Facile Synthesis and Characterization of Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticles for the Successful Removal of Safranine T Dye from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
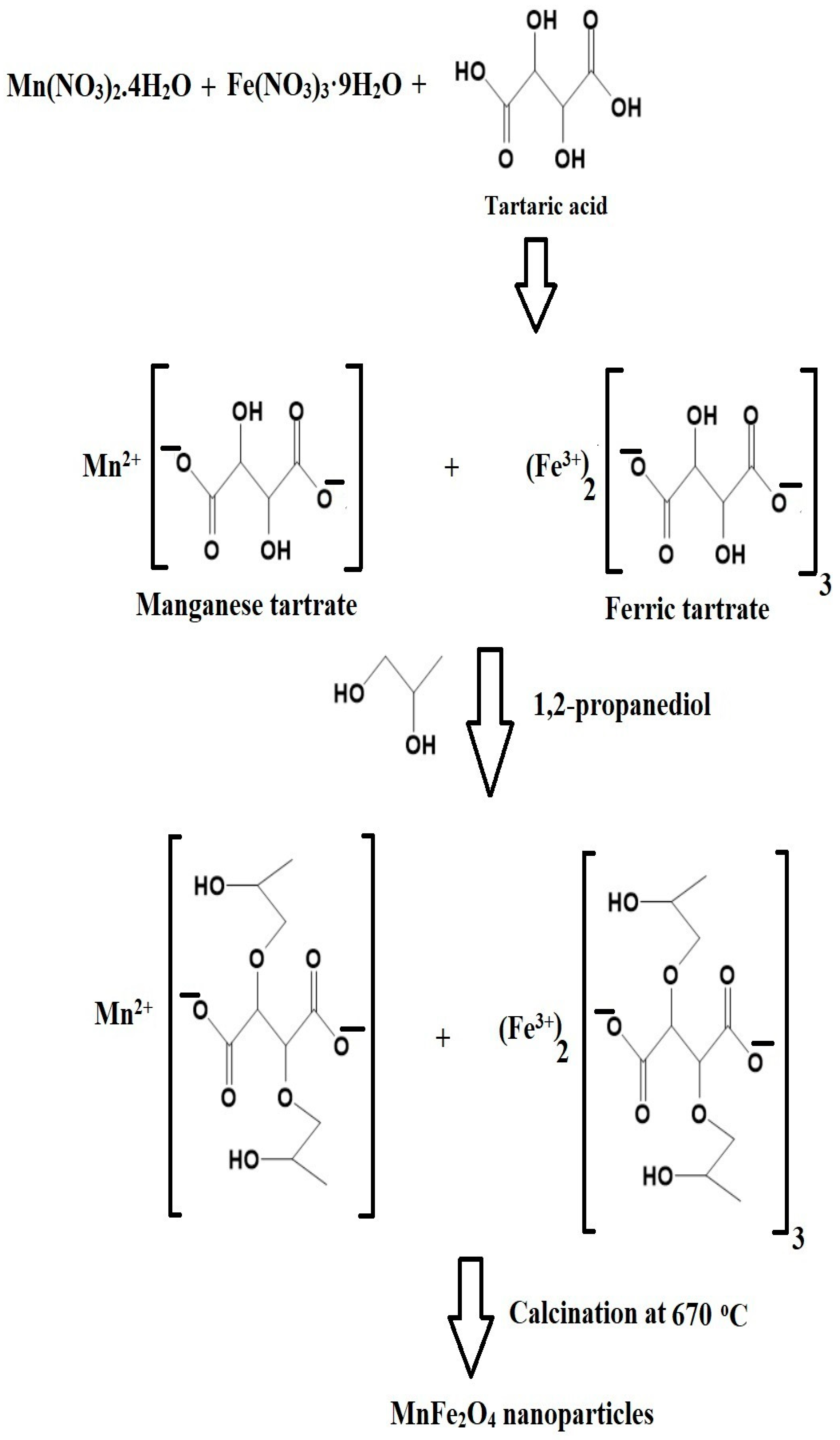
2.2. Synthesis of MnFe2O4 Nanoparticles
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Adsorption of Safranine T Dye from Aqueous Solutions
3. Results and Discussion
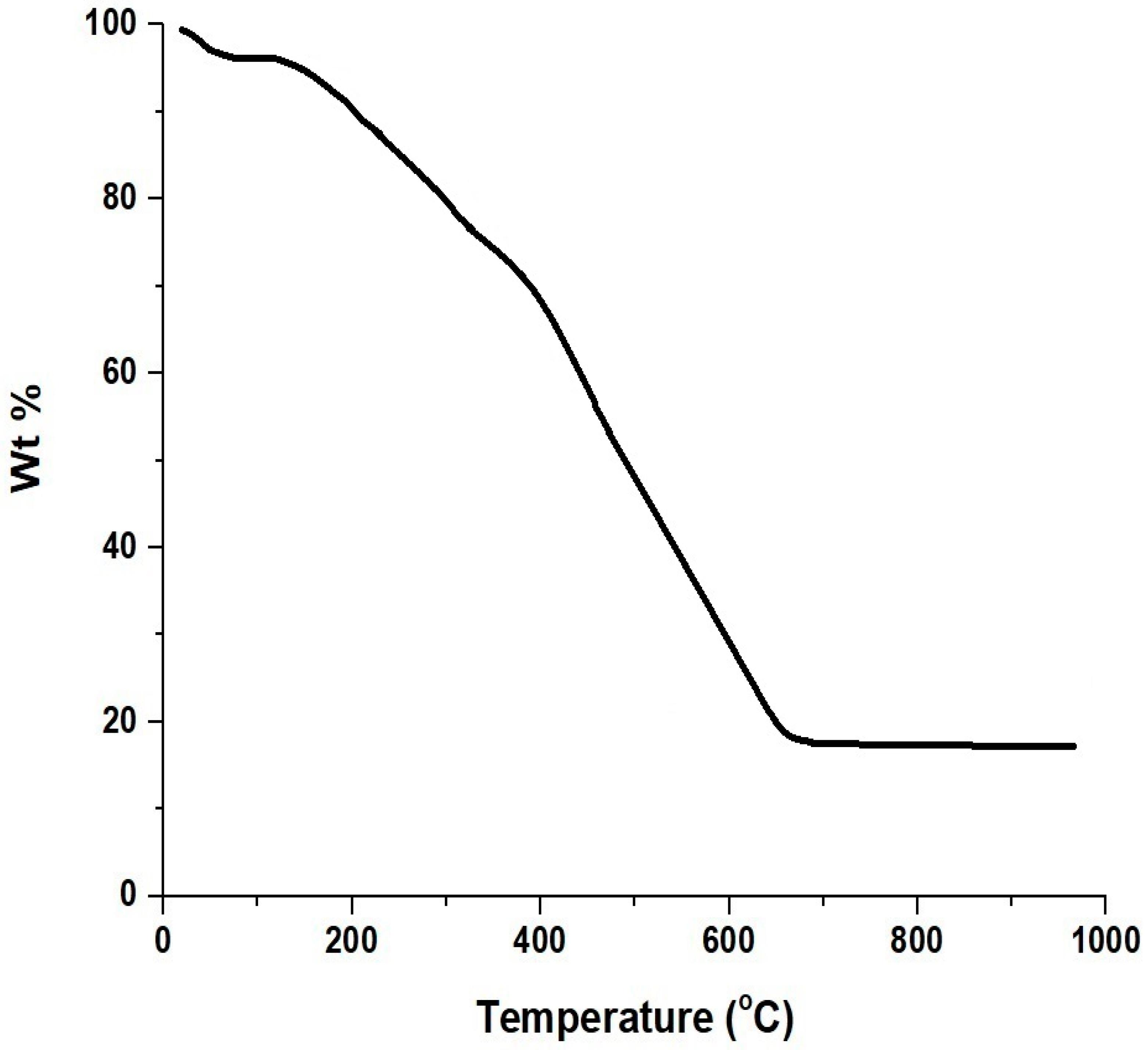
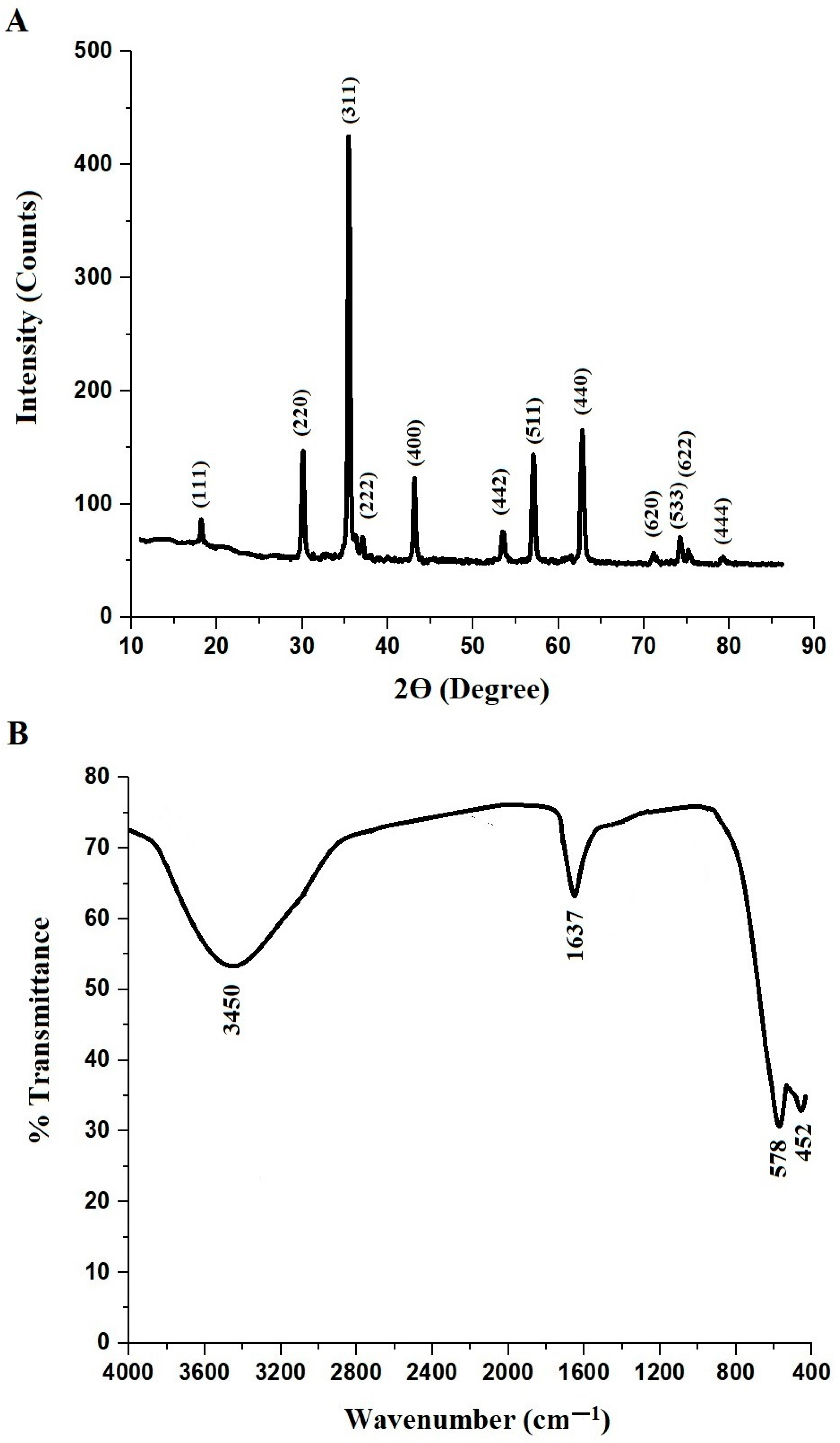
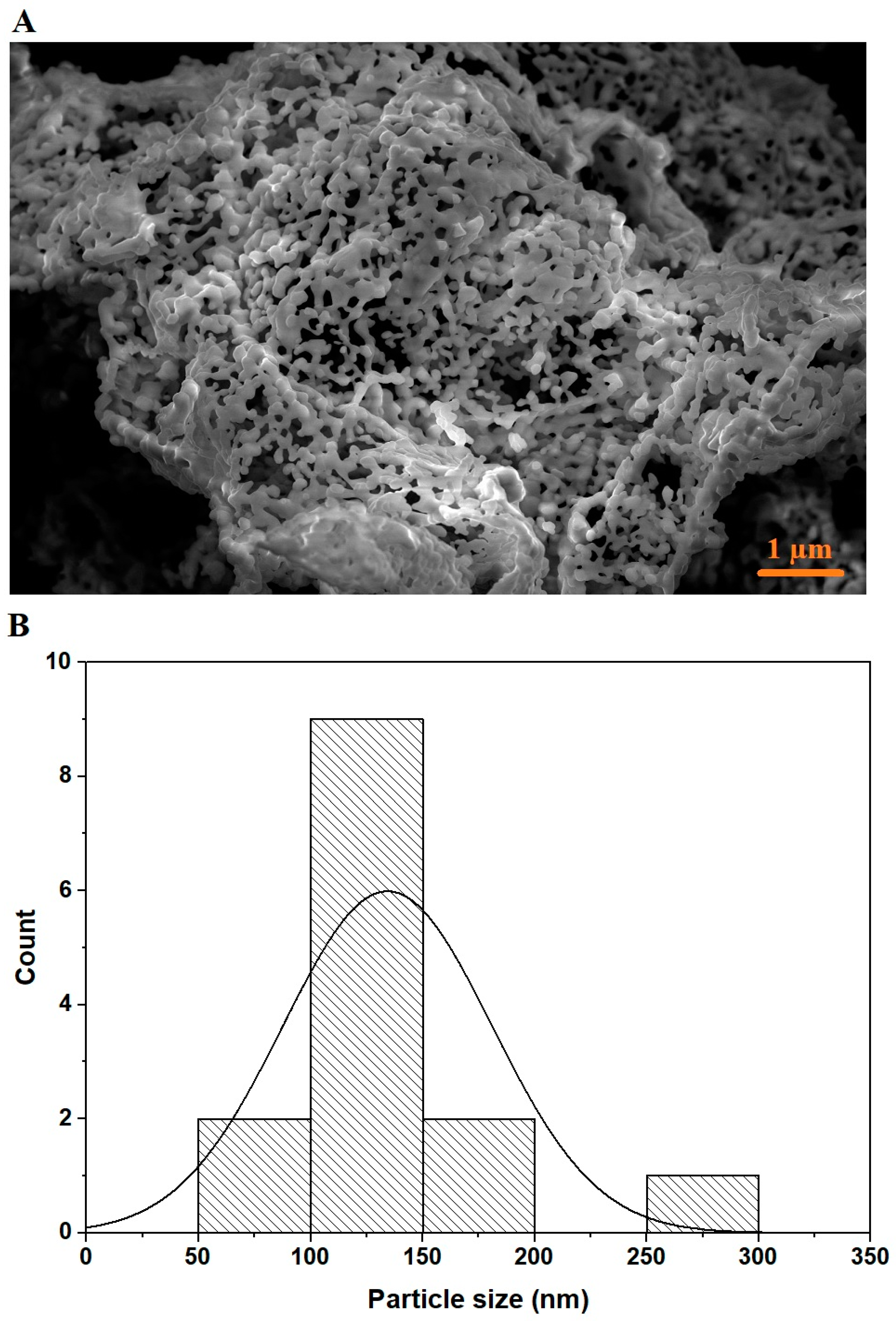
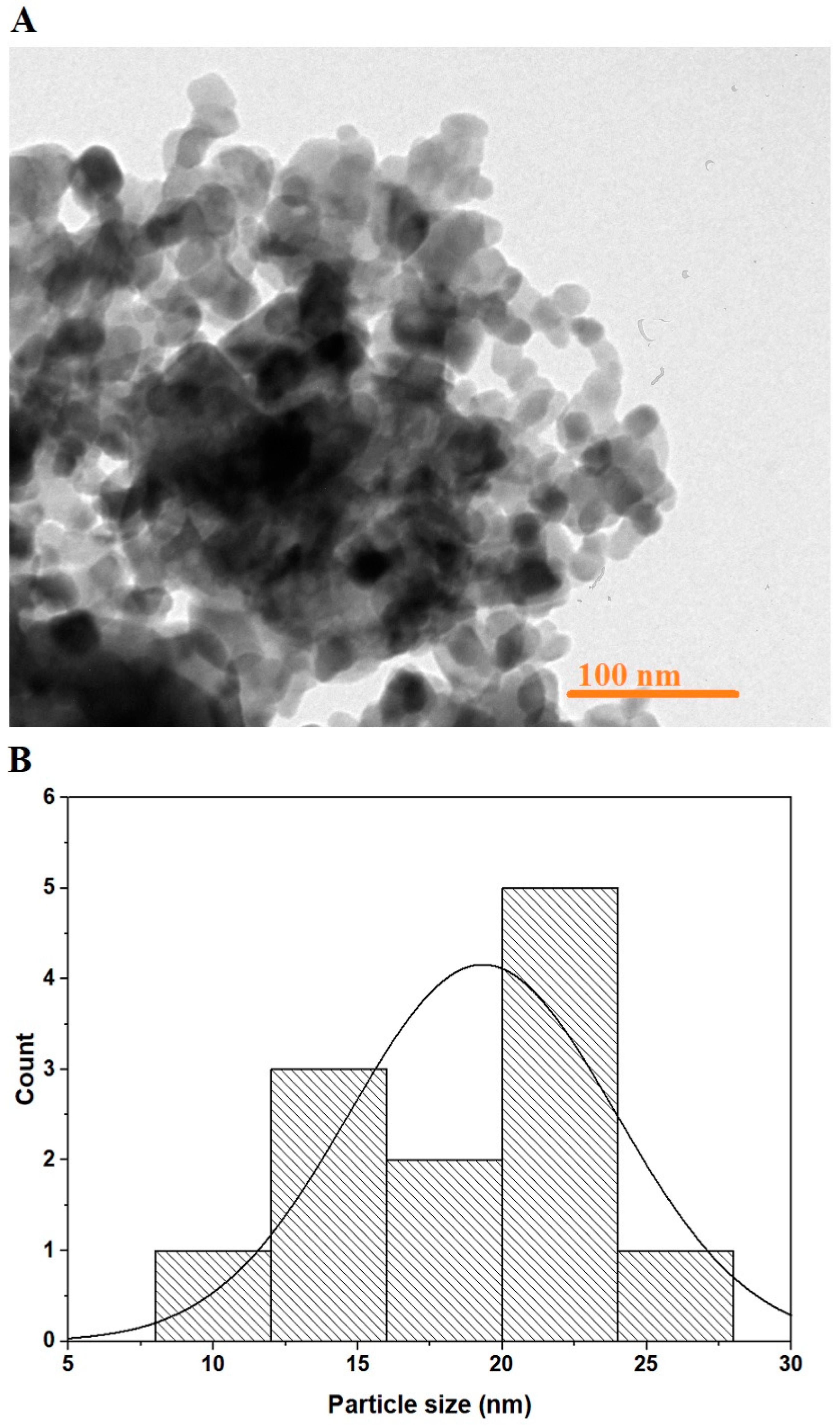
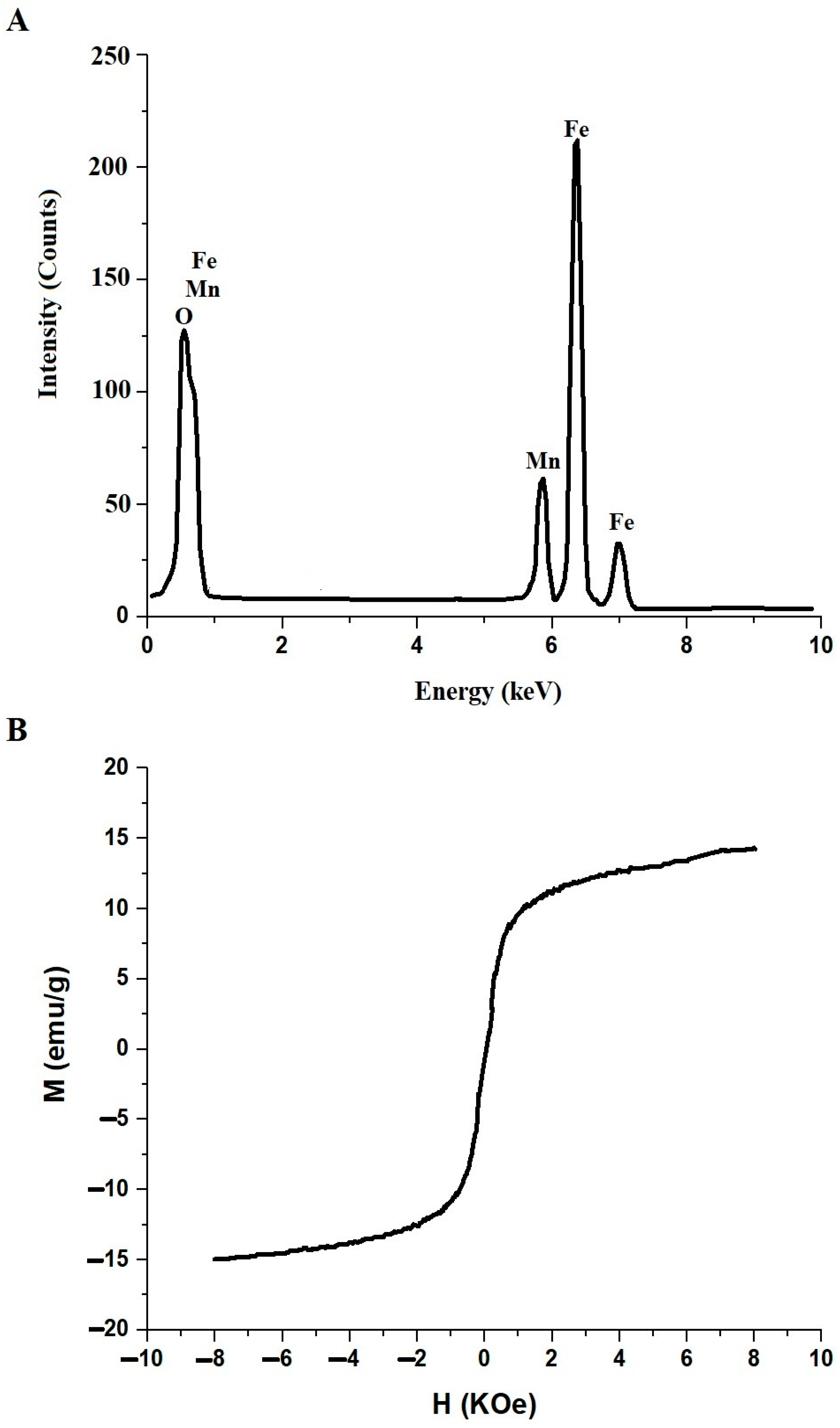
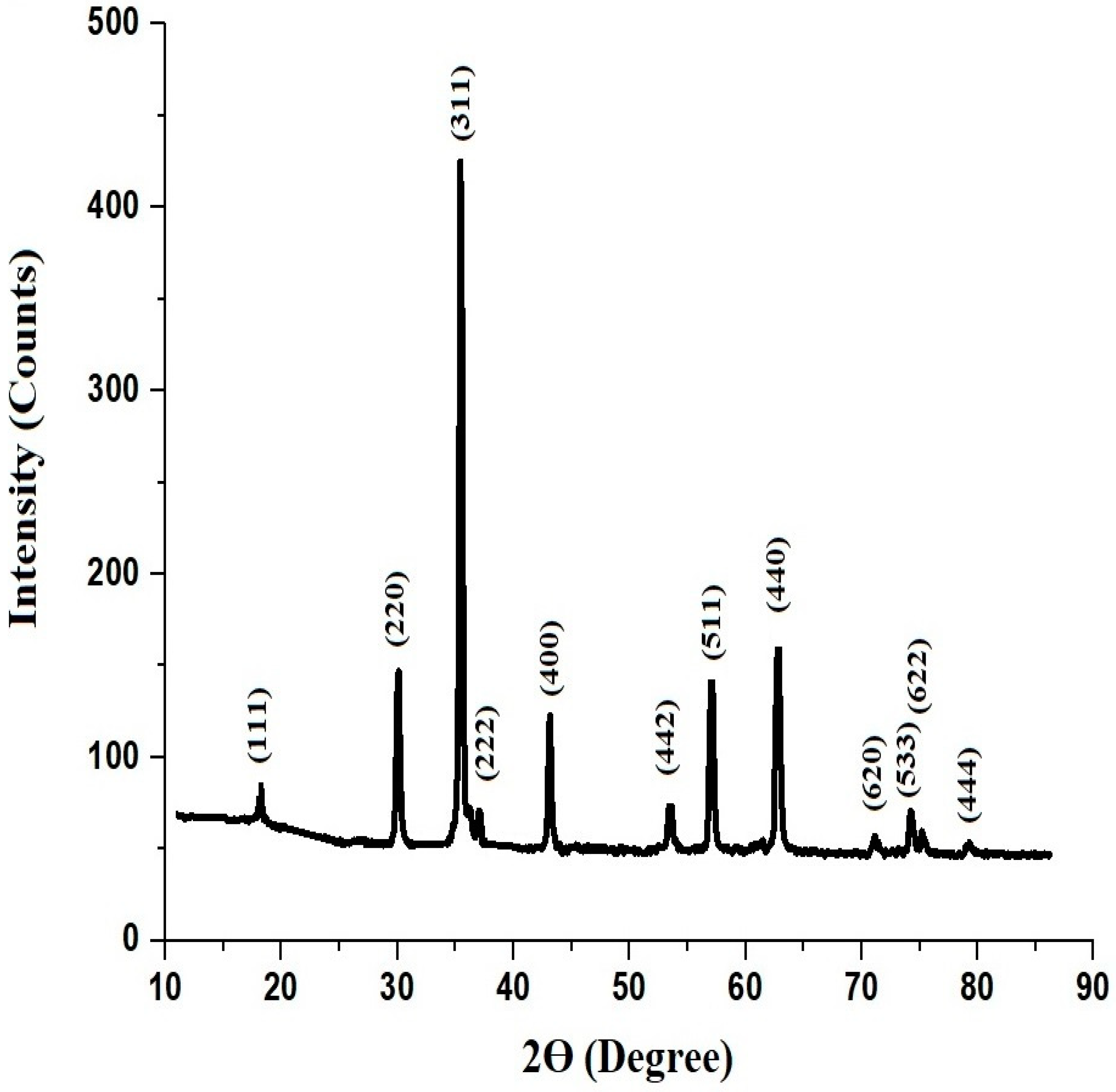
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of MnFe2O4 Nanoparticles
3.2. Safranine T Dye Removal from Aqueous Solutions
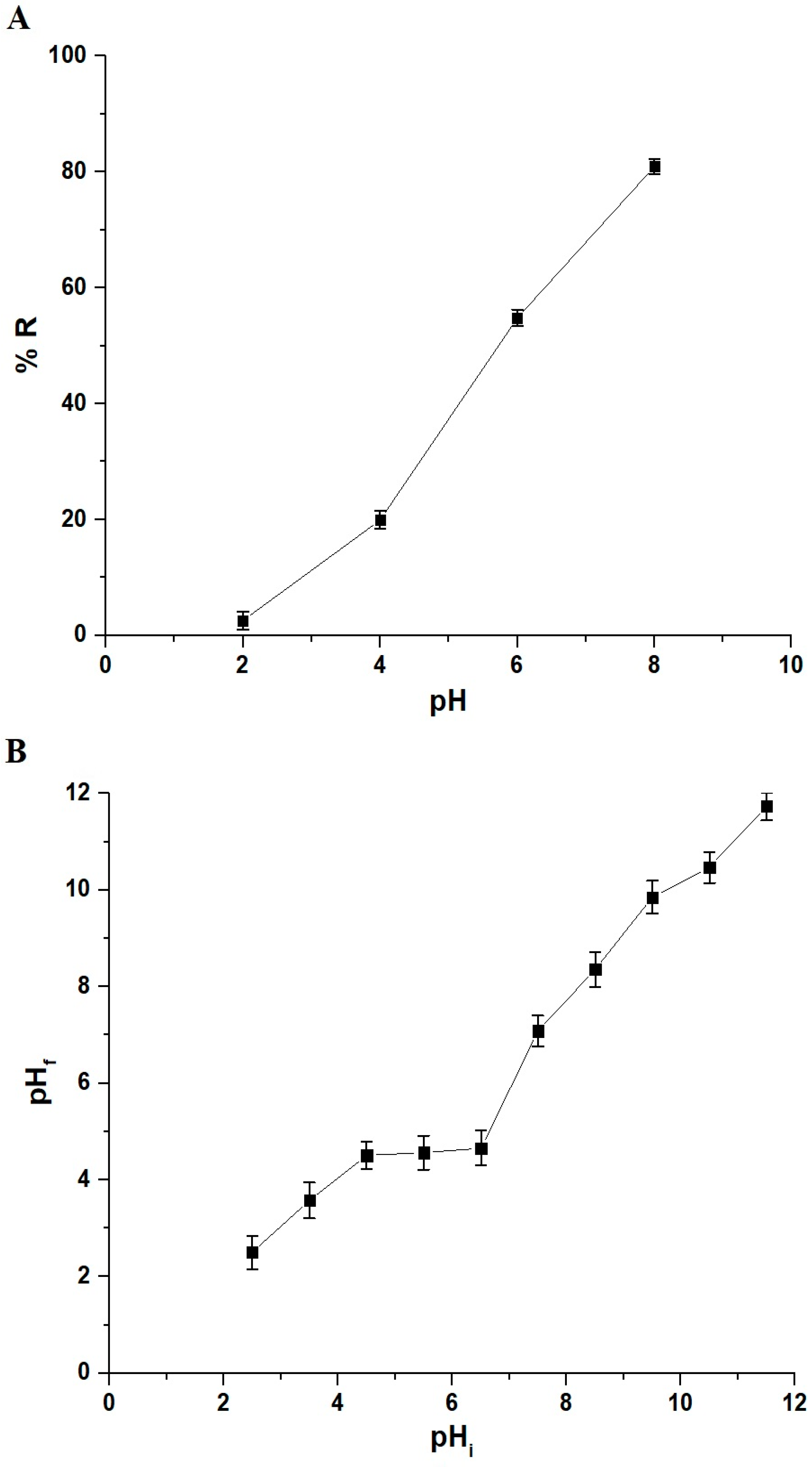
3.2.1. Influence of pH
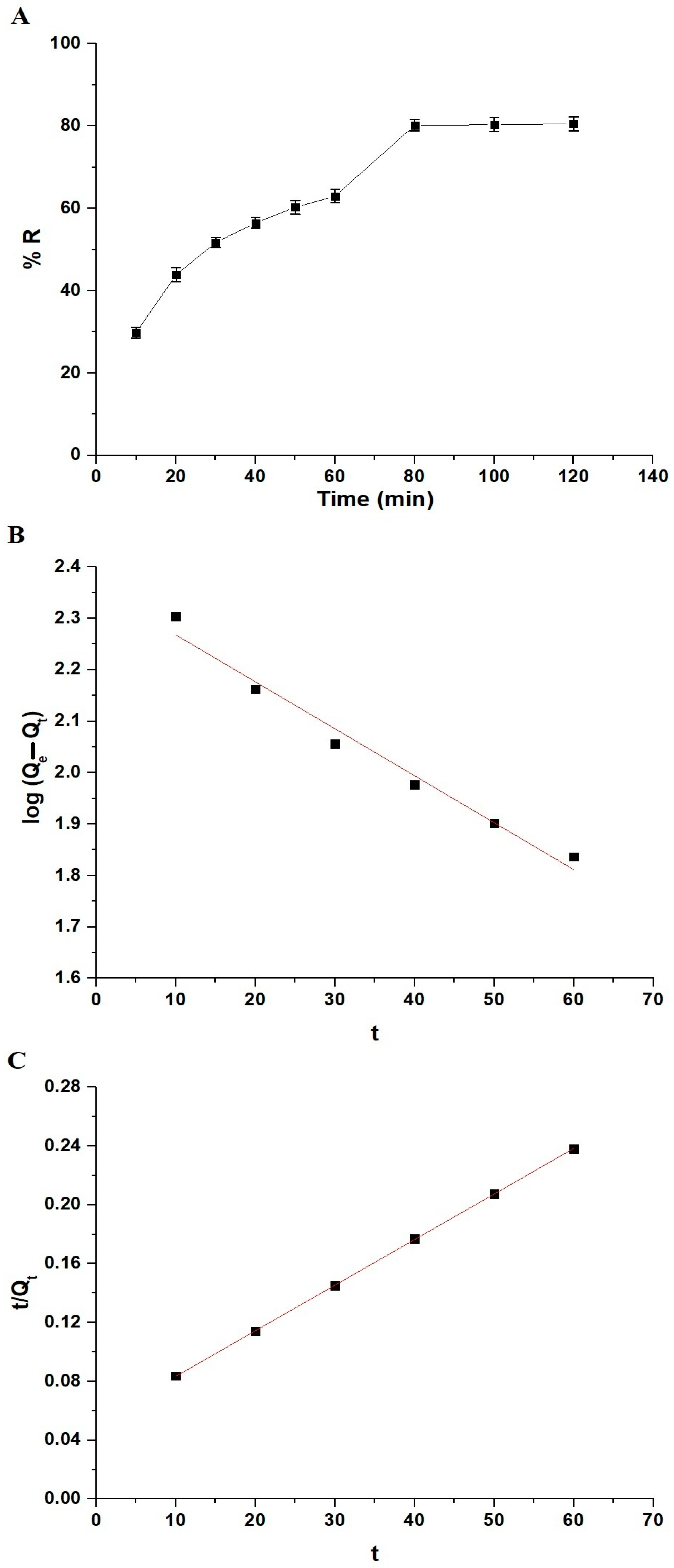
3.2.2. Influence of Adsorption Time and Adsorption Kinetics
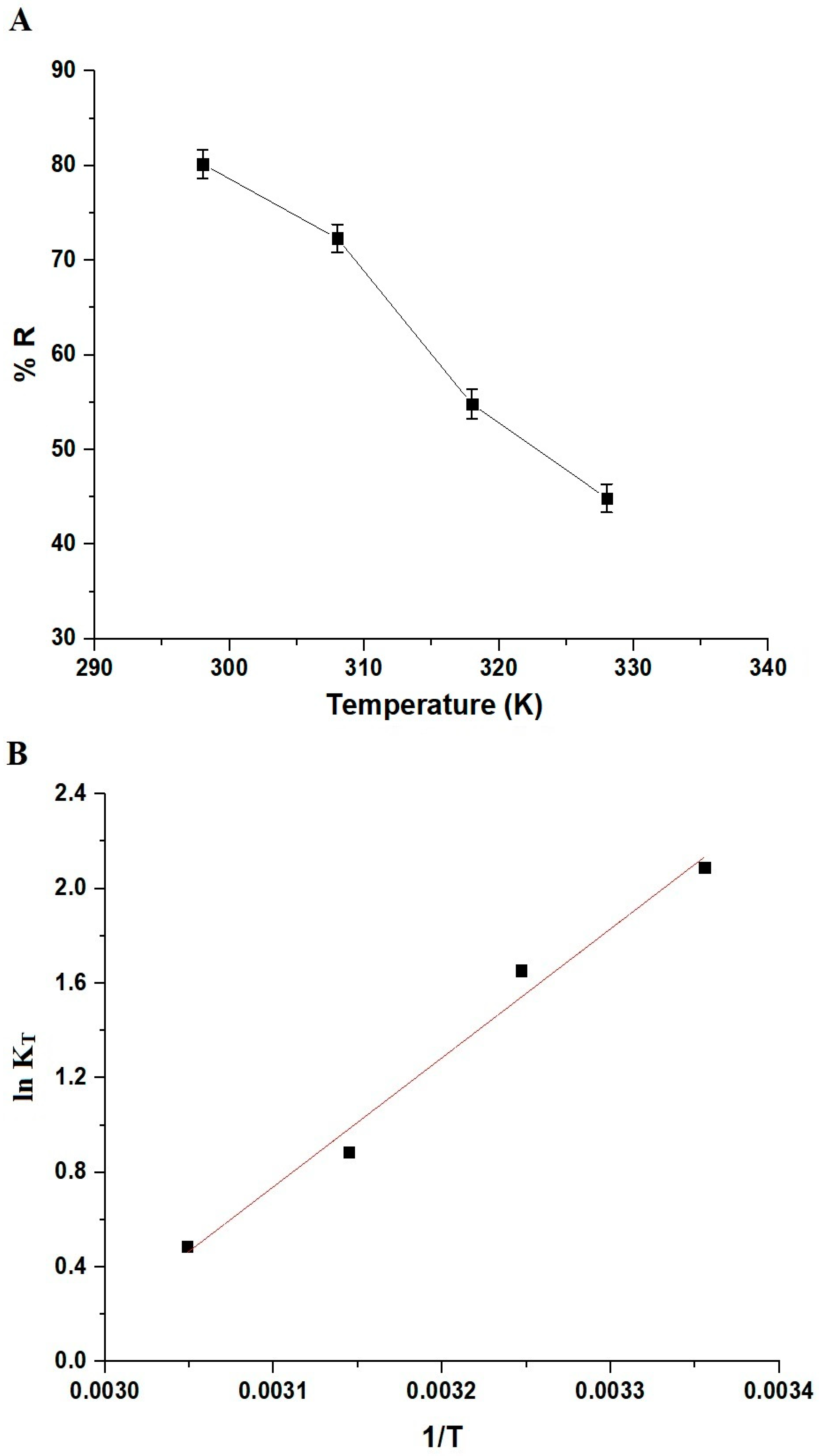
3.2.3. Influence of Solution Temperature and Thermodynamic Constants
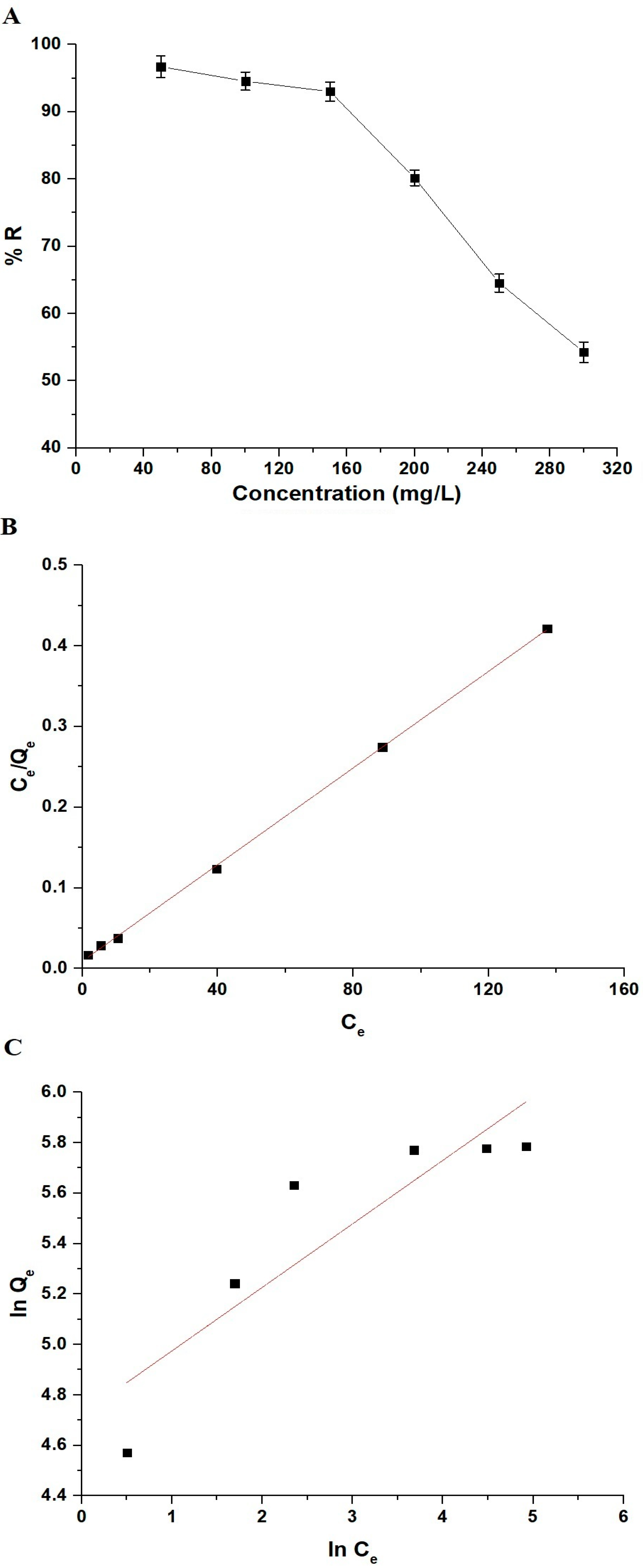
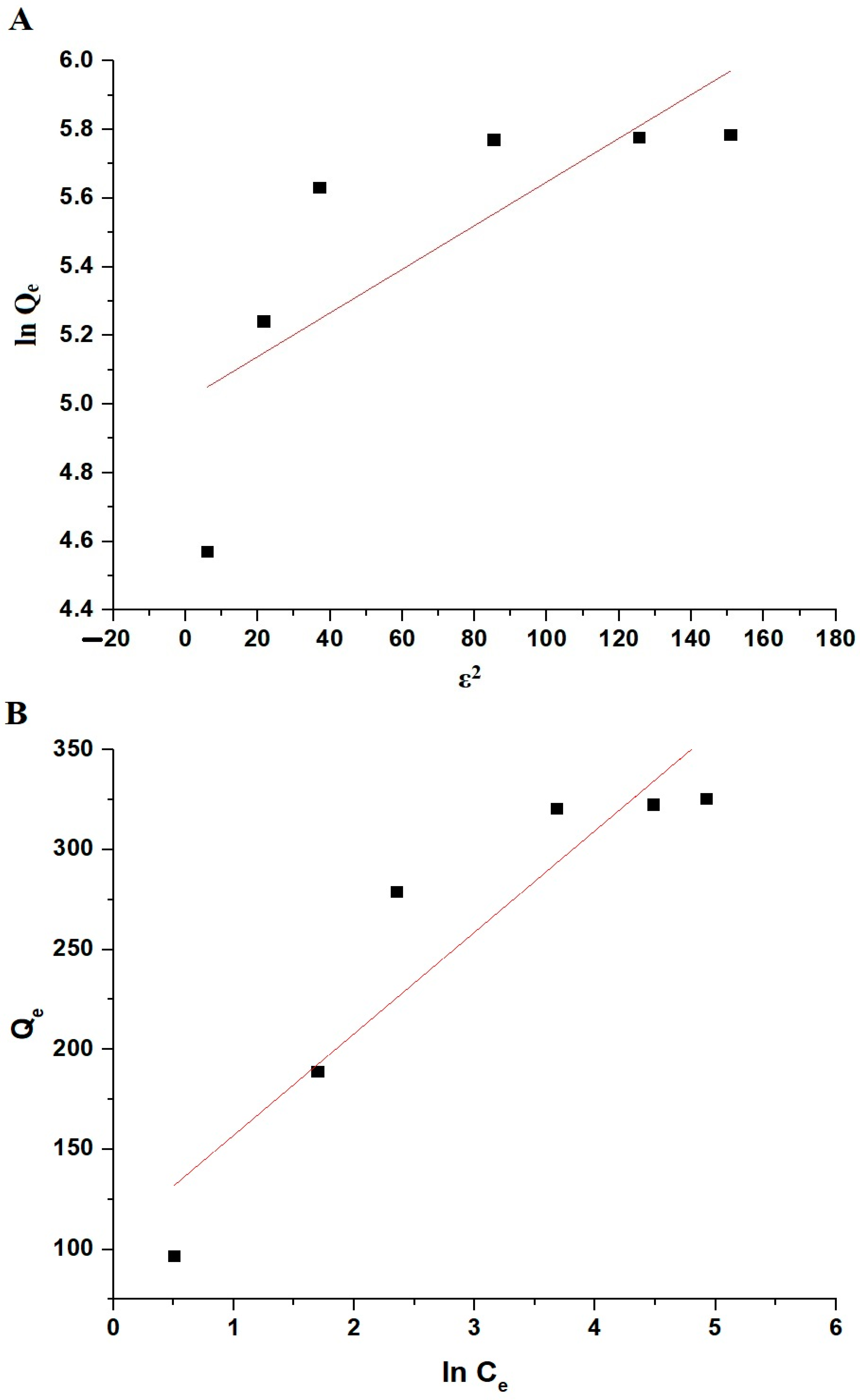
3.2.4. Influence of Initial Safranine T Dye Concentration and Adsorption Equilibrium Isotherms
3.2.5. Influence of Renewal and Reusability
3.2.6. Influence of Selectivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, N.; Pandey, A.; Sharma, Y.C. A Review on Sustainable Mesoporous Activated Carbon as Adsorbent for Efficient Removal of Hazardous Dyes from Industrial Wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 54, 104054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, M.; Jaymand, M. Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogels for Removal of Synthetic Dyes: A Comprehensive Review. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 486, 215152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Zohra, S.T.; Ijaz, S.; Iqbal, M.; Iqbal, J.; Bibi, I.; Nouren, S.; El Messaoudi, N.; Nazir, A. Cellulose-Based Materials and Their Adsorptive Removal Efficiency for Dyes: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 224, 1337–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaner, D.; Sarac, A. Removal of Dyes from Water Using Crosslinked Aminomethane Sulfonic Acid Based Resin. Environ. Geochem. Health 2010, 32, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Khan, U.; Ihsanullah, I. MXenes: The Emerging Adsorbents for the Removal of Dyes from Water. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 385, 122377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, M.; Ji, M.; Zhang, L.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, Y. Magnetic Graphene Oxide-Containing Chitosan-Sodium Alginate Hydrogel Beads for Highly Efficient and Sustainable Removal of Cationic Dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 2221–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihaddaden, S.; Aberkane, D.; Boukerroui, A.; Robert, D. Removal of Methylene Blue (Basic Dye) by Coagulation-Flocculation with Biomaterials (Bentonite and Opuntia Ficus Indic). J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 102952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, H.; Kusumoto, R. Journal of Water Process Engineering Removal of Anionic Dyes in Aqueous Solution by Flocculation with Cellulose Ampholytes. J. Water Process Eng. 2015, 7, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, A.; Ding, L.; Wei, J.; Liu, Y.; Niu, Y. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects Simultaneous and Ultrafast Removal of Anionic and Cationic Dyes from Aqueous Solution by Zr-Based MOFs Hybridized by Attapulgite and Adsorption Performance Research. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 680, 132643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semwal, N.; Mahar, D.; Chatti, M.; Dandapat, A.; Chandra, M. Heliyon “Adsorptive Removal of Congo Red Dye from Its Aqueous Solution by Ag-Cu-CeO2 Nanocomposites: Adsorption Kinetics, Isotherms, and Thermodynamics”. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlangu, O.T.; Mamba, G.; Mamba, B.B. A Facile Synthesis Approach for GO-ZnO/PES Ultrafiltration Mixed Matrix Photocatalytic Membranes for Dye Removal in Water: Leveraging the Synergy between Photocatalysis and Membrane Filtration. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subrahmanya, T.M.; Widakdo, J.; Mani, S.; Faye, H.; Hung, W.; Makari, H.K.; Nagar, J.K.; Hu, C.; Lai, J. An Eco-Friendly and Reusable Syringe Filter Membrane for the Efficient Removal of Dyes from Water via Low Pressure Filtration Assisted Self-Assembling of Graphene Oxide and SBA-15/PDA. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 349, 131425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Qiu, X.; Deng, X.; Ren, X.; Ge, W.; Yuan, H. Coagulation Performance and Floc Properties for Synchronous Removal of Reactive Dye and Polyethylene Terephthalate Microplastics. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 165, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcyotto, F.; Wei, Q.; Macharia, D.K.; Huang, M.; Shen, C.; Chow, C.W.K. Effect of dye structure on color removal efficiency by coagulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yin, W.; Zhao, T.; Yao, Q.; Fu, S.; Zhou, G. High-Efficient Removal of Organic Dyes from Model Wastewater Using Mg(OH)2-MnO2 Nanocomposite: Synergistic Effects of Adsorption, Precipitation, and Photodegradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 272, 118901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, M.; Javanbakht, V.; Esmaili, J. Synthesis of zeolite/nickel ferrite/sodium alginate bionanocomposite via a co-precipitation technique for efficient removal of water-soluble methylene blue dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, S.; Guelli, D.A.; De