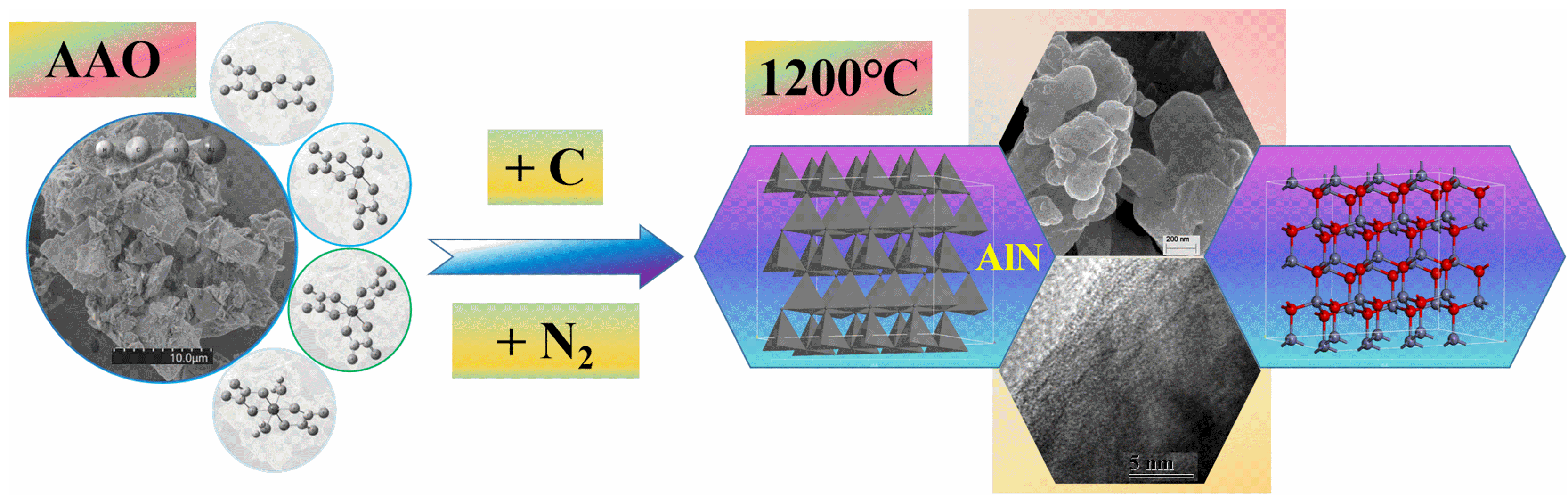
Abstract
Aluminum nitride (AlN) powder, a cornerstone material for advanced ceramics. This study examines the low-temperature formation of AlN crystals as well as their phase transformation by employing amorphous aluminum oxalate (AAO) as a novel precursor for carbothermal reduction, contrasting it with conventional aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3). Through characterization using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscope (HRTEM), 27Al Magic-Angle Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (27Al-MAS-NMR) energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), we unraveled the phase evolution pathways and the formation of AlN. Key findings reveal striking differences between the two precursors. When Al(OH)3 was used, no AlN phase was detected at 1350 °C, and even at 1500 °C, the AlN obtained with significant residual alumina impurities. In contrast, the AAO precursor demonstrated exceptional efficiency: nano-sized α-Al2O3 formed at 1050 °C, followed by the emergence of AlN phases at 1200 °C, ultimately gaining the pure AlN at 1500 °C. The phase transformation sequence—Al(OH)3 → γ-Al2O3 (950 °C) → (α-Al2O3 + δ-Al2O3) (1050 °C) → (AlN + α-Al2O3) (1200 °C~ 1350 °C) → AlN (≥1500 °C)—highlights the pivotal role of nano-sized α-Al2O3 in enabling low-temperature nano AlN synthesis. By leveraging the unique properties of AAO, we offer a transformative strategy for synthesizing nano-sized AlN powders, with profound implications for the ceramics industry.
1. Introduction
Aluminum nitride (AlN), as a wide-bandgap semiconductor material, has emerged as a critical material in high-power electronic packaging, deep-ultraviolet optoelectronic devices, and microwave radio frequency components due to its exceptional thermal conductivity (theoretical value up to 320 W·m−1·K−1), low dielectric loss (tanδ < 0.001), and thermal expansion coefficient compatible with silicon (4.5 × 10−6 K−1) [1,2,3,4]. With the rapid development of 6G communication, new energy vehicles, and aerospace technologies, the global ceramic substrate market is projected to grow. However, traditional substrate materials such as Al2O3 (thermal conductivity of only 20–30 W·m−1·K−1) and SiC (poor electrical insulation) struggle to meet the heat dissipation requirements of high-power-density devices, making AlN an ideal alternative due to its superior comprehensive performance. Despite this, the production of AlN powders faces significant technical bottlenecks: existing synthesis methods (e.g., self-propagating high-temperature synthesis, chemical vapor deposition) are plagued by high reaction temperatures (>1700 °C), high energy consumption, difficulties in controlling powder morphology, and impurity residues, leading to high production costs and inconsistent product performance [5,6,7,8,9,10]. Achieving low-temperature, high-efficiency synthesis of AlN powders has thus become a central challenge limiting their large-scale application.
AlN synthesis technologies primarily focus on carbothermal reduction (CR) and direct nitridation [11,12,13,14,15,16]. The CR method, using Al2O3 and a carbon source as raw materials to generate AlN in a nitrogen atmosphere at 1600–1800 °C, can produce high-purity, near-spherical powders but suffers from slow reaction kinetics and the need for secondary carbon removal treatment (decarburization temperature > 600 °C). To reduce energy consumption, researchers have attempted to improve reaction activity through ball milling (reducing the reaction temperature to 1400 °C) or by adding fluxes (e.g., Y2O3), but powder morphology control still relies on complex post-processing techniques [17,18,19,20]. Direct nitridation, on the other hand, is hindered by the oxide layer on aluminum powder surfaces, yet the resulting products often exhibit irregular particle shapes and significant purity fluctuations [21,22,23].
Some researchers have explored alternative aluminum or carbon sources to lower the reaction temperature for AlN powder synthesis [24,25]. Chu et al. [26] synthesized pure AlN powder using a precursor derived from the combustion of a mixed solution of aluminum nitrate, glucose, and urea. Hu et al. [27] used Al(OH)3 or Al(NO3)3·9H2O as aluminum sources and highly reactive carbon black as a reactant, achieving pure AlN powder after holding for two hours. Mylinh et al. [28] used phenolic resin and α-Al2O3 as precursors to produce AlN powder at 1700 °C. Miki et al. synthesized the AlN at a low temperature of 900–1000 °C from the anhydrous aluminum chloride-melamine complex of a ratio of 1 to 3 [29]. Li et al. yielded AlN powder with a particle size of 0.50 ± 0.18 µm at 1400 °C, benefiting from the direct nitridation of η-Al2O3 and θ-Al2O3 [30]. Overall, existing technologies face a “low-temperature-efficiency-morphology control” trilemma: lowering the temperature often results in incomplete reactions (conversion rate < 80%), while improving efficiency sacrifices powder uniformity. Therefore, developing novel precursors to reconstruct the reaction pathway has become a key direction for overcoming the low-temperature synthesis bottleneck.
