The Analytical Application of Quenching Phenomena of CdTe Quantum Dot Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
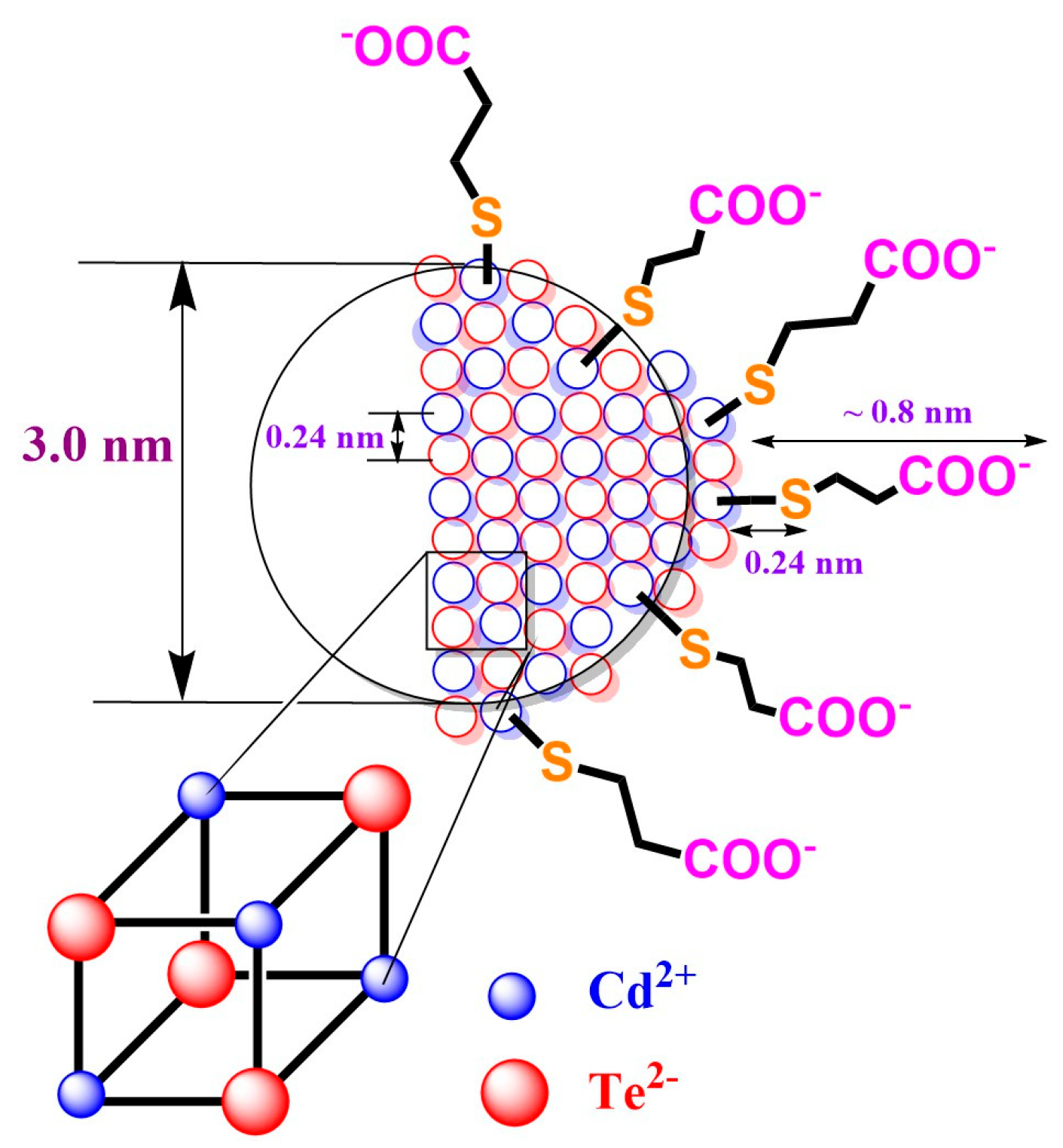
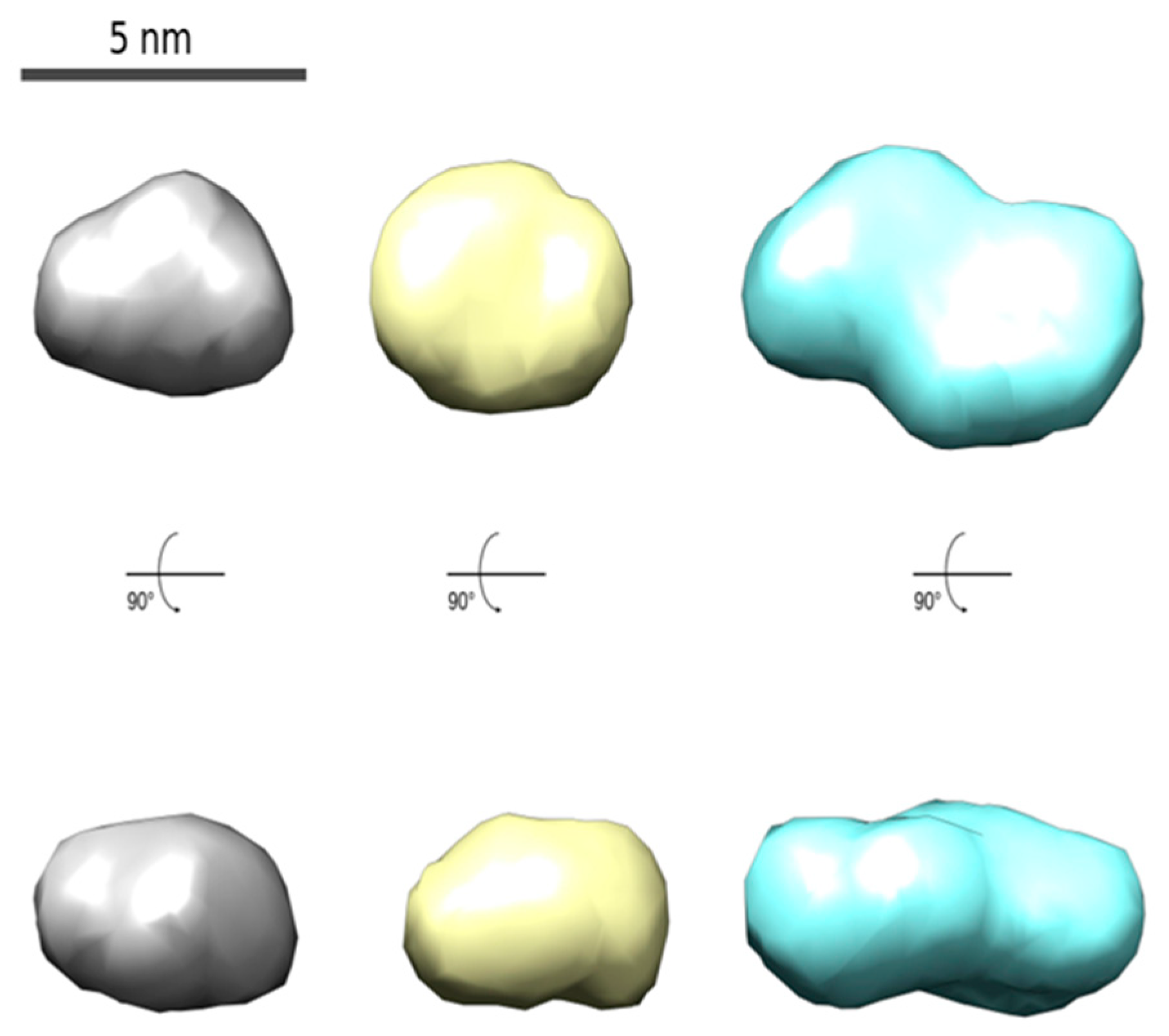
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of CdTe QD Nanoparticles
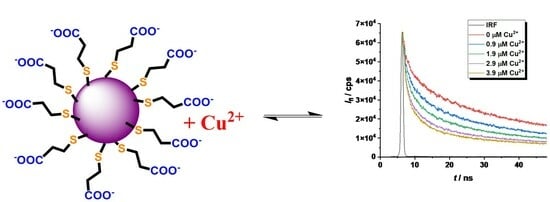
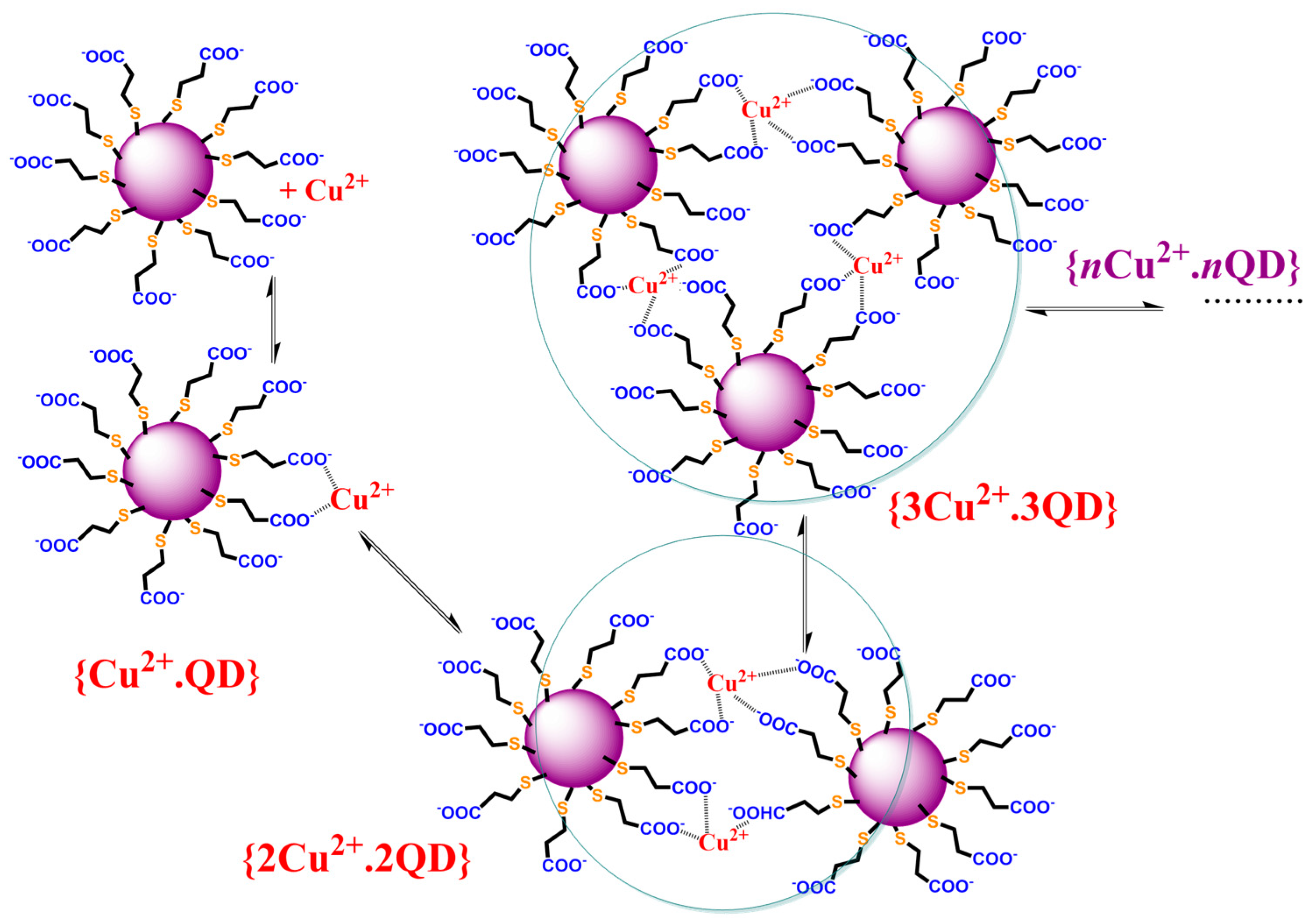
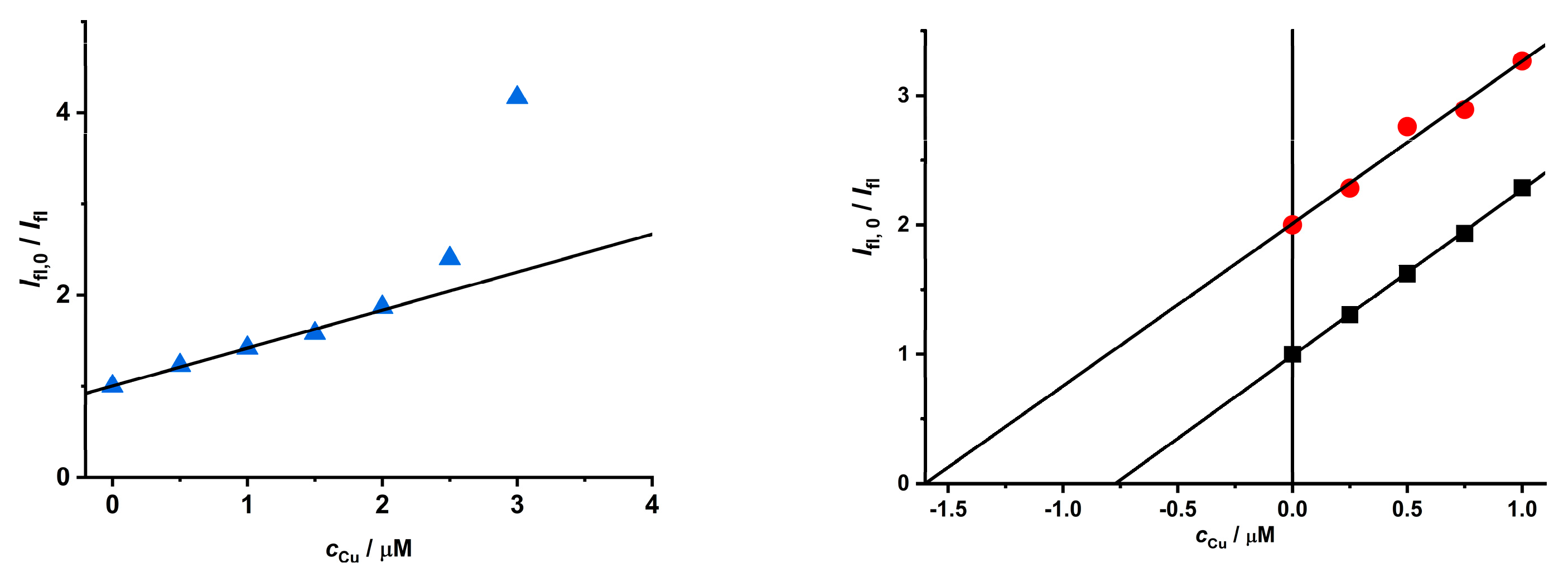
2.2. Study of the Quenching Phenomena of CdTe QD Nanoparticles
2.3. Analytical Applications of CdTe QDs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents for the Synthesis of CdTe QD Nanoparticles
4.2. Synthesis of CdTe QD Nanoparticles
4.3. Characterization of CdTe QD Nanoparticles
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cademartiri, L.; Ozin, G.A. Concepts of Nanochemistry; WILEY-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; ISBN 978-3-527-32597-9. [Google Scholar]
- Merkoçi, A. (Ed.) Biosensing Using Nanomaterials; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-470-18309-0. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, A. Nanotechnology Cookbook: Practical, Reliable and Jargon-Free Experimental Procedures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 978-0-08-097172-8. [Google Scholar]
- Shabbir, H.; Csapó, E.; Wojnicki, M. Carbon Quantum Dots: The Role of Surface Functional Groups and Proposed Mechanisms for Metal Ion Sensing. Inorganics 2023, 11, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesnyak, V.; Gaponik, N.; Eychmüller, A. Colloidal Semiconductor Nanocrystals: The Aqueous Approach. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2905–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiss, P.; Protière, M.; Li, L. Core/Shell Semiconductor Nanocrystals. Small 2009, 5, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ealias, A.M.; Saravanakumar, M.P. A Review on the Classification, Characterisation, Synthesis of Nanoparticles and Their Application. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 263, 032019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadreza Alizadeh-Ghodsi, M.; Pourhassan-Moghaddam, M.; Zavari-Nematabad, A.; Walker, B.; Annabi, N.; Akbarzadeh, A. State-of-the-Art and Trends in Synthesis, Properties, and Application of Quantum Dots-Based Nanomaterials. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2019, 36, 1800302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvin, A.P.; Martynenko, I.V.; Purcell-Milton, F.; Baranov, A.V.; Fedorov, A.V.; Gun’ko, Y.K. Colloidal Quantum Dots for Optoelectronics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 26, 13252–13275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; Tang, W. Surface Ligands Engineering of Semiconductor Quantum Dots for Chemosensory and Biological Applications. Mater. Today 2017, 20, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkhani, S.M.; Valizadeh, A. Review: Three Synthesis Methods of CdX (X = Se, S or Te) Quantum Dots. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2014, 8, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Cai, F.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.-X.; Chen, J.-F. Colloidal Synthesis of Semiconductor Quantum Dots towards Large- Scale Production: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 1790–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Yang, B.; Mohwald, H. Manipulation of Aqueous Growth of CdTe Nanocrystals to Fabricate Colloidally Stable One-Dimensional Nanostructures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 31, 10171–10180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-J.; Ruedas-Rama, M.J.; Hall, E.A.H. The emerging use of quantum dots in analysis. Anal. Lett. 2007, 40, 1497–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.J. Optical Sensing with Quantum Dots. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 520A–526A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biranje, A.; Azmi, N.; Tiwari, A.; Chaskar, A. Quantum Dots Based Fluorescent Probe for the Selective Detection of Heavy Metal Ions. J. Fluoresc. 2021, 31, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittar, D.B.; Ribeiro, D.S.M.; Pascoa, R.N.M.J.; Soares, J.X.; Rodrigues, S.S.M.; Castro, R.C.; Pezza, L.; Pezza, H.R.; Santos, J.L.M. Multiplexed analysis combining distinctly-sized CdTe-MPA quantum dots and chemometrics for multiple mutually interfering analyte determination. Talanta 2017, 174, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, D.S.M.; Castro, R.C.; Pascoa, R.N.M.J.; Soares, J.X.; Rodrigues, S.S.M.; Santos, J.L.M. Tuning CdTe quantum dots reactivity for multipoint detection of mercury(II), silver(I) and copper(II). J. Lum. 2019, 207, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, C.; Ping, Z. A new determining method of copper(II) ions at ng ml–1 levels based on quenching of the water-soluble nanocrystals fluorescence. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 381, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zhu, C. Aqueous synthesis of type-II core/shell CdTe/CdSe quantum dots for near-infrared fluorescent sensing of copper(II). Analyst 2008, 133, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Priyam, A.; Bhattacharya, S.C.; Saha, A. Mechanistic Aspects of Quantum Dot Based Probing of Cu (II) Ions: Role of Dendrimer in Sensor Efficiency. J. Fluoresc. 2009, 19, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.-X.; Liu, H.-Y.; Zhang, J.