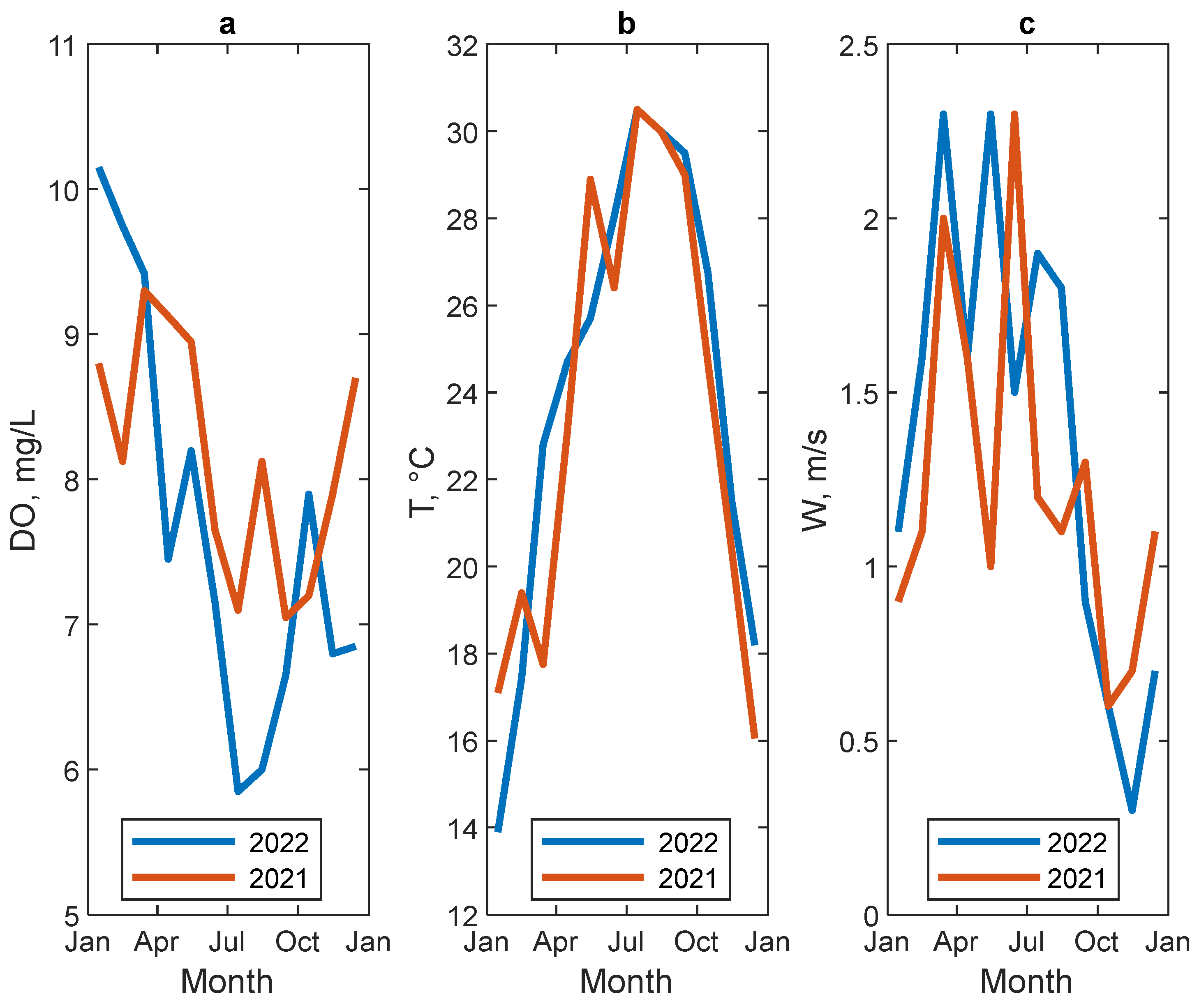
2.2. Study Area and Field Data
2.3. Development of the Numerical Model
3. Results and Discussion
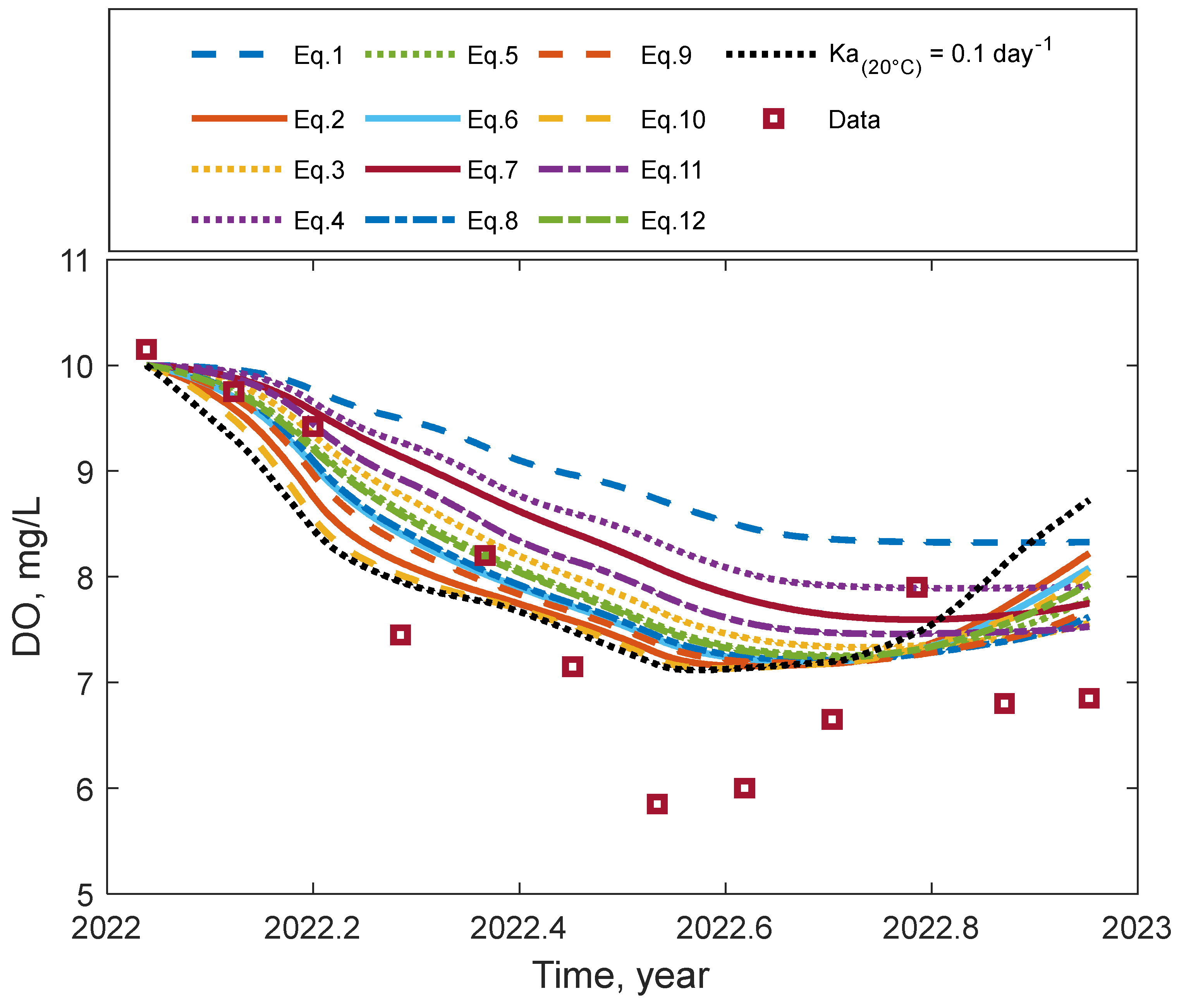
3.1. DO and Ka Numerical Determinations
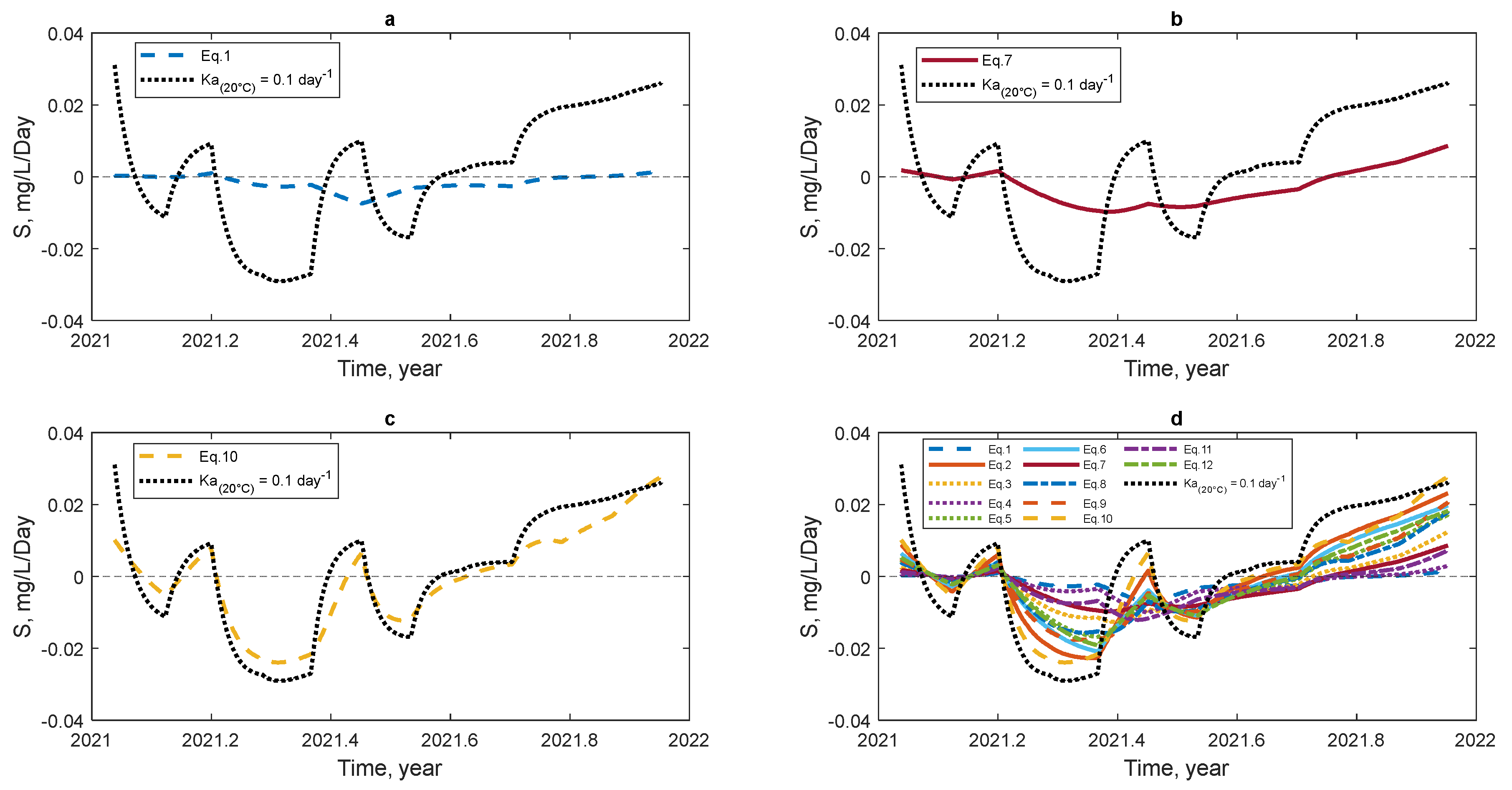
3.2. DO Source–Sink Response to Change Ka Equation
3.3. The Temporal Variation of Reaeration Coefficient
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chapra, S.C. Surface Water-Quality Modeling; Waveland Press, Inc.: Long Grove, IL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Abouelsaad, O.; Matta, E.; Omar, M.; Hinkelmann, R. Numerical simulation of Dissolved Oxygen as a water quality indicator in artificial lagoons–Case lagoons—Case study El Gouna, Egypt. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 56, 102697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.D.S.; Soeira, T.V.R.; Ferreira, D.C.; da Luz, M.S.; Poleto, C.; Gonçalves, J.C.d.S.I. The effect of sds surfactant on surface reaeration coefficient: A laboratory scale approach. Ambient. Agua-Interdiscip. J. Appl. Sci. 2020, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Hanipah, A.H.; Guo, Z.R. Reaeration Caused by Intense Boat Traffic. Asian J. Water Environ. Pollut. 2019, 16, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, V.; Parrella, L.; Falcucci, M. Modelling dissolved oxygen dynamics in coastal lagoons. Ecol. Model. 2008, 211, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-González, J.C.; Chávez-Parga, M.d.C.; Cortés, J.A.; Pérez-Munguía, R.M. Photosynthesis, respiration and reaeration in a stream with complex dissolved oxygen pattern and temperature dependence. Ecol. Model. 