Our team previously synthesized corundum at low temperatures of 1000 °C using amorphous aluminum oxalate (AAO) [31]. Building on this, we propose using AAO as a precursor to achieve low-temperature synthesis of AlN powders through molecular structure design and reaction kinetics regulation. To validate this approach, this study employs XRD, SEM, EDS, and FTIR to thoroughly analyze calcined samples using AAO as the aluminum source, comparing them with aluminum hydroxide (AH) to explore the phase transformation mechanism of aluminum oxalate and elucidate its conversion pathway to AlN.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Experimental Procedure
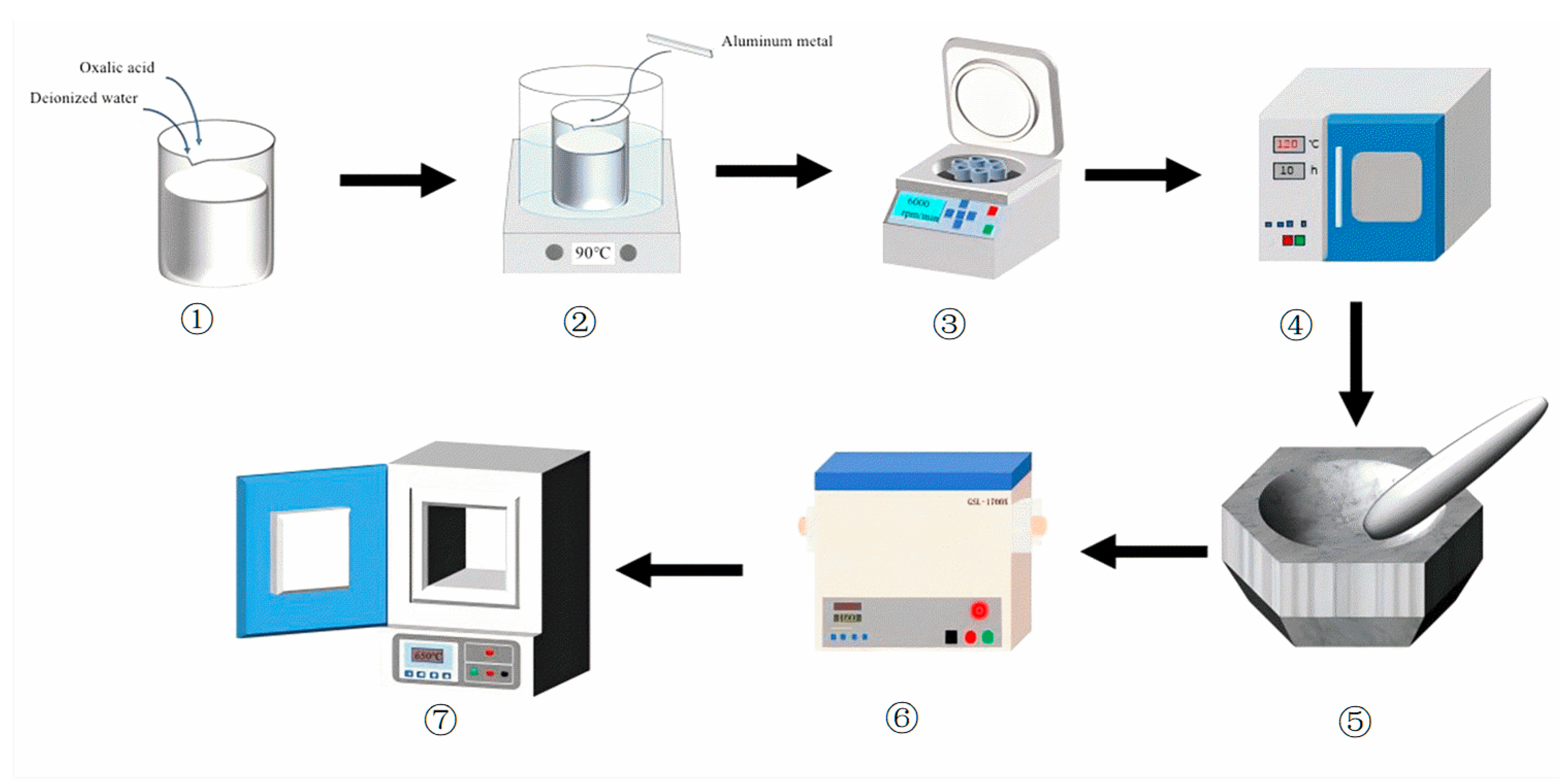
The experimental procedure is illustrated in Figure 1. 2.7 g of high-purity aluminum metal (Al ≥ 99.99%, Anhui Zhengying Technology Co., Ltd., Hefei, China) was first treated with dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl, Xilong Science Co., Ltd., Shantou, China) to remove surface impurities, followed by immediate rinsing with 100 mL of oxalic acid solution (1.5 mol/L, Xilong Science Co., Ltd., Shantou, China). The reaction was conducted at 90 °C under continuous stirring. After the reaction was complete, the resulting mixture was subjected to liquid-solid separation via centrifugation at 6000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was then filtered through a 1 μm membrane filter to remove residual particulates. The filtrate was subsequently evaporated in a drying oven at 105 °C to obtain the solid product (AAO). The dried AAO precursor was finely ground using an agate mortar and sieved through an 80-mesh sieve to ensure uniform particle size before storage.
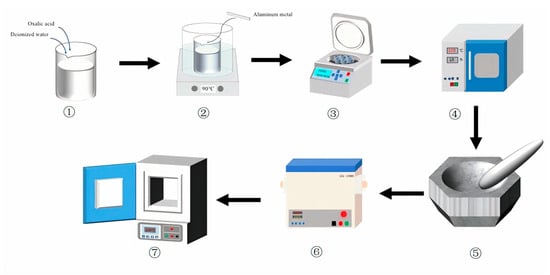
Figure 1.
The flow-process diagram of the experiment.
The phase transformation behavior of aluminum oxide from Al-Oxalate and aluminum hydroxide Al(OH)3 (Xilong Science Co., Ltd., Shantou, China; ~1 μm) was investigated. The samples (2g) were placed in alumina crucibles and covered with alumina lids. The crucibles were then subjected to calcination at various temperatures (300 °C, 500 °C, 700 °C, 800 °C, 900 °C, 1000 °C, 1100 °C, 1200 °C, and 1300 °C) for 2 h in a controlled atmosphere. After calcination, the samples were allowed to cool down inside the furnace.
The phase transformation behavior of AAO powders or aluminum hydroxide Al(OH)3 mixed with carbon black (100 nm~500 nm), was investigated in N2 atmosphere. In the experiment, the aluminum source (amorphous aluminum oxalate or Al(OH)3) and carbon black were combined in a agate mortar at an Al:C molar ratio of 1:3, followed by the addition of a small amount (2–6 wt %) of anhydrous ethanol. The mixture was ground with a agate pestle for 60 min, dried at 80 °C, and then lightly reground. The resulting black powder mixture was passed through a 200-mesh sieve and stored for subsequent use.
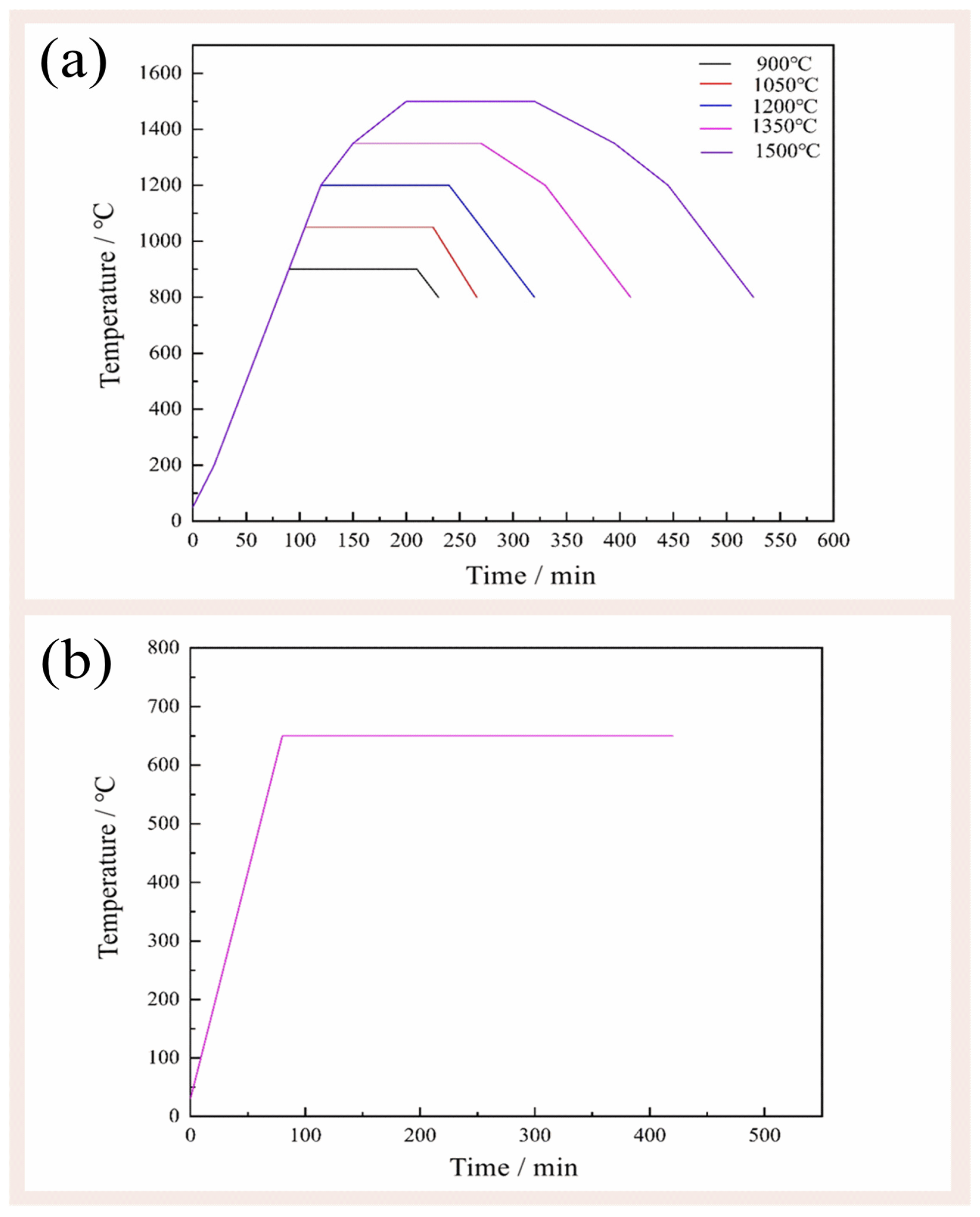
The mixture (1.5 g) was placed in alumina crucibles. The crucibles were put in the tube furnace and the nitrogen flow rate was controlled at 65 mL/min. The crucibles were then subjected to calcination at various temperatures (900 °C, 1050 °C, 1200 °C, 1350 °C, and 1500 °C) for 2 h (Figure 2a) in the N2 atmosphere with the flow rate of 80 mL/min. After calcination, the samples were cooled down inside the furnace. The calcined samples containing carbon residue were put into a muffle furnace under flowing air at 650 °C for 6 h to remove the carbon black (Figure 2b). To systematically investigate the influence of carbon addition on the reaction products, a carbon-free control group was meticulously established.
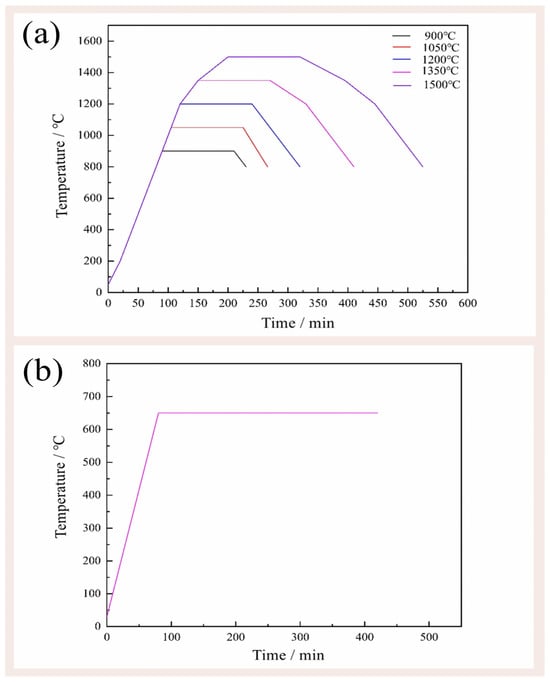
Figure 2.
