Optical Manipulation of Fibroblasts with Femtosecond Pulse and CW Laser
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
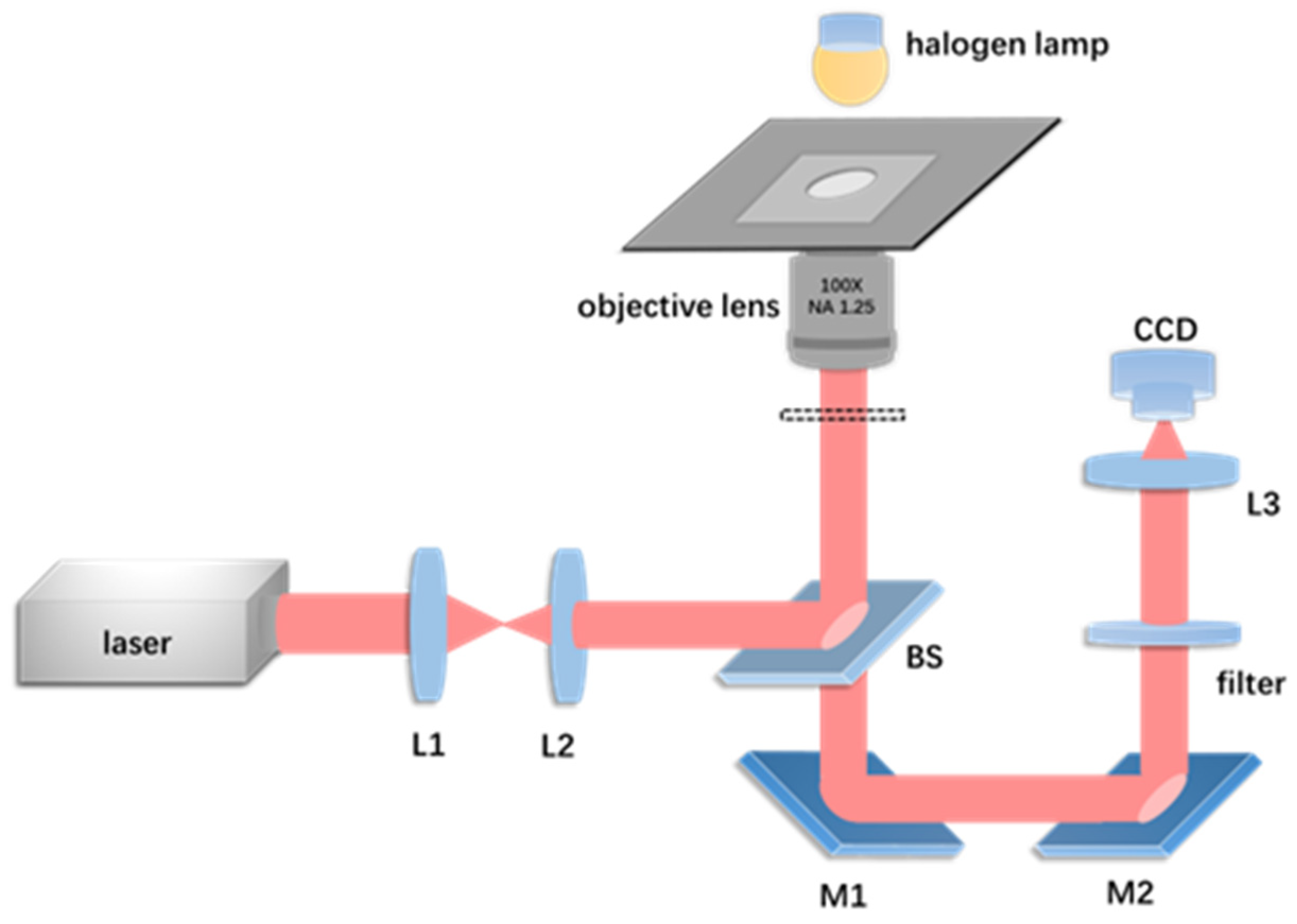
2.1. Experimental Setup and Materials
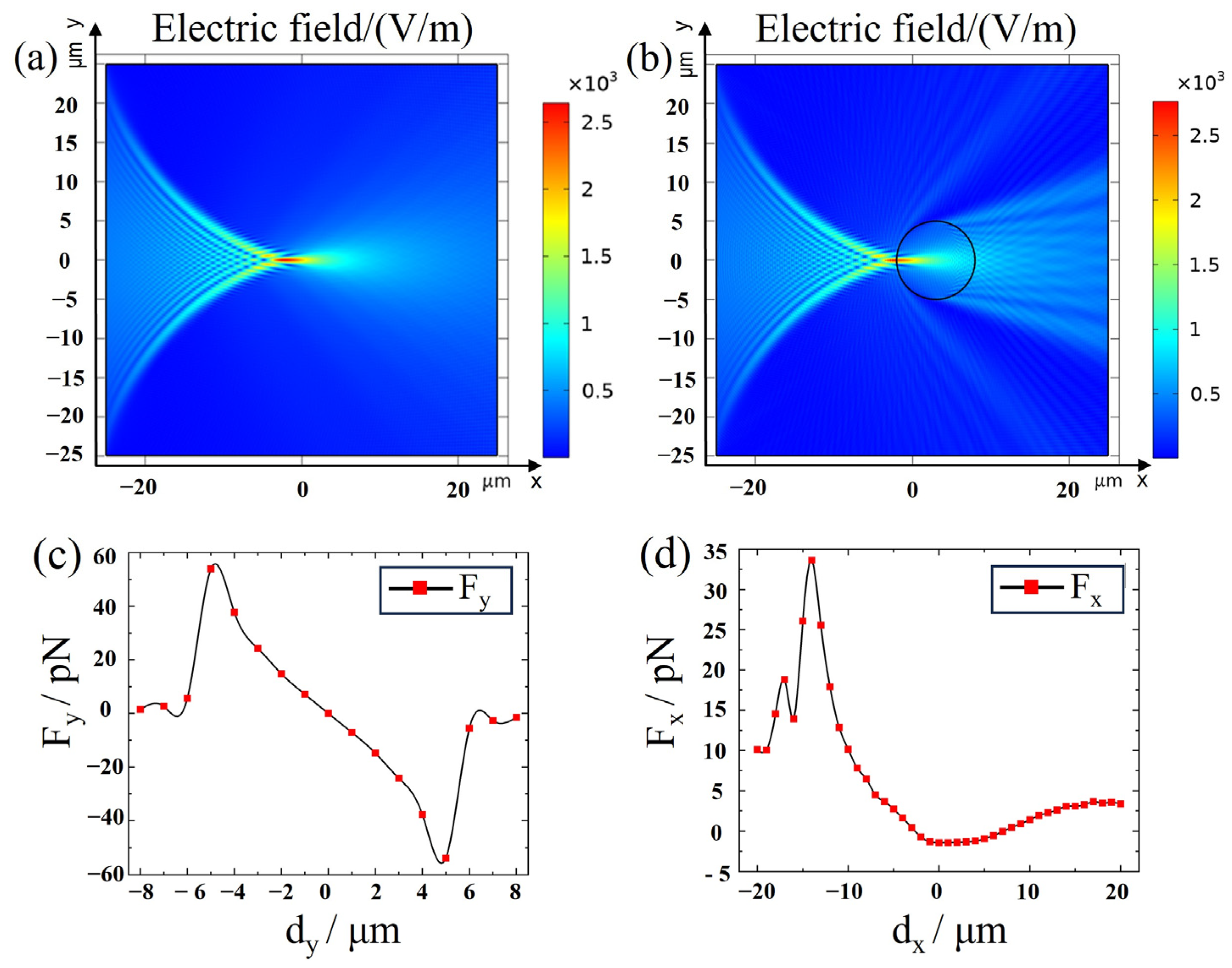
2.2. Electromagnetic Theory Model
3. Results and Discussion
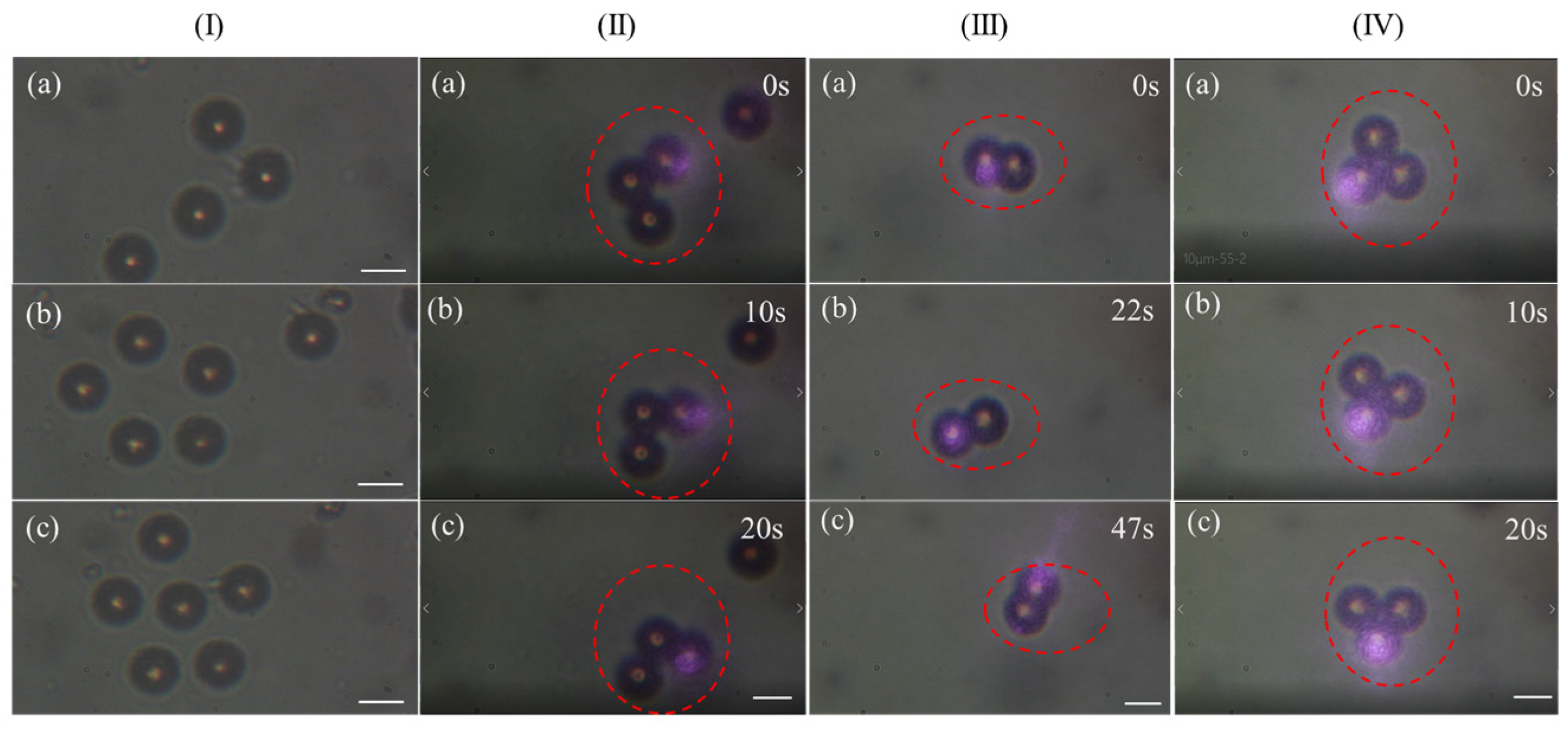
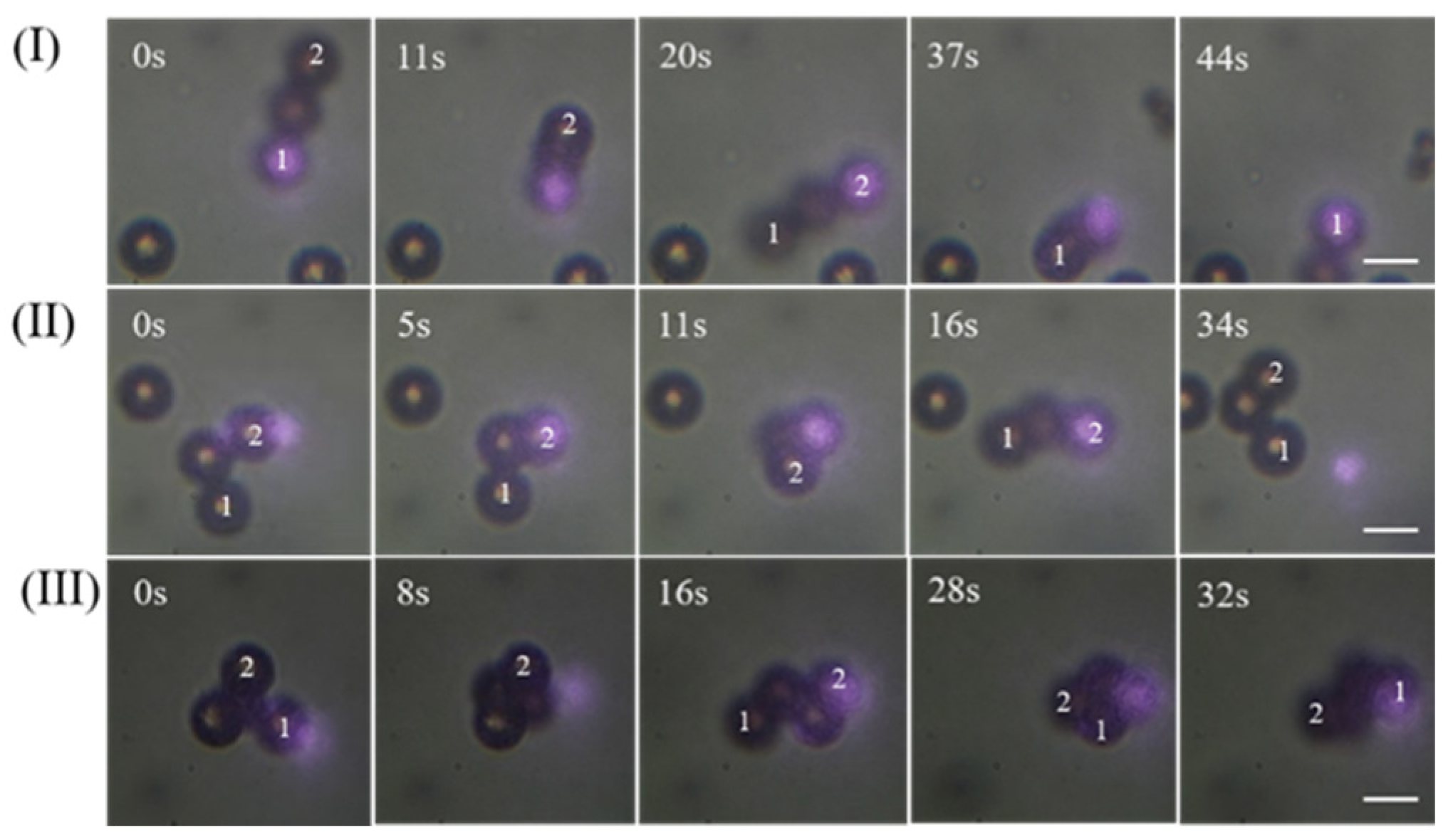
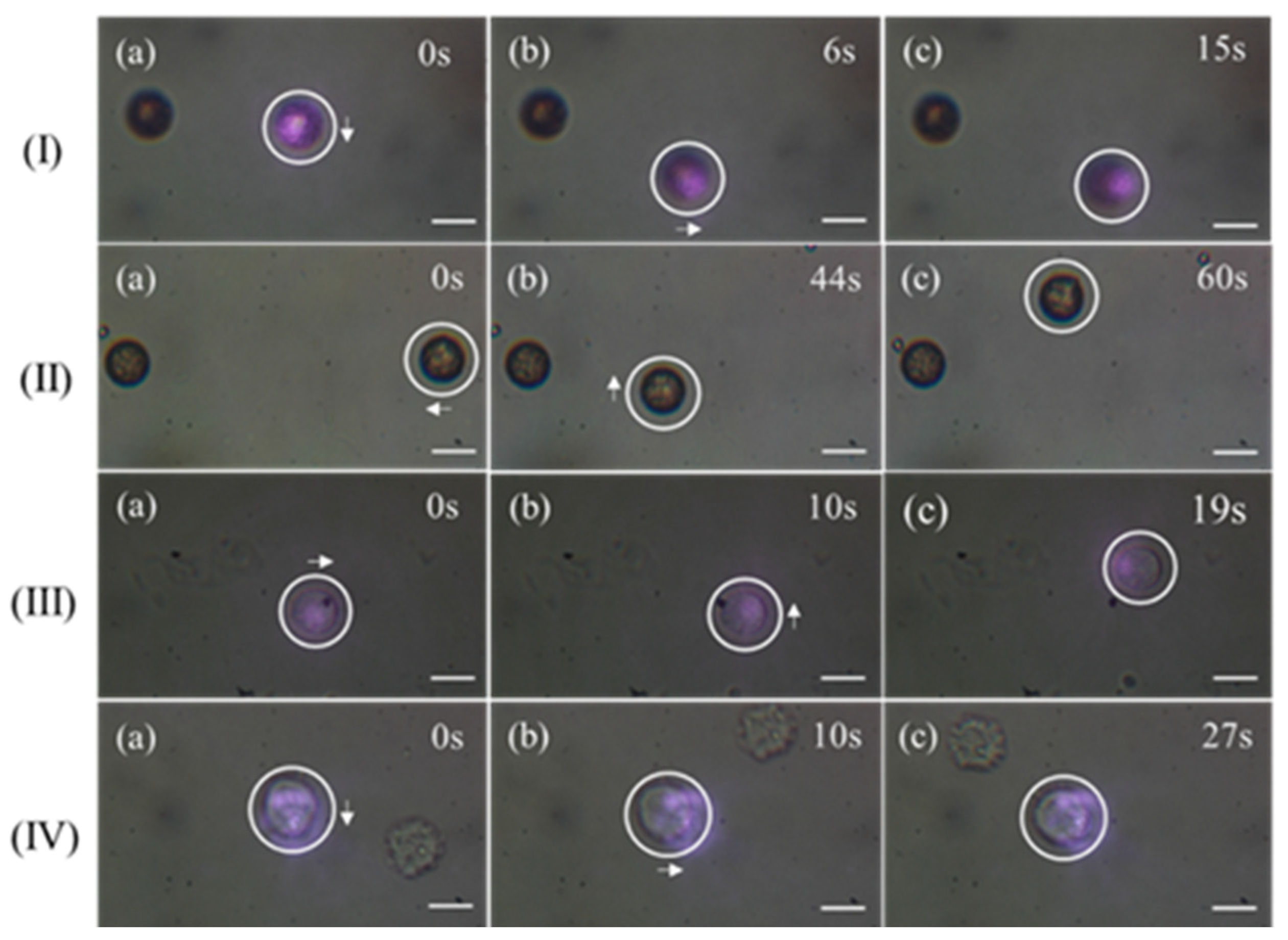
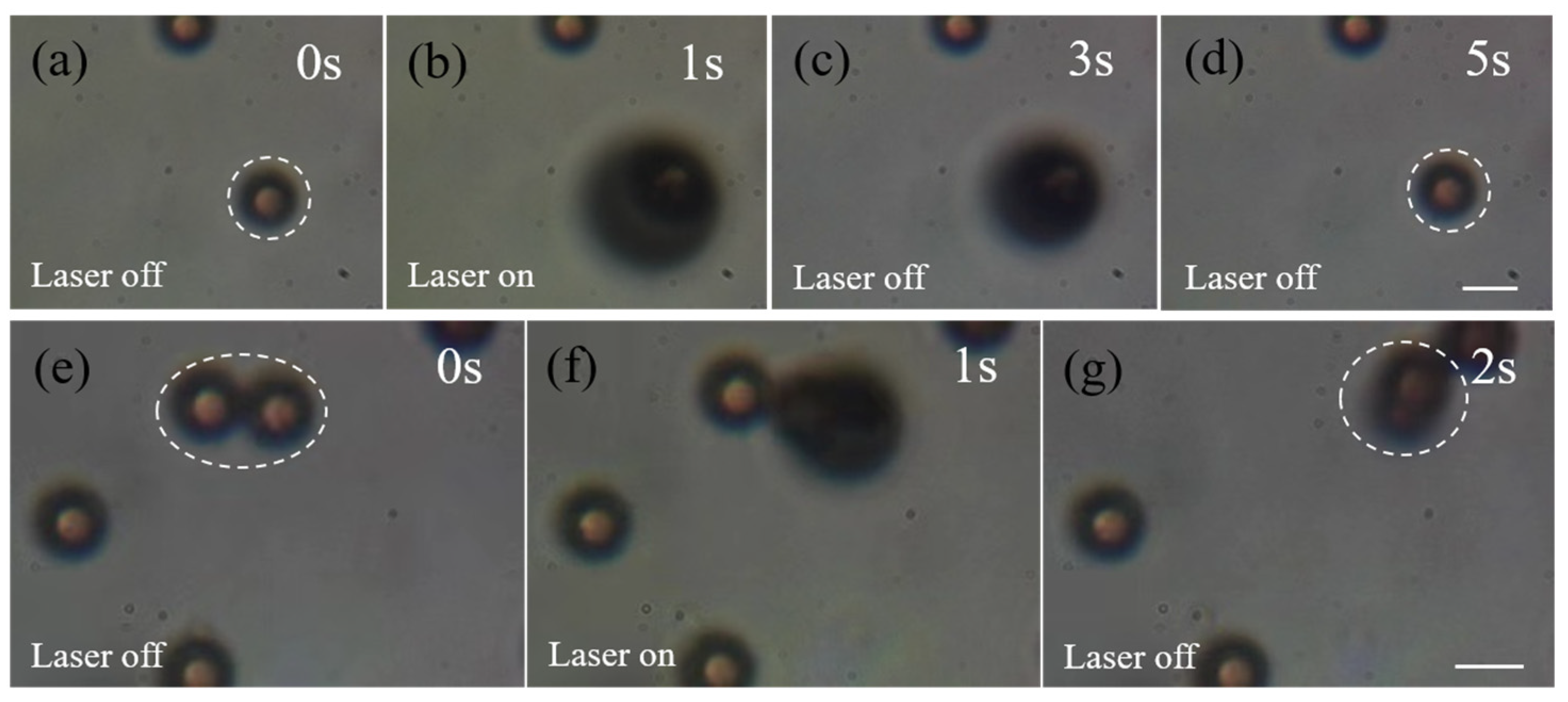
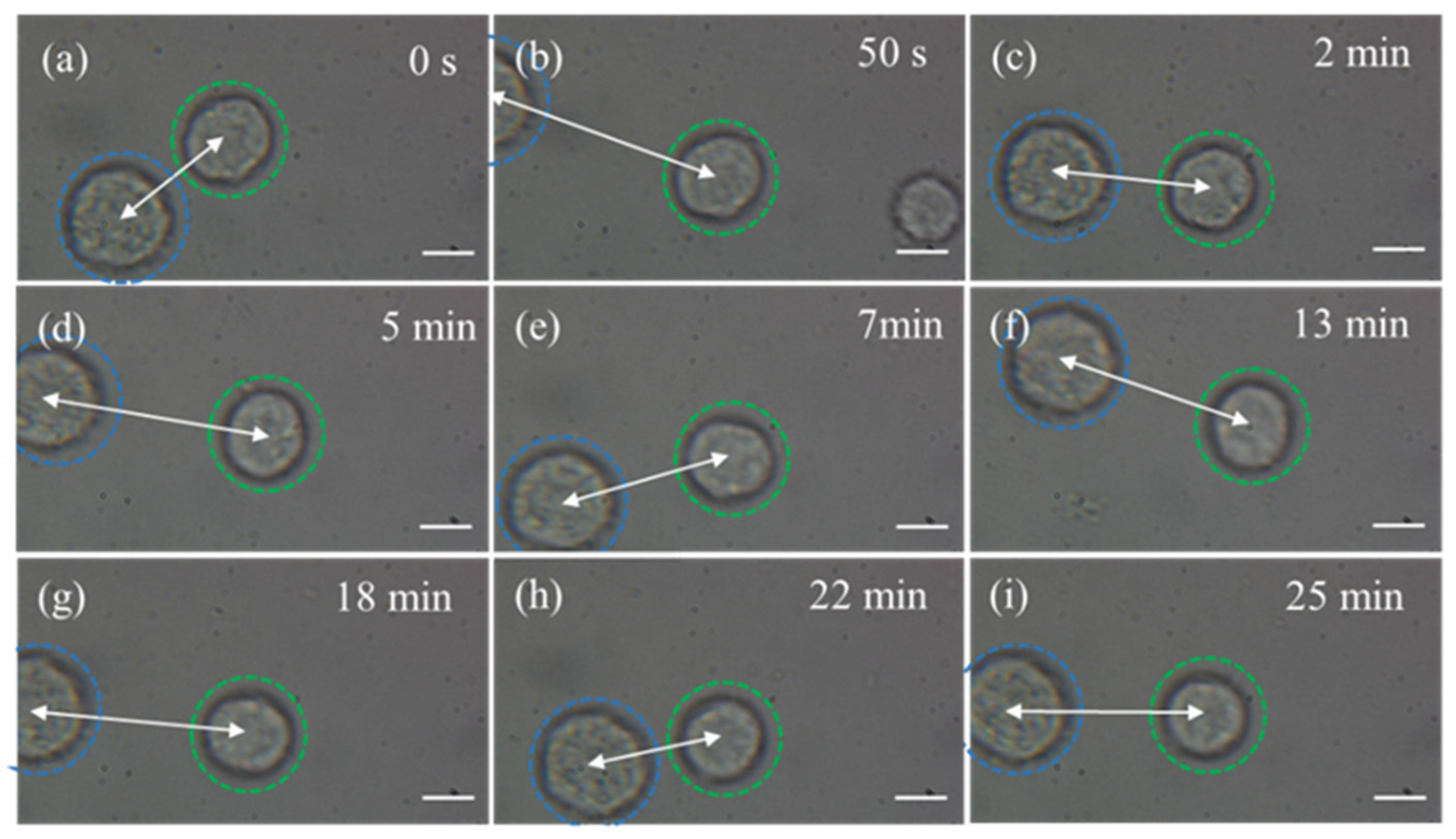
3.1. Capturing Objects with 808 nm CW Laser
3.2. Capturing Objects with 1030 nm Femtosecond Pulse Laser
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, F.; Gong, L.; Kuai, Y.; Tang, X.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, D. Controllable Optofluidic Assembly of Biological Cells Using an All-Dielectric One-Dimensional Photonic Crystal. Photonics Res. 2021, 10, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghoff, K.; Gross, W.; Eisentraut, M.; Kress, H. Using Blinking Optical Tweezers to Study Cell Rheology During Initial Cell-Particle Contact. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 3527–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsetti, S.; Dholakia, K. Optical manipulation: Advances for biophotonics in the 21st century. J. Biomed. Opt. 2021, 26, 070602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesce, G.; Jones, P.H.; Maragò, O.M.; Volpe, G. Optical Tweezers: Theory and Practice. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2020, 135, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maragò, O.M.; Jones, P.H.; Gucciardi, P.G.; Volpe, G.; Ferrari, A.C. Optical Trapping and Manipulation of Nanostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashkin, A. Acceleration and Trapping of Particles by Radiation Pressure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1970, 24, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkin, A. Atomic-Beam Deflection by Resonance-Radiation Pressure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1970, 25, 1321–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkin, A. History of Optical Trapping and Manipulation of Small-Neutral Particle, Atoms, and Molecules. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2000, 6, 841–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, J.E.; McLeod, E. Fundamental Limits of Optical Tweezer Nanoparticle Manipulation Speeds. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 2440–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshina, M.; Yokoshi, N.; Ishihara, H. Nanoscale Rotational Optical Manipulation. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 14980–14993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, O.E.C.; Qiu, H.; Lunn, D.J.; Rowden, J.; Harniman, R.L.; Hudson, Z.M.; Winnik, M.A.; Miles, M.J.; Manners, I. Transformation and Patterning of Supermicelles Using Dynamic Holographic Assembly. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, Y.; Qi, H.; Ruan, L. Manipulation of Microscale Fluid Using Laser-Irradiated Nanoparticle Arrays. Plasmonics 2019, 14, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Kong, M.; Wang, Z.; Costa, K.D.; Li, R.A.; Sun, D. Enhanced Cell Sorting and Manipulation with Combined Optical Tweezer and Microfluidic Chip Technologies. Lab A Chip 2011, 11, 3656–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsaidov, U.; Scrimgeour, J.; Timp, W.; Beck, K.; Mir, M.; Matsudaira, P.; Timp, G. Live Cell Lithography: Using Optical Tweezers to Create Synthetic Tissue. Lab A Chip 2008, 8, 2174–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouger, V.; Bordet, G.; Couillault, C.; Monneret, S.; Mailfert, S.; Ewbank, J.J.; Pujol, N.; Marguet, D. Independent Synchronized Control and Visualization of Interactions between Living Cells and Organisms. Biophys. J. 2014, 106, 2096–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Yuan, L. HACF-Based Optical Tweezers Available for Living Cells Manipulating and Sterile Transporting. Opt. Commun. 2018, 427, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Ge, C.-X.; Wu, Z.-S. Optical Trapping of Chiral Particles by Dual Laser Beams. Photonics 2023, 10, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Tang, X.; Min, C.; Rui, G.; Kuai, Y.; Lu, F.; Wang, P.; Ming, H.; Zhan, Q.; Yuan, X.; et al. Optical Trapping with Focused Surface Waves. Ann. Der Phys. 2020, 