-R.; Jun-Jie Zhu, J.-J. Ultrasensitive Cu2+ sensing by near-infrared-emitting CdSeTe alloyed quantum dots. Talanta 2010, 80, 2172–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.S.; Rodrigues, S.S.M.; Korn, M.G.A.; Ribeiro, D.S.M.; Santos, J.L.M.; Teixeira, L.S.G. Determination of copper in biodiesel samples using CdTe-GSH quantum dots as photoluminescence probes. Microchem. J. 2014, 117, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamideh Elmizadeh, H.; Soleimani, M.; Faridbod, F.; Bardajee, G.R. Ligand-Capped CdTe Quantum Dots as a Fluorescent Nanosensor for Detection of Copper Ions in Environmental Water Sample. J. Fluoresc. 2017, 27, 2323–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.; Wang, B.; Wen, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. Fluorometric determination of copper(II) by using 3-aminophenylboronic acid-functionalized CdTe quantum dot probes. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Liang, J.; Han, H. A novel method for the determination of Pb2+ based on the quenching of the fluorescence of CdTe quantum dots. Microchim. Acta 2008, 161, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.-S.; Zhu, C.-Q. Use of surface-modified CdTe quantum dots as fluorescent probes in sensing mercury (II). Talanta 2008, 75, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniyan, S.B.; Veerappan, A. Water soluble cadmium selenide quantum dots for ultrasensitive detection of organic, inorganic and elemental mercury in biological fluids and live cells. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 22274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liu, H.; Qi, J.; Xiang, J.; Fu, L.