The (a) firing temperature curve and (b) decarbonize temperature curve.
2.2. Characterization Methods
The morphology of the samples was examined by using a transmission electron microscope (TEM, JEM-2100F, Tokyo, Japan) operated at 200 kV. The micrographs of the samples were obtained from powdered samples deposited on a holey Cu grid.
X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) patterns were obtained using a Miniflex600 diffractometer (RIGAKU, Tokyo, Japan) operated at 30 kV and 10 mA with Cu Kα (0.15418 nm) filtered radiation, a curved graphite secondary monochromator, a scan range of 5°2θ to 90°2θ, a step width of 0.02°2θ, and a scan speed of 10 °/min.
The microstructure of the samples was examined using a SU 5000 scanning electron microscope (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) with a field emission gun operating normally at 5–10 kV of acceleration voltage in a high vacuum environment.
Energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS; Bruker Quantax, Karlsruhe, Germany) was employed to study the distribution of elements in the sample.
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) was carried out on the INVENIO-S spectrometer produced by Bruker corporation in the MIR range (4000–400 cm−1); the samples were prepared by KBr pellets methods (2 mg of sample dispersed in 200 mg KBr).
27Al magic angle spinning (MAS) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy was recorded on a Bruker AVANCE III 400 WB spectrometer (Karlsruhe, Germany) equipped with a 4 mm standard bore CP MAS probehead. The dried and finely powdered samples were packed in the ZrO2 rotor closed with Kel-F cap.
3. Results
3.1. The Formation of AlN from Al(OH)3
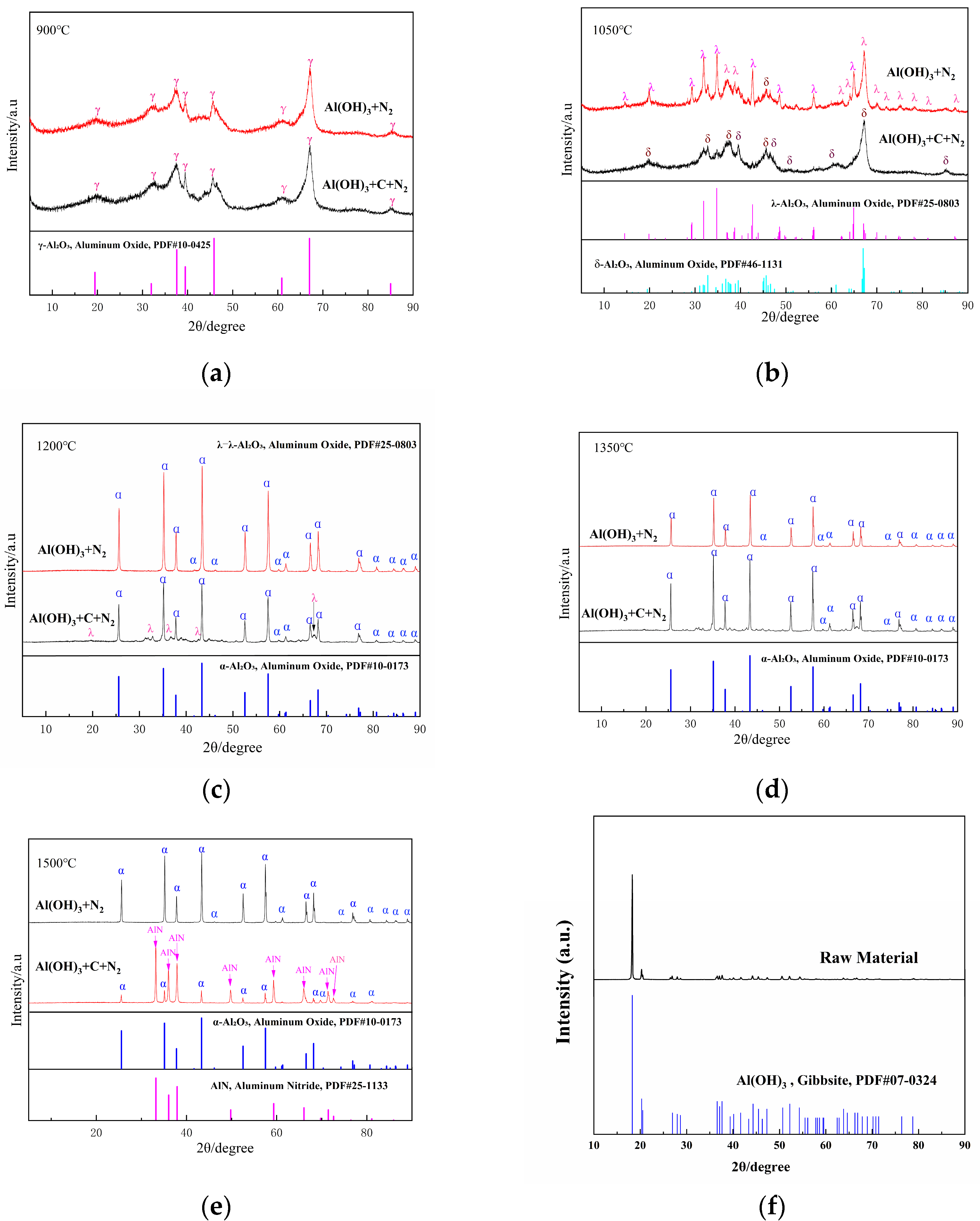
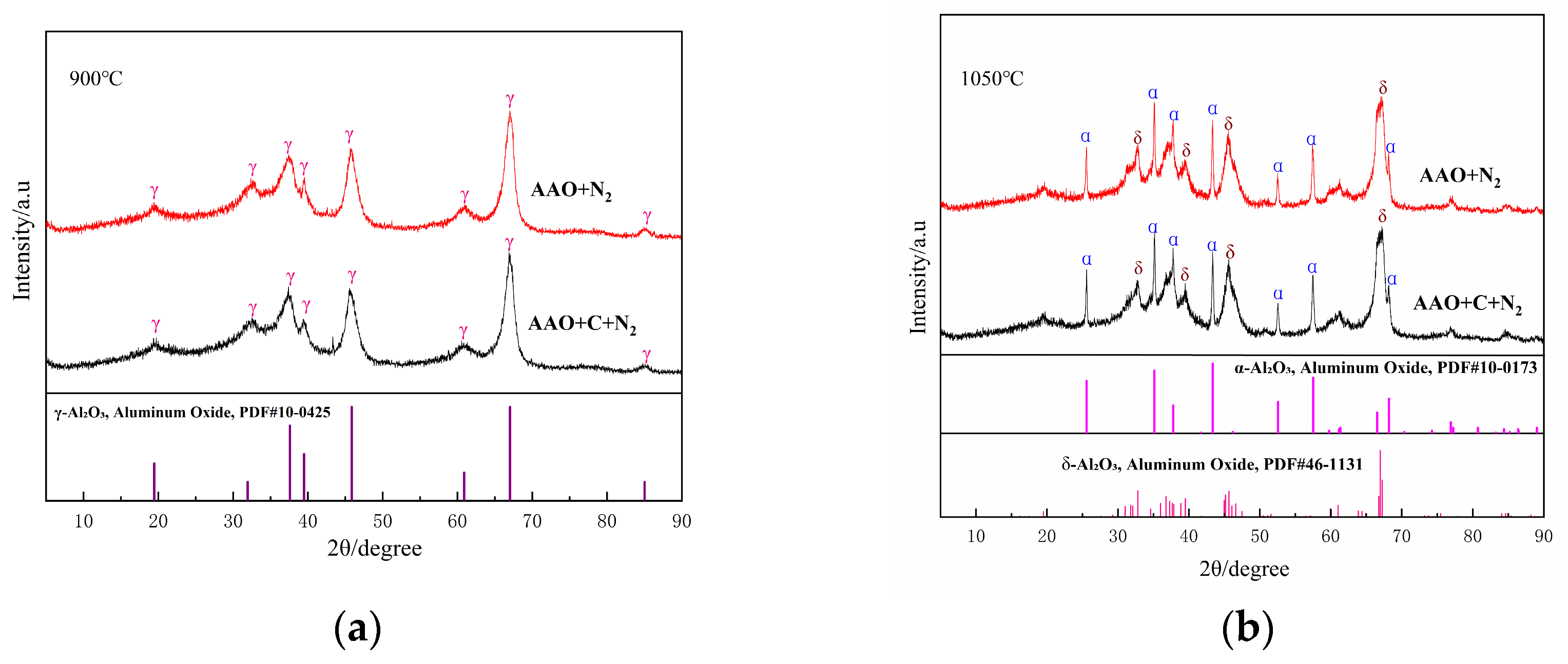
Carbon source variation shows limited impact on phase formation (<900 °C), γ-Al2O3 (PDF#10-0425) emerges as the thermodynamically preferred phase across all systems (Figure 3a). When heated to 1050 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere, the product derived from pure Al(OH)3 consists of δ-Al2O3 (PDF#46-1131) and λ-Al2O3 (PDF#25-0803), whereas the product from the Al(OH)3 and carbon mixture exhibits only δ-Al2O3 (PDF#46-1131, Figure 3b). At 1200 °C and 1350 °C, the pure Al(OH)3 raw material transforms into α-Al2O3 (PDF#10-0173, Figure 3c,d), while the product from the Al(OH)3 and carbon mixture exhibits some impurities. At 1500 °C, the carbon-doped material yields AlN (PDF#25-1133) as the primary phase. In comparison, the carbon-free raw material remains entirely in the α-Al2O3 phase (Figure 3e).
