Sacrificial Zinc Oxide Strategy-Enhanced Mesoporosity in MIL-53-Derived Iron–Carbon Composite for Methylene Blue Adsorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
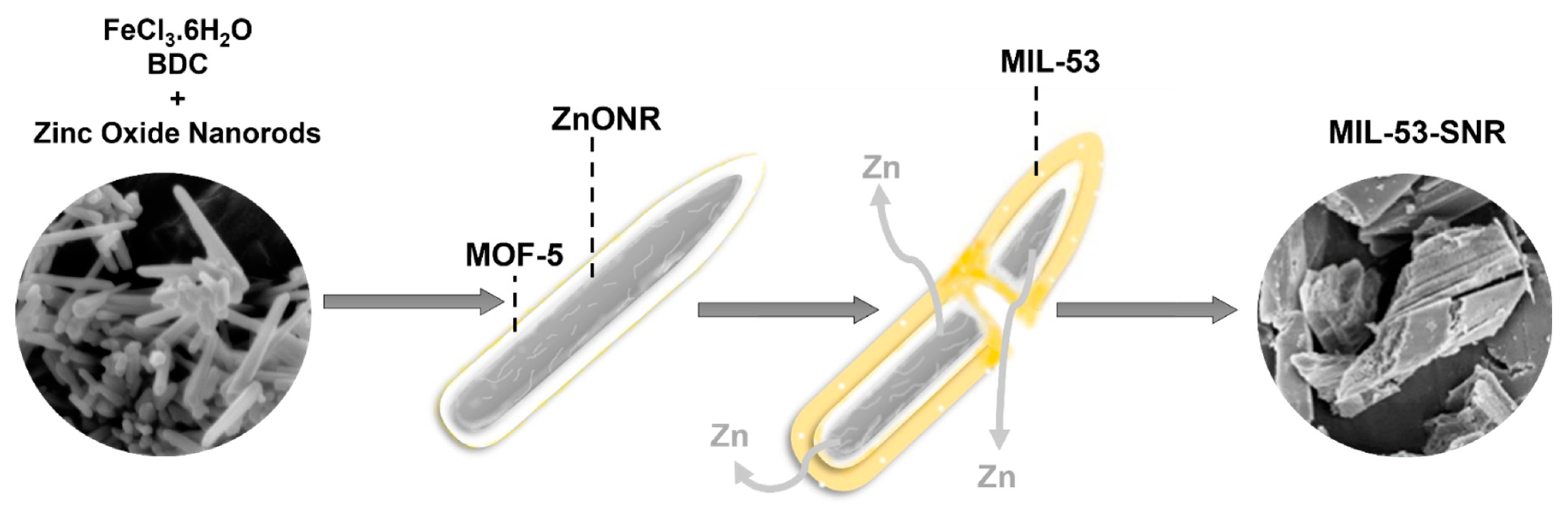
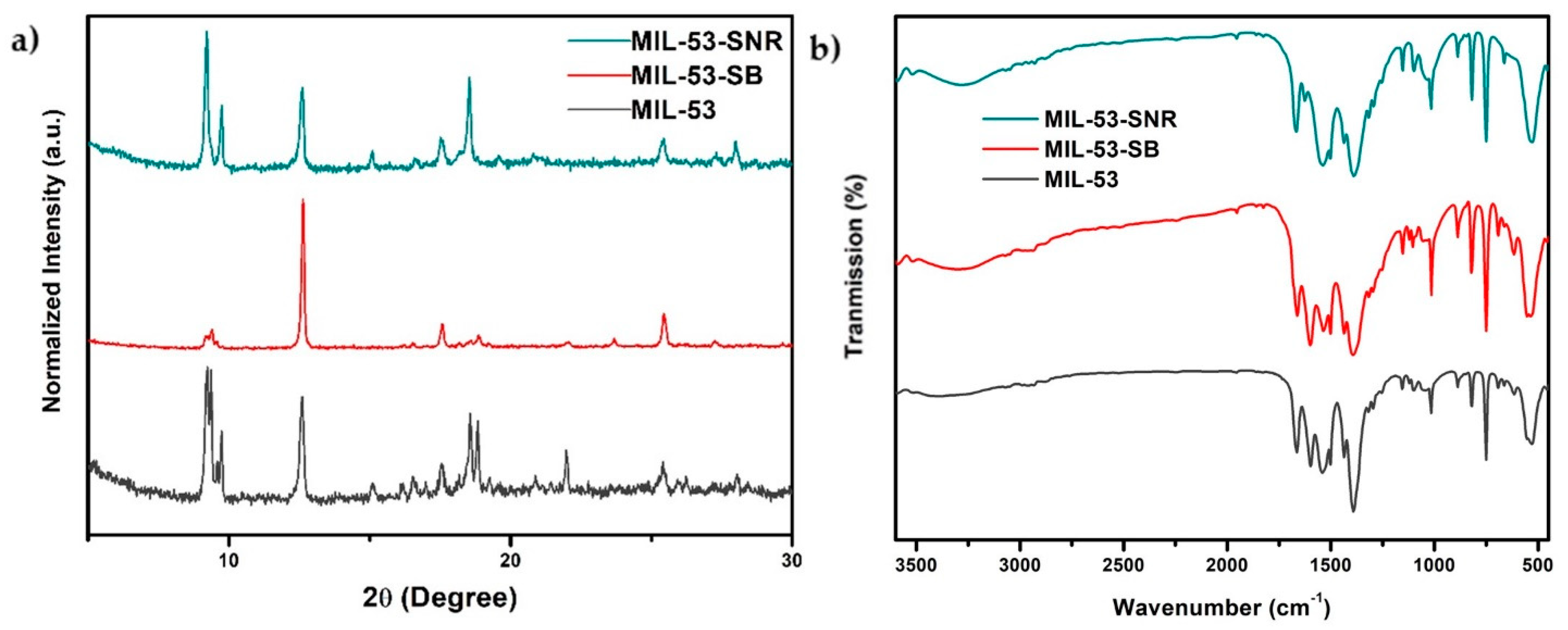
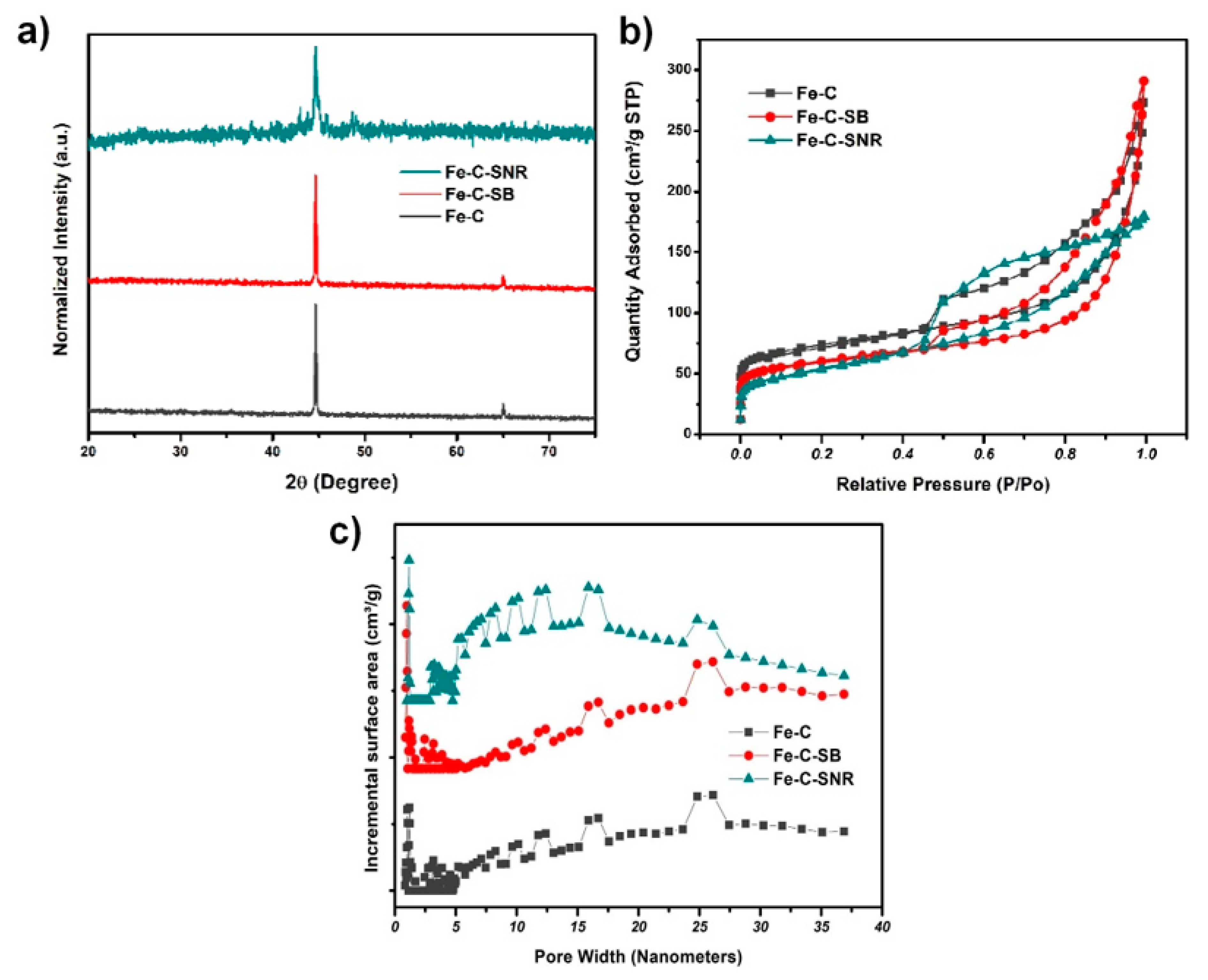
2.1. Characterizations
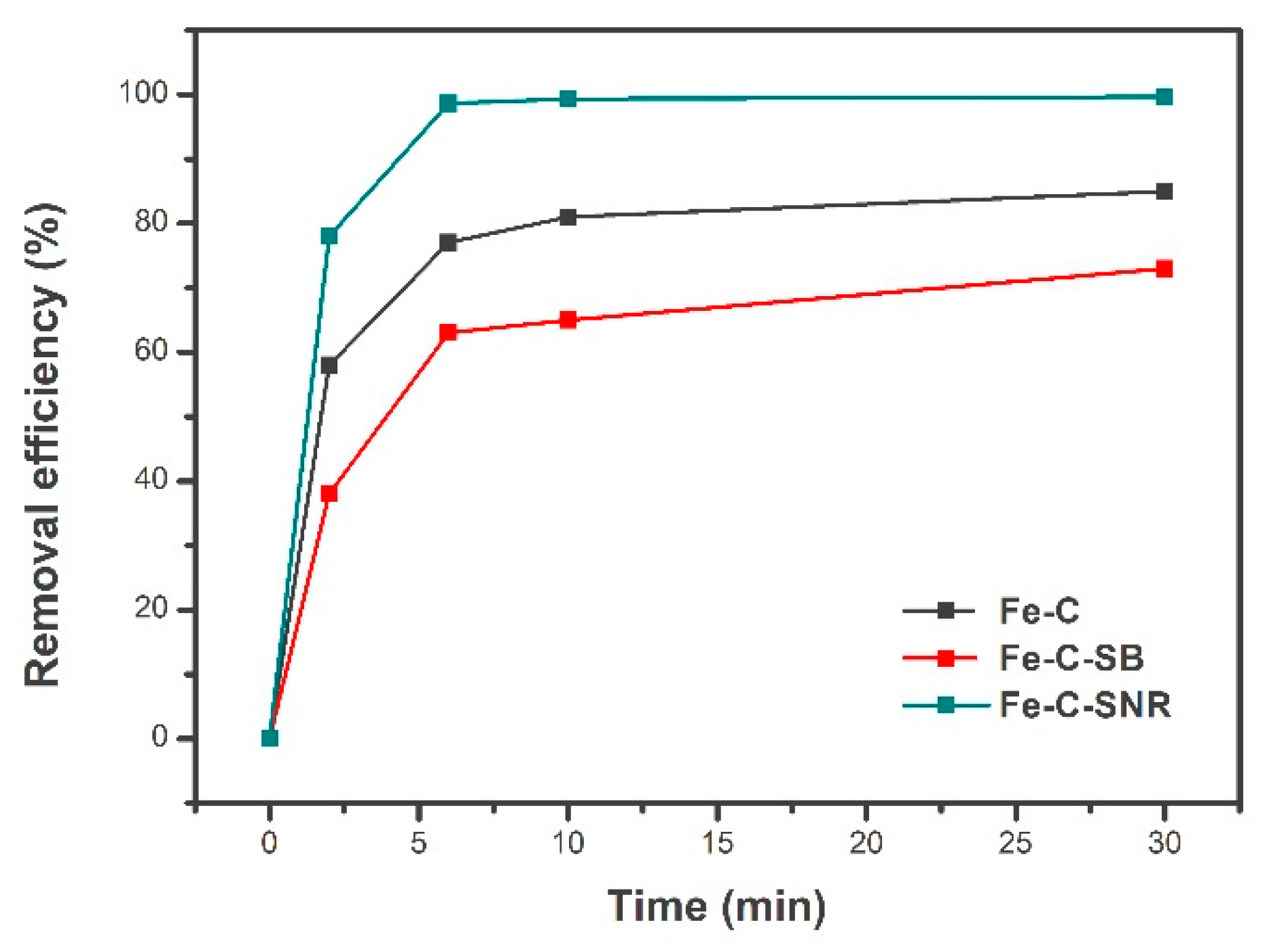
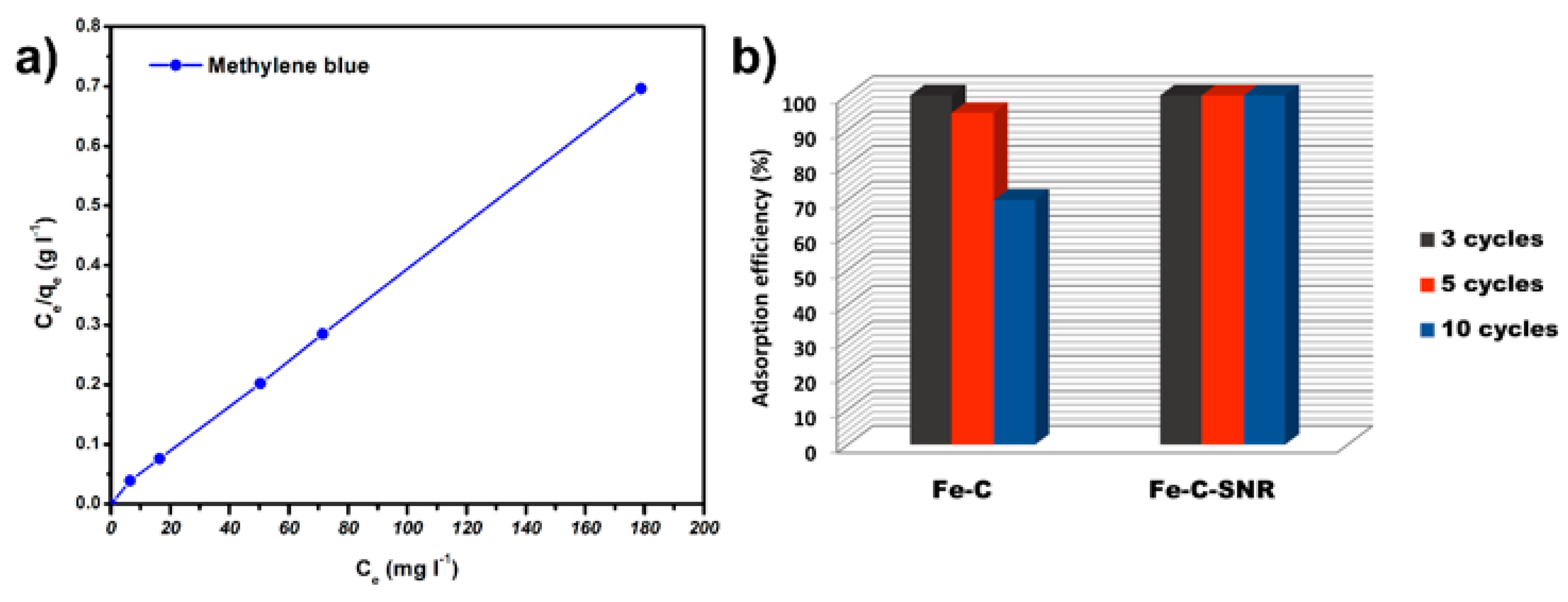
2.2. Adsorption Properties
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Methods
3.2. Characterizations
3.3. Adsorption Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Mwamulima, T.; Song, S.; Peng, C. Removal of Crystal Violet and Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions Using the Fly Ash-Based Adsorbent Material-Supported Zero-Valent Iron. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 250, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Hashim, R. Scavenging Behaviour of Meranti Sawdust in the Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katheresan, V.; Kansedo, J.; Lau, S.Y. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4676–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.-D.; Le, H.T.T.; Nguyen, D.A.; Duc, D.; Dinh, L.; Nguyen, D. A Magnetic Hierarchical Zero-Valent Iron Nanoflake-Decorated Graphene Nanoplate Composite for Simultaneous Adsorption and Reductive Degradation of Rhodamine B. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 9083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Ida, S.; Staykov, A.; Akbay, T.; Hagiwara, H.; Matsuda, J.; Kaneko, K.; Ishihara, T. Ni-Fe Nitride Nanoplates on Nitrogen-Doped Graphene as a Synergistic Catalyst for Reversible Oxygen Evolution Reaction and Rechargeable Zn-Air Battery. Small 2017, 13, 1700099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yue, Q.; Kong, W.; Gao, B.; Wang, W.; Jiang, W. Degradation of Chlortetracycline with Simultaneous Removal of Copper (II) from Aqueous Solution Using Wheat Straw-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, K.; Liu, W.; Xu, Y.; Liang, P.