Combined Effect of Halogenation and SiO2 Addition on the Li-Ion Conductivity of LiBH4
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXD)
2.3. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. h-Li(BH4)1−xXx Solid Solutions
3.2. (h-Li(BH4)1−α(X)α)1−β-(SiO2)β Systems
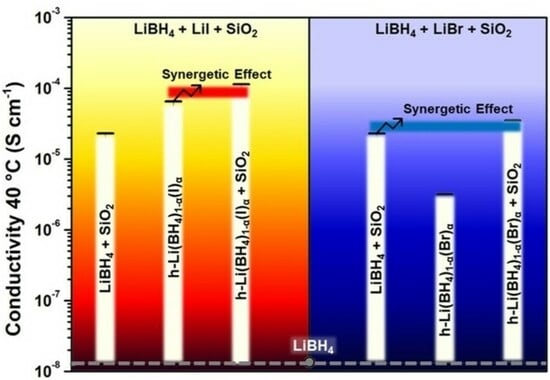
3.3. Synergetic Effect
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goodenough, J.B.; Kim, Y. Challenges for Rechargeable Li Batteries. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachman, J.C.; Muy, S.; Grimaud, A.; Chang, H.-H.; Pour, N.; Lux, S.F.; Paschos, O.; Maglia, F.; Lupart, S.; Lamp, P.; et al. Inorganic Solid-State Electrolytes for Lithium Batteries: Mechanisms and Properties Governing Ion Conduction. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 140–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manthiram, A.; Yu, X.; Wang, S. Lithium Battery Chemistries Enabled by Solid-State Electrolytes. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 16103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, J.B.; Singh, P. Review—Solid Electrolytes in Rechargeable Electrochemical Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A2387–A2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, S.P.; Koerver, R.; Krauskopf, T.; Zeier, W.G. Designing Ionic Conductors: The Interplay between Structural Phenomena and Interfaces in Thiophosphate-Based Solid-State Batteries. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 4179–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muldoon, J.; Bucur, C.B.; Gregory, T. Quest for Nonaqueous Multivalent Secondary Batteries: Magnesium and Beyond. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11683–11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeshoji, T.; Tsuchida, E.; Morishita, T.; Ikeda, K.; Matsuo, M.; Kawazoe, Y.; Orimo, S.-I. Fast-ionic conductivity of Li+ in LiBH4. Phys. Rev. B-Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2011, 83, 144301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kharbachi, A.; Pinatel, E.; Nuta, I.; Baricco, M. A Thermodynamic Assessment of LiBH4. Calphad 2012, 39, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, M.; Nakamori, Y.; Orimo, S.; Maekawa, H.; Takamura, H. Lithium Superionic Conduction in Lithium Borohydride Accompanied by Structural Transition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 224103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulino, V.; Wolczyk, A.; Golov, A.A.; Eremin, R.A.; Palumbo, M.; Nervi, C.; Blatov, V.A.; Proserpio, D.M.; Baricco, M. Combined DFT and Geometrical–Topological Analysis of Li-Ion Conductivity in Complex Hydrides. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 3115–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulino, V.; Brighi, M.; Dematteis, E.M.; Murgia, F.; Nervi, C.; Černý, R.; Baricco, M. Phase Stability and Fast Ion Conductivity in the Hexagonal LiBH4–LiBr–LiCl Solid Solution. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 5133–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, R.; Duchêne, L.; Kühnel, R.-S.; Remhof, A.; Hagemann, H.; Battaglia, C. Electrochemical Oxidative Stability of Hydroborate-Based Solid-State Electrolytes. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 6924–6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveinbjörnsson, D.; Myrdal, J.S.G.; Blanchard, D.; Bentzen, J.J.; Hirata, T.; Mogensen, M.B.; Norby, P.; Orimo, S.; Vegge, T. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Lithium Ion Conduction of the LiBH4–LiI Solid Solution. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 3249–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unemoto, A.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Matsuo, M.; Ikeshoji, T.; Orimo, S.I. Pseudo-Binary Electrolyte, LiBH4-LiCl, for Bulk-Type All-Solid-State Lithium-Sulfur Battery. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 254001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekawa, H.; Matsuo, M.; Takamura, H.; Ando, M.; Noda, Y.; Karahashi, T.; Orimo, S.-I. Halide-stabilized LiBH4, a room-temperature lithium fast-ion conductor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 894–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, M.; Remhof, A.; Martelli, P.; Caputo, R.; Ernst, M.; Miura, Y.; Sato, T.; Oguchi, H.; Maekawa, H.; Takamura, H.; et al. Complex Hydrides with (BH4)− and (NH2)− Anions as New Lithium Fast-Ion Conductors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16389–16391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Bolarin, J.A.; Zhang, B.; Liu, W. Evaluation of a new lithium complex hydride: A derivative of BH4- and NH2- for fast Li-ion conduction and H2 sorption. Dalton Trans. 