Souza, U.; Angela, K.; Bonilla, S.; Augusto, A.; Souza, U. Removal of COD and Color from Hydrolyzed Textile Azo Dye by Combined Ozonation and Biological Treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijannarong, S.; Aroonsrimorakot, S.; Thavipoke, P. Removal of Reactive Dyes from Textile Dyeing Industrial Effluent by Ozonation Process. APCBEE Procedia 2013, 5, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, W.; Li, S.; Han, L.; Lu, X.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Lv, Z.; et al. Enhanced Electrochemical Removal of Dye Wastewater by PbO2 Anodes Using Halloysite Nanotubes with Different Surface Charge Properties. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 923, 116816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Q.; Xu, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Jin, D.; Wang, P.; Wu, D.; Dong, F. Electrochemical Removal of Synthetic Methyl Orange Dyeing Wastewater by Reverse Electrodialysis Reactor: Experiment and Mineralizing Model. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 114064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, J.M.; Alyahya, S.A.; Govindan, R.; Kanisha, C. Laccase Producing Bacteria Influenced the High Decolorization of Textile Azo Dyes with Advanced Study. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, E.; Talip, B.A.; Al-gheethi, A.; Mohamed, R.; Nagao, H. Materials Today: Proceedings Decolourisation of Dyes in Greywater by Mycoremediation and Mycosorption Process of Fungi from Peatland: Primary Study. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 31, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wasidi, A.S.; Khairy, M.; Abdulkhair, B.Y.