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X. Versatile Zero Valent Iron Applied in Anaerobic Membrane Reactor for Treating Municipal Wastewater: Performances and Mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 123000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, T.; Guan, X. The Influences of Iron Characteristics, Operating Conditions and Solution Chemistry on Contaminants Removal by Zero-Valent Iron: A Review. Water Res. 2016, 100, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Liu, H. The Use of Zero-Valent Iron for Groundwater Remediation and Wastewater Treatment: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 267, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaibu, S.E.; Adekola, F.A.; Adegoke, H.I.; Ayanda, O.S. A Comparative Study of the Adsorption of Methylene Blue onto Synthesized Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron-Bamboo and Manganese-Bamboo Composites. Materials 2014, 7, 4493–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ezzatahmadi, N.; Ayoko, G.A.; Millar, G.J.; Speight, R.; Yan, C.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Xi, Y. Clay-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Composite Materials for the Remediation of Contaminated Aqueous Solutions: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 312, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, H.; Park, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, S. Effects of Washing Solution and Drying Condition on Reactivity of Nano-Scale Zero Valent Irons (NZVIs) Synthesized by Borohydride Reduction. Chemosphere 2014, 97, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, W.; Fan, J.; Wang, W.; Bai, N.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Kong, B.; Yang, J.; Zhao, D.; et al. Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron in Mesoporous Carbon (NZVI@C): Stable Nanoparticles for Metal Extraction and Catalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 4478–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Damtie, M.M.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Wei, W.; Jin, J.; Phong Vo, H.N.; Ye, J.S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.F.; Yu, Z.M.; et al. Bentonite-Supported Nano Zero-Valent Iron Composite as a Green Catalyst for Bisphenol A Degradation: Preparation, Performance, and Mechanism of Action. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhao, L.; Yang, X. Enhanced Chitosan/Fe 0-Nanoparticles Beads for Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 189–190, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zheng, S.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L.; Xi, Y. Degradation of Simazine from Aqueous Solutions by Diatomite-Supported Nanosized Zero-Valent Iron Composite Materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Li, T.; Zhou, C.; Qi, C. Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles (NZVI) Supported by Kaolinite for CuII and NiII Ion Removal by Adsorption: Kinetics, Thermodynamics, and Mechanism. Aust. J. Chem. 2015, 68, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mystrioti, C.; Sparis, D.; Papasiopi, N.; Xenidis, A.; Dermatas, D.; Chrysochoou, M. Assessment of Polyphenol Coated Nano Zero Valent Iron for Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Contaminated Waters. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 94, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.Y.; Chang, M.C.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, P.E. Using Resin Supported Nano Zero-Valent Iron Particles for Decoloration of Acid Blue 113 Azo Dye Solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; Bi, D. The Removal of Chromium (VI) and Lead (II) from Groundwater Using Sepiolite-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (S-NZVI). Chemosphere 2015, 138, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavian, S.; An, H.; Chun, D.; Moon, J. Activated Carbon Impregnated by Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles (AC/NZVI) Optimized for Simultaneous Adsorption and Reduction of Aqueous Hexavalent Chromium: Material Characterizations and Kinetic Studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lei, M. Recyclable Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron-Based Magnetic Polydopamine Coated Nanomaterials for the Adsorption and Removal of Phenanthrene and Anthracene. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2017, 18, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tristão, J.C.; de Mendonça, F.G.; Lago, R.M.; Ardisson, J.D. Controlled Formation of Reactive Fe Particles Dispersed in a Carbon Matrix Active for the Oxidation of Aqueous Contaminants with H2O2. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tran, T.; Bui, Q.T.P.; Nguyen, T.D.; Thanh Ho, V.T.; Bach, L.G. Application of Response Surface Methodology to Optimize the Fabrication of ZnCl2-Activated Carbon from Sugarcane Bagasse for the Removal of Cu2+. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 2047–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Thuan, T.; Quynh, B.T.P.; Nguyen, T.D.; Ho, V.T.T.; Bach, L.G. Response Surface Methodology Approach for Optimization of Cu2+, Ni2+ and Pb2+ Adsorption Using KOH-Activated Carbon from Banana Peel. Surf. Interfaces 2017, 6, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Ruan, W.; Hu, J.; Fan, M.; Cao, R.; Wei, X. Optimizing the Removal of Rhodamine B in Aqueous Solutions by Reduced Graphene Oxide-Supported Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron (NZVI/RGO) Using an Artificial Neural Network-Genetic Algorithm (ANN-GA). Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefaniuk, M.; Oleszczuk, P.; Ok, Y.S. Review on Nano Zerovalent Iron (NZVI): From Synthesis to Environmental Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Gu, J. In Situ Carbothermal Synthesis of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Functionalized Porous Carbon from Metal-Organic Frameworks for Efficient Detoxification of Chromium(VI). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 2018, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, J.; Song, H.; Zuo, S.; Chen, X.; Xia, D.; Li, D. MIL-53(Fe)-Derived Fe2O3 with Oxygen Vacancy as Fenton-like Photocatalysts for the Elimination of Toxic Organics in Wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 246, 118971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Jing, F.; Shen, L.; Qin, N.; Wu, L. MIL-53(Fe) as a Highly Efficient Bifunctional Photocatalyst for the Simultaneous Reduction of Cr(VI) and Oxidation of Dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 287, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.A.; Le, G.H.; Dao, C.D.; Dang, L.Q.; Nguyen, K.T.; Nguyen, Q.K.; Dang, P.T.; Tran, H.T.K.; Duong, Q.T.; Nguyen, T.V.; et al. Arsenic Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption Using Novel MIL-53(Fe) as a Highly Efficient Adsorbent. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 5261–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serre, C.; Millange, F.; Thouvenot, C.; Noguès, M.; Marsolier, G.; Louër, D.; Férey, G. Very Large Breathing Effect in the First Nanoporous Chromium(III)-Based Solids: MIL-53 or CrIII(OH)·{O2C-C6H4- CO2}·{HO2C-C6H4 -CO2H}x·H2Oy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 13519–13526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.; Park, S.; Oh, M. Coordination Polymer Nanorods of Fe-MIL-88B and Their Utilization for Selective Preparation of Hematite and Magnetite Nanorods. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 4138–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherb, C.; Schödel, A.; Bein, T. Metal-Organic Frameworks Directing the Structure of Metal-Organic Frameworks by Oriented Surface Growth on an Organic Monolayer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 5777–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.; Ramos, K.; Sua, A.; Acuna, J.; Slowinska, K.; Nguyen, T.; Bui, A.; Weber, M.D.R.; Tian, F. Tuning Crystal Structures of Iron-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks for Drug Delivery Applications. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 3418–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, X.; Lin, J.; Pang, M. Facile Synthesis of Highly Uniform Fe-MIL-88B Particles. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 3565–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeimi, S.; Faghihian, H. Application of Novel Metal Organic Framework, MIL-53(Fe) and Its Magnetic Hybrid: For Removal of Pharmaceutical Pollutant, Doxycycline from Aqueous Solutions. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 53, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Gokhale, R.; Bhatnagar, S.; Jog, J.; Bhardwaj, M.; Lefez, B.; Hannoyer, B.; Ogale, S. MOF Derived Porous Carbon-Fe3O4 Nanocomposite as a High Performance, Recyclable Environmental Superadsorbent. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 19694–19699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stassen, I.; Campagnol, N.; Fransaer, J.; Vereecken, P.; De Vos, D.; Ameloot, R. Solvent-Free Synthesis of Supported ZIF-8 Films and Patterns through Transformation of Deposited Zinc Oxide Precursors. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 9308–9311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, R.; Peng, Q.; Zhao, H.; Fan, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q. Effect of Pore Structure on the Adsorption Capacities to Different Sizes of Adsorbates by Ferrocene-Based Conjugated Microporous Polymers. Polymer 2021, 233, 124192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhuo, S.P.; Xing, W.; Cui, H.Y.; Dai, X.D.; Liu, X.M.; Yan, Z.F. Aqueous Dye Adsorption on Ordered Mesoporous Carbons. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 310, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horzum, N.; Hilal, M.E.; Isık, T. Enhanced Bactericidal and Photocatalytic Activities of ZnO Nanostructures by Changing the Cooling Route. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 11831–11838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, R.L.; Xi, Y.; He, H. Synthesis, Characterization of Palygorskite Supported Zero-Valent Iron and Its Application for Methylene Blue Adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 341, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H. Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution Using Mg-Fe, Zn-Fe, Mn-Fe Layered Double Hydroxide. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 2522–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, A.; Hamdy, M.K.; Nasr, M. Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles for Methylene Blue Removal from Aqueous Solutions and Textile Wastewater Treatment, with Cost Estimation. Water Sci. Technol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gao, B.