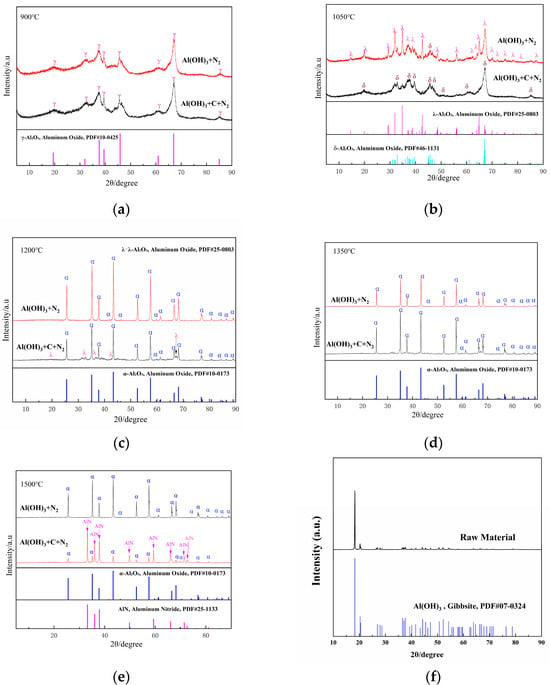
Figure 3.
XRD patterns of the samples obtained from Al(OH)3 with and without the carbon at various sintering temperatures ((a), 900 °C; (b), 1050 °C; (c), 1200 °C; (d), 1350 °C; (e), 1500 °C; (f), the raw materials).
The phase evolution of Al(OH)3 under a nitrogen atmosphere within the temperature range of 900–1500 °C exhibits distinct pathways depending on the presence of a carbon source. In the absence of carbon, the transformation sequence follows: Al(OH)3 → γ-Al2O3 (950 °C) → (δ-Al2O3 + λ-Al2O3) (1050 °C) → α-Al2O3 (≥1200 °C). However, when a carbon source is introduced, the phase progression shifts to: Al(OH)3 → γ-Al2O3 (950 °C) → δ-Al2O3 (1050 °C) → α-Al2O3 (≥1200 °C) → AlN (1500 °C).
3.2. The Formation of AlN from AAO
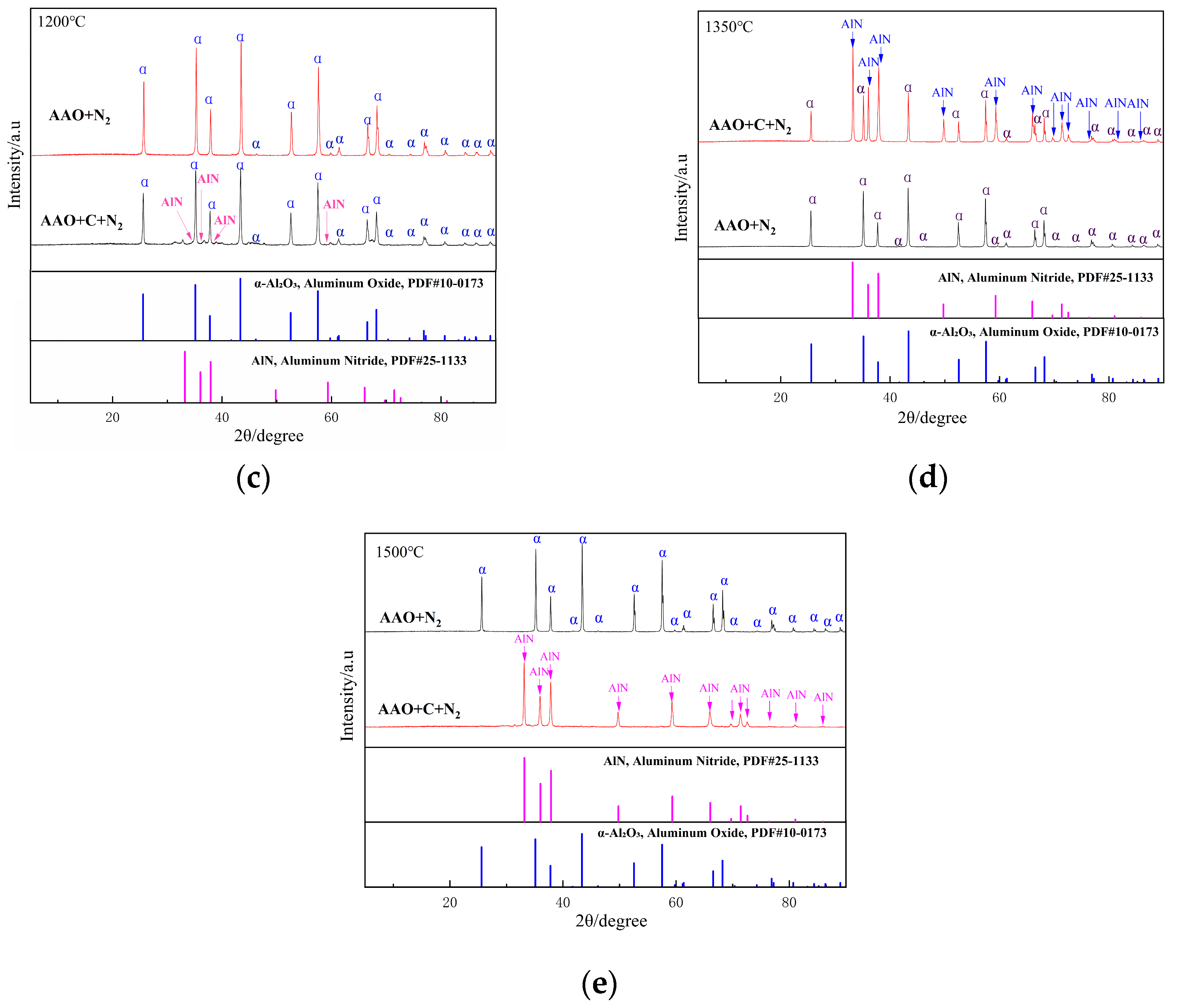
As illustrated in Figure 4a,b, the influence of the carbon source on the phase composition of the samples is negligible at 900 °C and 1050 °C. At 1050 °C, a substantial amount of α-Al2O3 is formed in the AAO-derived samples. In contrast to Al(OH)3, AAO generated highly reactive intermediates during the thermal decomposition process. This observation aligns with previous studies demonstrating that AAO undergo transformation to α-Al2O3 at lower temperatures in an air atmosphere; the present study confirms that this behavior persists under a nitrogen atmosphere. At 1200–1500 °C, the non-carbon-doped samples exhibit a single-phase α-Al2O3 (Figure 4c–e); upon the introduction of carbon, a weak diffraction peak corresponding to aluminum nitride emerges at 1200 °C (Figure 4c). As the temperature rises, the intensity of the AlN diffraction peaks progressively increases, while the alumina (α-Al2O3) peaks diminish. By 1500 °C (Figure 4e), the alumina diffraction peaks vanish entirely, and the product consists exclusively of the aluminum nitride phase.
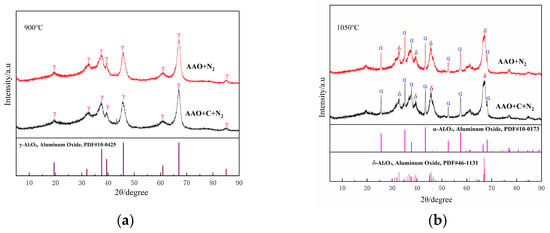
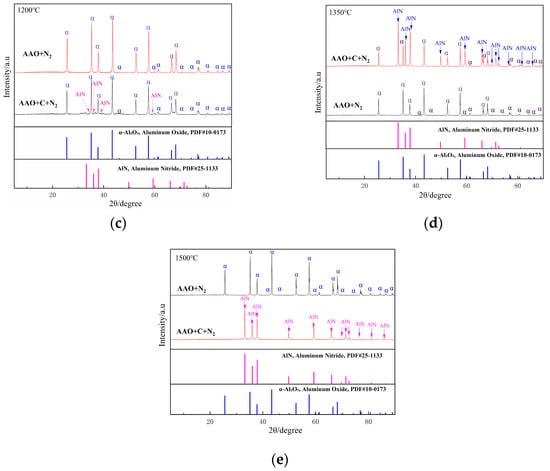
Figure 4.
XRD patterns of the samples obtained from AAO with and without the carbon at various sintering temperatures ((a), 900 °C; (b), 1050 °C; (c), 1200 °C; (d), 1350 °C; (e), 1500 °C).
The crystallographic transformation pathways of AAO as the aluminum source are systematically analyzed as follows:
In the absence of a carbon source, the phase evolution of AAO with increasing temperature follows the sequence:
Al(OH)3 → γ-Al2O3 (950 °C) → (α-Al2O3 + δ-Al2O3) (1050 °C) → α-Al2O3 (≥1200 °C)
In contrast, when a carbon source is introduced, the phase transformation pathway shifts to:
Al(OH)3 → γ-Al2O3 (950 °C) → (α-Al2O3 + δ-Al2O3) (1050 °C) → (AlN + α-Al2O3) (1200 °C~ 1350 °C) → AlN (≥1500 °C)
It is noteworthy that AAO alone do not form aluminum nitride at elevated temperatures. This is primarily due to the complete oxidation of organic functional groups, predominantly carboxylate ions (-COO−), at high temperatures, leaving no residual carbon to participate in the carbothermal reduction reaction.