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Chen, L. A Simple and Effective Visual Fluorescent Sensing Paper-Based Chip for the Ultrasensitive Detection of Mercury Ions in Environmental Water. Sensors 2023, 23, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnathambi, S.; Shirahata, N. Recent advances on fluorescent biomarkers of near-infrared quantum dots for in vitro and in vivo imaging. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2019, 20, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, K.; Vaishanav, S.K.; Korram, J.; Nagwanshi, R.; Karbhal, I.; Dewangan, L.; Ghosh, K.K.; Satnami, M.L. Interaction of Folic Acid with Mn(II) Doped CdTe/ZnS Quantum Dots In Situ Detection of Folic Acid. J. Fluoresc. 2021, 31, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sławski, J.; Białek, R.; Burdziński, G.; Gibasiewicz, K.; Worch, R.; Grzyb, J. Competition between Photoinduced Electron Transfer and Resonance Energy Transfer in an Example of Substituted Cytochrome c–Quantum Dot Systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 3307–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zou, P.; Li, J.; Lu, D.; Wang, X.-J.; Ma, L. Photoluminescent CdTe Quantum Dot-Polynitroxylated Albumin Composites for Glutathione Detection. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 4677–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Řezáčová, L.; Rybáková, S.; Lubal, P. Quantum Dot-Based Fluorosensor for Determination of Cu(II) and Pb(II) Ions. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Nanomaterials-Research & Application–NanoCon 2015, Brno, Czech Republic, 14–16 October 2015; pp. 650–654. [Google Scholar]
- Huhey, J.E.; Keiter, E.A.; Keiter, R.L. Inorganic Chemistry: Principles of Structure and Reactivity, 4th ed.; Harper Collins: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Modlitbová, P.; Novotný, K.; Pořízka, P.; Klus, J.; Lubal, P.; Zlámalová-Gargošová, H.; Kaiser, J. Comparative investigation of toxicity and bioaccumulation of Cd-based quantum dots and Cd salt in freshwater plant Lemna minor L. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlaváček, A.; Skládal, P. Isotachophoretic purification of nanoparticles: Tuning optical properties of quantum dots. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 1427–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Křížková, S.; Dostálová, S.; Michálek, P.; Nejdl, L.; Komínková, M.; Milosavljevič, V.; Moulick, A.; Vaculovičová, M.; Kopel, P.; Adam, V.; et al. SDS-PAGE as a Tool for Hydrodynamic Diameter-Dependent Separation of Quantum Dots. Chromatografia 2015, 78, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voráčová, I.; Klepárník, K.; Lišková, M.; Foret, F. Determination of zeta-potential, charge, and number of organic ligands on the surface of water-soluble quantum dots by capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepárník, K.; Voráčová, I.; Lišková, M.; Přikryl, J.; Hezinová, V.; Foret, F. Capillary electrophoresis immunoassays with conjugated quantum dots. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lišková, M.; Voráčová, I.; Klepárník, K.; Hezinová, V.; Přikryl, J.; Foret, F. Conjugation reactions in the preparations of quantum dot-based immunoluminescent probes for analysis of proteins by capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-387-31278-1. [Google Scholar]
- Valeur, B.; Berberan-Santos, M.N. Molecular Fluorescence. Principles and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2001; ISBN 3-527-29919-X. [Google Scholar]
- Kotrlý, S.; Šůcha, L. Handbook of Chemical Equilibria in Analytical Chemistry; Ellis Horwood: Chichester, UK, 1985; ISBN 0470274794. [Google Scholar]
