Low-Cost Carbon Nanoparticles for Removing Hazardous Organic Pollutants from Water: Complete Remediation Study and Multi-Use Investigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of TPCNPs
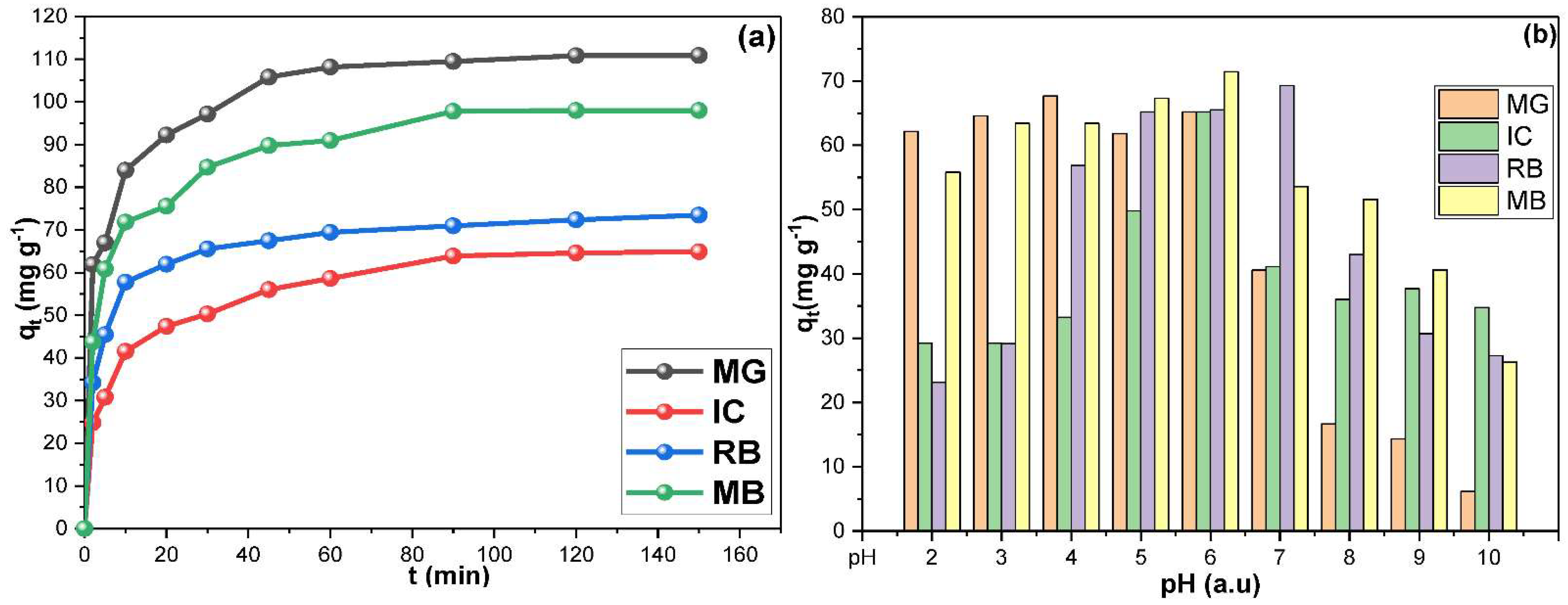
2.2. Adsorption of Organic Dyes by TPCNPs
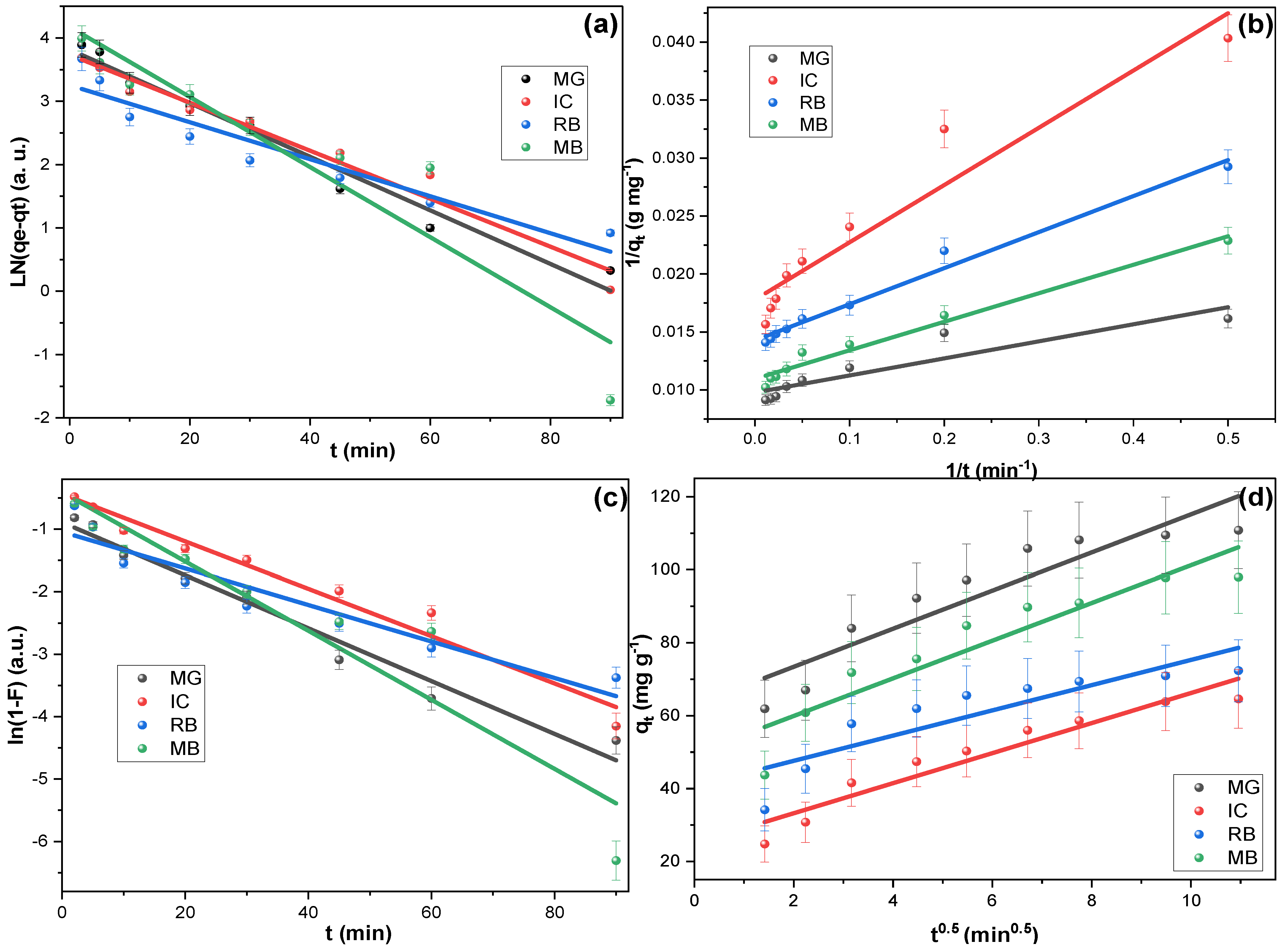
2.3. Adsorption Kinetics
2.4. Adsorption Isotherms
2.5. Adsorption Thermodynamics
2.6. Application to Natural Water Samples and Regeneration of TPCNPs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Carbon Nanoparticles
3.3. Characterization of Carbon Nanoparticles
3.4. Adsorption Investigation
3.5. Application to Natural Water Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahbar-Shamskar, K.; Azar, P.A.; Rashidi, A.; Baniyaghoob, S.; Yousefi, M. Synthesis of micro/mesoporous carbon adsorbents by in-situ fast pyrolysis of reed for recovering gasoline vapor. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.R.; Cavaleiro, A.J.; Soares, O.S.G.; Braga, C.S.; Salvador, A.F.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Alves, M.M.; Pereira, L. Detoxification of ciprofloxacin in an anaerobic bioprocess supplemented with magnetic carbon nanotubes: Contribution of adsorption and biodegradation mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bożęcka, A.; Orlof-Naturalna, M.; Kopeć, M. Methods of Dyes Removal from Aqueous Environment. J. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 22, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.; Protection, E. Removal of Dyes from Wastewater by Adsorption onto Activated Carbon: Mini Review. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2020, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaprakasha, S.; Kumarb, P.S.; Krishnac, S. Adsorption study of various dyes on Activated Carbon Fe3O4 Magnetic Nano Composite. Int. J. Appl. Chem. 2017, 13, 255–266. [Google Scholar]
- Topare, N.S.; Bokil, S.A. Adsorption of textile industry effluent in a fixed bed column using activated carbon prepared from agro-waste materials. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurtsever, A.; Basaran, E.; Ucar, D.; Sahinkaya, E. Self-forming dynamic membrane bioreactor for textile industry wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q.; Guo, K. Flocculation performance of papermaking sludge-based flocculants in different dye wastewater treatment: Comparison with commercial lignin and coagulants. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, M.H.D.; Adam, M.R.; Kamaludin, R.; Ismail, N.J.; Rahman, M.A.; Jaafar, J. Advanced Membrane Technology for Textile Wastewater Treatment. In Membrane Technology Enhancement for Environmental Protection and Sustainable Industrial Growth; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 91–108. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.F.; Khandaker, S.; Sarker, F.; Islam, A.; Rahman, M.T.; Awual, M.R. Current treatment technologies and mechanisms for removal of indigo carmine dyes from wastewater: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 318, 114061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrache, Z.; Abbas, M.; Aksil, T.; Trari, M. Thermodynamic and kinetics studies on adsorption of Indigo Carmine from aqueous solution by activated carbon. Microchem. J. 2019, 144, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberoi, A.S.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Khanal, S.K.; Lu, H. Insights into the fate and removal of antibiotics in engineered biological treatment systems: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7234–7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, O.A.; Lester, J.N.; Voulvoulis, N. Pharmaceuticals: A threat to drinking water? Trends Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussin, F.; Aroua, M.K.; Kassim, M.A.; Ali, U.F. Transforming Plastic Waste into Porous Carbon for Capturing Carbon Dioxide: A Review. Energies 2021, 14, 8421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, T.; Ahmad, N.; Ali, J.; Hassan, A.A.; Sher, F.; Rizwan, K.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Bilal, M. Nano and micro architectured cues as smart materials to mitigate recalcitrant pharmaceutical pollutants from wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabzehmeidani, M.M.; Mahnaee, S.; Ghaedi, M.; Heidari, H.; Roy, V.A.L. Carbon based materials: A review of adsorbents for inorganic and organic compounds. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 598–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jjagwe, J.; Olupot, P.W.; Menya, E.; Kalibbala, H.M. Synthesis and application of Granular activated carbon from biomass waste materials for water treatment: A review. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 292–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, R.; Peighambardoust, S.J.; Peighambardoust, S.H.