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Efficient Disposal of Basic Fuchsin Dye from Aqueous Media Using ZrO2/MgMn2O4/Mg(Mg0.333Mn1.333)O4 as a Novel and Facilely Synthesized Nanocomposite. Inorganics 2023, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, E.A.; Algethami, F.K.; Alsalem, H.S.; Binkadem, M.S. Facile Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Nanostructures for the Efficient Disposal of Crystal Violet Dye from Aqueous Media. Inorganics 2023, 11, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-wasidi, A.S.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Simple Synthesis and Characterization of Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles for the Successful Adsorption of Indigo Carmine Dye from Aqueous Media. Inorganics 2023, 11, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirtimala, N.; Wareppam, B.; Herojit, L. Materials Today: Proceedings Effect of Sintering Temperature on the Magnetic Properties of ZnFe2O4 Composite with Cobaltic Oxide Synthesized by Chemical Co Precipitation Method. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 68, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Mei, S.; Yang, L.; Yang, L.; Lu, Z.; Shuang, W. Effect of Synthesis Conditions on the Structure and Properties of LiFeO2/ZnFe2O4 Nanocomposites Prepared by a Sol-Gel Method. Solid State Commun. 2021, 334–335, 114379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, N.; Kadam, S.; Ingole, R.; Kulkarni, S. Facile Hydrothermal Synthesis of ZnFe2O4 Nanostructures for High-Performance Supercapacitor Application. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 29478–29483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srihari, S.; Panda, S.; Gandi, S.; Reddy, S.; Panigrahi, T. Facile Hydrothermal Synthesis of Bio-Inspired ZnO/Fe2O3/ZnFe2O4 Heterostructure: Effect of Microwave Absorption Properties. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 42, 103490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, T.G.; Tuokkola, A.R.; Yu, M.; Laine, R.M. Liquid-Feed Flame Spray Pyrolysis Enabled Synthesis of Co- and Cr-Free, High-Entropy Spinel Oxides as Li-Ion Anodes. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iljinas, A.; Brucas, R.; Stankus, V.; Dudonis, J. Synthesis of Fe3O4 Thin Films by Solid State Reactions. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2005, 25, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, X.; Liao, T.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, H.; Li, T.; Song, J. ScienceDirect Facile Electrochemical Fabrication of Magnetic Fe3O4 for Electrocatalytic Synthesis of Ammonia Used for Hydrogen Storage Application. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 24128–24134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Wijayantha, K.G.U.; Mazhar, M.; Mckee, V. ZnFe2O4 Thin Fi Lms from a Single Source Precursor by Aerosol Assisted Chemical Vapour Deposition. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 3664–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.Y.; Baek, E.; You, C.Y.; Choi, H.J. Magnetic-Stimuli Rheological Response of Soft-Magnetic Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticle Suspension. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2021, 4, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, E.A.; Abou El-Reash, Y.G.; Youssef, H.M.; Kotp, Y.H.; Hegazey, R.M. Utilization of Rice Husk and Waste Aluminum Cans for the Synthesis of Some Nanosized Zeolite, Zeolite/Zeolite, and Geopolymer/Zeolite Products for the Efficient Removal of Co(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) Ions from Aqueous Media. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayazi, M.; Afzali, D.; Taher, M.A.; Mostafavi, A.; Gupta, V.K. Removal of Safranin Dye from Aqueous Solution Using Magnetic Mesoporous Clay: Optimization Study. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 212, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.; Kumar, S. Removal of Safranine T and Brilliant Cresyl Blue Dyes from Water by Carboxy Methyl Cellulose Incorporated Acrylic Hydrogels: Isotherms, Kinetics and Thermodynamic Study. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 60, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abukhadra, M.R.; Mohamed, A.S. Adsorption Removal of Safranin Dye Contaminants from Water Using Various Types of Natural Zeolite. Silicon 2019, 11, 1635–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, M.; Abukhadra, M.R.; Shahien, M.G.; Khan, A.A.P. Upgraded Modified Forms of Bituminous Coal for the Removal of Safranin-T Dye from Aqueous Solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 18135–18151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Effect | Concentration of Safranine T Dye (mg/L) | Volume of Safranine T Dye (mL) | Amount of Adsorbent (g) | Temperature (K) | Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH (2–8) | 200 | 100 | 0.05 | 298 | 180 |
| Time (10–120 min) | 200 | 100 | 0.05 | 298 | 10–120 |
| Temperature (298–328 K) | 200 | 100 | 0.05 | 298–328 | 80 |
| Concentration (50–300 mg/L) | 50–300 | 100 | 0.05 | 298 | 80 |
| Experimental Qexp (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe (mg/g) | K1 (1/min) | R2 | Qe (mg/g) | K2 (g/mg.min) | R2 | |
| 320.7 | 228.57 | 0.0210 | 0.9724 | 322.58 | 0.00018 | 0.9993 |
| △H° (KJ/mol) | △S° (KJ/molK) | △G° (KJ/mol) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 308 | 318 | 328 | ||
| −45.56 | 0.1350 | −85.80 | −87.15 | −88.50 | −89.85 |
| Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax (mg/g) | K3 (L/mg) | R2 | Qmax (mg/g) | K4 (mg/g)(L/mg)1/n | R2 |
| 334.45 | 0.3229 | 0.9996 | 426.99 | 112.43 | 0.7465 |
| Dubinin–Radushkevich Isotherm | Temkin Isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qmax (mg/g) | K5 (mol2/KJ2) | R2 | B | K6 (L/g) | R2 |
| 150.17 | 0.00636 | 0.5007 | 50.80 | 8.11 | 0.8317 |
| Adsorbents | Maximum Sorption Capacity (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic graphene oxide-containing chitosan-sodium alginate hydrogel | 44.313 | [6] |
