TPDNet: Texture-Guided Phase-to-DEPTH Networks to Repair Shadow-Induced Errors for Fringe Projection Profilometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
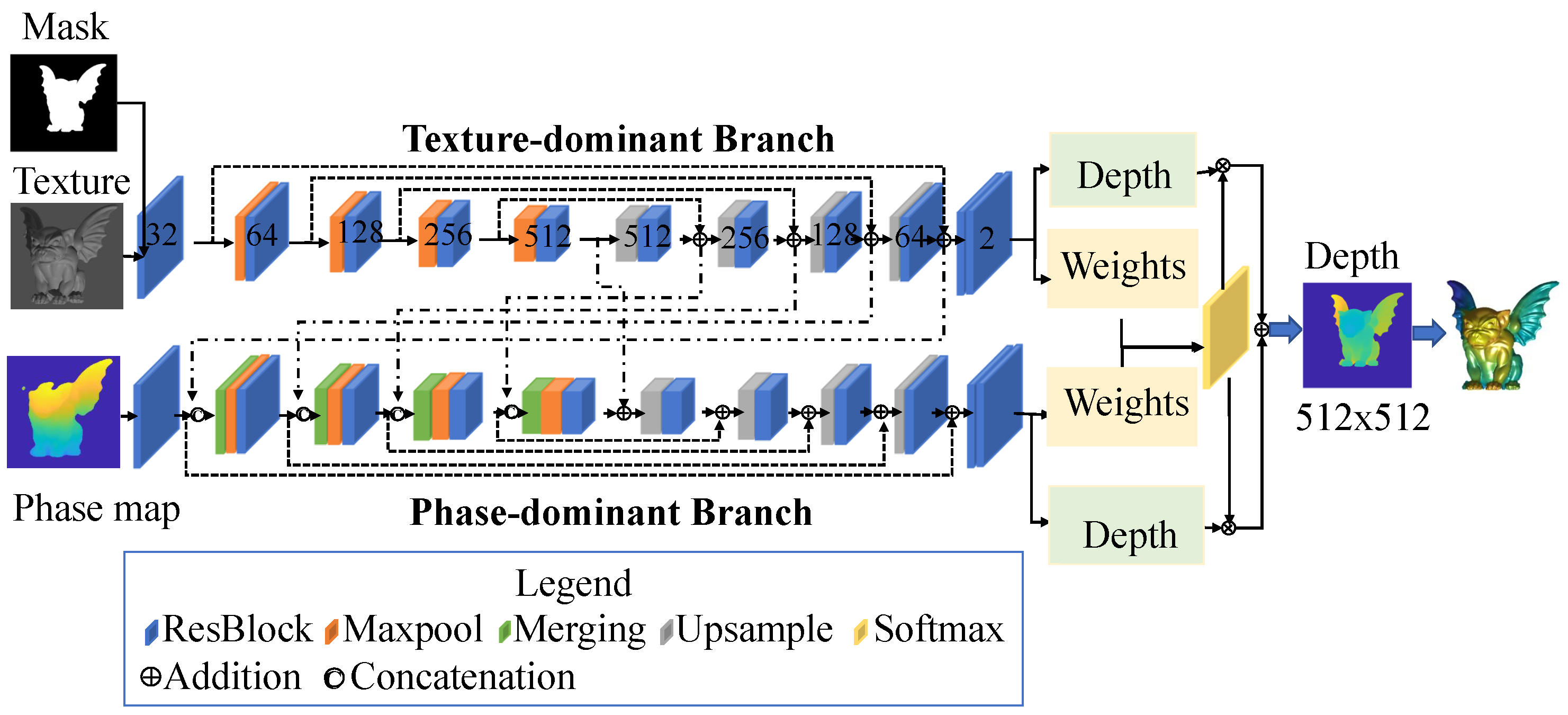
- Each layer in the encoder stage of the phase-dominant branch is fused with a layer from the decoder stage of the other branch via concatenation and addition
- At the end of the decoder stage, depth maps from two branches are fused by multiplying the respective weights.
