Metal-Free Reduction of Phosphine Oxides Using Polymethylhydrosiloxane
Abstract
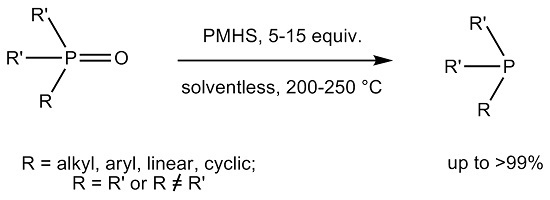
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Methods and Substrates
4.1.1. Synthesis of 3
4.1.2. Synthesis of 8
4.2. Reduction Protocol
Detailed Procedure for the Reduction of 1
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheldon, R.A. The E Factor: Fifteen years on. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, P.J.A.; Elser, J.J.; Hilton, J.; Ohtake, H.; Schipper, W.J.; van Dijk, K.C. Greening the global phosphorus cycle: How green chemistry can help achieve planetary P sustainability. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2087–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamer, P.C.J.; Van Leeuwen, P.W.N.M. (Eds.) Phosphorus(III) Ligands in Homogeneous Catalysis: Design and Synthesis; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2012.
- Peruzzini, M.; Gonsalvi, L. (Eds.) Phosphorus Compounds: Advanced Tools in Catalysis and Material Sciences, 1st ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2011; Volume 37.
- Johnson, A.W. Ylides and Imines of Phosphorus; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Cornils, B.; Hermann, W.A. (Eds.) Aqueous-Phase Organometallic Catalysis: Concepts and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2005.
- Herault, D.; Nguyen, D.H.; Nuel, D.; Buono, G. Reduction of secondary and tertiary phosphine oxides to phosphines. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2508–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritzsche, H.; Hasserodt, U.; Korte, F.; Friese, G.; Adrian, K.; Arenz, H.J. Reduktion organischer Verbindungen des fünfwertigen Phosphors zu Phosphinen, I. Reduktion tertiärer Phosphinoxyde zu tertiären Phosphinen mit Silanen. Chem. Ber. 1964, 97, 1988–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shell Internationale Research Maatschappij N.V. te ’s-Gravenhage. Werkwijze ter Bereiding van Fosfinen. Dutch Patent NL295914A, May 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Fritzsche, H.; Hasserodt, U.; Korte, F. Verfahren zur Herstellung von Tertiaeren Phosphinen. German Patent DE1203773B, October 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Keglevich, G.; Kovács, T.; Csatlós, F. The Deoxygenation of Phosphine Oxide under Green Chemical Conditions. Heteroat. Chem. 2015, 26, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsche, H.; Hasserodt, U.; Korte, F.; Friese, G.; Adrian, K. Reduktion organischer Verbindungen des fünfwertigen Phosphors zu Phosphinen, II. Reduktion tertiärer Phosphinoxyde zu tertiären Phosphinen mit Trichlorsilan. Chem. Ber. 1965, 98, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumbe, T.; Lawrence, N.J.; Muhammad, F. Titanium(IV) catalysis in the reduction of phosphine oxides. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthod, M.; Favre-Reguillon, A.; Mohamad, J.; Mignani, G.; Docherty, G.; Lemaire, M. A Catalytic Method for the Reduction of Secondary and Tertiary Phosphine Oxides. Synlett 2007, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Das, S.; Zhou, S.; Junge, K.; Beller, M. General and Selective Copper-Catalyzed Reduction of Tertiary and Secondary Phosphine Oxides: Convenient Synthesis of Phosphines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9727–9732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lu, L.Q.; Das, S.; Pisiewicz, S.; Junge, K.; Beller, M. Highly Chemoselective Metal-Free Reduction of Phosphine Oxides to Phosphines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 18325–18329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirmer, M.-L.; Jopp, S.; Holz, J.; Spannenberg, A.; Werner, T. Organocatalyzed Reduction of Tertiary Phosphine Oxides. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2016, 358, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, A.D.; Gonsalvi, L.; Romerosa, A.; Vizza, F.; Peruzzini, M. Coordination chemistry of 1,3,5-Triaza-7-phosphaadamantane (PTA): Transition metal complexes and related catalytic, medicinal and photo-luminescent applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2004, 248, 955–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.; Bolaño, S.; Gonsalvi, L.; Peruzzini, M. Coordination chemistry of 1,3,5-Triaza-7-phosphaadamantane (PTA) and derivatives. Part II. The quest for tailored ligands, complexes and related applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 555–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carenco, S.; Portehault, D.; Boissiere, C.; Mézailles, N.; Sanchez, C. Nanoscaled Metal Borides and Phosphides: Recent Developments and Perspectives. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 7981–8065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, E.; Rickelton, W. A Review of the Industrial and Recent Potential Applications of Trioctylphosphine Oxide. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 1992, 10, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, C.J.; Tellez, J.L.; Nixon, Z.S.; Kang, L.J.; Carter, A.L.; Kunkel, S.R.; Przeworski, K.C.; Chass, G.A. Recycling the Waste: The Development of a Catalytic Wittig Reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6836–6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirmer, M.-L.; Adomeit, S.; Spannenberg, A.; Werner, T. Novel Base-Free Catalytic Wittig Reaction for the Synthesis of Highly Functionalized Alkenes. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 2458–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilliard, C.R.; Bhuvanesh, N.; Gladysz, J.A.; Blümel, J. Synthesis, purification, and characterization of phosphine oxides and their hydrogen peroxide adducts. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 1742–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, A.P.; Lees, A.M.J.; Platt, A.W.G. Synthesis, structures and mass spectrometry of lanthanide nitrate complexes with tricyclohexylphosphine oxide. Polyhedron 2007, 26, 4865–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, C.J.; Nixon, Z.S.; Holohan, A.J.; Kunkel, S.R.; Tellez, J.L.; Doonan, B.J.; Coyle, E.E.; Lavigne, F.; Kang, L.J.; Przeworski, K.C. Part I: The Development of the Catalytic Wittig Reaction. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 15281–15289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daigle, D.J.; Pepperman, A.B. Chemical proof for the preferred nitrogen quarternization in 1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphaadamantane. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1975, 12, 579–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigle, D.J. 1,3,5-Triaza-7-Phosphatricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]Decane and Derivatives. Inorg. Synth. 1998, 32, 40–45. [Google Scholar]





| Entry | Substrate | PMHS (equiv.) | T (°C) | t (h) | Yield (%) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 5 | 250 | 0.5 | 24 |
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 250 | 1 | 45 |
| 3 | 1 | 5 | 250 | 1.5 | 86 (84) |
| 4 | 1 | 15 | 250 | 1 | 90 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 200 | 24 | 90 |
| 6 | 1 | 5 | 220 | 24 | 100 |
| 7 | 2 | 5 | 220 | 1 | 100 |
| 8 | 3 | 5 | 250 | 6 | 0 |
| 9 | 3 | 10 | 200 | 3 | 7 |
| 10 | 3 | 10 | 200 | 6 | <1 * |
| 11 | 3 | 15 | 200 | 6 | 10 |
| 12 | 3 | 15 | 250 | 2 | 20 |
| 13 | 3 | 15 | 250 | 6 | 5 |
| 14 | 3 | 15 | 250 | 7 | <1 * |
| 15 | 4 | 10 | 200 | 3 | 4 |
| 16 | 4 | 10 | 200 | 6 | 33 |
| 17 | 4 | 10 | 250 | 3 | 12 |
| 18 | 4 | 10 | 250 | 6 | 53 |
| 19 | 4 | 15 | 200 | 3 | 30 |
| 20 | 4 | 15 | 200 | 7 | 87 |
| 21 | 4 | 15 | 250 | 3 | 13 |
| 22 | 4 | 15 | 250 | 7 | 82 |
| 23 | 5 | 5 | 250 | 1 | 100 |
| 24 | 6 | 5 | 250 | 1 | 100 |
| 25 | 6 | 5 | 220 | 1 | 100 |
| 26 | 7 | 5 | 220 | 1 | 83 (78) |
| 27 | 8 | 10 | 250 | 1 | <1 * |
| 28 | 8 | 15 | 200 | 6 | <1 |
| 29 | 8 | 15 | 200 | 20 | <1 * |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicolas, E.; Guerriero, A.; Lyaskovskyy, V.; Peruzzini, M.; Lammertsma, K.; Gonsalvi, L.; Slootweg, J.C. Metal-Free Reduction of Phosphine Oxides Using Polymethylhydrosiloxane. Inorganics 2016, 4, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics4040034
Nicolas E, Guerriero A, Lyaskovskyy V, Peruzzini M, Lammertsma K, Gonsalvi L, Slootweg JC. Metal-Free Reduction of Phosphine Oxides Using Polymethylhydrosiloxane. Inorganics. 2016; 4(4):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics4040034
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicolas, Emmanuel, Antonella Guerriero, Volodymyr Lyaskovskyy, Maurizio Peruzzini, Koop Lammertsma, Luca Gonsalvi, and J. Chris Slootweg. 2016. "Metal-Free Reduction of Phosphine Oxides Using Polymethylhydrosiloxane" Inorganics 4, no. 4: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics4040034
APA StyleNicolas, E., Guerriero, A., Lyaskovskyy, V., Peruzzini, M., Lammertsma, K., Gonsalvi, L., & Slootweg, J. C. (2016). Metal-Free Reduction of Phosphine Oxides Using Polymethylhydrosiloxane. Inorganics, 4(4), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics4040034