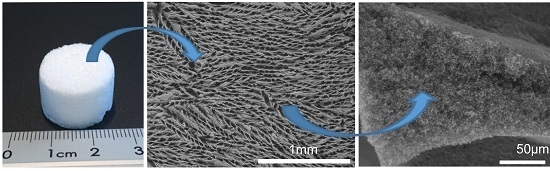
A Reliable Method for the Preparation of Multiporous Alumina Monoliths by Ice-Templating
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Determination of Synthesis Parameters
2.1.1. P123/Al Ratio
2.1.2. Acid Source and Acid/Al Ratio
2.1.3. Impact of Peptization Duration and Temperature
2.2. Process Parameters
2.2.1. Water Content
2.2.2. Cooling Speed
2.3. Thermal Stability
2.4. Macroporosity
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Synthesis
3.2. Materials Processing
3.3. Material Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rouquerol, J.; Avnir, D.; Fairbridge, C.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haynes, J.H.; Pernicone, N.; Ramsay, J.D.F.; Sing, K.S.W.; Unger, K.K. Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids. Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 1739–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresge, C.T.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Roth, W.J.; Vartuli, J.C.; Beck, J.S. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 1992, 359, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Kresge, C.T.; Schmitt, K.D.; Chu, C.T.-W.; Olson, D.H.; Sheppard, E.W.; McCullen, S.B.; et al. A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiola, V.; Ritsko, J.E.; Clarence, D. Process for Producing Low-Bulk Density Silica. U.S. Patent 3,556,725, 19 January 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Vaudry, F.; Khodabandeh, S.; Davis, M.E. Synthesis of pure alumina mesoporous materials. Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagshaw, S.A.; Prouzet, E.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Templating of mesoporous molecular sieves by nonionic polyethylene oxide surfactants. Science 1995, 269, 1242–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagshaw, S.A.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Mesoporous alumina molecular sieves. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1996, 35, 1102–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler-Illia, G.J.D.A.; Sanchez, C.; Lebeau, B.; Patarin, J. Chemical strategies to design textured materials: From microporous and mesoporous oxides to nanonetworks and hierarchical structures. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4093–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, C.; Boissière, C.; Grosso, D.; Laberty, C.; Nicole, L. Design, synthesis, and properties of inorganic and hybrid thin films having periodically organized nanoporosity. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 682–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez-Alvarez, C.; Žilková, N.; Pérez-Pariente, J.; Čejka, J. Synthesis, characterization and catalytic applications of organized mesoporous aluminas. Catal. Rev. 2008, 50, 222–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoldas, B. Alumina sol preparation from alkoxides. Ceram. Bull. 1975, 54, 289–290. [Google Scholar]
- Yoldas, B.E. Alumina gels that form porous transparent Al2O3. J. Mater. Sci. 1975, 10, 1856–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, C.J.; Lu, Y.; Sellinger, A.; Fan, H. Evaporation-induced self-assembly: Nanostructures made easy. Adv. Mater. 1999, 11, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Yin, A.-X.; Luo, C.; Sun, L.-D.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Duan, W.-T.; Liu, H.-C.; Yan, C.-H. Facile synthesis for ordered mesoporous γ-aluminas with high thermal stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 3465–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valange, S.; Barrault, J.; Derouault, A.; Gabelica, Z. Binary Cu–Al mesophases precursors to uniformly sized copper particles highly dispersed on mesoporous alumina. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2001, 44–45, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Gao, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Synthesis, characterization and catalytic applications of mesoporous γ-alumina from boehmite sol. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 111, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looi, P.Y.; Mohamed, A.R.; Tye, C.T. Hydrocracking of residual oil using molybdenum supported over mesoporous alumina as a catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 181–182, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleel, A. Methanol dehydration to dimethyl ether over highly porous xerogel alumina catalyst: Flow rate effect. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newnham, J.; Mantri, K.; Amin, M.H.; Tardio, J.; Bhargava, S.K. Highly stable and active Ni-mesoporous alumina catalysts for dry reforming of methane. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 1454–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Meng, A.; Yu, J.; Jaroniec, M. Hierarchically macro-mesoporous Pt/γ-Al2O3 composite microspheres for efficient formaldehyde oxidation at room temperature. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikawa, T.; Ookoshi, T.; Tanaka, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Onaka, M. A new heterogeneous olefin metathesis catalyst composed of rhenium oxide and mesoporous alumina. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 74, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamtil, R.; Žilková, N.; Balcar, H.; Čejka, J. Rhenium oxide supported on organized mesoporous alumina—A highly active and versatile catalyst for alkene, diene, and cycloalkene metathesis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2006, 302, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghiu, S.; Coppens, M.-O. Optimal bimodal pore networks for heterogeneous catalysis. AIChE J. 2004, 50, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacquin, J.-P.; Dhainaut, J.; Duprez, D.; Royer, S.; Lee, A.F.; Wilson, K. An efficient route to highly organized, tunable macroporous-mesoporous alumina. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 12896–12897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.-L.; Duan, W.-T.; Yuan, Q.; Li, Z.-X.; Duan, H.-H.; Yan, C.-H. Hierarchical γ-Al2O3 monoliths with highly ordered 2D hexagonal mesopores in macroporous walls. Chem. Commun. 2009, 6174–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabuki, M.; Takahashi, R.; Sato, S.; Sodesawa, T.; Ogura, K. Silica-alumina catalysts prepared in sol-gel process of TEOS with organic additives. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2002, 4, 4830–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Z.; Liu, S. Hierarchically ordered meso/macroporous γ-alumina for enhanced hydrodesulfurization performance. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 158, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, V.V.; Vinogradov, A.V.; Kraev, A.S.; Agafonov, A.V.; Kessler, V.G. Sol-gel synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity of γ-alumina with bimodal mesopore distribution. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, C.Y.; Liang, H.; Liu, Y. Macroporous monolithic Pt/γ-Al2O3 and K–Pt/γ-Al2O3 catalysts used for preferential oxidation of CO. Catal. Lett. 2008, 127, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhainaut, J.; Piana, G.; Deville, S.; Guizard, C.; Klotz, M. Freezing-induced ordering of block-copolymer micelles. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 12572–12574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deville, S. Ice-templating, freeze casting: Beyond materials processing. J. Mater. Res. 2013, 28, 2202–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüth, F. Non-siliceous mesostructured and mesoporous materials. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3184–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hicks, R.W.; Pauly, T.R.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Mesostructured forms of γ-Al2O3. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 1592–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, S.; Sachse, A.; Galarneau, A. Challenges and strategies in the synthesis of mesoporous alumina powders and hierarchical alumina monoliths. Materials 2012, 5, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharchenya, R.I. Influence of peptization on the properties of alumina produced from boehmite sols. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 1996, 6, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.C.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, H.; Park, I.; Choy, J.H. Tailoring porosity of colloidal boehmite sol by controlling crystallite size. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, 33, 1962–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manet, S.; Lecchi, A.; Impéror-Clerc, M.; Zholobenko, V.; Durand, D.; Oliveira, C.L.P.; Pedersen, J.S.; Grillo, I.; Meneau, F.; Rochas, C. Structure of micelles of a nonionic block copolymer determined by SANS and SAXS. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 11318–11329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manet, S.; Schmitt, J.; Impéror-Clerc, M.; Zholobenko, V.; Durand, D.; Oliveira, C.L.P.; Pedersen, J.S.; Gervais, C.; Baccile, N.; Babonneau, F.; et al. Kinetics of the formation of 2D-hexagonal silica nanostructured materials by nonionic block copolymer templating in solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 11330–11344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulvio, P.F.; Brosey, R.I.; Jaroniec, M. Synthesis of mesoporous alumina from boehmite in the presence of triblock copolymer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamorategui, A.; Martinez, J.M.; Tanaka, S. Maximum solid loading dispersion of pseudoboehmite. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. Vol. 2015, 51, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Klotz, M.; Amirouche, I.; Guizard, C.; Viazzi, C.; Deville, S. Ice templating—An alternative technology to produce micromonoliths. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2012, 14, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, W.N.; Kloprogge, J.T.; Frost, R.L.; Bartlett, J.R. A crystallite packing model for pseudoboehmite formed during the hydrolysis of trisecbutoxyaluminium to explain the peptizability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 247, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Formulation | Synthesis | Ice-Templating | Thermal Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2O/Al ratio | Temperature | Freezing speed | Heating rate |
| Acid/Al ratio | Peptization duration | H2O/Al ratio | Dwelling temperature |
| Acid source | Ageing duration | Dwelling time | |
| Surfactant/Al ratio | |||
| Surfactant source | |||
| Alumina source |
| Acid | Aspect of Al Sol | H+/Al Ratio | Peak (nm) | SSA (m2/g) | Vporous (cm3/g) | dporous (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfuric acid | Yellow opaque | 0.10 | Could not be ice-templated | |||
| Acetic acid | White opaque | 0.10 | No peak | 222 | 0.64 | 10.6 |
| Citric acid | White opaque | 0.10 | 17.7 | 310 | 1.13 | 10.7 |
| Propionic acid | translucent | 0.10 | 13.8 | 324 | 0.94 | 8.4 |
| Chlorhydric acid | translucent | 0.10 | 15.7 | 328 | 0.91 | 8.1 |
| Nitric acid | translucent | 0.038 | 16.7 | 317 | 1.11 | 10.9 |
| Nitric acid | translucent | 0.07 | 11.18 | 317 | 0.90 | 8.4 |
| Nitric acid | translucent | 0.10 | 10.8 | 327 | 1.00 | 8.9 |
| Nitric acid | translucent | 0.13 | 10.6 | 287 | 0.72 | 7.4 |
| Calcination Temperature (°C) | SSA (m2/g) | Vporous (cm3/g) | dpores (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 550 | 317 | 0.90 | 8.4 |
| 850 | 260 | 0.95 | 11.2 |
| 900 | 236 | 0.91 | 11.1 |
| 950 | 188 | 0.71 | 11.6 |
| 1000 | 210 | 0.82 | 11.7 |
| 1050 | 127 | 0.54 | 14.4 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dhainaut, J.; Deville, S.; Amirouche, I.; Klotz, M. A Reliable Method for the Preparation of Multiporous Alumina Monoliths by Ice-Templating. Inorganics 2016, 4, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics4010006
Dhainaut J, Deville S, Amirouche I, Klotz M. A Reliable Method for the Preparation of Multiporous Alumina Monoliths by Ice-Templating. Inorganics. 2016; 4(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics4010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleDhainaut, Jérémy, Sylvain Deville, Idris Amirouche, and Michaela Klotz. 2016. "A Reliable Method for the Preparation of Multiporous Alumina Monoliths by Ice-Templating" Inorganics 4, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics4010006
APA StyleDhainaut, J., Deville, S., Amirouche, I., & Klotz, M. (2016). A Reliable Method for the Preparation of Multiporous Alumina Monoliths by Ice-Templating. Inorganics, 4(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics4010006