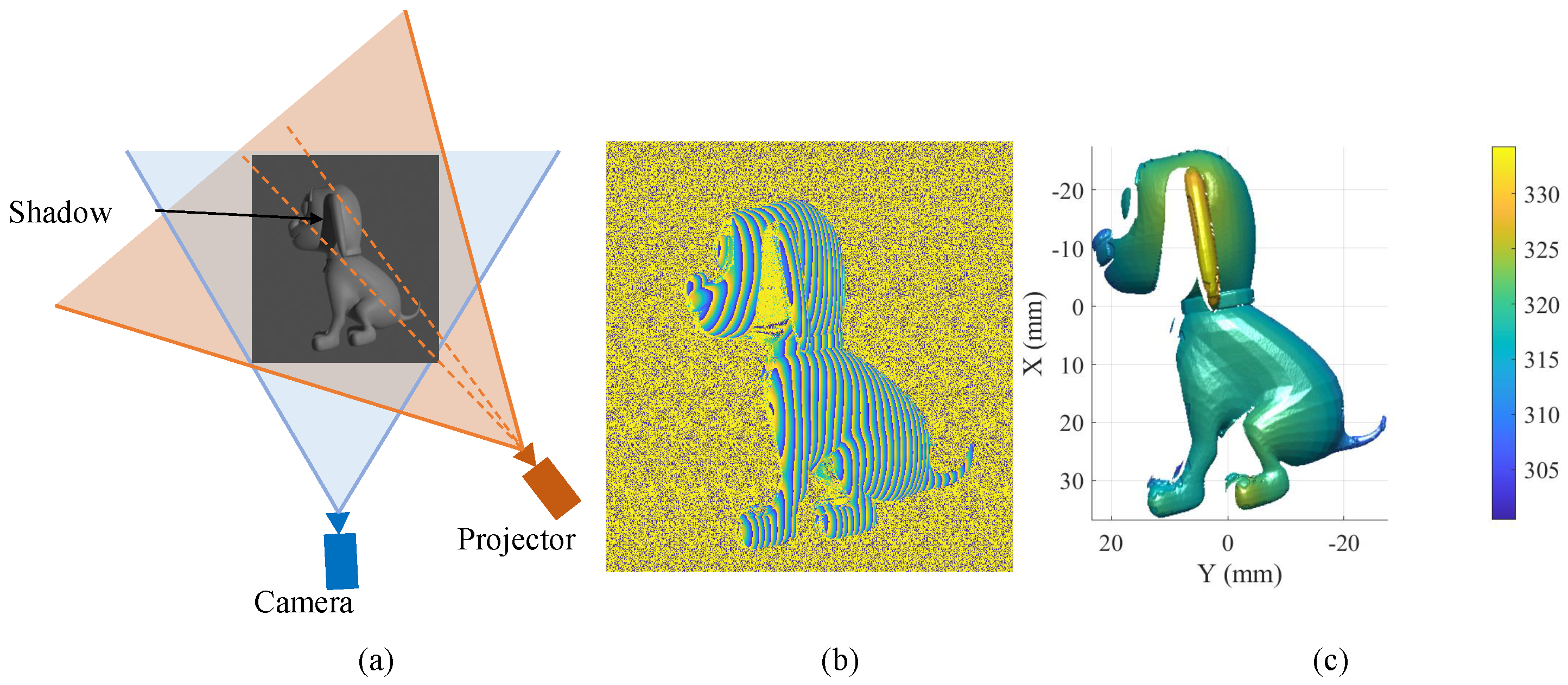
2. Principles
2.1. FPP Model
2.2. Virtual FPP Model
3. Proposed Model
3.1. Network Architecture
3.2. Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset Preparation
4.2. Training
4.3. Results with Data from the Virtual System
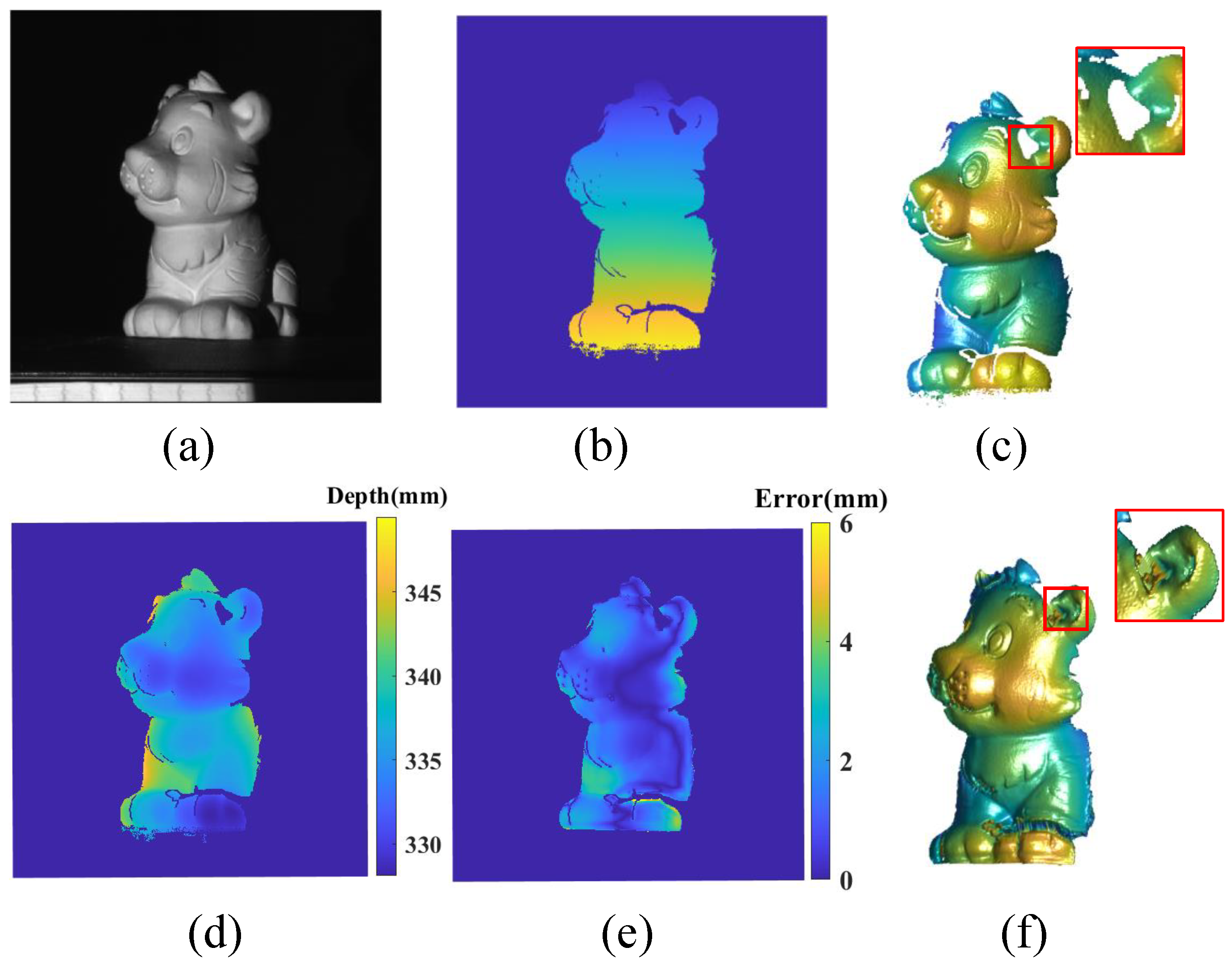
4.4. Results with Data from the Real-World System
5. Discussion
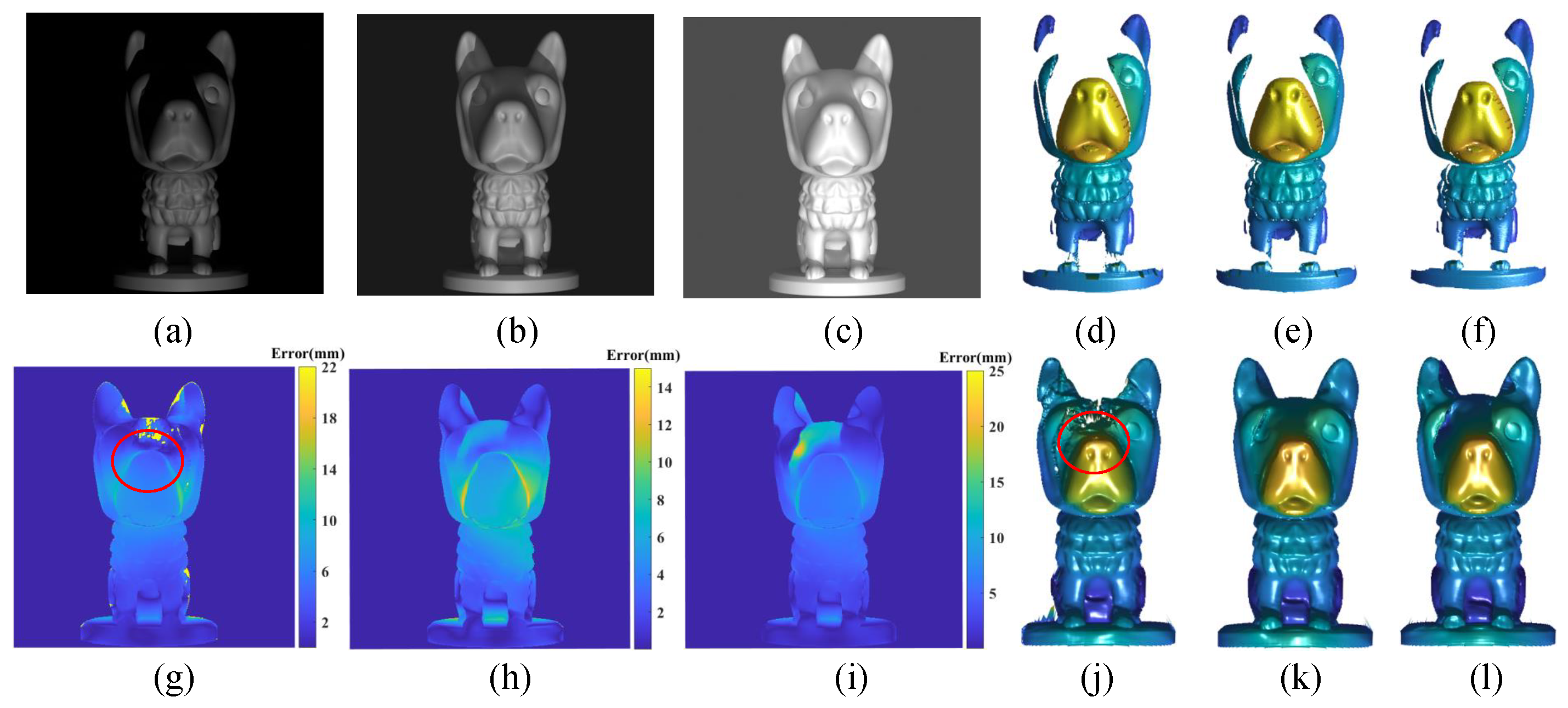
5.1. Influence of Environment Light on Prediction
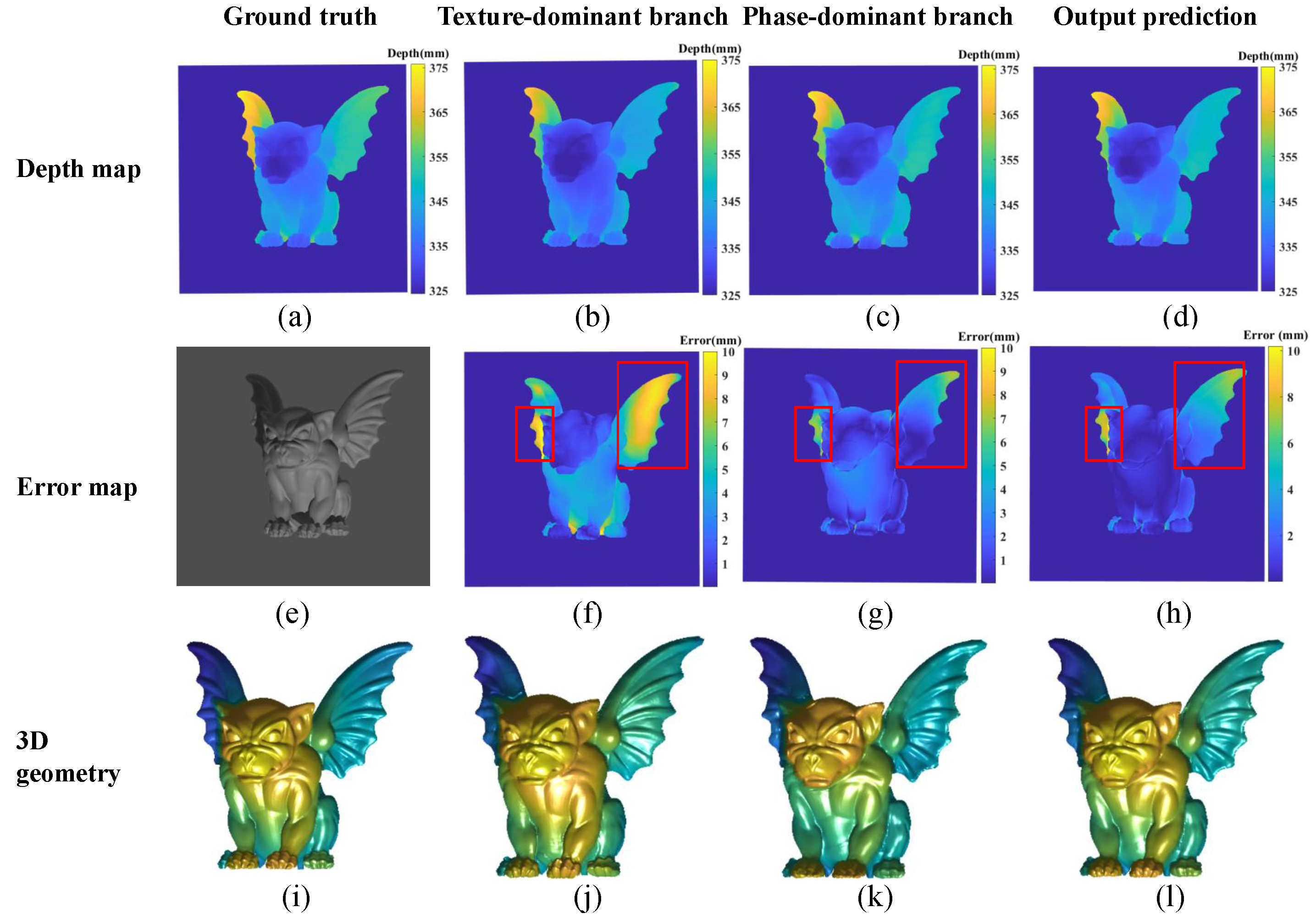
5.2. Function Comparison of the Two Branch Networks
6. Conclusions
- Texture images are leveraged as guidance for shadow-induced error removal, and information from phase maps and texture images are combined at two stages.
- A specified loss function that combines image edge details and structural similarity is designed to better train the model.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zuo, C.; Feng, S.; Huang, L.; Tao, T.; Yin, W.; Chen, Q. Phase shifting algorithms for fringe projection profilometry: A review. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2018, 109, 23–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, S. Status, challenges, and future perspectives of fringe projection profilometry. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 135, 106193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Su, X.; You, Z. Uniaxial three-dimensional shape measurement with multioperation modes for different modulation algorithms. Opt. Eng. 2017, 56, 034115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, B. Uniaxial High-Speed Microscale Three-Dimensional Surface Topographical Measurements Using Fringe Projection. J. Micro Nano-Manuf. 2020, 8, 041007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Quanyao, H.; Yongkai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Qijian, T.; Xiang, P.; Xiaoli, L. Large DOF microscopic fringe projection profilometry with a coaxial light-field structure. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 8015–8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skydan, O.A.; Lalor, M.J.; Burton, D.R. Using coloured structured light in 3-D surface measurement. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2005, 43, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinmann, M.; Schwartz, C.; Ruiters, R.; Klein, R. A multi-camera, multi-projector super-resolution framework for structured light. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on 3D Imaging, Modeling, Processing, Visualization and Transmission, Hangzhou, China, 16–19 May 2011; pp. 397–404. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Asundi, A.K. Phase invalidity identification framework with the temporal phase unwrapping method. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 035304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Xi, J.; Yu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Yin, Y.; Song, L. Shadow removal method for phase-shifting profilometry. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 6059–6064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, B.; Ma, Z.; Liu, J.; Ni, X.; Xiao, W.; Liu, H. Shadow Extraction Method Based on Multi-Information Fusion and Discrete Wavelet Transform. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. Phase unwrapping error reduction framework for a multiple-wavelength phase-shifting algorithm. Opt. Eng. 2009, 48, 105601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Su, X.; Xiang, L. Analysis and identification of phase error in phase measuring profilometry. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 11300–11307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Jin, Y.; Duan, M.; Kan, Y.; Zhu, C.; Chen, E. Discriminative repair approach to remove shadow-induced error for typical digital fringe projection. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 26076–26090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, C.; Qian, J.; Feng, S.; Yin, W.; Li, Y.; Fan, P.; Han, J.; Qian, K.; Chen, Q. Deep learning in optical metrology: A review. Light. Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, K.; Yu, Y.; Huang, C.; Sui, L.; Qian, K.; Asundi, A. Fringe pattern denoising based on deep learning. Opt. Commun. 