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Chen, H.; Zhang, M.; Cao, X. Biochar-Supported Zerovalent Iron for Removal of Various Contaminants from Aqueous Solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, S.; Sohrabi, M.R. Removal of Methylene Blue, a Basic Dye, from Aqueous Solutions Using Nano-Zerovalent Iron. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S.; Zeng, J.; Subhan, F.; Li, M.; Lyu, F.; Li, Y.; Yan, Z.; Aslam, S.; Zeng, J.; Subhan, F.; et al. Accepted Manuscript In Situ One-Step Synthesis of Fe3O4 @MIL-100(Fe) Core-Shells for Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Water In Situ One-Step Synthesis of Fe3O4 @MIL-100(Fe) Core-Shells for Adsorption of Methylene Blue from Water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Liu, L.-H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Xie, J.; Yu, B.; Ma, X.; Yang, S.-T.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Hydrothermal Preparation of Magnetic Fe3O4 @C Nanoparticles for Dye Adsorption. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 2, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dekyvere, S.; Hilal, M.E.; Chaemchuen, S.; Zhuiykov, S.; Verpoort, F. Sacrificial Zinc Oxide Strategy-Enhanced Mesoporosity in MIL-53-Derived Iron–Carbon Composite for Methylene Blue Adsorption. Inorganics 2022, 10, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10050059
Dekyvere S, Hilal ME, Chaemchuen S, Zhuiykov S, Verpoort F. Sacrificial Zinc Oxide Strategy-Enhanced Mesoporosity in MIL-53-Derived Iron–Carbon Composite for Methylene Blue Adsorption. Inorganics. 2022; 10(5):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10050059
Chicago/Turabian StyleDekyvere, Sander, Mohamed Elhousseini Hilal, Somboon Chaemchuen, Serge Zhuiykov, and Francis Verpoort. 2022. "Sacrificial Zinc Oxide Strategy-Enhanced Mesoporosity in MIL-53-Derived Iron–Carbon Composite for Methylene Blue Adsorption" Inorganics 10, no. 5: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10050059
APA StyleDekyvere, S., Hilal, M. E., Chaemchuen, S., Zhuiykov, S., & Verpoort, F. (2022). Sacrificial Zinc Oxide Strategy-Enhanced Mesoporosity in MIL-53-Derived Iron–Carbon Composite for Methylene Blue Adsorption. Inorganics, 10(5), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10050059