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Adsorption of Crystal Violet Dye Using Activated Carbon of Lemon Wood and Activated Carbon/Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanocomposite from Aqueous Solutions: A Kinetic, Equilibrium and Thermodynamic Study. Molecules 2021, 26, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafil, M.; Nasab, B.; Moazed, H.; Jokiniemi, J.; Laehde, A.; Bhatnagar, A. Efficient removal of azo dyes from water with chitosan/carbon nanoflower as a novel nanocomposite synthesized by pyrolysis technique. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 142, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Bi, H.; Sun, L. Graphene and carbon-based nanomaterials as highly efficient adsorbents for oils and organic solvents. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2016, 5, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakkoli, M.; Flahaut, E.; Peljo, P.; Sainio, J.; Davodi, F.; Lobiak, E.V.; Mustonen, K.; Kauppinen, E.I. Mesoporous single-atom-doped graphene–carbon nanotube hybrid: Synthesis and tunable electrocatalytic activity for oxygen evolution and reduction reactions. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 4647–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Dong, X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, N.; Zheng, B.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, Y. Controllable Synthesis of MoS2/Carbon Nanotube Hybrids with Enlarged Interlayer Spacings for Efficient Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 13603–13608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Chen, X.; Liu, P. Preparation of CNTs/Cu composites with good electrical conductivity and excellent mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 771, 138656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, B.; Goel, S.; Balomajumder, C. Multiwalled CNTs for Cr (VI) removal from industrial wastewater: An advanced study on adsorption, kinetics, thermodynamics for the comparison between the embedded and non-embedded carboxyl group. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 99, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, M.R.; Abdulkhair, B.Y.; Elzupir, A.O. Insight to aspirin sorption behavior on carbon nanotubes from aqueous solution: Thermodynamics, kinetics, influence of functionalization and solution parameters. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Supriya, S.; Sriram, G.; Ngaini, Z.; Kavitha, C.; Kurkuri, M.; De Padova, I.P.; Hegde, G. The role of temperature on physical–chemical properties of green synthesized porous carbon nanoparticles. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 11, 3821–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahimov, H.; Amirov, F.; Huseynov, H.; Ibragimova, Z.; Zamanova, L.; Asadzadeh, R.; Jabarov, S.H. Carbon nanotubes obtained from natural gas by CVD. J. Surf. Investig. X-ray Synchrotron Neutron Tech. 2019, 13, 1244–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almufarij, R.S.; Abdulkhair, B.Y.; Salih, M.; Aldosari, H.; Aldayel, N.W. Optimization, Nature, and Mechanism Investigations for the Adsorption of Ciprofloxacin and Malachite Green onto Carbon Nanoparticles Derived from Low-Cost Precursor via a Green Route. Molecules 2022, 27, 4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breland, O.P.J.S. A Laboratory Manual Of Comparative Anatomy/ Barker, Kenneth & Breland, Osmond; Mcgraw-Hill Book Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Mote, V.; Purushotham, Y.; Dole, B.N. Williamson-Hall analysis in estimation of lattice strain in nanometer-sized ZnO particles. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2012, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.; Abdullah, B.; Tahir, D. X-ray diffraction analysis of nanocomposite Fe3O4/activated carbon by Williamson–Hall and size-strain plot methods. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2019, 20, 100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Bassler, G.C. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds; State University New York: Albany, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pavia, D.L.; Lampman, G.M.; Kriz, G.S.; Vyvyan, J.A. Introduction to Spectroscopy; Cengage Learning Acquisitions, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-C. Fine Activated Carbon from Rubber Fruit Shell Prepared by Using ZnCl2 and KOH Activation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3994. [Google Scholar]
- Bandura, L.; Panek, R.; Madej, J.; Franus, W. Synthesis of zeolite-carbon composites using high-carbon fly ash and their adsorption abilities towards petroleum substances. Fuel 2020, 283, 119173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Dai, W.; Lian, X.; Cui, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, K.; Lin, M.; Zou, R.; Loh, K.; et al. From micropores to ultra-micropores inside hard carbon: Toward enhanced capacity in room-/low-temperature sodium-ion storage. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-Z.; Huang, X.