| Magnetic mesoporous clay | 37.97 | [36] |
| Carboxy methyl cellulose incorporated acrylic hydrogels | 63.25 | [37] |
| Clinoptilolite | 42.90 | [38] |
| Phillipsite | 65.35 | [38] |
| Heulandite | 41.66 | [38] |
| Modified bituminous activated carbon with nitric acid | 27.40 | [39] |
| Modified bituminous activated carbon with zinc oxide | 32.46 | [39] |
| Porous graphite | 33.67 | [39] |
| MnFe2O4 nanoparticles | 334.45 | This study |
| Interfering Ion | Tolerance Limit (µg/L) |
|---|---|
| K(I) | 1000 |
| Na(I) | 1100 |
| Ca(II) | 105 |
| Mg(II) | 110 |
| Cd(II) | 80 |
| Ni(II) | 90 |
| SO42− | 1450 |
| CO32− | 1450 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhalili, Z.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Facile Synthesis and Characterization of Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticles for the Successful Removal of Safranine T Dye from Aqueous Solutions. Inorganics 2024, 12, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12010030
Alhalili Z, Abdelrahman EA. Facile Synthesis and Characterization of Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticles for the Successful Removal of Safranine T Dye from Aqueous Solutions. Inorganics. 2024; 12(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhalili, Zahrah, and Ehab A. Abdelrahman. 2024. "Facile Synthesis and Characterization of Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticles for the Successful Removal of Safranine T Dye from Aqueous Solutions" Inorganics 12, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12010030
APA StyleAlhalili, Z., & Abdelrahman, E. A. (2024). Facile Synthesis and Characterization of Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticles for the Successful Removal of Safranine T Dye from Aqueous Solutions. Inorganics, 12(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12010030