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparation of Phase-Transformation from AAO and Al(OH)3
Combined XRD patterns and the refined data in Table 1 reveal that, below 1050 °C, increasing temperature not only drives the successive γ → λ → δ → α phase transitions but also promotes continuous grain growth, because elevated temperatures accelerate bulk diffusion. Consequently, the mean crystallite size of each polymorph becomes larger at higher temperatures, while the absolute size follows the order γ-Al2O3 < λ-Al2O3 ≈ δ-Al2O3 < α-Al2O3, reflecting the intrinsic crystallisation habit of each phase. Notably, when the OAA precursor is subjected to carbothermal reduction at 1200 °C, the nascent AlN crystallites already reach 13.33 nm, indicating a high nucleation density and rapid growth even at this relatively low temperature. For the Al(OH)3 precursor, α-Al2O3 is already the dominant crystalline phase at 1200 °C.

Table 1.
The primary crystalline phase and crystallite size for the different samples.
Above 1350 °C the specimen is essentially biphasic, containing only α-Al2O3 and/or AlN; consequently, temperatures beyond this point were used to track phase assemblage and quantify the relative fractions, from which the AlN yield was derived.
Quantitative phase analysis of the patterns shown in Figure 3d,e and Figure 4d,e was further performed by the external-standard method coupled with Rietveld refinement (Table 2). With Al(OH)3 as the aluminium source, the AlN yield after carbothermal reduction at 1500 °C is only 43.24 wt % (i.e., <50 wt %). In contrast, the aluminium–organic precursor furnishes 51.93 wt % AlN at 1350 °C—an increment of 20.09% relative to the hydroxide route at 1500 °C—and boosts the AlN fraction to ≥95 wt % at 1500 °C. Under a pure N2 atmosphere the same precursor delivers ≥99 wt % AlN, surpassing the 90.02 wt % achieved with commercial alumina. Taken together, these data demonstrate that the OAA source enhances product yield and lowers the formation temperature in both reductive and neutral atmospheres, an advantage ascribed to its superior calcination reactivity.

Table 2.
Mass fractions of the phase in the samples (wt %).
Compared with the data compiled by our group [30], samples derived from alumina show no detectable Al2O3 crystalline phase at ~1350 °C, yet their AlN conversion at 1500 °C remains below 50 wt % (Table 3). In sharp contrast, the AAO precursor introduced here attains ≥95 wt % AlN at the same temperature. Literature values report that ≥90 wt % AlN is only achieved at 1550 °C or higher [8,9,14,30,32,33]. The present OAA route therefore offers a conspicuously lower conversion temperature, while being inexpensive, readily available and intrinsically impurity-free.

Table 3.
AlN yield (wt %) obtained with different aluminium sources and synthesis conditions.
4.2. The Formation Mechanism of Aluminum Nitride from AAO at Low Temperatures
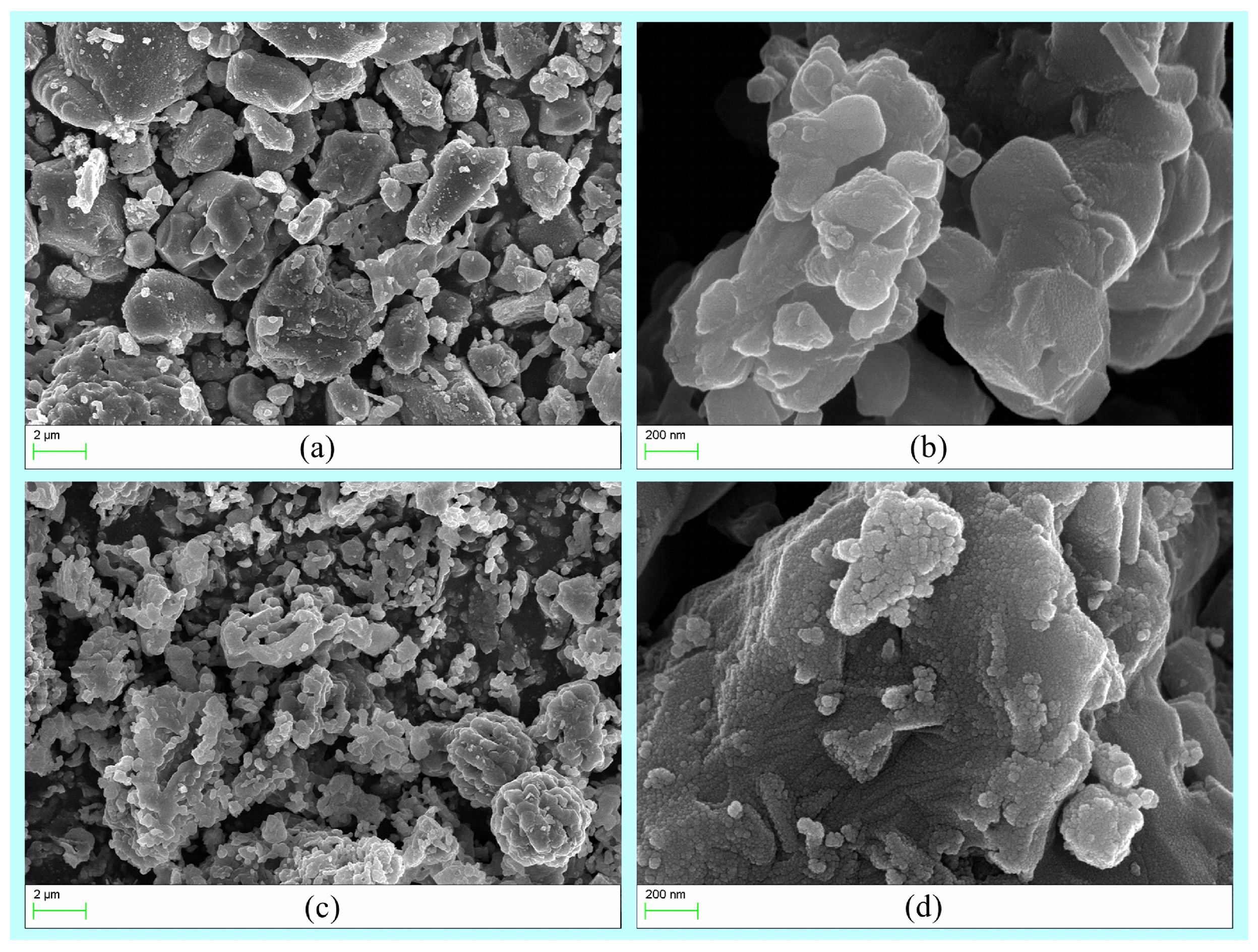
Figure 5 presents the SEM images of AAO at various temperatures. At 1200 °C, cavities (Figure 5a) and nanoparticles (Figure 5a) on the surface of large particles were discernible, predominantly attributed to the decomposition of AAO into α-Al2O3 [29] and the formation of nano-sized AlN. At 1350 °C, a substantial quantity of ~50 nm grains were observed on the surface of large particle samples (Figure 5d). In accordance with the XRD results, these grains are primarily nano-sized aluminum nitride (AlN).
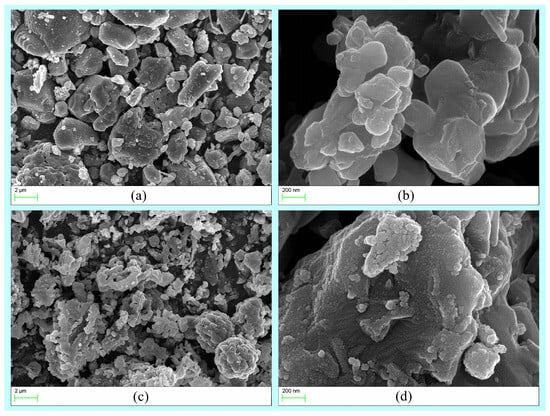

Figure 5.
The SEM pictures of the samples from AAO at different temperatures ((a,b), 1200 °C; (c,d), 1350 °C).