- Christian, G.D. Analytical Chemistry; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-0-471-21472-4. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.L.; Song, L.X.; Zhan, J.H. One-Pot Synthesis of Highly Luminescent CdTe Quantum Dots by Microwave Irradiation Reduction and Their Hg2+-Sensitive Properties. Nano Res. 2009, 2, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.F.; Wang, E.K.; Dong, S.J. One-pot synthesis of CdTe nanocrystals and shape control of luminescent CdTe-cystine nanocomposites. Small 2006, 2, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škarková, P.; Novotný, K.; Lubal, P.; Jebavá, A.; Pořízka, P.; Klus, J.; Farka, Z.; Hrdlička, A.; Kaiser, J. 2D distribution mapping of quantum dots injected onto filtration paper by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta B 2017, 131, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Řezáčová, L.; Runowski, M.; Lubal, P.; Szyczewski, A.; Lis, S. Synthesis of highly luminescent nanocomposite LaF3:Ln3+/QD-CdTe system, exhibiting tunable red-to-green emission. Chem. Pap. 2019, 73, 2907–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

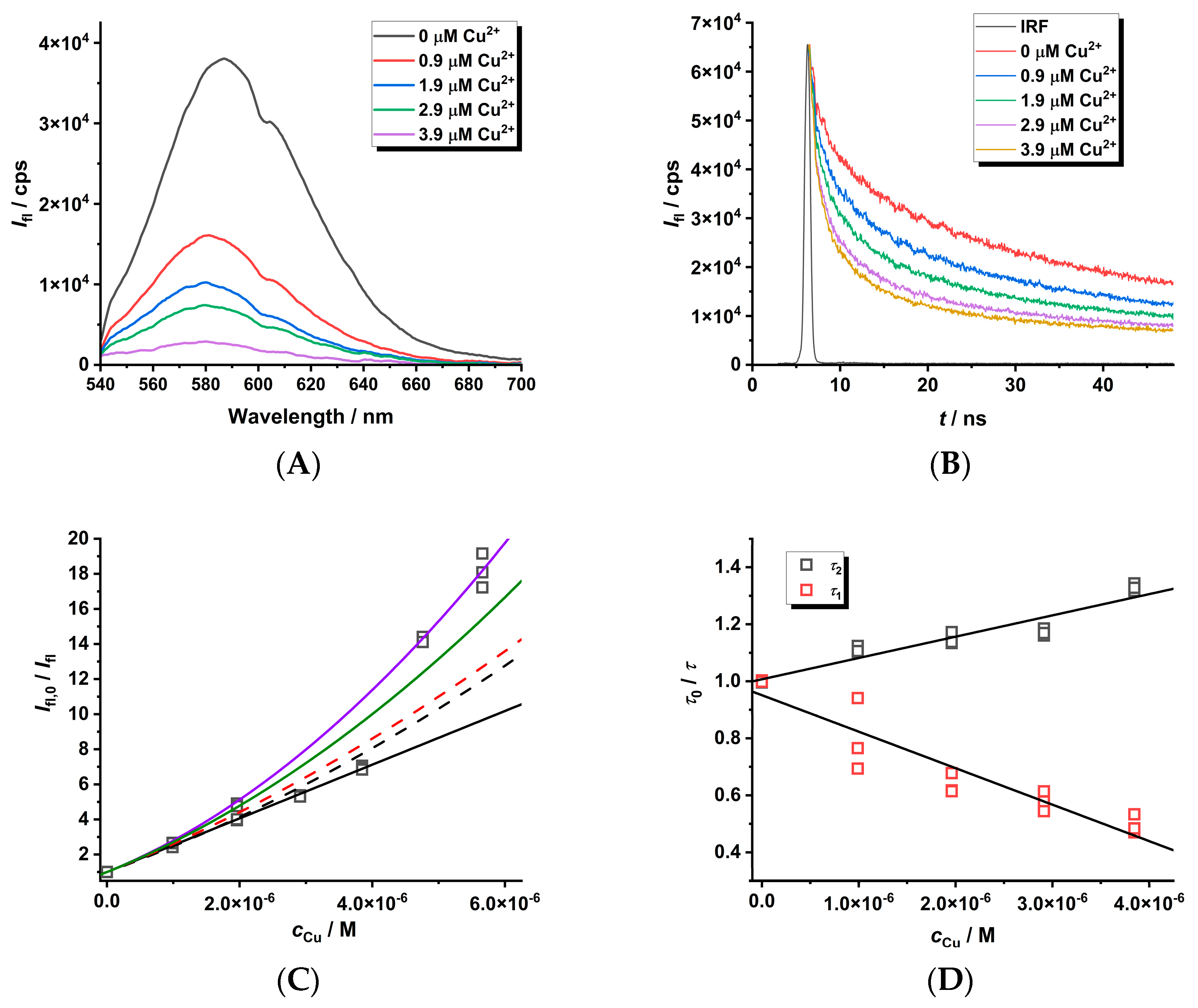
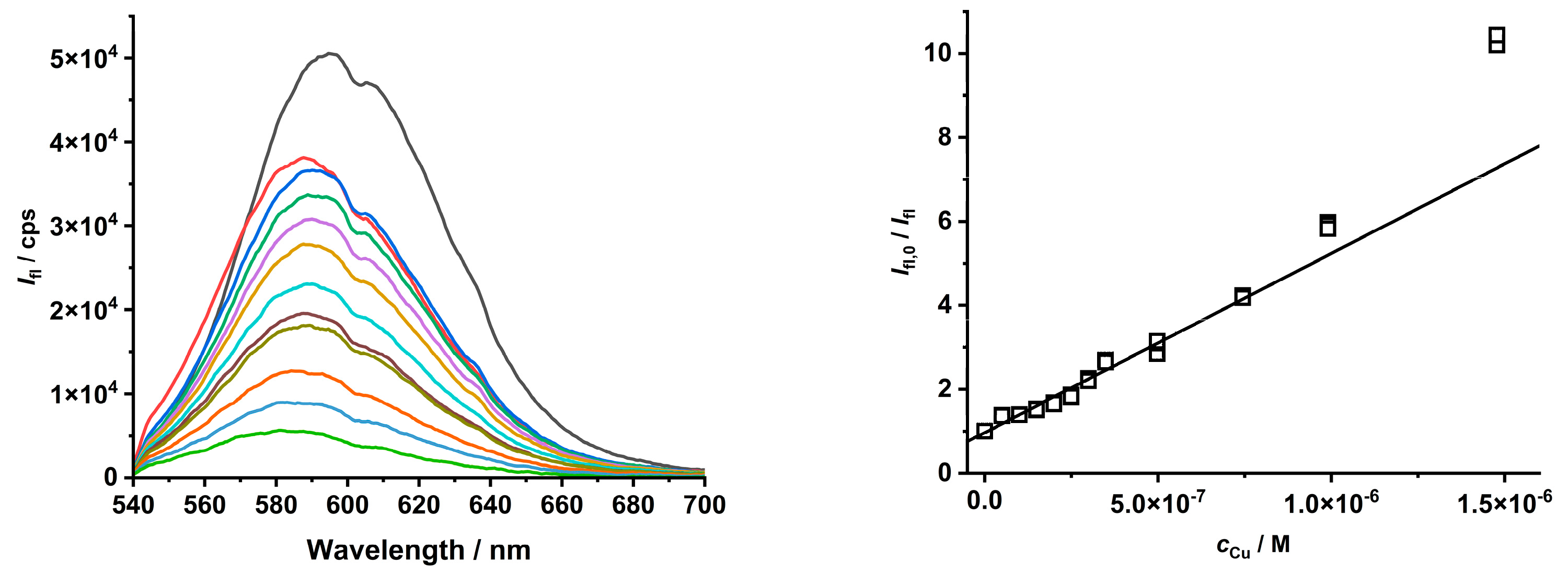
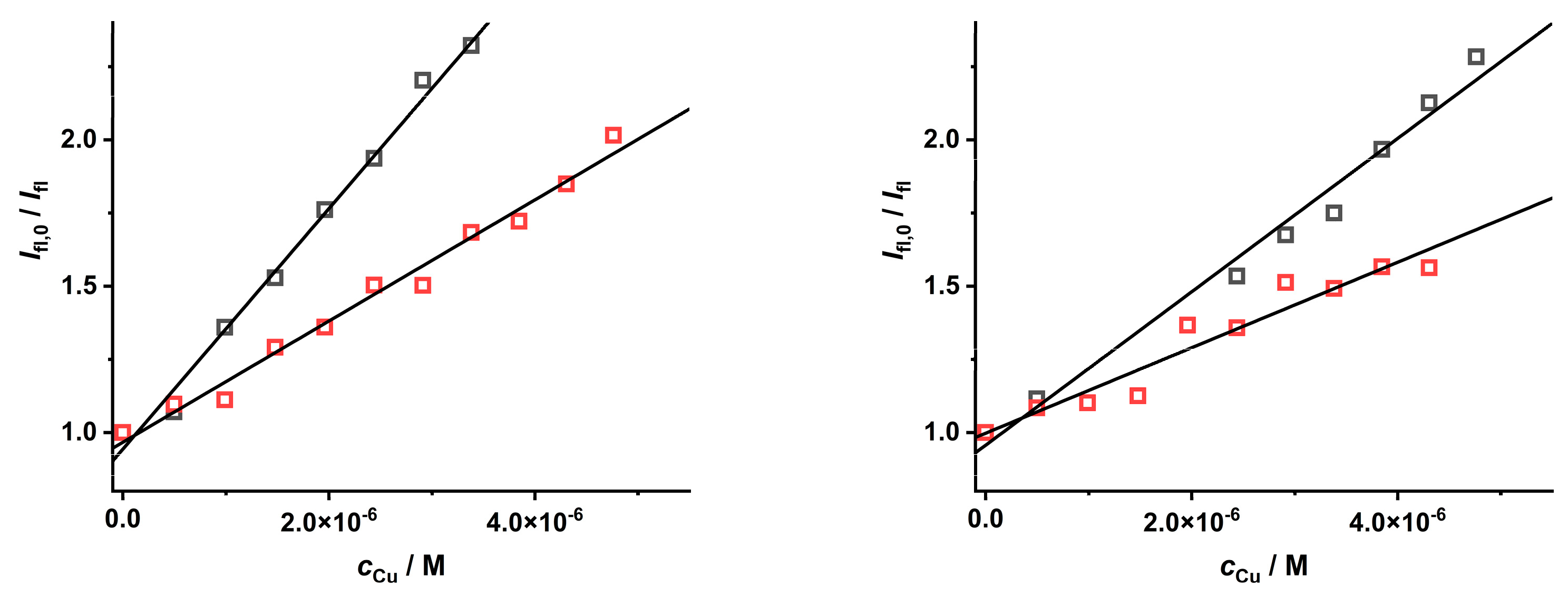
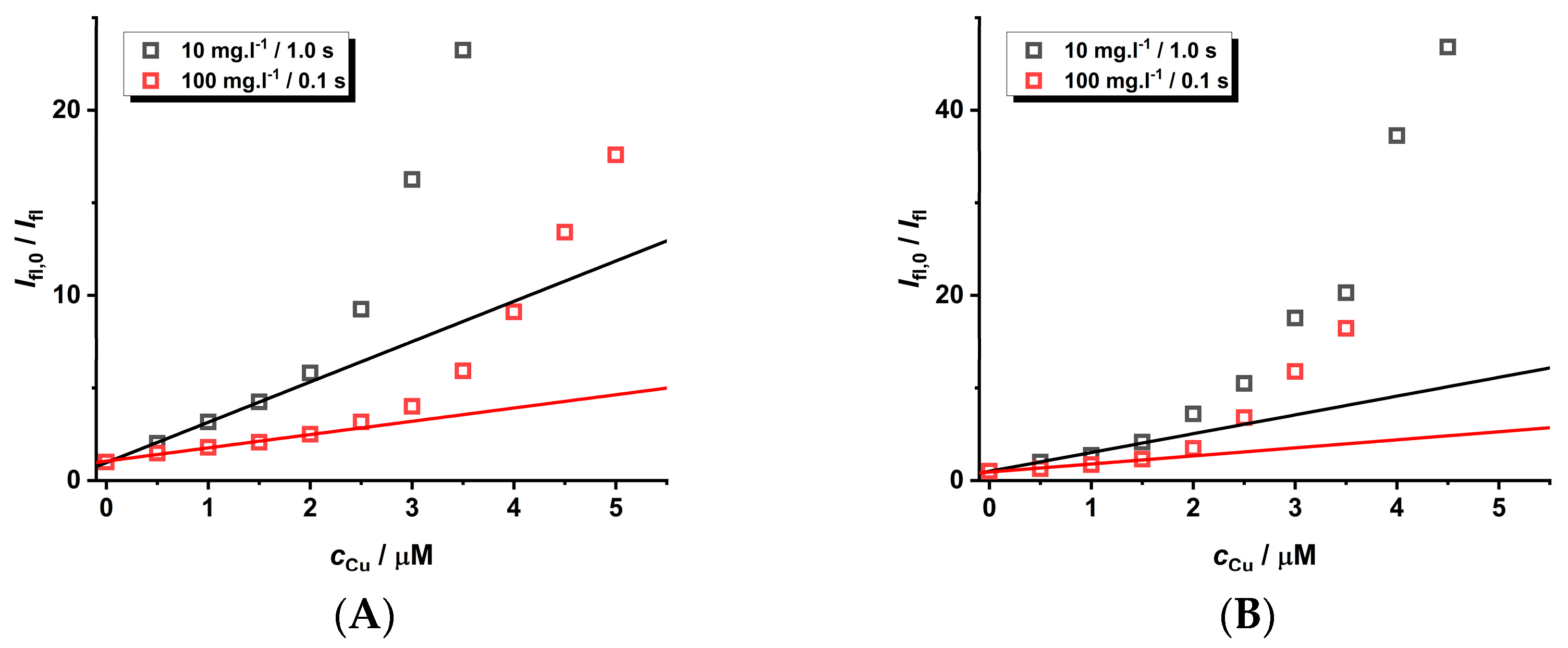

| Ratio Pic−/Cu2+ | KD+S/μM−1 b | LOD/nM |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.51 ± 0.01 | 11 |
| 1 | 5.3 ± 0.4 | 40 |
| 3 | 4.7 ± 0.2 | 29 |
| 5 | 4.3 ± 0.1 | 98 |
| Ratio Pic−/M2+ | Hg(II) | Pb(II) |
|---|---|---|
| KD+S/μM−1 b | ||
| 0 | 1.01 ± 0.09 | 0.38 ± 0.06 |
| 1 | 0.58 ± 0.05 | 0.38 ± 0.04 |
| 3 | 0.43 ± 0.04 | - |
| 5 | 0.37 ± 0.01 | 0.323 ± 0.003 |
| Species | MPA | GSH |
|---|---|---|
| KD+S/μM−1 a | ||
| [Cu(H2O)4]2+ | 0.41 ± 0.01 | 0.26 ± 0.01 |
| [Cu(NH3)4]2+ | 0.207 ± 0.009 | 0.16 ± 0.02 |
| Heating Time/min (λem/nm) | cQD/mg·L−1 a | |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 100 | |