2019, 437, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Zhou, X. Single-shot phase extraction for fringe projection profilometry using deep convolutional generative adversarial network. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 32, 015007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qian, J.; Feng, S.; Chen, Q.; Zuo, C. Single-shot spatial frequency multiplex fringe pattern for phase unwrapping using deep learning. In Proceedings of the Optics Frontier Online 2020: Optics Imaging and Display, Shanghai, China, 19–20 June 2020; Volume 11571, pp. 314–319. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Lu, S.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Li, D.; Lu, X.; Zhong, L.; Tian, J. Deep phase shifter for quantitative phase imaging. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.03027. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Kemao, Q.; Di, J.; Zhao, J. One-step robust deep learning phase unwrapping. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 15100–15115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoorthi, G.; Gorthi, S.; Gorthi, R.K.S.S. PhaseNet: A deep convolutional neural network for two-dimensional phase unwrapping. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 26, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Yu, Y.; Sun, T.; Asundi, A.; Kemao, Q. Wrapped phase denoising using convolutional neural networks. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 128, 105999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montresor, S.; Tahon, M.; Laurent, A.; Picart, P. Computational de-noising based on deep learning for phase data in digital holographic interferometry. APL Photonics 2020, 5, 030802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.w.; Shi, Y.s.; Wang, C.j.; Qin, D.h.; Huang, K. Complex object 3D measurement based on phase-shifting and a neural network. Opt. Commun. 2009, 282, 2699–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Jeught, S.; Dirckx, J.J. Deep neural networks for single shot structured light profilometry. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 17091–17101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Single-shot 3D shape reconstruction using structured light and deep convolutional neural networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Li, B. Fringe projection profilometry by conducting deep learning from its digital twin. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 36568–36583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elharrouss, O.; Almaadeed, N.; Al-Maadeed, S.; Akbari, Y. Image inpainting: A review. Neural Process. Lett. 2020, 51, 2007–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Team, B.D. Blender—A 3D Modelling and Rendering Package; Blender Foundation, Stichting Blender Foundation: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Pang, Q. The elimination of errors caused by shadow in fringe projection profilometry based on deep learning. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2022, 159, 107203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malacara, D. Optical Shop Testing; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; Volume 59. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Oliver, J.H. 3D shape measurement technique for multiple rapidly moving objects. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 8539–8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Qin, H.; Li, B. Similarity evaluation of topography measurement results by different optical metrology technologies for additive manufactured parts. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 126, 105920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, M.; Wang, S.; Li, B.; Ning, S.; Fan, L.; Gong, X. Penet: Towards precise and efficient image guided depth completion. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 13656–13662. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Van Gansbeke, W.; Neven, D.; De Brabandere, B.; Van Gool, L. Sparse and noisy lidar completion with rgb guidance and uncertainty. In Proceedings of the 2019 16th International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA), Tokyo, Japan, 27–31 May 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Gallo, O.; Frosio, I.; Kautz, J. Loss functions for image restoration with neural networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2016, 3, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bojanowski, P.; Joulin, A.; Lopez-Paz, D.; Szlam, A. Optimizing the latent space of generative networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.05776. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Jacobson, A. Thingi10K: A Dataset of 10,000 3D-Printing Models. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1605.04797. [Google Scholar]
- Free 3D Models. Available online: https://free3d.com/3d-models/ (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc. (NeurIPS): Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Robbins, H.; Monro, S. A stochastic approximation method. Ann. Math. Stat. 1951, 22, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Guan, Q. Single-shot fringe projection profilometry based on deep learning and computer graphics. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 8024–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Parameters | Virtual Camera | Virtual Projector (Spot Light) |
|---|---|---|
| Extrinsic matrix Location | (0.0227 m, 0.0885 m, −0.1692 m) | |
| Rotation | ||
| Scale |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Li, B. TPDNet: Texture-Guided Phase-to-DEPTH Networks to Repair Shadow-Induced Errors for Fringe Projection Profilometry. Photonics 2023, 10, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030246
Li J, Li B. TPDNet: Texture-Guided Phase-to-DEPTH Networks to Repair Shadow-Induced Errors for Fringe Projection Profilometry. Photonics. 2023; 10(3):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030246
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiaqiong, and Beiwen Li. 2023. "TPDNet: Texture-Guided Phase-to-DEPTH Networks to Repair Shadow-Induced Errors for Fringe Projection Profilometry" Photonics 10, no. 3: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030246
APA StyleLi, J., & Li, B. (2023). TPDNet: Texture-Guided Phase-to-DEPTH Networks to Repair Shadow-Induced Errors for Fringe Projection Profilometry. Photonics, 10(3), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030246