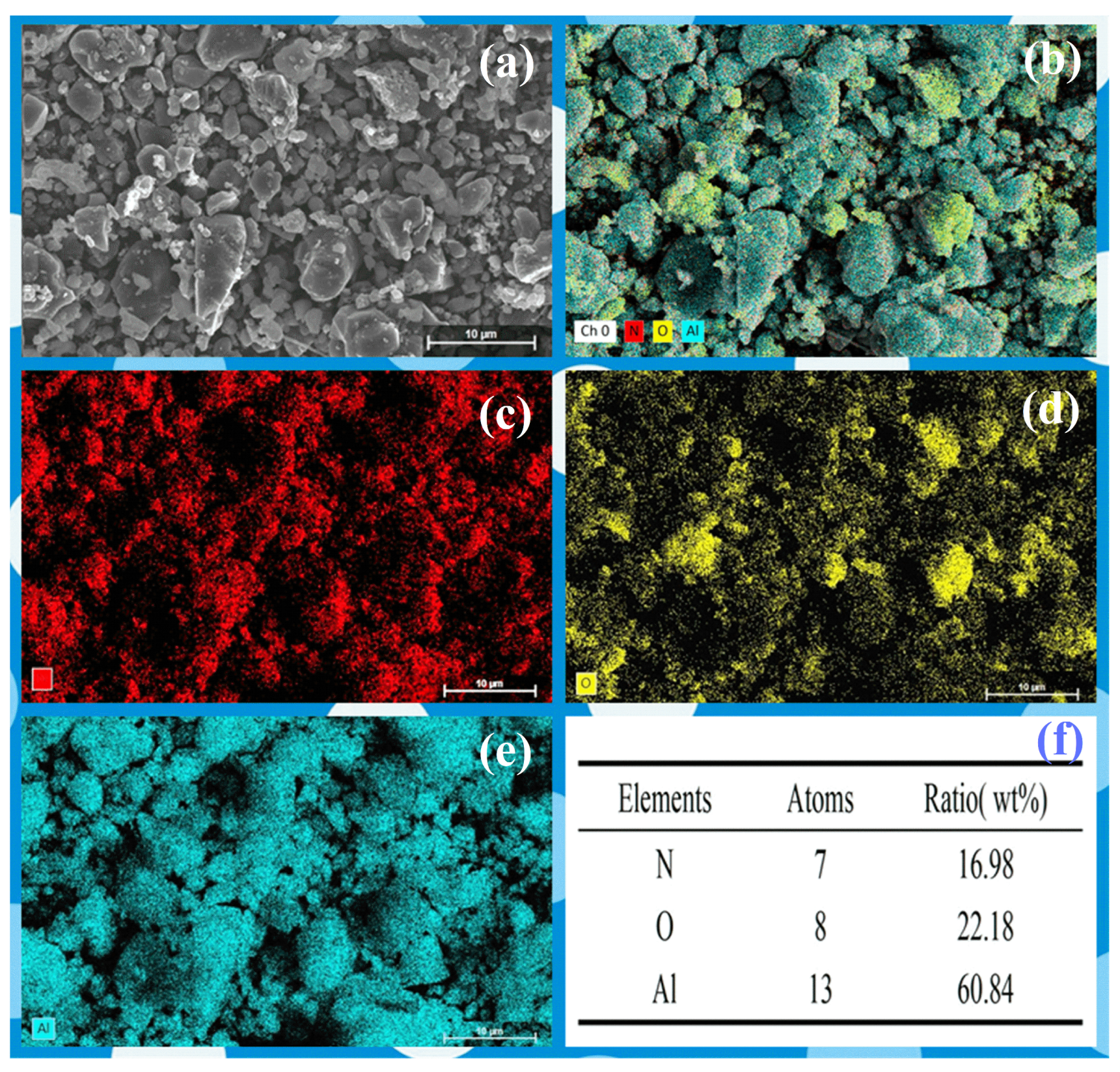
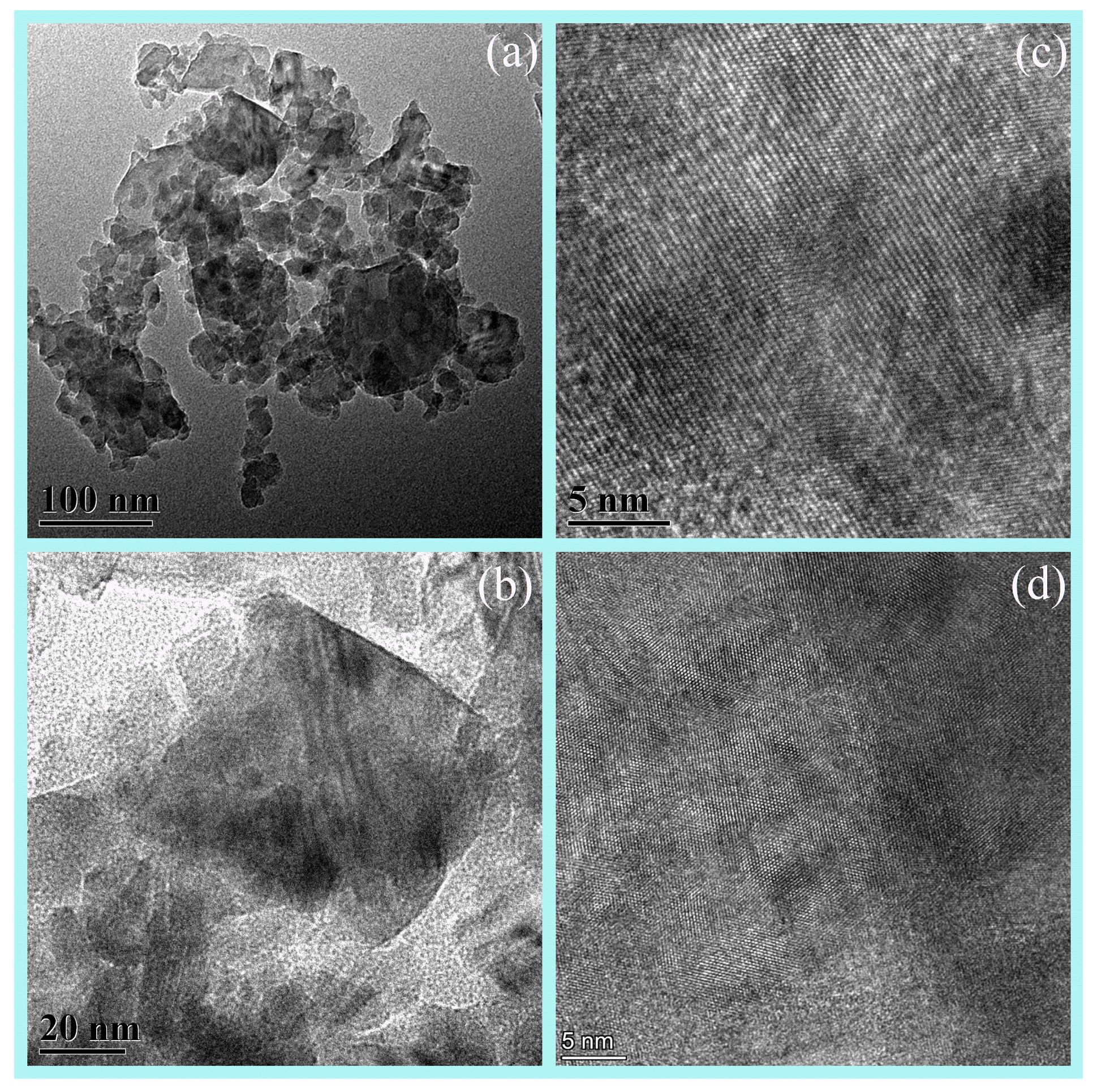
Due to the low content of AlN at 1200 °C, it is challenging to observe. Therefore, Element mapping (EDS) and HRTEM of the samples 1350 °C was conducted, which contains a significant amount of AlN. The analysis revealed a rich presence of nitrogen in the sample, indicating a substantial formation of nano-sized AlN grains at 1350 °C (Figure 6). The TEM images reveal grains ~50 nm in diameter (Figure 7), consistent with the SEM and the crystallite size extracted from XRD line-broadening. Two distinct phases with well-resolved lattice fringes are identified; occasional fringe bending and contrast loss are also observed, indicating local lattice distortion that most likely originates from structural rearrangement during the phase transition.
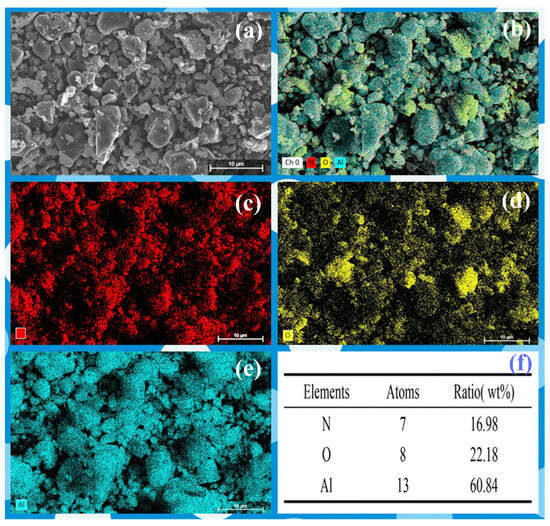
Figure 6.
The (a) SEM image, (b–e) mapping and (f) EDS analysis of the AAO at 1350 °C.
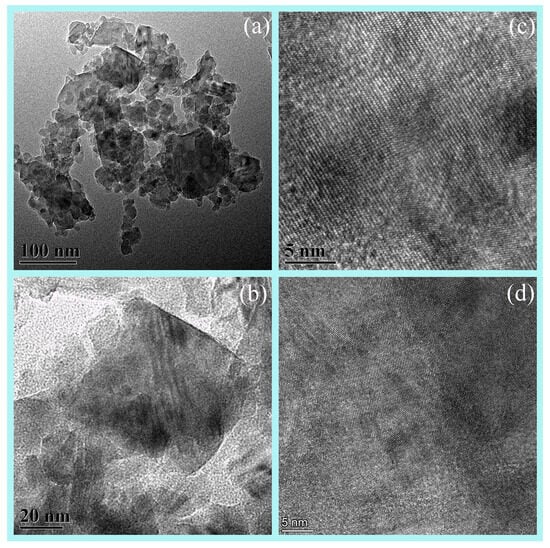
Figure 7.
The (a,b) TEM and (c,d) HRTEM images of AAO under carbothermal reduction at 1350 °C.