-L. Effect of temperature and salinity on phosphate sorption on marine sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 6831–6837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flower, H.; Rains, M.; Lewis, D.; Zhang, J.-Z.; Price, R. Saltwater intrusion as potential driver of phosphorus release from limestone bedrock in a coastal aquifer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 184, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, M.R.; Abdulkhair, B.Y.; Elzupir, A.O. Removal of ciprofloxacin and indigo carmine from water by carbon nanotubes fabricated from a low-cost precursor: Solution parameters and recyclability. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2022, 101844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwegbe, C.A.; Oba, S.N.; Aniagor, C.O.; Adeniyi, A.G.; Ighalo, J.O. Adsorption of ciprofloxacin from water: A comprehensive review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 93, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Brito, S.M.; Andrade, H.M.C.; Soares, L.F.; de Azevedo, R.P. Brazil nut shells as a new biosorbent to remove methylene blue and indigo carmine from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmi, U.R.; Srivastava, V.C.; Mall, I.D.; Lataye, D.H. Rice husk ash as an effective adsorbent: Evaluation of adsorptive characteristics for Indigo Carmine dye. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Mittal, J.; Kurup, L. Batch and bulk removal of hazardous dye, indigo carmine from wastewater through adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, A.G.; Torres, J.D.; Faria, E.A.; Dias, S.C. Comparative adsorption studies of indigo carmine dye on chitin and chitosan. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 277, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.H.; Abdulhameed, A.S.; Wilson, L.D.; Syed-Hassan, S.S.A.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Khan, M.R. High surface area and mesoporous activated carbon from KOH-activated Dragon fruit peels for methylene blue dye adsorption: Optimization and mechanism study. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 32, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Hossain, M.A. Optimization of a fixed bed column adsorption of Fast Green dye on used black tea leaves from aqueous solution. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2022, 19, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renita, A.A.; Amarnath, D.J.; Duraikannu, S.L. Synthesis of peanut-shell magnetized biocarbon for acid fuchsin dye removal. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 3075–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghizadeh, A.; Karimi, A.; Derakhshani, E.; Esform, A. Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) as an efficient adsorbent for removal of reactive dyes from water solution: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2021, 31, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofomaja, A.E.; Naidoo, E.B.; Pholosi, A. Intraparticle diffusion of Cr (VI) through biomass and magnetite coated biomass: A comparative kinetic and diffusion study. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 32, 39–55. [Google Scholar]
- An, B. Cu (II) and As (V) adsorption kinetic characteristic of the multifunctional amino groups in chitosan. Processes 2020, 8, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdy, Y.; Altaher, H. Kinetic analysis of the adsorption of dyes from high strength wastewater on cement kiln dust. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konggidinata, M.I.; Chao, B.; Lian, Q.; Subramaniam, R.; Zappi, M.; Gang, D.D. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for adsorption of BTEX onto Ordered Mesoporous Carbon (OMC). J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 336, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayyun, T.S.; Mseer, A.H. Comparison of the experimental results with the Langmuir and Freundlich models for copper removal on limestone adsorbent. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, J.; Sahu, J.; Mohanty, C.; Meikap, B. Removal of lead (II) from wastewater by activated carbon developed from Tamarind wood by zinc chloride activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 149, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letshwenyo, M.W.; Mokgosi, S. Investigation of water treatment sludge from drinking water treated with Zetafloc 553I coagulant for phosphorus removal from wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 282, 111909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirbas, O.; Calimli, M.H.; Kuyuldar, E.; Alma, M.H.; Nas, M.S.; Sen, F. Equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic of adsorption of enzymes on diatomite clay materials. BioNanoScience 2019, 9, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarab, N.; Hsini, A.; Essekri, A.; Laabd, M.; Lakhmiri, R.; Albourine, A. Removal of an emerging pharmaceutical pollutant (metronidazole) using PPY-PANi copolymer: Kinetics, equilibrium and DFT identification of adsorption mechanism. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, S.; Lakshmi, J. Studies relating to an electrochemically assisted coagulation for the removal of chromium from water using zinc anode. Water Supply 2011, 11, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Zorpas, A.A. Heat of adsorption, adsorption energy and activation energy in adsorption and ion exchange systems. Desalin. Water Treat. 2012, 39, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Han, Y.; Li, S. Adsorption characteristic of Cr (VI) onto different activated coal fly ashes: Kinetics, thermodynamic, application feasibility, and error analysis. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.; El-Khaiary, M. Malachite green adsorption by rattan sawdust: Isotherm, kinetic and mechanism modeling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 159, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
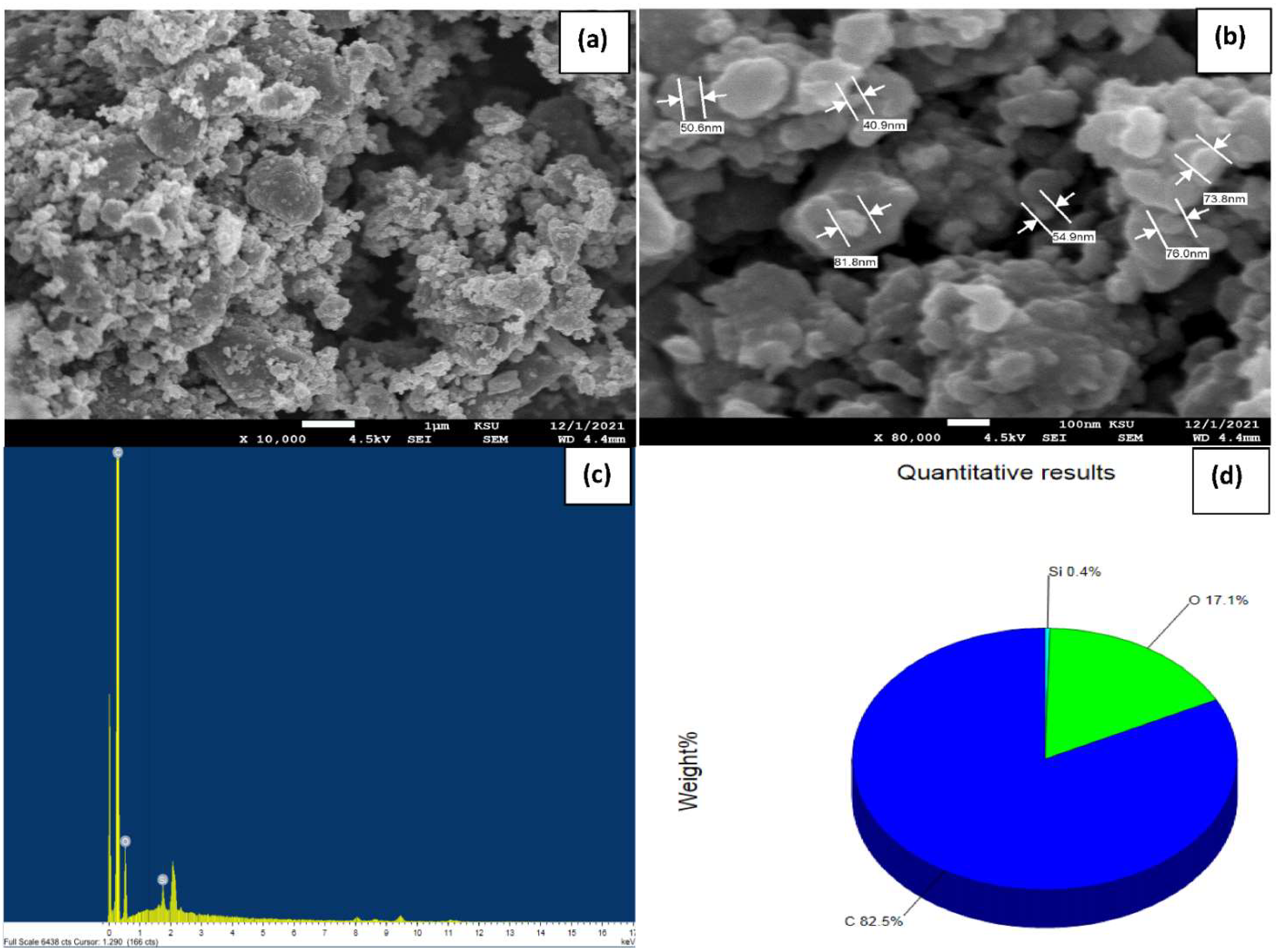
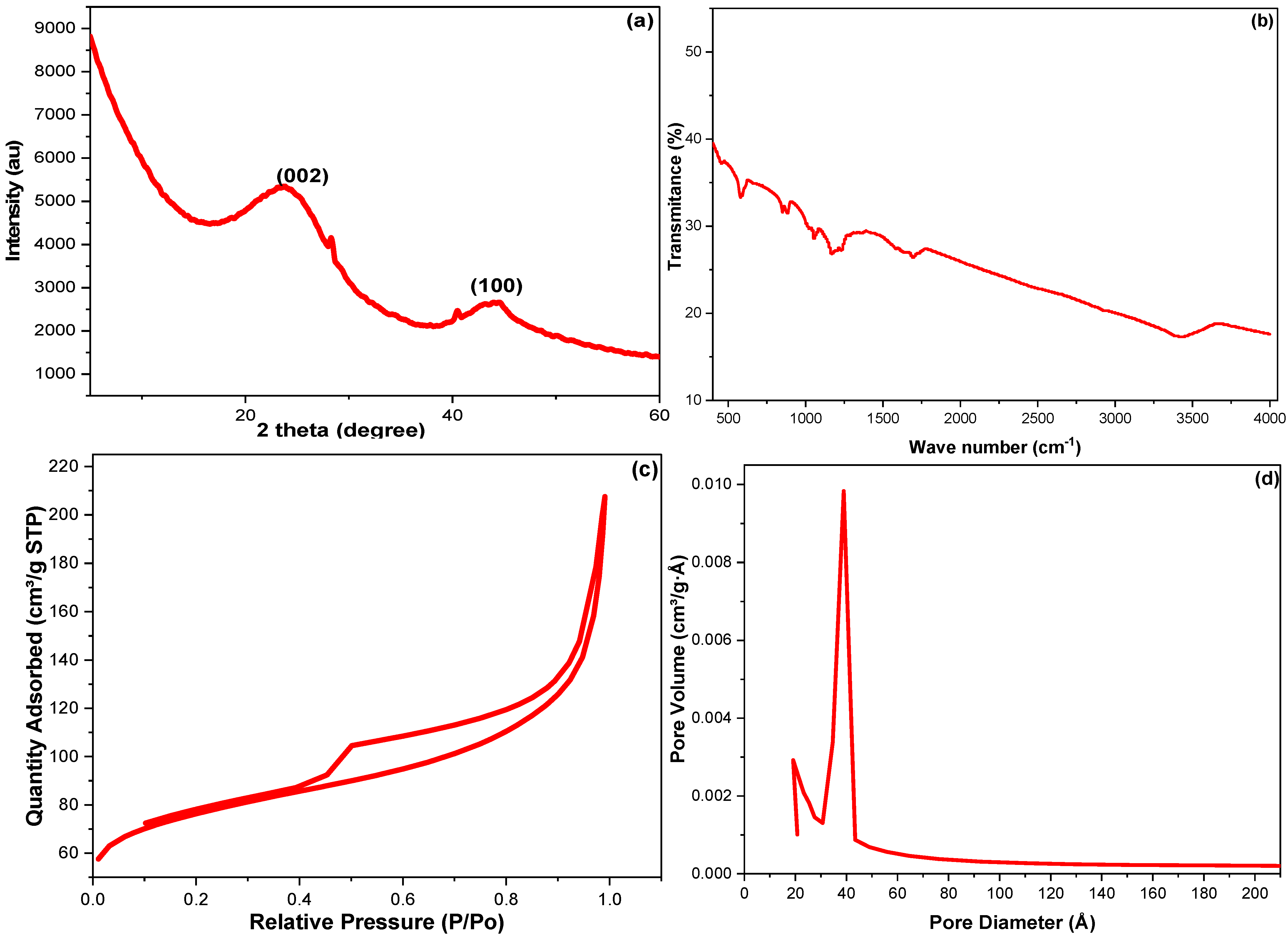


| Parameters | 23.7083 (2θ°) | 44.4823 (2θ°) | Avge |
|---|---|---|---|
| D (nm) | 0.414 | 2.079 | 1.246 |
| a (nm) | 0.183 | 0.337 | 0.260 |
| c (nm) | 7.500 | 4.070 | 5.785 |
| ε (Arbutary) | 0.377 | 0.356 | 0.367 |
| Adsorption Kinetic | ||||||||
| Adsorption Rate Order | ||||||||
| PSFO | PSSO | |||||||
| Dye | MG | IC | RB | MB | MG | IC | RB | MB |
| qe exp. (mg g−1) | 110.852 | 64.883 | 73.452 | 97.974 | 110.852 | 64.883 | 73.452 | 97.974 |
| qe cal. (mg g−1) | 45.480 | 41.885 | 25.887 | 65.048 | 102.249 | 56.180 | 69.979 | 91.241 |
| R2 (Arbutary) | 0.971 | 0.973 | 0.905 | 0.891 | 0.840 | 0.920 | 0.984 | 0.975 |
| Rate constant | 0.042 | 0.038 | 0.029 | 0.055 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.005 |
| Adsorption Mechanism | ||||||||
| Pollutant ↓ | Intraparticle Diffusion Model (IPDM) | Liquid Film Diffusion Model (LFDM) | ||||||
| KIP (mg g−1 min0.5) | C (mg g−1) | R2 | KLF (min–1) | R2 | ||||
| MG | 5.218 | 62.980 | 0.854 | −0.042 | 0.972 | |||
| IC | 4.124 | 24.983 | 0.919 | −0.038 | 0.967 | |||
| RB | 3.461 | 40.689 | 0.770 | −0.029 | 0.905 | |||
| MB | 5.162 | 49.595 | 0.862 | −0.055 | 0.892 | |||
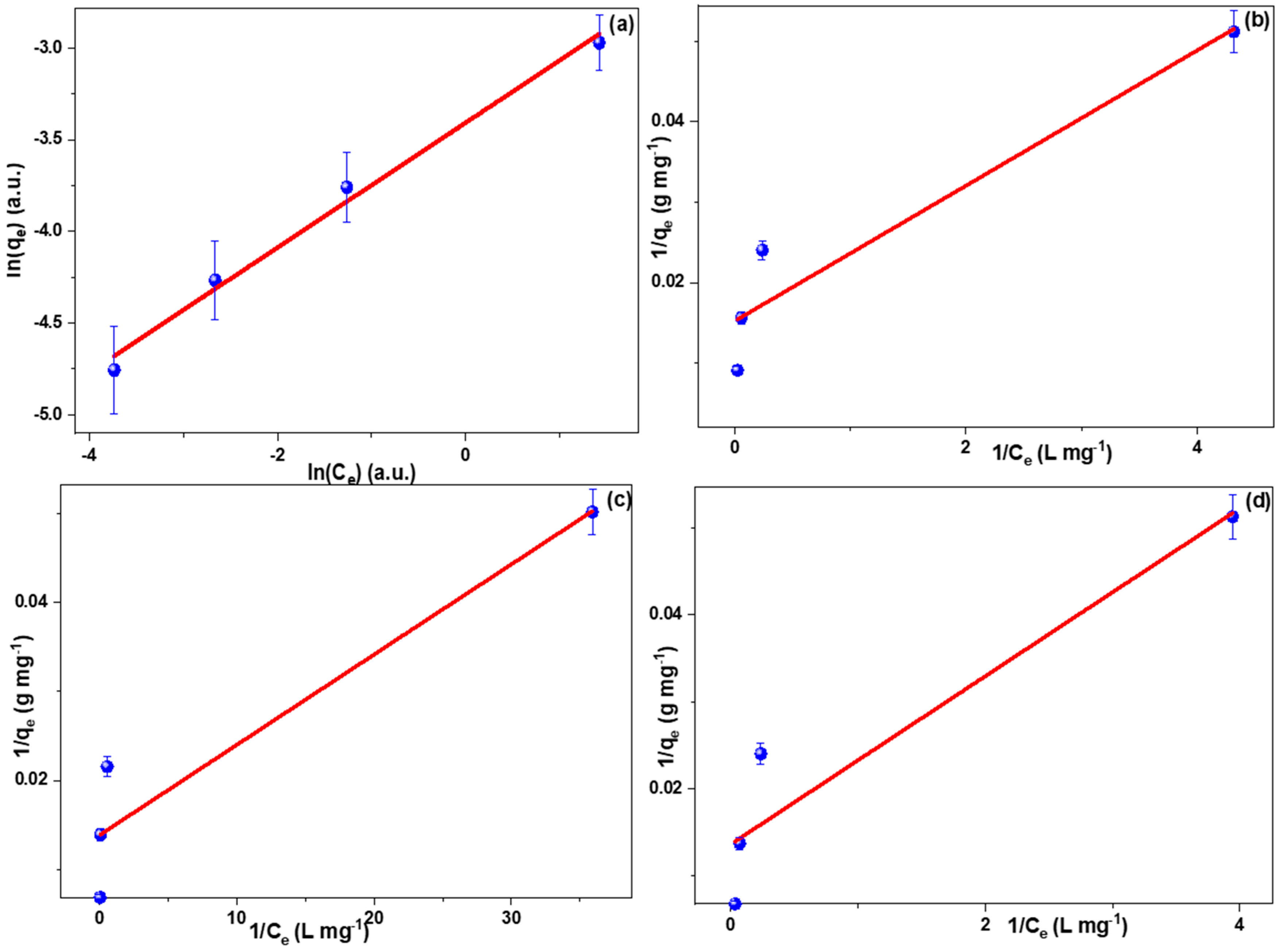
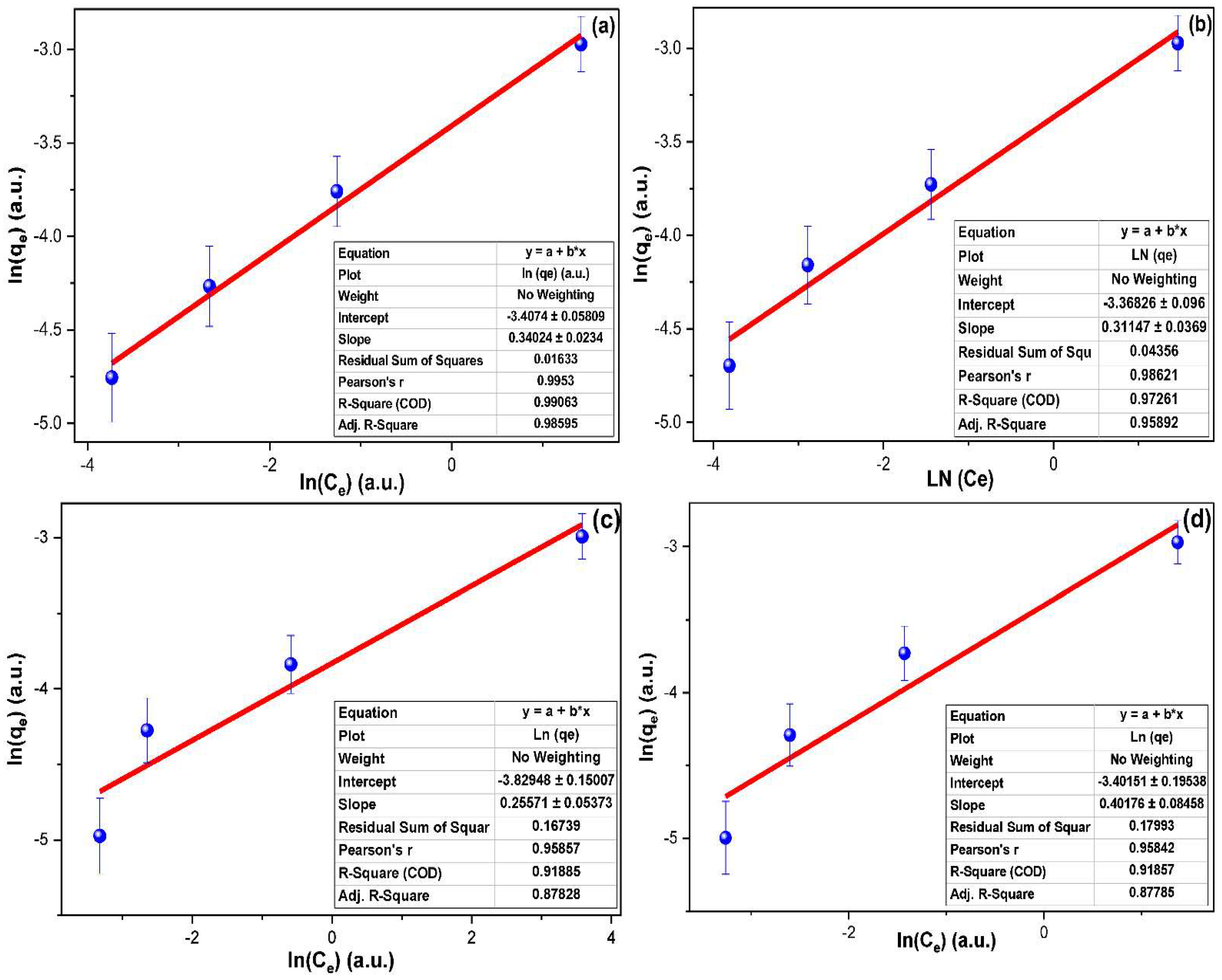
| Adsorption Isotherms | ||||||
| Isotherm Model → | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
| Dye ↓ | R2 (a.u.) | KL (L mg−1) | qm (mg g−1) | R2(a.u.) | Kf (L mg−1) | n−1 (a.u.) |
| MG | 0.928 | 71.276 | 1.542 | 0.991 | 0.033 | 0.340 |
| IC | 0.916 | 65.445 | 1.821 | 0.973 | 0.034 | 0.311 |