2014, 273, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.R.; Jirka, G.H. Wind and Stream Flow Induced Reaeration. J. Environ. Eng. 2003, 129, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Inácio Gonçalves, J.C.; Silveira, A.; Lopes Júnior, G.B.; da Luz, M.S.; Simões, A.L.A. Reaeration Coefficient Estimate: New Parameter for Predictive Equations. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, R.O.; Egbe, J.G. Comparative Empirical Analysis for Determination of Re-Aeration Rate Constant of Otamiri and Kaduna Rivers. Int. J. Water Resour. 2024, 6, 168. [Google Scholar]
- Klaus, M.; Vachon, D. Challenges of predicting gas transfer velocity from wind measurements over global lakes. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 82, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.; Bade, D.L.; Bastviken, D.; Pace, M.L.; Van de Bogert, M. Multiple approaches to estimating air-water gas exchange in small lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2010, 8, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelda, R.K.; Auer, M.T.; Effler, S.W.; Chapra, S.C.; Storey, M.L. Determination of Reaeration Coefficients: Whole Lake Approach. J. Environ. Eng. 1996, 122, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, A.; Zane, M.; Becker, T.E.; Visser, A.; Uriostegui, S.H.; DeRubeis, E.; Moran, J.E.; Esser, B.K.; Clark, J.F. Quantifying reaeration rates in alpine streams using deliberate gas tracer experiments. Water 2014, 6, 1013–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, T.M.; Wells, S.A. CE-QUAL-W2: A Two-Dimensional, Laterally Averaged, Hydrodynamic and Water Quality Model, 2006; Version 3.5. Available online: https://pdxscholar.library.pdx.edu/cengin_fac (accessed on 18 June 2024).