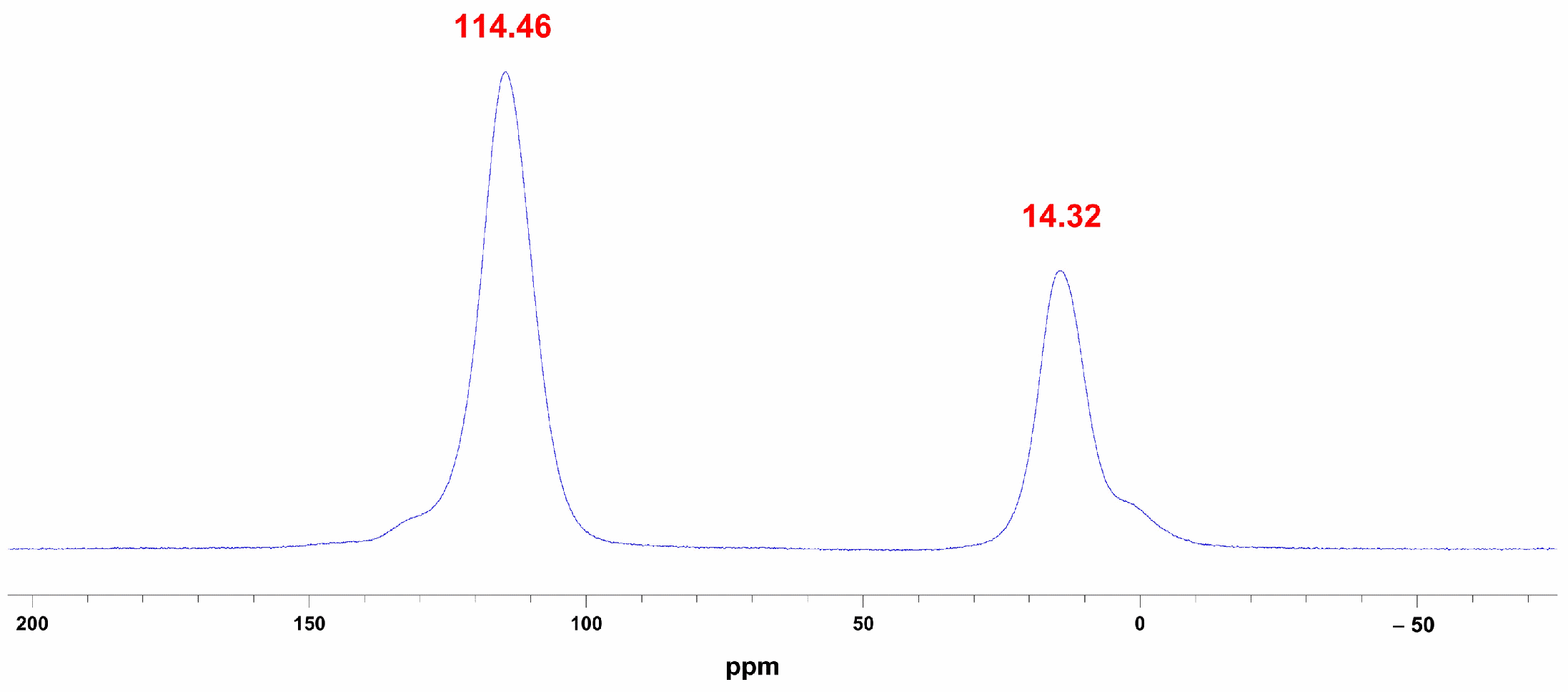
Furthermore, to gain deeper insight into the characteristics of the resultant aluminum nitride, we performed 27Al-MAS-NMR measurements. The results indicate that under carbothermal reduction conditions, at 1350 °C, the characteristic chemical shift of [AlN4] at 114.46 ppm appears (Figure 8), together with a resonance assigned to [AlO6] at 14.32 ppm [14]. However, the evolution of aluminum coordination number and chemical environment during AlN formation when AAO serves as the aluminum source remains to be further investigated by our team.
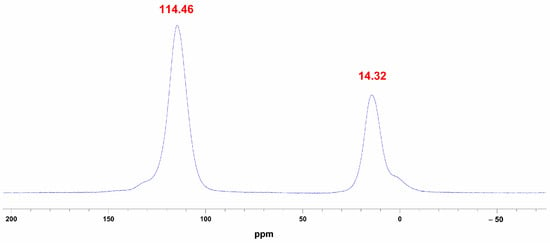
Figure 8.
27Al-MAS-NMR spectra of AAO at 1350 °C under carbothermal reduction conditions.
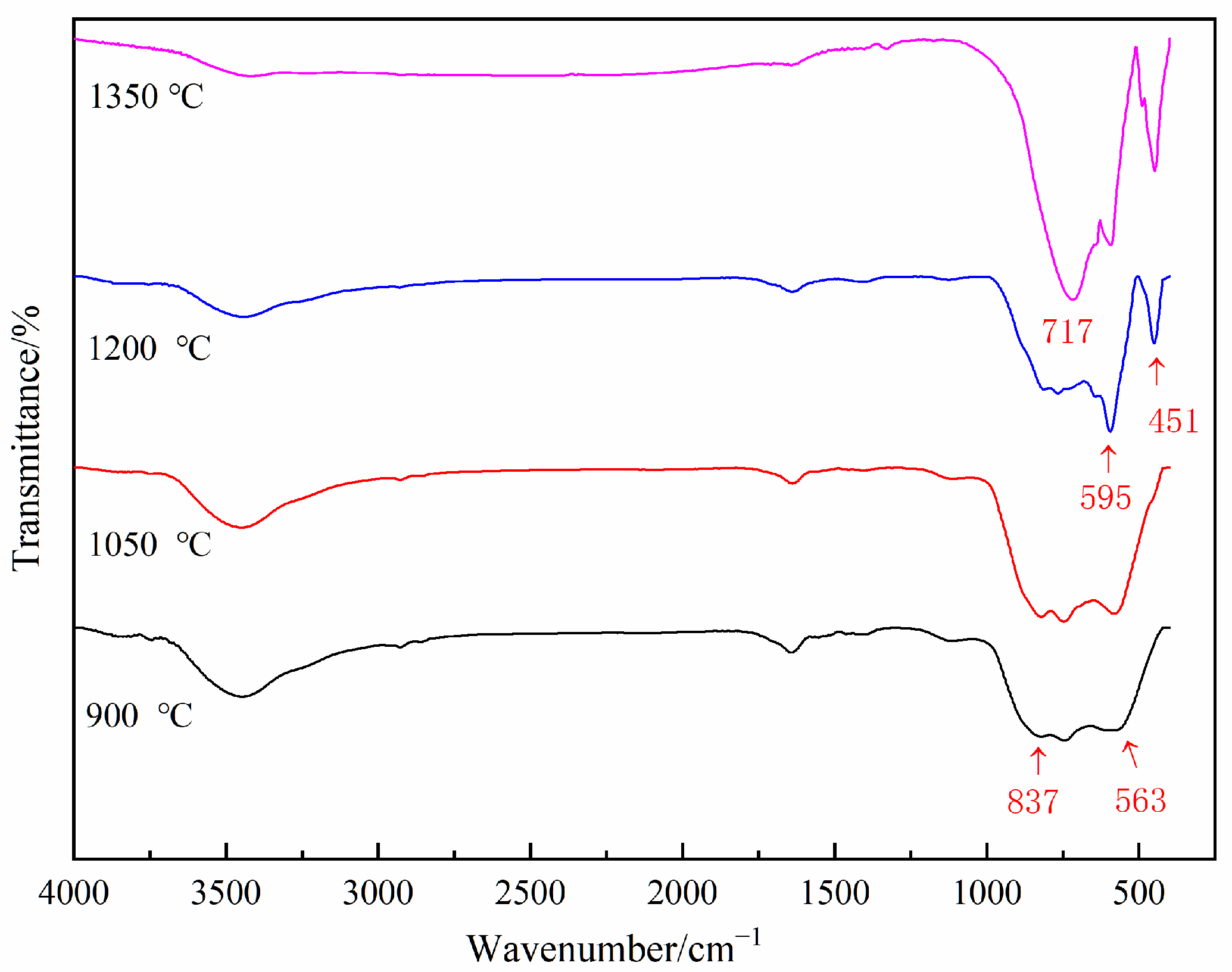
To further investigate the low-temperature formation mechanism of aluminum nitride, vibrational spectroscopy with higher sensitivity was employed to analyze the chemical bonds of the samples. Figure 9 presents the FTIR spectra of the AAO at 900 °C, 1050 °C, 1200 °C, and 1350 °C. At 900 °C and 1050 °C, the broad peaks are observed in the 500–900 cm−1 region, attributed to the characteristic peaks of γ-Al2O3. At 1200 °C and 1350 °C, absorption peaks at 595 cm−1 and 451 cm−1 are attributed to the vibration of Al-O bonds in α-Al2O3, while the absorption peak at 717 cm−1 is due to the vibration of Al-N bonds. This reaffirms that AAO can form aluminum nitride phases at the relatively low temperature of 1200 °C under carbothermal reduction conditions.
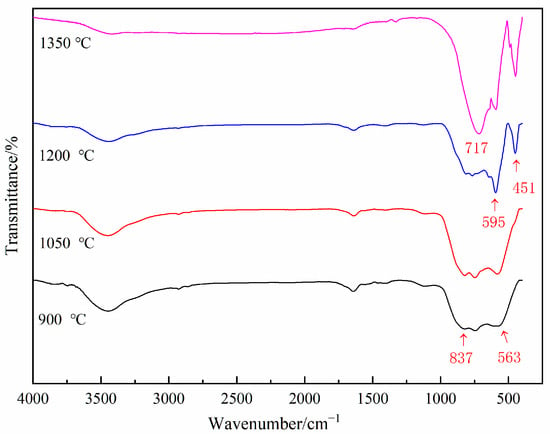
Figure 9.
The FTIR spectra of the AAO samples at different temperatures.
Comparative analysis with Al(OH)3 reveals that, under carbothermal conditions, AAO facilitate the formation of aluminum nitride at significantly lower temperatures. The AAO with high reactivity, being comfirmed by to the ability of AAO to generate nano α-Al2O3 at lower temperatures, facilitates the low-temperature formation of aluminum nitride under carbothermal reduction (Figure 10).
Figure 10.
The diagram of the predicted configuration for low-temperature phase transition of AlN derived from the AAO.