| KD+S/μM−1 | ||
| 60 (543) | 2.18 ± 0.03 b | 0.72 ± 0.04 c |
| 120 (547) | 2.0 ± 0.2 b | 0.87 ± 0.09 c |
| 180 (552) | 1.6 ± 0.2 b | 0.42 ± 0.06 c |
| 240 (562) | 1.8 ± 0.1 b | 0.46 ± 0.03 c |
| 360 (577) | 5 ± 1 c 4.9 ± 0.6 b 2.8 ± 0.2 d | 4.1 ± 0.3 c 2.3 ± 0.3 b |
| Metal Ion | Tap Water | Svratka River Water | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluorosensor | ICP-OES | Fluorosensor | ICP-OES | |
| Cu(II) | 47 ± 6 ppm 0.7 ± 0.1 μM | 76.0 ppm 1.20 μM | 51 ± 4 ppm 0.80 ± 0.06 μM | 31.0 ppm 0.488 μM |
| Pb(II) | 58 ± 30 ppm 0.3 ± 0.1 μM | 48.9 ppm 0.236 μM | 80 ± 14 ppm 0.39 ± 0.07 μM | 69.0 ppm 0.333 μM |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Humajová, P.; Baliak, P.; Yumdjo Youmbissi, I.L.; Jebavá, A.; Řezáčová, L.; Lubal, P. The Analytical Application of Quenching Phenomena of CdTe Quantum Dot Nanoparticles. Inorganics 2023, 11, 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11090373
Humajová P, Baliak P, Yumdjo Youmbissi IL, Jebavá A, Řezáčová L, Lubal P. The Analytical Application of Quenching Phenomena of CdTe Quantum Dot Nanoparticles. Inorganics. 2023; 11(9):373. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11090373
Chicago/Turabian StyleHumajová, Petra, Patrik Baliak, Ivan Landry Yumdjo Youmbissi, Alžběta Jebavá, Lenka Řezáčová, and Přemysl Lubal. 2023. "The Analytical Application of Quenching Phenomena of CdTe Quantum Dot Nanoparticles" Inorganics 11, no. 9: 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11090373
APA StyleHumajová, P., Baliak, P., Yumdjo Youmbissi, I. L., Jebavá, A., Řezáčová, L., & Lubal, P. (2023). The Analytical Application of Quenching Phenomena of CdTe Quantum Dot Nanoparticles. Inorganics, 11(9), 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11090373