Frequency Comb Generation Based on Brillouin Random Lasing Oscillation and Four-Wave Mixing Assisted with Nonlinear Optical Loop Mirror
Abstract
:1. Introduction
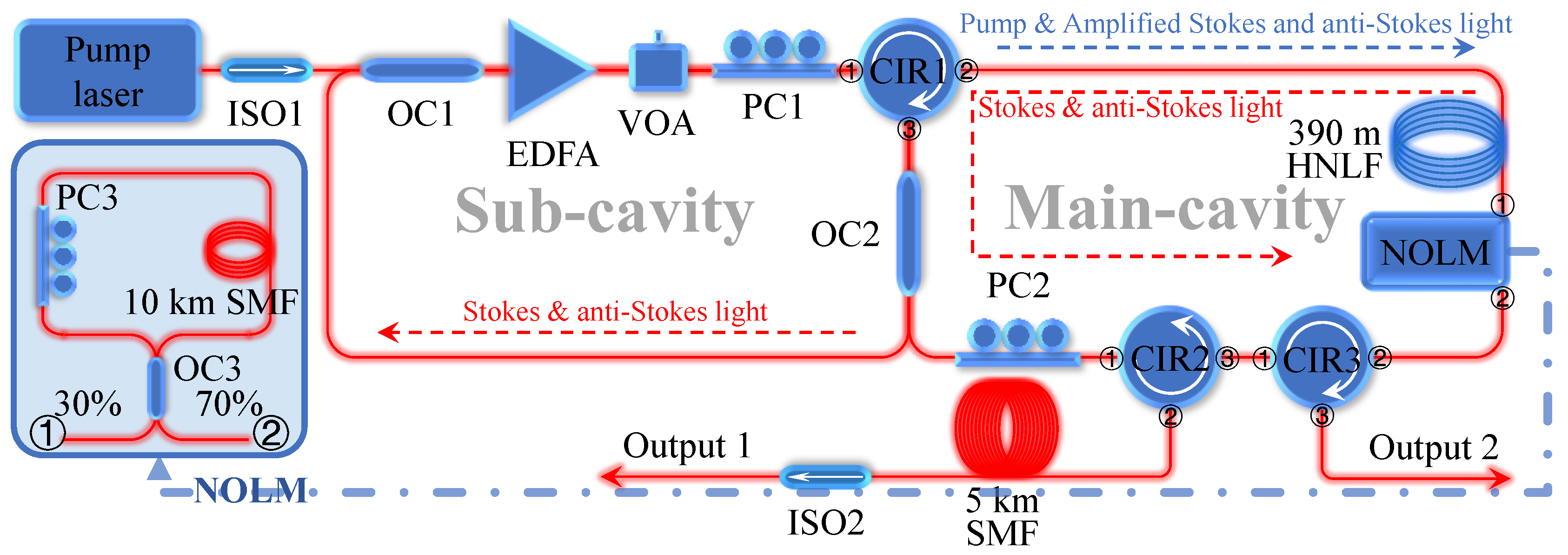
2. Experimental Setup and Operation Principle
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.1. Optical Spectrum
3.2. Linewidth
3.3. Relative Intensity Noise
3.4. Frequency Noise
3.5. Temporal Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Veselka, J.J.; Korotky, S.K. A Multiwavelength Source Having Precise Channel Spacing for WDM Systems. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 1998, 10, 958–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.-C.; Tseng, H.-Y.; Chi, S. Long-Distance FBG Sensor System Using a Linear-Cavity Fiber Raman Laser Scheme. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2004, 16, 575–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J. Microwave Photonics. J. Light. Technol. 2009, 27, 314–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, S.; Harun, S.W.; Ahmad, H. Multi-Wavelength Brillouin Fiber Laser Using Brillouin-Rayleigh Scatterings in Distributed Raman Amplifier. Laser Phys. Lett. 2009, 6, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gong, Y. Tunable and Switchable Multi-Wavelength Erbium-Brillouin Random Fiber Laser Incorporating a Highly Nonlinear Fiber. J. Light. Technol. 2020, 38, 4093–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellemare, A.; Karasek, M.; Rochette, M.; LRochelle, S.; Tetu, M. Room Temperature Multifrequency Erbium-Doped Fiber Lasers Anchored on the ITU Frequency Grid. J. Light. Technol. 2000, 18, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Chu, M.J.; Lee, J.H. Wideband Multiwavelength Erbium-Doped Fiber Ring Laser with Frequency Shifted Feedback. Opt. Commun. 2001, 190, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhou, D.; Dong, F.; Ngo, N.Q. Room-Temperature Multiwavelength Erbium-Doped Fiber Ring Laser Employing Sinusoidal Phase-Modulation Feedback. Opt. Lett. 2003, 28, 893–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasseur, J.; Hanna, M.; Dudley, J.M.; Barry, J.R. Numerical and Theoretical Analysis of an Alternate Multiwavelength Mode-Locked Fiber Laser. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2005, 17, 2295–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, W.; Zhu, L.; Dong, M.; Lou, X.; Luo, F. Wavelength-Switchable and Stable-Ring-Cavity, Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser Based on Mach–Zehnder Interferometer and Tunable Filter. Laser Phys. 2018, 28, 045104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.-P.; Luo, Z.-C.; Xu, W.-C. Tunable and Switchable Multiwavelength Erbium-Doped Fiber Ring Laser Based on a Modified Dual-Pass Mach-Zehnder Interferometer. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 2135–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Kang, Z.; Qi, Y.; Jian, S. Tunable Dual-Wavelength Fiber Laser Based on an MMI Filter in a Cascaded Sagnac Loop Interferometer. Laser Phys. 2014, 24, 045102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.W.; Zhang, Z.X. All-Normal-Dispersion Multi-Wavelength Dissipative Soliton Yb-Doped Fiber Laser. Laser Phys. Lett. 2013, 10, 085105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Lou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Z. Random Distributed Feedback Fiber Laser at 2.1 μm. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 4923–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dong, X.; Shum, P.P.; Su, H. Tunable Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser Based on Random Distributed Feedback. IEEE Photonics J. 2014, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Quan, X.; Wu, H.; Gao, W.; Huang, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, S.; Fan, D.; Liu, J. 20 Watt-Level Single Transverse Mode Narrow Linewidth and Tunable Random Fiber Laser at 1.5 Μm Band. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 28795–28804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, P.; Mihailov, S.; Chen, L.; Bao, X. Time-Delay Signature Concealed Broadband Gain-Coupled Chaotic Laser with Fiber Random Grating Induced Distributed Feedback. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 109, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, M.; Bao, X.; Chen, L. Observation of Narrow Linewidth Spikes in the Coherent Brillouin Random Fiber Laser. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 1866–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Gao, S.; Saxena, B.; Chen, L.; Bao, X. Linearly Polarized Low-Noise Brillouin Random Fiber Laser. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Han, B.; Liu, Y. Tunable Narrowband Cascaded Random Raman Fiber Laser. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 21539–21550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lu, P.; Bao, X. Compact Single-End Pumped Brillouin Random Fiber Laser with Enhanced Distributed Feedback. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 4236–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Bao, X. Single-Mode SOA-Based 1kHz-Linewidth Dual-Wavelength Random Fiber Laser. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 15828–15837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovar, P.; Temporão, G.; Weid, J.P. von der Longitudinal Mode Dynamics in SOA-Based Random Feedback Fiber Lasers. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 31001–31012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawki, H.; Kotb, H.; Khalil, D. Modeling and Characterization of a Dual-Wavelength SOA-Based Single Longitudinal Mode Random Fiber Laser with Tunable Separation. OSA Contin. 2019, 2, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Wang, Z.; Wu, H.; Sun, W.; Zhang, L. Low-Threshold, High-Efficiency Random Fiber Laser with Linear Output. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2015, 27, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Han, M.; Xu, Z.; Du, Y.; Shu, X. Stable and Low-Threshold Random Fiber Laser via Anderson Localization. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 12987–12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, Z.; Sun, W.; He, Q.; Wei, Z.; Rao, Y.-J. 1.5 μm Low Threshold, High Efficiency Random Fiber Laser with Hybrid Erbium–Raman Gain. J. Light. Technol. 2018, 36, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, H.; Fan, M.; Zhang, L.; Rao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jia, X. High Power Random Fiber Laser with Short Cavity Length: Theoretical and Experimental Investigations. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2015, 21, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, L.; Song, J.; Wu, H.; Zhou, P.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; et al. Quasi-Kilowatt Random Fiber Laser. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 2613–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Li, J.Q.; Guo, J.Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H.H.; Hu, B.; Rao, Y.J.; Zhang, W.L. High-Power Low Spatial Coherence Random Fiber Laser. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 8738–8744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babin, S.A.; El-Taher, A.E.; Harper, P.; Podivilov, E.V.; Turitsyn, S.K. Tunable Random Fiber Laser. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 84, 021805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, J.; Ye, J.; Xu, J.; Yao, T.; Zhou, P. Tunable Random Raman Fiber Laser at 1.7 μm Region with High Spectral Purity. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 28800–28807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, P. Tunable Random Distributed Feedback Fiber Laser Operating at 1 μm. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 908–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, P. Powerful Narrow Linewidth Random Fiber Laser. Photonic Sens. 2017, 7, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhao, X.; Qin, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y. Single-Longitudinal-Mode Short-Cavity Brillouin Random Fiber Laser via Frequency Auto-Tracking with Unpumped-EDF Sagnac Loop. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 127, 104461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, S.; Lu, P.; Mihailov, S.; Chen, L.; Bao, X. Low-Noise Brillouin Random Fiber Laser with a Random Grating-Based Resonator. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 3197–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Qin, Z.; Liu, Z. Low-Noise Brillouin Random Fiber Laser with Auto-Tracking Dynamic Fiber Grating Based on a Saturable Absorption Ring. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 122, 104088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Qin, Z.; Liu, Z. Low-Noise Narrow-Linewidth Brillouin Random Fiber Laser with Dynamic Fiber Grating. In Proceedings of the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (2022), Paper JW3B.34, San Jose, CA, USA, 15 May 2022; Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; p. JW3B.34. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Z. Temporally Stable Random Fiber Laser Operates at 1070 Nm. IEEE Photonics J. 2015, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Qin, Z.; Liu, Z. Stabilized Narrow-Linewidth Brillouin Random Fiber Laser with a Double-Coupler Fiber Ring Resonator. J. Light. Technol. 2022, 40, 2988–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xiang, D.; Ou, Z.; Lu, P.; Bao, X. Random Fabry–Perot Resonator-Based Sub-KHz Brillouin Fiber Laser to Improve Spectral Resolution in Linewidth Measurement. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Lu, P.; Chen, L.; Bao, X. Tapered Fiber Based Brillouin Random Fiber Laser and Its Application for Linewidth Measurement. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 28353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Lu, C.; Tam, H.Y.; Wai, P.K.A. Reconfigurable Microwave Photonic Filter Using Multiwavelength Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2007, 19, 1334–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, R.; Pu, T. A Novel Technique to Generate High-Frequency Microwave Signal Based on High-Order Stimulated Brillouin Scattering. Acta Opt. Sin. 2010, 30, 1571–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehler, A.E.H.; Zeller, S.C.; Weingarten, K.J.; Keller, U. Broad Multiwavelength Source with 50 GHz Channel Spacing for Wavelength Division Multiplexing Applications in the Telecom C Band. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, S.H.; Shin, J.-U.; Park, Y.-J.; Kim, S.-B.; Park, S.; Sung, H.-K.; Baek, Y.-S.; Oh, K.-R. Multiwavelength Lasers for WDM-PON Optical Line Terminal Source by Silica Planar Lightwave Circuit Hybrid Integration. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2007, 19, 1622–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lu, P.; Mihailov, S.; Bao, X. Real-Time Physical Random Bit Generation at Gbps Based on Random Fiber Lasers. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 4796–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Ke, T.; Rao, Y.; Chiang, K.S. Fabry–Perot Optical Fiber Tip Sensor for High Temperature Measurement. Opt. Commun. 2010, 283, 3683–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-G.; Tran, T.V.A.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, S.B. Multiwavelength Raman-Fiber-Laser-Based Long-Distance Remote Sensor for Simultaneous Measurement of Strain and Temperature. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lu, P.; Mihailov, S.; Bao, X. Multi-Parameter Sensor Based on Random Fiber Lasers. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 095009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lu, P.; Mihailov, S.; Bao, X. Multi-Parameter Fiber-Optic Sensors Based on Fiber Random Grating. In Proceedings of the 2017 25th Optical Fiber Sensors Conference (OFS), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 24–28 April 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, S.; Lu, P.; Mihailov, S.; Bao, X. Highly Sensitive Fiber Random-Grating-Based Random Laser Sensor for Ultrasound Detection. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 1353–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Lu, P.; Gao, S.; Xiang, D.; Lu, P.; Mihailov, S.; Bao, X. Optical Fiber Random Grating-Based Multiparameter Sensor. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 5514–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Han, B.; Wang, Z.; Genty, G.; Feng, G.; Liang, H. Temporal Ghost Imaging with Random Fiber Lasers. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 9957–9964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.S.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.L. Novel Illumination for Imaging Using Self-Modulated Coherent Random Fiber Laser. In Proceedings of the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (2022), Paper JW3B.192, San Jose, CA, USA, 15 May 2022; Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; p. JW3B.192. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.; Bao, X. High-Speed Random Bit Generation via Brillouin Random Fiber Laser with Non-Uniform Fibers. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2017, 29, 1352–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Lu, P.; Xu, Y.; Gao, S.; Chen, L.; Bao, X. Truly Random Bit Generation Based on a Novel Random Brillouin Fiber Laser. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, S.W.; Shirazi, M.R.; Ahmad, H. A New Configuration of Multi-Wavelength Brillouin Fiber Laser. Laser Phys. Lett. 2008, 5, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Gao, S.; Saxena, B.; Chen, L.; Bao, X. Multiwavelength Coherent Brillouin Random Fiber Laser with Ultrahigh Optical Signal-to-Noise Ratio. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2018, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.; Bao, X. Linearly Polarized Multi-Wavelength Comb via Rayleigh Scattering Induced Brillouin Random Lasing Resonance. In Proceedings of the 2018 Optical Fiber Communications Conference and Exposition (OFC), San Diego, CA, USA, 11–15 March 2018; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Chen, L.; Bao, X. Linearly Polarized Multi-Wavelength Fiber Laser Comb via Brillouin Random Lasing Oscillation. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2018, 30, 1005–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Lu, P.; Mihailov, S.; Chen, L.; Bao, X. Multi-Wavelength Brillouin Random Fiber Laser via Distributed Feedback From a Random Fiber Grating. J. Light. Technol. 2018, 36, 2122–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gong, Y. Switchable Wide-Band Multi-Wavelength Brillouin-Erbium Fiber Laser Based on Random Distributed Feedback. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 218614–218620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Parameter Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Dispersion (D) @1550 nm | 0.5753183 ps/nm‧km |
| Pump wavelength (λp) | 1550 nm |
| Signal wavelength (λs) @15th-Stokes | 1551.14 nm |
| Zero-dispersion wavelength (λ0) | 1521.78962 nm |
| Nonlinear coefficient (γ) | 10 W−1‧km−1 |
| Pump power (P) | 50 mW |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, Y.; Ma, S.; Ji, Q.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Qin, Z.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y. Frequency Comb Generation Based on Brillouin Random Lasing Oscillation and Four-Wave Mixing Assisted with Nonlinear Optical Loop Mirror. Photonics 2023, 10, 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030296
Pang Y, Ma S, Ji Q, Zhao X, Li Y, Qin Z, Liu Z, Xu Y. Frequency Comb Generation Based on Brillouin Random Lasing Oscillation and Four-Wave Mixing Assisted with Nonlinear Optical Loop Mirror. Photonics. 2023; 10(3):296. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030296
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Yuxi, Shaonian Ma, Qiang Ji, Xian Zhao, Yongfu Li, Zengguang Qin, Zhaojun Liu, and Yanping Xu. 2023. "Frequency Comb Generation Based on Brillouin Random Lasing Oscillation and Four-Wave Mixing Assisted with Nonlinear Optical Loop Mirror" Photonics 10, no. 3: 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030296
APA StylePang, Y., Ma, S., Ji, Q., Zhao, X., Li, Y., Qin, Z., Liu, Z., & Xu, Y. (2023). Frequency Comb Generation Based on Brillouin Random Lasing Oscillation and Four-Wave Mixing Assisted with Nonlinear Optical Loop Mirror. Photonics, 10(3), 296. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030296