- Antonopoulos, V.Z.; Gianniou, S.K. Simulation of water temperature and dissolved oxygen distribution in Lake Vegoritis, Greece. Ecol. Model. 2003, 160, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Stefan, H.G. Interaction between Oxygen Transfer Mechanisms in Lake Models. J. Environ. Eng. 1995, 121, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, C. Verification of wind-driven volatilization models. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2006, 6, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zubaidi, H.A.; Wells, S.A. 3D numerical temperature model development and calibration for lakes and reservoirs: A case study. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resource Congress, Sacramento, CA, USA, 18 May 2017; pp. 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowjood, M.I.M.; Kasubuchi, T. Effect of convection on the exchange coefficient of oxygen and estimation of net production rate of oxygen in ponded water of a paddy field. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2002, 48, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zubaidi, H.A.; Naje, A.S.; Al-Ridah, Z.A.; Chelliapan, S.; Sopian, K. Numerical Modeling of Reaeration Coefficient for Lakes: A Case Study of Sawa Lake, Iraq. Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2024, 25, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ro, K.S.; Hunt, P.G. New Unified Equation for Wind-Driven Surficial Oxygen Transfer into Stationary Water Bodies. Trans. ASABE 2006, 49, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, S.M.; Willmott, C.J. Decomposition of the mean absolute error (MAE) into systematic and unsystematic components. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0279774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, T.; Draxler, R.R. Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)?—Arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugume, I.; Basalirwa, C.; Waiswa, D.; Reuder, J.; Mesquita, M.D.S.; Tao, S.; Ngailo, T.J. Comparison of Parametric and Nonparametric Methods for Analyzing the Bias of a Numerical Model. Model. Simul. Eng. 2016, 2016, 7530759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, Y. Analysis of the Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) in Assessing Rounding Model. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 324, 012049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dalimy, S.Z.; Al-Zubaidi, H.A.M. Application of QUAL2K Model for Simulating Water Quality in Hilla River, Iraq. J. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 24, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, L.; Ali-Maher, O. The dependence of the consumption of dissolved oxygen on lake morphology in ice covered lakes. Hydrol. Res. 2020, 51, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shi, X.; Zhao, S.; Arvola, L.; Huotari, J.; Hao, R. Equilibrium simulation and driving factors of dissolved oxygen in a shallow eutrophic Inner Mongolian lake (UL) during open-water period. Water Supply 2022, 22, 6013–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwuma, A.N.; Ugbebor, J.; Ugwoha, E. Modeling of re-aeration coefficient For Nkisa River, Egbema, Rivers State, Nigeria. Water Pract. Technol. 2024, 19, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palshin, N.; Zdorovennova, G.; Efremova, T.; Bogdanov, S.; Terzhevik, A.; Zdorovennov, R. Dissolved oxygen stratification in a small lake depending on water temperature and density and wind impact. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 937, 032019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, N.B.; Riha, S.J.; Walter, M.T. Temperature dependence of daily respiration and reaeration rates during baseflow conditions in a northeastern U.S. stream. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 19, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zubaidi, H.A.M.; Wells, S.A. Comparison of a 2D and 3D Hydrodynamic and Water Quality Model for Lake Systems. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2018: Watershed Management. Irrigation and Drainage, and Water Resources Planning and Management, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 31 May 2018; pp. 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demars, B.O.L.; Manson, J.R. Temperature dependence of stream aeration coefficients and the effect of water turbulence: A critical review. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





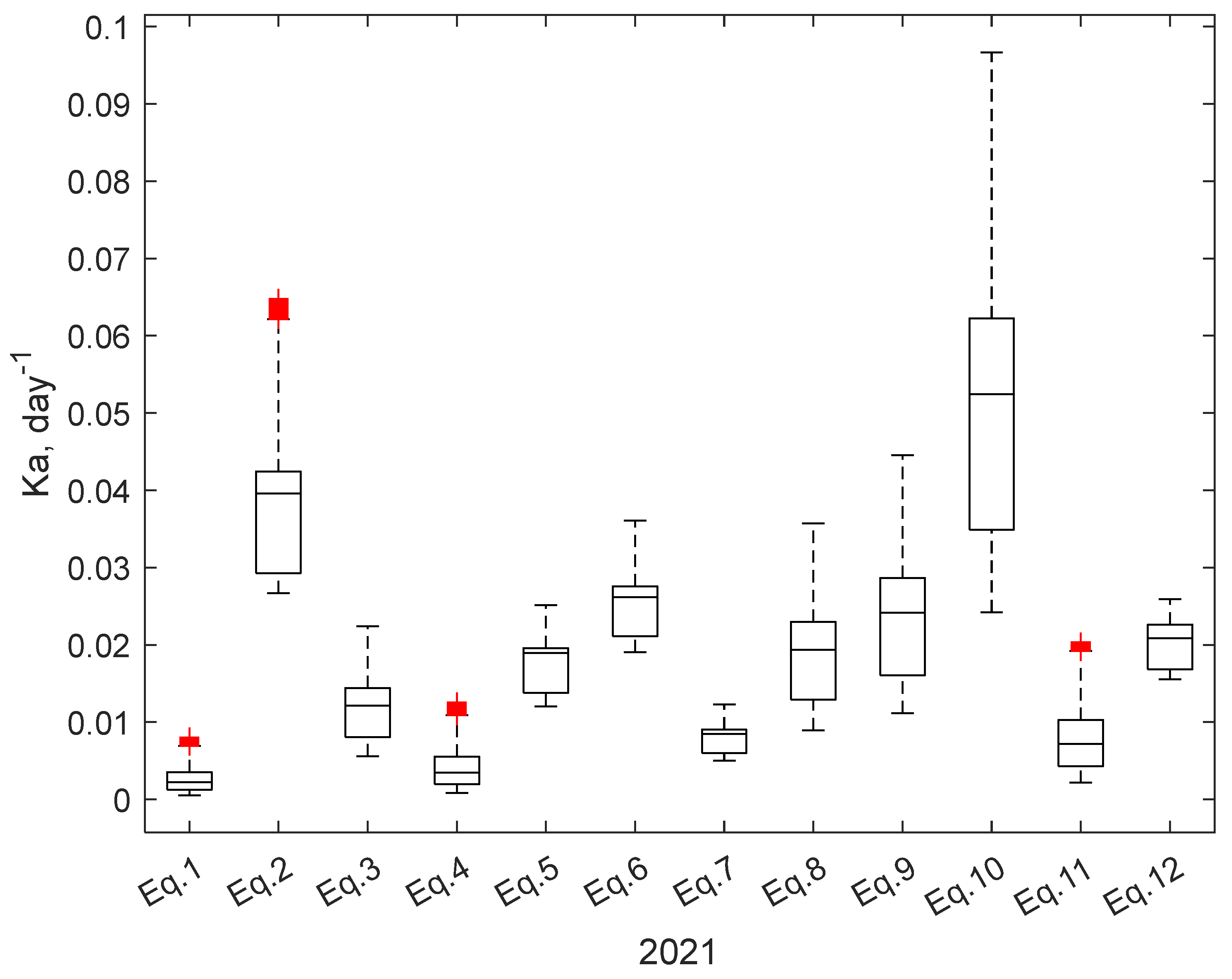


| Ka Equation | 2021 | 2022 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE (mg/L) | MAE (mg/L) | RMSE (mg/L) | MAE (mg/L) | |
| Equation (1) | 0.7897 | 0.6455 | 1.1773 | 1.0680 |
| Equation (2) | 0.2275 | 0.1686 | 0.2209 | 0.1744 |
| Equation (3) | 0.5103 | 0.4084 | 0.5868 | 0.5134 |
| Equation (4) | 0.6991 | 0.5762 | 0.9183 | 0.8358 |
| Equation (5) | 0.4164 | 0.3272 | 0.4866 | 0.4195 |