2023. accepted manuscript. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Rawal, A.; Aguey-Zinsou, K.-F. Investigating the factors affecting the ionic conduction in nanoconfined NaBH4. Inorganics 2021, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefevr, J.; Cervini, L.; Griffin, J.M.; Blanchard, D. Lithium Conductivity and Ions Dynamics in LiBH4/SiO2 Solid Electrolytes Studied by Solid-State NMR and Quasi-Elastic Neutron Scattering and Applied in Lithium-Sulfur Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 15264–15275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Xie, C.; Li, Y.; Li, H.-W.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q. Enhancement of the ionic conductivity of lithium borohydride by silica supports. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 15352–15358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulino, V.; Barberis, L.; Ngene, P.; Baricco, M.; de Jongh, P.E. Enhancing Li-Ion Conductivity in LiBH4-Based Solid Electrolytes by Adding Various Nanosized Oxides. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 4941–4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwarno, S.; Nale, A.; Suwarta, P.; Wijayanti, I.D.; Ismail, M. Designing Nanoconfined LiBH4 for Solid-State Electrolytes. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 866959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Rawal, A.; Salman, M.S.; Aguey-Zinsou, K.-F. Core–Shell NaBH4@Na2B12H12 Nanoparticles as Fast Ionic Conductors for Sodium-Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Lee, Y.-S.; Oh, K.H.; Cho, Y.W. Interface-enhanced Li ion conduction in a LiBH4-SiO2 solid electrolyte. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 22540–22547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kort, L.M.; Gulino, V.; de Jongh, P.E.; Ngene, P. Ionic Conductivity in Complex Metal Hydride-Based Nanocomposite Materials: The Impact of Nanostructuring and Nanocomposite Formation. J Alloys Compd. 2022, 901, 163474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kort, L.; Ngene, P.; Baricco, M.; de Jongh, P.; Gulino, V. Improving the Cycle Life of Solid-State Batteries by Addition of Oxide Nanoparticles to a Complex Hydride Solid Electrolyte. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 3988–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, V.; Sakka, S. Electronic Oxide Polarizability and Optical Basicity of Simple Oxides. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 79, 1736–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutterotti, L.; Matthies, S.; Wenk, H.R. MAUD: A Friendly Java Program for Material Analysis Using Diffraction. Newsletter CPD 1999, 21, 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Boukamp, B.A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy in Solid State Ionics: Recent Advances. Solid State Ion. 2004, 169, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukamp, B.A. A Package for Impedance/Admittance Data Analysis. Solid State Ion. 1986, 19, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xiang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, W. Lithium Migration Pathways at the Composite Interface of LiBH4 and Two-Dimensional MoS2 Enabling Superior Ionic Conductivity at Room Temperature. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 4096–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascallana-Matias, I.; Keen, D.A.; Cussen, E.J.; Gregory, D.H. Phase Behavior in the LiBH4–LiBr System and Structure of the Anion-Stabilized Fast Ionic, High Temperature Phase. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 7780–7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filinchuk, Y.; Chernyshov, D.; Cerny, R. Lightest Borohydride Probed by Synchrotron X-Ray Diffraction: Experiment Calls for a New Theoretical Revision. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 10579–10584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paskevicius, M.; Jepsen, L.H.; Schouwink, P.; Černý, R.; Ravnsbæk, D.B.; Filinchuk, Y.; Dornheim, M.; Besenbacher, F.; Jensen, T.R. Metal Borohydrides and Derivatives–Synthesis, Structure and Properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 1565–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguchi, H.; Matsuo, M.; Hummelshøj, J.S.; Vegge, T.; Nørskov, J.K.; Sato, T.; Miura, Y.; Takamura, H.; Maekawa, H.; Orimo, S. Experimental and Computational Studies on Structural Transitions in the LiBH4–LiI Pseudobinary System. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 141912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sveinbjörnsson, D.; Christiansen, A.S.; Viskinde, R.; Norby, P.; Vegge, T. The LiBH4-LiI solid solution as an electrolyte in an all-solid-state battery. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, A1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, R.; Karahashi, T.; Kumatani, N.; Noda, Y.; Ando, M.; Takamura, H.; Matsuo, M.; Orimo, S.; Maekawa, H. Room Temperature Lithium Fast-Ion Conduction and Phase Relationship of LiI Stabilized LiBH4. Solid State Ion. 2011, 192, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rude, L.H.; Zavorotynska, O.; Arnbjerg, L.M.; Ravnsbæk, D.B.; Malmkjær, R.A.; Grove, H.; Hauback, B.C.; Baricco, M.; Filinchuk, Y.; Besenbacher, F.; et al. Bromide Substitution in Lithium Borohydride, LiBH4–LiBr. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 15664–15672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, P.; Remhof, A.; Borgschulte, A.; Ackermann, R.; Strässle, T.; Embs, J.P.; Ernst, M.; Matsuo, M.; Orimo, S.-I.; Züttel, A. Rotational Motion in LiBH4/LiI Solid Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 5329–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchter, F.; Łodziana, Z.; Mauron, P.; Remhof, A.; Friedrichs, O.; Borgschulte, A.; Züttel, A.; Sheptyakov, D.; Strässle, T.; Ramirez-Cuesta, A.J. Dynamical Properties and Temperature Induced Molecular Disordering of LiBH4 and LiBD4. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 094302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Lee, H.R.; Hsu, P.-C.; Liu, K.; Cui, Y. High Ionic Conductivity of Composite Solid Polymer Electrolyte via In Situ Synthesis of Monodispersed SiO2 Nanospheres in Poly(Ethylene Oxide). Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, D.; Nale, A.; Sveinbjörnsson, D.; Eggenhuisen, T.M.; Verkuijlen, M.H.W.; Suwarno; Vegge, T.; Kentgens, A.P.M.; De Jongh, P.E. Nanoconfined LiBH4 as a Fast Lithium Ion Conductor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Name | Halide | Oxide | ρ 1 | Fraction of Pore Filling 2 | Thickness of h-Li(BH4)1−α(X)α 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molar Fraction | wt.% | v/v % | g/cm3 | % | nm | ||
| I0.2 | I | 0.2 | / | / | 1.30 | / | / |
| I0.2-13 | I | 0.2 | 20 | 13 | 1.30 | 134 | 10.5 |
| I0.2-16 | I | 0.2 | 25 | 16 | 1.30 | 100 | 7.8 |
| I0.2-20 | I | 0.2 | 30 | 20 | 1.30 | 78 | 6.1 |
| I0.2-33 | I | 0.2 | 45 | 33 | 1.30 | 41 | 3.2 |
| I0.2-47 | I | 0.2 | 60 | 47 | 1.30 | 22 | 1.7 |
| I0.3 | I | 0.3 | / | / | 1.66 | / | / |
| I0.3-24 | I | 0.3 | 30 | 24 | 1.66 | 61 | 4.8 |
| I0.3-38 | I | 0.3 | 45 | 38 | 1.66 | 32 | 2.5 |
| I0.4 | I | 0.4 | / | / | 1.95 | / | / |
| I0.4-28 | I | 0.4 | 30 | 28 | 1.95 | 52 | 4.1 |
| I0.4-42 | I | 0.4 | 45 | 42 | 1.95 | 27 | 2.1 |
| I0.5 | I | 0.5 | / | / | 2.23 | / | / |
| I0.5-45 | I | 0.5 | 45 | 45 | 2.23 | 24 | 1.9 |
| Br0.3 | Br | 0.3 | / | / | 1.36 | / | / |
| Br0.3-13 | Br | 0.3 | 20 | 13 | 1.36 | 128 | 10.0 |
| Br0.3-21 | Br | 0.3 | 30 | 21 | 1.36 | 75 | 5.8 |
| Br0.3-34 | Br | 0.3 | 45 | 34 | 1.36 | 39 | 3.1 |
| Br0.3-48 | Br | 0.3 | 60 | 48 | 1.36 | 21 | 1.7 |
| Br0.4 | Br | 0.4 | / | / | 1.60 | / | / |
| Br0.4-24 | Br | 0.4 | 30 | 24 | 1.60 | 63 | 5.0 |
| Br0.4-37 | Br | 0.4 | 45 | 37 | 1.60 | 33 | 2.6 |
| Br0.5 | Br | 0.5 | / | / | 1.83 | / | / |
| Br0.5-26 | Br | 0.5 | 30 | 26 | 1.83 | 55 | 4.3 |
| Br0.5-40 | Br | 0.5 | 45 | 40 | 1.83 | 29 | 2.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gulino, V.; de Kort, L.; Ngene, P.; de Jongh, P.; Baricco, M. Combined Effect of Halogenation and SiO2 Addition on the Li-Ion Conductivity of LiBH4. Inorganics 2023, 11, 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11120459
Gulino V, de Kort L, Ngene P, de Jongh P, Baricco M. Combined Effect of Halogenation and SiO2 Addition on the Li-Ion Conductivity of LiBH4. Inorganics. 2023; 11(12):459. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11120459
Chicago/Turabian StyleGulino, Valerio, Laura de Kort, Peter Ngene, Petra de Jongh, and Marcello Baricco. 2023. "Combined Effect of Halogenation and SiO2 Addition on the Li-Ion Conductivity of LiBH4" Inorganics 11, no. 12: 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11120459
APA StyleGulino, V., de Kort, L., Ngene, P., de Jongh, P., & Baricco, M. (2023). Combined Effect of Halogenation and SiO2 Addition on the Li-Ion Conductivity of LiBH4. Inorganics, 11(12), 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11120459