532, 1900497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, F.; Zhang, W.; Yu, W.; Zhu, W.; Premaratne, M.; Mei, T.; Xiao, F.; Zhao, J. Optical Trapping of Single Nano-Size Particles Using a Plasmonic Nanocavity. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2020, 32, 475301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarshar, M.; Wong, W.T.; Anvari, B. Comparative study of methods to calibrate the stiffness of a single-beam gradient-force optical tweezers over various laser trapping powers. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 115001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Mameren, J.; Gross, P.; Farge, G.; Hooijman, P.; Modesti, M.; Falkenberg, M.; Wuite, G. Unraveling the structure of DNA during overstretching by using multicolor, single-molecule fluorescence imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18231–18236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, C.; Alexander, L.; Maciuba, K.; Kaiser, C.M. Single-Molecule Studies of Protein Folding with Optical Tweezers. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2020, 89, 443–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiner, S.M.; Koo, P.K.; Zhao, Y.; Mochrie, S.G.J.; King, M.C. The tethering of chromatin to the nuclear envelope supports nuclear mechanics. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.-C.; Wei, X.-B.; Zhou, J.-H.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Li, Y.-M. Trapping red blood cells in living animals using optical tweezers. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, P.; Liu, Y.; Keeler, E.G.; Cruz, N.M.; Freedman, B.S.; Lin, L.Y. Optical tweezers system for live stem cell organization at the single-cell level. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wu, T.; Gong, Z.; Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ferraro, P.; Li, B. Lipid droplets as endogenous intracellular microlenses. Light Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-C.; Cheng, C.-J. Holographic Optical Tweezers: Techniques and Biomedical Applications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Chen, Q.; He, M.; Zhang, X.; Qi, H.; Yan, Y. Plasmonic Optical Tweezers for Particle Manipulation: Principles, Methods, and Applications. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 6105–6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, R.; Shao, S.; Xie, F.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, S. Capture Dynamics of Dielectric Microparticles in Hollow-Core-Fiber-Based Optical Traps. Photonics 2023, 10, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Chen, Z.; Ponce, C.; Zheng, Y. Optothermal rotation of micro-/nano-objects. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 2208–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Peng, X.; Wei, X.; Mao, Z.; Xie, C.; Zheng, Y. Thermophoretic Tweezers for Low-Power and Versatile Manipulation of Biological Cells. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3147–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delinassios, J.G.; Hoffman, R.M. The cancer-inhibitory effects of proliferating tumor-residing fibroblasts. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.B.; Chan, C.T. Lateral Optical Force on Chiral Particles Near a Surface. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y.; He, M.; Gao, B.; Qi, H. Nanoparticle manipulation using plasmonic optical tweezers based on particle sizes and refractive indices. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 34092–34105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghese, F.; Denti, P.; Saija, R.; Lati, M.A. Optical trapping of nonspherical particles in the T-matrix formalism. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 11984–11998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhongfu, W.; Zhihai, L.; Chengkai, G.; Jun, Y.; Libo, Y. Numerical Simulation and Experiments of Two Fiber Optical Tweezers. Acta Opt. Sin. 2008, 28, 1971–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minjun, Y.; Wei, Z.; Wuzhou, S. Photothermal Effect Based Single Fiber Trapping Method and Simulation Analysis. Chin. J. Lasers 2019, 46, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.-C.; Liu, A.-Y.; Ji, F. Opto-thermal oscillation and trapping of light absorbing particles. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 29730–29737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmler, M.; Fratz, M.; Giel, D.M.; Saum, N.; Brandenburg, A.; Hoffmann, C. Noninvasive time-dependent cytometry monitoring by digital holography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2007, 12, 064002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabuig, A.; Mugnano, M.; Miccio, L.; Grilli, S.; Ferraro, P. Investigating fibroblast cells under “safe” and “injurious” blue-light exposure by holographic microscopy. J. Biophotonics 2016, 10, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.-L.; Xing, Q.-R.; Wang, K.; Lang, L.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Chai, L.; Wang, Q.-Y. Optical trapping of red blood cells and two-photon excitation-based photodynamic study using a femtosecond laser. Opt. Commun. 2005, 256, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Sosa, V.; Quinto-Su, P.A. Transient trapping of two microparticles interacting with optical tweezers and cavitation bubbles. J. Opt. 2016, 18, 105301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakhov, A.; Astafiev, A.; Nadtochenko, V. Microparticle manipulation using femtosecond photonic nanojet-assisted laser cavitation. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 1858–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 808 nm PS | 808 nm Fibroblasts | 1030 nm PS | 1030 nm Fibroblasts | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power (mW) | Velocity (μm/s) | Power (mW) | Velocity (μm/s) | Power (mW) | Velocity (μm/s) | Power (mW) | Velocity (μm/s) |