| Equation (6) | 0.3195 | 0.2469 | 0.3492 | 0.2962 |
| Equation (7) | 0.5841 | 0.4808 | 0.7938 | 0.7156 |
| Equation (8) | 0.4217 | 0.3202 | 0.4477 | 0.3649 |
| Equation (9) | 0.3750 | 0.2769 | 0.3918 | 0.3047 |
| Equation (10) | 0.2005 | 0.1347 | 0.2324 | 0.1400 |
| Equation (11) | 0.5830 | 0.4771 | 0.6708 | 0.5999 |
| Equation (12) | 0.3760 | 0.2956 | 0.4492 | 0.3875 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Saadi, B.J.M.; Al-Zubaidi, H.A.M. Reaeration Coefficient Empirical Equation Selection for Water Quality Modeling in Surface Waterbodies: An Integrated Numerical-Modeling-Based Technique with Field Case Study. Limnol. Rev. 2025, 25, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25020015
Al-Saadi BJM, Al-Zubaidi HAM. Reaeration Coefficient Empirical Equation Selection for Water Quality Modeling in Surface Waterbodies: An Integrated Numerical-Modeling-Based Technique with Field Case Study. Limnological Review. 2025; 25(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Saadi, Balsam J. M., and Hussein A. M. Al-Zubaidi. 2025. "Reaeration Coefficient Empirical Equation Selection for Water Quality Modeling in Surface Waterbodies: An Integrated Numerical-Modeling-Based Technique with Field Case Study" Limnological Review 25, no. 2: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25020015
APA StyleAl-Saadi, B. J. M., & Al-Zubaidi, H. A. M. (2025). Reaeration Coefficient Empirical Equation Selection for Water Quality Modeling in Surface Waterbodies: An Integrated Numerical-Modeling-Based Technique with Field Case Study. Limnological Review, 25(2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25020015