The solid-state carbothermal reduction in AAO is proposed to proceed as follows. First, the highly reactive AAO decomposes at relatively low temperatures to yield a porous, Al- and O-rich substance (DAAO). This substance then reacts with carbon, during which Al–O bonds are cleaved and intermediate or transient species containing Al–C or Al–O–C bonds (or other related chemical linkages) are formed. Under a nitrogen atmosphere, nitrogen atoms subsequently displace carbon or oxygen, leading to the formation of aluminum nitride at a markedly reduced temperature. The underlying chemical reaction can be expressed as:
5. Conclusions
High-end aluminum nitride (AlN) products require high-performance AlN powder. In this study, we utilized self-synthesized amorphous aluminum-oxalate (AAO) and employed the carbothermal reduction method to synthesize nano-sized AlN powder at a relatively low temperature of 1200 °C. Al(OH)3 was used as a comparative sample. XRD, SEM, HRTEM, EDS, 27Al-MAS-NMR, and FTIR were employed to investigate the crystallographic phase transformation process and the low-temperature synthesis mechanism. When using AAO as the aluminum source, the non-carbon-doped samples exhibit a single-phase α-Al2O3 at 1500 °C in N2 atmosphere. For the carbon-doped samples, α-Al2O3 forms from AAO at 1050 °C. At 1200 °C, an absorption peak at 717 cm−1 attributed to Al-N bond vibration and the crystalline diffraction peaks of AlN were also observed; at 1350°C, a large number of 50 nm AlN nanoparticles were observed; at 1500 °C, the AlN was obtained with no impurities. The crystallographic phase transformation sequence for AAO is: AAO → γ-Al2O3 (950 °C) → (α-Al2O3 + δ-Al2O3) (1050 °C) → (AlN + α-Al2O3) (1200 °C~ 1350 °C) → AlN (≥1500 °C). These findings indicate that AAO decompose easily, forming reactive species during heating, which leads to the formation of a significant amount of nano α-Al2O3 at a lower temperature, meanwhile, the highly reactive AAO decomposes, and reacts with carbon to form intermediate or transient species containing Al–C or Al–O–C bonds. Under a nitrogen atmosphere, nitrogen atoms subsequently displace carbon or oxygen, promoting the generation and growth of AlN at lower temperatures. This study provides a novel approach for the low-temperature preparation of AlN powder using low-cost AAO.
Author Contributions
Drafting and the manuscript, W.T.; investigation, W.T. and Y.Y.; analysis and interpretation of the data, C.Z. and Z.H.; formal analysis, W.W.; writing—review and editing, C.Z. and Z.Z.; conception and planning of the work, S.L. and J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21207027, and 51372090), the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (2017B090921002), the Scientific Research Foundation of Hanshan Normal University (XN201919), the Scientific Research Project of the Department of Education of Guangdong Province (2022KQNCX046), the Special Project in Key Fields of General Universities in Guangdong Province (2024ZDZX3030 and 2024ZDZX3029), and the Mentorship Support Program of Hanshan Normal University (XWT2025101).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request.
Acknowledgments
Advanced Ceramic Materials Innovation Research Center are acknowledged. The Guangdong Chaoshan Institute of Higher Education and Technology are acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lin, C.; Liu, S.; Jiang, B.; Zhou, L.; Cui, H.; Liu, M.; Wen, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Li, S.; et al. A review on the wettability and residual stress of AMB AlN/metal joints. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2024, 174, 108181. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.; Fu, R.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, H. Enhanced adhesion strength of silver paste on AlN ceramic substrate via sintered nano-CuO. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 9471–9476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, H.; Sun, D.; Tian, C.; Guo, J.; Cui, S.; Tang, W. Studies on the Al2OC mesophase in synthesized AlN powder and its effects on properties of AlN ceramic substrates. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 21172–21181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwema, F.M.; Akinlabi, E.T.; Oladijo, O.P. A systematic review of magnetron sputtering of AlN thin films for extreme condition sensing. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 1546–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, K.; Wei, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S.; Huang, X.; Lin, S.; Plucknett, K.P.; Lin, H. Reaction mechanisms of nano-sized AlN powders synthesized from dicyandiamide and its optical property. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 253, 123376. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Lu, K.; Zhou, X.; Zhouchen, Z.; Huang, X.; Qi, J.; Lu, T. High sphericity AlN powder carbothermal reduced from spray granulated Al2O3/C precursor. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 7336–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, H.; Zhou, G.; Huang, D.; Ling, L.; Qin, X. Synthesis of fine AlN powders by carbothermal reduction and nitridation from nano-alumina/carbon foam. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 8291–8298. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.M.; Ayman, M.T.; Jang, S.M.; Park, S.; Yoon, D.H. Synthesis of pure fine AlN powder via CRN using nitridation promoter. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, S.M.; Jang, S.M.; Yoon, D.H. Effect of starting materials’ dispersion on the properties of AlN powder synthesized by carbothermal reduction and nitridation. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 16836–16843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Shan, Y.; Han, X.; Xu, J.; Li, J. Preparation of single phase nano-sized AlN powder by carbothermal reduction and nitridation of hydrothermal synthesized carbon coated γ-Al2O3 from glucose via fast heating. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 22128–22138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Yi, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Ko, Y.N.; Hong, Y.J.; Kang, Y.C. Preparation of nanometer AlN powders by combining spray pyrolysis with carbothermal reduction and nitridation. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 1967–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z. Preparation of spherical AlN powders by combined microemulsion method and carbothermal method. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 12708–12715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthisabarimoorthi, A.; Ayman, M.T.; Ryu, S.S.; Yoon, D.H. Synthesis of hollow AlN microsphere by hydrothermal and carbothermal reduction–nitridation hybrid technique. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 35154–35160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Xu, J.; Sun, X.; Hong, C.; Shi, L.; Xu, J.; Li, J. Preparation of AlN powder of low oxygen content via carbothermal reduction and nitridation by active gas exchange technique. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 21182–21189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiao, L.; Zheng, J.; Ying, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, W.; Che, S. Preparation of AlN with low agglomeration using polyethylene glycol and emulsifier to disperse the ultrafine raw powders. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Q.; Jia, G.; Lei, R.; Wang, S.; Xu, S. Influence of yttrium dopant on the synthesis of ultrafine AlN powders by CRN route from a sol–gel low temperature combustion precursor. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.; Hassan, N.; Raju, K.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.; Moon, S.; Kim, M.; Shin, S.; Kwak, Y.; et al. Flash sintering of AlN ceramics with Y2O3 additive. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 55042–55054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.Y.; Hotta, Y.; Watari, K.; Mitsuishi, K.; Yamazaki, M. Low-temperature sintering behavior of the nano-sized AlN powder achieved by super-fine grinding mill with Y2O3 and CaO additives. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 26, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Gu, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, S.; Li, T.; Ma, J.; Guan, J.; Qin, M. Influence of Y2O3 sintering aids on performance of c-BN-reinforced AlN/BN composite ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 24425–24432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, U.; Kim, S.G.; Kwak, Y.; Ryu, S.S.; Cho, J. Ultrafast high-temperature sintering of aluminum nitride. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2025, 45, 117025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.G.; Wang, K.Y.; Guo, S.M. Large-scale synthesis of AlN nanofibers by direct nitridation of aluminum. Ceram. Int. 2010, 36, 2209–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashhadi, M.; Mearaji, F.; Tamizifar, M. The effects of NH4Cl addition and particle size of Al powder in AlN whiskers synthesis by direct nitridation. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2014, 46, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.B.; Kim, J.; Shim, C.H.; Kim, Y.; Choi, H.; Ahn, J.P. Low-temperature synthesis of high-purity AlN from Al powder. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 4526–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Lou, B.; Shen, H. Formation of aluminum nitride in dross by contact-diffusion reaction during aluminum recycling. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 177432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, A.; Qin, M.; Rafi-ud-din, R.; Jia, R.; Lu, H.; He, X.; Qu, X. Effect of aluminum source on the synthesis of AlN powders from combustion synthesis precursors. Mater. Res. Bull. 2012, 47, 2475–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, A.; Qin, M.; Rafi-ud-din, R.; Lu, H.; He, X.; Qu, X. Effect of urea on the size and morphology of AlN nanoparticles synthesized from combustion synthesis precursors. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 530, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Huang, Q.; Yang, X.; Peng, H.; Tian, X.; Peng, Y. Effects of different aluminum sources and calcination temperatures on the synthesis of ultrafine AlN powder via carbothermal reduction nitridation. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 2017, 18, 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- Mylinh, M.D.T.; Yoon, D.H.; Kim, C.Y. Aluminum Nitride Formation From Aluminum Oxide/Phenol Resin Solid-Gel Mixture by Carbothermal Reduction Nitridation Method. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2015, 60, 1551–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, U.; Takahiro, T.; Nobuhiro, K.; Hideyuki, T.; Kazuki, A.; Takashi, T. Low temperature synthesis of aluminum nitride from anhydrous aluminum chloride-organic amine complex. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2022, 130, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, B.; Ren, B.; Chen, H.; Zhu, B.; Chen, J. Synthesis of Aluminum Nitride Using Sodium Aluminate as Aluminum Source. Processes 2023, 11, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhong, M.; Yang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liang, C.; Song, C.; Xu, W.; Lin, S.; Zhang, Z. Low temperature phase transition mechanism of amorphous Al-oxalate to nano α-alumina. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 35457–35464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.X.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.L.; Xu, Y.G.; Wang, S.W. Synthesis of AlN powder by carbothermal reduction–nitridation of alumina/carbon black foam. J. Inorg. Mater. 2017, 32, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.Z.; Song, S.D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, J.S.; Tang, Z.X. Investigation on synthesis AlN powder by carbothermal reduction. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 33, 289–293. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).