| RB | 0.908 | 72.098 | 13.733 | 0.919 | 0.022 | 0.256 |
| MB | 0.897 | 73.801 | 1.400 | 0.919 | 0.033 | 0.402 |
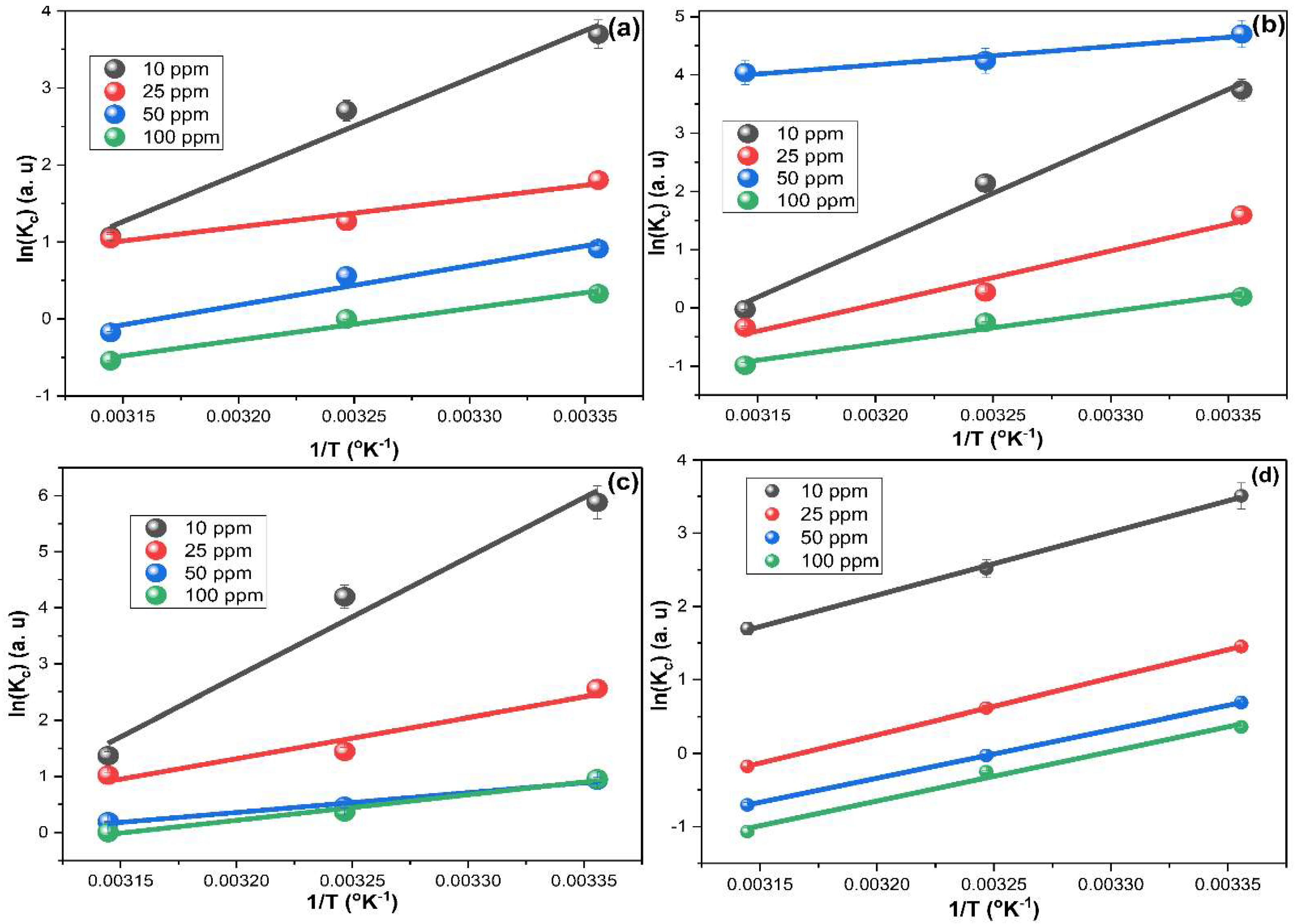
| Thermodynamic Parameters | ||||||
| MG | ||||||
| Fed conc. (mg L−1) | ΔH° (Kj mol−1) | ΔS° (kJ mol−1) | ΔG° (kJ mol−1) 298 K | ΔG° (kJ mol−1) 308 K | ΔG° (kJ mol−1) 318 K | R2 |
| 10 | −103.125 | −0.314 | −9.453 | −6.309 | −3.166 | 0.975 |
| 25 | −30.022 | −0.086 | −4.351 | −3.490 | −2.628 | 0.954 |
| 50 | −42.628 | −0.135 | −2.424 | −1.075 | 0.274 | 0.953 |
| 100 | −34.139 | −0.112 | −0.906 | 0.209 | 1.324 | 0.975 |
| IC | ||||||
| 10 | −148.286 | −0.466 | −9.547 | −4.892 | −0.236 | 0.989 |
| 25 | −76.294 | −0.244 | −3.688 | −1.251 | 1.185 | 0.964 |
| 50 | −26.268 | −0.049 | −11.556 | −11.062 | −10.568 | 0.961 |
| 100 | −46.201 | −0.153 | −0.606 | 0.924 | 2.454 | 0.974 |
| RB | ||||||
| 10 | −182.242 | −0.564 | −14.138 | −8.497 | −2.856 | 0.970 |
| 25 | −67.406 | −0.210 | −4.915 | −2.818 | −0.721 | 0.955 |
| 50 | −46.729 | −0.156 | −0.368 | 1.188 | 2.744 | 0.995 |
| 100 | −64.772 | −0.216 | −0.503 | 1.654 | 3.811 | 0.999 |
| MB | ||||||
| 10 | −71.474 | −0.211 | −8.646 | −6.538 | −4.430 | 0.999 |
| 25 | −64.006 | −0.203 | −3.596 | −1.568 | 0.459 | 0.999 |
| 50 | −54.862 | −0.178 | −1.709 | 0.075 | 1.859 | 0.999 |
| 100 | −56.198 | −0.185 | −0.997 | 0.855 | 2.707 | 0.990 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdulkhair, B.Y.; Elamin, M.R. Low-Cost Carbon Nanoparticles for Removing Hazardous Organic Pollutants from Water: Complete Remediation Study and Multi-Use Investigation. Inorganics 2022, 10, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10090136
Abdulkhair BY, Elamin MR. Low-Cost Carbon Nanoparticles for Removing Hazardous Organic Pollutants from Water: Complete Remediation Study and Multi-Use Investigation. Inorganics. 2022; 10(9):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10090136
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdulkhair, Babiker Y., and Mohamed R. Elamin. 2022. "Low-Cost Carbon Nanoparticles for Removing Hazardous Organic Pollutants from Water: Complete Remediation Study and Multi-Use Investigation" Inorganics 10, no. 9: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10090136
APA StyleAbdulkhair, B. Y., & Elamin, M. R. (2022). Low-Cost Carbon Nanoparticles for Removing Hazardous Organic Pollutants from Water: Complete Remediation Study and Multi-Use Investigation. Inorganics, 10(9), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10090136