| 15.34 | 1.719 | 62.88 | 0.879 | 0.96 | 2.344 | 4.30 | 1.758 |
| 18.65 | 1.914 | 67.56 | 1.270 | 1.16 | 2.637 | 5.90 | 2.246 |
| 21.53 | 2.109 | 71.76 | 1.456 | 1.18 | 2.832 | 7.36 | 2.441 |
| 24.65 | 2.246 | 75.79 | 1.563 | 1.36 | 3.223 | 8.62 | 3.555 |
| 27.40 | 2.441 | 80.26 | 1.718 | 1.59 | 3.613 | 9.68 | 3.809 |
| 32.81 | 2.637 | 84.42 | 1.855 | 1.78 | 3.809 | 10.16 | 4.004 |
| 36.04 | 2.832 | 88.60 | 1.914 | 1.99 | 4.004 | 10.60 | 4.590 |
| 41.42 | 3.223 | 92.39 | 1.992 | 2.19 | 4.199 | 11.44 | 4.883 |
| 44.53 | 3.418 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Cai, S.; Feng, G. Optical Manipulation of Fibroblasts with Femtosecond Pulse and CW Laser. Photonics 2024, 11, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11030248
Zhang X, Wu Y, Cai S, Feng G. Optical Manipulation of Fibroblasts with Femtosecond Pulse and CW Laser. Photonics. 2024; 11(3):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11030248
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xia, Yi Wu, Siao Cai, and Guoying Feng. 2024. "Optical Manipulation of Fibroblasts with Femtosecond Pulse and CW Laser" Photonics 11, no. 3: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11030248
APA StyleZhang, X., Wu, Y., Cai, S., & Feng, G. (2024). Optical Manipulation of Fibroblasts with Femtosecond Pulse and CW Laser. Photonics, 11(3), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11030248




